MicroRNA-1258 Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells through Suppressing CKS1B Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Gene Expression Analysis
2.3. Protein Expression
2.4. Transfection of miR-1258 Mimic, miR-1258 Inhibitor, Stable miR-1258 Expression Vector and CKS1B siRNA
2.5. Cell Proliferation and Migration Assays
2.6. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.7. Xenograft Mouse Model
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
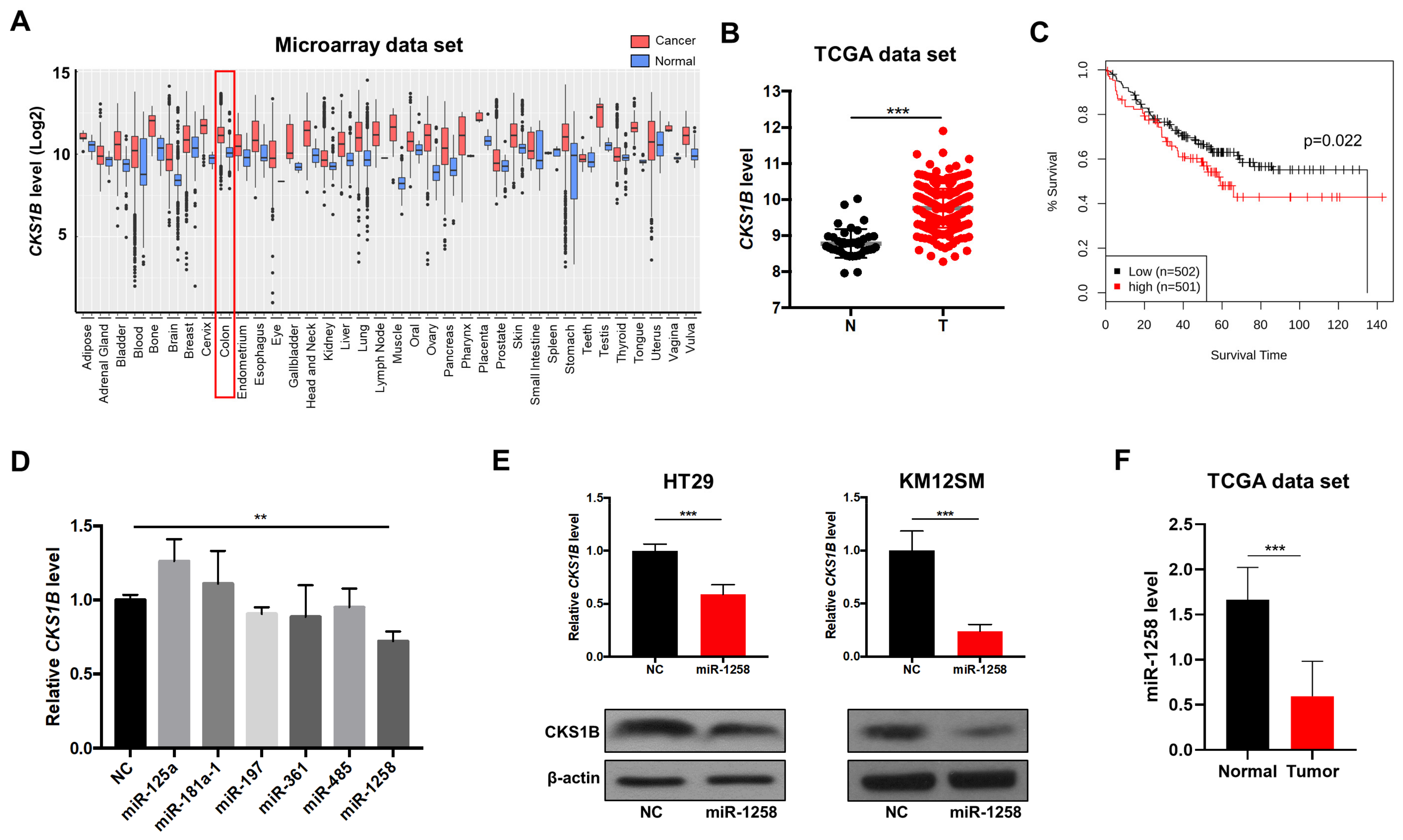
3.1. miR-1258 Negatively Regulates CKS1B Expression, Which Is Highly Upregulated in CRC Tumor Tissues
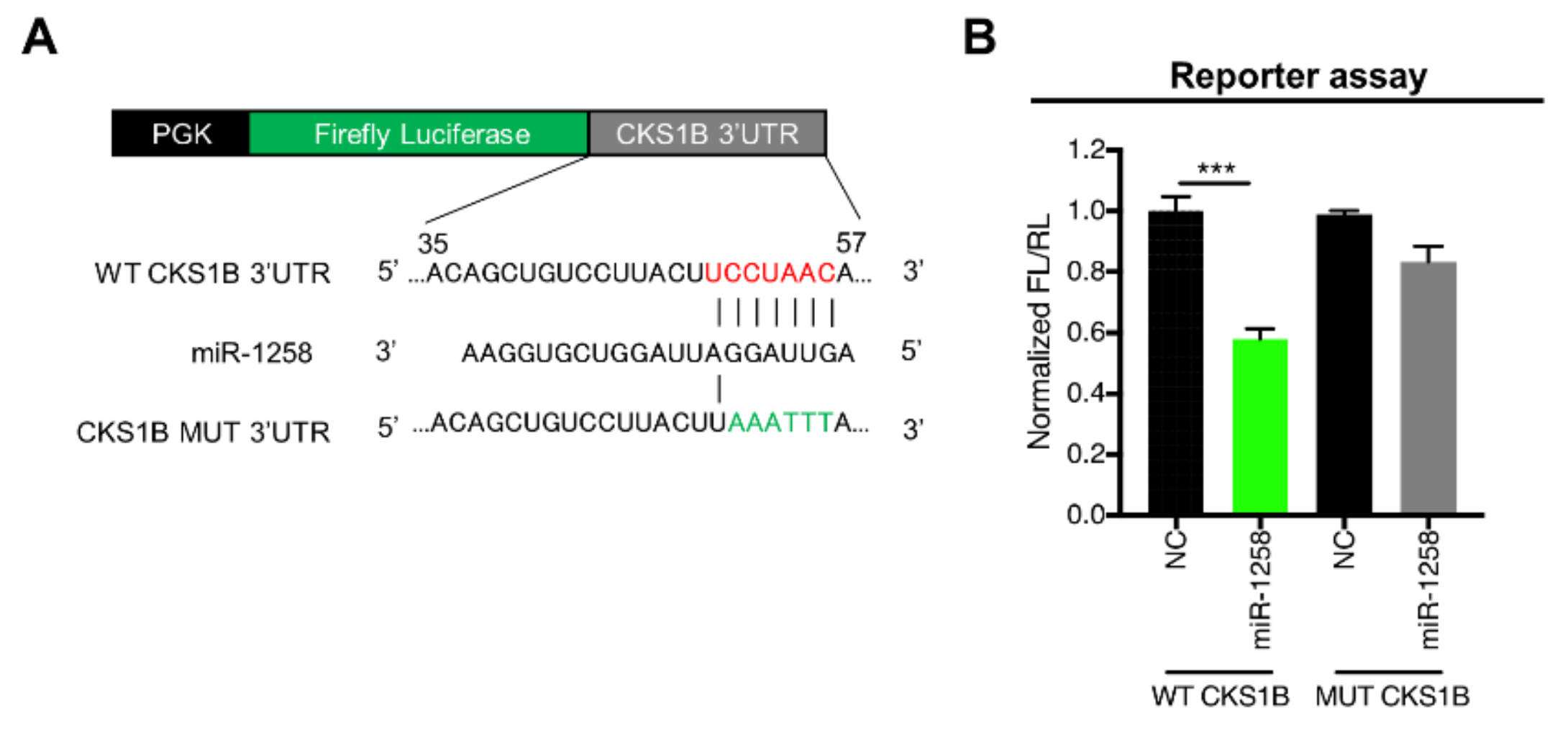
3.2. CKS1B Is Directly Regulated by miR-1258
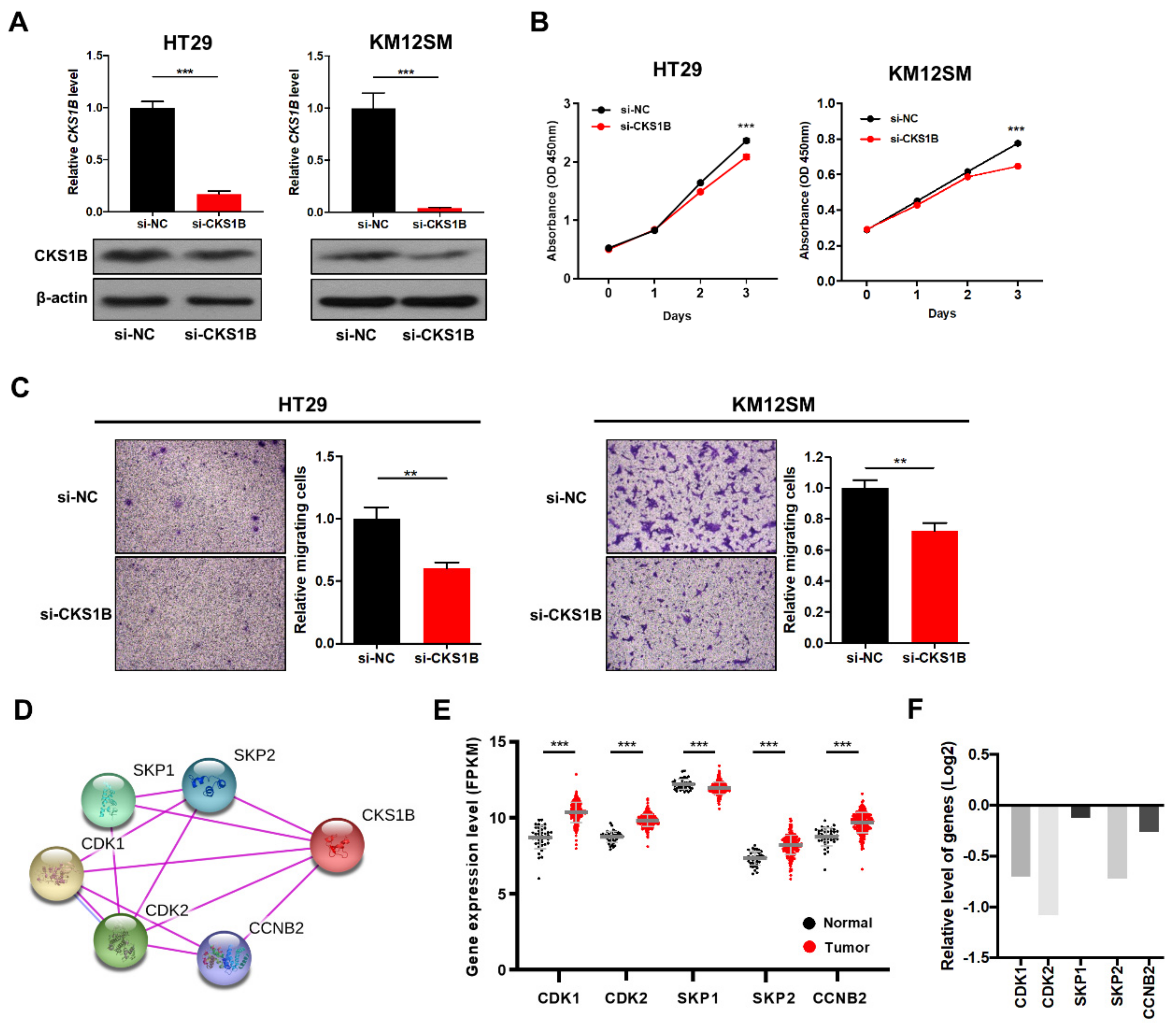
3.3. miR-1258 Inhibited Cell Proliferation, Motility and Tumorigenicity
3.4. CKS1B Knockdown Suppressed CRC Cell Proliferation and Migration
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luebeck, E.G.; Moolgavkar, S.H. Multistage carcinogenesis and the incidence of colorectal cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15095–15100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, W.A.; Swaika, A.; Mody, K. Pharmacologic resistance in colorectal cancer: A review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 8, 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayles, J.; Beach, D.; Durkacz, B.; Nurse, P. The fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2: Isolation of a sequence suc1 that suppresses cdc2 mutant function. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1986, 202, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.K.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, Y. Cell-cycle regulator Cks1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by supporting NF-kappaB-dependent expression of interleukin-8. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6827–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganoth, D.; Bornstein, G.; Ko, T.K.; Larsen, B.; Tyers, M.; Pagano, M.; Hershko, A. The cell-cycle regulatory protein Cks1 is required for SCF (Skp2)-mediated ubiquitinylation of p27. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruck, C.; Strohmaier, H.; Watson, M.; Smith, A.P.; Ryan, A.; Krek, T.W.; Reed, S.I. A CDK-independent function of mammalian Cks1: Targeting of SCF (Skp2) to the CDK inhibitor p27Kip1. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, F.; Colla, S.; Wu, X.; Chen, B.; Stewart, J.P.; Kuehl, W.M.; Barlogie, B.; Shaughnessy, J.D., Jr. CKS1B, overexpressed in aggressive disease, regulates multiple myeloma growth and survival through SKP2- and p27Kip1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Blood 2007, 109, 4995–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.S.; Jeong, E.J.; Seok, H.J.; Kim, S.K.; Hwang, J.S.; Choi, M.L.; Jo, D.G.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. Cks1 regulates human hepatocellular carcinoma cell progression through osteopontin expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 508, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doma, M.K.; Parker, R. Endonucleolytic cleavage of eukaryotic mRNAs with stalls in translation elongation. Nature 2006, 440, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, N.C.; Lim, L.P.; Weinstein, E.G.; Bartel, D.P. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 2001, 294, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 2001, 294, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.S.; Hur, K.; Xu, G.; Choi, B.; Okugawa, Y.; Toiyama, Y.; Oshima, H.; Oshima, M.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, V.N.; et al. MicroRNA-29c mediates initiation of gastric carcinogenesis by directly targeting ITGB1. Gut 2015, 64, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.X.; Wu, Q.N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Liao, D.Z.; Hou, J.H.; Fu, J.; Zeng, M.S.; Yun, J.P.; Wu, Q.L.; et al. Knockdown of miR-21 in human breast cancer cell lines inhibits proliferation, in vitro migration and in vivo tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujambio, A.; Calin, G.A.; Villanueva, A.; Ropero, S.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M.; Blanco, D.; Montuenga, L.M.; Rossi, S.