Determination of Suitable RT-qPCR Reference Genes for Studies of Gene Functions in Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing and Virus Acquisition
2.2. Preparation of Insect Samples for RT-qPCR
- (1)
- L. striatellus at different developmental stages: Embryos (24 h post laying), second instar nymphs, fifth instar nymphs, and adult L. striatellus were collected. Approximately 50 individual insects at a specific developmental stage were collected for the assay and each treatment included three biological replicates.
- (2)
- Different insect tissues: Head, cuticle, midgut, and fat body from RBSDV-V and RBSDV-NV third instar L. striatellus were collected using a fine-pointed tweezer (Dumont, Switzerland). Insects were immerged in the 1× PBS (pH 7.2), and tissues were collected under stereo microscope. RBSDV-V L. striatellus used for tissue collection was prepared by allowing second instar L. striatellus nymphs to feed on RBSDV-infected rice seedlings for 7 days, and then on healthy rice seedlings for 7 days. This experiment was repeated three times and in each experiment around 200 insects were used.
- (3)
- RBSDV-V L. striatellus was prepared by allowing second instar L. striatellus nymphs to feed on RBSDV-infected rice seedlings for 2 days. The insects were then allowed to feed on healthy rice seedlings for 7, 14, and 21 days, respectively. Insects at the same developmental stage reared on healthy rice seedlings were used as controls. Progenies of RSV-V or RSV-NV L. striatellus were collected and used as the RSV-V or RSV-NV samples for the assays. The presence of RBSDV or RSV in viruliferous L. striatellus was confirmed by RT-PCR using RBSDV P10- or RSV CP-specific primers prior to sampling (Table S1). For each treatment, three groups with 50 insects each were used.
- (4)
- Lssynaptojanin 1 (LsSYNJ1)-silenced and RBSDV-V L. striatellus was prepared for reference gene analysis, and the Lssynaptojanin 1 (LsSYNJ1)-silenced insect was used as control. A fragment (654 bp) representing a partial sequence of LsSYNJ1 was RT-PCR amplified using specific primers (Table S1). A similar-sized fragment representing a partial sequence of GFP gene was also amplified. The two fragments were cloned individually into the pMD18-T vector (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) and sequenced. dsRNA from the two vectors was synthesized using the Transcript Aid T7 High Yield Transcription kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The resulting dsRNA was injected into third instar nymphs (100 ng per nymph) using a FemtoJet express instrument (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). Efficiency of LsSYNJ1 silencing was determined by RT-qPCR at 3 days post injection. After analysing the knockdown efficiency of LsSYNJ1, the dsRNA-injected insects were divided into two groups. One group fed on RBSDV-infected rice seedlings for 2 days to acquire virus and then fed on healthy rice seedlings for another 2 days. Another group was grown on healthy rice seedlings for 4 days, and then used for analyses of reference gene expression. Approximately 30 insects were collected as a group, and three replications were applied for each treatment. The experiment was repeated three times.
