Secretome of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevents Myofibroblasts Differentiation by Transferring Fibrosis-Associated microRNAs within Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Conditioned Medium Harvesting and Fractioning
2.3. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
2.4. TEM Imaging
2.5. Immunofluorescent Analysis
2.6. Collagen Gel Contraction Assay
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. mRNA Level Evaluation by Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.9. MSC-EV RNA High-Throughput Sequencing
2.10. microRNA Level Evaluation by Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.11. MSC-EV Transfection
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Components of MSC Secretome Modulate the TGFbeta-Induced Differentiation of Fibroblasts into Myofibroblasts
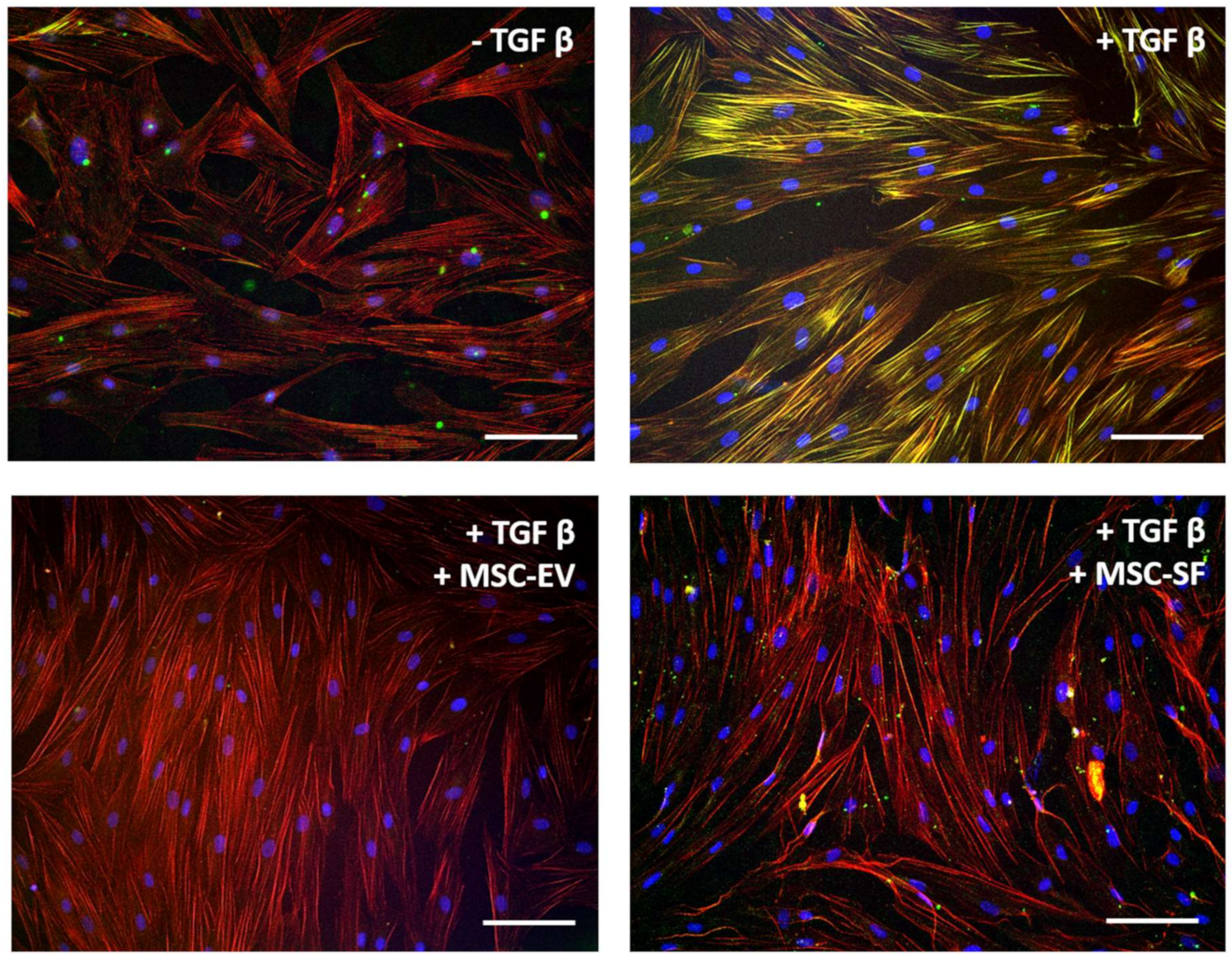
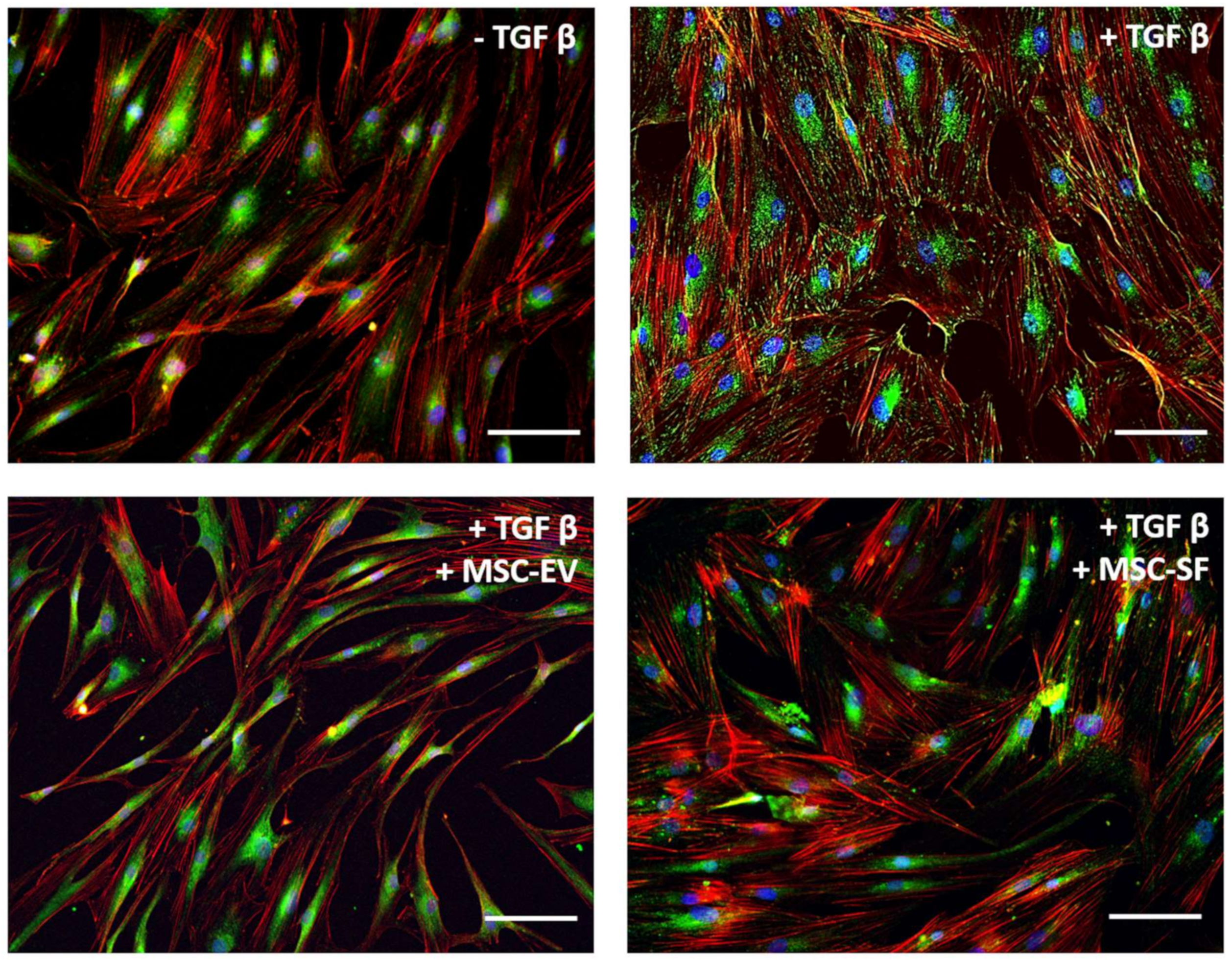
3.1.1. Acquisition of Myofibroblasts Phenotype Is Inhibited by Fractions of MSC-CM
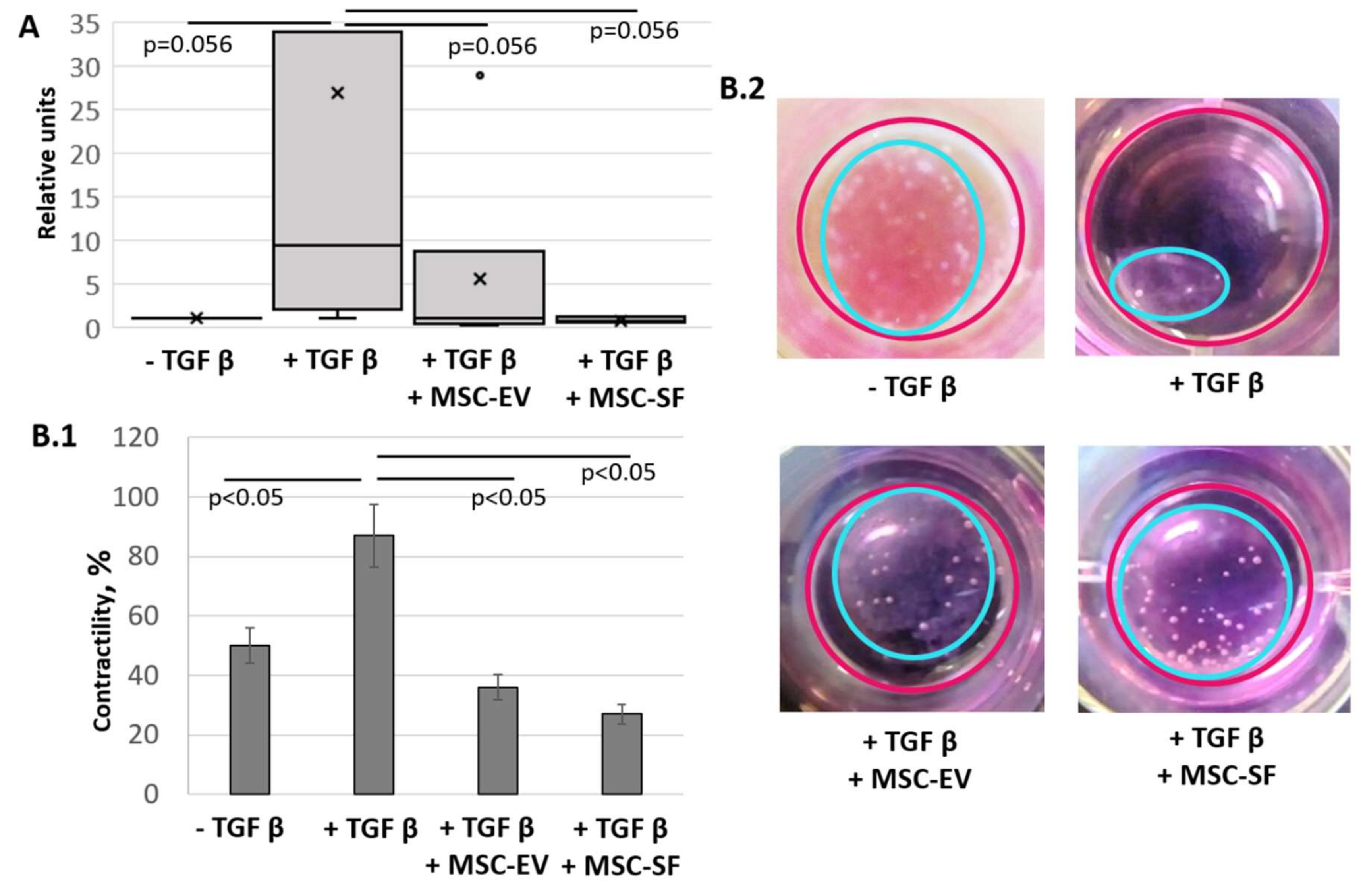
3.1.2. MSC-CM Fractions Suppress Contractile Activity of Myofibroblasts
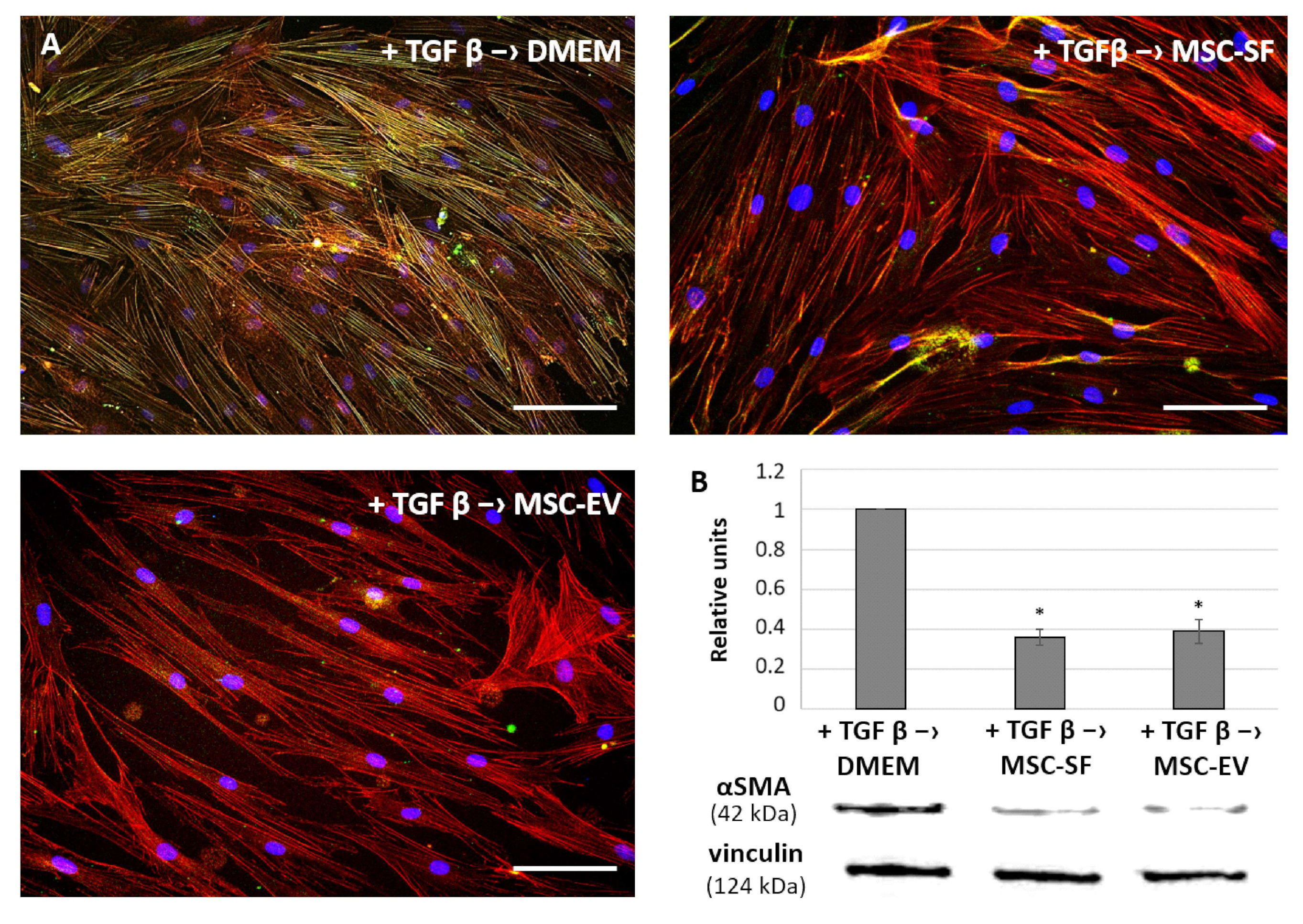
3.1.3. MSC-CM Fractions induce the Re-Differentiation of Myofibroblasts
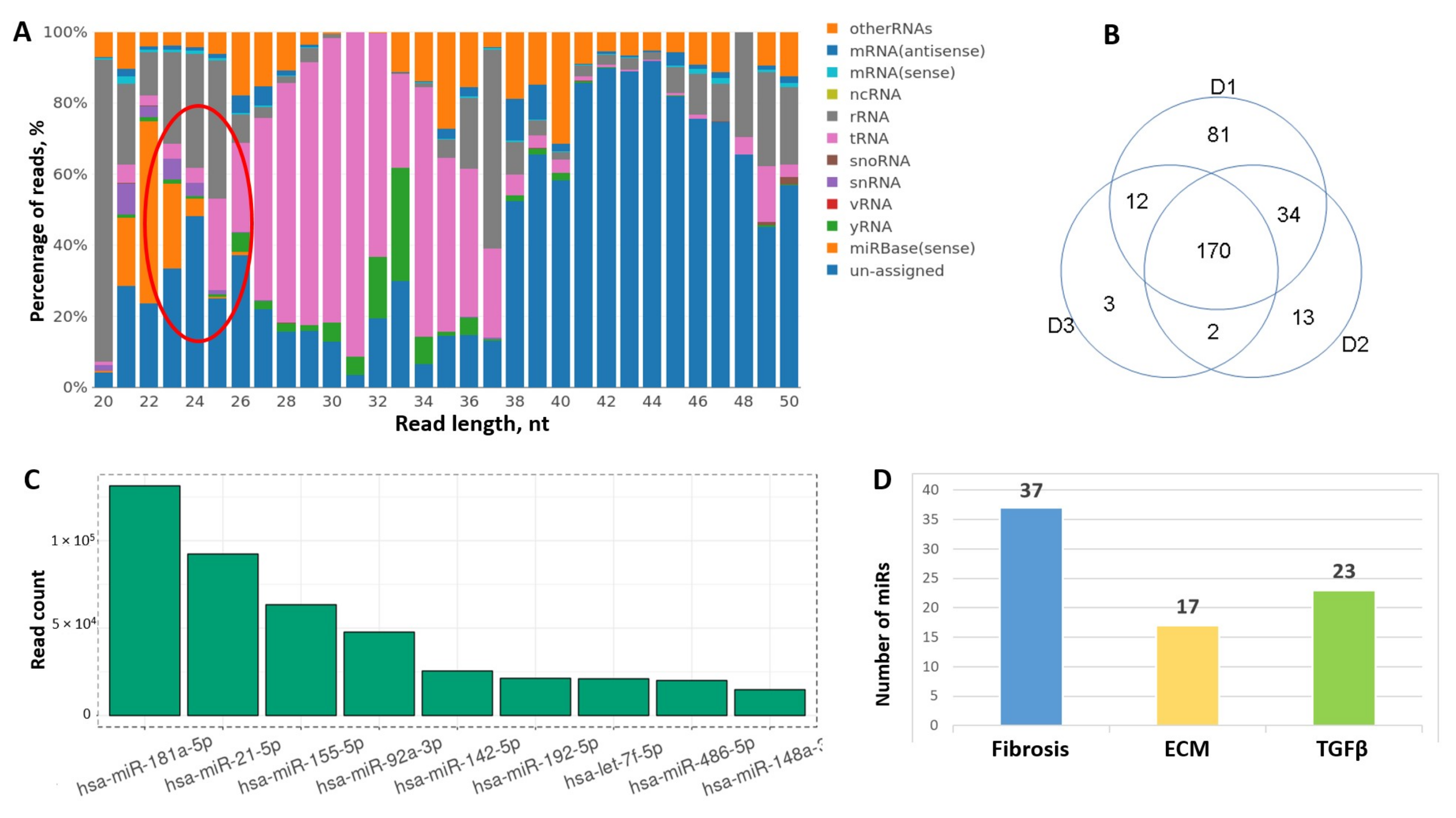
3.2. RNA Sequencing Reveal miRs Associated with Fibrosis in MSC-EV
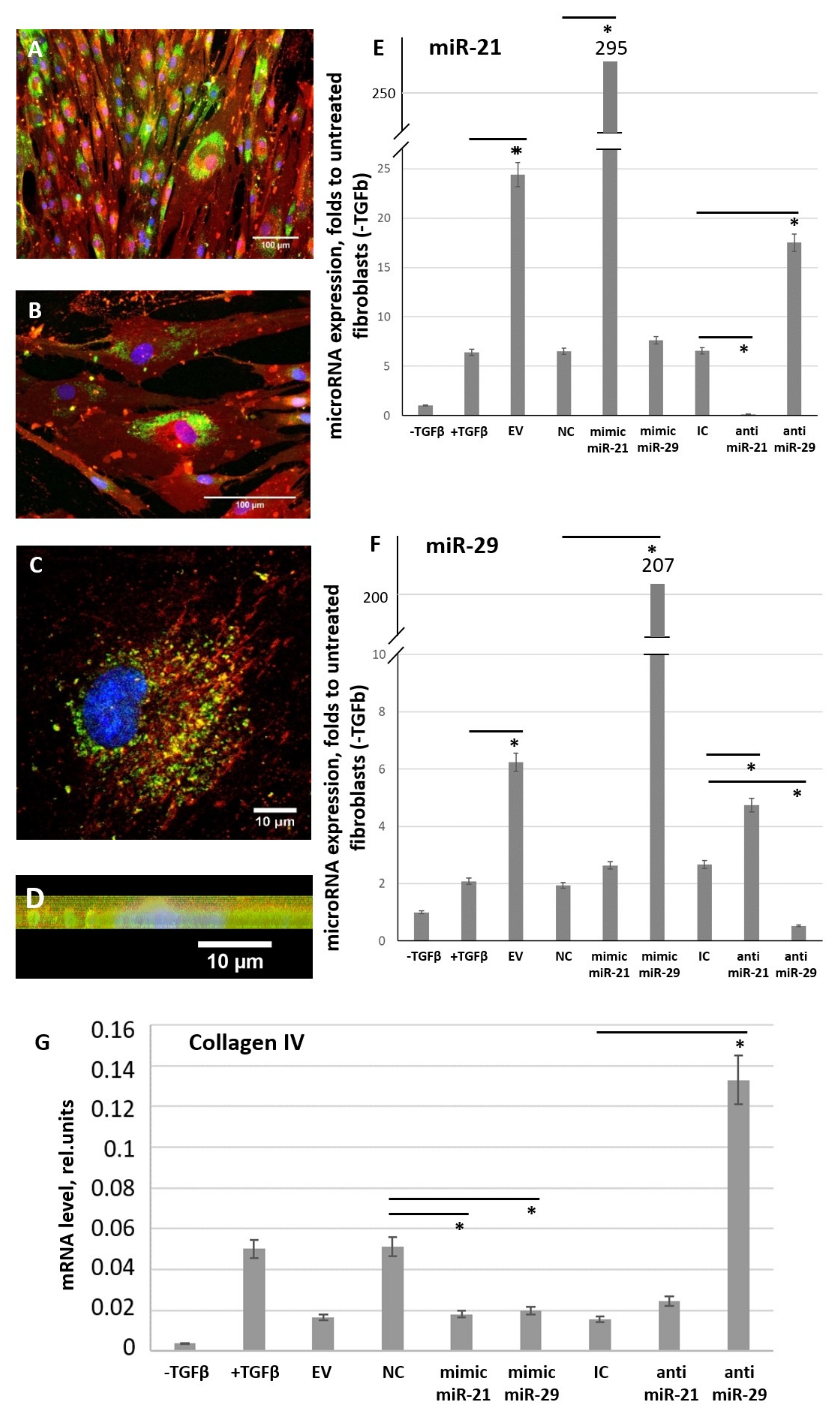
3.3. MSC-EV Are Able to Transfer miRs from MSC to Fibroblasts
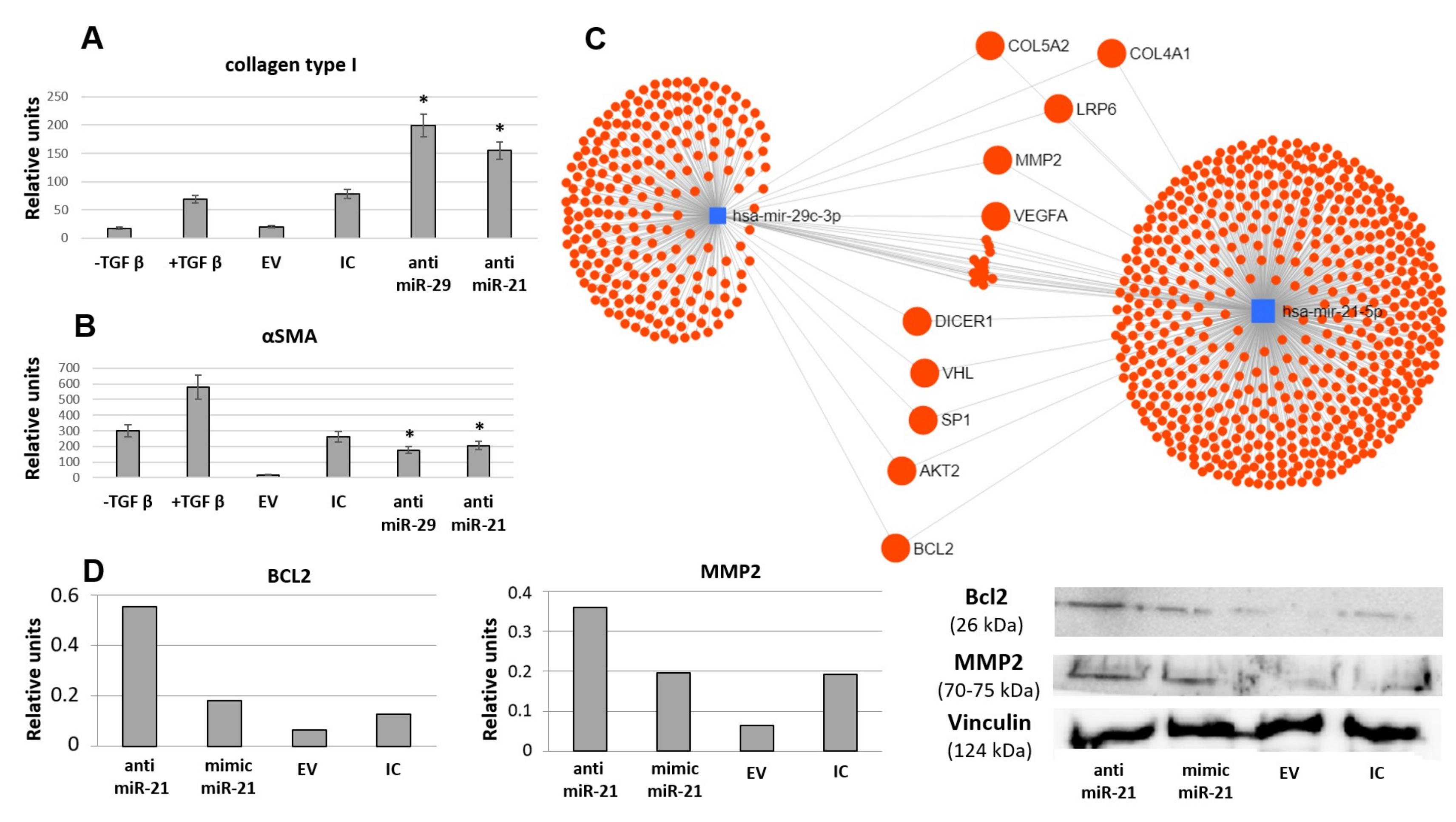
