Macrophage Activation Markers, CD163 and CD206, in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction: Macrophages, Inflammatory Liver Diseases, and ACLF
2. Macrophages
Scavenger Receptors—Structure and Function
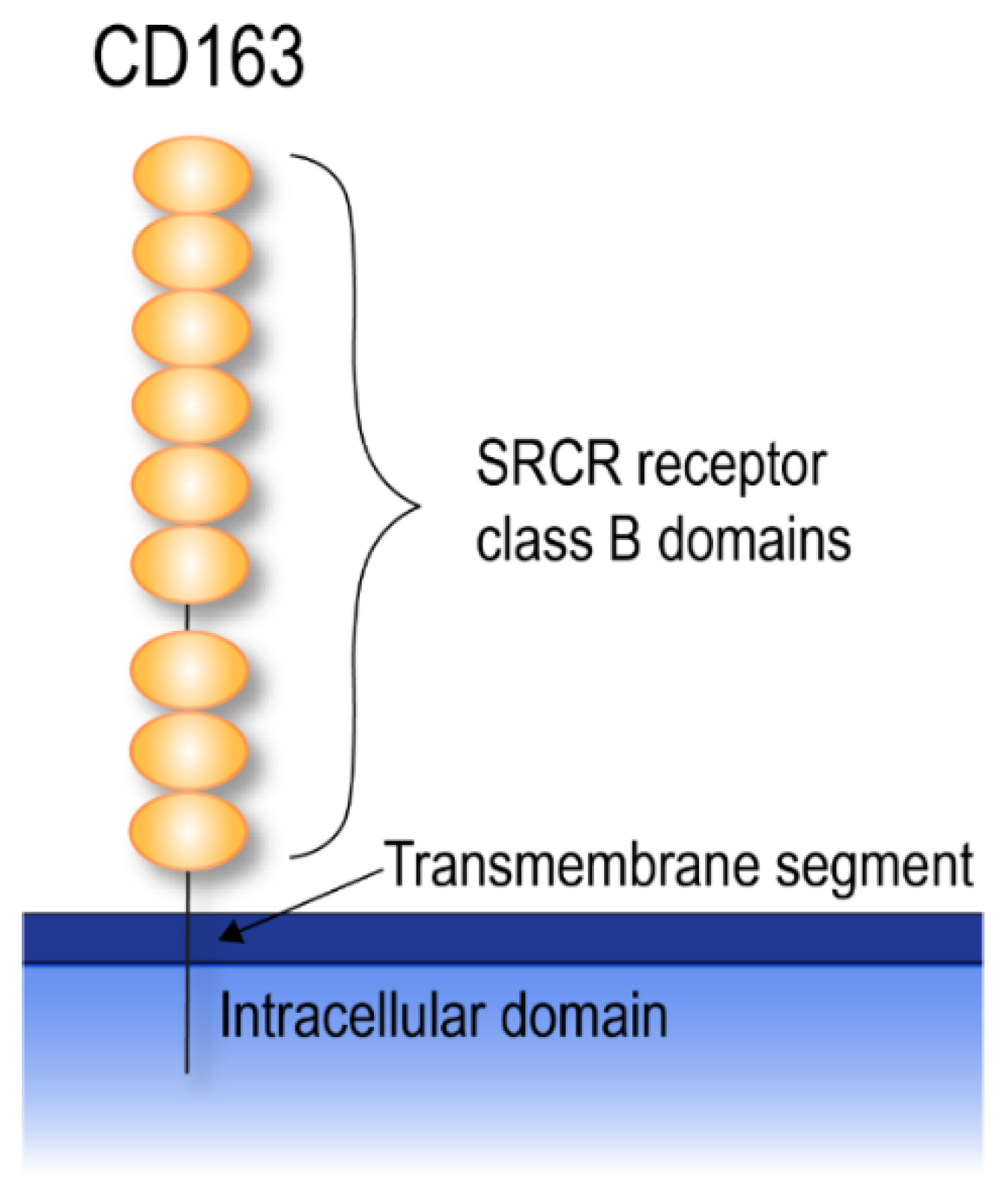
3. CD163
3.1. CD163 Shedding
3.2. Soluble CD163 Function
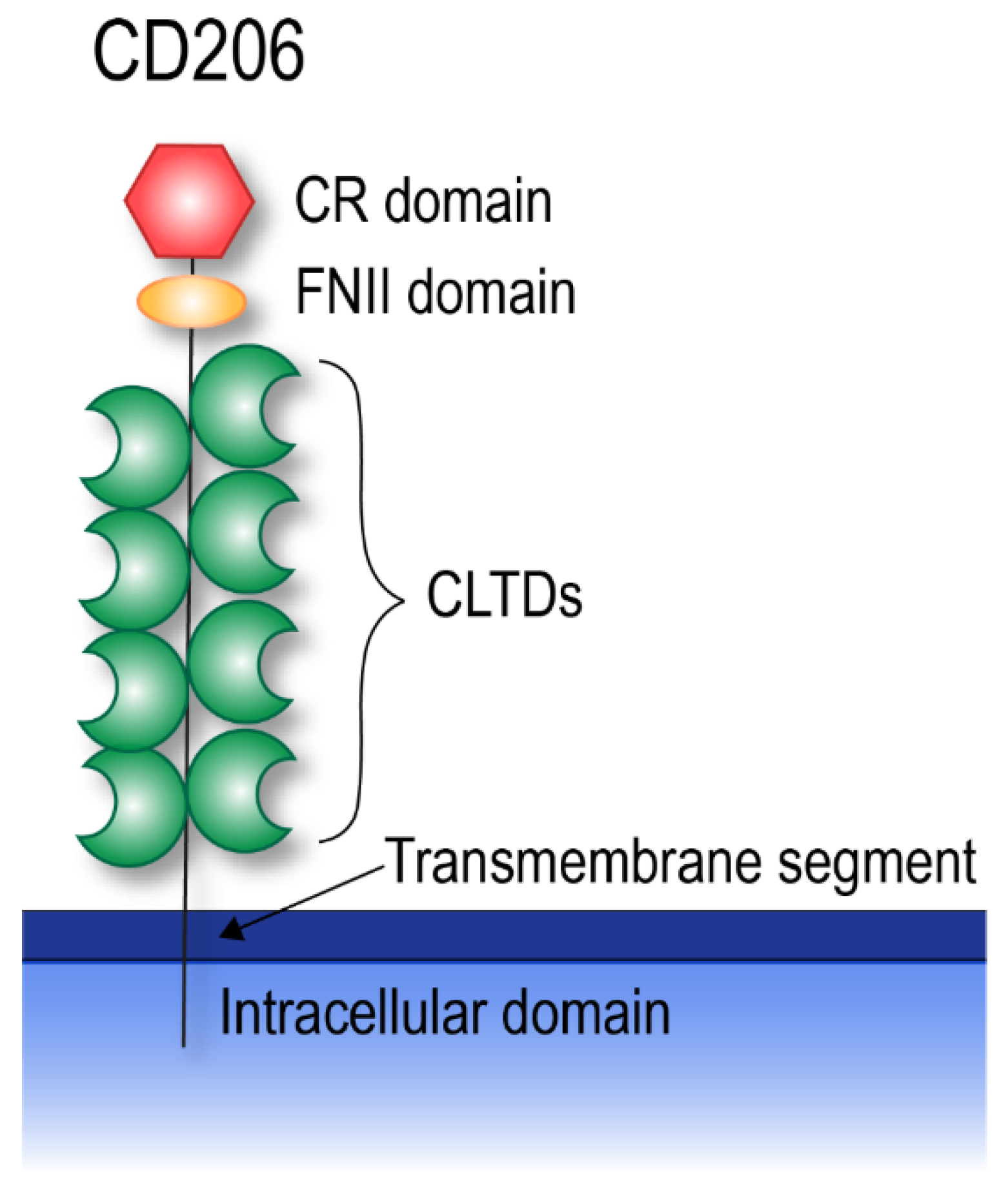
4. CD206
4.1. CD206 Shedding
4.2. sCD206 Function
5. sCD163 and sCD206 in Liver Disease
5.1. sCD163 in Liver Diseases
5.2. sCD206 in Liver Diseases
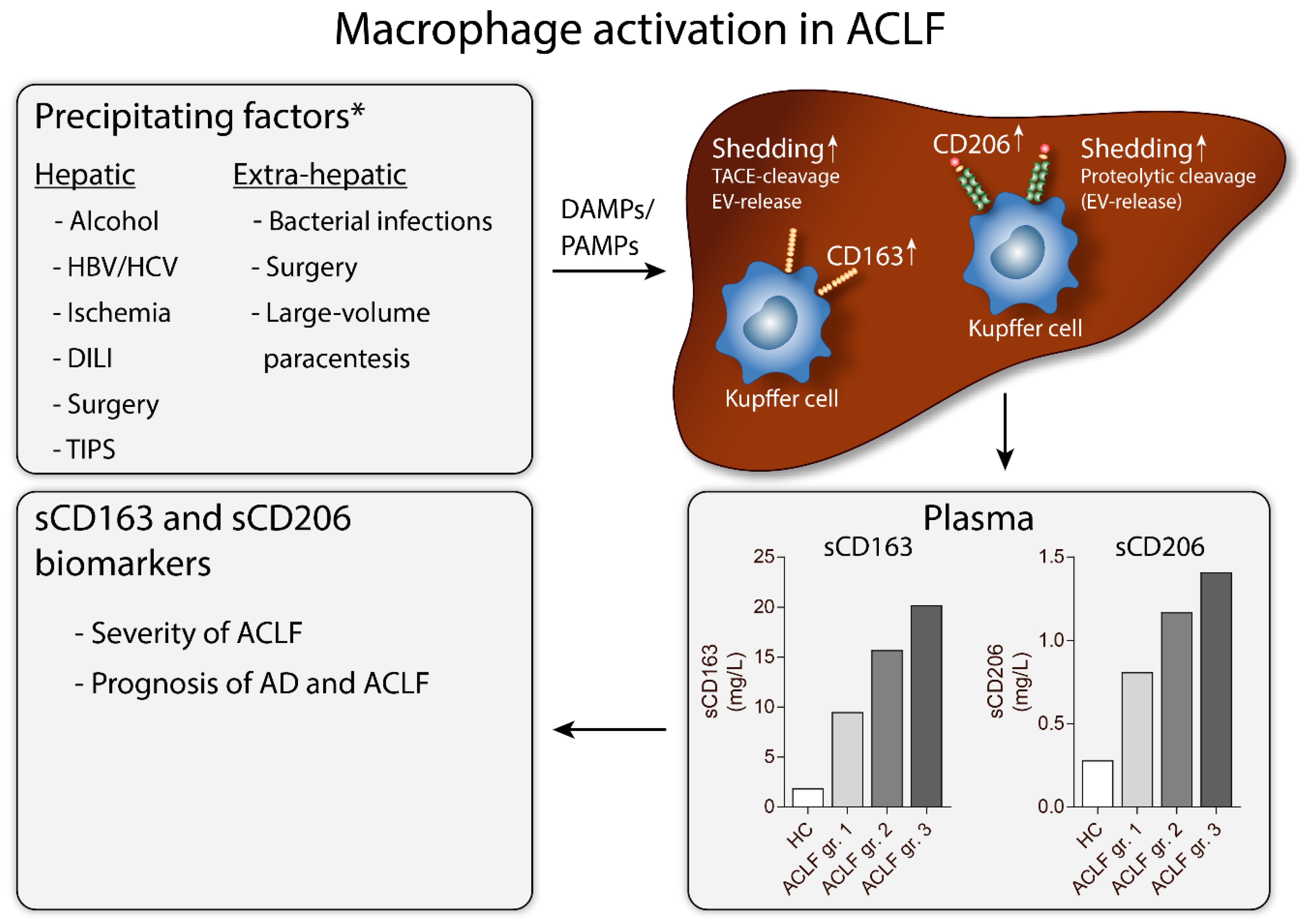
6. Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure
6.1. sCD163 in ACLF
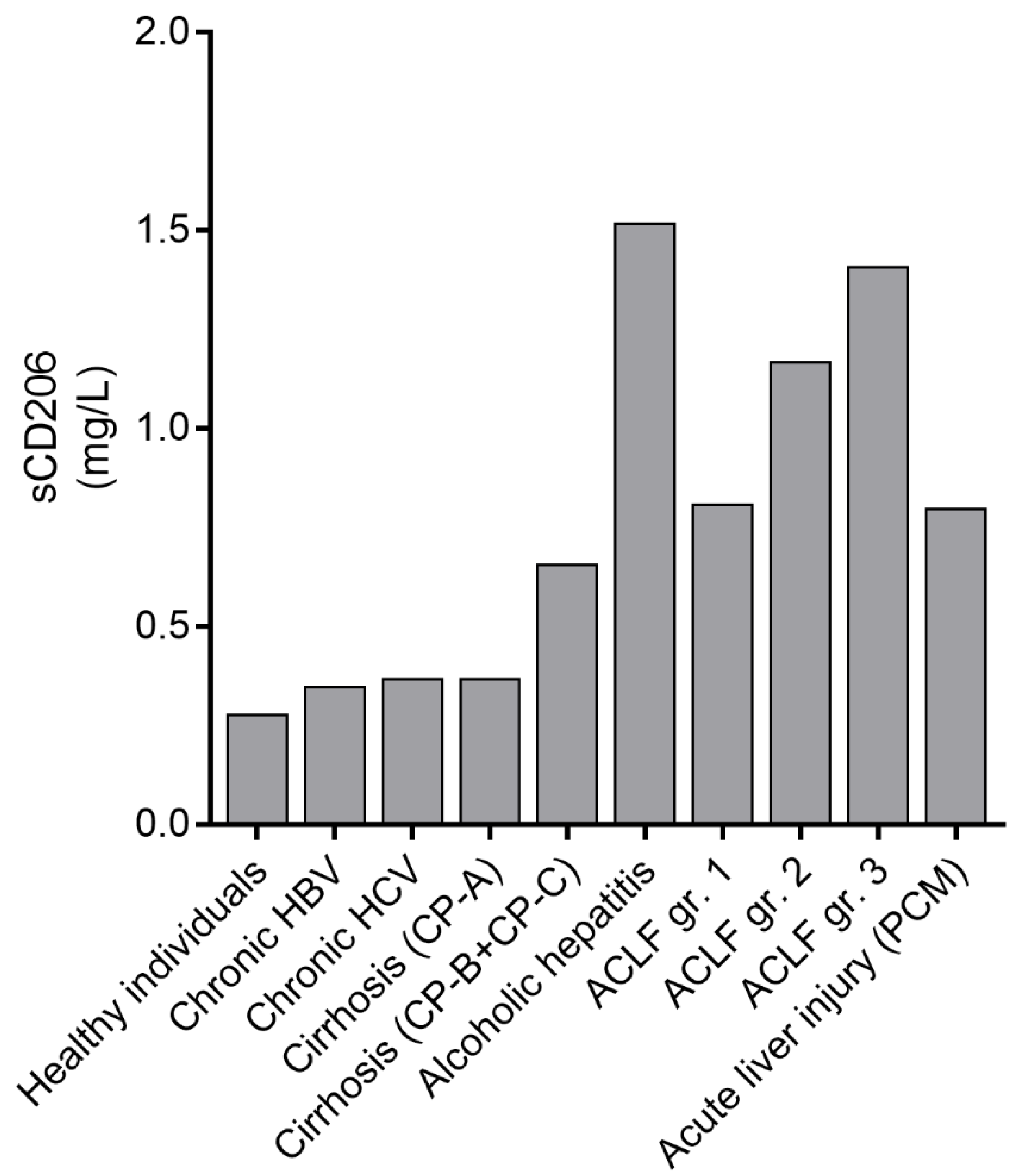
6.2. sCD206 in ACLF
6.3. Similarities and Differences in sCD163 and sCD206 in AD and ACLF
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Ginès, P.; Pavesi, M.; Angeli, P.; Cordoba, J.; Durand, F.; Gustot, T.; Saliba, F.; Domenicali, M.; et al. Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Is a Distinct Syndrome That Develops in Patients With Acute Decompensation of Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1426–1437.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebayo, D.; Morabito, V.; Jalan, R. Acute-on-chronic liver failure. Cirrhosis A Pract. Guide Manag. 2015, 57, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, N.; Kaplan, D.; Taddei, T.H.; Goldberg, D.S. Incidence and Mortality of Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Using Two Definitions in Patients with Compensated Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2150–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalan, R.; Saliba, F.; Pavesi, M.; Amorós, A.; Moreau, R.; Ginès, P.; Lévesque, É.; Durand, F.; Angeli, P.; Caraceni, P.; et al. Development and validation of a prognostic score to predict mortality in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V.; Moreau, R.; Kamath, P.; Jalan, R.; Ginès, P.; Nevens, F.; Fernández, J.; To, U.; García-Tsao, G.; Schnabl, B. Acute-on-chronic liver failure in cirrhosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grønbæk, H.; Rødgaard-Hansen, S.; Aagaard, N.K.; Arroyo, V.; Moestrup, S.K.; Garcia, E.; Solà, E.; Domenicali, M.; Piano, S.; Vilstrup, H.; et al. Macrophage activation markers predict mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis without or with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzerodt, A.; Maniecki, M.B.; Moller, K.; Møller, H.J.; Moestrup, S.K. Tumor necrosis factor α-converting enzyme (TACE/ADAM17) mediates ectodomain shedding of the scavenger receptor CD163. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzerodt, A.; Berg, R.M.G.; Plovsing, R.R.; Andersen, M.N.; Bebien, M.; Habbeddine, M.; Lawrence, T.; Møller, H.J.; Moestrupa, S.K. Soluble ectodomain CD163 and extracellular vesicle-associated CD163 are two differently regulated forms of “soluble CD163” in plasma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.C.; Andersen, M.N.; Rittig, N.; Rødgaard-Hansen, S.; Grønbaek, H.; Moestrup, S.K.; Møller, H.J.; Etzerodt, A.; Grønbæk, H. The macrophage-related biomarkers sCD163 and sCD206 are released by different shedding mechanisms. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Martinez-Pomares, L. Physiological roles of macrophages. Pflüger, Archiv für die Gesammte Physiologie des Menschen und der Thiere 2017, 469, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosser, D.; Edwards, J. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhudas, M.; Baldwin, C.L.; Bollyky, P.L.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Drickamer, K.; Febbraio, M.; Herz, J.; Kobzik, L.; Krieger, M.; Loike, J.; et al. A Consensus Definitive Classification of Scavenger Receptors and Their Roles in Health and Disease. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 3775–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, S.K.A.; Micklem, K.J.; Shaw, J.M.; Zhang, X.-P.; Dong, Y.; Willis, A.C.; Mason, D.Y. A new macrophage differentiation antigen which is a member of the scavenger receptor superfamily. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gröger, M.; Holnthoner, W.; Maurer, D.; Lechleitner, S.; Wolff, K.; Mayr, B.B.; Lubitz, W.; Petzelbauer, P. Dermal microvascular endothelial cells express the 180-kDa macrophage mannose receptor in situ and in vitro. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5428–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcheray, F.; Viaud, S.; Rimaniol, A.-C.; Leone, C.; Samah, B.; Dereuddre-Bosquet, N.; Dormont, D.; Gras, G. Macrophage activation switching: An asset for the resolution of inflammation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 142, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Kuang, H.; Ansari, S.; Liu, T.; Gong, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, L.; et al. Landscape of Intercellular Crosstalk in Healthy and NASH Liver Revealed by Single-Cell Secretome Gene Analysis. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 644–660.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, P.; Dobie, R.; Wilson-Kanamori, J.R.; Dora, E.F.; Henderson, B.E.P.; Luu, N.T.; Portman, J.R.; Matchett, K.P.; Brice, M.; Marwick, J.A.; et al. Resolving the fibrotic niche of human liver cirrhosis at single-cell level. Nature 2019, 575, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulford, K.; Micklem, K.; McCarthy, S.; Cordell, J.; Jones, M.; Mason, D.Y. A monocyte/macrophage antigen recognized by the four antibodies GHI/61, Ber-MAC3, Ki-M8 and SM4. Immunology 1992, 75, 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Backé, E.; Schwarting, R.; Gerdes, J.; Ernst, M.; Stein, H. Ber-MAC3: New monoclonal antibody that defines human monocyte/macrophage differentiation antigen. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 44, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, M.; Graversen, J.H.; Jacobsen, C.; Sonne, O.; Hoffman, H.-J.; Law, S.A.; Moestrup, S.K. Identification of the haemoglobin scavenger receptor. Nature 2001, 409, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.J.; Møller, H.J.; Moestrup, S.K.; Madsen, M. The macrophage scavenger receptor CD163: Endocytic properties of cytoplasmic tail variants. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rother, R.P.; Bell, L.; Hillmen, P.; Gladwin, M.T. The Clinical Sequelae of Intravascular Hemolysis and Extracellular Plasma Hemoglobin. JAMA 2005, 293, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbé, E.; Huitinga, I.; A Döpp, E.; Bauer, J.; Dijkstra, C.D. A novel bone marrow frozen section assay for studying hematopoietic interactions in situ: The role of stromal bone marrow macrophages in erythroblast binding. J. Cell Sci. 1996, 109, 2937–2945. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fabriek, B.O.; Polfliet, M.M.; Vloet, R.P.M.; Van Der Schors, R.C.; Ligtenberg, A.J.M.; Weaver, L.; Geest, C.; Matsuno, K.; Moestrup, S.K.; Dijkstra, C.D.; et al. The macrophage CD163 surface glycoprotein is an erythroblast adhesion receptor. Blood 2007, 109, 5223–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabriek, B.O.; Van Bruggen, R.; Deng, D.M.; Ligtenberg, A.J.M.; Nazmi, K.; Schornagel, K.; Vloet, R.P.M.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Berg, T.K.V.D. The macrophage scavenger receptor CD163 functions as an innate immune sensor for bacteria. Blood 2009, 113, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bover, L.C.; Cardó-Vila, M.; Kuniyasu, A.; Sun, J.; Rangel, R.; Takeya, M.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Arap, W.; Arap, W. A previously unrecognized protein-protein interaction between TWEAK and CD163: Potential biological implications. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 8183–8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.A.; Muñoz-Garcia, B.; Martin-Ventura, J.L.; Madrigal-Matute, J.; Orbe, J.; Paramo, J.A.; Ortega, L.; Egido, J.; Blanco-Colio, L.M. The CD163-expressing macrophages recognize and internalize TWEAK. Atherosclerosis 2009, 207, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, H.J.; Peterslund, N.A.; Graversen, J.H.; Moestrup, S.K. Identification of the hemoglobin scavenger receptor/CD163 as a natural soluble protein in plasma. Blood 2002, 99, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulahian, T.H.; Hintz, K.A.; Wardwell, K.; Guyre, P.M. Development of an ELISA to measure soluble CD163 in biological fluids. J. Immunol. Methods 2001, 252, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, L.; Hintz-Goldstein, K.A.; Pioli, P.A.; Wardwell, K.; Qureshi, N.; Vogel, S.N.; Guyre, P.M. Pivotal Advance: Activation of cell surface Toll-like receptors causes shedding of the hemoglobin scavenger receptor CD163. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droste, A.; Sorg, C.; Högger, P. Shedding of CD163, a Novel Regulatory Mechanism for a Member of the Scavenger Receptor Cysteine-Rich Family. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 256, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, H.J.; Nielsen, M.J.; Maniecki, M.B.; Madsen, M.; Moestrup, S.K. Soluble macrophage-derived CD163: A homogenous ectodomain protein with a dissociable haptoglobin–hemoglobin binding. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandahl, T.D.; Grønbæk, H.; Møller, H.J.; Støy, S.; Thomsen, K.L.; Dige, A.K.; Agnholt, J.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Thiel, S.; Vilstrup, H. Hepatic Macrophage Activation and the LPS Pathway in Patients With Alcoholic Hepatitis: A Prospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, H.J.; Grønbæk, H.; Schiødt, F.V.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Schilsky, M.; Muñoz, S.; Hassanein, T.; Lee, W.M.; Grønbaek, H.; the US Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Soluble CD163 from activated macrophages predicts mortality in acute liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazankov, K.; Barrera, F.; Møller, H.J.; Bibby, B.M.; Vilstrup, H.; George, J.; Grønbaek, H. Soluble CD163, a macrophage activation marker, is independently associated with fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis B and C. Hepatology 2014, 60, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdo, T.H.; Lentz, M.R.; Autissier, P.; Krishnan, A.; Halpern, E.; Letendre, S.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Ellis, R.J.; Williams, K.C. Soluble CD163 made by monocyte/macrophages is a novel marker of HIV activity in early and chronic infection prior to and after anti-retroviral therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.N.; Abildgaard, N.; Maniecki, M.B.; Møller, H.J.; Andersen, N.F. Monocyte/macrophage-derived soluble CD163: A novel biomarker in multiple myeloma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 93, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, J.H.; Moon, J.M.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.B. Prognostic Significance of Serum Soluble CD163 Level in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2013, 75, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaer, D.J.; Schleiffenbaum, B.; Kurrer, M.; Imhof, A.; Bachli, E.; Fehr, J.; Møller, H.J.; Moestrup, S.K.; Schaffner, A. Soluble hemoglobin-haptoglobin scavenger receptor CD163 as a lineage-specific marker in the reactive hemophagocytic syndrome. Eur. J. Haematol. 2005, 74, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hønge, B.L.; Andersen, M.N.; Jespersen, S.; Medina, C.; Correira, F.G.; Jakobsen, M.R.; Laursen, A.; Erikstrup, C.; Møller, H.J.; Wejse, C. Brief Report: Macrophage Activation in HIV-2-Infected Patients Is Less Affected by Antiretroviral Treatment-sCD163 in HIV-1, HIV-2, and HIV-1/2 Dually Infected Patients. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2016, 72, 254–258. [Google Scholar]
- Moller, H.J. Soluble CD163. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2012, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvorning, S.L.; Nielsen, M.C.; Andersen, N.F.; Hokland, M.; Andersen, M.N.; Møller, H.J. Circulating extracellular vesicle-associated CD163 and CD206 in multiple myeloma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020, 104, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzerodt, A.; Rasmussen, M.R.; Svendsen, P.; Chalaris, A.; Schwarz, J.; Galea, I.; Møller, H.J.; Moestrup, S.K. Structural Basis for Inflammation-driven Shedding of CD163 Ectodomain and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Macrophages*. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 289, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Högger, P.; Sorg, C. Soluble CD163 Inhibits Phorbol Ester-Induced Lymphocyte Proliferation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 288, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneidl, J.; Löffler, B.; Erat, M.C.; Kalinka, J.; Peters, G.; Roth, J.; Barczyk, K. Soluble CD163 promotes recognition, phagocytosis and killing of Staphylococcus aureus via binding of specific fibronectin peptides. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 914–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Cheng, Y.; Emrich, S.; Schorey, J.S. Activation of endothelial cells by extracellular vesicles derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis infected macrophages or mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, P.K.; Schorey, J.S. Exosomes Derived from M. Bovis BCG Infected Macrophages Activate Antigen-Specific CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, S.A.; Martinez-Pomares, L.; Stahl, P.D.; Gordon, S. Mannose Receptor and Its Putative Ligands in Normal Murine Lymphoid and Nonlymphoid Organs: In Situ Expression of Mannose Receptor by Selected Macrophages, Endothelial Cells, Perivascular Microglia, and Mesangial Cells, but not Dendritic Cells. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, D.B.; Songu-Mize, E.; Pontow, S.E.; Stahl, P.D.; Rattazzi, M.C. A mannose receptor mediates mannosyl-rich glycoprotein-induced mitogenesis in bovine airway smooth muscle cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shepherd, V.L.; I Tarnowski, B.; McLaughlin, B.J. Isolation and characterization of a mannose receptor from human pigment epithelium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1991, 32, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M.E.; Conary, J.T.; Lennartz, M.R.; Stahl, P.D.; Drickamer, K. Primary structure of the mannose receptor contains multiple motifs resembling carbohydrate-recognition domains. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 12156–12162. [Google Scholar]
- Boskovic, J.; Arnold, J.; Stilion, R.; Gordon, S.; Sim, R.; Rivera-Calzada, A.; Wienke, D.; Isacke, C.; Martinez-Pomares, L.; Llorca, O. Structural Model for the Mannose Receptor Family Uncovered by Electron Microscopy of Endo180 and the Mannose Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8780–8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Bakker, T.; Harris, J.; Tsang, C.; Brown, G.D.; Wormald, M.; Gordon, S.; Dwek, R.A.; Rudd, P.M.; Martinez-Pomares, L. Glycosylation Influences the Lectin Activities of the Macrophage Mannose Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 32811–32820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Shi, X.; Yu, B.; Li, N.; Huang, Y.; He, Y. Structural Insights into the pH-Dependent Conformational Change and Collagen Recognition of the Human Mannose Receptor. Structure 2018, 26, 60–71.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, C.; He, Y. Structural basis of the pH-dependent conformational change of the N-terminal region of human mannose receptor/CD206. J. Struct. Biol. 2019, 208, 107384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Pomares, L. The mannose receptor. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leteux, C.; Chai, W.; Loveless, R.W.; Yuen, C.T.; Uhlin-Hansen, L.; Combarnous, Y.; Jankovic, M.; Maric, S.C.; Misulovin, Z.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; et al. The cysteine-rich domain of the macrophage mannose receptor is a multispecific lectin that recognizes chondroitin sulfates A and B and sulfated oligosaccharides of blood group Lewis(a) and Lewis(x) types in addition to the sulfated N-glycans of lutropin. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chirino, A.J.; Misulovin, Z.; Leteux, C.; Feizi, T.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Bjorkman, P.J. Crystal Structure of the Cysteine-Rich Domain of Mannose Receptor Complexed with a Sulfated Carbohydrate Ligand. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Pomares, L.; Wienke, D.; Stillion, R.; McKenzie, E.J.; Arnold, J.; Harris, J.; McGreal, E.; Sim, R.; Isacke, C.; Gordon, S. Carbohydrate-independent recognition of collagens by the macrophage mannose receptor. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, C.E.; Drickamer, K.; Taylor, M.E. Collagen binding by the mannose receptor mediated through the fibronectin type II domain. Biochem. J. 2006, 395, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.E.; Bezouska, K.; Drickamer, K. Contribution to ligand binding by multiple carbohydrate-recognition domains in the macrophage mannose receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar]