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Faller, W.J.; et al. A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13556–13561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.S.; Ban, H.S.; Hur, K.; Cho, H.S. The Epigenetic Regulation of HCC Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.S.; Voon, D.C.; Oshima, H.; Nakayama, M.; Echizen, K.; Sakai, E.; Yong, Z.W.E.; Murakami, K.; Yu, L.; Minamoto, T.; et al. Interleukin 1 Upregulates MicroRNA 135b to Promote Inflammation-associated Gastric Carcinogenesis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, M. Cyclin-dependent kinases. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warfel, N.A.; Dolloff, N.G.; Dicker, D.T.; Malysz, J.; El-Deiry, W.S. CDK1 stabilizes HIF-1alpha via direct phosphorylation of Ser668 to promote tumor growth. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3689–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurikar, N.; Thompson, R.; Montano, R.; Eastman, A. A subset of cancer cell lines is acutely sensitive to the Chk1 inhibitor MK-8776 as monotherapy due to CDK2 activation in S phase. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 1380–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubbar, E.; Kovacs, A.; Hajizadeh, S.; Parris, T.Z.; Nemes, S.; Gunnarsdottir, K.; Einbeigi, Z.; Karlsson, P.; Helou, K. Elevated cyclin B2 expression in invasive breast carcinoma is associated with unfavorable clinical outcome. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yin, Y.; Cai, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, G.; Ba, Y.; et al. Role of miR-143 targeting KRAS in colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2009, 28, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, C. MiR-21 regulates biological behavior through the PTEN/PI-3 K/Akt signaling pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, R.; le Sage, C.; Diosdado, B.; van der Waal, M.; Oude Vrielink, J.A.; Bolijn, A.; Meijer, G.A.; Agami, R. Regulation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene by the miR-135 family in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chen, P.; Sun, J.; Song, Y.; Ma, B.; Gao, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. MicroRNA-1258: An invasion and metastasis regulator that targets heparanase