Genetic Insights and Diagnostic Challenges in Highly Attenuated Lysosomal Storage Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results (Overview)
4. Clinical Manifestations
4.1. Cardiac Manifestations
4.2. Neurology Manifestations
4.3. Dental and Craniofacial Abnormalities
4.4. ENT and Respiratory Manifestations
4.5. Hepatic and Splenic Manifestations
4.6. Musculoskeletal Manifestations
4.7. Cutaneous Features
4.8. Ophthalmic Manifestations
4.9. Summary
5. Biomarkers
5.1. Specific Enzyme Activity
5.2. Primary Storage Metabolites
5.3. Biomarkers of Macrophage Activation
5.4. Downstream and Secondary Biomarkers
5.5. Summary
6. Molecular Analysis
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARSB | arylsulfatase B |
| ASMD | acid sphingomyelinase deficiency |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CMR | cardiac magnetic resonance imaging |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CTS | carpal tunnel syndrome |
| ECG | electrocardiogram |
| ECHO | echocardiogram |
| EF | ejection fraction |
| FLAIR | fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
| GAGs | glycosaminoglycans |
| GALNS | N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase |
| GALC | galactosylceramidase |
| Ht | height |
| ID | intellectual disability |
| IDUA | alpha-L-iduronidase |
| IDS | iduronate 2-sulfatase |
| LALD | lysosomal acid lipase deficiency |
| LSD | lysosomal storage disease |
| LVH | left ventricular hypertrophy |
| MANBA | mannosidase beta |
| MAN2B1 | mannosidase alpha class 2B member 1 |
| MLD | metachromatic luekodystrophy |
| MPS | mucopolysaccharidosis |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NCS | nerve conduction studies |
| NPC | Niemann–Pick C |
| OSA | obstructive sleep apnoea |
| PFTs | pulmonary function test |
| SMPD1 | sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1 |
| SUMF1 | sulfatase modifying factor 1 |
| RBBB | right bundle branch block |
| RP | retinitis pigmentosa |
| SHSH | N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase |
| VUS | variant of unknown significance |
| USS | ultrasound |
| Wt | weight |
References
- Ferreira, C.R.; Gahl, W.A. Lysosomal storage diseases. Transl. Sci. Rare Dis. 2017, 2, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.M.; Cachón-González, M.B. The cellular pathology of lysosomal diseases. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, F.M.; d’Azzo, A.; Davidson, B.L.; Neufeld, E.F.; Tifft, C.J. Lysosomal storage diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.J.; Fuller, M. Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders in Australia from 2009 to 2020. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2021, 19, 100344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, G.; Medina, D.L.; Ballabio, A. The rapidly evolving view of lysosomal storage diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigoldi, M.; Verrecchia, E.; Manna, R.; Mascia, M.T. Clinical hints to diagnosis of attenuated forms of Mucopolysaccharidoses. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gort, L.; Santamaria, R.; Grinberg, D.; Vilageliu, L.; Chabás, A. Identification of a novel pseudodeficiency allele in the GLB1 gene in a carrier of GM1 gangliosidosis. Clin. Genet. 2007, 72, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filocamo, M.; Morrone, A. Lysosomal storage disorders: Molecular basis and laboratory testing. Hum. Genom. 2011, 5, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Young, S.P.; Millington, D.S. Quantification of Glycosaminoglycans in Urine by Isotope-Dilution Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Curr. Protoc. 2023, 3, e701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpi, N.; Galeotti, F.; Gatto, F. High-throughput glycosaminoglycan extraction and UHPLC-MS/MS quantification in human biofluids. Nat. Protoc. 2025, 20, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaño, A.M.; Sukegawa, K.; Kato, Z.; Carrozzo, R.; Di Natale, P.; Christensen, E.; Orii, K.O.; Orii, T.; Kondo, N.; Tomatsu, S. Effect of ‘attenuated’ mutations in mucopolysaccharidosis IVA on molecular phenotypes of N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doerr, A.; Farooq, M.; Faulkner, C.; Gould, R.; Perry, K.; Pulikottil-Jacob, R.; Rajasekhar, P. Diagnostic odyssey for patients with acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD): Exploring the potential indicators of diagnosis using quantitative and qualitative data. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2024, 38, 101052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchan, M.; Lehman, A.; van Dussen, L.; Langendonk, J.G.; Janssen, M.C.H.; Langeveld, M.; Murphy, E.; Ryder, B.; Glamuzina, E.; Merkel, M.; et al. The Frequencies of Different Inborn Errors of Metabolism in Adult Metabolic Centres: 10 Years Later, Another Report from the SSIEM Adult Metabolic Physicians Group. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2025, 48, e70005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, F.M.; Boland, B.; van der Spoel, A.C. The cell biology of disease: Lysosomal storage disorders: The cellular impact of lysosomal dysfunction. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oussoren, E.; van Eerd, D.; Murphy, E.; Lachmann, R.; van der Meijden, J.C.; Hoefsloot, L.H.; Verdijk, R.; Ruijter, G.J.G.; Maas, M.; Hollak, C.E.M.; et al. Mucolipidosis type III, a series of adult patients. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, O.I.; Timmermans, R.G.; Nemes, A.; Vletter, W.B.; Wilson, J.H.; ten Cate, F.J.; Geleijnse, M.L. Cardiac abnormalities in adults with the attenuated form of mucopolysaccharidosis type I. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- García Del Rey, M.D.C.; Castrodeza, J.; Pinto, Á.; Espinosa Castro, M.; Muñoz Delgado, C.; Fernández-Avilés, F. Heart valve disease in Hurler-Scheie syndrome. Cardiol. J. 2022, 29, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golda, A.; Jurecka, A.; Tylki-Szymanska, A. Cardiovascular manifestations of mucopolysaccharidosis type VI (Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome). Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 158, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaio, C.R.; Grinberg, H.; Vieira, M.L.; Paula, A.C.; Leal, G.N.; Gomy, I.; Leistner-Segal, S.; Giugliani, R.; Bertola, D.R.; Kim, C.A. Report of a Large Brazilian Family With a Very Attenuated Form of Hunter Syndrome (MPS II). JIMD Rep. 2012, 4, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golda, A.; Jurecka, A.; Opoka-Winiarska, V.; Tylki-Szymańska, A. Mucopolysaccharidosis type VI: A cardiologist’s guide to diagnosis and treatment. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moog, U.; van Mierlo, I.; van Schrojenstein Lantman-de Valk, H.M.; Spaapen, L.; Maaskant, M.A.; Curfs, L.M. Is Sanfilippo type B in your mind when you see adults with mental retardation and behavioral problems? Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2007, 145C, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarron, E.P.; Chinnadurai, R.; Meyer, J.; Anderson, T.; Stepien, K.M.; Sharma, R.; Woolfson, P.; Jovanovic, A. Real-world clinical outcomes in adult patients with Fabry disease: A 20-year retrospective observational cohort study from a single centre. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2025, 43, 101229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debs, R.; Froissart, R.; Aubourg, P.; Papeix, C.; Douillard, C.; Degos, B.; Fontaine, B.; Audoin, B.; Lacour, A.; Said, G.; et al. Krabbe disease in adults: Phenotypic and genotypic update from a series of 11 cases and a review. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, E.P.; Oldham, A.; Herwadkar, A.; Jenkinson, S.; Campbell, C.; Neal, K.; Church, H.J.; Cooper, J.A.; Stepien, K.M. Natural History and Diagnostic Findings in an Adult Man Diagnosed With Attenuated Krabbe Disease. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2025, 197, e64031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-C.; Eichinger, C.S.; Field, P. The natural history and burden of illness of metachromatic leukodystrophy: A systematic literature review. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthane, U.; Chickabasaviah, Y.; Kaneski, C.; Shankar, S.K.; Narayanappa, G.; Christopher, R.; Govindappa, S.S. Clinical features of adult GM1 gangliosidosis: Report of three Indian patients and review of 40 cases. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopshire, M.C.; Tifft, C.; Burns, J.; Gould, R.; Zheng, R.; Batsu, I. The diagnostic journey for patients with late-onset GM2 Gangliosidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2023, 37, 101014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutschalk, A.; Harting, I.; Cantz, M.; Springer, C.; Rohrschneider, K.; Meinck, H.M. Adult alpha-mannosidosis: Clinical progression in the absence of demyelination. Neurology 2004, 63, 1744–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollak, C.E.; Weinreb, N.J. The attenuated/late onset lysosomal storage disorders: Therapeutic goals and indications for enzyme replacement treatment in Gaucher and Fabry disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, E.G.; Nestrasil, I.; Delaney, K.A.; Rudser, K.; Kovac, V.; Nair, N.; Richard, C.W., 3rd; Haslett, P.; Whitley, C.B. A Prospective Natural History Study of Mucopolysaccharidosis Type IIIA. J. Pediatr. 2016, 170, 278.e4–287.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijmeijer, S.C.M.; van den Born, L.I.; Kievit, A.J.A.; Stepien, K.M.; Langendonk, J.; Marchal, J.P.; Roosing, S.; Wijburg, F.A.; Wagenmakers, M. The attenuated end of the phenotypic spectrum in MPS III: From late-onset stable cognitive impairment to a non-neuronopathic phenotype. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Guerrero, J.L.; Gómez Higuera, P.J.; Arias Flórez, J.S.; Contreras-García, G.A. Mucopolysaccharidosis: Clinical features, diagnosis and management. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2016, 87, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avanzo, F.; Rigon, L.; Zanetti, A.; Tomanin, R. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II: One Hundred Years of Research, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videbæk, C.; Stokholm, J.; Sengeløv, H.; Fjeldborg, L.U.; Larsen, V.A.; Krarup, C.; Nielsen, J.E.; Grønborg, S. Allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in two siblings with adult metachromatic leukodystrophy and a systematic literature review. JIMD Rep. 2021, 60, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, M.L.; Levy, T.; Lakhani, S.; Wang, C.; Ross, M.E. Adult-onset Niemann–Pick disease type C masquerading as spinocerebellar ataxia. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2022, 10, e1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannebley, J.S.; Silveira-Moriyama, L.; Bastos, L.O.; Steiner, C.E. Clinical Findings and Natural History in Ten Unrelated Families with Juvenile and Adult GM1 Gangliosidosis. JIMD Rep. 2015, 24, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooten, W.I.; Muhlebach, M.S.; Muenzer, J.; Loughlin, C.E.; Vaughn, B.V. Progression of Polysomnographic Abnormalities in Mucolipidosis II (I-Cell Disease). J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 1695–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Santamaria, F.; Andreucci, M.V.; Parenti, G.; Polverino, M.; Viggiano, D.; Montella, S.; Cesaro, A.; Ciccarelli, R.; Capaldo, B.; Andria, G. Upper airway obstructive disease in mucopolysaccharidoses: Polysomnography, computed tomography and nasal endoscopy findings. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żuber, Z.; Kieć-Wilk, B.; Kałużny, Ł.; Wierzba, J.; Tylki-Szymańska, A. Diagnosis and Management of Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II (Hunter Syndrome) in Poland. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, D.; Nilssen, Ø. Alpha-mannosidosis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2008, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiyrzhanov, R.; Guliyeva, U.; Gulieva, S.; Salayev, K.; Mursalova, A.; Allahyarova, P.; Ferla, M.P.; Houlden, H. GM1-Gangliosidosis Type III Associated Parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2021, 8, S21–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerves Serrano, T.; Gold, J.; Cooper, J.A.; Church, H.J.; Tylee, K.L.; Wu, H.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Stepien, K.M. Hepatomegaly and Splenomegaly: An Approach to the Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Las Heras, J.; Almohalla, C.; Blasco-Alonso, J.; Bourbon, M.; Couce, M.L.; de Castro Lopez, M.J.; Garcia Jimenez, M.C.; Gil Ortega, D.; Gonzalez-Dieguez, L.; Meavilla, S.; et al. Practical Recommendations for the Diagnosis and Management of Lysosomal Acid Lipase Deficiency with a Focus on Wolman Disease. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viskochil, D.; Muenzer, J.; Guffon, N.; Garin, C.; Munoz-Rojas, M.V.; Moy, K.A.; Hutchinson, D.T. Carpal tunnel syndrome in mucopolysaccharidosis I: A registry-based cohort study. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2017, 59, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly-Pen, D.; Andreu, J.L. Response to: Arthropathy-like findings and a carpal tunnel syndrome as the presenting features of Scheie syndrome: Three cases from the same family. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2019, 61, 982–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökay, S.; Kardaş, F.; Kendirci, M.; Sözeri, B. Arthropathy-like findings and a carpal tunnel syndrome as the presenting features of Scheie syndrome: Three cases from the same family. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2018, 60, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.; Kim, T.; Neufeld, J.A. Clinical assessment and treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome in the mucopolysaccharidoses. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 3, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuts, I.; Potgieter, D.; van der Westhuizen, F.H. Combined tarsal and carpal tunnel syndrome in mucolipidosis type III. A case study and review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1151, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, F.S.; Jones, D.H.; Vellodi, A.; Kane, N.; Pitt, M.C. Carpal tunnel syndrome in the mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1997, 79, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazifehdan, F.; Karantzoulis, V.G.; Ebner, R.; Igoumenou, V.G. A Unique Case of Cervical Myelopathy in an Adult Patient with Scheie Syndrome. J. Orthop. Case Rep. 2017, 7, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Illsinger, S.; Lücke, T.; Hartmann, H.; Mengel, E.; Müller-Forell, W.; Donnerstag, F.; Das, A.M. Scheie syndrome: Enzyme replacement therapy does not prevent progression of cervical myelopathy due to spinal cord compression. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2009, 32 (Suppl. S1), S321–S325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, R.; Bonosi, L.; Porzio, M.; Paolini, F.; Brunasso, L.; Giovannini, A.E.; Silven, M.P.; Giammalva, G.R.; Umana, G.E.; Scalia, G.; et al. Burden of Surgical Treatment for the Management of Cervical Myelopathy in Mucopolysaccharidoses: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2022, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Dajnoki, A.; Bodamer, O. Diagnosis of lysosomal storage disorders: Gaucher disease. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2014, 82, 17.15.11–17.15.16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodny, E.H.; Raghavan, S.; Krivit, W. Late-Onset Krabbe Disease (Globoid Cell Leukodystrophy): Clinical and Biochemical Features of 15 Cases. Dev. Neurosci. 1991, 13, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wraith, J.E. The clinical presentation of lysosomal storage disorders. Acta Neurol. Taiwan. 2004, 13, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Frischhut, N.; Zelger, B.; Andre, F.; Zelger, B.G. The spectrum of melanocytic nevi and their clinical implications. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2022, 20, 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos Martins, T.G.; de Azevedo Costa, A.L.F.; Pimentel, S.L.G.; Oyamada, M.K.; Finzi, S. Retinitis pigmentosa and nanophthalmos in a patient with attenuated Hunter’s syndrome. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2023, 146, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Schiff, E.; Arno, G.; Mahroo, O.A.; Webster, A.R. Unveiling hidden genetic complexity: Coexistence of HGSNAT and EYS variants in a patient with retinal dystrophy. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2024, 194, e63805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahnehjelm, K.T.; Ashworth, J.L.; Pitz, S.; Olsson, M.; Törnquist, A.L.; Lindahl, P.; Summers, C.G. Clinical guidelines for diagnosing and managing ocular manifestations in children with mucopolysaccharidosis. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012, 90, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, O.; Au, L.; Ashworth, J. Management of Corneal Clouding in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haer-Wigman, L.; Newman, H.; Leibu, R.; Bax, N.M.; Baris, H.N.; Rizel, L.; Banin, E.; Massarweh, A.; Roosing, S.; Lefeber, D.J.; et al. Non-syndromic retinitis pigmentosa due to mutations in the mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIC gene, heparan-alpha-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase (HGSNAT). Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 3742–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvucci, I.D.M.; Finzi, S.; Oyamada, M.K.; Kim, C.A.; Pimentel, S.L.G. Multimodal image analysis of the retina in Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II): Case report. Ophthalmic Genet. 2018, 39, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majmudar, I.P.; Ismail, H.O.; Dang, S.; Gill, M.K. Posterior segment findings in Hunter Syndrome: Case report and review. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2024, 36, 102189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkin, J.; Kerr, N.C.; Byrd, K.W.; Ward, J.C.; Iannaccone, A. Characterization of a Case of Pigmentary Retinopathy in Sanfilippo Syndrome Type IIIA Associated with Compound Heterozygous Mutations in the SGSH Gene. Ophthalmic Genet. 2016, 37, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzetzi, D.; Hamilton, R.; Robinson, P.H.; Dutton, G.N. Negative ERGs in mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) Hurler-Scheie (I-H/S) and Hurler (I-H)-syndromes. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2007, 114, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Robson, A.G.; Thompson, D.A.; Stepien, K.M.; Lachmann, R.; Footitt, E.; Czyz, O.; Chandrasekhar, S.; Schiff, E.; Iosifidis, C.; et al. Non-syndromic retinal dystrophy associated with biallelic variation of SUMF1 and reduced leukocyte sulfatase activity. Clin. Genet. 