Long Non-Coding RNAs Target Pathogenetically Relevant Genes and Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Microarray Analysis
2.3. Protein‒Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Construction and Network Clustering
2.4. Gene Functional Classification and Enrichment Analysis
2.5. Real-Time PCR of LncRNA
2.6. Real-Time PCR of Genes Modulated in RA Patients
2.7. Real-Time PCR of MicroRNA
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. High-Throughput Gene and Long Non-Coding RNA Expression Profiling in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of RA Patients
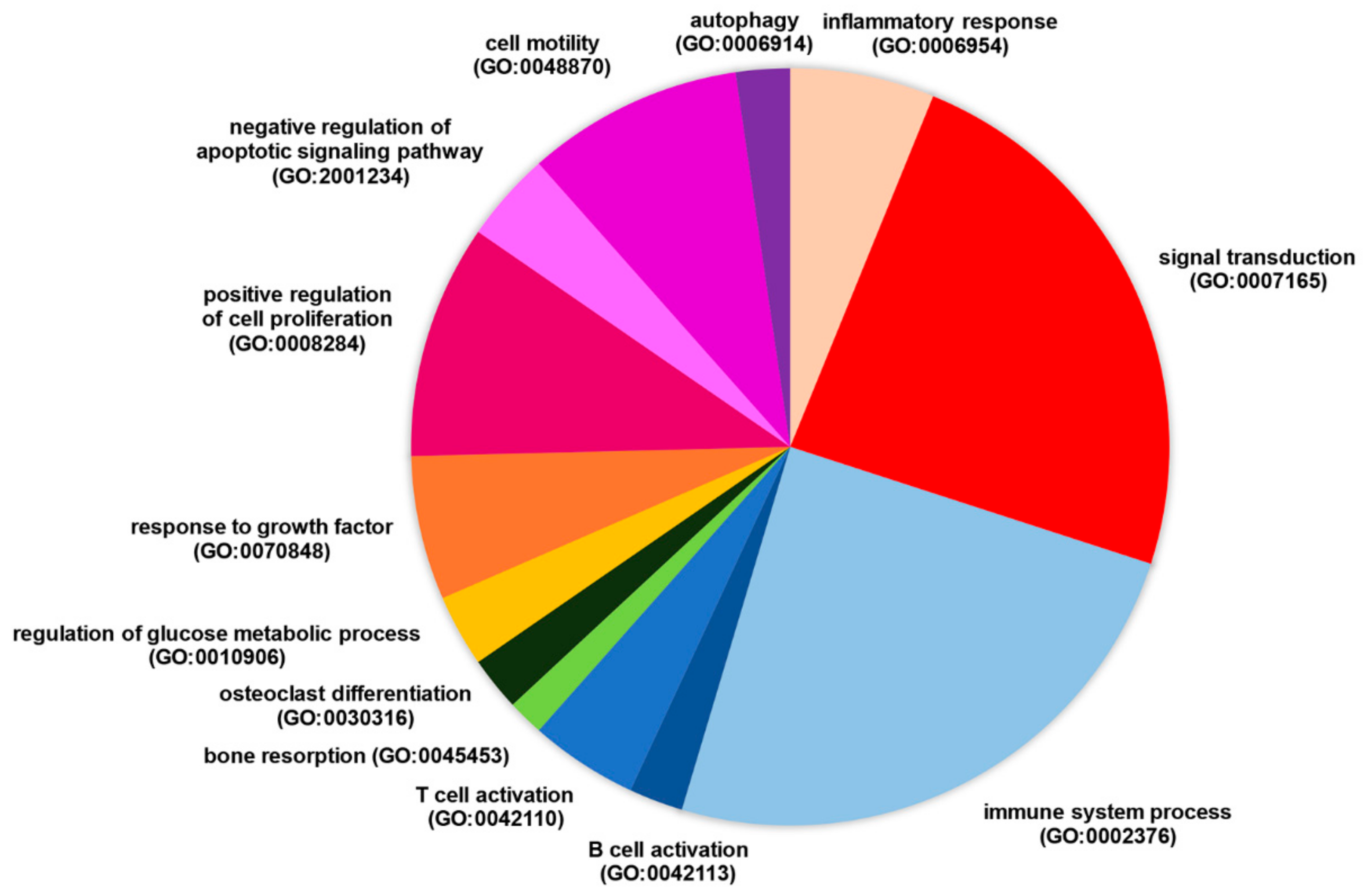
3.2. Selected Long Non-Coding RNAs Modulated in RA Patients Have the Potential to Regulate Genes Differentially Expressed in the Disease
3.3. LncRNA RP11-498C9.15 Targets RA-Associated Meaningful Signalling Pathways
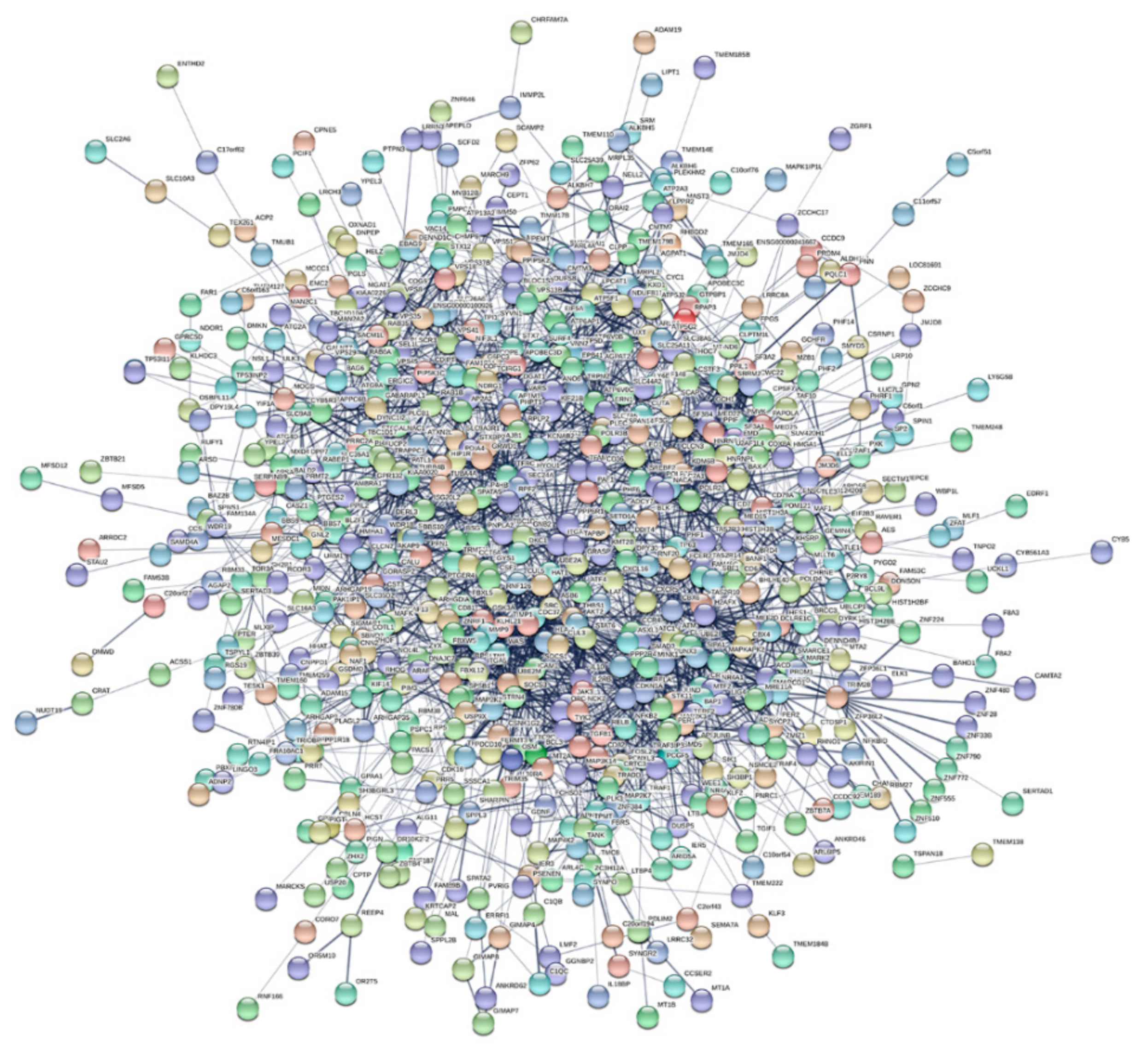
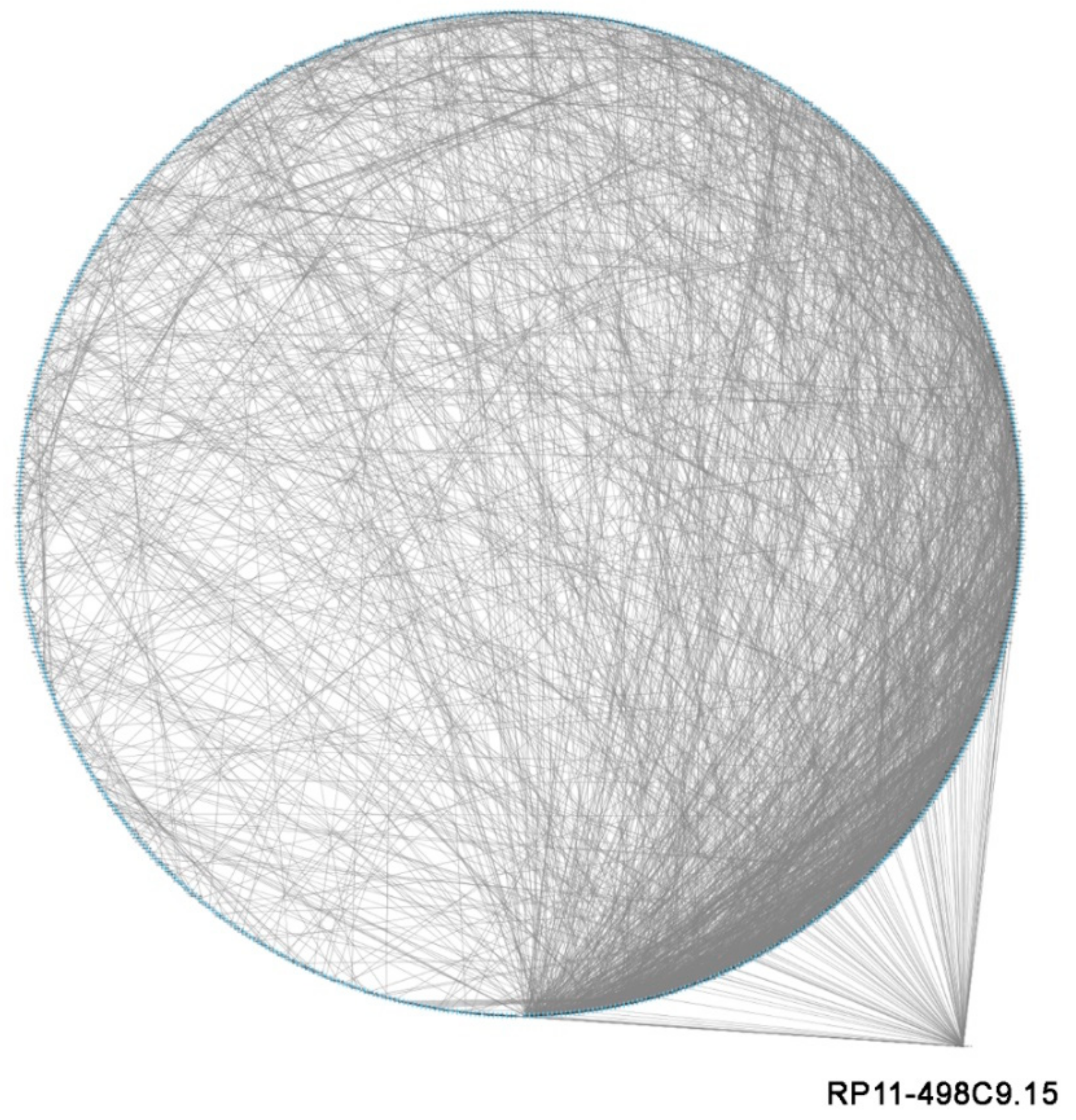
3.4. LncRNA RP11-498C9.15 Targets Highly Connected Genes in the RA Transcriptome
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croia, C.; Bursi, R.; Sutera, D.; Petrelli, F.; Alunno, A.; Puxeddu, I. One year in review 2019: Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, R.; Zwergel, C.; Artico, M.; Taurone, S.; Ralli, M.; Greco, A.; Mai, A. The emerging role of epigenetics in human autoimmune disorders. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.C.; Pan, H.F.; Leng, R.X.; Wang, D.G.; Li, X.P.; Li, X.M.; Ye, D.Q. Emerging role of long noncoding RNAs in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, M.J.; Jamshidi, A.; Chopra, A.; Aslani, S.; Akhlaghi, M.; Mahmoudi, M. Implications of the noncoding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 234, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Zeng, L.; Ye, J.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J. Comprehensive analysis of long non-coding RNA and mRNA expression profiles in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5965–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Qu, B.; Xu, L.; Liu, L.; Sun, H.; Li, C.; Shi, Y.; Liu, H. Long noncoding RNA profiling revealed differentially expressed lncRNAs associated with disease activity in PBMCs from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. StarBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97, StarBase v2.0. Available online: http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/starbase2/index.php (accessed on 6 April 2019). [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.; Keerthikumar, S.; Ang, C.S.; Gangoda, L.; Quek, C.Y.; Williamson, N.A.; Mouradov, D.; Sieber, O.M.; Simpson, R.J.; Salim, A.; et al. Funrich: An open access standalone functional enrichment and interaction network analysis tool. Proteomics 2015, 15, 2597–2601, Funrich. Available online: http://www.funrich.org/ (accessed on 12 April 2019). [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.J.; Kuhn, M.; Stark, M.; Chaffron, S.; Creevey, C.; Muller, J.; Doerks, T.; Julien, P.; Roth, A.; Simonovic, M.; et al. String 8-a global view on proteins and their functional interactions in 630 organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D412–D416, String. Available online: http://string-db.org/ (accessed on 15 April 2019). [CrossRef]
- Cline, M.S.; Smoot, M.; Cerami, E.; Kuchinsky, A.; Landys, N.; Workman, C.; Christmas, R.; Avila-Campilo, I.; Creech, M.; Gross, B.; et al. Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using cytoscape. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2366–2382, Cytoscape. Available online: http://www.cytoscape.org/ (accessed on 25 April 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Casagrande, J.T.; Thomas, P.D. Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1551–1566, Panther. Available online: http://pantherdb.org/ (accessed on 29 June 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.Q.; Feng, S.; Chen, W.; Zhao, H.; Paulson, C.; Li, Y.P. V-ATPase subunit ATP6AP1 (Ac45) regulates osteoclast differentiation, extracellular acidification, lysosomal trafficking, and protease exocytosis in osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotake, S.; Nanke, Y.; Kawamoto, M.; Yago, T.; Udagawa, N.; Ichikawa, N.; Kobashigawa, T.; Saito, S.; Momohara, S.; Kamatani, N.; et al. T-cell leukemia translocation-associated gene (TCTA) protein is required for human osteoclastogenesis. Bone 2009, 45, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, K.; Uematsu, S.; Kondo, T.; Takeuchi, O.; Martino, M.M.; Kawasaki, T.; Akira, S. Strawberry notch homologue 2 regulates osteoclast fusion by enhancing the expression of DC-STAMP. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, J.M.; Kirkland, M.A.; Nicholson, G.C. Multiple roles of M-CSF in human osteoclastogenesis. J. Cell Biochem. 2007, 102, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazzotti, G.; Bavelloni, A.; Blalock, W.; Piazzi, M.; Cocco, L.; Faenza, I. BMP-2 Induced Expression of PLCβ1 That is a Positive Regulator of Osteoblast Differentiation. J. Cell Physiol. 2016, 231, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, R.G.; Xin, G.; Schauder, D.M.; Cossette, S.M.; Bordas, M.; Cui, W.; Ramchandran, R. Dual Specificity Phosphatase 5 Is Essential for T Cell Survival. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.A.; Millán, J. The role of lipid rafts in signalling and membrane trafficking in T lymphocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3957–3965. [Google Scholar]
- Balagopalan, L.; Yi, J.; Nguyen, T.; McIntire, K.M.; Harned, A.S.; Narayan, K.; Samelson, L.E. Plasma membrane LAT activation precedes vesicular recruitment defining two phases of early T-cell activation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagi, Y.; Landrigan, A.; Levy, R.; Levy, S. Complementary costimulation of human T-cell subpopulations by cluster of differentiation 28 (CD28) and CD81. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, S.; Thomson, B.P.; Remmers, E.F.; Eyre, S.; Hinks, A.; Guiducci, C.; Catanese, J.J.; Xie, G.; Stahl, E.A.; Chen, R.; et al. Genetic variants at CD28, PRDM1 and CD2/CD58 are associated with rheumatoid arthritis risk. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herglotz, J.; Unrau, L.; Hauschildt, F.; Fischer, M.; Kriebitzsch, N.; Alawi, M.; Indenbirken, D.; Spohn, M.; Müller, U.; Ziegler, M.; et al. Essential control of early B-cell development by Mef2 transcription factors. Blood 2016, 127, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, X.M.; Wang, J. Regulation of the Development and Function of B Cells by ZBTB Transcription Factors. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, S.; Arai, Y.; Mori, H.; Matsushita, Y.; Kubo, T.; Nakanishi, T. Small interfering RNA targeting CD81 ameliorated arthritis in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.; Park, M.; Park, W.; Kim, S.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, T.; Jung, J.; et al. REDD-1 aggravates endotoxin-induced inflammation via atypical NF-κB activation. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4585–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M.J.; Jones, S.W. Review: Long Noncoding RNAs in the Regulation of Inflammatory Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.A.; Satpathy, S.; Beli, P.; Choudhary, C. SPATA2 links CYLD to the TNF-α receptor signaling complex and modulates the receptor signaling outcomes. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 1868–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakonjac, M.; Fischer, L.; Provost, P.; Werz, O.; Steinhilber, D.; Samuelsson, B.; Rådmark, O. Coactosin-like protein supports 5-lipoxygenase enzyme activity and up-regulates leukotriene A4 production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13150–131555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, A.; Gogarty, M.; Crean, D.; Murphy, E.P. Subcellular Localization of NR4A2 Orphan Nuclear Receptor Expression in Human and Mouse Synovial Joint Tissue. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1966, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, K.P.; O’Donoghue, G.; Adams, C.; Mulcahy, H.; Molloy, C.; Silke, C.; Molloy, M.; Shanahan, F.; O’Gara, F. High levels of Lymphotoxin-Beta (LT-Beta) gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovium: Clinical and cytokine correlations. Rheumatol. Int. 2008, 28, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caselli, G.; Bonazzi, A.; Lanza, M.; Ferrari, F.; Maggioni, D.; Ferioli, C.; Giambelli, R.; Comi, E.; Zerbi, S.; Perrella, M.; et al. Pharmacological characterisation of CR6086, a potent prostaglandin E(2) receptor 4 antagonist, as a new potential disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsaidi, A.; Tiaden, A.N.; Richards, P.J. Prostaglandin E(2) inhibits matrix mineralization by human bone marrow stromal cell-derived osteoblasts via Epac-dependent cAMP signaling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.M.; Jeon, W.J.; Kim, E.J.; Jang, W.G. CRTC2 suppresses BMP2-induced osteoblastic differentiation via Smurf1 expression in MC3T3-E1 cells. Life Sci. 2018, 214, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, E.F.; Matsuo, K. Signalling in osteoclasts and the role of Fos/AP1 proteins. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinne, R.W.; Boehm, S.; Iftner, T.; Aigner, T.; Vornehm, S.; Weseloh, G.; Bravo, R.; Emmrich, F.; Kroczek, R.A. Synovial fibroblast-like cells strongly express jun-B and C-fos proto-oncogenes in rheumatoid- and osteoarthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1995, 101, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, T.M.; Wheaton, J.D.; Houtz, G.M.; Ciofani, M. JunB promotes Th17 cell identity and restrains alternative CD4(+) T-cell programs during inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vomero, M.; Barbati, C.; Colasanti, T.; Perricone, C.; Novelli, L.; Ceccarelli, F.; Spinelli, F.R.; Di Franco, M.; Conti, F.; Valesini, G.; et al. Autophagy and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Knowledges and Future Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, J.Y.; Park, H.J.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, Y.A.; Choi, I.A.; Chung, J.H.; Hong, S.J. Association of forkhead box J3 (FOXJ3) polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malemud, C.J. Intracellular Signaling Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Cell Immunol. 2013, 4, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaigirdar, S.A.; Benson, R.A.; Elmesmari, A.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.S.; McInnes, I.B.; Garside, P.; MacLeod, M.K.L. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Promotes the Persistence of Activated CD4 T Cells in Inflamed Sites. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowin, T.; Straub, R.H. Integrins and their ligands in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanki, T.; Shimaoka, T.; Hayashida, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Yonehara, S.; Miyasaka, N. Pathogenic role of the CXCL16-CXCR6 pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3004–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohba, T.; Takase, Y.; Ohhara, M.; Kasukawa, R. Thrombin in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis mediates proliferation of synovial fibroblast-like cells by induction of platelet derived growth factor. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 23, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau, M.; Lavoie, R.R.; Lauzier, A.; Harper, K.; McDonald, P.P.; Dubois, C.M. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Activation Promotes the Prodestructive Invadosome-Forming Phenotype of Synoviocytes from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, N.; Hamilton, J.A. Extravascular coagulation and the plasminogen activator/plasmin system in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2268–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pache, M.; Schwarz, H.A.; Kaiser, H.J.; Wüest, P.; Klöti, M.; Dubler, B.; Flammer, J. Elevated plasma endothelin-1 levels and vascular dysregulation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2002, 8, CR616–CR619. [Google Scholar]
- Mythreye, K.; Blobe, G.C. Proteoglycan signaling co-receptors: Roles in cell adhesion, migration and invasion. Cell Signal. 2009, 21, 1548–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoureux, F.; Baud’huin, M.; Duplomb, L.; Heymann, D.; Rédini, F. Proteoglycans: Key partners in bone cell biology. Bioessays 2007, 29, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekanecz, Z.; Besenyei, T.; Szentpétery, A.; Koch, A.E. Angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2010, 22, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelef, M.A.; Bennin, D.A.; Yasmin, N.; Warner, T.F.; Ludwig, T.; Beggs, H.E.; Huttenlocher, A. Focal adhesion kinase is required for synovial fibroblast invasion, but not murine inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.L.; Li, X.; Lu, W.G.; Sun, J.M.; Jiang, D.L.; Xu, R.S. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) as a therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, B.M.; Cho, M.L.; Lee, S.H. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Matsuo, K. Regulation of osteoclasts by membrane-derived lipid mediators. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3341–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandaunet, B.; Syversen, S.W.; Hoff, M.; Sundan, A.; Haugeberg, G.; van Der Heijde, D.; Kvien, T.K.; Standal, T. Association between high plasma levels of hepatocyte growth factor and progression of radiographic damage in the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, H.; Zhou, H.; Jin, H.; Ning, Y.; Wang, Y. Abnormal Glucose Metabolism in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9670434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias de la Rosa, I.; Escudero-Contreras, A.; Rodríguez-Cuenca, S.; Ruiz-Ponce, M.; Jiménez-Gómez, Y.; Ruiz-Limón, P.; Pérez-Sánchez, C.; Ábalos-Aguilera, M.C.; Cecchi, I.; Ortega, R.; et al. Defective glucose and lipid metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis is determined by chronic inflammation in metabolic tissues. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagakis, I.; Bertsias, G.; Karvounaris, S.; Kavousanaki, M.; Virla, D.; Raptopoulou, A.; Kardassis, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Sidiropoulos, P.I. Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy improves insulin resistance, beta cell function and insulin signaling in active rheumatoid arthritis patients with high insulin resistance. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Higgs, B.W.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Wu, Y.; Karsdal, M.A.; Kuziora, M.; Godwood, A.; Close, D.; Ryan, P.C.; Roskos, L.K.; et al. Blockade of GM-CSF pathway induced sustained suppression of myeloid and T cell activities in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brühl, H.; Cihak, J.; Niedermeier, M.; Denzel, A.; Rodriguez Gomez, M.; Talke, Y.; Goebel, N.; Plachý, J.; Stangassinger, M.; Mack, M. Important role of interleukin-3 in the early phase of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isomäki, P.; Alanärä, T.; Isohanni, P.; Lagerstedt, A.; Korpela, M.; Moilanen, T.; Visakorpi, T.; Silvennoinen, O. The expression of SOCS is altered in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.; Shi, Q.; Wang, M. MiR-650 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts by targeting AKT2. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamata, A.; Izu, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Amagasa, T.; Wagner, E.F.; Nakashima, K.; Ezura, Y.; Hayata, T.; Noda, M. JunD suppresses bone formation and contributes to low bone mass induced by estrogen depletion. J. Cell Biochem. 2008, 103, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, S.S. NF-kappa B in rheumatoid arthritis: A pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and tissue destruction. Arthritis Res. 2001, 3, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ID | Fold Change | FDR p-Value | Gene Symbol | Description | mRNA Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apoptosis | |||||
| TC0300009843.hg.1 | 2.12 | 0.050 | TP63 | tumour protein p63 | NM_001114978 |
| TC2200007783.hg.1 | 5.34 | 0.008 | PIM3 | Pim-3 proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase | NM_001001852 |
| TC0300010770.hg.1 | 12.5 | 0.008 | CSRNP1 | cysteine-serine-rich nuclear protein 1 | NM_033027 |
| TC1900009429.hg.1 | 2.3 | 0.018 | KHSRP | KH-type splicing regulatory protein | NM_003685 |
| TC0600011441.hg.1 | 3.47 | 0.008 | BAG6 | BCL2-associated athanogene 6 | NM_001199697 |
| TC1100013230.hg.1 | 2.08 | 0.023 | BCL9L | B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9-like | NM_182557 |
| TC0100007449.hg.1 | 2.2 | 0.049 | SH3BGRL3 | SH3 domain binding glutamate-rich protein like 3 | NM_031286 |
| TC1100006815.hg.1 | 3 | 0.037 | WEE1 | WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase | NM_001143976 |
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| TC0300009702.hg.1 | 2.49 | 0.044 | EIF4G1 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma, 1 | NM_001194946 |
| TC0X00007132.hg.1 | 3.18 | 0.008 | CDK16 | cyclin-dependent kinase 16 | NM_001170460 |
| TC0200015764.hg.1 | 3.79 | 0.004 | CNPPD1 | cyclin Pas1/PHO80 domain containing 1 | NM_015680 |
| TC0200016494.hg.1 | 2.04 | 0.046 | CNNM4 | cyclin and CBS domain divalent metal cation transport mediator 4 | NM_020184 |
| TC1900010696.hg.1 | 5.13 | 0.007 | AKT2 | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 2 | NM_001243027 |
| Cell migration | |||||
| TC1500010018.hg.1 | 2.3 | 0.018 | SEMA7A | semaphorin 7A, GPI membrane anchor | NM_001146029 |
| TC1200012859.hg.1 | 3.65 | 0.006 | RHOF | ras homolog family member F (in filopodia) | NM_019034 |
| TC1100009864.hg.1 | 3.29 | 0.004 | RHOG | ras homolog family member G | NM_001665 |
| TC1700009528.hg.1 | 2.46 | 0.028 | CXCL16 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16 | NM_001100812 |
| Inflammatory response | |||||
