Functions and the Emerging Role of the Foetal Liver into Regenerative Medicine
Abstract
1. Foetal Liver Embryogenesis and Foetal Functions
1.1. Foetal Liver Functions
1.2. Cardiovascular Function
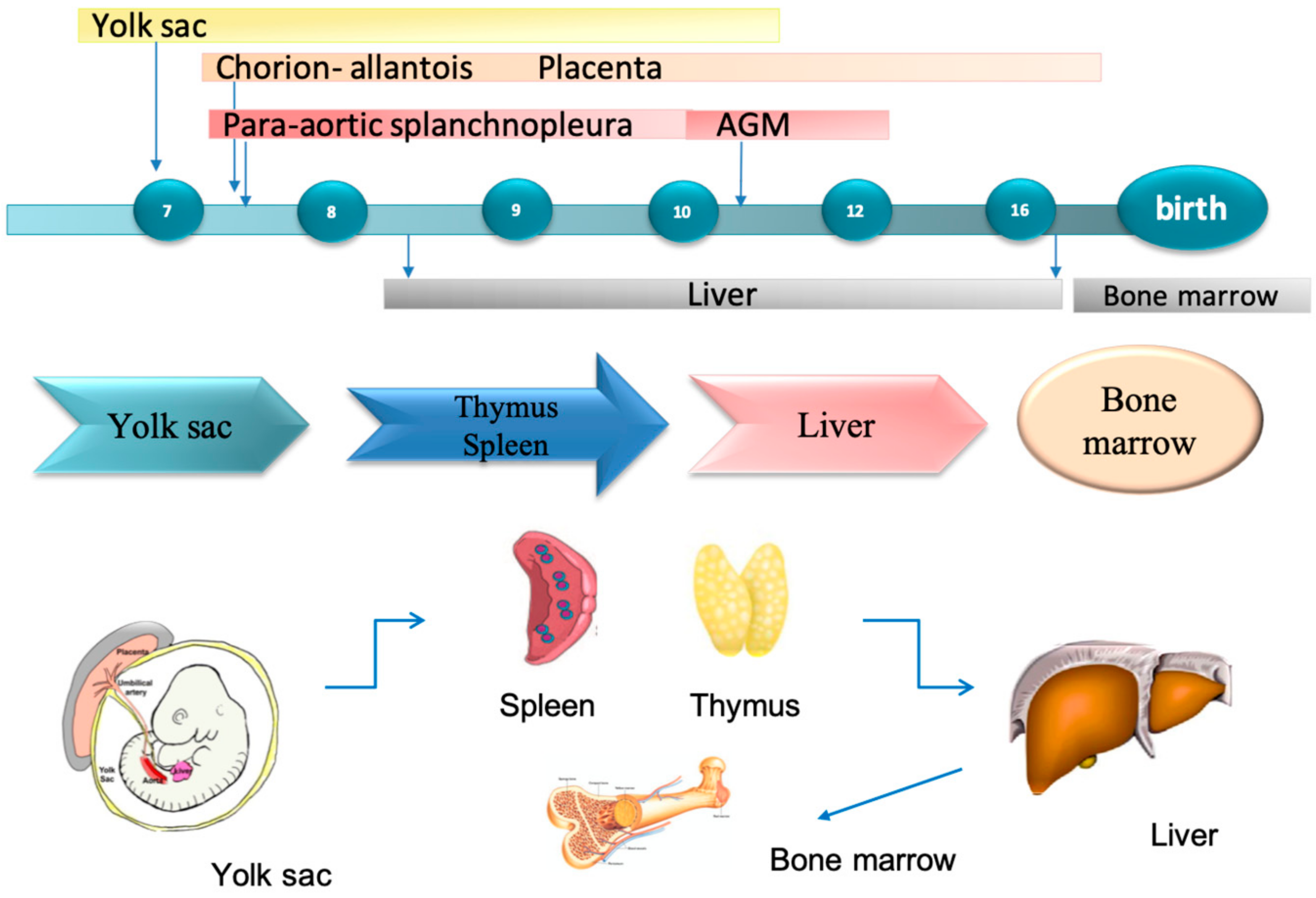
1.3. Haematopoiesis
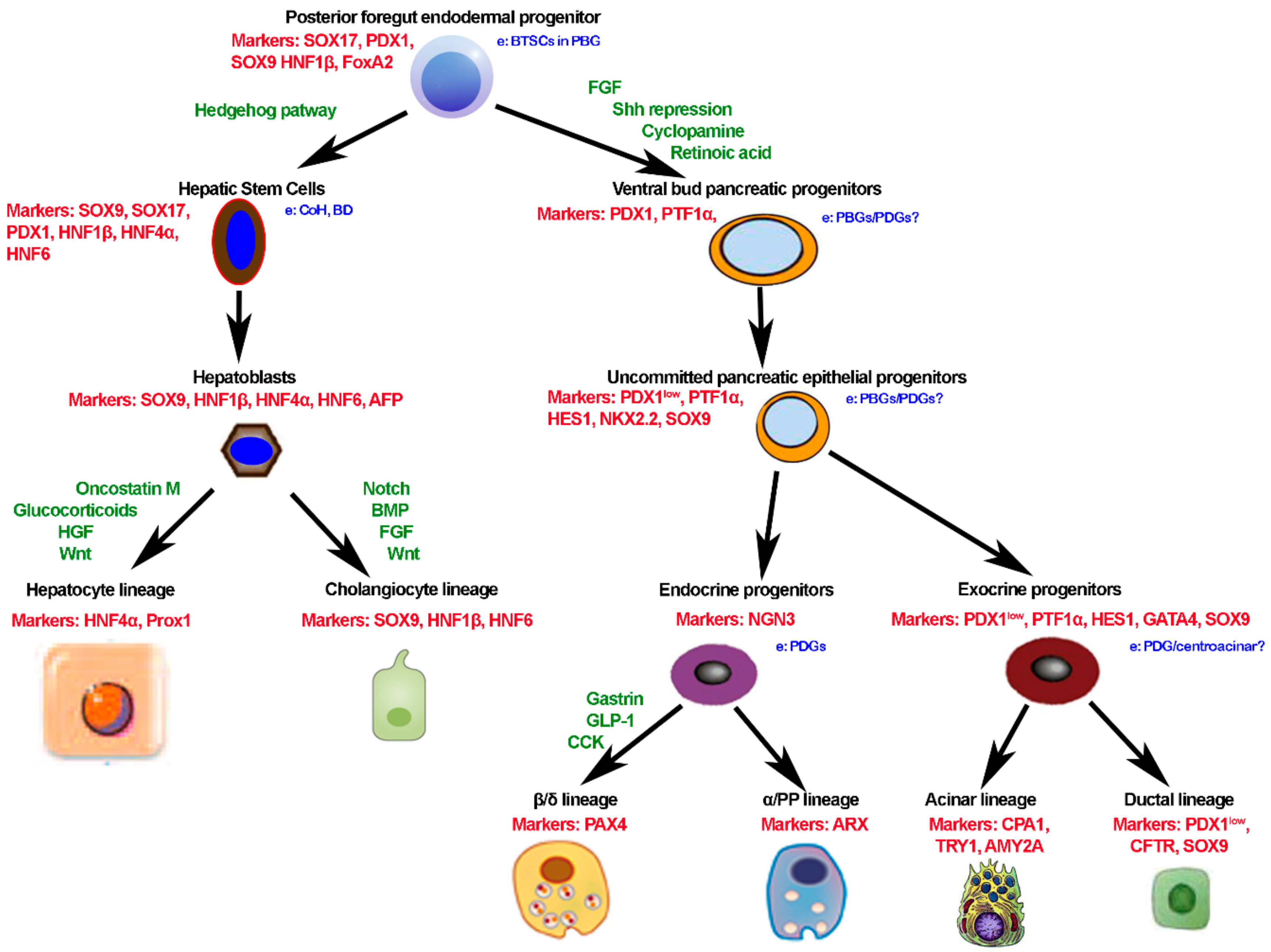
1.4. Foetal Liver Embryology
1.5. Molecular Regulation of Liver Induction
1.6. Common Embryogenesis of Liver and Pancreas and Remnant Stem Cells in Adult Life
2. Regenerative Medicine of the Liver
2.1. Controversy on Liver Regeneration
2.2. State of Art of the Use of Hepatocytes and Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine of the Liver
2.3. Foetal Liver as a Cell Source for Regenerative Medicine: Preclinical and Clinical Evidences
2.4. Organoids are Powerful Tool to Study Liver and Bile Duct Regeneration
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Si-Tayeb, K.; Lemaigre, F.P.; Duncan, S.A. Organogenesis and Development of the Liver. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautt, W.W. Hepatic Circulation: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wladimiroff, J.W.; vd Wijngaard, J.A.; Degani, S.; Noordam, M.J.; van Eyck, J.; Tonge, H.M. Cerebral and umbilical arterial blood flow velocity waveforms in normal and growth-retarded pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol. 1987, 69, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zapol, W.M.; Liggins, G.C.; Schneider, R.C.; Qvist, J.; Snider, M.T.; Creasy, R.K.; Hochachka, P.W. Regional blood flow during simulated diving in the conscious Weddell seal. J. Appl. Physiol. 1979, 47, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellotti, M.; Pennati, G.; De Gasperi, C.; Bozzo, M.; Battaglia, F.C.; Ferrazzi, E. Simultaneous measurements of umbilical venous, fetal hepatic, and ductus venosus blood flow in growth-restricted human fetuses. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 190, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiserud, T.; Kessler, J.; Ebbing, C.; Rasmussen, S. Ductus venosus shunting in growth-restricted fetuses and the effect of umbilical circulatory compromise. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 28, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, K.M.; Haugen, G.; Kiserud, T.; Inskip, H.M.; Cooper, C.; Harvey, N.C.W.; Crozier, S.R.; Robinson, S.M.; Davies, L.; Hanson, M.A. Fetal Liver Blood Flow Distribution: Role in Human Developmental Strategy to Prioritize Fat Deposition versus Brain Development. PLoS ONE 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanni, D.; Angotzi, F.; Lai, F.; Gerosa, C.; Senes, G.; Fanos, V.; Faa, G. Four stages of hepatic hematopoiesis in human embryos and fetuses. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2018, 31, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, L.W.; Foley, J.F.; Elmore, S.A. Histology Atlas of the Developing Mouse Hepatobiliary System with Emphasis on Embryonic Days 9.5–18.5. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 38, 872–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordes, C.; Haussinger, D. Hepatic stem cell niches. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payushina, O.V. Hematopoietic Microenvironment in the Fetal Liver: Roles of Different Cell Populations. ISRN Cell Boil. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaccio, G.; Migliaccio, A.R.; Petti, S.; Mavilio, F.; Russo, G.; Lazzaro, D.; Testa, U.; Marinucci, M.; Peschle, C. Human embryonic hemopoiesis. Kinetics of progenitors and precursors underlying the yolk sac–liver transition. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emura, I.; Sekiya, M.; Ohnishi, Y. Four Types of Presumptive Hemopoietic Stem Cells in the Human Fetal Liver. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 1983, 46, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikhina, K.; Tsuneto, M.; Melchers, F. Environments of hematopoiesis and B-lymphopoiesis in foetal liver. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Mendt, M.; Cardier, J.E. Stromal-derived factor-1 and its receptor, CXCR4, are constitutively expressed by mouse liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Implications for the regulation of hematopoietic cell migration to the liver during extramedullary hematopoiesis. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Pati, H.P.; Ahuja, R.K.; Takkar, D.; Kochupillai, V. Haemopoietic cell composition of human fetal liver, spleen and thymus. Med. Oncol. 1997, 14, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzan, H.; Takahashi, H.; Kawakami, A.; Yamashitat, S.; Ohkit, T.; Yamamoto, M. Light and electron microscopic observations of hepatic hematopoiesis of human fetuses. Pathol. Int. 1980, 30, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T. Fetal hemopoiesis. II. Electron microscopic studies on human hepatic hemopoiesis. Virchows Arch. B Cell Pathol. 1974, 16, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, H.; Ohmura, K.; Hattori, N.; Katsura, Y. Hemopoietic progenitors in the murine fetal liver capable of rapidly generating T cells. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 3118–3124. [Google Scholar]
- Lacaud, G.; Carlsson, L.; Keller, G. Identification of a Fetal Hematopoietic Precursor with B Cell, T Cell, and Macrophage Potential. Immunity 1998, 9, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Kawamoto, H.; Katsube, Y.; Ikawa, T.; Katsura, Y. The Common Myelolymphoid Progenitor: A Key Intermediate Stage in Hemopoiesis Generating T and B Cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3519–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, S.K.; Ulirsch, J.C.; Sankaran, V.G. Advances in Understanding Erythropoiesis: Evolving Perspectives. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douagi, I. Identification of the earliest prethymic bipotent T/NK progenitor in murine fetal liver. Blood 2002, 99, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, H.; Ohmura, K.; Fujimoto, S.; Katsura, Y. Emergence of T cell progenitors without B cell or myeloid differentiation potential at the earliest stage of hematopoiesis in the murine fetal liver. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 2725–2731. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Aiba, Y.; Katsura, Y. T Cell Progenitors in the Murine Fetal Liver: Differences from Those in the Adult Bone Marrow. Cell. Immunol. 1997, 177, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugh, R. The mouse. Its reproduction and development; Burgess Publishing Co.: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, K.; Kondo, M. Developmental switch of mouse hematopoietic stem cells from fetal to adult type occurs in bone marrow after birth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17852–17857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifkind, R.A. An ultrastructural study of early morphogenetic events during the establishment of fetal hepatic erythropoiesis. J. Cell Biol. 1969, 40, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langaman, J. Medical Embryology; Human Development—Normal and Abnormal. Postgrad. Med. J. 1964, 40, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, L.; Moore, T.V.N.P.; Mark, G. The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology. Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, A.K. Essentials of Human Embryology, 3rd ed.; Current Books International: Kolkata, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, E.L.C. Pathology of the Fetus and the Infant; Year Book Medical Publisher: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Rouiller, C.H. THE LIVER (Morphology, Biochemistry, Physiology); Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, H.I. Development of liver and biliary duct (in Japanese). Shusanki Igaku 1983, 13, 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- Achiron, R.; Gindes, L.; Kivilevitch, Z.; Kuint, J.; Kidron, D.; Boyanover, Y.; Yakobson, J.; Heggesh, J. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital agenesis of the fetal portal venous system. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 34, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoazec, J.-Y.; Collardeau-Frachon, S. Vascular Development and Differentiation During Human Liver Organogenesis. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Boil. 2008, 291, 614–627. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinale, V.; Wang, Y.; Carpino, G.; Mendel, G.; Alpini, G.; Gaudio, E.; Reid, L.M.; Alvaro, D. The biliary tree—A reservoir of multipotent stem cells. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaret, K.S.; Grompe, M. Generation and Regeneration of Cells of the Liver and Pancreas. Science 2008, 322, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, R.; Suñer, R.E.; Van Hul, N.; Kopp, J.L.; Beaudry, J.; Cordi, S.; Antoniou, A.; Raynaud, P.; Lepreux, S.; Jacquemin, P.; et al. Embryonic Ductal Plate Cells Give Rise to Cholangiocytes, Periportal Hepatocytes and Adult Liver Progenitor Cells. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskams, T.; Desmet, V. Embryology of Extra- and Intrahepatic Bile Ducts, the Ductal plate. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2008, 291, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.R.; Lange, A.W.; Lin, S.-C.J.; Kaestner, K.H.; Lowy, A.M.; Kim, I.; Whitsett, J.A.; Wells, J.M. Sox17 regulates organ lineage segregation of ventral foregut progenitor cells. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, M.; Rustgi, A.K. Pancreatic ductal cells in development, regeneration, and neoplasia. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4572–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, V.; Wang, Y.; Carpino, G.; Gatto, M.; Rossi, M.; Berloco, P.B.; Cantafora, A.; Wauthier, E.; Furth, M.E.; Inverardi, L.; et al. Multipotent stem/progenitor cells in human biliary tree give rise to hepatocytes, cholangiocytes, and pancreatic islets. Hepatology 2011, 54, 2159–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Cardinale, V.; Gentile, R.; Onori, P.; Semeraro, R.; Franchitto, A.; Wang, Y.; Bosco, D.; Iossa, A.; Napoletano, C.; et al. Evidence for multipotent endodermal stem/progenitor cell populations in human gallbladder. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Cardinale, V.; Onori, P.; Franchitto, A.; Berloco, P.B.; Rossi, M.; Wang, Y.; Semeraro, R.; Anceschi, M.; Brunelli, R.; et al. Biliary tree stem/progenitor cells in glands of extrahepatic and intraheptic bile ducts: An anatomical in situ study yielding evidence of maturational lineages. J. Anat. 2012, 220, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeraro, R.; Carpino, G.; Cardinale, V.; Onori, P.; Gentile, R.; Cantafora, A.; Franchitto, A.; Napoli, C.; Anceschi, M.; Brunelli, R.; et al. Multipotent stem/progenitor cells in the human foetal biliary tree. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lanzoni, G.; Carpino, G.; Cui, C.-B.; Dominguez-Bendala, J.; Wauthier, E.; Cardinale, V.; Oikawa, T.; Pileggi, A.; Gerber, D.; et al. Biliary Tree Stem Cells, Precursors to Pancreatic Committed Progenitors: Evidence for Possible Life-long Pancreatic Organogenesis. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 1966–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, Y. Sox9 and programming of liver and pancreatic progenitors. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzoni, G.; Oikawa, T.; Wang, Y.; Cui, C.B.; Carpino, G.; Cardinale, V.; Gerber, D.; Gabriel, M.; Dominguez-Bendala, J.; Furth, M.E.; et al. Concise review: Clinical programs of stem cell therapies for liver and pancreas. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huch, M.; Gehart, H.; Van Boxtel, R.; Hamer, K.; Blokzijl, F.; Verstegen, M.M.; Ellis, E.; Van Wenum, M.; Fuchs, S.A.; De Ligt, J.; et al. Long-Term Culture of Genome-Stable Bipotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Liver. Cell 2015, 160, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, A.; Tanaka, M.; Itoh, T. Stem/Progenitor Cells in Liver Development, Homeostasis, Regeneration, and Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelzer, E.; Zhang, L.; Bruce, A.; Wauthier, E.; Ludlow, J.; Yao, H.