2024, 106, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.M.; Kallemeijn, W.W.; Wegdam, W.; Joao Ferraz, M.; van Breemen, M.J.; Dekker, N.; Kramer, G.; Poorthuis, B.J.; Groener, J.E.; Cox-Brinkman, J.; et al. Biomarkers in the diagnosis of lysosomal storage disorders: Proteins, lipids, and inhibodies. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrousse, P.; Chien, Y.H.; Pomponio, R.J.; Keutzer, J.; Lee, N.C.; Akmaev, V.R.; Scholl, T.; Hwu, W.L. Genetic heterozygosity and pseudodeficiency in the Pompe disease newborn screening pilot program. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 99, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, S.D.; Langereis, E.J.; de Klerk, C.M.; Zoetekouw, L.; Wagemans, T.; IJlst, L.; Wanders, R.J.; Wijburg, F.A.; van Vlies, N. An algorithm to predict phenotypic severity in mucopolysaccharidosis type I in the first month of life. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussoren, E.; Keulemans, J.; van Diggelen, O.P.; Oemardien, L.F.; Timmermans, R.G.; van der Ploeg, A.T.; Ruijter, G.J. Residual α-L-iduronidase activity in fibroblasts of mild to severe Mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2013, 109, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, O.L.M.; Welling, L.; Valstar, M.J.; Hoefsloot, L.H.; Bruggenwirth, H.T.; van der Ploeg, A.T.; Ruijter, G.J.G.; Wagemans, T.; Wijburg, F.A.; van Vlies, N. Residual N-acetyl-alpha-glucosaminidase activity in fibroblasts correlates with disease severity in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C. Chapter 10—Lysosomal storage disorders: Sphingolipidoses. In Biomarkers in Inborn Errors of Metabolism; Garg, U., Smith, L.D., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 211–233. [Google Scholar]
- Giuffrida, G.; Markovic, U.; Condorelli, A.; Calafiore, V.; Nicolosi, D.; Calagna, M.; Grasso, S.; Ragusa, M.T.V.; Gentile, J.; Napolitano, M. Glucosylsphingosine (Lyso-Gb1) as a reliable biomarker in Gaucher disease: A narrative review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, V.; Chuang, W.L.; Liu, J.; Lischuk, A.; Kacena, K.; Lin, H.; Pastores, G.M.; Yang, R.; Keutzer, J.; Zhang, K.; et al. Glucosylsphingosine is a key biomarker of Gaucher disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlina, A.; Brand, E.; Hughes, D.; Kantola, I.; Krӓmer, J.; Nowak, A.; Tøndel, C.; Wanner, C.; Spada, M. An expert consensus on the recommendations for the use of biomarkers in Fabry disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2023, 139, 107585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.M.; Groener, J.E.; Kuiper, S.; Donker-Koopman, W.E.; Strijland, A.; Ottenhoff, R.; van Roomen, C.; Mirzaian, M.; Wijburg, F.A.; Linthorst, G.E.; et al. Elevated globotriaosylsphingosine is a hallmark of Fabry disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2812–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smid, B.E.; van der Tol, L.; Biegstraaten, M.; Linthorst, G.E.; Hollak, C.E.; Poorthuis, B.J. Plasma globotriaosylsphingosine in relation to phenotypes of Fabry disease. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuchman, E.H.; Desnick, R.J. Types A and B Niemann-Pick disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 120, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escolar, M.L.; Kiely, B.T.; Shawgo, E.; Hong, X.; Gelb, M.H.; Orsini, J.J.; Matern, D.; Poe, M.D. Psychosine, a marker of Krabbe phenotype and treatment effect. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 121, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Lee, C.L.; Lo, Y.T.; Wang, T.J.; Huang, S.F.; Chen, T.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Niu, D.M.; Chuang, C.K.; Lin, S.P. The relationships between urinary glycosaminoglycan levels and phenotypes of mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2018, 6, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouiri, G.; Rhouda, H.; Kriouile, Y. c.754T>A homozygous mutation described for the first time in three Moroccan patients with Gaucher disease. Arch. Pediatr. 2024, 31, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubaski, F.; Osago, H.; Mason, R.W.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Tsuchiya, M.; Orii, T.; Tomatsu, S. Glycosaminoglycans detection methods: Applications of mass spectrometry. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 120, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubaski, F.; de Oliveira Poswar, F.; Michelin-Tirelli, K.; Burin, M.G.; Rojas-Malaga, D.; Brusius-Facchin, A.C.; Leistner-Segal, S.; Giugliani, R. Diagnosis of Mucopolysaccharidoses. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, Z.M.; Hong, X.; Sadilek, M.; Fuller, M.; Gelb, M.H. Newborn screening for the full set of mucopolysaccharidoses in dried blood spots based on first-tier enzymatic assay followed by second-tier analysis of glycosaminoglycans. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2023, 140, 107698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggink, C.; Poorthuis, B.J.; Deelder, A.M.; Wuhrer, M. Analysis of urinary oligosaccharides in lysosomal storage disorders by capillary high-performance anion-exchange chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Rios, A.; Stepien, K.M.; Gibbs, L.H.; Hall, K.; Hall, P.L.; Pino, G.B.; Wang, R.; Pillai, N.R.; Lund, T.C.; Orchard, P.J.; et al. Expanding the phenotype spectrum of β-mannosidosis. medRxiv 2025, 2025.2001.2013.24316445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spacil, Z.; Babu Kumar, A.; Liao, H.-C.; Auray-Blais, C.; Stark, S.; Suhr, T.R.; Scott, C.R.; Turecek, F.; Gelb, M.H. Sulfatide Analysis by Mass Spectrometry for Screening of Metachromatic Leukodystrophy in Dried Blood and Urine Samples. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.H.Y.; Brown, H.A.; Church, H.J.; Kershaw, C.J.; Hutton, R.; Egerton, C.; Cooper, J.; Tylee, K.; Cohen, R.N.; Gokhale, D.; et al. Improving newborn screening test performance for metachromatic leukodystrophy: Recommendation from a pre-pilot study that identified a late-infantile case for treatment. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2024, 142, 108349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekri, S.; Bley, A.; Brown, H.A.; Chanson, C.; Church, H.J.; Gelb, M.H.; Hong, X.; Janzen, N.; Kasper, D.C.; Mechtler, T.; et al. Higher precision, first tier newborn screening for metachromatic leukodystrophy using 16:1-OH-sulfatide. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2024, 142, 108436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaff, A.; Basheeruddin, K.; Bekri, S.; Brown, H.A.; Church, H.J.; Gianares, J.; Hong, X.; Jones, S.A.; Kappell, T.; Kubaski, F.; et al. Newborn screening for metachromatic leukodystrophy: Preparation of reagents and methodology for measurement of sulfatides and arylsulfatase A enzymatic activity in dried blood spots. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2025, 145, 109138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natowicz, M.R.; Prence, E.M.; Chaturvedi, P.; Newburg, D.S. Urine sulfatides and the diagnosis of metachromatic leukodystrophy. Clin. Chem. 1996, 42, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.H.; Lee, N.C.; Huang, H.J.; Thurberg, B.L.; Tsai, F.J.; Hwu, W.L. Later-onset Pompe disease: Early detection and early treatment initiation enabled by newborn screening. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 1023.e1–1027.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saville, J.T.; Fuller, M. Experience with the Urinary Tetrasaccharide Metabolite for Pompe Disease in the Diagnostic Laboratory. Metabolites 2021, 11, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajner, A.; Michelin, K.; Burin, M.G.; Pires, R.F.; Pereira, M.L.S.; Giugliani, R.; Coelho, J.C. Biochemical characterization of chitotriosidase enzyme: Comparison between normal individuals and patients with Gaucher and with Niemann–Pick diseases. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussen, L.; Hendriks, E.; Groener, J.; Boot, R.; Hollak, C.; Aerts, J. Value of plasma chitotriosidase to assess non-neuronopathic Gaucher disease severity and progression in the era of enzyme replacement therapy. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2014, 37, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, M.E.; Balwani, M.; Nazarenko, I.; Prakash-Cheng, A.; Desnick, R.J. Type 1 Gaucher disease: Null and hypomorphic novel chitotriosidase mutations—Implications for diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, R.G.; Verhoek, M.; de Fost, M.; Hollak, C.M.; Maas, M.; Bleijlevens, B.; van Breemen, M.J.; van Meurs, M.; Boven, L.A.; Laman, J.D.; et al. Marked elevation of the chemokine CCL18/PARC in Gaucher disease: A novel surrogate marker for assessing therapeutic intervention. Blood 2004, 103, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Breemen, M.J.; de Fost, M.; Voerman, J.S.; Laman, J.D.; Boot, R.G.; Maas, M.; Hollak, C.E.; Aerts, J.M.; Rezaee, F. Increased plasma macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha and MIP-1beta levels in type 1 Gaucher disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1772, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Takahashi, T.; Toyono, M.; Tamura, M.; Harada, K.; Yoshida, M.; Nishikawa, Y.; Enomoto, K.; Takada, G. Acid sphingomyelinase deficiency: Cardiac dysfunction and characteristic findings of the coronary arteries. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserstein, M.P.; Desnick, R.J.; Schuchman, E.H.; Hossain, S.; Wallenstein, S.; Lamm, C.; McGovern, M.M. The natural history of type B Niemann-Pick disease: Results from a 10-year longitudinal study. Pediatrics 2004, 114, e672–e677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giese, A.K.; Mascher, H.; Grittner, U.; Eichler, S.; Kramp, G.; Lukas, J.; te Vruchte, D.; Al Eisa, N.; Cortina-Borja, M.; Porter, F.D.; et al. A novel, highly sensitive and specific biomarker for Niemann-Pick type C1 disease. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Fukumoto, H.; Utsumi, K.; Hirai, Y. Cardiovascular manifestations of Fabry disease and the novel therapeutic strategies. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2005, 72, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, S.; Crisamore, K.; Schuck, R.; Pacanowski, M. Evaluation of the landscape of pharmacodynamic biomarkers in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPC). Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2024, 19, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, S.; Crisamore, K.; Li, R.J.; Pacanowski, M.; Schuck, R. Evaluation of the Landscape of Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers in GM1 and GM2 Gangliosidosis. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2025, 18, e70176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.A.; Giugliani, R.; Guffon, N.; Jones, S.A.; Keenan, H.A.; Munoz-Rojas, M.V.; Okuyama, T.; Viskochil, D.; Whitley, C.B.; Wijburg, F.A.; et al. Genotype-phenotype relationships in mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I): Insights from the International MPS I Registry. Clin. Genet. 2019, 96, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazna, A.; Beesley, C.; Berna, L.; Stolnaja, L.; Myskova, H.; Bouckova, M.; Vlaskova, H.; Poupetova, H.; Zeman, J.; Magner, M.; et al. Mucopolysaccharidosis type I in 21 Czech and Slovak patients: Mutation analysis suggests a functional importance of C-terminus of the IDUA protein. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2009, 149a, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valstar, M.J.; Neijs, S.; Bruggenwirth, H.T.; Olmer, R.; Ruijter, G.J.; Wevers, R.A.; van Diggelen, O.P.; Poorthuis, B.J.; Halley, D.J.; Wijburg, F.A. Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA: Clinical spectrum and genotype-phenotype correlations. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuga, M.; Mashima, R.; Hirakiyama, A.; Fuji, N.; Kumagai, T.; Seo, J.H.; Nikaido, M.; Saito, S.; Ohno, K.; Sakuraba, H.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of 65 families with mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome) characterized by 16 novel mutations in the IDS gene: Genetic, pathological, and structural studies on iduronate-2-sulfatase. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016, 118, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorakova, L.; Vlaskova, H.; Sarajlija, A.; Ramadza, D.P.; Poupetova, H.; Hruba, E.; Hlavata, A.; Bzduch, V.; Peskova, K.; Storkanova, G.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation in 44 Czech, Slovak, Croatian and Serbian patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II. Clin. Genet. 