Metabolomic Profiling of Plasma and Erythrocytes in Sickle Mice Points to Altered Nociceptive Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sampling Procedures
2.2. Red Blood Cell Extraction
2.3. Metabolomic Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
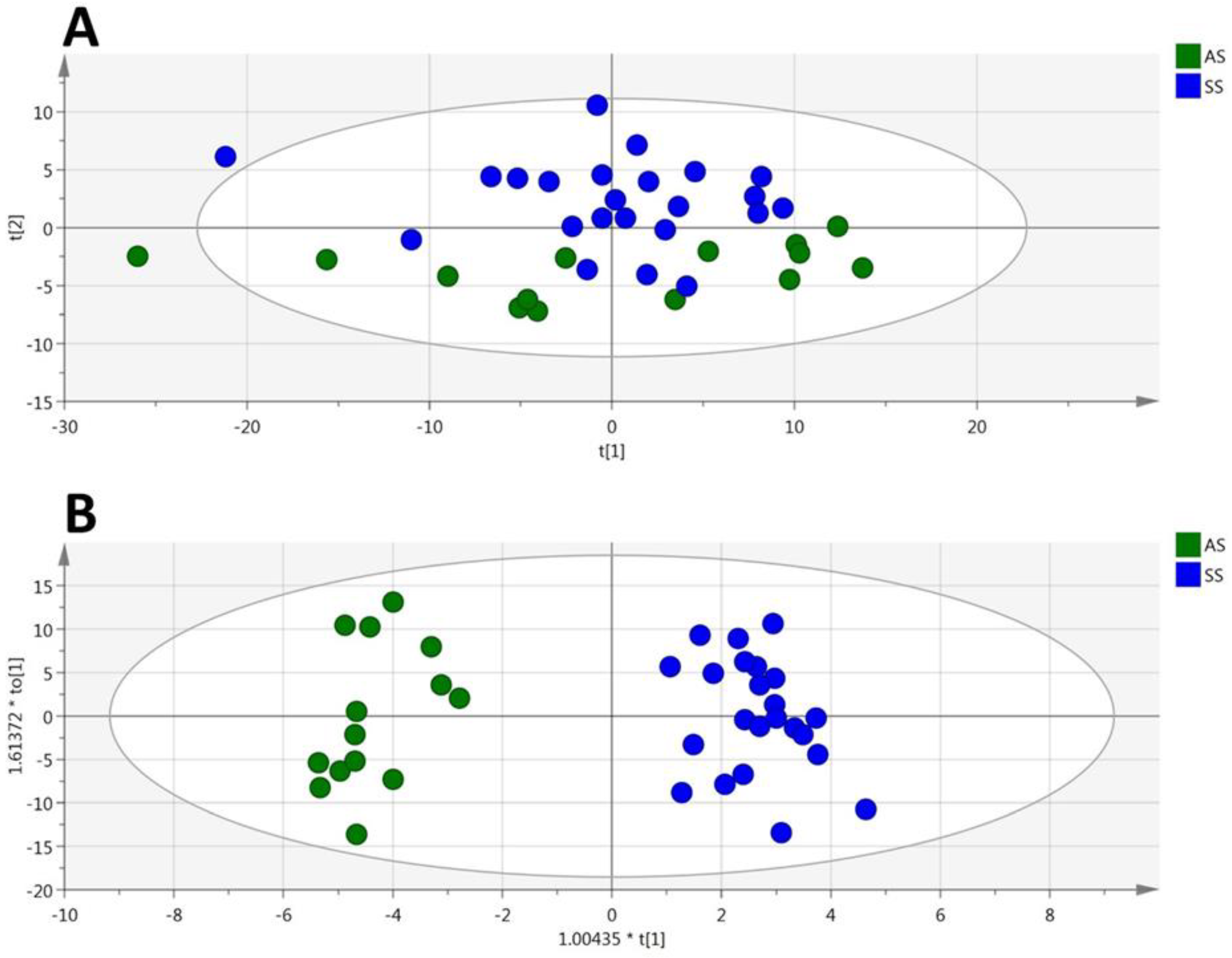
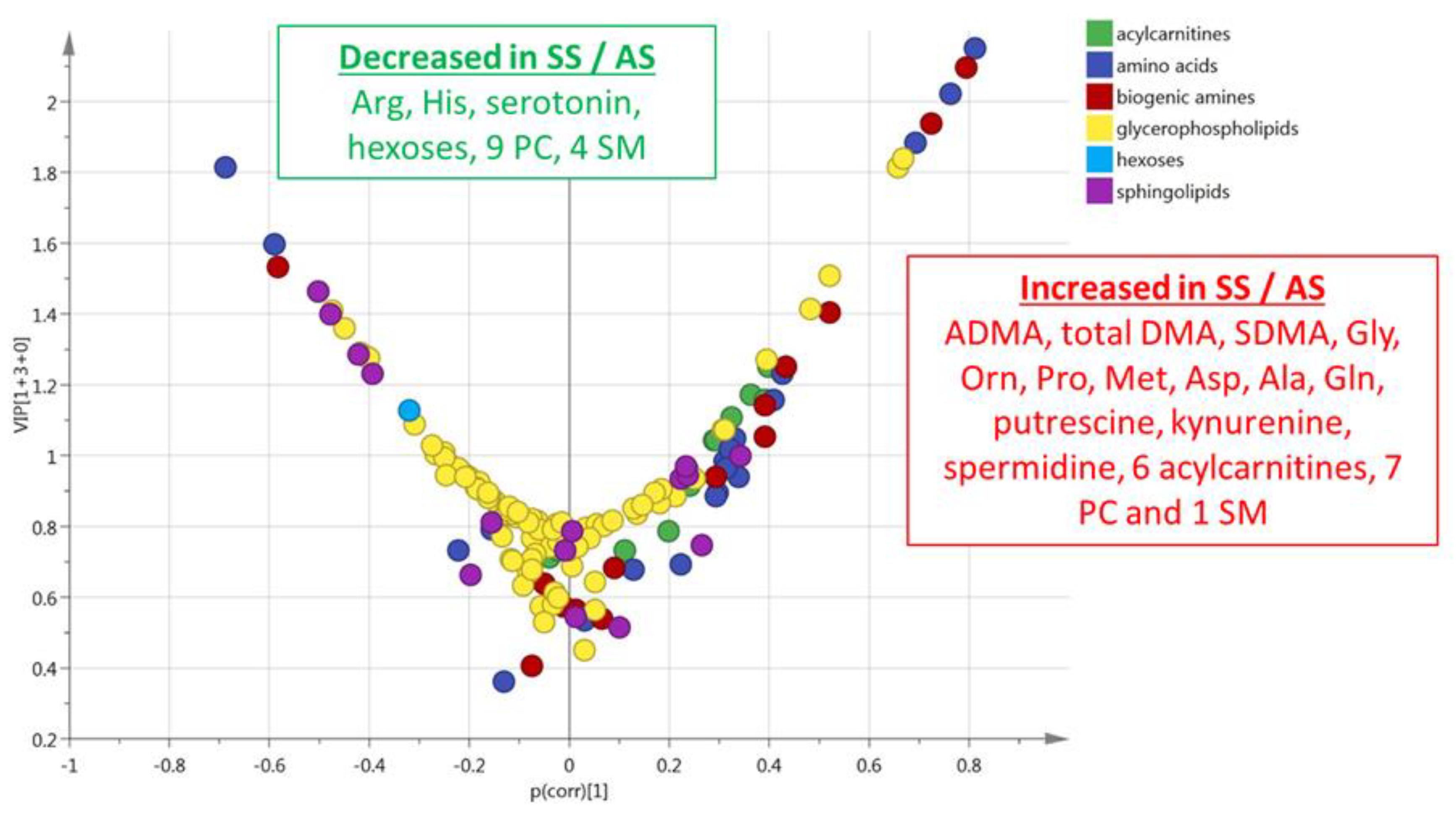
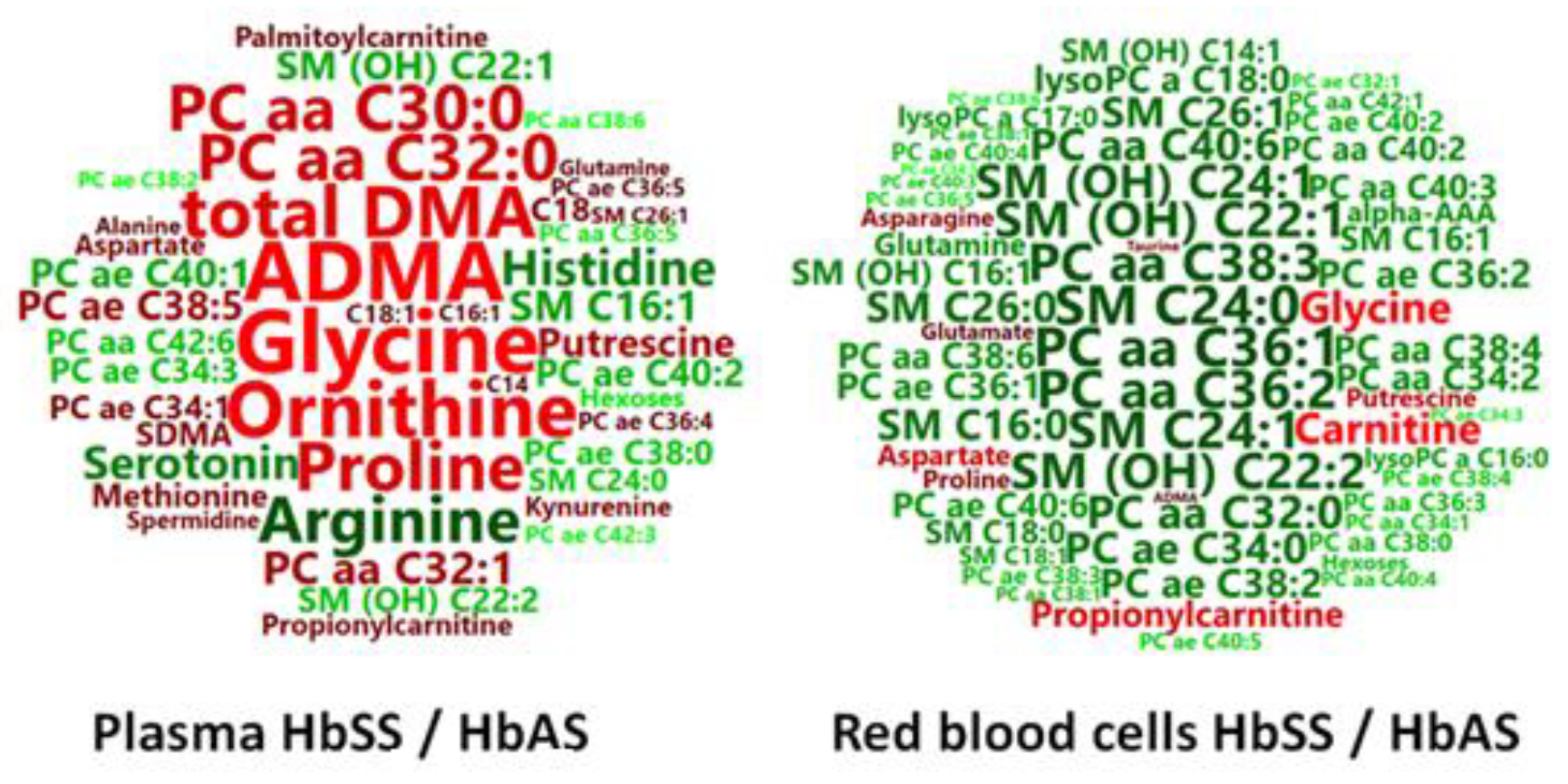
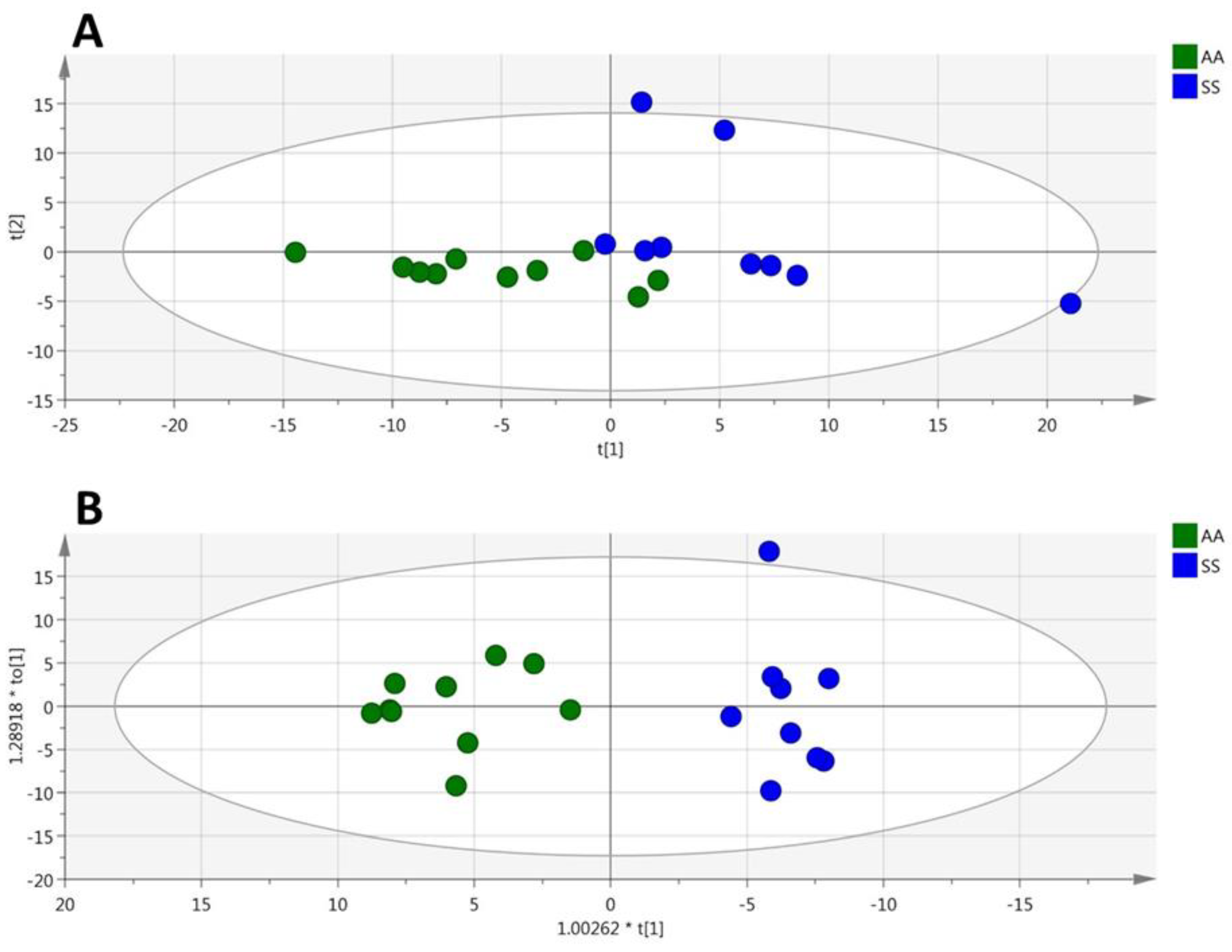
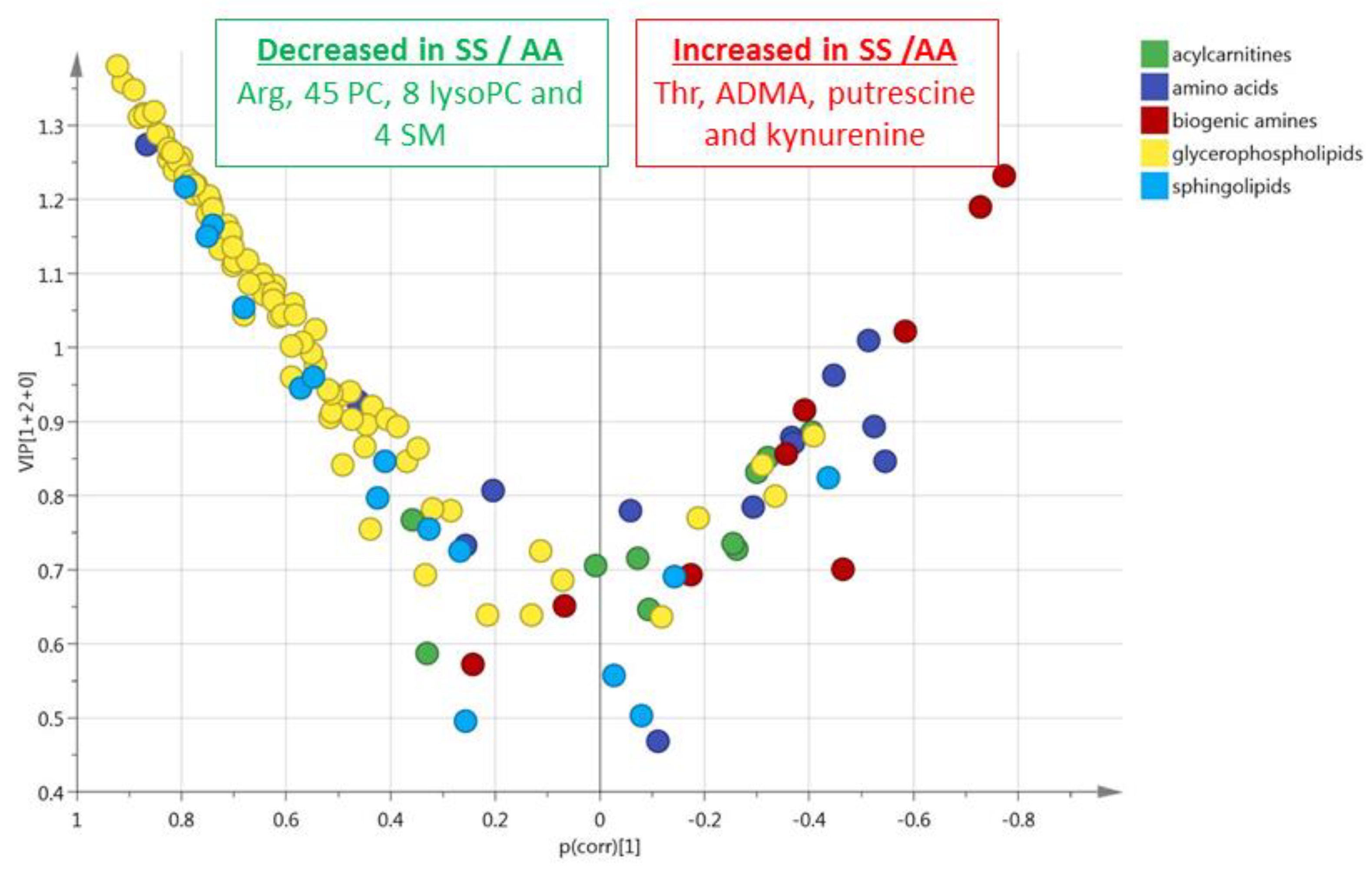
3.1. HbSS/HbAS Plasma Signature
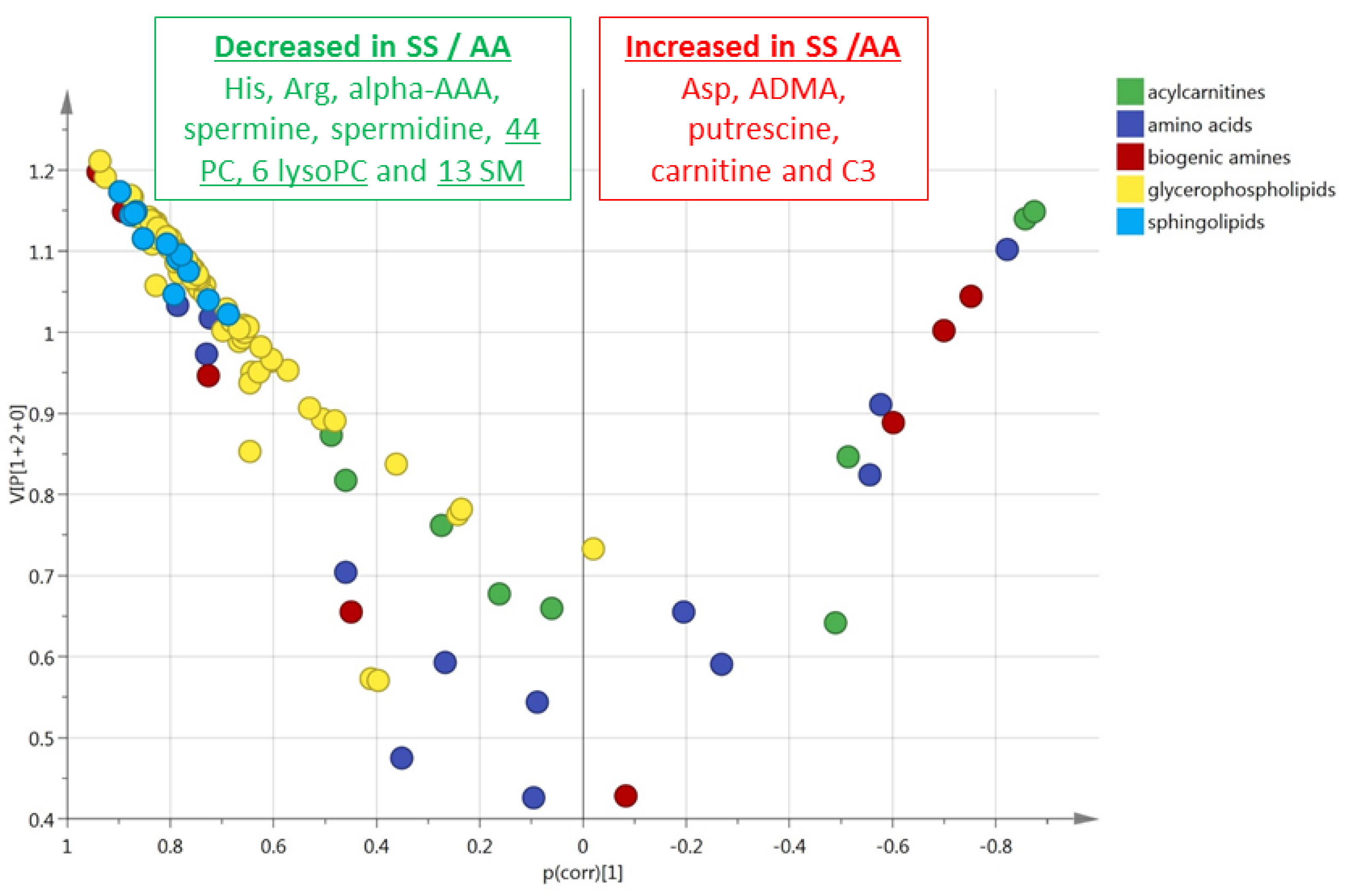
3.2. HbSS/HbAS Red Blood Cells Signature
3.3. Summary of the HbSS/HbAS Signature
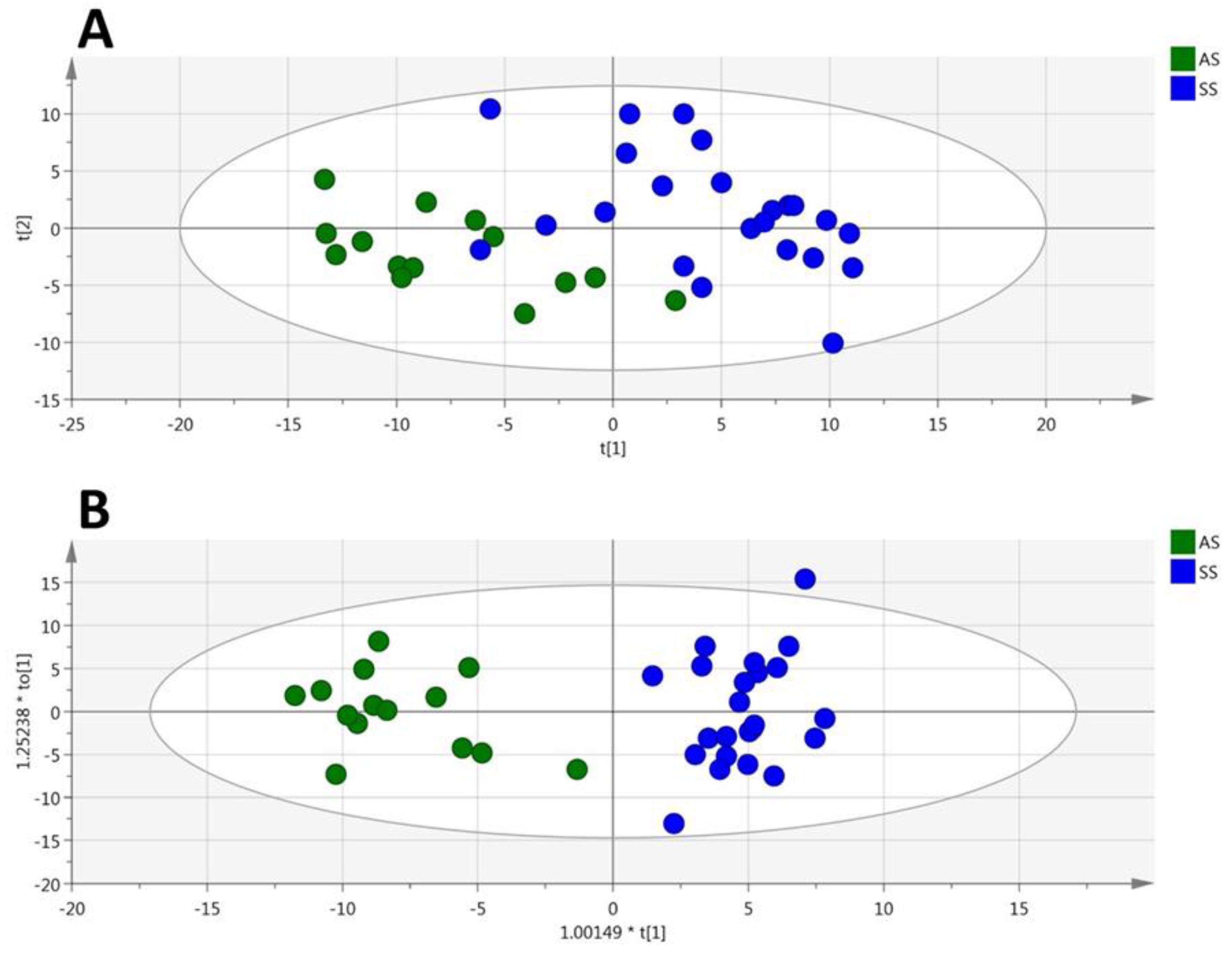
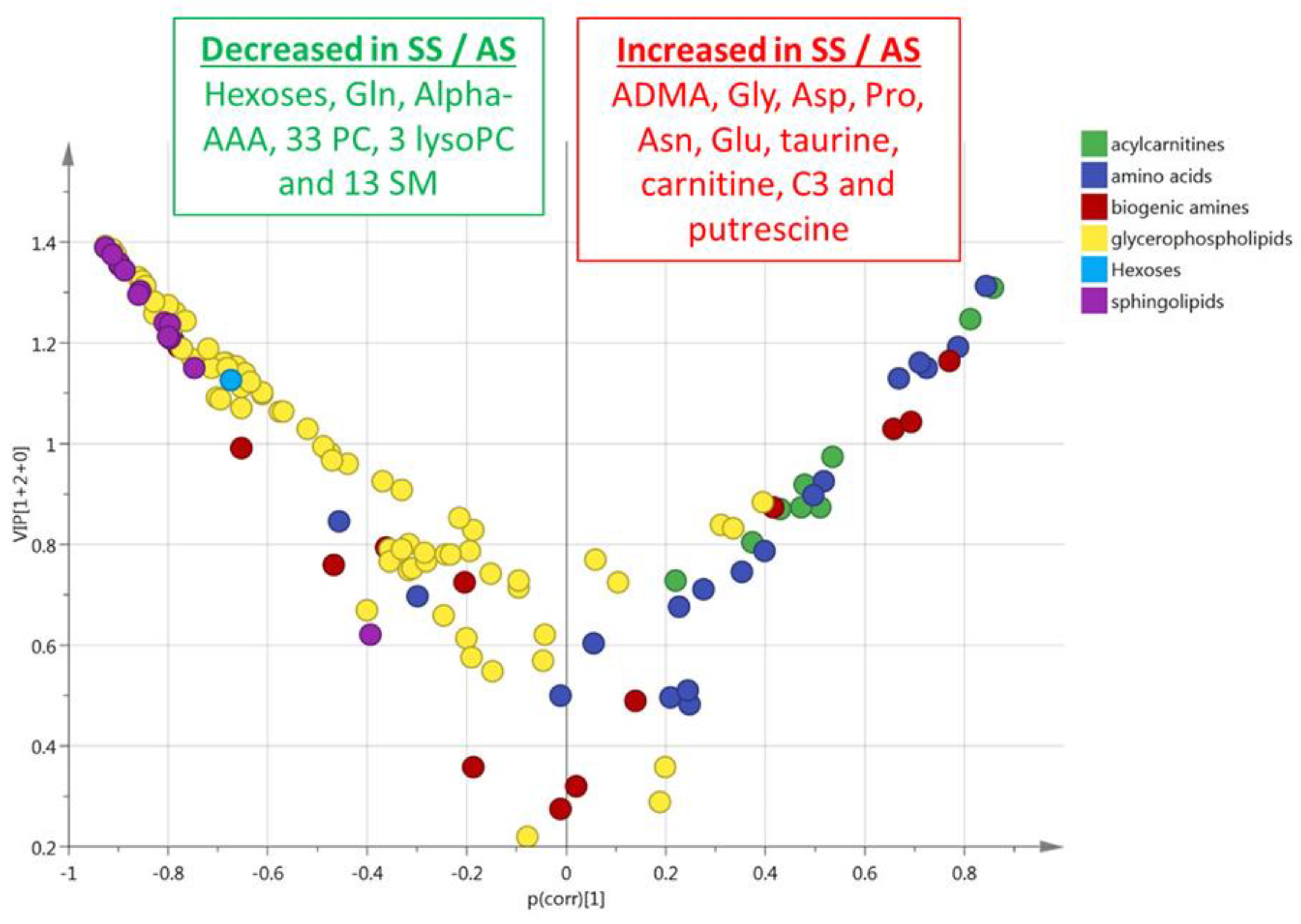
3.4. HbSS/HbAA Plasma Signature
3.5. HbSS/HbAA Red Blood Cell Signature
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ingram, V.M. Gene mutations in human haemoglobin: The chemical difference between normal and sickle cell haemoglobin. Nature 1957, 180, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, S.R.; Pace, B.S.; Hansen, K.C.; D’alessandro, A.; Xia, Y.; Daescu, O.; Glatt, S.J. Minireview: Multiomic candidate biomarkers for clinical manifestations of sickle cell severity: Early steps to precision medicine. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2016, 241, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebiyi, M.G.; Manalo, J.M.; Xia, Y. Metabolomic and molecular insights into sickle cell disease and innovative therapies. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darghouth, D.; Koehl, B.; Madalinski, G.; Heilier, J.F.; Bovee, P.; Xu, Y.; Olivier, M.F.; Bartolucci, P.; Benkerrou, M.; Pissard, S.; et al. Pathophysiology of sickle cell disease is mirrored by the red blood cell metabolome. Blood 2011, 117, e57–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wen, J.; Zhang, W.; Grenz, A.; Sun, H.; Tao, L.; Lu, G.; Alexander, D.C.; Milburn, M.V.; et al. Detrimental effects of adenosine signaling in sickle cell disease. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Berka, V.; Song, A.; Sun, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Ning, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Bogdanov, M.; et al. Elevated sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes sickling and sickle cell disease progression. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 2750–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Adebiyi, M.G.; Zhang, Y.; Couturier, J.P.; Fan, X.; Zhang, H.; Kellems, R.E.; Lewis, D.E.; Xia, Y. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 mediates elevated IL-6 signaling to promote chronic inflammation and multitissue damage in sickle cell disease. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 2855–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherif, L.; Pathmasiri, W.; McRitchie, S.; Archer, D.R.; Ataga, K.I.; Townes, T.M. Plasma metabolomics analysis in sickle cell disease patients with albuminuria–an exploratory study. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 620–623. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.C.; Sun, C.W.; Ryan, T.M.; Pawlik, K.M.; Ren, J.; Townes, T.M. Correction of sickle cell disease by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Blood 2006, 108, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.; Johansson, E.; Kettaneh-Wold, N.; Trygg, J.; Wiksström, C.; Wold, S. Part