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.4. Primer Design
2.5. Quantitative PCR
2.6. Analyses of Candidate Gene Expression
2.7. Validation of Candidate Gene Expression
3. Results
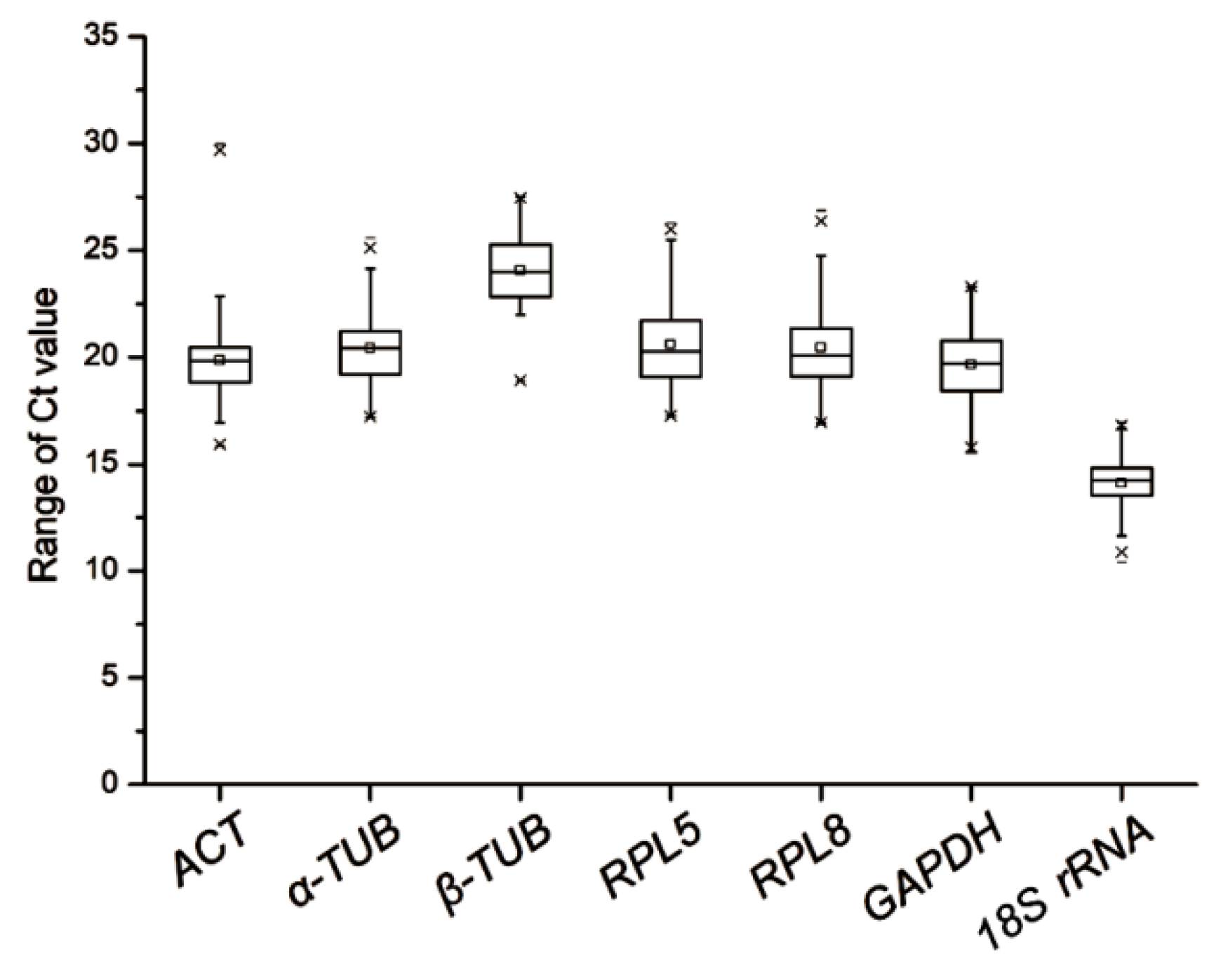
3.1. Expression Profiles of Candidate Reference Genes
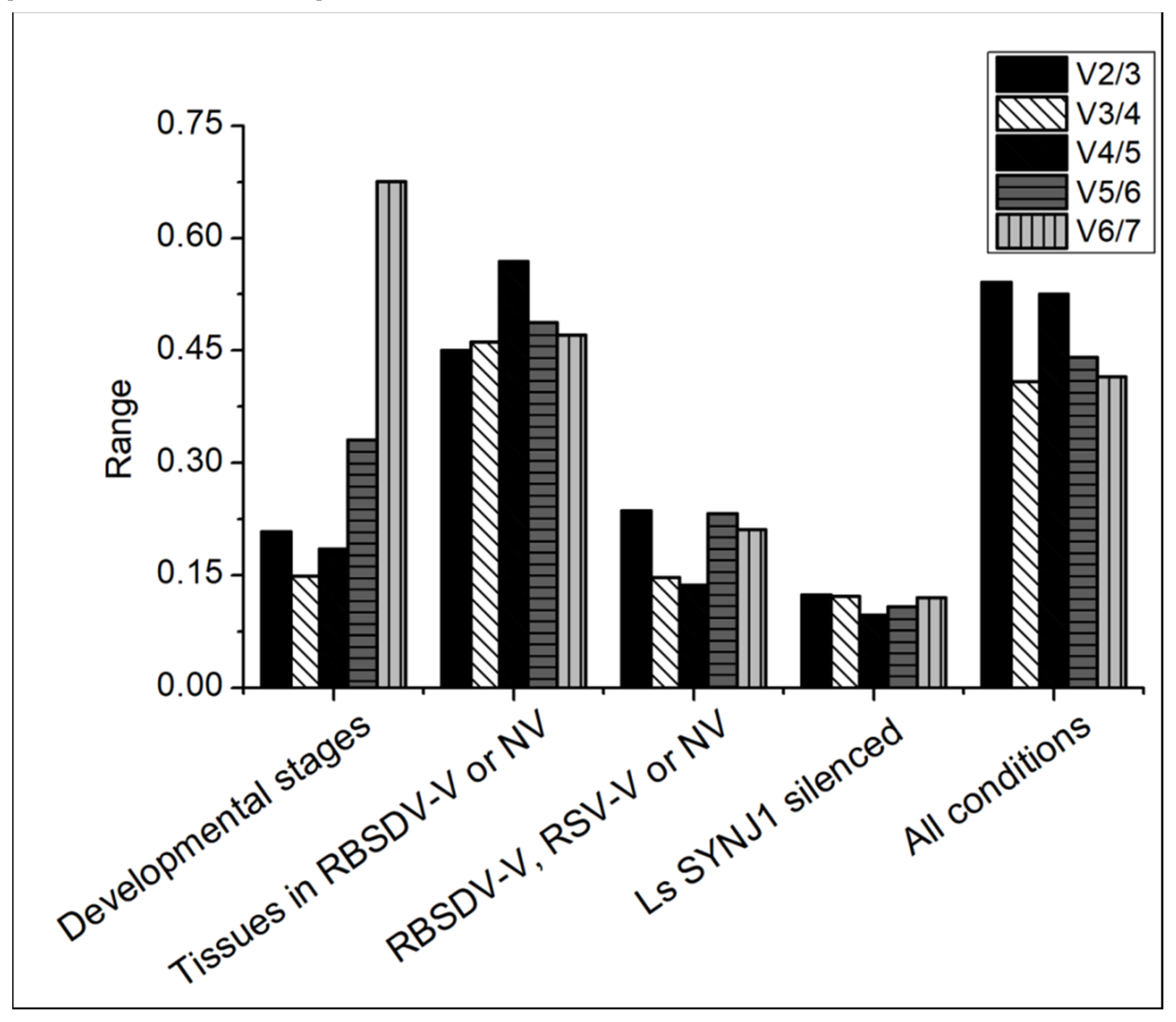
3.2. Expression of Candidate Genes in L. striatellus at Different Developmental Stages
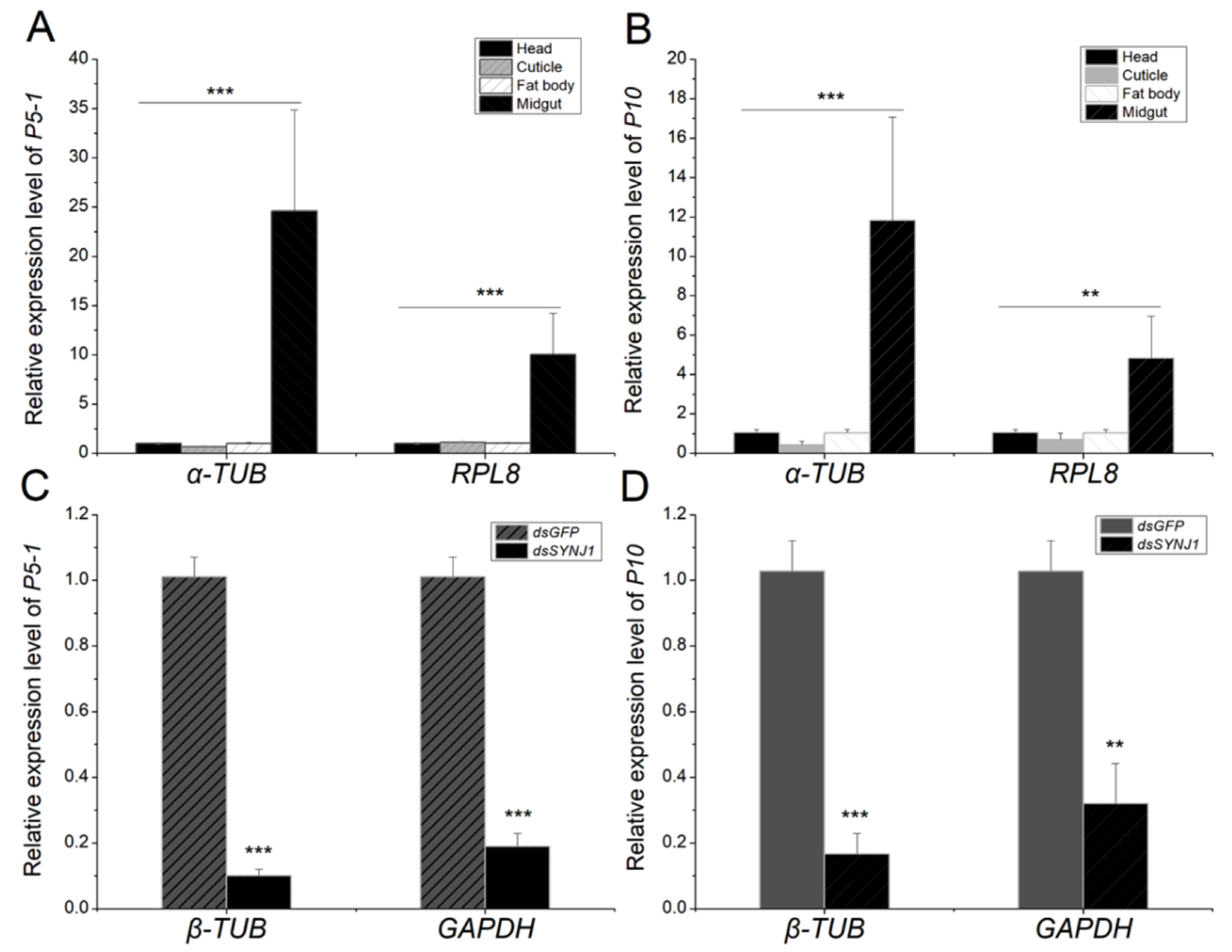
3.3. Expression of the Candidate Genes in Different L. striatellus Tissues
3.4. Expression of the Candidate Genes in RBSDV-V or RSV-V L. striatellus
3.5. Expression of the Candidate Genes in RBSDV-V and LsSYNJ1-Silenced L. striatellus
3.6. Overall Ranking of the Candidate Genes
3.7. Determination of the Optimal Number of Reference Genes Needed for RT-qPCR Normalization
3.8. Normalization of RT-qPCR Data From Different L. striatellus Tissues Using Reference Gene Lsα-TUB and LsRPL8
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Z.G.; Liu, Y.Q.; Xiao, S.Z.; Hu, J.L.; Pan, G.; He, J.; Xu, T.T.; Huang, J.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Fan, D.J.; et al. Identification of quantitative trait loci for resistance to rice black-streaked dwarf virus disease and small brown planthopper in rice. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.F.; Liu, H.Q.; Yuan, P.P.; Zhang, X.X.; Chen, Q.Q.; Jiang, X.L.; Zhou, Y.J. Development of a simplified RT-PCR without RNA isolation for rapid detection of RNA viruses in a single small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus Fallen). Virol. J. 2017, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, R.Q.; Lu, C.X.; Han, X.H.; Guo, S.L.; Yan, S.F.; Liu, L.; Fu, X.L.; Chen, N.N.; Guo, X.H.; Chi, H.F.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings under rice black-streaked dwarf virus infection. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiba, T.; Hirae, M.; Hayano-Saito, Y.; Ohto, Y.; Uematsu, H.; Sugiyama, A.; Okuda, M. Spread and yield loss mechanisms of rice stripe disease in rice paddies. Field Crops Res. 2018, 217, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.D.; Chen, J.P.; Zhang, H.M.; Sun, X.L.; Zhu, J.L.; Wang, A.G.; Sheng, W.X.; Adams, M.J. Recent rice stripe virus epidemics in Zhejiang province, China, and experiments on sowing date, disease yield loss relationships, and seedling susceptibility. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Tao, X.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, W.; Je, Y.H. Transcriptome analysis of the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus carrying rice stripe virus. Plant Pathol. J. 2013, 29, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.J.; Guo, H.Y.; Zheng, H.J.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, Y.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Fang, R.X.; Qian, W.; Chen, X.Y. Massively parallel pyrosequencing-based transcriptome analyses of small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus), a vector insect transmitting rice stripe virus (RSV). BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.B.; Qin, F.L.; Liu, W.W.; Wang, X.F. Differential proteomics profiling of the ova between healthy and Rice stripe virus-infected female insects of Laodelphax striatellus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Lu, L.X.; Yang, P.C.; Cui, N.; Kang, L.; Cui, F. Organ-specific transcriptome response of the small brown planthopper toward rice stripe virus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 70, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Andika, I.B.; Shen, J.F.; Lv, Y.D.; Ji, Y.Q.; Sun, L.Y.; Chen, J.P. Characterization of rice black-streaked dwarf virus- and rice stripe virus-derived siRNAs in singly and doubly infected insect vector Laodelphax striatellus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.L.; Xu, Z.T.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Lu, L.; Liu, R.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Cui, F. Rice stripe virus-derived siRNAs play different regulatory roles in rice and in the insect vector Laodelphax striatellus. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, A.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, D.; Jia, R.; Luo, Q.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. Establishment of real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay for transcriptional analysis of duck enteritis virus UL55 gene. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Ogasawara, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Takano, K.; Shiraishi, T.; Sato, T.; Tsutsumi, H.; Himi, T.; Yokota, S.I. Evaluation of consistency in quantification of gene copy number by real-time reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction and virus titer by plaque-forming assay for human respiratory syncytial virus. