Aspirin Mitigated Tumor Growth in Obese Mice Involving Metabolic Inhibition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Caspase 3 Activity Assay
2.4. Syngeneic Tumor Model Study
2.5. Colony Formation Assay
2.6. Blood Sample Collection and Analyses
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
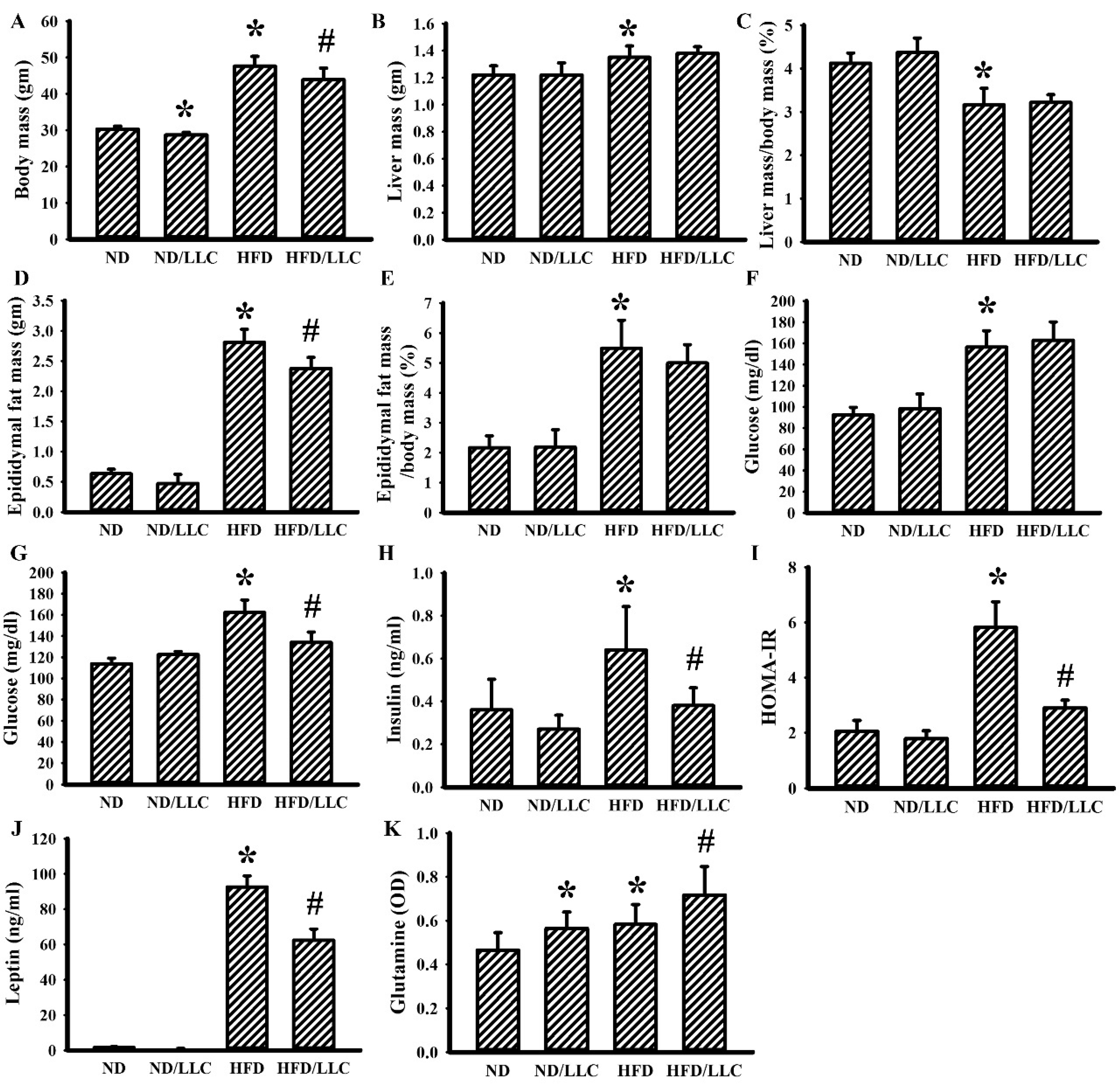
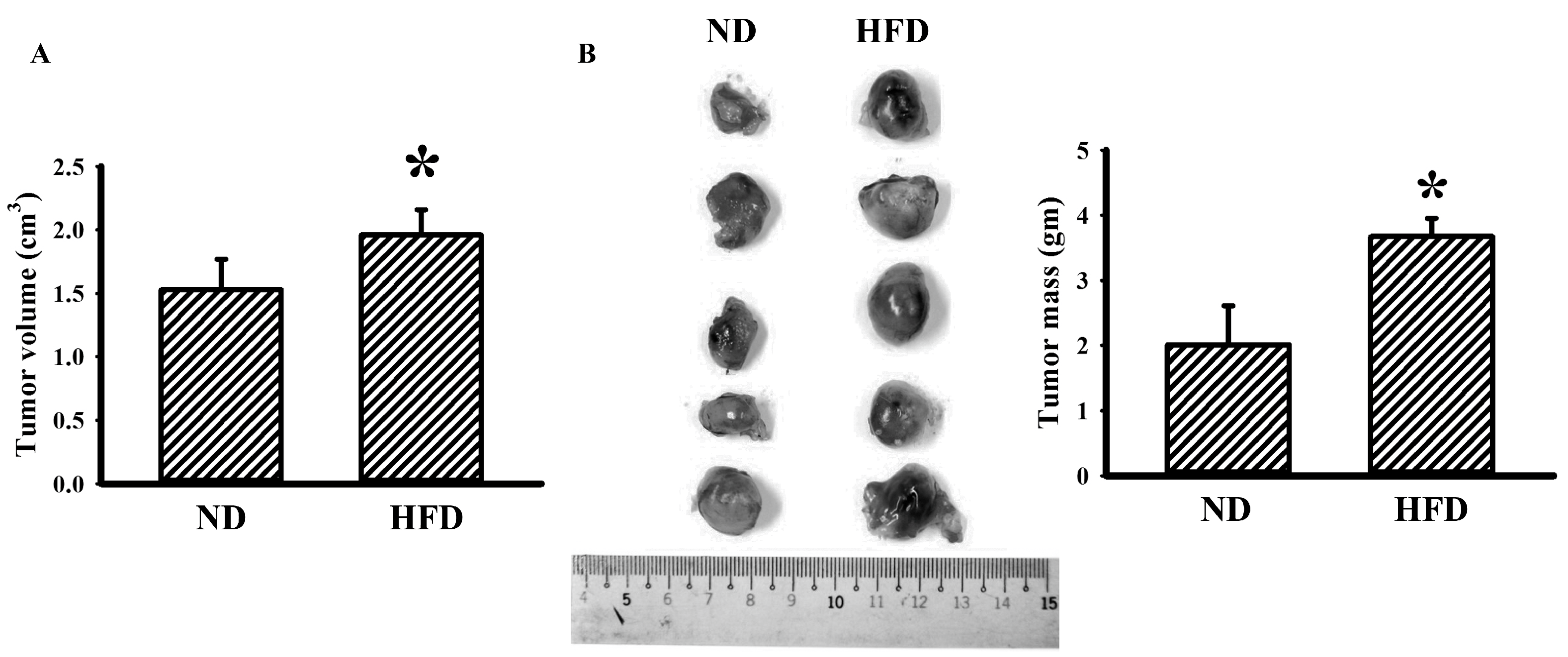
3.1. Tumor Improved Glucose Metabolism in Obese Mice
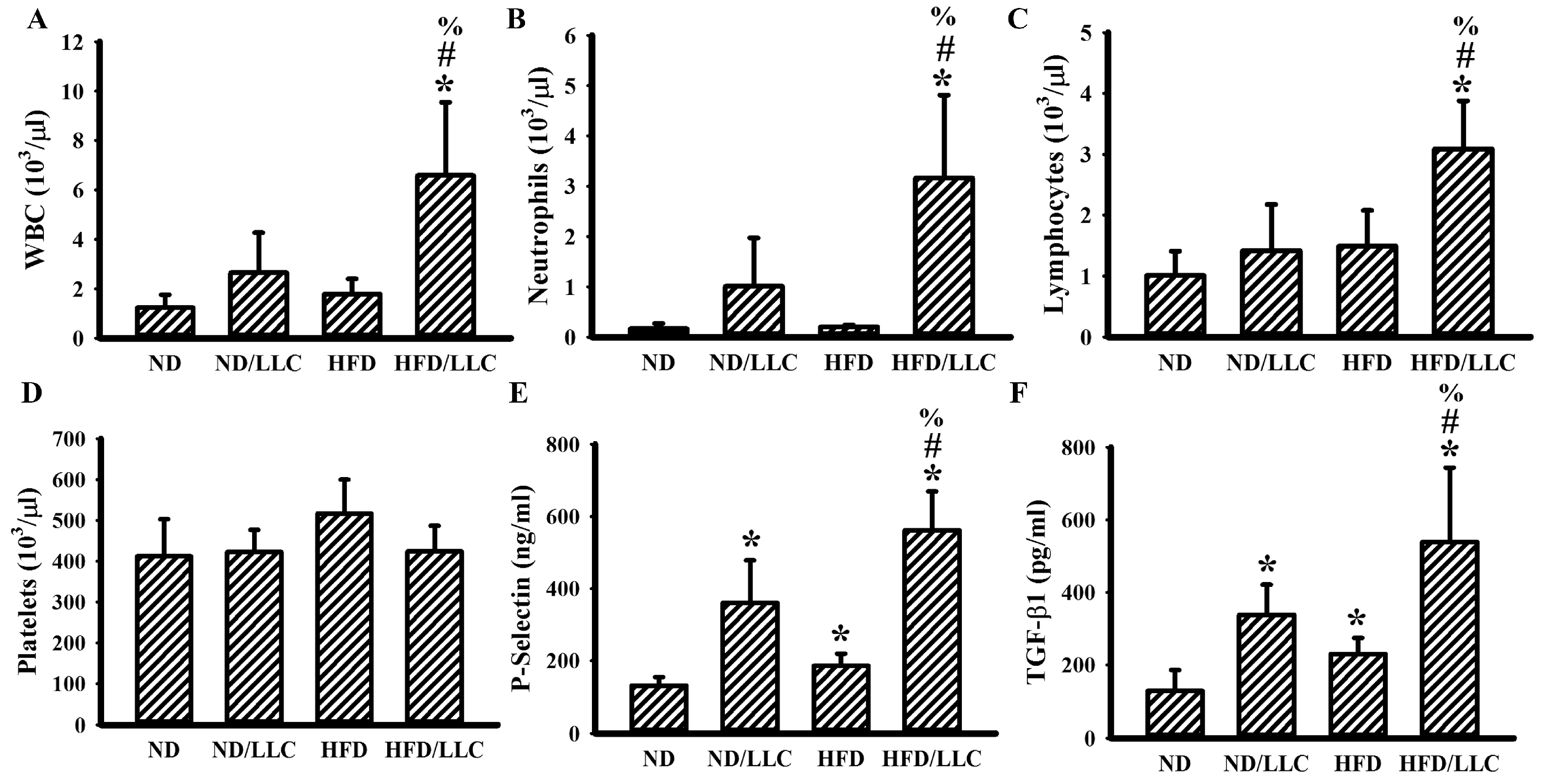
3.2. Tumor Elevated Circulating Leukocytes in Obese Mice
3.3. Aspirin Improved Metabolic and Inflammatory Alterations in Tumor-Bearing HFD-Fed Mice
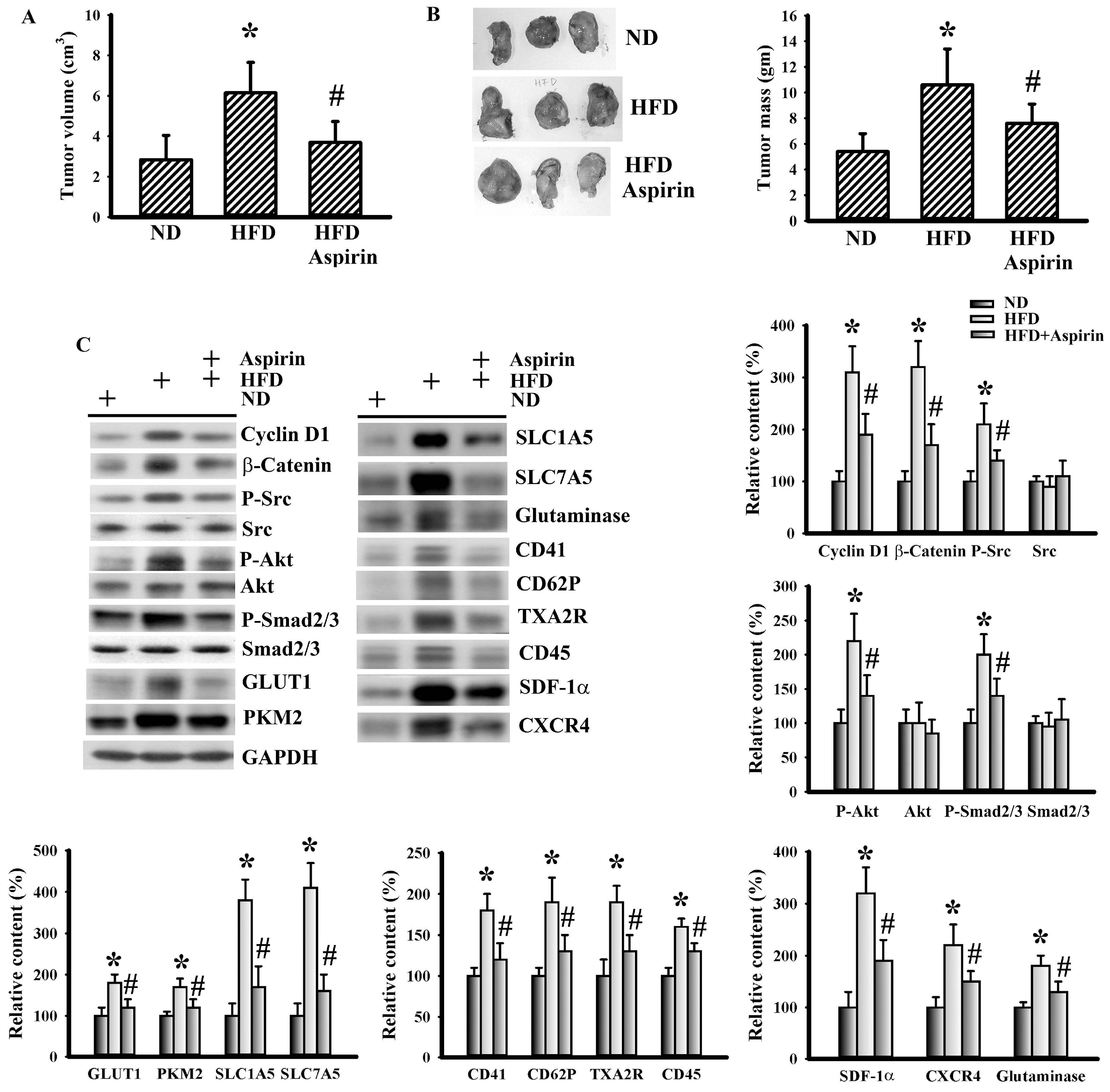
3.4. Aspirin Mitigated Cellular Metabolic Capacity and Cell Growth in Tumor-Bearing HFD-Fed Mice
3.5. Aspirin Mitigated LLC Cell Proliferation and Metabolism
3.6. Glutamine Promoted LLC Cell Proliferation and Metabolism
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allott, E.H.; Hursting, S.D. Obesity and cancer: Mechanistic insights from transdisciplinary studies. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, R365–R386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Kong, W.; Zhang, L.; Han, J.; Clark, L.H.; Yin, Y.; Fang, Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Gilliam, T.P.; et al. Reversal of obesity-driven aggressiveness of endometrial cancer by metformin. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2170–2193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, S.; Li, J.; Bao, W.; Zhang, P.; Huang, Y.; Ling, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q. Effects of high-fat diet-induced adipokines and cytokines on colorectal cancer development. FEBS Open Bio. 2019, 9, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; He, X.; Ding, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, L. Statin uses and mortality in colorectal cancer patients: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 3305–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri, A.R.; Rodrigues, M.R.; Li, Z.; Leitner, B.P.; Perry, R.J. SGLT2 inhibition slows tumor growth in mice by reversing hyperinsulinemia. Cancer Metab. 