2017, 91, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuokkanen, E.; Riise Stensland, H.M.; Smith, W.; Kjeldsen Buvang, E.; Van Nguyen, L.; Nilssen, Ø.; Heikinheimo, P. Molecular and cellular characterization of novel {alpha}-mannosidosis mutations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 2651–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertola, F.; Filocamo, M.; Casati, G.; Mort, M.; Rosano, C.; Tylki-Szymanska, A.; Tüysüz, B.; Gabrielli, O.; Grossi, S.; Scarpa, M.; et al. IDUA mutational profiling of a cohort of 102 European patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type I: Identification and characterization of 35 novel α-L-iduronidase (IDUA) alleles. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, E2189–E2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Las Heras, M.; Szenfeld, B.; Ballout, R.A.; Buratti, E.; Zanlungo, S.; Dardis, A.; Klein, A.D. Understanding the phenotypic variability in Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC): A need for precision medicine. NPJ Genom. Med. 2023, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amartino, H.; Ceci, R.; Masllorens, F.; Gal, A.; Arberas, C.; Bay, L.; Ilari, R.; Dipierri, J.; Specola, N.; Cabrera, A.; et al. Identification of 17 novel mutations in 40 Argentinean unrelated families with mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome). Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2014, 1, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvis, J.; González, J.; Uribe, A.; Velasco, H. Deep Genotyping of the IDS Gene in Colombian Patients with Hunter Syndrome. JIMD Rep. 2015, 19, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semyachkina, A.N.; Voskoboeva, E.Y.; Nikolaeva, E.A.; Zakharova, E.Y. Analysis of long-term observations of the large group of Russian patients with Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II). BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, J.J.; Aronovich, E.L.; Braun, S.E.; Whitley, C.B. Molecular diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome) by automated sequencing and computer-assisted interpretation: Toward mutation mapping of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1995, 56, 597–607. [Google Scholar]
- Sukegawa, K.; Tomatsu, S.; Fukao, T.; Iwata, H.; Song, X.Q.; Yamada, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Isogai, K.; Orii, T. Mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter disease): Identification and characterization of eight point mutations in the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in Japanese patients. Hum. Mutat. 1995, 6, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T.C.; Eiken, H.G.; Knappskog, P.M.; Kase, B.F.; Månsson, J.E.; Boman, H.; Apold, J. Mutations in the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in five Norwegians with Hunter syndrome. Hum. Genet. 1996, 97, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gort, L.; Chabás, A.; Coll, M.J. Hunter disease in the Spanish population: Molecular analysis in 31 families. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1998, 21, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Kuzenkova, L.M.; Savost’anov, K.V.; Gevorkyan, A.K.; Pushkov, A.A.; Nikitin, A.G.; Vashakmadze, N.D.; Zhurkova, N.V.; Podkletnova, T.V.; Namazova-Baranova, L.S.; et al. Genetic analysis of 17 children with Hunter syndrome: Identification and functional characterization of four novel mutations in the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene. J. Genet. Genom. 2014, 41, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josahkian, J.A.; Brusius-Facchin, A.C.; Netto, A.B.O.; Leistner-Segal, S.; Málaga, D.R.; Burin, M.G.; Michelin-Tirelli, K.; Trapp, F.B.; Cardoso-Dos-Santos, A.C.; Ribeiro, E.M.; et al. Genotype-phenotype studies in a large cohort of Brazilian patients with Hunter syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2021, 187, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xie, T.; Sheng, H.; Shao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, M.; Xu, A.; Su, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; et al. Genetic analysis of 63 Chinese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II: Functional characterization of seven novel IDS variants. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 491, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzano, N.; Villani, G.R.; Grosso, M.; Izzo, P.; Di Natale, P. Detection of four novel mutations in the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene. Mutations in brief no. 123. Online. Hum. Mutat. 1998, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Guo, X.-H.; Wraith, J.E.; Cooper, A.; Kleijer, W.J.; Bunge, S.; Hopwood, J.J. Novel Mutations in Sanfilippo a Syndrome: Implications for Enzyme function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, T.; Masuda, N.; Waragai, M.; Motoyoshi, Y.; Kurokawa, K.; Yuasa, T. An adult Japanese Sanfilippo A patient with novel compound heterozygous S347F and D444G mutations in the sulphamidase gene. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 777–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, P.; Villani, G.R.; Di Domenico, C.; Daniele, A.; Dionisi Vici, C.; Bartuli, A. Analysis of Sanfilippo A gene mutations in a large pedigree. Clin. Genet. 2003, 63, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, O.; Coppa, G.V.; Bruni, S.; Villani, G.R.; Pontarelli, G.; Di Natale, P. An adult Sanfilippo type A patient with homozygous mutation R206P in the sulfamidase gene. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2005, 133A, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, N.S.; Schreiber, K.; Pröpper, K.; Becker, S.; Usón, I.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Gärtner, J.; Krätzner, R.; Steinfeld, R. Structure of sulfamidase provides insight into the molecular pathology of mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarrubia, J.; Munoz, G.; Ciubotariu, C.; Dominguez-Ruiz, M.; Piris-Villaespesa, M.; Unceta, M.; Ceberio, L.; Church, H.; Norouzi, M.; Ross, M. Adult acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (Niemann-Pick disease type B): A difficult pathway to a diagnosis in 4 novel cases. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2022, 135, S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Hao, N.