-L.; Moss, N.; Melhem, A.; McClelland, R.; Turner, W.; et al. Human hepatic stem cells from fetal and postnatal donors. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1973–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.; Lozoya, O.; Wang, Y.; Cardinale, V.; Gaudio, E.; Alpini, G.; Mendel, G.; Wauthier, E.; Barbier, C.; Alvaro, D.; et al. Human Hepatic Stem Cell and Maturational Liver Lineage Biology. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, V.; Puca, R.; Carpino, G.; Scafetta, G.; Renzi, A.; De Canio, M.; Sicilia, F.; Nevi, L.; Casa, D.; Panetta, R.; et al. Adult Human Biliary Tree Stem Cells Differentiate to beta-Pancreatic Islet Cells by Treatment with a Recombinant Human Pdx1 Peptide. PLoS ONE 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tarlow, B.D.; Pelz, C.; Naugler, W.E.; Wakefield, L.; Wilson, E.M.; Finegold, M.J.; Grompe, M. Bipotential adult liver progenitors are derived from chronically injured mature hepatocytes. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicent, S.; Lieshout, R.; Saborowski, A.; Verstegen, M.M.A.; Raggi, C.; Recalcati, S.; Invernizzi, P.; Laan, L.J.W.; Alvaro, D.; Calvisi, D.F.; et al. Experimental models to unravel the molecular pathogenesis, cell of origin and stem cell properties of cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, D.M.; Drill, E.; Shen, R.; Taylor, A.M.; Schneider, B.G.; Malta, T.M.; Benz, C.C.; Caesar-Johnson, S.J.; Demchok, J.A.; Felau, I.; et al. Cell-of-Origin Patterns Dominate the Molecular Classification of 10,000 Tumors from 33 Types of Cancer. Cell 2018, 173, 291–304. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzoni, G.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G. The hepatic, biliary, and pancreatic network of stem/progenitor cell niches in humans: A new reference frame for disease and regeneration. Hepatology 2016, 64, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spee, B.; Carpino, G.; Schotanus, B.A.; Katoonizadeh, A.; Vander Borght, S.; Gaudio, E.; Roskams, T. Characterisation of the liver progenitor cell niche in liver diseases: Potential involvement of Wnt and Notch signalling. Gut 2010, 59, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasetti, C.; Vogelstein, B. Cancer etiology. Variation in cancer risk among tissues can be explained by the number of stem cell divisions. Science 2015, 347, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, A.; Lu, W.-Y.; Man, T.Y.; Ferreira-Gonzalez, S.; O’Duibhir, E.; Dwyer, B.J.; Thomson, J.P.; Meehan, R.R.; Bogorad, R.; Koteliansky, V.; et al. Cholangiocytes act as Facultative Liver Stem Cells during Impaired Hepatocyte Regeneration. Nature 2017, 547, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizarani, N.; Saviano, A.; Sagar; Mailly, L.; Durand, S.; Herman, J.S.; Pessaux, P.; Baumert, T.F.; Grün, D. A human liver cell atlas reveals heterogeneity and epithelial progenitors. Nature 2019, 572, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.J.; Gupta, S.; Dhawan, A. Cell therapy for liver disease: From liver transplantation to cell factory. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannoun, Z.; Steichen, C.; Dianat, N.; Weber, A.; Dubart-Kupperschmitt, A. The potential of induced pluripotent stem cell derived hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xingshun, Q.; Xiaozhong, G.; Chunping, S. Clinical Outcomes of the Transplantation of Stem Cells from Various Human Tissue Sources in the Management of Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 10, 166–180. [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan, A. Clinical human hepatocyte transplantation: Current status and challenges. Liver Transplant. 