3.4. miR-21 and miR-29 Are Involved in MSC-EV-Mediated Antifibrotic Effects of MSC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lemos, D.R.; Duffield, J.S. Tissue-resident mesenchymal stromal cells: Implications for tissue-specific antifibrotic therapies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Agha, E.; Kramann, R.; Schneider, R.K.; Li, X.; Seeger, W.; Humphreys, B.D.; Bellusci, S. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Fibrotic Disease. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usunier, B.; Benderitter, M.; Tamarat, R.; Chapel, A. Management of fibrosis: The mesenchymal stromal cells breakthrough. Stem Cells Int. 2014, 2014, 340257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spees, J.L.; Lee, R.H.; Gregory, C.A. Mechanisms of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell function. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozito, T.P.; Tuan, R.S. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit both endogenous and exogenous MMPs via secreted TIMPs. J. Cell Physiol. 2011, 226, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, A.I.; Correa, D. The MSC: An injury drugstore. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Time to Change the Name! Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrigal, M.; Rao, K.S.; Riordan, N.H. A review of therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell secretions and induction of secretory modification by different culture methods. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, N.; Kharlampieva, D.; Loguinova, M.; Butenko, I.; Pobeguts, O.; Efimenko, A.; Ageeva, L.; Sharonov, G.V.; Ischenko, D.; Alekseev, D.; et al. Characterization of secretomes provides evidence for adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells subtypes. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, A.M.; Mott, J.L. Overview of microRNA biology. Semin. Liver Dis. 2015, 35, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Zheng, G.; Ge, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, R.; Shu, Q.; Xu, J. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles affect disease outcomes via transfer of microRNAs. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinney, D.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Njah, J.; Sala-Llinas, E.; Shiva, S.; Croix, C.M.S.; Stolz, N.B.; Watkins, S.C.; Di, Y.P.; Leikauf, G.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM E2834-12(2018), Standard Guide for Measurement of Particle Size Distribution of Nanomaterials in Suspension by Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA); ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Silachev, D.N.; Goryunov, K.V.; Shpilyuk, M.A.; Beznoschenko, O.S.; Morozova, N.Y.; Kraevaya, E.E.; Popkov, V.A.; Pevzner, I.B.; Zorova, L.D.; Evtushenko, E.A.; et al. Effect of MSCs and MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Human Blood Coagulation. Cells 2019, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, P.; Ramalingam, P.; Phillips, J.A.; Furuta, G.T. Collagen gel contraction assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006, 341, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Snowdon, V.K.; Fallowfield, J.A. Models and mechanisms of fibrosis resolution. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, V.D.; Hsia, H.C.; Schwarzbauer, J.E. Reversible modulation of myofibroblast differentiation in adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.W.; Wang, J.; Lee, C.J.; Liu, M.; Neelamegham, S.; Canty, J.M.; Nguyen, J. The microRNA regulatory landscape of MSC-derived exosomes: A systems view. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, I.A.; Laverdet, B.; Bonté, F.; Desmoulière, A. Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in wound healing. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 7, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, R.T.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A. Fibroblasts in fibrosis: Novel roles and mediators. Front Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, T.T.A.; Liguori, G.R.; Moreira, L.F.P.; Harmsen, M.C. Fibroblast growth factor-2, but not the adipose tissue-derived stromal cells secretome, inhibits TGF-β1-induced differentiation of human cardiac fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, B.; Phan, S.H.; Thannickal, V.J.; Galli, A.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.L.; Gabbiani, G. The myofibroblast: One function, multiple origins. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakihara, T.; Horiguchi, K.; Miyazawa, K.; Ehata, S.; Shibata, T.; Morita, I.; Miyazono, K.; Saitoh, M. TGF-β regulates isoform switching of FGF receptors and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Ryan, A.E.; Griffin, M.D.; Ritter, T. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles: Toward Cell-free Therapeutic Applications. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, H.R.; Tuan, R.S. Secreted trophic factors of mesenchymal stem cells support neurovascular and musculoskeletal therapies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, D.S.; Tieu, A.; Lalu, M.; Burger, D. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Regenerative Therapy and Immune Modulation: Progress and Challenges Toward Clinical Application. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Bandeira, E.; Shelke, G.V.; Lässer, C.; Lötvall, J. Enhancement of therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yan, Y.; Wang, B.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglio, S.R.; Rooijers, K.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; Verweij, F.J.; Pérez Lanzón, M.; Zini, N.; Naaijkens, B.; Perut, F.; Niessen, H.W.; Baldini, N.; et al. Human bone marrow- and adipose-mesenchymal stem cells secrete exosomes enriched in distinctive miRNA and tRNA species. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Yang, C.; Bi, H.; Qian, X.; Wu, M.; Ji, K.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shentu, T.P.; Huang, T.S.; Cernelc-Kohan, M.; Chan, J.; Wong, S.S.; Espinoza, C.R.; Tan, C.; Gramaglia, I.; van der Heyde, H.; Chien, S.; et al. Thy-1 dependent uptake of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles blocks myofibroblastic differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Friggeri, A.; Yang, Y.; Milosevic, J.; Ding, Q.; Thannickal, V.J.; Kaminski, N.; Abraham, E. miR-21 mediates fibrogenic activation of pulmonary fibroblasts and lung fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakhlallah, D.; Batte, K.; Wang, Y.; Cantemir-Stone, C.Z.; Yan, P.; Nuovo, G.; Mikhail, A.; Hitchcock, C.L.; Wright, V.P.; Nana-Sinkam, S.P.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of miR-17~92 contributes to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zang, A.