Identification and Computational Analysis of Rare Variants of Known Hearing Loss Genes Present in Five Deaf Members of a Pakistani Kindred
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement and Clinical Evaluation
2.2. Whole Exome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analyses
2.3. Structural Modeling
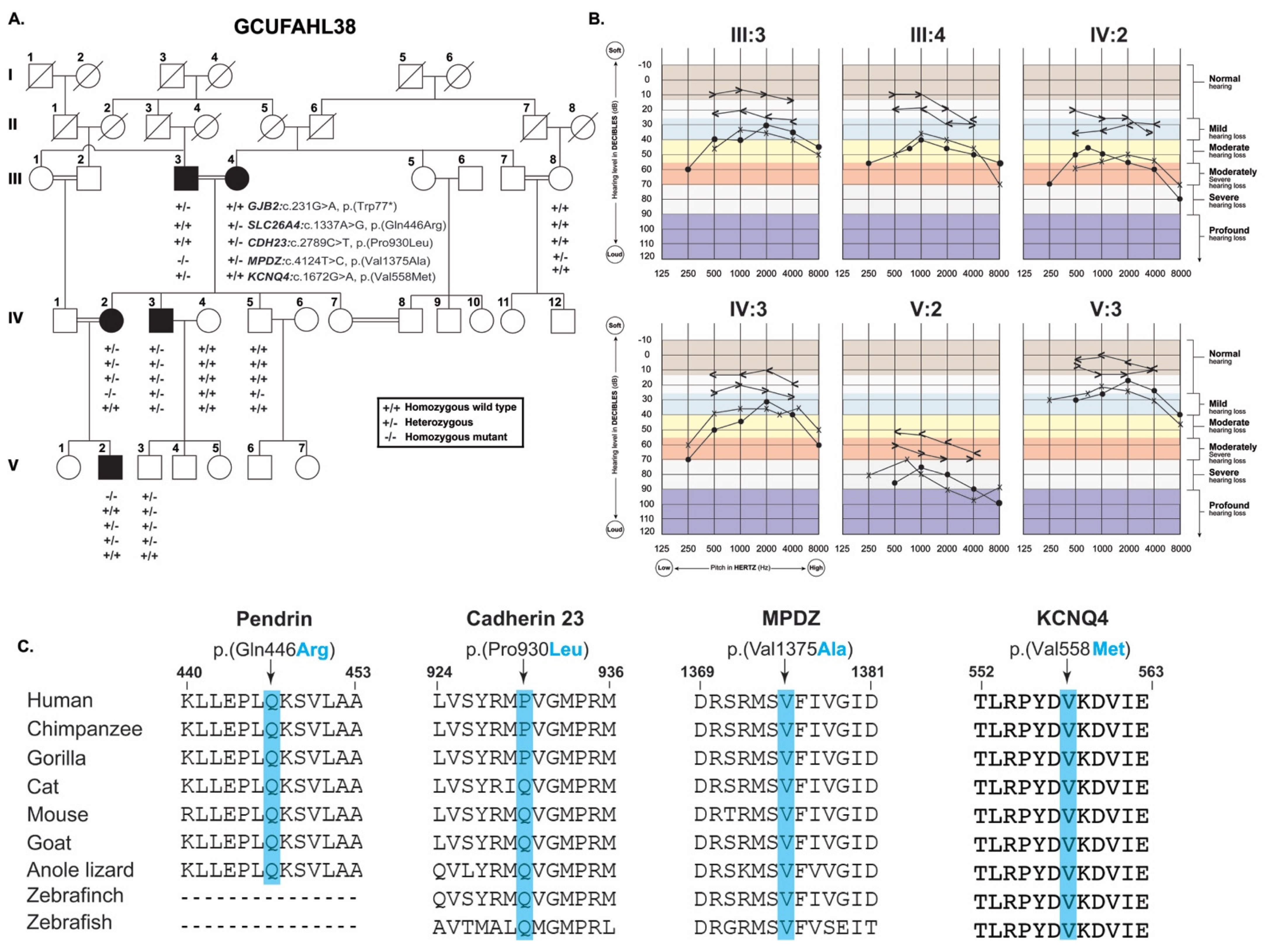
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Presentation
3.2. Genetic Analysis
3.3. Protein Secondary Structure Modeling
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mittal, R.; Patel, A.P.; Nguyen, D.; Pan, D.R.; Jhaveri, V.M.; Rudman, J.R.; Dharmaraja, A.; Yan, D.; Feng, Y.; Chapagain, P. Genetic basis of hearing loss in Spanish, Hispanic and Latino populations. Gene 2018, 647, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Addressing the Rising Prevalence of Hearing Loss; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liaqat, K.; Schrauwen, I.; Raza, S.I.; Lee, K.; Hussain, S.; Chakchouk, I.; Nasir, A.; Acharya, A.; Abbe, I.; Umair, M.; et al. Identification of CACNA1D variants associated with sinoatrial node dysfunction and deafness in additional Pakistani families reveals a clinical significance. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 64, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Peng, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, A.; Lu, Y. Association between the p. V37I variant of GJB2 and hearing loss: A pedigree and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schrauwen, I.; Chakchouk, I.; Acharya, A.; Liaqat, K.; Nickerson, D.A.; Bamshad, M.J.; Shah, K.; Ahmad, W.; Leal, S.M. Novel digenic inheritance of PCDH15 and USH1G underlies profound non-syndromic hearing impairment. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, S.; Lin, X.; Liu, X.Z. Genetics of hearing and deafness. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2012, 295, 1812–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rehman, A.U.; Santos-Cortez, R.L.; Drummond, M.C.; Shahzad, M.; Lee, K.; Morell, R.J.; Ansar, M.; Jan, A.; Wang, X.; Aziz, A.; et al. Challenges and solutions for gene identification in the presence of familial locus heterogeneity. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noman, M.; Ishaq, R.; Bukhari, S.A.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Riazuddin, S. Delineation of homozygous variants associated with Prelingual Sensorineural hearing loss in Pakistani families. Genes 2019, 10, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubisch, C.; Schroeder, B.C.; Friedrich, T.; Lutjohann, B.; El-Amraoui, A.; Marlin, S.; Petit, C.; Jentsch, T.J. KCNQ4, a novel potassium channel expressed in sensory outer hair cells, is mutated in dominant deafness. Cell 1999, 96, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, H.Y.; Alipanahi, B.; Lee, L.J.; Bretschneider, H.; Merico, D.; Yuen, R.K.; Hua, Y.; Gueroussov, S.; Najafabadi, H.S.; Hughes, T.R.; et al. RNA splicing. The human splicing code reveals new insights into the genetic determinants of disease. Science 2015, 347, 1254806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavithra, A.; Jeffrey, J.M.; Chandru, J.; Ramesh, A.; Srisailapathy, C.R. High incidence of GJB2 gene mutations among assortatively mating hearing impaired families in Kerala: Future implications. J. Genet. 2014, 93, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleha, S.; Ajmal, M.; Jamil, M.; Nasir, M.; Hameed, A. In silico analysis of a disease-causing mutation in PCDH15 gene in a consanguineous Pakistani family with Usher phenotype. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 9, 662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azaiez, H.; Booth, K.T.; Ephraim, S.S.; Crone, B.; Black-Ziegelbein, E.A.; Marini, R.J.; Shearer, A.E.; Sloan-Heggen, C.M.; Kolbe, D.; Casavant, T.; et al. Genomic landscape and mutational signatures of deafness-associated genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oza, A.M.; DiStefano, M.T.; Hemphill, S.E.; Cushman, B.J.; Grant, A.R.; Siegert, R.K.; Shen, J.; Chapin, A.; Boczek, N.J.; Schimmenti, L.A.; et al. Expert specification of the ACMG/AMP variant interpretation guidelines for genetic hearing loss. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 1593–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venselaar, H.; Te Beek, T.A.; Kuipers, R.K.; Hekkelman, M.L.; Vriend, G. Protein structure analysis of mutations causing inheritable diseases. An e-Science approach with life scientist friendly interfaces. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadi, A.; Aghaei, S.; Amiri, B.; Hashemzadeh-Chaleshtori, M. An update of spectrum and frequency of GJB2 mutations causing hearing loss in the south of Iran: A literature review. Int. J. Pediatric Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 119, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, E.M.; Santos-Cortez, R.L.P.; Faridi, R.; Rehman, A.U.; Lee, K.; Shahzad, M.; Acharya, A.; Khan, A.A.; Imtiaz, A.; Chakchouk, I. Global genetic insight contributed by consanguineous Pakistani families segregating hearing loss. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erickson, T.; Pacentine, I.V.; Venuto, A.; Clemens, R.; Nicolson, T. The lhfpl5 ohnologs lhfpl5a and lhfpl5b are required for mechanotransduction in distinct populations of sensory hair cells in zebrafish. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 12, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bharadwaj, T.; Schrauwen, I.; Rehman, S.; Liaqat, K.; Acharya, A.; Giese, A.P.J.; Nouel-Saied, L.M.; Nasir, A.; Everard, J.L.; Pollock, L.M.; et al. ADAMTS1, MPDZ, MVD, and SEZ6: Candidate genes for autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarysta, A.; Tarchini, B. Multiple PDZ domain protein maintains patterning of the apical cytoskeleton in sensory hair cells. bioRxiv 2021, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, R.; Sebai, M.A.; Patel, N.; Ewida, N.; Kurdi, W.; Altweijri, I.; Sogaty, S.; Almardawi, E.; Seidahmed, M.Z.; Alnemri, A. The genetic landscape of familial congenital hydrocephalus. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eyken, E.; Van Laer, L.; Fransen, E.; Topsakal, V.; Lemkens, N.; Laureys, W.; Nelissen, N.; Vandevelde, A.; Wienker, T.; Van De Heyning, P.; et al. KCNQ4: A gene for age-related hearing impairment? Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, Z.; Xu, K.; Huang, X.; Long, S.; Wu, M.; McManus, O.B.; Le Engers, J.; Mattmann, M.E.; Engers, D.W.; et al. Identification of a novel, small molecule activator of KCNQ1 channels. In Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich, M.; Lechner, S.G.; Vardanyan, V.; Wetzel, C.; Cremers, C.W.; De Leenheer, E.M.; Aranguez, G.; Moreno-Pelayo, M.A.; Jentsch, T.J.; Lewin, G.R. KCNQ4 K+ channels tune mechanoreceptors for normal touch sensation in mouse and man. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 15, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Lin, H.; Koh, Y.I.; Ryu, K.; Lee, J.S.; Rim, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Yu, S.; et al. Rare KCNQ4 variants found in public databases underlie impaired channel activity that may contribute to hearing impairment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walls, W.D.; Moteki, H.; Thomas, T.R.; Nishio, S.Y.; Yoshimura, H.; Iwasa, Y.; Frees, K.L.; Nishimura, C.J.; Azaiez, H.; Booth, K.T.; et al. A comparative analysis of genetic hearing loss phenotypes in European/American and Japanese populations. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Subject | III:3 | III:4 | IV:3 | IV:2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | M | F | M | F | |