2015, 21, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, I.J.; Chowdhury, J.R.; Kaufman, S.S.; Goertzen, T.C.; Chowdhury, N.R.; Warkentin, P.I.; Dorko, K.; Sauter, B.V.; Strom, S.C. Treatment of the Crigler–Najjar Syndrome Type I with Hepatocyte Transplantation. New Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansel, M.C.; Gramignoli, R.; Skvorak, K.J.; Dorko, K.; Marongiu, F.; Blake, W.; Davila, J.; Strom, S.C. The history and use of human hepatocytes for the treatment of liver diseases: The first 100 patients. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2014, 62, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Parveen, N.; Mahaboob, V.; Rajendraprasad, A.; Ravindraprakash, H.; Venkateswarlu, J.; Rao, P.; Pande, G.; Narusu, M.L.; Khaja, M.; et al. Treatment of Crigler-Najjar Syndrome Type 1 by Hepatic Progenitor Cell Transplantation: A Simple Procedure for Management of Hyperbilirubinemia. Transplant. Proc. 2008, 40, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysy, P.; Najimi, M.; Stéphenne, X.; Bourgois, A.; Smets, F.; Sokal, E.M. Liver cell transplantation for Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I: Update and perspectives. World, J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 3464–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyburg, J.; Das, A.M.; Hoerster, F.; Lindner, M.; Kriegbaum, H.; Engelmann, G.; Schmidt, J.; Ott, M.; Pettenazzo, A.; Luecke, T.; et al. One Liver for Four Children: First Clinical Series of Liver Cell Transplantation for Severe Neonatal Urea Cycle Defects. Transplantation 2009, 87, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyburg, J.; Hoerster, F.; Schmidt, J.; Poeschl, J.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Schenk, J.-P. Monitoring of Intraportal Liver Cell Application in Children. Cell Transplant. 2010, 19, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevi, L.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Costantini, D.; Di Matteo, S.; Cantafora, A.; Melandro, F.; Brunelli, R.; Bastianelli, C.; Aliberti, C.; et al. Cryopreservation protocol for human biliary tree stem/progenitors, hepatic and pancreatic precursors. Sci. Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevi, L.; Carpino, G.; Costantini, D.; Cardinale, V.; Riccioni, O.; Di Matteo, S.; Melandro, F.; Berloco, P.B.; Reid, L.; Gaudio, E.; et al. Hyaluronan coating improves liver engraftment of transplanted human biliary tree stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, J.; Strom, S.C.; Hughes, R.D.; Bansal, S.; Castell, J.V.; Dagher, I.; Ellis, E.C.S.; Nowak, G.; Ericzon, B.-G.; Fox, I.J.; et al. Improving the Techniques for Human Hepatocyte Transplantation: Report from a Consensus Meeting in London. Cell Transplant. 2012, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, A.; Puppi, J.; Hughes, R.D.; Mitry, R.R. Human hepatocyte transplantation: Current experience and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.Y.; Jang, Y.J.; Lim, H.-J.; Han, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, G.; Park, J.Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, J.H.; Do, B.-R.; et al. Milk Fat Globule-EGF Factor 8, Secreted by Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Protects Against Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreone, P.; Catani, L.; Margini, C.; Brodosi, L.; Lorenzini, S.; Sollazzo, D.; Nicolini, B.; Giordano, R.; Montemurro, T.; Rizzi, S.; et al. Reinfusion of highly purified CD133+ bone marrow-derived stem/progenitor cells in patients with end-stage liver disease: A phase I clinical trial. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.; Barton, D.; Beard, N.; Than, J.; Moore, C.; Corbett, J.; Thomas, K.; Guo, I.; Guha, I.; Hollyman, D.; et al. REpeated AutoLogous Infusions of STem cells In Cirrhosis (REALISTIC): A multicentre, phase II, open-label, randomised controlled trial of repeated autologous infusions of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF) mobilised CD133+ bone marrow stem cells in patients with cirrhosis. A study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanthier, N.; Lin-Marq, N.