| TC1500006925.hg.1 | 24.36 | 0.018 | THBS1 | thrombospondin 1 | NM_003246 |
| TC1900006977.hg.1 | 11.9 | 0.050 | ICAM1 | intercellular adhesion molecule 1 | NM_000201 |
| TC0500007231.hg.1 | 3.28 | 0.022 | PTGER4 | prostaglandin E receptor 4 (subtype EP4) | NM_000958 |
| TC0100011384.hg.1 | 2.52 | 0.025 | MAPKAPK2 | mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 | NM_004759 |
| TC0100009364.hg.1 | 3.82 | 0.008 | CSF1 | colony stimulating factor 1 (macrophage) | NM_000757 |
| TC0300006985.hg.1 | 6.3 | 0.034 | CCR4 | chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 4 | NM_005508 |
| TC1900010743.hg.1 | 2.7 | 0.019 | TGFB1 | transforming growth factor beta 1 | NM_000660 |
| TC1000007990.hg.1 | 4.92 | 0.020 | DDIT4 | DNA damage inducible transcript 4 | NM_019058 |
| TC1600011060.hg.1 | 2.28 | 0.017 | COTL1 | coactosin-like F-actin binding protein 1 | NM_021149 |
| TC2000009401.hg.1 | 3.54 | 0.011 | SPATA2 | Spermatogenesis-associated 2 | NM_00113577 |
| TC1100011243.hg.1 | 4.25 | 0.007 | RELA | v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A | NM_001145138 |
| TC0900011623.hg.1 | 2.16 | 0.030 | PTGES2 | prostaglandin E synthase 2 | NM_001256335 |
| TC0200014672.hg.1 | 7.65 | 0.042 | NR4A2 | nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | NM_006186 |
| TC1900007270.hg.1 | 6.2 | 0.007 | KLF2 | Kruppel-like factor 2 | NM_016270 |
| TC1700011903.hg.1 | 4.41 | 0.046 | SOCS3 | suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 | NM_003955 |
| TC1600009395.hg.1 | 3.76 | 0.010 | SOCS1 | suppressor of cytokine signalling 1 | NM_003745 |
| TC0100017107.hg.1 | 2.71 | 0.041 | IL10 | interleukin 10 | NM_000572 |
| TC1100009225.hg.1 | 7.04 | 0.006 | CXCR5 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 5 | NM_001716 |
| TC1100013178.hg.1 | 2.22 | 0.023 | MAP4K2 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 2 | NM_001307990 |
| TC1700007262.hg.1 | 4.43 | 0.023 | MAP2K3 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 | NM_002756 |
| TC1900009325.hg.1 | 3.56 | 0.038 | MAP2K2 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | NM_030662 |
| TC0600011438.hg.1 | 2.07 | 0.045 | LTB | lymphotoxin beta (TNF superfamily, member 3) | NM_002341 |
| TC1700011903.hg.1 | 4.41 | 0.046 | SOCS3 | suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 | NM_003955 |
| Immune response | |||||
| TC0200008452.hg.1 | 2.85 | 0.024 | MAL | mal, T-cell differentiation protein | NM_002371 |
| TC1100006576.hg.1 | 3.74 | 0.015 | CD81 | CD81 molecule | NM_001297649 |
| TC0600007495.hg.1 | 2.08 | 0.037 | HLA-A | major histocompatibility complex, class I, A | NM_001242758 |
| TC0100007291.hg.1 | 2.08 | 0.028 | C1QC | complement component 1, q subcomponent, C chain | NM_001114101 |
| TC1100007787.hg.1 | 3.29 | 0.035 | CD6 | CD6 molecule | NM_001254750 |
| TC1600011368.hg.1 | 3.14 | 0.008 | LAT | linker for activation of T-cells | NM_001014987 |
| TC1900008279.hg.1 | 5.58 | 0.006 | BCL3 | B-cell CLL/lymphoma 3 | NM_005178 |
| TC1900008166.hg.1 | 3.13 | 0.004 | CD79A | CD79a molecule, immunoglobulin-associated alpha | NM_001783 |
| TC1200010950.hg.1 | 2.47 | 0.034 | STAT6 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 6, interleukin-4 induced | NM_001178078 |
| TC1000008891.hg.1 | 10.97 | 0.008 | DUSP5 | dual specificity phosphatase 5 | NM_004419 |
| TC0600008972.hg.1 | 5.51 | 0.018 | PRDM1 | PR domain containing 1, with ZNF domain | NM_001198 |
| TC0100016000.hg.1 | 4.15 | 0.004 | MEF2D | myocyte enhancer factor 2D | NM_001271629 |
| TC0900008891.hg.1 | 2.21 | 0.023 | LRRC8A | leucine rich repeat containing 8 family, member A | NM_001127244 |
| TC1900009320.hg.1 | 2.71 | 0.045 | ZBTB7A | zinc finger and BTB domain containing 7A | NM_015898 |
| TC1900008505.hg.1 | 2.93 | 0.018 | BAX | BCL2-associated X protein | NM_001291428 |
| TC1800007805.hg.1 | 2.22 | 0.027 | NFATC1 | nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1 | NM_001278669 |
| TC2200008637.hg.1 | 3.64 | 0.015 | IL2RB | interleukin 2 receptor, beta | NM_000878 |
| Angiogenesis | |||||
| TC1200010839.hg.1 | 2 | 0.029 | ITGA5 | integrin alpha 5 | NM_002205 |
| TC2000007336.hg.1 | 2.83 | 0.015 | PPP1R16B | protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 16B | NM_001172735 |
| TC1600008971.hg.1 | 2.83 | 0.018 | JMJD8 | jumonji domain containing 8 | NM_001005920 |
| TC1700011818.hg.1 | 2.6 | 0.050 | JMJD6 | jumonji domain containing 6 | NM_001081461 |
| TC0100007832.hg.1 | 17.12 | 0.008 | ZC3H12A | zinc finger CCCH-type containing 12A | NM_025079 |
| TC0100018300.hg.1 | 2.44 | 0.032 | ADAM15 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 15 | NM_001261464 |