- Fiete, D.J.; Beranek, M.C.; Baenziger, J.U. A cysteine-rich domain of the "mannose" receptor mediates GalNAc-4-SO4 binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J. Mannose Receptor-Mediated Regulation of Serum Glycoprotein Homeostasis. Science 2002, 295, 1898–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maródi, L.; Forehand, J.R.; Johnston, R.B. Mechanisms of host defense against Candida species. II. Biochemical basis for the killing of Candida by mononuclear phagocytes. J. Immunol. 1991, 146, 2790–2794. [Google Scholar]
- O’Riordan, D.M.; Standing, J.E.; Limper, A.H. Pneumocystis carinii glycoprotein A binds macrophage mannose receptors. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Hildreth, J.E.K. Involvement of macrophage mannose receptor in the binding and transmission of HIV by macrophages. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamze, S.; Martinez-Pomares, L.; Jones, H.; Taylor, P.R.; Stillion, R.J.; Gordon, S.; Wong, S.Y.C. Recognition of Bacterial Capsular Polysaccharides and Lipopolysaccharides by the Macrophage Mannose Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41613–41623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseman, A.P.; Moseman, E.A.; Schworer, S.; Smirnova, I.; Volkova, T.; von Andrian, U.; Poltorak, A. Mannose receptor 1 mediates cellular uptake and endosomal delivery of CpG-motif containing oligodeoxynucleotides. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5615–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, U.; Martinez-Pomares, L. Influence of the mannose receptor in host immune responses. Immunobiology 2009, 214, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.R.; Gordon, S.; Martinez-Pomares, L. The mannose receptor: Linking homeostasis and immunity through sugar recognition. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, U.; Rosas, M.; Singh, S.; Heinsbroek, S.; Haq, I.; Johnson, S.R.; Brown, G.D.; Williams, D.L.; Taylor, P.R.; Martinez-Pomares, L. Fungal recognition enhances mannose receptor shedding through dectin-1 engagement. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7822–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Pomares, L.; Mahoney, J.A.; Káposzta, R.; Linehan, S.A.; Stahl, P.D.; Gordon, S.; Martínez-Pomares, L. A Functional Soluble Form of the Murine Mannose Receptor Is Produced by Macrophagesin Vitroand Is Present in Mouse Serum. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 23376–23380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordens, R.; Thompson, A.; Amons, R.; Koning, F. Human dendritic cells shed a functional, soluble form of the mannose receptor. Int. Immunol. 1999, 11, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fraser, I.P.; Takahashi, K.; Koziel, H.; Fardin, B.; Harmsen, A.; Ezekowitz, R.B. Pneumocystis carinii enhancessoluble mannose receptor production by macrophages. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødgaard-Hansen, S.; Rafique, A.; Christensen, P.A.; Maniecki, M.B.; Sandahl, T.D.; Nexø, E.; Møller, H.J. A soluble form of the macrophage-related mannose receptor (MR/CD206) is present in human serum and elevated in critical illness. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødgaard-Hansen, S.; Rafique, A.; Weis, N.; Wejse, C.; Nielsen, H.; Pedersen, S.S.; Møller, H.J.; Kronborg, G. Increased concentrations of the soluble mannose receptor in serum from patients with pneumococcal bacteraemia, and prediction of survival. Infect. Dis. 2015, 47, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.N.; Andersen, N.F.; Rødgaard-Hansen, S.; Hokland, M.; Abildgaard, N.; Møller, H.J. The novel biomarker of alternative macrophage activation, soluble mannose receptor (sMR/sCD206): Implications in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandahl, T.D.; Støy, S.H.; Laursen, T.L.; Rødgaard-Hansen, S.; Møller, H.J.; Møller, S.; Vilstrup, H.; Grønbæk, H. The soluble mannose receptor (sMR) is elevated in alcoholic liver disease and associated with disease severity, portal hypertension, and mortality in cirrhosis patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainer, F.; Horvath, A.; Sandahl, T.D.; Leber, B.; Schmerboeck, B.; Blesl, A.; Groselj-Strele, A.; Stauber, R.E.; Fickert, P.; Stiegler, P.; et al. Soluble CD163 and soluble mannose receptor predict survival and decompensation in patients with liver cirrhosis, and correlate with gut permeability and bacterial translocation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 47, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, T.L.; Wong, G.L.H.; Kazankov, K.; Sandahl, T.D.; Møller, H.J.