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 62, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, T.; Miyauchi, A.; Yokozawa, T.; Matsuzuka, F.; Maeda, I.; Kuma, K.; Amino, N. Preoperative diagnosis of thyroid papillary and anaplastic carcinomas by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction of oncofet al fibronectin messenger RNA. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4542–4545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Song, Z.; Chen, X.; Fang, R.; Zhang, L. Insect tissue-specific vitellogenin facilitates transmission of plant virus. PLoS Pathogens 2018, 14, e1006909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.T.; Liu, C.C.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.Q.; Li, F.; Dong, S.L. Validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in Laodelphax striatellus. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, D.H.; Park, M.G.; Woo, R.M.; Lee, B.R.; Kim, W.J.; Li, S.; et al. RNA interference of E75 nuclear receptor gene suppresses transmission of rice stripe virus in Laodelphax striatellus. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Lin, K.J.; Ding, S.M.; Wang, G.R.; Li, F. The vitellogenin receptor has an essential role in vertical transmission of rice stripe virus during oogenesis in the small brown plant hopper. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.J.; Li, F.Q.; Bai, Y.L.; Shi, X.X.; Zhu, M.F.; Zhang, M.J.; Mao, C.G.; Zhu, Z.R. Rice stripe virus infection alters mRNA levels of sphingolipid-metabolizing enzymes and sphingolipids content in Laodelphax striatellus. J. Insect Sci. 2017, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wu, S.F.; Gao, C.F. Molecular characterization and expression pattern of three GABA receptor-like subunits in the small brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 136, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, M.; Shiba, T.; Hirae, M. Quantitative analysis of rice stripe virus in a transovarial transmission cycle during the development and reproduction of its vector, Laodelphax striatellus. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.; Chen, L.; Su, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Fang, R.; Zhang, L. Artificial feeding Rice stripe virus enables efficient virus infection of Laodelphax striatellus. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 235, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Lu, Y.H.; Zhu, X.; Wan, H.; Shakeel, M.; Zhan, S.; Jin, B.R.; Li, J.H. Selection and evaluation of potential reference genes for gene expression analysis in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) using reverse-transcription quantitative PCR. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.K.; Hou, M.L.; Liu, Y.D. Reference gene selection and evaluation for gene expression studies using qRT-PCR in the white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroniche, G.A.; Sagadin, M.; Mongelli, V.C.; Truol, G.A.; Vas, D.M. Reference gene selection for gene expression studies using RT-qPCR in virus-infected planthoppers. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Gregoire, J.C.; Vaillancourt, C. A simple method to assess group difference in RT-qPCR reference gene selection using GeNorm: The case of the placental sex. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.L.; Jensen, J.L.; Orntoft, T.F. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5245–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Tichopad, A.; Prgomet, C.; Neuvians, T.P. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper--Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liang, H.; Niu, M.; Guo, B.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Selection and validation of novel RT-qPCR reference genes under hormonal stimuli and in different tissues of Santalum album. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Zhou, Y.R.; Sun, Z.T.; Wang, X.; Xie, L.; Chen, J.P. Identification and profiling of conserved and novel microRNAs in Laodelphax striatellus in response to rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) infection. Genom. Data 2015, 3, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, F.L.; Liu, W.W.; Wu, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.K.; Zhou, X.P.; Wang, X.F. Invasion of midgut epithelial cells by a persistently transmitted virus is mediated by sugar transporter 6 in its insect vector. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarza, P.; Yilmaz, P.; Panzer, K.; Glockner, F.O.; Reich, M. A phylogenetic framework for the kingdom Fungi based on 18S rRNA gene sequences. Mar. Genom. 