Interleukin-6 Derived from the Central Nervous System May Influence the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in a Cell-Dependent Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Conditional IL-6 KO Mice
2.2. Genotyping
2.3. Animals Used for EAE and Tamoxifen Treatment
2.4. Induction of EAE and Clinical Evaluation
2.5. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.6. Histology
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
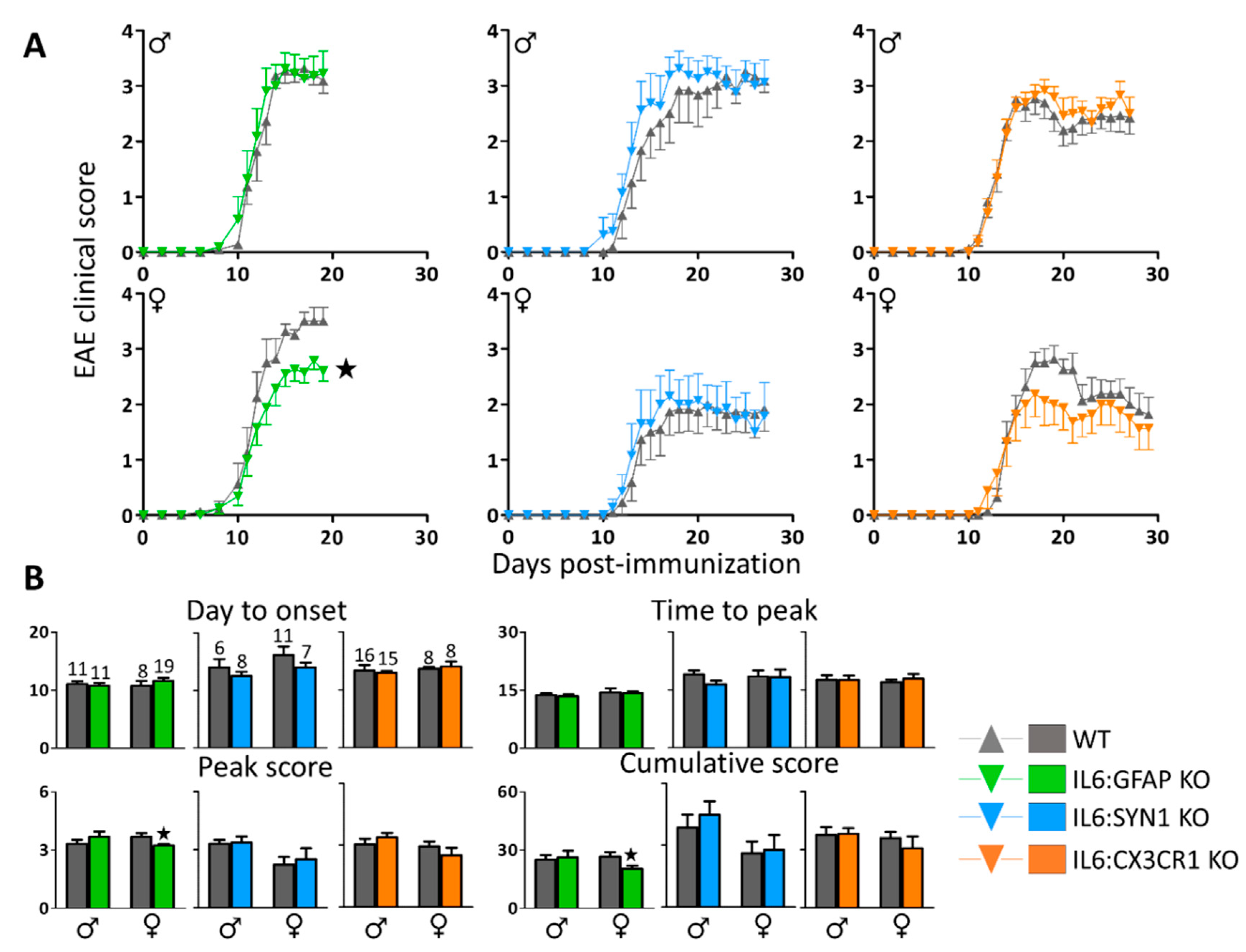
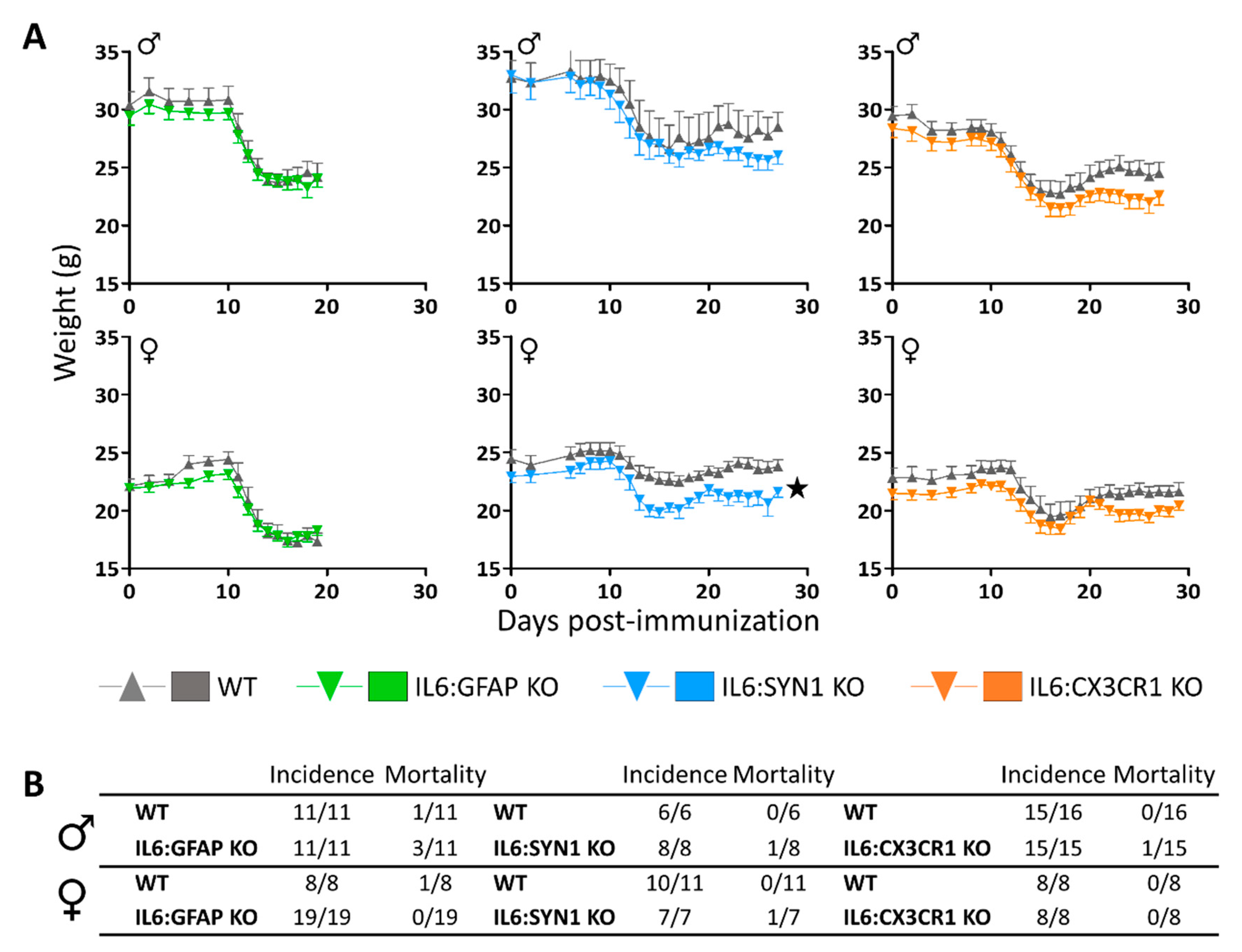
3.1. IL6:GFAP KO, but not IL6:SYN1 KO and IL6:CX3CR1 KO Mice, Present an Ameliorated EAE Symptomatology in a Sex-Dependent Manner
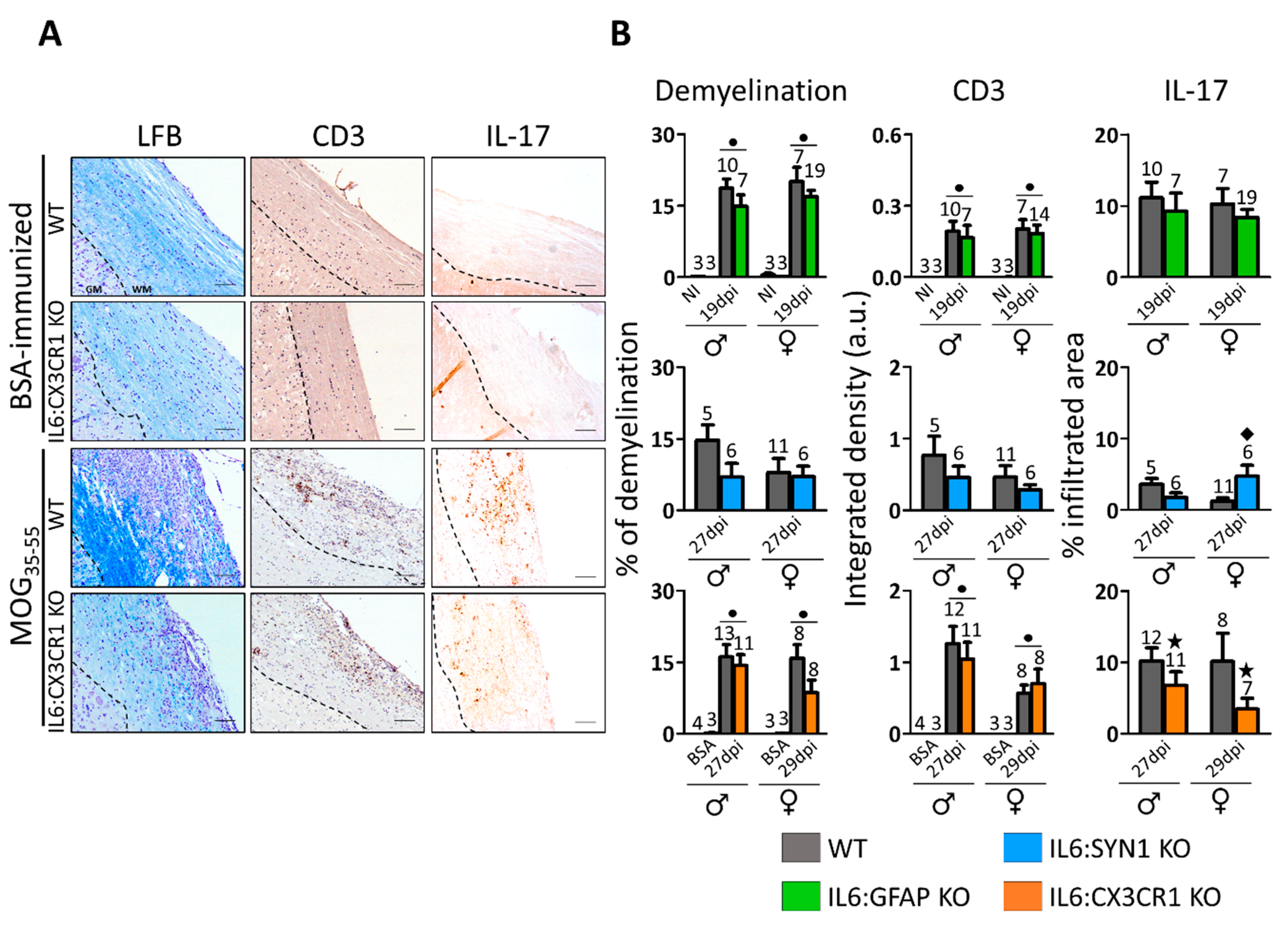
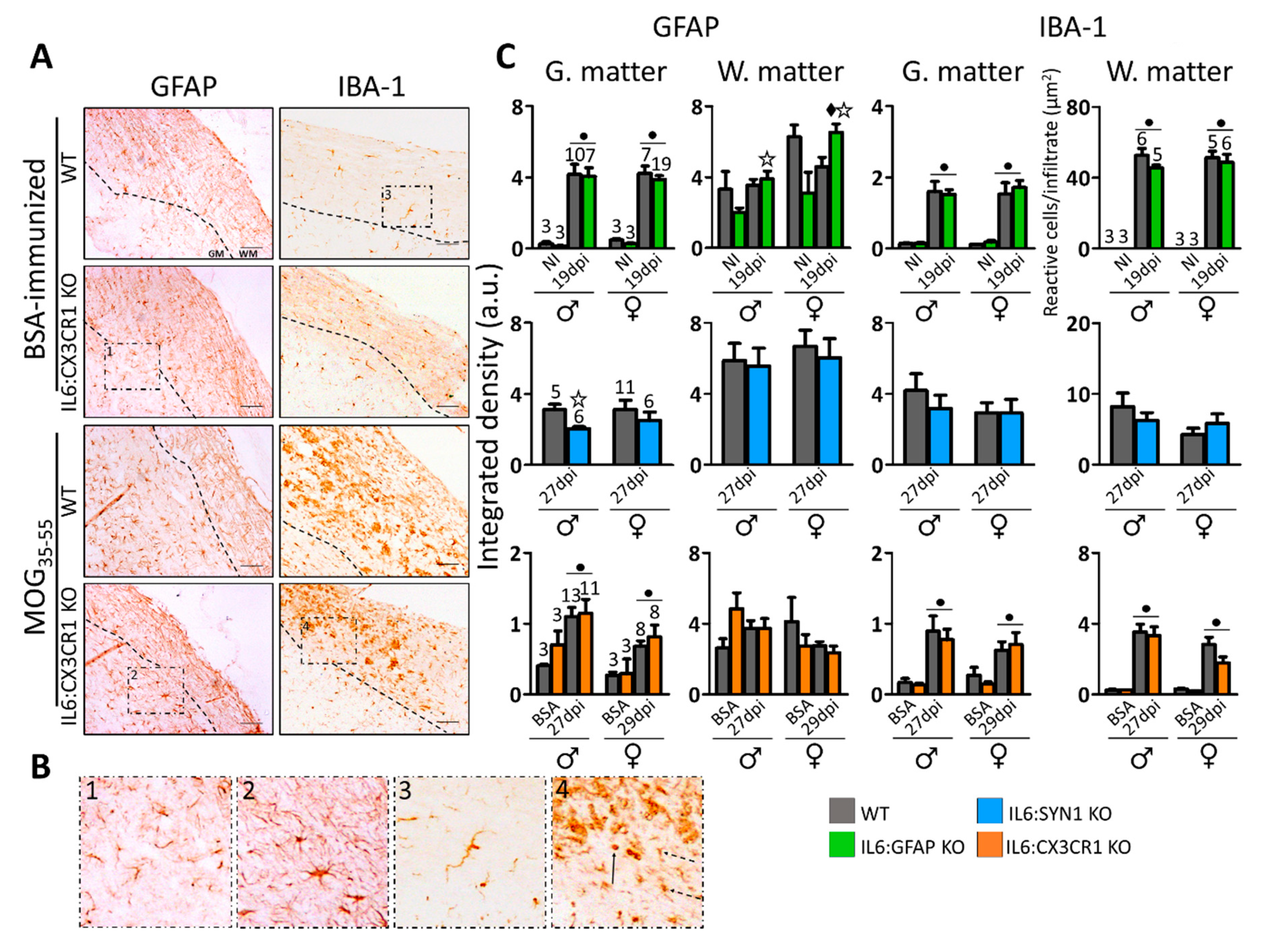
3.2. Demyelination, Infiltrates, and Gliosis in the Spinal Cord of MOG35-55-Immunized Mice are Regulated in Sex- and Cellular IL-6 Source-Dependent Manner
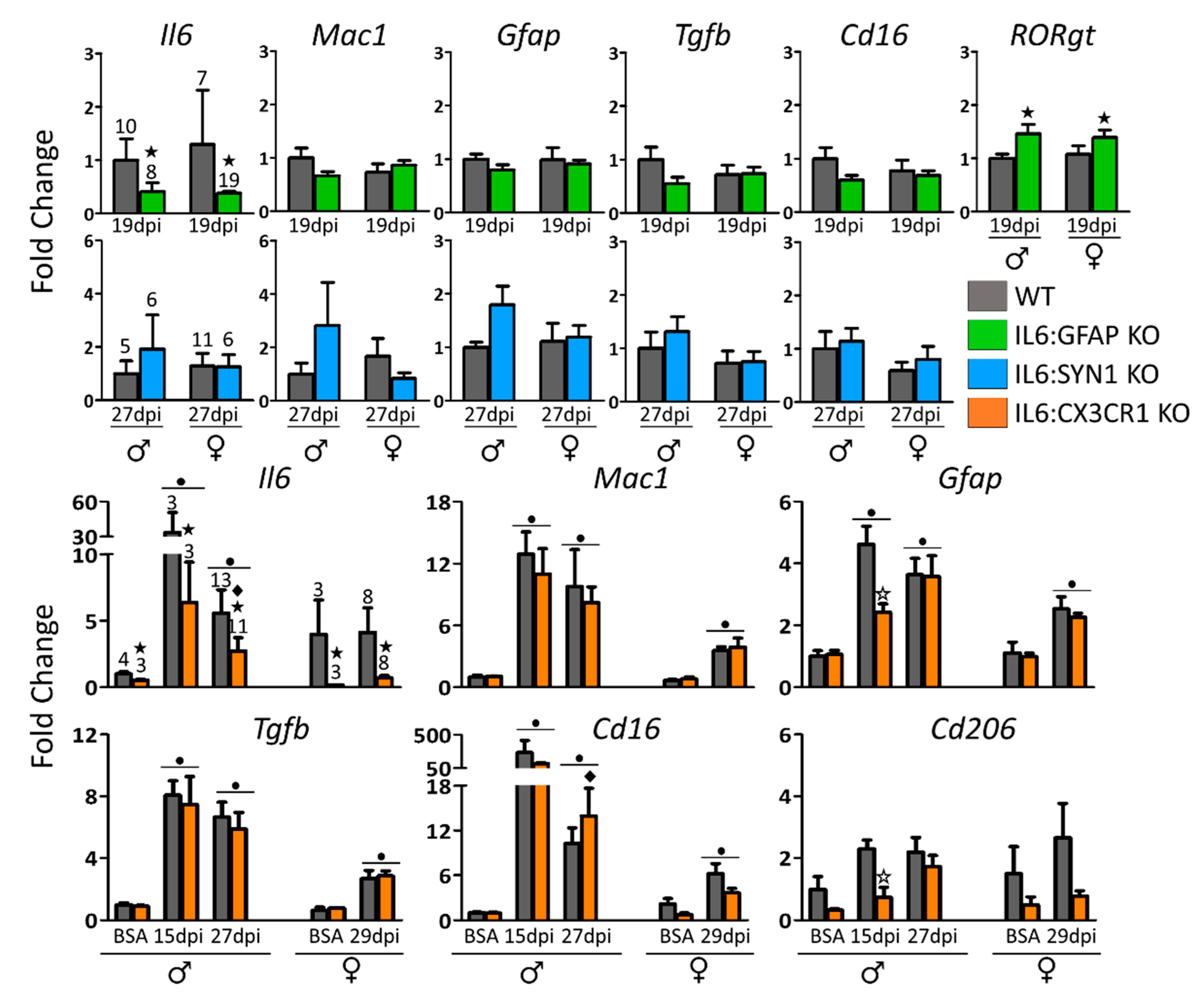
3.3. IL6:GFAP KO and IL6:CX3CR1 KO, but not IL6:SYN1 KO Mice, Present an Altered Expression of Some Inflammation-Related Genes During EAE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erta, M.; Quintana, A.; Hidalgo, J. Interleukin-6, a major cytokine in the central nervous system. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1254–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mycko, M.P.; Papoian, R.; Boschert, U.; Raine, C.S.; Selmaj, K.W. cDNA microarray analysis in multiple sclerosis lesions: Detection of genes associated with disease activity. Brain 2003, 126, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimone, D.; Guazzi, G.C.; Annunziata, P. IL-6 detection in multiple sclerosis brain. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 146, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, M.T.; Culpepper, W.J.; Nichols, E.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Gebrehiwot, T.T.; Hay, S.I.; Khalil, I.A.; Krohn, K.J.; Liang, X.; Naghavi, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of multiple sclerosis 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.P.D.; Barnett, M.H.; Parratt, J.D.E.; Prineas, J.W. Multiple sclerosis: Distribution of inflammatory cells in newly forming lesions. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourbakhsh, B.; Mowry, E.M. Multiple sclerosis risk factors and pathogenesis. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2019, 25, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönrock, L.M.; Gawlowski, G.; Brück, W. Interleukin-6 expression in human multiple sclerosis lesions. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 294, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmasiak, Z.; Kozioł-Montewka, M.; Dobosz, B.; Rejdak, K. IL-6 and sIL-6R concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of MS patients. Med. Sci. Monit. 2001, 7, 914–918. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Liu, J.; Lin, C.Y.; Scott, R.J.; Brown, M.A.; Booth, D.R.; Stewart, G.J.; Broadley, S.; Mason, D.; Griffiths, L.; et al. Interleukin-6 gene promoter-572 C allele may play a role in rate of disease progression in multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13667–13679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.-D.; Li, F.-J.; Shu, Q.-F.; Liu, X.-L.; Jiang, S.-F. Association netween IL-6 -174G/C polymorphism and risk of Multiple Sclerosis: A meta-Analysis. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2013, 18, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirowska-Guzel, D.; Gromadzka, G.; Mach, A.; Czlonkowski, A.; Czlonkowska, A. Association of IL-1A, IL-1B, IL-RN, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α polymorphisms with risk and clinical course of multiple sclerosis in a Polish population. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 236, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, H.; Bradl, M. Multiple sclerosis: Experimental models and reality. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giralt, M.; Molinero, A.; Hidalgo, J. Active induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) with MOG35–55 in the mouse. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1791, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Siffrin, V.; Radbruch, H.; Glumm, R.; Niesner, R.; Paterka, M.; Herz, J.; Leuenberger, T.; Lehmann, S.M.; Luenstedt, S.; Rinnenthal, J.L.; et al. In Vivo imaging of partially reversible Th17 cell-induced neuronal dysfunction in the course of encephalomyelitis. Immunity 2010, 33, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giralt, M.; Ramos, R.; Quintana, A.; Ferrer, B.; Erta, M.; Castro-Freire, M.; Comes, G.; Sanz, E.; Unzeta, M.; Pifarré, P.; et