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; George, J.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Grønbæk, H. Soluble CD163 and mannose receptor associate with chronic hepatitis B activity and fibrosis and decline with treatment. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Torre-Minguela, C.; Barberà-Cremades, M.; Gómez, A.I.; Martín-Sánchez, F.; Pelegrín, P. Macrophage activation and polarization modify P2X7 receptor secretome influencing the inflammatory process. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Pomares, L.; Gordon, S. Potential role of the mannose receptor in antigen transport. Immunol. Lett. 1999, 65, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazankov, K.; Tordjman, J.; Møller, H.J.; Vilstrup, H.; Poitou, C.; Bedossa, P.; Bouillot, J.; Clement, K.; Grønbaek, H. Macrophage activation marker soluble CD163 and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in morbidly obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazankov, K.; Barrera, F.; Møller, H.J.; Rosso, C.; Bugianesi, E.; David, E.; Jouness, R.I.K.; Esmaili, S.; Eslam, M.; McLeod, D.; et al. The macrophage activation marker sCD163 is associated with morphological disease stages in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, J.L.; Feeney, E.R.; Zheng, H.; Misdraji, J.; Kruger, A.J.; Alatrakchi, N.; King, L.Y.; Gelrud, L.; E Corey, K.; Chung, R.T. Circulating Soluble CD163 is Associated with Steatohepatitis and Advanced Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazankov, K.; Møller, H.J.; Lange, A.; Birkebaek, N.H.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Solvig, J.; Hørlyck, A.; Kristensen, K.; Rittig, S.; Handberg, A.; et al. The macrophage activation marker sCD163 is associated with changes in NAFLD and metabolic profile during lifestyle intervention in obese children. Pediatr. Obes. 2014, 10, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødgaard-Hansen, S.; George, A.S.; Kazankov, K.; Bauman, A.; George, J.; Grønbæk, H.; Møller, H.J. Effects of lifestyle intervention on soluble CD163, a macrophage activation marker, in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2017, 77, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dultz, G.; Gerber, L.; Farnik, H.; Berger, A.; Vermehren, J.; Pleli, T.; Zeuzem, S.; Piiper, A.; Kronenberger, B.; Waidmann, O. Soluble CD163 is an indicator of liver inflammation and fibrosis in patients chronically infected with the hepatitis B virus. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 22, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dultz, G.; Gerber, L.; Zeuzem, S.; Sarrazin, C.; Waidmann, O. The macrophage activation marker CD163 is associated with IL28B genotype and hepatic inflammation in chronic hepatitis C virus infected patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 23, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, T.L.; Siggard, C.B.; Kazankov, K.; Sandahl, T.D.; Moller, H.J.; Ong, A.; Douglas, M.; George, J.; Tarp, B.; Kristensen, L.H.; et al. Rapid and persistent decline in soluble CD163 with successful direct-acting antiviral therapy and associations with chronic hepatitis C histology. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, T.L.; Siggaard, C.B.; Kazankov, K.; Sandahl, T.D.; Møller, H.J.; Tarp, B.; Kristensen, L.H.; Laursen, A.L.; Leutscher, P.; Grønbæk, H. Time-dependent improvement of liver inflammation, fibrosis and metabolic liver function after successful direct-acting antiviral therapy of chronic hepatitis C. J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 27, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grønbaek, H.; Sandahl, T.D.; Mortensen, C.; Vilstrup, H.; Møller, H.J.; Møller, S.; Grønbæk, H. Soluble CD163, a marker of Kupffer cell activation, is related to portal hypertension in patients