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Clément, S.; Goossens, N.; Spahr, L. Autologous bone marrow-derived cell transplantation in decompensated alcoholic liver disease: What is the impact on liver histology and gene expression patterns? Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.K.; Stutchfield, B.M.; Forbes, S.J. Systematic review: The effects of autologous stem cell therapy for patients with liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Fox, R.; King, A.L.; Barton, D.; Than, N.-N.; Moore, J.; Corbett, C.; Townsend, S.; Thomas, J.; Guo, K.; et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and autologous CD133-positive stem-cell therapy in liver cirrhosis (REALISTIC): An open-label, randomised, controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Xie, D.-Y.; Lin, B.-L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.-P.; Xie, C.; Zheng, Y.-B.; Gao, Z.-L. Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in liver failure patients caused by hepatitis B: Short-term and long-term outcomes. Hepatology 2011, 54, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, E.M.; Lombard, C.A.; Roelants, V.; Najimi, M.; Varma, S.; Sargiacomo, C.; Ravau, J.; Mazza, G.; Jamar, F.; Versavau, J.; et al. Biodistribution of Liver-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells After Peripheral Injection in a Hemophilia A Patient. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahr, L.; Chalandon, Y.; Terraz, S.; Kindler, V.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Frossard, J.-L.; Bréguet, R.; Lanthier, N.; Farina, A.; Passweg, J.; et al. Autologous Bone Marrow Mononuclear Cell Transplantation in Patients with Decompensated Alcoholic Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, P.; Cao, X.; Frenette, P.S.; Mao, J.J.; Robey, P.G.; Simmons, P.J.; Wang, C.-Y. The meaning, the sense and the significance: Translating the science of mesenchymal stem cells into medicine. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanthier, N. Haemopoietic stem cell therapy in cirrhosis: The end of the story? Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Fibroblasts by Defined Factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.J.; Newsome, P.N. New horizons for stem cell therapy in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Rezvani, M.; Harbell, J.; Mattis, A.N.; Wolfe, A.R.; Benet, L.Z.; Willenbring, H.; Ding, S. Mouse liver repopulation with hepatocytes generated from human fibroblasts. Nature 2014, 508, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, M.; Grimm, A.; Willenbring, H. Assessing the Therapeutic Potential of Lab-Made Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; He, Z.; Yao, D.; Wu, Z.; Cen, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; et al. Direct Reprogramming of Human Fibroblasts to Functional and Expandable Hepatocytes. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, J.; Song, N.; Xiang, C.; Xu, J.; Hou, Z.; Su, X.; Liu, B.; Jiang, T.; et al. Human Hepatocytes with Drug Metabolic Function Induced from Fibroblasts by Lineage Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, F.; Chang, M.; Liu, X.; et al. Conversion of Human Gastric Epithelial Cells to Multipotent Endodermal Progenitors using Defined Small Molecules. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiskinis, E.; Eggan, K. Progress toward the clinical application of patient-specific pluripotent stem cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, W.; Zhou, H.; Wei, W.; Ambasudhan, R.; Lin, T.; Kim, J.; Zhang, K.; Ding, S. Reprogramming of Human Primary Somatic Cells by OCT4 and Chemical Compounds. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Do, J.T.; Desponts, C.; Hahm, H.S.; Scholer, H.R.; Ding, S. A Combined Chemical and Genetic Approach for the Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Guan, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, T.; Ye, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, K.; et al. Pluripotent Stem Cells Induced from Mouse Somatic Cells by Small-Molecule Compounds. Science 2013, 341, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Qiu, B.; Guan, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Gao, L.; Shen, L.; Huang, Y.; Xie, G.; et al. Direct Conversion of Normal and Alzheimer’s Disease Human Fibroblasts into Neuronal Cells by Small Molecules. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Zhang, Y. Genetic and epigenetic variations in iPSCs: Potential causes and implications for application. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 13, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Miyajima, A. Liver regeneration by stem/progenitor cells. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huch, M.; Bonfanti, P.; Boj, S.F.; Sato, T.; Loomans, C.J.M.; Van De Wetering, M.; Sojoodi, M.; Li, V.S.W.; Schuijers, J.; Gracanin, A.; et al. Unlimited in vitro expansion of adult bi-potent pancreas progenitors through the Lgr5/R-spondin axis. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2708–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Puca, R.; Cardinale, V.; Renzi, A.; Scafetta, G.; Nevi, L.; Rossi, M.; Berloco, P.B.; Corradini, S.G.; Reid, L.M.; et al. Peribiliary Glands as a Niche of Extrapancreatic Precursors Yielding Insulin-Producing Cells in Experimental and Human Diabetes. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Gentile, R.; Napoletano, C.; Rahimi, H.; Franchitto, A.; Semeraro, R.; Nuti, M.; Onori, P.; Berloco, P.B.; et al. Transplantation of human fetal biliary tree stem/progenitor cells into two patients with advanced liver cirrhosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Renzi, A.; Cardinale, V.; Franchitto, A.; Onori, P.; Overi, D.; Rossi, M.; Berloco, P.B.; Alvaro, D.; Reid, L.M.; et al. Progenitor cell niches in the human pancreatic duct system and associated pancreatic duct glands: An anatomical and immunophenotyping study. J. Anat. 2016, 228, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, M.; Carnevale, G.; Cardinale, V.; Gibellini, L.; De Biasi, S.; Pisciotta, A.; Carpino, G.; Gentile, R.; Berloco, P.B. The Fas/Fas ligand apoptosis pathway underlies immunomodulatory properties of human biliary tree stem/progenitor cells. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.S.; Khan, A.A.; Parveen, N.; Habeeb, M.A.; Habibullah, C.M.; Pande, G. Characterization of hepatic progenitors from human fetal liver during second trimester. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 5730–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-A.; Lee, D.-H.; Noh, J.-K.; Kwon, C.; Jung, S.-M.; Lee, S.-K.; Kwon, C.H.D. Differentiation and Major Histocompatibility Complex Antigen Expression in Human Liver–Derived Stem Cells. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 1113–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-M.; Gerasimidou, D.; Kuwahara, R.; Hytiroglou, P.; Yoo, J.E.; Park, Y.N.; Theise, N.D. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) marks hepatocytes newly derived from stem/progenitor cells in humans. Hepatology 2011, 53, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Shaik, M.V.; Parveen, N.; Rajendraprasad, A.A.; Aleem, M.; Aejaz, M.; Srinivas, G.; Avinash, T.; Tiwari, S.K.; Kumaresan, K.; et al. Human fetal liver derived stem cell transplantation as supportive modality in the management of end stage decompensated liver cirrhosis. Cell Transplant. 2010, 19, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrosi, G.; Cintorino, D.; Amico, G.; Chinnici, C.; Conaldi, P.G.; Triolo, F.; Gridelli, B.; Vizzini, G.; Luca, A.; Spada, M.; et al. Efficient human fetal liver cell isolation protocol based on vascular perfusion for liver cell–based therapy and case report on cell transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2012, 18, 226–237. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrosi, G.; Vizzini, G.; Gerlach, J.; Chinnici, C.; Luca, A.; Amico, G.; D’Amato, M.; Conaldi, P.G.; Petri, S.L.; Spada, M.; et al. Phases I-II Matched Case-Control Study of Human Fetal Liver Cell Transplantation for Treatment of Chronic Liver Disease. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevi, L.; Safarikia, S.; Di Matteo, S.; Biancaniello, F.; Chiappetta, M.F.; Cardinale, V. Hyaluronan-Based Grafting Strategies for Liver Stem Cell Therapy and Tracking Methods. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Renzi, A.; Franchitto, A.; Cardinale, V.; Onori, P.; Reid, L.; Alvaro, D.; Gaudio, E. Stem/Progenitor Cell Niches Involved in Hepatic and Biliary Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhaus, R.A. Gene therapy meets stem cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusa, K.; Rashid, S.T.; Strick-Marchand, H.; Varela, I.; Liu, P.Q.; Paschon, D.E.; Miranda, E.; Ordóñez, A.; Hannan, N.R.; Rouhani, F.J.; et al. Targeted gene correction of alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency in induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2011, 478, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Vries, R.G.; Snippert, H.J.; Van De Wetering, M.; Barker, N.; Stange, D.E.; Van Es, J.H.; Abo, A.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.J.; et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009, 459, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, N.; Huch, M.; Kujala, P.; van de Wetering, M.; Snippert, H.J.; van Es, J.H.; Sato, T.; Stange, D.E.; Begthel, H.; van den Born, M.; et al. Lgr5(+ve) stem cells drive self-renewal in the stomach and build long-lived gastric units in vitro. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Hansen, N.F.; Zhao, L.; Du, Y.; Zou, C.; Donovan, F.X.; Chou, B.-K.; Zhou, G.; Li, S.; Dowey, S.N.; et al. Low incidence of DNA sequence variation in human induced pluripotent stem cells generated by non-integrating plasmid expression. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, D.; Baptista, P.M.; Brovold, M.; Moran, E.; Gaston, B.; Booth, C.; Samuel, M.; Atala, A.; Soker, S. Self-assembled liver organoids recapitulate hepatobiliary organogenesis in vitro. Hepatology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Nevi, L.; Overi, D.; Cardinale, V.; Lu, W.; Di Matteo, S.; Safarikia, S.; Berloco, P.B.; Venere, R.; Onori, P.; et al. Peribiliary gland niche participates in biliary tree regeneration in mouse and in human primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaziotis, F.; Justin, A.W.; Tysoe, O.C.; Sawiak, S.; Godfrey, E.M.; Upponi, S.S.; Gieseck, R.L.; De Brito, M.C.; Berntsen, N.L.; Gómez-Vázquez, M.J.; et al. Reconstruction of the mouse extrahepatic biliary tree using primary human extrahepatic cholangiocyte organoids. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giancotti, A.; Monti, M.; Nevi, L.; Safarikia, S.; D’Ambrosio, V.; Brunelli, R.; Pajno, C.; Corno, S.; Di Donato, V.; Musella, A.; et al. Functions and the Emerging Role of the Foetal Liver into Regenerative Medicine. Cells 2019, 8, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080914
Giancotti A, Monti M, Nevi L, Safarikia S, D’Ambrosio V, Brunelli R, Pajno C, Corno S, Di Donato V, Musella A, et al. Functions and the Emerging Role of the Foetal Liver into Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2019; 8(8):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080914
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiancotti, Antonella, Marco Monti, Lorenzo Nevi, Samira Safarikia, Valentina D’Ambrosio, Roberto Brunelli, Cristina Pajno, Sara Corno, Violante Di Donato, Angela Musella, and et al. 2019. "Functions and the Emerging Role of the Foetal Liver into Regenerative Medicine" Cells 8, no. 8: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080914
APA StyleGiancotti, A., Monti, M., Nevi, L., Safarikia, S., D’Ambrosio, V., Brunelli, R., Pajno, C., Corno, S., Di Donato, V., Musella, A., Chiappetta, M. F., Bosco, D., Benedetti Panici, P., Alvaro, D., & Cardinale, V. (2019). Functions and the Emerging Role of the Foetal Liver into Regenerative Medicine. Cells, 8(8), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080914