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pergola, G.; Giagulli, V.A.; Guastamacchia, E.; Bartolomeo, N.; Tatoli, R.; Lampignano, L.; Silvestris, F.; Triggiani, V. Platelet number is positively and independently associated with glycated hemoglobin in non-diabetic overweight and obese subjects. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, R.; Dovizio, M.; Marcone, S.; Szklanna, P.B.; Bruno, A.; Ebhardt, H.A.; Cassidy, H.; Ní Áinle, F.; Caprodossi, A.; Lanuti, P.; et al. Platelet-derived microparticles from obese individuals: Characterization of number, size, proteomics, and crosstalk with cancer and endothelial cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, P.; Liani, R.; Tripaldi, R.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Guagnano, M.T.; Tartaro, A.; Bonadonna, R.C.; Federico, V.; Cipollone, F.; Consoli, A.; et al. Thromboxane-dependent platelet activation in obese subjects with prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes: Effects of liraglutide- or lifestyle changes-induced weight loss. Nutrients 2018, 10, E1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakis, G.; Fritsche, H.M.; Hassan, F.; Kluth, L.; Miller, F.; Soave, A.; Otto, W.; Schwentner, C.; Todenhofer, T.; Dahlem, R.; et al. Prognostic relevance of postoperative platelet count in upper tract urothelial carcinoma after radical nephroureterectomy. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, T.; Tajima, H.; Makino, I.; Nakagawara, H.; Kitagawa, H.; Fushida, S.; Harmon, J.W.; Ohta, T. Metastasis-promoting role of extravasated platelet activation in tumor. J. Urol. Res. 2015, 193, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M.; Ishiwata, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Takashi, H.; Saito, K.; Fujii, Y.; Kihara, K.; Yasuhara, M. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis of sunitinib-induced thrombocytopenia in Japanese patients with renal cell carcinoma. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachidi, S.; Wallace, K.; Day, T.A.; Alberg, A.J.; Li, Z. Lower circulating platelet counts and antiplatelet therapy independently predict better outcomes in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Väyrynen, J.P.; Väyrynen, S.A.; Sirniö, P.; Minkkinen, I.; Klintrup, K.; Karhu, T.; Mäkelä, J.; Herzig, K.H.; Karttunen, T.J.; Tuomisto, A.; et al. Platelet count, aspirin use, and characteristics of host inflammatory responses in colorectal cancer. J. Transl Med. 2019, 17, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Liu, Z.W.; Woolf, D.; Hargreaves, S.; Michalarea, V.; Menashy, R.; Kooner, I.; Wilson, E. Change in platelet levels during radiotherapy with concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide for the treatment of glioblastoma: A novel prognostic factor for survival. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contursi, A.; Sacco, A.; Grande, R.; Dovizio, M.; Patrignani, P. Platelets as crucial partners for tumor metastasis: From mechanistic aspects to pharmacological targeting. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3491–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, M.; Hoeksema, M.D.; Shiota, M.; Qian, J.; Harris, B.K.; Chen, H.; Clark, J.E.; Alborn, W.E.; Eisenberg, R.; Massion, P.P. SLC1A5 mediates glutamine transport required for lung cancer cell growth and survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 19, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, S.; Chacko, B.; Sawada, H.; Kramer, P.A.; Johnson, M.S.; Benavides, G.A.; O’Donnell, V.; Marques, M.B.; Darley-Usmar, V.M. Metabolic plasticity in resting and thrombin activated platelets. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0123597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasta, V.; Meacci, E.; Farnararo, M.; Bruni, P. Glutamine transport and enzymatic activities involved in glutaminolysis in human platelets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1243, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, N.M.; Spillane, C.D.; Sheils, O.; O’Leary, J.; Kenny, D. Aspirin and P2Y12 inhibition attenuate platelet-induced ovarian cancer cell invasion. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.E.; Ceglowski, J.R.; Roweth, H.G.; Forward, J.A.; Tippy, M.D.; El-Husayni, S.; Kulenthirarajan, R.; Malloy, M.W.; Machlus, K.R.; Chen, W.Y.; et al. Aspirin inhibits platelets from reprogramming breast tumor cells and promoting metastasis. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucotti, S.; Cerutti, C.; Soyer, M.; Gil-Bernabé, A.M.; Gomes, A.L.; Allen, P.D.; Smart, S.; Markelc, B.; Watson, K.; Armstrong, P.C.; et al. Aspirin blocks formation of metastatic intravascular niches by inhibiting platelet-derived COX-1/thromboxane A2. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 1845–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xu, R.; Xia, J.; Huang, J.; Su, B.; Wang, S. Aspirin inhibits hypoxia-mediated lung cancer cell stemness and exosome function. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Yan, J.; Fu, X.; Pan, Q.; Sun, D.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Nie, L.; Tong, L.; Shen, A.; et al. Aspirin inhibits cancer metastasis and angiogenesis via targeting heparanase. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6267–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Aspirin suppresses chemoresistance and enhances antitumor activity of 5-Fu in 5-Fu-resistant colorectal cancer by abolishing 5-Fu-induced NF-κB activation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Wu, X. Aspirin inhibits colon cancer cell line migration through regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Wnt signaling. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4675–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, W.; Cao, Q.; Shu, Y. Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 inhibits TGF-β1-induced EMT through the inhibition of the mTOR pathway by reducing the expression of PKM2 and is closely linked to oxidative stress. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzoli, G.; Petrucci, G.; Navarra, P.; Marei, H.E.; Cenciarelli, C. Aspirin inhibits proliferation and promotes differentiation of neuroblastoma cells via p21Waf1 protein up-regulation and Rb1 pathway modulation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7078–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.F.; Yang, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Wu, B.C.; Huang, S.C.; Liu, C.M.; Chen, S.L.; Pan, Y.F.; Chou, S.S.; Chou, M.Y.; et al. Aspirin-induced inhibition of adipogenesis was p53-dependent and associated with inactivation of pentose phosphate pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 738, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisada, Y.; Mackman, N. Mouse models of cancer-associated thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2018, 164, S48–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.; Hasselwander, S.; Li, H.; Xia, N. Effects of different diets used in diet-induced obesity models on insulin resistance and vascular dysfunction in C57BL/6 mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Kuan, Y.H.; Ou, Y.C.; Li, J.R.; Wu, C.C.; Pan, P.H.; Chen, W.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Chen, C.J. Autophagy contributes to gefitinib-induced glioma cell growth inhibition. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 327, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hoske, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, A.; Neuberger, E.; Esch-Heisser, L.; Haller, N.; Jorgensen, M.M.; Baek, R.; Möbius, W.; Simon, P.; Krämer-Albers, E.M. Platelets, endothelial cells and leukocytes contribute to the exercise-triggered release of extracellular vesicles into the circulation. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2019, 8, 1615820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frere, C.; Lejeune, M.; Kubicek, P.; Faille, D.; Marjanovic, Z.; Groupe Francophone Thrombose et Cancer. Antiplatelet agents for cancer prevention: Current evidences and continuing controversies. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, E1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Tseng, H.C.; Yu, S.H.; Lin, J.T.; Wu, M.S.; Wu, C.Y. Association of daily aspirin therapy with risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.Y.; Chen, C.J.; Liu, C.H.; Mao, F.C. Chromium supplementation enhances insulin signaling in skeletal muscle of obese KK/HlJ diabetic mice. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2009, 11, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganapathy-Kanniappan, S. Molecular intricacies of aerobic glycolysis in cancer: Current insights into the classic metabolic phenotype. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 53, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matés, J.M.; Campos-Sandoval, J.A.; Santos-Jiménez, J.L.; Márquez, J. Dysregulation of glutaminase and glutamine synthetase in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 467, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitaloka, D.M.I.; Ko, C.H.; Lin, M.T.; Yeh, S.L.; Yeh, C.L. Glutamine administration promotes hepatic glucose homeostasis through regulating the PI3K/Akt pathway in high-fat diet-induced obese mice with limb ischemia. Nutr. Res. 2019, 68, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garabet, L.; Ghanima, W.; Monceyron Jonassen, C.; Skov, V.; Holst, R.; Mowinckel, M.C.; C Hasselbalch, H.; A Kruse, T.; Thomassen, M.; Liebman, H.; et al. Effect of thrombopoietin receptor agonists on markers of coagulation and P-selectin in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. Platelets 2019, 30, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Ning, Y.; Lin, X.; Guo, S.; Chen, M.; Han, M. Glutaminolysis was induced by TGF-β1 through PP2Ac regulated Raf-MEK-ERK signaling in endothelial cells. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0162658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, D.; Chatterjee, M.; Holtkamp, A.; Tekath, N.; Borst, O.; Vogel, S.; Müller, K.; Gawaz, M.; Geisler, T. Evidence of an interaction between TGF-β1 and the SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in human platelets. Thromb. Res. 2016, 144, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Xiao, C.H.; Tan, L.D.; Wang, Q.S.; Li, X.Q.; Feng, Y.M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells through paracrine TGF-β signaling. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bako, H.Y.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Isah, M.S.; Ibrahim, S. Inhibition of JAK-STAT and NF-κB signaling systems could be a novel therapeutic target against insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.-D.; Chen, W.-Y.; Li, J.-R.; Lin, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Liao, S.-L.; Ko, C.-C.; Chen, C.-J. Aspirin Mitigated Tumor Growth in Obese Mice Involving Metabolic Inhibition. Cells 2020, 9, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030569
Wang J-D, Chen W-Y, Li J-R, Lin S-Y, Wang Y-Y, Wu C-C, Liao S-L, Ko C-C, Chen C-J. Aspirin Mitigated Tumor Growth in Obese Mice Involving Metabolic Inhibition. Cells. 2020; 9(3):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030569
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiaan-Der, Wen-Ying Chen, Jian-Ri Li, Shih-Yi Lin, Ya-Yu Wang, Chih-Cheng Wu, Su-Lan Liao, Chiao-Chen Ko, and Chun-Jung Chen. 2020. "Aspirin Mitigated Tumor Growth in Obese Mice Involving Metabolic Inhibition" Cells 9, no. 3: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030569
APA StyleWang, J.-D., Chen, W.-Y., Li, J.-R., Lin, S.-Y., Wang, Y.-Y., Wu, C.-C., Liao, S.-L., Ko, C.-C., & Chen, C.-J. (2020). Aspirin Mitigated Tumor Growth in Obese Mice Involving Metabolic Inhibition. Cells, 9(3), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030569