| Bone resorption | |||||
| Positive regulation of bone resorption | |||||
| TC0X00008831.hg.1 | 2.62 | 0.021 | ATP6AP1 | ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal accessory protein 1 | NM_001183 |
| TC2000007283.hg.1 | 2.11 | 0.026 | SRC | SRC proto-oncogene, non-receptor tyrosine kinase | NM_005417 |
| TC0300009916.hg.1 | 4.17 | 0.030 | HES1 | hes family bHLH transcription factor 1 | NM_005524 |
| TC0100015891.hg.1 | 2.76 | 0.008 | CRTC2 | CREB regulated transcription coactivator 2 | NM_181715 |
| TC1900010009.hg.1 | 3.41 | 0.023 | JUND | jun D proto-oncogene | NM_001286968 |
| Positive regulation of osteoclast proliferation/differentiation | |||||
| TC0300007380.hg.1 | 2.4 | 0.027 | TCTA | T-cell leukaemia translocation altered | NM_022171 |
| TC1900009134.hg.1 | 9.56 | 0.002 | SBNO2 | strawberry notch homolog 2 | NM_014963 |
| TC0100009364.hg.1 | 3.82 | 0.008 | CSF1 | colony stimulating factor 1 (macrophage) | NM_000757 |
| TC0X00008831.hg.1 | 2.62 | 0.021 | ATP6AP1 | ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal accessory protein 1 | NM_001183 |
| TC0300009916.hg.1 | 4.17 | 0.030 | HES1 | hes family bHLH transcription factor 1 | NM_005524 |
| TC0500007231.hg.1 | 3.28 | 0.022 | PTGER4 | prostaglandin E receptor 4 (subtype EP4) | NM_000958 |
| TC1900007096.hg.1 | 5.16 | 0.032 | JUNB | jun B proto-oncogene | NM_002229 |
| Osteoblast differentiation | |||||
| TC2000009887.hg.1 | −2.8 | 0.0172 | PLCB1 | phospholipase C, beta 1 (phosphoinositide-specific) | NM_015192 |
| Extracellular matrix degradation | |||||
| TC2000007514.hg.1 | 3.14 | 0.041 | MMP9 | matrix metallopeptidase 9 | NM_004994 |
| TC0500012599.hg.1 | 1.9 | 0.040 | ADAM19 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 19 | NM_033274 |
| TC0100018300.hg.1 | 2.44 | 0.032 | ADAM15 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 15 | NM_001261464 |
| TC1900006470.hg.1 | 3.01 | 0.011 | BSG | basigin | NM_001728 |
| ID | Fold Change | FDR p-Value | Gene Symbol | Description | mRNA Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wnt signalling pathway | |||||
| TC1900009272.hg.1 | 2.4 | 0.018 | AES | amino-terminal enhancer of split | NM_001130 |
| TC1100008181.hg.1 | 2.03 | 0.029 | LRP5 | LDL-receptor-related protein 5 | NM_001291902 |
| TC0200014672.hg.1 | 7.65 | 0.042 | NR4A2 | nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | NM_006186 |
| TC1100007913.hg.1 | 2.69 | 0.048 | MARK2 | MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 2 | NM_001039469 |
| TC1200007595.hg.1 | 2.88 | 0.023 | SMARCD1 | SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily d, member 1 | NM_003076 |
| TC1900011639.hg.1 | 2.1 | 0.032 | STK11 | serine/threonine kinase 11 | NM_000455 |
| TC1100008181.hg.1 | 2.03 | 0.029 | LRP5 | LDL-receptor-related protein 5 | NM_001291902 |
| TNF signalling pathway | |||||
| TC0900011385.hg.1 | −1.99 | 0.040 | PSMD5 | proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase 5 | NM_001270427 |
| TC0600011438.hg.1 | 2.07 | 0.045 | LTB | lymphotoxin beta (TNF superfamily, member 3) | NM_002341 |
| TC1700010879.hg.1 | 2.36 | 0.026 | MAP3K14 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 14 | NM_003954 |
| TC1600010616.hg.1 | 2.14 | 0.035 | TRADD | TNFRSF1A-associated via death domain | NM_003789 |
| TC1100011243.hg.1 | 4.25 | 0.007 | RELA | v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A | NM_001145138 |
| Type I interferon signalling | |||||
| TC0600007495.hg.1 | 2.08 | 0.037 | HLA-A | major histocompatibility complex, class I, A | NM_001242758 |
| TC0200008452.hg.1 | 2.85 | 0.024 | MAL | mal, T-cell differentiation protein | NM_002371 |
| TC0100017107.hg.1 | 2.71 | 0.041 | IL10 | interleukin 10 | NM_000572 |
| TC1600009395.hg.1 | 3.76 | 0.010 | SOCS1 | suppressor of cytokine signalling 1 | NM_003745 |
| TC1100011243.hg.1 | 4.25 | 0.007 | RELA | v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A | NM_001145138 |
| TC1900009627.hg.1 | 2.63 | 0.040 | TYK2 | tyrosine kinase 2 | NM_003331 |
| TC1000008727.hg.1 | 2.64 | 0.024 | NFKB2 | nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 2 (p49/p100) | NM_001077494 |
| p38 MAP kinase signalling | |||||
| TC1400009524.hg.1 | 2.91 | 0.029 | ZFP36L1 | ZFP36 ring finger protein-like 1 | NM_001244698 |
| TC1700007262.hg.1 | 4.43 | 0.023 | MAP2K3 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 | NM_002756 |
| TC0100011384.hg.1 | 2.52 | 0.025 | MAPKAPK2 | mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 | NM_004759 |