I: Basic Principles and Applications PLS. Multi- and Magavariate Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Umetrics Ed: Umea, Sweden, 2006; p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, C.D.; Gladwin, M.T. An emerging role for nitric oxide in sickle cell disease vascular homeostasis and therapy. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2003, 10, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnog, J.J.; Jager, E.H.; van der Dijs, F.P.; Duits, A.J.; Moshage, H.; Muskiet, F.D.; Muskiet, F.A. Evidence for a metabolic shift of arginine metabolism in sickle cell disease. Ann. Hematol. 2004, 83, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natta, C.L.; Kremzner, L.T. Polyamines and membrane proteins in sickle cell disease. Blood Cells 1982, 8, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kato, G.J.; Wang, Z.; Machado, R.F.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Taylor, J.G., 6th; Hazen, S.L. Endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in sickle cell disease: Abnormal levels and correlations with pulmonary hypertension, desaturation, haemolysis, organ dysfunction and death. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsikas, D. Does the inhibitory action of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) on the endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity explain its importance in the cardiovascular system? The ADMA paradox. J Controv. Biomed. Res. 2017, 3, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Closs, E.I.; Basha, F.Z.; Habermeier, A.; Forstermann, U. Interference of L-arginine analogues with L-arginine transport mediated by the y+ carrier hCAT-2B. Nitric Oxide 1997, 1, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, M.O.; Lüneburg, N.; Schwedhelm, E.; Ayers, C.R.; Anderssohn, M.; Khera, A.; Atzler, D.; de Lemos, J.A.; Grant, P.J.; McGuire, D.K.; et al. Symmetrical dimethylarginine predicts mortality in the general population: Observations from the Dallas heart study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2682–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripepi, G.; Mattace, R.F.; Sijbrands, E.; Seck, M.S.; Maas, R.; Boger, R.; Witteman, J.; Rapisarda, F.; Malatino, L.; Mallamaci, F.; et al. Inflammation and asymmetric dimethylarginine for predicting death and cardiovascular events in ESRD patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnog, J.B.; Teerlink, T.; van der Dijs, F.P.; Duits, A.J.; Muskiet, F.A.; CURAMA Study Group. Plasma levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), an endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, are elevated in sickle cell disease. Ann. Hematol. 2005, 84, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, N.; Morris, C.R. The role of the arginine metabolome in pain: Implications for sickle cell disease. J Pain Res. 2016, 9, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Eleutério, R.M.N.; Nascimento, F.O.; Araújo, T.G.; Castro, M.F.; Filho, T.P.A.; Filho, P.A.M.; Eleutério, J., Jr.; Elias, D.B.D.; Lemes, R.P.G. Double-Blind Clinical Trial of Arginine Supplementation in the Treatment of Adult Patients with Sickle Cell Anaemia. Adv. Hematol. 