in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3739–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Kangping, L.; Song, Y.; Zhao, L.; Kang, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, S. The expression and clinical significance of microRNA-1258 and heparanase in human breast cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sullivan, P.S.; Goodman, J.C.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Marchetti, D. MicroRNA-1258 suppresses breast cancer brain metastasis by targeting heparanase. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Gao, W.; Jiang, G. The expression of heparanase and microRNA-1258 in human non-small cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 2012, 33, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Yagishita, S.; Hagiwara, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Takeshita, F.; Fujiwara, T.; Tsuta, K.; Nokihara, H.; Tamura, T.; et al. The clinical relevance of the miR-197/CKS1B/STAT3-mediated PD-L1 network in chemoresistant non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Yang, C.D.; Hong, H.C.; Chou, C.H.; Tai, C.S.; Chiew, M.Y.; Chen, W.L.; Weng, S.L.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, Y.A.; et al. Integrated MicroRNA-mRNA Analysis Reveals miR-204 Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Gastric Cancer by Targeting CKS1B, CXCL1 and GPRC5A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ferreira, J.; Ramalho-Carvalho, J.; Gomez, A.; Menezes, F.D.; Freitas, R.; Oliveira, J.; Antunes, L.; Bento, M.J.; Esteller, M.; Henrique, R.; et al. MiR-193b promoter methylation accurately detects prostate cancer in urine sediments and miR-34b/c or miR-129-2 promoter methylation define subsets of clinically aggressive tumors. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, E.A.; Loginov, V.I.; Burdennyi, A.M.; Filippova, E.A.; Pronina, I.V.; Kurevlev, S.V.; Kazubskaya, T.P.; Kushlinskii, D.N.; Utkin, D.O.; Ermilova, V.D.; et al. Five Hypermethylated MicroRNA Genes as Potential Markers of Ovarian Cancer. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 164, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Kao, S.C.; Pavlakis, N.; Brahmbhatt, H.; MacDiarmid, J.; Clarke, S.; Boyer, M.; van Zandwijk, N. Clinical development of TargomiRs, a miRNA mimic-based treatment for patients with recurrent thoracic cancer. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primers | Sequences (5′–3′) | Restriction Enzyme | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CKS1B | Forward | TATTCGGACAAATACGACGACG | |