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fan, W.; Feng, J.; Duan, M.; Zhang, L.; Huo, R.; Jiao, J.; et al. Triptolide reduces proliferation and enhances apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer cells through PTEN by targeting miR-21. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2763–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, R.L.; Yu, G.; Latimer, P.A.; Stack, C.; Robinson, K.; Dalby, C.M.; Kaminski, N.; van Rooij, E. MicroRNA mimicry blocks pulmonary fibrosis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, L.; Kuang, P.; Lü, J. The role of miR-29 in pulmonary fibrosis. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Long, X.; Deng, W.; Wang, Z. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21 protects C-kit+ cardiac stem cells from oxidative injury through the PTEN/PI3K/Akt axis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.M.; Png, C.Y.; Lee, D.J. Type V Collagen in Health, Disease, and Fibrosis. Anat. Rec. 2016, 299, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldred, J.A.; Hodgkinson, L.M.; Dawes, L.J.; Reddan, J.R.; Edwards, D.R.; Wormstone, I.M. MMP2 activity is critical for TGFβ2-induced matrix contraction--implications for fibrosis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 4085–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Johnson, B.G.; Kida, Y.; Ip, C.; Davidson, K.C.; Lin, S.L.; Kobayashi, A.; Lang, R.A.; Hadjantonakis, A.K.; Moon, R.T.; et al. LRP-6 is a co-receptor for multiple fibrogenic signaling pathways in pericytes and myofibroblasts that are inhibited by DKK-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.S.; Liu, C.C.; Lin, J.H.; Hsu, T.W.; Hsu, J.W.; Su, K.; Hung, S.C. Involvement