2017, 36, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillery, M.M.L.; Blake-Hedges, C.; Zheng, Y.; Buchwalter, R.A.; Megraw, T.L. Centrosomal and non-centrosomal microtubule-organizing centers (MTOCs) in Drosophila melanogaster. Cells 2018, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.F.; Zhang, J.F.; Li, S.; Ni, H.P.; Zhou, Y.J. Screening of RBSDV p10 interacting proteins in small brown planthopper by yeast two hybrid system. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2013, 27, 633–638. [Google Scholar]
- Akanuma, G.; Nanamiya, H.; Natori, Y.; Yano, K.; Suzuki, S.; Omata, S.; Ishizuka, M.; Sekine, Y.; Kawamura, F. Inactivation of ribosomal protein genes in Bacillus subtilis reveals importance of each ribosomal protein for cell proliferation and cell differentiation. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 6282–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orelle, C.; Carlson, E.D.; Szal, T.; Florin, T.; Jewett, M.C.; Mankin, A.S. Protein synthesis by ribosomes with tethered subunits. Nature 2015, 524, U119–U289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J.; Hao, P.Y.; Lu, C.F.; Ma, Y.; Feng, Y.L.; Yu, X.P. Expression and RNA interference of ribosomal protein L5 gene in Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J. Insect Sci. 2017, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiong, R.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Zhou, Y.J. Five proteins of Laodelphax striatellus are potentially involved in the interactions between rice stripe virus and vector. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Jia, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hou, M. Transcriptomic and expression analysis of the salivary glands in brown planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2884–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| actin | ACT | AY192151 | F: TGAGCGTGAAATCGTAAGAGACAT | 187 |
| R: GAAGGAAGGCTGGAATAGGG | ||||
| alpha-1-tubulin | α-TUB | AY550922 | F: AGACAATGAGGCTATCTACGACA | 296 |
| R: CCATCTGGTTGGCGGGTT | ||||
| beta-tubulin | β-TUB | AY334072 | F: TACCGCCCATTGGTCTGC | 167 |
| R: CGGCTTCAGTGAACTCCATCT | ||||
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GAPDH | HQ385974 | F: ACGCACCCATGTTCGTGT | 193 |
| R: CGGTCCGTCAACAGTCTTCT | ||||
| Ribosome protein L5 | RPL5 | HQ385973 | F: CCGAAGTGACAGGCGAGGAG | 164 |
| R: CACGCTGTGCGGGATGTT | ||||