2019, 2019, 4397150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.A.; Klafke, J.Z.; Rossato, M.F.; Gewehr, C.; Guerra, G.P.; Rubin, M.A.; Ferreira, J. Role of peripheral polyamines in the development of inflammatory pain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivat, C.; Richebé, P.; Laboureyras, E.; Laulin, J.P.; Havouis, R.; Noble, F.; Moulinoux, J.P.; Simonnet, G. Polyamine deficient diet to relieve pain hypersensitivity. Pain 2008, 137, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänggi, P.; Makhro, A.; Gassmann, M.; Schmugge, M.; Goede, J.S.; Speer, O.; Bogdanova, A. Red blood cells of sickle cell disease patients exhibit abnormally high abundance of N-methyl D-aspartate receptors mediating excessive calcium uptake. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 167, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Chen, S.R.; Pan, H.L. Targeting N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors for treatment of neuropathic pain. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 4, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lötsch, J.; Hummel, T.; Warskulat, U.; Coste, O.; Häussinger, D.; Geisslinger, G.; Tegeder, I. Congenital taurine deficiency in mice is associated with reduced sensitivity to nociceptive chemical stimulation. Neuroscience 2014, 259, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Leek, A.P.; Yanishevsky, Y.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. The Kynurenine Pathway as a Novel Link between Allergy and the Gut Microbiome. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; McKenzie, G.; Witting, P.K.; Stasch, J.P.; Hahn, M.; Changsirivathanathamrong, D.; Wu, B.J.; Ball, H.J.; Thomas, S.R.; et al. Kynurenine is an endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced during inflammation. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Rojewska, E.; Ciapała, K.; Piotrowska, A.; Makuch, W.; Mika, J. Pharmacological Inhibition of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-2 and Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase, Enzymes of the Kynurenine Pathway, Significantly Diminishes Neuropathic Pain in a Rat Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballas, S.K. Current issues in sickle cell pain and its management. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2007, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.M.; Hebbel, R.P.; Gupta, K.; Haynes, C.L. Carbon-fiber microelectrode amperometry reveals sickle-cell-induced inflammation and chronic morphine effects on single mast cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Jarrett, S.; Nguyen, J.; Badgaiyan, R.; Gupta, K. Activation of the Central Serotonergic System Reduces Hyperalgesia in Sickle Mice. Blood 2016, 128, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Vilchez, I.; Diaz-Ricart, M.; White, J.G.; Escolar, G.; Galan, A.M. Serotonin enhances platelet procoagulant properties antheir activation induced during platelet tissue factor upake. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 84, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Ngo, D.; Psychogios, N.; Dejam, A.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Ghorbani, A.; O’Sullivan, J.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; et al. 2-Aminoadipic acid is a biomarker for diabetes risk. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 4309–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinlade, K.S.; Kumuyi, A.S.; Rahamon, S.K.; Olaniyi, J.A. Insulin Sensitivity, Inflammation, and Basal Metabolic Rate in Adults with Sickle Cell Anemia. Int. J. Appl. Basic. Med. Res. 2018, 8, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Luo, X.; Qadri, M.Y.; Berta, T.; Ji, R.R. Sex-Dependent Glial Signaling in Pathological Pain: Distinct Roles of Spinal Microglia and Astrocytes. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, A.; Mancinelli, G.; Radatti, G.L.; Dottori, S.; Molajoni, F.; Ramsay, R.R. Role of carnitine and carnitine palmitoyltransferase as integral components of the pathway for membrane phospholipid fatty acid turnover in intact human erythrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 12673–12681. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, M.; Kıraç, E.; Kaya, S.; Özcan, F.; Salim, O.; Küpesiz, O.A. Decreased Serum Levels of Sphingomyelins and Ceramides in Sickle Cell Disease Patients. Lipids 2018, 53, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.J.; Yanes, O.; Shriver, L.P.; Courade, J.P.; Tautenhahn, R.; Manchester, M.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics implicates altered sphingolipids in chronic pain of neuropathic origin. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembélé, K.C.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Aldiouma, G.; Chupin, S.; Goïta, Y.; Homedan, C.; Mirebeau-Prunier, D.; Cissé, B.; Simard, G.; Diallo, D.; et al. Sickle cell disease: Metabolomic profiles of vaso-occlusive crisis in plasma and erythrocytes. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglie, G.; Di Mauro, M.; Tarissi De Jacobis, I.; de Gennaro, F.; Quaranta, M.; Baronci, C.; Villani, A.; Palumbo, G. Gender-Related Differences in Sickle Cell Disease in a Pediatric Cohort: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Front Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dembélé, K.C.; Mintz, T.