of ER stress, PI3K/AKT activation, and lung fibroblast proliferation in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weder, B.; Mamie, C.; Rogler, G.; Clarke, S.; McRae, B.; Ruiz, P.A.; Hausmann, M. BCL2 Regulates Differentiation of Intestinal Fibroblasts. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaurav, R.; Black, B.; Edelman, B.; Redente, E.; Riches, D. Bcl-2 Overexpression in Fibroblasts Promotes Persistent Fibrosis in a Normally Resolving Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, A4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, T.; Zhang, W.; Bozkanat, M.; Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; van Breemen, R.B.; Christman, J.W.; Sznajder, J.I.; Zhou, G. Suppression of von Hippel-Lindau Protein in Fibroblasts Protects against Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, K.Q.; An, G.; Ji, S.Y.; Chen, Q.K. Anti-fibrotic effects via regulation of transcription factor Sp1 on hepatic stellate cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, F.; Rossert, J.; Mauviel, A. Blocking sp1 transcription factor broadly inhibits extracellular matrix gene expression in vitro and in vivo: Implications for the treatment of tissue fibrosis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, J.; Beisang, D.J.; Peterson, M.; Forster, C.; Gilbertsen, A.; Benyumov, A.; Smith, K.; Korenczuk, C.E.; Barocas, V.H.; Guenther, K.; et al. Dicer1 Deficiency in the Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Fibroblastic Focus Promotes Fibrosis by Suppressing MicroRNA