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, Z.; Mao, A.; Meng, W.; Liu, J. Long-read sequencing enables comprehensive molecular genetic diagnosis of Fabry disease. Hum. Genomics 2024, 18, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cognata, V.; Cavallaro, S. Detection of Structural Variants by NGS: Revealing Missing Alleles in Lysosomal Storage Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, M.; Bellettato, C.M.; Lampe, C.; Begley, D.J. Neuronopathic lysosomal storage disorders: Approaches to treat the central nervous system. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loret, A.; Jacob, C.; Mammou, S.; Bigot, A.; Blasco, H.; Audemard-Verger, A.; Schwartz, I.V.; Mulleman, D.; Maillot, F. Joint manifestations revealing inborn metabolic diseases in adults: A narrative review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridova, N.; Trajkova, S.; Chonevska, B.; Stojanoski, Z.; Ivanovski, M.; Popova-Labachevska, M.; Stojanovska-Jakimovska, S.; Filipche, V.; Sofijanova, A.; Panovska-Stavridis, I. Gaucher disease in North Macedonia: Unexpected prevalence of the N370S GBA1 allele with attenuated disease expression. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2022, 32, 100895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meikle, P.J.; Hopwood, J.J. Lysosomal storage disorders: Emerging therapeutic options require early diagnosis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2003, 162 (Suppl. S1), S34–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Belanger, E.C.; Veinot, J.P. Lysosomal storage disorders affecting the heart: A review. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2019, 39, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger-Plantinga, E.G.; Vanneste, J.A.; Groener, J.E.; van Schooneveld, M.J. Adult-onset dementia and retinitis pigmentosa due to mucopolysaccharidosis III-C in two sisters. J. Neurol. 2004, 251, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkley, S.U.; Vanier, M.T. Secondary lipid accumulation in lysosomal disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sornalingam, K.; Javed, A.; Aslam, T.; Sergouniotis, P.; Jones, S.; Ghosh, A.; Ashworth, J. Variability in the ocular phenotype in mucopolysaccharidosis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.H.; Kubaski, F.; Arno, G.; Phinney, W.; Wood, T.C.; Flanagan-Steet, H.; Pollard, L.M.; Steet, R. Functional assessment of IDUA variants of uncertain significance identified by newborn screening. NPJ Genom. Med. 2024, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

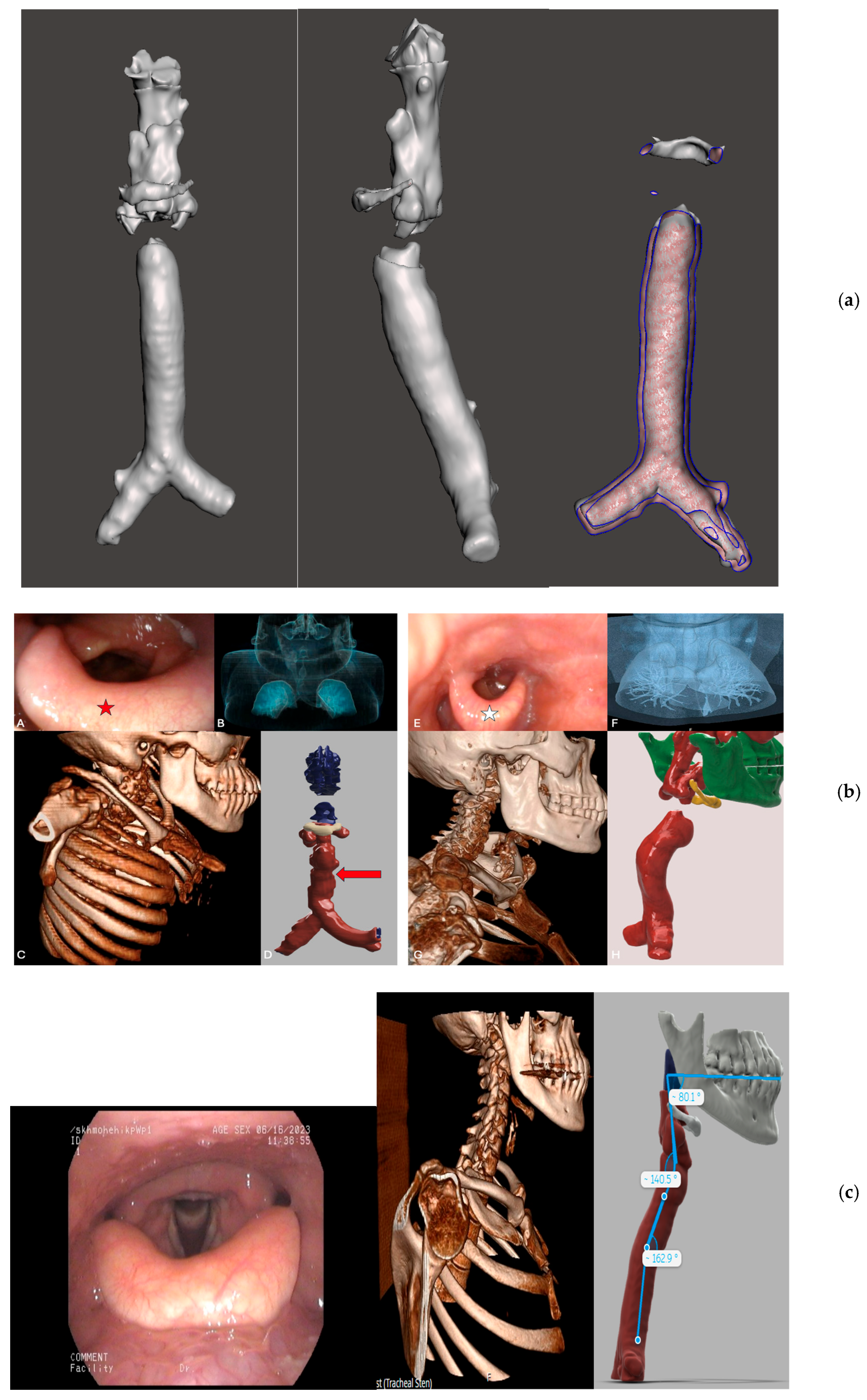
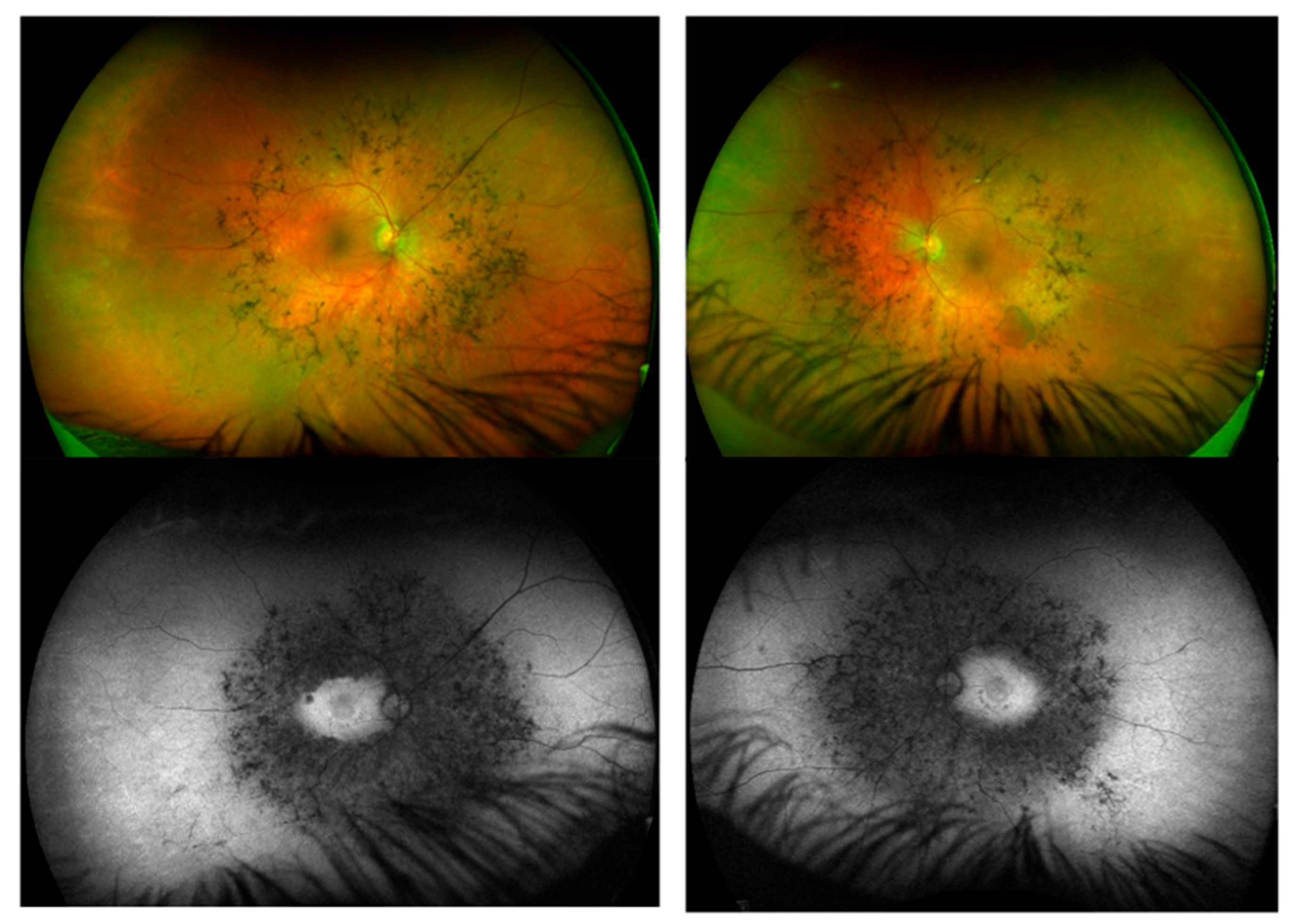
| LSD | Age at Onset of Symptoms | Age at Diagnosis/Gender | Ht (cm) | Wt (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | Enzyme Activity | Cardiovascular | Respiratory/ENT/Airways | Liver/Spleen/ Hernia | Orthopaedics | Neurology/ CNS/ID | Ophthalmology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPS I (Case 1) | 40s—vision impairment, gradual deterioration over time | 56/M | 177 | 84 | 26.9 | Alpha- iduronidase 0.3 nmol/mg/h (13.0–111.0) | ECG: LVH on voltage criteria | Chest infections + Right sensorineural deafness ++ PFTs N | USS: N | Changes in lumbar spine: ++ | No ID | RP ++ (pericentral subtype) Corneas clear |
| MPS II (Case 2) | 50s—hernia and AF | 52/M | 181 | 98 | 29.8 | Iduronate sulfatase 2 nmol/mL/4 h (494–1113) | ECG:AF ECHO: LVH, mild MR CMR: Focal myocardial fibrosis | ENT: Mild narrowing of right main bronchus Bilateral sensory neural hearing loss ++ PFTs N | No hepatosplenomegaly Left inguinal hernia repair in infancy and repeated in his 50s | Retrolisthesis of L2–L3 and L3 on L4 + Small central disc protrusion at C3/C4 + Multilevel loss of disc space height + Degenerative changes in right MTPJ + | No ID Carpal tunnel syndrome + Ulnar neuropathies + Bilateral C4 nerve root compression + | RP + |
| MPS IIIA (Case 3) | ID and hearing impairment since childhood | 40/M * | 179 | 73 | 22.8 | Sulfamidase 0.2 nmol/mg/17 h (3.2–20) | ECG: RBBB, LVH ECHO: N | Chest infections + Mild hearing impairment + Ear infections and grommets + adenoid removed in childhood | Hepatomegaly + | CTS + | ID + Lived independently until 42 yrs, communicative Sudden neurocognitive decline after that: Disturbed sleep, acute psychosis | RP ++ |
| MPS IVA (Case 4) | Childhood—skeletal deformities and pain | 8/M * | 133 | 46 | 26 | Galactose 6 sulfatase 0.3 nmol/20 h/mg (4–11) | ECG: Short PR ECHO: N | Conductive hearing impairment + ENT: Contracted nasopharynx, restricted neck extension, high anterior larynx, bulky supraglottis PFTs N | No | Thoracolumbar, spinal and chest deformities +++ Hip fracture Left tibia fracture Foot drop in the right. | No ID He is independent Bilateral weakness, not being able to walk 10 m in 2024 | None |
| MPS IVA (Case 5) | Adolescence—bone deformities and pain | 33/M * | 160 | 93 | 36.4 | Galactose 6 sulfatase 0.3 nmol/20 h/mg (4–11) | ECG: SR 101/min normal ECHO: N | ENT: Large tongue, small maxilla, large mandible, poor dentition, high anterior larynx, bulky supraglottis, short neck, restricted neck extension, short cervical spine, curved lower trachea, mild flattening of lower trachea | Splenomegaly and fatty liver + | Dysplastic hips and severe bilateral OA; bilateral OA changes in both knees; orthopaedic intervention of left hip at 11 y/o 2025: Mild degenerative changes in spine | No neurological impairments | None |
| MPS VI (Case 6) | Childhood—hip replacement and hearing impairment | 46/F | 147 | 54 | 25.2 | Arylsulfatase B 0.6 nmol/mg/h (7–108) | ECG: N ECHO: Severe AS, mitral thickening, mild mitral regurgitation | ENT: Adenoidectomy at 29 yr Crowded oropharynx, high anterior larynx, bulky epiglottis Short cervical spine, restricted neck extension Sensorineural hearing | None | Right hip replacement Maxillary slightly hypoplastic | Poor memory, no other cognitive impairment; mild syrinx at C7 no gross cord signal abnormalities; possible Chiari I malformation. | None |
| Alpha -mannosidosis (Case 7) | Childhood—ID and hearing impairment since age of 3 | 31/F * | 148 | 68 | 30.6 | 2 nmol/h/h (20–100) | ECG: N ECHO: Mild AS, mitral thickening | ENT: Bulky tonsils almost occluding oropharynx; supraglottis moderately bulky Small epiglottis High anterior larynx, mild flattening and curved trachea; restricted neck extension Sensorineural hearing problems | None | CTS: ++ L hip AO Bilateral Genu valgum | Moderate ID Speech impairment; broad-based ataxic gait pattern | Likely retinal changes |