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Chabrun, F.; Chupin, S.; Tessier, L.; Simard, G.; Henrion, D.; Mirebeau-Prunier, D.; Chao de la Barca, J.M.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling of Plasma and Erythrocytes in Sickle Mice Points to Altered Nociceptive Pathways. Cells 2020, 9, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061334
Dembélé KC, Mintz T, Veyrat-Durebex C, Chabrun F, Chupin S, Tessier L, Simard G, Henrion D, Mirebeau-Prunier D, Chao de la Barca JM, et al. Metabolomic Profiling of Plasma and Erythrocytes in Sickle Mice Points to Altered Nociceptive Pathways. Cells. 2020; 9(6):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061334
Chicago/Turabian StyleDembélé, Klétigui Casimir, Thomas Mintz, Charlotte Veyrat-Durebex, Floris Chabrun, Stéphanie Chupin, Lydie Tessier, Gilles Simard, Daniel Henrion, Delphine Mirebeau-Prunier, Juan Manuel Chao de la Barca, and et al. 2020. "Metabolomic Profiling of Plasma and Erythrocytes in Sickle Mice Points to Altered Nociceptive Pathways" Cells 9, no. 6: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061334
APA StyleDembélé, K. C., Mintz, T., Veyrat-Durebex, C., Chabrun, F., Chupin, S., Tessier, L., Simard, G., Henrion, D., Mirebeau-Prunier, D., Chao de la Barca, J. M., Tharaux, P.-L., & Reynier, P. (2020). Metabolomic Profiling of Plasma and Erythrocytes in Sickle Mice Points to Altered Nociceptive Pathways. Cells, 9(6), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061334