| TC0X00009581.hg.1 | 2.99 | 0.013 | ELK1 | ELK1, member of ETS oncogene family | NM_001114123 |
| TC0100016000.hg.1 | 4.15 | 0.004 | MEF2D | myocyte enhancer factor 2D | NM_001271629 |
| NF-kB signalling pathway | |||||
| TC1900008300.hg.1 | 2.78 | 0.034 | RELB | v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog B | NM_006509 |
| TC1900008279.hg.1 | 5.58 | 0.006 | BCL3 | B-cell CLL/lymphoma 3 | NM_005178 |
| TC1600010616.hg.1 | 2.14 | 0.035 | TRADD | TNFRSF1A-associated via death domain | NM_003789 |
| TC1100011243.hg.1 | 4.25 | 0.007 | RELA | v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A | NM_001145138 |
| TC1700010879.hg.1 | 2.36 | 0.026 | MAP3K14 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 14 | NM_003954 |
| TC0800012190.hg.1 | 3.65 | 0.018 | SHARPIN | SHANK-associated RH domain interactor | NM_030974 |
| TOLL-like receptors signalling pathways | |||||
| TC0200008452.hg.1 | 2.85 | 0.024 | MAL | mal, T-cell differentiation protein | NM_002371 |
| TC0X00009581.hg.1 | 2.99 | 0.013 | ELK1 | ELK1, member of ETS oncogene family | NM_001114123 |
| TC0100011384.hg.1 | 2.52 | 0.025 | MAPKAPK2 | mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 | NM_004759 |
| TC1000008727.hg.1 | 2.64 | 0.024 | NFKB2 | nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 2 | NM_001077494 |
| TC1700007262.hg.1 | 4.43 | 0.023 | MAP2K3 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 | NM_002756 |
| TC1100011243.hg.1 | 4.25 | 0.007 | RELA | v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A | NM_001145138 |
| Jak-Stat signalling pathway | |||||
| TC1600009395.hg.1 | 3.76 | 0.010 | SOCS1 | suppressor of cytokine signalling 1 | NM_003745 |
| TC1700011903.hg.1 | 4.41 | 0.046 | SOCS3 | suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 | NM_003955 |
| TC1900009991.hg.1 | 2.63 | 0.042 | JAK3 | Janus kinase 3 | NM_000215 |
| TC1200010950.hg.1 | 2.47 | 0.034 | STAT6 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 6, interleukin-4 induced | NM_001178078 |
| PI3K signalling pathway | |||||
| TC1900010696.hg.1 | 5.13 | 0.007 | AKT2 | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 2 | NM_001243027 |
| TC1100008136.hg.1 | 2.31 | 0.023 | RPS6KB2 | ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 70kDa, polypeptide 2 | NM_003952 |
| TC1000007990.hg.1 | 4.92 | 0.020 | DDIT4 | DNA damage inducible transcript 4 | NM_019058 |
| TC1000008891.hg.1 | 10.97 | 0.008 | DUSP5 | dual specificity phosphatase 5 | NM_004419 |
| TC0700008560.hg.1 | 3.76 | 0.026 | GNB2 | guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 2 | NM_005273 |
| TC1900010009.hg.1 | 3.41 | 0.023 | JUND | jun D proto-oncogene | NM_001286968 |
| TC1900007096.hg.1 | 5.16 | 0.032 | JUNB | jun B proto-oncogene | NM_002229 |
| TC0600008972.hg.1 | 5.51 | 0.018 | PRDM1 | PR domain containing 1, with ZNF domain | NM_001198 |
| mTOR signalling pathway | |||||
| TC0300013684.hg.1 | 2.21 | 0.043 | TFRC | transferrin receptor | NM_001128148 |
| TC1200007595.hg.1 | 2.88 | 0.023 | SMARCD1 | SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily d, member 1 | NM_003076 |
| TC1700011903.hg.1 | 4.41 | 0.046 | SOCS3 | suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 | NM_003955 |
| TC2000007283.hg.1 | 2.11 | 0.026 | SRC | SRC proto-oncogene, non-receptor tyrosine kinase | NM_005417 |
| TC0400009765.hg.1 | 3.06 | 0.018 | MXD4 | MAX dimerization protein 4 | NM_006454 |
| TC0100016000.hg.1 | 4.15 | 0.004 | MEF2D | myocyte enhancer factor 2D | NM_001271629 |
| Biological Pathway | Bonferroni Corrected p-Value |
|---|---|
| Proteoglycan syndecan-mediated signalling events | 0.006 |
| Alpha9 beta1 integrin signalling events | 0.020 |
| GMCSF-mediated signalling events | 0.025 |
| Beta1 integrin cell surface interactions | 0.026 |
| IL3-mediated signalling events | 0.027 |
| IFN-gamma pathway | 0.028 |
| PAR1-mediated thrombin signalling events | 0.031 |
| Thrombin/protease-activated receptor (PAR) pathway | 0.032 |
| Syndecan-1-mediated signalling events | 0.032 |
| Integrin family cell surface interactions | 0.032 |
| Plasma membrane oestrogen receptor signalling | 0.033 |
| Endothelins | 0.040 |
| Signalling events mediated by focal adhesion kinase | 0.040 |
| PDGFR-beta signalling pathway | 0.040 |
| Arf6 trafficking events | 0.040 |
| Class I PI3K signalling events mediated by Akt | 0.040 |
| mTOR signalling pathway | 0.040 |
| Internalization of ErbB1 | 0.040 |
| EGF receptor (ErbB1) signalling pathway | 0.040 |
| Class I PI3K signalling events | 0.040 |
| Arf6 signalling events | 0.040 |