with liver cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 36, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodé, A.; Nicoll, A.; Møller, H.J.; Lim, L.; Angus, P.W.; Kronborg, I.; Arachchi, N.; Gorelik, A.; Liew, D.; Kazankov, K.; et al. Hepatic macrophage activation predicts clinical decompensation in chronic liver disease. Gut 2013, 62, 1231–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waidmann, O.; Brunner, F.; Herrmann, E.; Zeuzem, S.; Piiper, A.; Kronenberger, B. Macrophage activation is a prognostic parameter for variceal bleeding and overall survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland-Fischer, P.; Riggio, O.; Ridola, L.; Vilstrup, H.; Grønbæk, H.; Møller, H.J.; Sandahl, T.D.; Moestrup, S.K.; Aagaard, N.K. Kupffer cells are activated in cirrhotic portal hypertension and not normalised by TIPS. Gut 2011, 60, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Tornai, D.; Kodys, K.; Adejumo, A.; Lowe, P.; McClain, C.; Mitchell, M.; McCullough, A.; Dasarathy, S.; Kroll-Desrosiers, A.; et al. Biomarkers of Macrophage Activation and Immune Danger Signals Predict Clinical Outcomes in Alcoholic Hepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1134–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Horiike, N.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Michitaka, K.; Matsuyama, T.; Onji, M. Soluble CD163 in patients with liver diseases: Very high levels of soluble CD163 in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, S.S.; Zhu, H.H.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, W.X.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.; Xia, C.X.; et al. Expression of serum sCD163 in patients with liver diseases and inflammatory disorders. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 8419–8425. [Google Scholar]
- Siggaard, C.B.; Kazankov, K.; Rødgaard-Hansen, S.; Møller, H.J.; Donnelly, M.C.; Simpson, K.J.; Grønbæk, H. Macrophage markers soluble CD163 and soluble mannose receptor are associated with liver injury in patients with paracetamol overdose. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, E.S.; Rødgaard-Hansen, S.; Moessner, B.; Christensen, P.B.; Møller, H.J.; Weis, N. Macrophage-related serum biomarkers soluble CD163 (sCD163) and soluble mannose receptor (sMR) to differentiate mild liver fibrosis from cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C: A pilot study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 33, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, T.L.; Rødgaard-Hansen, S.; Møller, H.J.; Mortensen, C.; Karlsen, S.; Nielsen, D.T.; Frevert, S.; Clemmesen, J.O.; Møller, S.; Jensen, J.S.; et al. The soluble mannose receptor is released from the liver in cirrhotic patients, but is not associated with bacterial translocation. Liver Int. 2016, 37, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stengel, S.; Quickert, S.; Lutz, P.; Ibidapo-Obe, O.; Steube, A.; Köse-Vogel, N.; Yarbakht, M.; Reuken, P.A.; Busch, M.; Brandt, A.; et al. Peritoneal Level of CD206 Associates With Mortality and an Inflammatory Macrophage Phenotype in Patients With Decompensated Cirrhosis and Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1745–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wlodzimirow, K.A.; Eslami, S.; Abu-Hanna, A.; Nieuwoudt, M.; Chamuleau, R.A.F.M. A systematic review on prognostic indicators of acute on chronic liver failure and their predictive value for mortality. Liver Int. 2012, 33, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernsmeier, C.; Pop, O.T.; Singanayagam, A.; Triantafyllou, E.; Patel, V.C.; Weston, C.; Curbishley, S.; Sadiq, F.; Vergis, N.; Khamri, W.; et al. Patients With Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Have Increased Numbers of Regulatory Immune Cells Expressing the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase MERTK. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 603–615.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clària, J.; Stauber, R.E.; Coenraad, M.J.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Pavesi, M.; Amorós, À.; Titos, E.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Oettl, K.; et al. Systemic inflammation in decompensated cirrhosis: Characterization and role in acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Wang, L.-Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, K. Increased CD163 expression is associated with acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2818–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.; Clària, J.; Aguilar, F.; Fenaille, F.; Lozano, J.J.; Junot, C.; Colsch, B.; Caraceni, P.; Trebicka, J.; Pavesi, M.; et al. Blood metabolomics uncovers inflammation-associated mitochondrial dysfunction as a potential mechanism underlying ACLF. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.-H.; Wu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, X.; Sun, W.; Shi, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, F.; Zhao, H.; Sun, S.; et al. Prognostic utility of novel biomarkers in acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) associated with hepatitis B: A multicenter prospective study. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 49, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, H.J.; Moestrup, S.K.; Weis, N.; Wejse, C.; Nielsen, H.; Pedersen, S.S.; Attermann, J.; Nexø, E.; Kronborg, G. Macrophage serum markers in pneumococcal bacteremia: Prediction of survival by soluble CD163*. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 2561–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalan, R.; Pavesi, M.; Saliba, F.; Amorós, A.; Fernandez, J.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Sawhney, R.; Mookerjee, R.; Caraceni, P.; Moreau, R.; et al. The CLIF Consortium Acute Decompensation score (CLIF-C ADs) for prognosis of hospitalised cirrhotic patients without acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-P.; Guan, S.-H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.-W.; Yang, K.; Zhang, H. Soluble mannose receptor as a predictor of prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5667–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebicka, J.; Amoros, A.; Pitarch, C.; Titos, E.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Schierwagen, R.; Deulofeu, C.; Fernandez-Gomez, J.; Piano, S.; Caraceni, P.; et al. Addressing Profiles of Systemic Inflammation Across the Different Clinical Phenotypes of Acutely Decompensated Cirrhosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, M.; Angeli, P.; Clària, J.; Moreau, R.; Gines, P.; Jalan, R.; Caraceni, P.; Fernandez, J.; Gerbes, A.L.; O’Brien, A.J.; et al. Albumin in decompensated cirrhosis: New concepts and perspectives. Gut 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korf, H.; Du Plessis, J.; Van Pelt, J.; De Groote, S.; Cassiman, D.; Verbeke, L.; Ghesquière, B.; Fendt, S.-M.; Bird, M.; Talebi, A.; et al. LBP-36-Inhibition of glutamine synthetase in monocytes from patients with Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure resuscitates their antibacterial and inflammatory capacity. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, L.; Deng, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; et al. Dynamic Changes of Lipopolysaccharide Levels in Different Phases of Acute on Chronic Hepatitis B Liver Failure. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nielsen, M.C.; Hvidbjerg Gantzel, R.; Clària, J.; Trebicka, J.; Møller, H.J.; Grønbæk, H. Macrophage Activation Markers, CD163 and CD206, in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Cells 2020, 9, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051175
Nielsen MC, Hvidbjerg Gantzel R, Clària J, Trebicka J, Møller HJ, Grønbæk H. Macrophage Activation Markers, CD163 and CD206, in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Cells. 2020; 9(5):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051175
Chicago/Turabian StyleNielsen, Marlene Christina, Rasmus Hvidbjerg Gantzel, Joan Clària, Jonel Trebicka, Holger Jon Møller, and Henning Grønbæk. 2020. "Macrophage Activation Markers, CD163 and CD206, in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure" Cells 9, no. 5: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051175
APA StyleNielsen, M. C., Hvidbjerg Gantzel, R., Clària, J., Trebicka, J., Møller, H. J., & Grønbæk, H. (2020). Macrophage Activation Markers, CD163 and CD206, in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Cells, 9(5), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051175