| Beta -mannosidosis (Case 8) | Childhood—ID | 30/F * | 163 | 64 | 24.1 | Leucocyte beta-mannosidase 2 nmol/mL/h (150–1500) | ECG: Short PR interval, RBBB ECHO: Moderate aortic and tricuspid regurgitation | Coarse facial features + Sensorineural hearing loss ++ | None | DEXA: Normal bone density | Moderate ID Tremor in upper limbs; Ataxia MRI: Normal | N/A |
| Krabbe disease (Case 9) | 30s—tendency to fall 55—difficulty walking | 55/M * | 171 | 95 kg | 32.1 | GALC 0.03 nmol/mg/h [0.4–4] | ECG: N | N/A | Umbilical hernia | No | Acroparesthesia Ataxia Brisk reflexes with bilateral clonus; Babinsky + bilateral. no saddle paraesthesia or anal sphincter dysfunction MRI: Signal changes in corticospinal tracts and symmetrical parietal white matter high signal intensities on FLAIR images NCS: Consistent with chronic L5 radiculopathy | None |
| Multiple sulfatases (Case 10) | 40s—progression of vision impairment | 52/F * | 165 | 73 | 25 | Several Arylsulfatase Alpha reduced ++ Heparin sulfamidase reduced + | ECG: ECHO: LVH, grade 1 diastolic dysfunction | None | Mild fatty liver and gallstones | None | No ID MRI: Non-specific white matter changes | Bilateral retinal dystrophy; Fuch’s corneal endothelial dystrophy Glaucoma |
| LSD | Gene | Molecular | Type | Protein Change | Classification | Inheritance Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPS I (Case 1) | IDUA | c.794G>A p and c.1205 G>A | Missense and Missense | p.(Gly265Asp) and p.(Trp402Ter) | Pathogenic and Pathogenic | Compound Heterozygous |
| MPS II (Case 2) | IDS | c.817C>T | Missense | p.(Arg273Trp) | Pathogenic | Homozygous |
| MPS IIIA (Case 3) | SGSH | c.1063G>A and c.220C>T | Missense and Missense | p.(Glu355Lys) and p.(Arg74Cys) | Pathogenic and Pathogenic | Compound Heterozygous |
| MPS IVA (Case 4) | GALNS | c.331C>T and N/A | Missense | p.(Gln111Ter) and p.(Ala241Ala) | Pathogenic Likely Pathogenic | Compound Heterozygous |
| MPS IVA (Case 5) | GALNS | c.604del and c.143T>G | Stop Codon and Missense | p.(Glu202LysfsTer117) and p.(Val48Gly) | Pathogenic and Likely Pathogenic | Compound Heterozygous |
| MPS VI (Case 6) | ARSB | c.629A>G and c.936G>T | Missense and Missense | p.(Tyr210Cys) and p.(Trp312Cys) | Likely Pathogenic and Likely Pathogenic | Compound Heterozygous |
| Alpha -mannosidosis (Case 7) | MAN2B1 | c.1388_1389del and c.2426T>C | Frameshift and Missense | p.(Arg463Profs53) and p.(Leu809Pro) | Pathogenic and Likely Pathogenic | Compound Heterozygous |
| Beta -mannosidosis (Case 8) | MANBA | c.1452_1453del and c.1753C>T | Frameshift and Stop Codon | p.(Tyr485CysfsTer27) and p.(Arg585Ter) | Pathogenic and Pathogenic | Compound Heterozygous |
| Krabbe disease (Case 9) | GALC | c.326C>T and c.391T>C | Missense and Missense | p.(Thr109Ile) and p.(Trp131Arg) | Pathogenic and Pathogenic | Compound Heterozygous |
| Multiple sulfatases (Case 10) | SUMF1 | c.866A>G | Missense | p.(Tyr289Cys) | Likely Pathogenic | Homozygous |
| LSD | Early-Onset (Classical) Presentation | Late-Onset (Attenuated) Presentation |
|---|---|---|
| MPS I | Coarse facial features, developmental delay, skeletal dysplasia, corneal clouding | Isolated retinal dystrophy, mild LVH, clear corneas, normal cognition |
| MPS II | Hepatosplenomegaly, cognitive decline, skeletal deformities, coarse facies | Cardiac fibrosis, atrial fibrillation, mild airway and joint changes |
| MPS IIIA | Severe neurodegeneration, behavioural disturbance, early cognitive loss | Late-onset psychosis, progressive cognitive decline after stable adult life |
| MPS IVA | Skeletal dysplasia, growth delay, short stature, joint stiffness | Orthopaedic issues, curved trachea, ENT abnormalities, preserved intellect |
| MPS VI | Joint contractures, coarse facial features, airway abnormalities, hepatosplenomegaly | Severe aortic stenosis, sensorineural hearing loss, Chiari I malformation |
| Alpha-mannosidosis | Intellectual disability, recurrent infections, hearing loss, skeletal abnormalities | Moderate intellectual disability, speech impairment, broad-based gait, airway abnormalities |
| Beta-mannosidosis | Intellectual disability, coarse features, hypotonia, seizures | Tremor, ataxia, moderate intellectual disability |
| Krabbe Disease | Developmental regression, irritability, spasticity, early death | Adult-onset spastic paraparesis, white matter changes |
| Multiple Sulfatase Deficiency | Developmental delay, ichthyosis, multisystem involvement | Retinal dystrophy, glaucoma, nonspecific brain imaging findings |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urizar, E.; McCarron, E.P.; Gadepalli, C.; Bentley, A.; Woolfson, P.; Lin, S.; Iosifidis, C.; Browning, A.C.; Bassett, J.; Senarathne, U.D.; et al. Genetic Insights and Diagnostic Challenges in Highly Attenuated Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Genes 2025, 16, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080915
Urizar E, McCarron EP, Gadepalli C, Bentley A, Woolfson P, Lin S, Iosifidis C, Browning AC, Bassett J, Senarathne UD, et al. Genetic Insights and Diagnostic Challenges in Highly Attenuated Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Genes. 2025; 16(8):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080915
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrizar, Elena, Eamon P. McCarron, Chaitanya Gadepalli, Andrew Bentley, Peter Woolfson, Siying Lin, Christos Iosifidis, Andrew C. Browning, John Bassett, Udara D. Senarathne, and et al. 2025. "Genetic Insights and Diagnostic Challenges in Highly Attenuated Lysosomal Storage Disorders" Genes 16, no. 8: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080915
APA StyleUrizar, E., McCarron, E. P., Gadepalli, C., Bentley, A., Woolfson, P., Lin, S., Iosifidis, C., Browning, A. C., Bassett, J., Senarathne, U. D., Indika, N.-L. R., Church, H. J., Cooper, J. A., Menendez Lorenzo, J., Farrugia, M. E., Jones, S. A., Black, G. C., & Stepien, K. M. (2025). Genetic Insights and Diagnostic Challenges in Highly Attenuated Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Genes, 16(8), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080915