| Reverse | CGCCAAGATTCCTCCATTCAGA | ||
| GAPDH | Forward | CTCTGCTCCTCCTGTTCGAC | |
| Reverse | TTAAAAGCAGCCCTGGTGAC | ||
| miR-1258 cloning primer | Forward | AAAGAGCTCGAGCGTGAGCAACAGCTTC | SacI |
| Reverse | AAGGTACCGGGACCTTCTCTCTGCTCCT | KpnI | |
| CKS1B WT 3′-UTR | Forward | AGCTTTACACAGCTGTCCTTACTTCCTAACATCTT | SacI |
| Reverse | TCGAAAGATGTTAGGAAGTAAGGACAGCTGTGTAAAGCTAGCT | XhoI | |
| CKS1B MUT 3′-UTR | Forward | AGCTTTACACAGCTGTCCTTACTTAAATTTATCTT | SacI |
| Reverse | TCGAAAGATAAATTTAAGTAAGGACAGCTGTGTAAAGCTAGCT | XhoI |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, J.-S.; Jeong, E.-J.; Choi, J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Jung, E.; Kim, S.-K.; Min, J.-K.; Han, T.-S.; Kim, J.-S. MicroRNA-1258 Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells through Suppressing CKS1B Expression. Genes 2019, 10, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110912
Hwang J-S, Jeong E-J, Choi J, Lee Y-J, Jung E, Kim S-K, Min J-K, Han T-S, Kim J-S. MicroRNA-1258 Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells through Suppressing CKS1B Expression. Genes. 2019; 10(11):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110912
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Jin-Seong, Eun-Jeong Jeong, Jinhyeon Choi, Yeo-Jin Lee, Eunsun Jung, Seon-Kyu Kim, Jeong-Ki Min, Tae-Su Han, and Jang-Seong Kim. 2019. "MicroRNA-1258 Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells through Suppressing CKS1B Expression" Genes 10, no. 11: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110912
APA StyleHwang, J.-S., Jeong, E.-J., Choi, J., Lee, Y.-J., Jung, E., Kim, S.-K., Min, J.-K., Han, T.-S., & Kim, J.-S. (2019). MicroRNA-1258 Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells through Suppressing CKS1B Expression. Genes, 10(11), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110912