al. Induction of atypical EAE mediated by transgenic production of IL-6 in astrocytes in the absence of systemic IL-6. Glia 2013, 61, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, Y.; Sakoda, S.; Bernard, C.C.A.; Fujimura, H.; Saeki, Y.; Kishimoto, T.; Yanagihara, T. IL-6-deficient mice are resistant to the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis provoked by myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. Int. Immunol. 1998, 10, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugster, H.P.; Frei, K.; Kopf, M.; Lassmann, H.; Fontana, A. IL-6-deficient mice resist myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brod, S.A.; Bauer, V.L. Ingested (oral) tocilizumab inhibits EAE. Cytokine 2014, 68, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serada, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Mihara, M.; Koike, N.; Ohsugi, Y.; Nomura, S.; Yoshida, H.; Nishikawa, T.; Terabe, F.; Ohkawara, T.; et al. IL-6 blockade inhibits the induction of myelin antigen-specific Th17 cells and Th1 cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9041–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijbels, K.; Brocke, S.; Abrams, J.; Steinman, L. Administration of neutralizing antibodies to Interleukin-6 (IL-6) reduces experimental autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and is associated with elevated levels of IL-6 bioactivity in central nervous system and circulation. Mol. Med. 1995, 1, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettelli, E.; Carrier, Y.; Gao, W.; Korn, T.; Strom, T.B.; Oukka, M.; Weiner, H.L.; Kuchroo, V.K. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 2006, 441, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.O.; Chang, S.H.; Nurieva, R.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Hood, L.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, Q.; et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing Interleukin 17. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Bak-Jensen, K.S.; Chen, Y.; Tato, C.M.; Blumenschein, W.; McClanahan, T.; Cua, D.J. TGF-β and IL-6 drive the production of IL-17 and IL-10 by T cells and restrain TH-17 cell-mediated pathology. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oukka, M. Interplay between pathogenic Th17 and regulatory T cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willenborg, O.D.; Fordham, A.S.; Cowden, B.W.; Ramshaw, A.I. Cytokines and murine autoimmune eEncephalomyelitis: Inhibition or enhancement of disease with antibodies to select cytokines, or by delivery of exogenous cytokines using a recombinant vaccinia virus system. Scand. J. Immunol. 2006, 41, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, R.; Khademi, M.; Wallstrom, E.; Iacobaeus, E.; Salvaggio, A.; Caracappa, S.; Papoian, R.; Nicoletti, F.; Olsson, T. Curative effects of recombinant human Interleukin-6 in DA rats with protracted relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2001, 116, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, R.; Persaud, T.; Hu, X.; Karmally, S.; Shestopalov, V.I.; Dvoriantchikova, G.; Ivanov, D.; Nathanson, L.; Barnum, S.R.; Bethea, J.R. Transgenic inhibition of astroglial NF-kB improves functional outcome in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing chronic central nervous system inflammation. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 2628–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnarfi, N.; Schulze-Topphoff, U.; Weber, M.S.; Patarroyo, J.C.; Prod’homme, T.; Varrin-Doyer, M.; Shetty, A.; Linington, C.; Slavin, A.J.; Hidalgo, J.; et al. MHC class II–dependent B cell APC function is required for induction of CNS autoimmunity independent of myelin-specific antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2921–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heink, S.; Yogev, N.; Garbers, C.; Herwerth, M.; Aly, L.; Gasperi, C.; Husterer, V.; Croxford, A.L.; Möller-Hackbarth, K.; Bartsch, H.S.; et al. Trans-Presentation of IL-6 by dendritic cells is required for the priming of pathogenic T H 17 cells. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskuhl, R.R.; Peterson, R.S.; Song, B.; Ao, Y.; Morales, L.B.J.; Tiwari-Woodruff, S.; Sofroniew, M.V. Reactive astrocytes form scar-like perivascular barriers to leukocytes during adaptive immune inflammation of the CNS. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 11511–11522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ayers, M.M.; Catmull, D.V.; Hazelwood, L.J.; Bernard, C.C.A.; Orian, J.M. Astrocyte-Associated axonal damage in pre-onset stages of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Glia 2005, 51, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijbels, K.; van Damme, J.; Proost, P.; Put, W.; Carton, H.; Billiau, A. Interleukin 6 production in the central nervous system during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 1990, 20, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarin, C.; Hinton, D.R.; Valentin-Torres, A.; Chen, Z.; Trapp, B.D.; Bergmann, C.C.; Stohlman, S.A. Astrocyte response to IFN-γ limits IL-6-mediated microglia activation and progressive autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erta, M.; Giralt, M.; Jiménez, S.; Molinero, A.; Comes, G.; Hidalgo, J. Astrocytic IL-6 influences the clinical symptoms of EAE in mice. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, U.K. Microglia as a source and target of cytokines. Glia 2002, 40, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marik, C.; Felts, P.A.; Bauer, J.; Lassmann, H.; Smith, K.J. Lesion genesis in a subset of patients with multiple sclerosis: A role for innate immunity? Brain 2007, 130, 2800–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, F.L.; Greter, M.; Marino, D.; Falsig, J.; Raivich, G.; Hövelmeyer, N.; Waisman, A.; Rülicke, T.; Prinz, M.; Priller, J.; et al. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis repressed by microglial paralysis. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, G.; Garzetti, L.; Gatta, A.T.; Finardi, A.; Maiorino, C.; Ruffini, F.; Martino, G.; Muzio, L.; Furlan, R. IL4 induces IL6-producing M2 macrophages associated to inhibition of neuroinflammation In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttler, E.; Tarabin, V.; Schwaninger, M. Interleukin-6 (IL-6): A possible neuromodulator induced by neuronal activity. Neuroscientist 2002, 8, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Gayol, O.; Sanchis, P.; Aguilar, K.; Navarro-Sempere, A.; Comes, G.; Molinero, A.; Giralt, M.; Hidalgo, J. Different responses to a high-fat diet in IL-6 conditional knockout mice driven by constitutive GFAP-Cre and Synapsin 1-Cre expression. Neuroendocrinology 2019, 109, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, A.; Erta, M.; Ferrer, B.; Comes, G.; Giralt, M.; Hidalgo, J. Astrocyte-Specific deficiency of interleukin-6 and its receptor reveal specific roles in survival, body weight and behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 27, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajenaru, M.L.; Zhu, Y.; Hedrick, N.M.; Donahoe, J.; Parada, L.F.; Gutmann, D.H. Astrocyte-Specific inactivation of the Neurofibromatosis 1 Gene (NF1) is insufficient for astrocytoma formation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 5100–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Romero, M.I.; Ghosh, P.; Ye, Z.; Charnay, P.; Rushing, E.J.; Marth, J.D.; Parada, L.F. Ablation of NF1 function in neurons induces abnormal development of cerebral cortex and reactive gliosis in the brain. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yona, S.; Kim, K.W.; Wolf, Y.; Mildner, A.; Varol, D.; Breker, M.; Strauss-Ayali, D.; Viukov, S.; Guilliams, M.; Misharin, A.; et al. Fate mapping reveals origins and dynamics of monocytes and tissue macrophages under homeostasis. Immunity 2013, 38, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, E.; Yang, L.; Su, T.; Morris, D.R.; McKnight, G.S.; Amieux, P.S. Cell-Type-Specific isolation of ribosome-associated mRNA from complex tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13939–13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia, B.; Ferrer, B.; Giralt, M.; Comes, G.; Carrasco, J.; Molinero, A.; Quintana, A.; Leclerc, J.; Viollet, B.; Señarís, R.M.; et al. Interleukin-6 deletion in mice driven by aP2-Cre-ERT2 prevents against high-fat diet-induced gain weight and adiposity in female mice. Acta Physiol. 2014, 211, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.J.; Palmiter, R.D. Detecting and avoiding problems when using the Cre-lox system. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis, P.; Fernández-Gayol, O.; Vizueta, J.; Comes, G.; Canal, C.; Escrig, A.; Molinero, A.; Giralt, M.; Hidalgo, J. Microglial cell-derived interleukin-6 influences behavior and inflammatory response in the brain following traumatic brain injury. Glia 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromnes, I.M.; Goverman, J.M. Passive induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1952–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, I.; Katz, A.; Kozak, N.; Ben-Nun, A.; Revel, M. Interleukin-6 functions in autoimmune encephalomyelitis: A study in gene-targeted mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, A.; Muller, M.; Frausto, R.F.; Ramos, R.; Getts, D.R.; Sanz, E.; Hofer, M.J.; Krauthausen, M.; King, N.J.C.; Hidalgo, J.; et al. Site-Specific Production of IL-6 in the central nervous system retargets and enhances the inflammatory response in experimental autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2079–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettenmann, H.; Hanisch, U.; Noda, M.; Verkhratsky, A. Physiology of microglia. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 461–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komiyama, Y.; Nakae, S.; Matsuki, T.; Nambu, A.; Ishigame, H.; Kakuta, S.; Sudo, K.; Iwakura, Y. IL-17 plays an important role in the development of experimental autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, T.; Mitsdoerffer, M.; Croxford, A.L.; Awasthi, A.; Dardalhon, V.A.; Galileos, G.; Vollmar, P.; Stritesky, G.L.; Kaplan, M.H.; Waisman, A.; et al. IL-6 controls Th17 immunity in vivo by inhibiting the conversion of conventional T cells into Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18460–18465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Reynolds, S.L.; Baker, B.J.; Li, X.; Benveniste, E.N.; Qin, H. IL-17 Enhancement of the IL-6 signaling cascade in astrocytes. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 4898–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, Á.C.; Lalor, S.J.; Lynch, M.A.; Mills, K.H.G. Infiltration of Th1 and Th17 cells and activation of microglia in the CNS during the course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Pang, R.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, W. IL-17-Triggered downregulation of miR-497 results in high HIF-1α expression and consequent IL-1β and IL-6 production by astrocytes in EAE mice. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I.L.; Abraham, C.R.; Masliah, E.; Kemper, P.; Inglis, J.D.; Oldstone, M.B.; Mucke, L. Neurologic disease induced in transgenic mice by cerebral overexpression of Interleukin 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10061–10065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Shi, M.; Zheng, C.; Shen, D.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, X.; Cui, L. The roles of macrophages and microglia in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 318, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, R.M. A polarizing question: Do M1 and M2 microglia exist. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, T.; Bettelli, E.; Gao, W.; Awasthi, A.; Jäger, A.; Strom, T.B.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-21 initiates an alternative pathway to induce proinflammatory T H17 cells. Nature 2007, 448, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, B.; Yang, M.X. Repression of the Interleukin-6 promoter by estrogen receptor is mediated by NF-kappa B and C/EBP beta. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 4971–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Mezei, G.; Nie, Y.; Rao, Y.; Choi, C.S.; Bechmann, I.; Leranth, C.; Toran-Allerand, D.; Priest, C.A.; Roberts, J.L.; et al. Anorectic estrogen mimics leptin’s effect on the rewiring of melanocortin cells and Stat3 signaling in obese animals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchis, P.; Fernández-Gayol, O.; Comes, G.; Escrig, A.; Giralt, M.; Palmiter, R.D.; Hidalgo, J. Interleukin-6 Derived from the Central Nervous System May Influence the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in a Cell-Dependent Manner. Cells 2020, 9, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020330
Sanchis P, Fernández-Gayol O, Comes G, Escrig A, Giralt M, Palmiter RD, Hidalgo J. Interleukin-6 Derived from the Central Nervous System May Influence the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in a Cell-Dependent Manner. Cells. 2020; 9(2):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020330
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchis, Paula, Olaya Fernández-Gayol, Gemma Comes, Anna Escrig, Mercedes Giralt, Richard D. Palmiter, and Juan Hidalgo. 2020. "Interleukin-6 Derived from the Central Nervous System May Influence the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in a Cell-Dependent Manner" Cells 9, no. 2: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020330
APA StyleSanchis, P., Fernández-Gayol, O., Comes, G., Escrig, A., Giralt, M., Palmiter, R. D., & Hidalgo, J. (2020). Interleukin-6 Derived from the Central Nervous System May Influence the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in a Cell-Dependent Manner. Cells, 9(2), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020330