Biogenesis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basalova, N.; Sagaradze, G.; Arbatskiy, M.; Evtushenko, E.; Kulebyakin, K.; Grigorieva, O.; Akopyan, Z.; Kalinina, N.; Efimenko, A. Secretome of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevents Myofibroblasts Differentiation by Transferring Fibrosis-Associated microRNAs within Extracellular Vesicles. Cells 2020, 9, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051272
Basalova N, Sagaradze G, Arbatskiy M, Evtushenko E, Kulebyakin K, Grigorieva O, Akopyan Z, Kalinina N, Efimenko A. Secretome of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevents Myofibroblasts Differentiation by Transferring Fibrosis-Associated microRNAs within Extracellular Vesicles. Cells. 2020; 9(5):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051272
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasalova, Nataliya, Georgy Sagaradze, Mikhail Arbatskiy, Evgeniy Evtushenko, Konstantin Kulebyakin, Olga Grigorieva, Zhanna Akopyan, Natalia Kalinina, and Anastasia Efimenko. 2020. "Secretome of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevents Myofibroblasts Differentiation by Transferring Fibrosis-Associated microRNAs within Extracellular Vesicles" Cells 9, no. 5: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051272
APA StyleBasalova, N., Sagaradze, G., Arbatskiy, M., Evtushenko, E., Kulebyakin, K., Grigorieva, O., Akopyan, Z., Kalinina, N., & Efimenko, A. (2020). Secretome of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevents Myofibroblasts Differentiation by Transferring Fibrosis-Associated microRNAs within Extracellular Vesicles. Cells, 9(5), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051272