| Age (years) | 86 | 85 | 45 | 50 | |
| Ethnicity | Punjab | ||||
| Status | Affected | Affected | Affected | Affected | |
| Comorbidity | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | |
| Hearing loss | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Thyroid profile | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | |
| Lipid profile | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | |
| Blood coagulation profile | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | |
| Cardiac enzymes profile | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | |
| Visual acuity | Right | 6/8 | 6/8 | 6/6 | 6/6 |
| Left | 6/9 | 6/6 | 6/6 | 6/6 | |
| Family | GCUFAHL38 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | GJB2 | SLC26A4 | CDH23 | MPDZ | KCNQ4 |
| Transcript ID | NM_004004.6 | NM_000441.2 | NM_022124.6 | NM_001378778 | NM_004700.4 |
| cDNA change | c.231G>A | c.1337A>G | c.2789C>T | c.4124T>C | c.1672G>A |
| Amino acid change | p.(Trp77 *) | p.(Gln446Arg) | p.(Pro930Leu) | p.(Val1375Ala) | p.(Val558Met) |
| gnomAD | 0.0001392 | 0.00007578 | 0.00006791 | 0.00002410 | 0.00001193 |
| ACMG (criteria used) | M1: Pathogenic (PVS1, PP5, PM2, PP3) | M2: Likely pathogenic (PS1, PS4, PM2, PM3, PP3) | M3: Unknown significance (PM1, PM2, BP4) | M3: Unknown significance (PP1, PM2, PM3, PP3, BP1) | M3: Unknown significance (PM1, PM2, PP3) |
| CADD | 39 | 26 | 21 | 33 | 28 |
| DANN | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| MutationTaster | Disease causing | Disease causing | Disease causing | Disease causing | Disease causing |
| FATHMM-MKL | Damaging | Damaging | Damaging | Damaging | Damaging |
| LRT | Deleterious | Deleterious | Deleterious | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| EIGEN PC | Pathogenic | Pathogenic | Benign | Pathogenic | Pathogenic |
| SIFT | NA | Tolerated | Tolerated | Damaging | Damaging |
| MutPred | NA | Pathogenic | Pathogenic | Pathogenic | Pathogenic |
| Provean | NA | Damaging | NA | Damaging | Damaging |
| GERP | 5.32 | 5.92 | 5.5 | 5.71 | 5.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleem, I.B.; Masoud, M.S.; Qasim, M.; Ali, M.; Ahmed, Z.M. Identification and Computational Analysis of Rare Variants of Known Hearing Loss Genes Present in Five Deaf Members of a Pakistani Kindred. Genes 2021, 12, 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121940
Saleem IB, Masoud MS, Qasim M, Ali M, Ahmed ZM. Identification and Computational Analysis of Rare Variants of Known Hearing Loss Genes Present in Five Deaf Members of a Pakistani Kindred. Genes. 2021; 12(12):1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121940
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleem, Irum Badshah, Muhammad Shareef Masoud, Muhammad Qasim, Muhammad Ali, and Zubair M. Ahmed. 2021. "Identification and Computational Analysis of Rare Variants of Known Hearing Loss Genes Present in Five Deaf Members of a Pakistani Kindred" Genes 12, no. 12: 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121940
APA StyleSaleem, I. B., Masoud, M. S., Qasim, M., Ali, M., & Ahmed, Z. M. (2021). Identification and Computational Analysis of Rare Variants of Known Hearing Loss Genes Present in Five Deaf Members of a Pakistani Kindred. Genes, 12(12), 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121940







