Cyclophilin A/EMMPRIN Axis Is Involved in Pro-Fibrotic Processes Associated with Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm of Marfan Syndrome Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Availability
2.2. Patients Enrollment
2.3. Immunostaining and Histological Assays
2.4. Aortic VSMC Isolation
2.5. ELISA Assays
2.6. MRNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Assay
2.7. Western Blot and Slot Blot Analyses
2.8. ImageStreamX Imaging Flow Cytometry
2.9. Sircol Assay
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
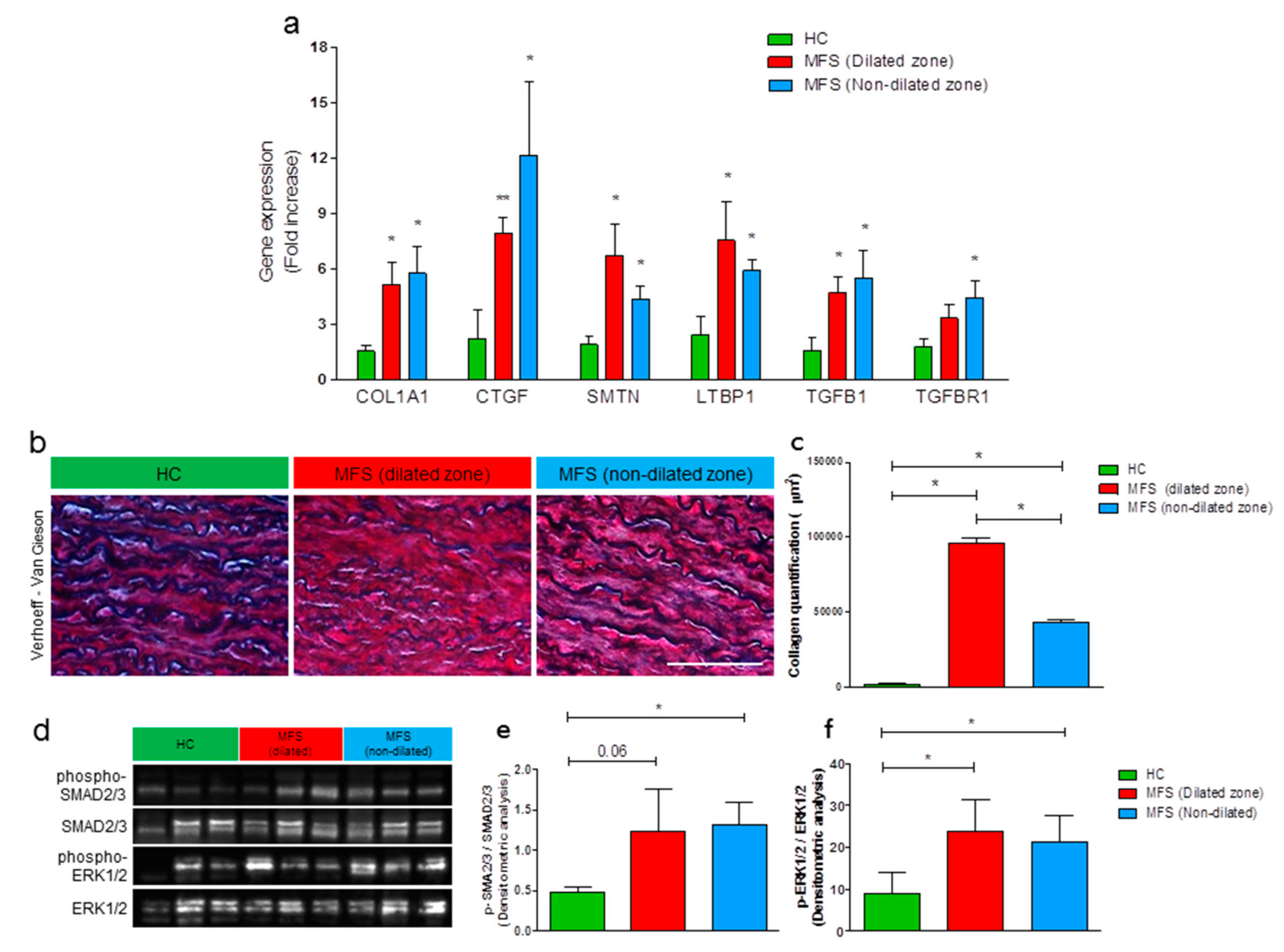
3.1. MFS Patients’ Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Shows Increased Fibrosis and Activation of TGF-β1 Signaling
3.2. Expression Levels of EMMPRIN Are Higher in MFS vs. HC, both in vivo and in vitro
3.3. MFS-VSMC Show A Higher Expression of AT1R, an Enhanced Secretion of CyPA, and MFS Patients Display Higher Plasmatic CyPA Levels
3.4. CyPA Stimulates EMMPRIN Expression and Activation
3.5. Blocking CyPA/EMMPRIN Axis Reverts the MFS-Related Expression of Pro-Fibrotic Mediators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Judge, D.P.; Dietz, H.C. Marfan’s syndrome. Lancet 2005, 366, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, H.C.; Cutting, G.R.; Pyeritz, R.E.; Maslen, C.L.; Sakai, L.Y.; Corson, G.M.; Puffenberger, E.G.; Hamosh, A.; Nanthakumar, E.J.; Curristin, S.M.; et al. Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo missense mutation in the fibrillin gene. Nature 1991, 352, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.R.; Summers, K.M. Structure and function of the mammalian fibrillin gene family: Implications for human connective tissue diseases. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 107, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, I.; Liu, W.; Brenn, T.; Furthmayr, H.; Francke, U. Cysteine substitutions in epidermal growth factor-like domains of fibrillin-1: Distinct effects on biochemical and clinical phenotypes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 65, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ammash, N.M.; Sundt, T.M.; Connolly, H.M. Marfan syndrome-diagnosis and management. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2008, 33, 7–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurali, E.; Perrucci, G.L.; Pilato, C.A.; Pini, A.; Gaetano, R.; Nigro, P.; Pompilio, G. Precise Therapy for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm in Marfan Syndrome: A Puzzle Nearing Its Solution. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 61, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashi, J.P.; Judge, D.P.; Holm, T.M.; Cohn, R.D.; Loeys, B.L.; Cooper, T.K.; Myers, L.; Klein, E.C.; Liu, G.; Calvi, C.; et al. Losartan, an AT1 antagonist, prevents aortic aneurysm in a mouse model of Marfan syndrome. Science 2006, 312, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holm, T.M.; Habashi, J.P.; Doyle, J.J.; Bedja, D.; Chen, Y.; van Erp, C.; Lindsay, M.E.; Kim, D.; Schoenhoff, F.; Cohn, R.D.; et al. Noncanonical TGFbeta signaling contributes to aortic aneurysm progression in Marfan syndrome mice. Science 2011, 332, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seizer, P.; Gawaz, M.; May, A.E. Cyclophilin A and EMMPRIN (CD147) in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 102, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seizer, P.; Geisler, T.; Bigalke, B.; Schneider, M.; Klingel, K.; Kandolf, R.; Stellos, K.; Schreieck, J.; Gawaz, M.; May, A.E. EMMPRIN and its ligand cyclophilin A as novel diagnostic markers in inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 163, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.F.; Wang, J.A.; Hou, J.; Gui, C.; Tang, L.J.; Chen, X.Q.; Xie, X.J.; Jiang, J.J.; Cai, J.F.; Chen, H.S.; et al. Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) is present in smooth muscle cells of human aneurysmal aorta and is induced by angiotensin II in vitro. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huet, E.; Gabison, E.E.; Mourah, S.; Menashi, S. Role of emmprin/CD147 in tissue remodeling. Connect. Tissue Res. 2008, 49, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huet, E.; Vallee, B.; Szul, D.; Verrecchia, F.; Mourah, S.; Jester, J.V.; Hoang-Xuan, T.; Menashi, S.; Gabison, E.E. Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer/CD147 promotes myofibroblast differentiation by inducing alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and collagen gel contraction: Implications in tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Ungern-Sternberg, S.N.I.; Zernecke, A.; Seizer, P. Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer EMMPRIN (CD147) in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, E507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nigro, P.; Pompilio, G.; Capogrossi, M.C. Cyclophilin A: A key player for human disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrucci, G.L.; Gowran, A.; Zanobini, M.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Pompilio, G.; Nigro, P. Peptidyl-prolyl isomerases: A full cast of critical actors in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 106, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satoh, K.; Nigro, P.; Matoba, T.; O’Dell, M.R.; Cui, Z.; Shi, X.; Mohan, A.; Yan, C.; Abe, J.; Illig, K.A.; et al. Cyclophilin A enhances vascular oxidative stress and the development of angiotensin II-induced aortic aneurysms. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Suk, K.; Lee, W.H. Activation of CD147 with cyclophilin a induces the expression of IFITM1 through ERK and PI3K in THP-1 cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 821940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Z.G.; Melaragno, M.G.; Liao, D.F.; Yan, C.; Haendeler, J.; Suh, Y.A.; Lambeth, J.D.; Berk, B.C. Cyclophilin A is a secreted growth factor induced by oxidative stress. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, J.; Jin, Z.G.; Meoli, D.F.; Matoba, T.; Berk, B.C. Cyclophilin A is secreted by a vesicular pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nataatmadja, M.; West, J.; Prabowo, S.; West, M. Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonism Reduces Transforming Growth Factor Beta and Smad Signaling in Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm. Ochsner J. 2013, 13, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Sowden, M.; Berk, B.C. Extracellular Cyclophilin, A.; Especially Acetylated, Causes Pulmonary Hypertension by Stimulating Endothelial Apoptosis, Redox Stress, and Inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, S.; Venugopal, A.; Kutty, V.R.; Vinitha, A.; Divya, G.; Chitrasree, V.; Kartha, C.C. Plasma level of cyclophilin A is increased in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and suggests presence of vascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Zang, X.; Chen, R.; Yuan, W.; Gong, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. The clinical implications of increased cyclophilin A levels in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, F. Extracellular cyclophilin A as a humoral factor modulating cardiovascular inflammatory responses. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2012, 53, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Ju, D.; Zhang, D.W.; Li, H.; Kong, L.M.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, Z.N.; Bian, H. Activation of TGF-beta1-CD147 positive feedback loop in hepatic stellate cells promotes liver fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Qiao, S.; Zhao, S.; Yu, L. Cyclophilin A is upregulated in small cell lung cancer and activates ERK1/2 signal. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2007, 361, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesevic, M.; Gutknecht, D.; Prell, E.; Klein, C.; Schumann, M.; Nowak, R.A.; Simon, J.C.; Schiene-Fischer, C.; Saalbach, A. Anti-inflammatory effects of extracellular cyclosporins are exclusively mediated by CD147. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 7302–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterss, S.; Mansour, A.M.; Ross, J.A.; Vaitkeviciute, I.; Charilaou, P.; Dumfarth, J.; Fang, H.; Ziganshin, B.A.; Rizzo, J.A.; Adeniran, A.J.; et al. Changing Pathology of the Thoracic Aorta From Acute to Chronic Dissection: Literature Review and Insights. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, H.; Rateri, D.L.; Cassis, L.A.; Daugherty, A. Conundrum of angiotensin II and TGF-beta interactions in aortic aneurysms. Curr. Opin. Pharm. 2013, 13, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhry, S.S.; Cain, S.A.; Morgan, A.; Dallas, S.L.; Shuttleworth, C.A.; Kielty, C.M. Fibrillin-1 regulates the bioavailability of TGFbeta1. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, K.; Matoba, T.; Suzuki, J.; O’Dell, M.R.; Nigro, P.; Cui, Z.; Mohan, A.; Pan, S.; Li, L.; Jin, Z.G.; et al. Cyclophilin A mediates vascular remodeling by promoting inflammation and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation 2008, 117, 3088–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satoh, K.; Nigro, P.; Zeidan, A.; Soe, N.N.; Jaffre, F.; Oikawa, M.; O’Dell, M.R.; Cui, Z.; Menon, P.; Lu, Y.; et al. Cyclophilin A Promotes Cardiac Hypertrophy in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, Y.W.; Kwon, H.M.; Hwang, K.C.; Choi, E.Y.; Hong, B.K.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.S.; Cho, S.H.; Song, K.S.; Sangiorgi, G. Upstream regulation of matrix metalloproteinase by EMMPRIN; extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer in advanced atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis 2005, 180, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seizer, P.; Schonberger, T.; Schott, M.; Lang, M.R.; Langer, H.F.; Bigalke, B.; Kramer, B.F.; Borst, O.; Daub, K.; Heidenreich, O.; et al. EMMPRIN and its ligand cyclophilin A regulate MT1-MMP, MMP-9 and M-CSF during foam cell formation. Atherosclerosis 2010, 209, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Satoh, K.; Ikeda, S.; Sunamura, S.; Otsuki, T.; Satoh, T.; Kikuchi, N.; Omura, J.; Kurosawa, R.; Nogi, M.; et al. Basigin Promotes Cardiac Fibrosis and Failure in Response to Chronic Pressure Overload in Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seizer, P.; Ochmann, C.; Schonberger, T.; Zach, S.; Rose, M.; Borst, O.; Klingel, K.; Kandolf, R.; MacDonald, H.R.; Nowak, R.A.; et al. Disrupting the EMMPRIN (CD147)-cyclophilin A interaction reduces infarct size and preserves systolic function after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rurali, E.; Perrucci, G.L.; Gaetano, R.; Pini, A.; Moschetta, D.; Gentilini, D.; Nigro, P.; Pompilio, G. Soluble EMMPRIN levels discriminate aortic ectasia in Marfan syndrome patients. Theranostics 2019, 9, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrucci, G.L.; Rurali, E.; Gowran, A.; Pini, A.; Antona, C.; Chiesa, R.; Pompilio, G.; Nigro, P. Vascular smooth muscle cells in Marfan syndrome aneurysm: The broken bricks in the aortic wall. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Gomez, D.; Bell, R.D.; Campbell, J.H.; Clowes, A.W.; Gabbiani, G.; Giachelli, C.M.; Parmacek, M.S.; Raines, E.W.; Rusch, N.J.; et al. Smooth muscle cell plasticity: Fact or fiction? Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Bai, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Wei, Y.; Huang, C. Proteomics identification of cyclophilin a as a potential prognostic factor and therapeutic target in endometrial carcinoma. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2008, 7, 1810–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunton, T.E.; Biery, N.J.; Myers, L.; Gayraud, B.; Ramirez, F.; Dietz, H.C. Phenotypic alteration of vascular smooth muscle cells precedes elastolysis in a mouse model of Marfan syndrome. Circ. Res. 2001, 88, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yurchenko, V.; Zybarth, G.; O’Connor, M.; Dai, W.W.; Franchin, G.; Hao, T.; Guo, H.; Hung, H.C.; Toole, B.; Gallay, P.; et al. Active site residues of cyclophilin A are crucial for its signaling activity via CD147. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22959–22965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venkatesan, B.; Valente, A.J.; Reddy, V.S.; Siwik, D.A.; Chandrasekar, B. Resveratrol blocks interleukin-18-EMMPRIN cross-regulation and smooth muscle cell migration. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H874–H886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, W.; Ge, H.; He, B. Pro-inflammatory activities induced by CyPA-EMMPRIN interaction in monocytes. Atherosclerosis 2010, 213, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Qie, G.; Zhou, J. The roles of CD147 and/or cyclophilin A in kidney diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 728673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, A.M.; Luna, R.E.; Horiba, K.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; McAllister, H.A., Jr.; Willerson, J.T.; Ferrans, V.J. Immunohistochemistry of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in thoracic aortic aneurysms and aortic valves of patients with Marfan’s syndrome. Circulation 1998, 98, II331–II337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Dai, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Jia, J.F.; Zheng, Z.H.; Ding, J.; Chen, Z.N.; Zhu, P. Expression of CD147 (EMMPRIN) on neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis enhances chemotaxis, matrix metalloproteinase production and invasiveness of synoviocytes. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrucci, G.L.; Rurali, E.; Pompilio, G. Cardiac fibrosis in regenerative medicine: Destroy to rebuild. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S2376–S2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.R.; Clayton, N.P.; Carta, L.; Galatioto, J.; Chiu, E.; Smaldone, S.; Nelson, C.A.; Cheng, S.H.; Wentworth, B.M.; Ramirez, F. Dimorphic effects of transforming growth factor-beta signaling during aortic aneurysm progression in mice suggest a combinatorial therapy for Marfan syndrome. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Li, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Qin, L.; Ali, R.; Zhou, J.; Ferruzzi, J.; Kim, R.W.; Geirsson, A.; Dietz, H.C.; et al. Tgfbr2 disruption in postnatal smooth muscle impairs aortic wall homeostasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milewicz, D.M.; Ramirez, F. Therapies for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms and Acute Aortic Dissections. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinzmann, D.; Bangert, A.; Muller, A.M.; von Ungern-Sternberg, S.N.; Emschermann, F.; Schonberger, T.; Chatterjee, M.; Mack, A.F.; Klingel, K.; Kandolf, R.; et al. The Novel Extracellular Cyclophilin A (CyPA)—Inhibitor MM284 Reduces Myocardial Inflammation and Remodeling in a Mouse Model of Troponin I -Induced Myocarditis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seizer, P.; Ungern-Sternberg, S.N.; Schonberger, T.; Borst, O.; Munzer, P.; Schmidt, E.M.; Mack, A.F.; Heinzmann, D.; Chatterjee, M.; Langer, H.; et al. Extracellular cyclophilin A activates platelets via EMMPRIN (CD147) and PI3K/Akt signaling, which promotes platelet adhesion and thrombus formation in vitro and in vivo. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Elastic Fiber Length Mean (μm ± SD) | p | |
|---|---|---|
| HC | 235.94 ± 64.78 | / |
| MFS (dilated zone) | 116.07 ± 54.64 | * |
| MFS (non-dilated zone) | 97.93 ± 37.68 | * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perrucci, G.L.; Rurali, E.; Corlianò, M.; Balzo, M.; Piccoli, M.; Moschetta, D.; Pini, A.; Gaetano, R.; Antona, C.; Egea, G.; et al. Cyclophilin A/EMMPRIN Axis Is Involved in Pro-Fibrotic Processes Associated with Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm of Marfan Syndrome Patients. Cells 2020, 9, 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010154
Perrucci GL, Rurali E, Corlianò M, Balzo M, Piccoli M, Moschetta D, Pini A, Gaetano R, Antona C, Egea G, et al. Cyclophilin A/EMMPRIN Axis Is Involved in Pro-Fibrotic Processes Associated with Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm of Marfan Syndrome Patients. Cells. 2020; 9(1):154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010154
Chicago/Turabian StylePerrucci, Gianluca L., Erica Rurali, Maria Corlianò, Maria Balzo, Michela Piccoli, Donato Moschetta, Alessandro Pini, Raffaella Gaetano, Carlo Antona, Gustavo Egea, and et al. 2020. "Cyclophilin A/EMMPRIN Axis Is Involved in Pro-Fibrotic Processes Associated with Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm of Marfan Syndrome Patients" Cells 9, no. 1: 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010154
APA StylePerrucci, G. L., Rurali, E., Corlianò, M., Balzo, M., Piccoli, M., Moschetta, D., Pini, A., Gaetano, R., Antona, C., Egea, G., Fischer, G., Malešević, M., Alamanni, F., Cogliati, E., Paolin, A., Pompilio, G., & Nigro, P. (2020). Cyclophilin A/EMMPRIN Axis Is Involved in Pro-Fibrotic Processes Associated with Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm of Marfan Syndrome Patients. Cells, 9(1), 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010154