| Ribosome protein L8 | RPL8 | HQ385976 | F: AGGGAGCGGGAAGTGTTTT | 267 |
| R: CCAATCTGTAGAGTGGCTTTC | ||||
| 18s ribosome RNA | 18s rRNA | AB085211 | F: GTAACCCGCTGAACCTCC | 169 |
| R: GTCCGAAGACCTCACTAAATCA |
| Rank | Delta Ct | geNorm | Bestkeeper | Normfinder | RefFinder | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene Name | Average Ct | SD | Gene Name | M | Gene Name | CV | Gene Name | SV | Gene Name | GM | |
| 1 | 18S rRNA | 14.10 | 1.22 | α-TUB | 1.67 | 18S rRNA | 1.17 | α-TUB | 1.34 | α-TUB | 1.41 |
| 2 | β-TUB | 24.07 | 1.62 | β-TUB | 1.67 | ACT | 1.28 | GAPDH | 1.45 | β-TUB | 2.28 |
| 3 | GAPDH | 19.66 | 1.81 | RPL5 | 1.81 | β-TUB | 1.29 | β-TUB | 1.47 | GAPDH | 2.99 |
| 4 | α-TUB | 20.44 | 1.86 | GAPDH | 2.12 | α-TUB | 1.47 | RPL5 | 1.71 | 18S rRNA | 3.98 |
| 5 | ACT | 19.87 | 2.10 | RPL8 | 2.19 | GAPDH | 1.50 | RPL8 | 1.94 | RPL5 | 4.28 |
| 6 | RPL5 | 20.61 | 2.10 | 18S rRNA | 2.32 | RPL8 | 1.66 | ACT | 1.98 | ACT | 4.92 |
| 7 | RPL8 | 20.46 | 2.22 | ACT | 2.39 | RPL5 | 1.69 | 18S rRNA | 1.99 | RPL8 | 5.23 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Liu, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, S.-M.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Q. Determination of Suitable RT-qPCR Reference Genes for Studies of Gene Functions in Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén). Genes 2019, 10, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110887
Wu W, Liu H, Dong Y, Zhang Y, Wong S-M, Wang C, Zhou Y, Xu Q. Determination of Suitable RT-qPCR Reference Genes for Studies of Gene Functions in Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén). Genes. 2019; 10(11):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110887
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wei, Haoqiu Liu, Yan Dong, Yun Zhang, Sek-Man Wong, Changchun Wang, Yijun Zhou, and Qiufang Xu. 2019. "Determination of Suitable RT-qPCR Reference Genes for Studies of Gene Functions in Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén)" Genes 10, no. 11: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110887
APA StyleWu, W., Liu, H., Dong, Y., Zhang, Y., Wong, S.-M., Wang, C., Zhou, Y., & Xu, Q. (2019). Determination of Suitable RT-qPCR Reference Genes for Studies of Gene Functions in Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén). Genes, 10(11), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110887