| ErbB1 downstream signalling | 0.040 |
| Arf6 downstream pathway | 0.040 |
| Insulin Pathway | 0.040 |
| Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and uPAR-mediated signalling | 0.040 |
| S1P1 pathway | 0.040 |
| EGFR-dependent Endothelin signalling events | 0.041 |
| IGF1 pathway | 0.044 |
| ErbB receptor signalling network | 0.045 |
| Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) pathway | 0.045 |
| IL5-mediated signalling events | 0.045 |
| Signalling events mediated by hepatocyte growth factor receptor (c-Met) | 0.047 |
| PDGF receptor signalling network | 0.047 |
| Nectin adhesion pathway | 0.049 |
| Signalling events mediated by VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 | 0.051 |
| Glypican 1 network | 0.056 |
| Glypican pathway | 0.055 |
| VEGF and VEGFR signalling network | 0.055 |
| Integrin-linked kinase signalling | 0.053 |
| ID | Fold Change | FDR p-Value | Gene Symbol | mRNA Accession | miRNA Targets | Targeted Modulated Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC0X00010064.hg.1 | −2.03 | 0.049 | FTX | NR_028379 | 64 | 96 |
| TC0100018570.hg.1 | −2.64 | 0.034 | HNRNPU-AS1 | NR_026778 | 55 | 161 |
| TC2200009240.hg.1 | −2 | 0.042 | MIATNB | NR_110543 | 16 | 11 |
| TC1700012077.hg.1 | 2.5 | 0.039 | RP11-498C9.15 | ENST00000582866.1 | 27 | 106 |
| TC0100009198.hg.1 | −3.23 | 0.008 | RP4-714D9.5 | ENST00000564623.1 | 6 | 27 |
| TC1400006883.hg.1 | 2.74 | 0.018 | RP11-73E17.2 | ENST00000557373.1 | 1 | 4 |
| Biological Pathway | Bonferroni Corrected p-Value |
|---|---|
| Beta1 integrin cell surface interactions | 0.004 |
| Integrin family cell surface interactions | 0.006 |
| IFN-gamma pathway | 0.008 |
| PAR1-mediated thrombin signalling events | 0.008 |
| Thrombin/protease-activated receptor (PAR) pathway | 0.009 |
| Plasma membrane oestrogen receptor signalling | 0.009 |
| Endothelins | 0.009 |
| Glypican pathway | 0.014 |
| Proteoglycan syndecan-mediated signalling events | 0.016 |
| Signalling events mediated by focal adhesion kinase | 0.030 |
| Class I PI3K signalling events mediated by Akt | 0.030 |
| Internalization of ErbB1 | 0.030 |
| Arf6 downstream pathway | 0.030 |
| Arf6 trafficking events | 0.030 |
| EGF receptor (ErbB1) signalling pathway | 0.030 |
| Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and uPAR-mediated signalling | 0.030 |
| ErbB1 downstream signalling | 0.030 |
| S1P1 pathway | 0.030 |
| Arf6 signalling events | 0.030 |
| mTOR signalling pathway | 0.030 |
| Insulin pathway | 0.030 |
| PDGFR-beta signalling pathway | 0.030 |
| Class I PI3K signalling events | 0.030 |
| EGFR-dependent Endothelin signalling events | 0.030 |
| IGF1 pathway | 0.031 |
| GMCSF-mediated signalling events | 0.031 |
| IL5-mediated signalling events | 0.031 |
| Signalling events mediated by hepatocyte growth factor receptor (c-Met) | 0.032 |
| PDGF receptor signalling network | 0.032 |
| IL3-mediated signalling events | 0.032 |
| Nectin adhesion pathway | 0.032 |
| Signalling events mediated by VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 | 0.033 |
| Glypican 1 network | 0.034 |
| Syndecan-1-mediated signalling events | 0.035 |
| VEGF and VEGFR signalling network | 0.036 |
| Alpha9 beta1 integrin signalling events | 0.037 |
| Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) pathway | 0.040 |
| ErbB receptor signalling network | 0.040 |
| Integrin-linked kinase signalling | 0.045 |
| Module | miRNAs | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | hsa-miR-23c (1.56 up) | CUL3 |
| hsa-miR-23b-3p (2.06 up) | CUL3 | |
| hsa-miR-23a-3p (1.74 down) | CUL3 | |
| hsa-miR-221-3p (2.34 up) | HNRNPA0 | |
| hsa-miR-302c-3p (2.48 down) | SOCS3 | |
| hsa-miR-221-3p (2.34 up) | SOCS3 | |
| M2 | hsa-miR-372-3p (1.63 up) | ANO6 |
| M3 | hsa-miR-101-3p (1.80 up) | ATP5G2 |
| hsa-miR-137 (2.54 up) | PTGES2 | |
| hsa-miR-101-3p (1.80 up) | TERF2 | |
| hsa-miR-613 (1.55 down) | TERF2 | |
| hsa-miR-221-3p (2.34 up) | TERF2 | |
| hsa-miR-206 (2.04 up) | TERF2 | |
| M4 | hsa-miR-4735-3p (2.53 up) | ATM |
| hsa-miR-101-3p (1.80 up) | NACA | |
| hsa-miR-137 (2.54 up) | PCGF5 | |
| hsa-miR-101-3p (1.80 up) | SEL1L | |
| hsa-miR-101-3p (1.80 up) | SURF4 | |
| hsa-miR-613 (1.55 down) | THBS1 | |
| hsa-miR-4735-3p (2.53 up) | THBS1 | |
| hsa-miR-221-3p (2.34 up) | THBS1 | |
| hsa-miR-206 (2.04 up) | THBS1 | |
| hsa-miR-18b-5p (1.67 down) | THBS1 | |
| hsa-miR-18a-5p (2.32 up) | THBS1 | |
| hsa-miR-613 (1.55 down) | VPS45 | |
| hsa-miR-206 (2.04 up) | VPS45 | |
| M5 | hsa-miR-137 (2.54 up) | AKT2 |
| hsa-miR-613 (1.55 down) | JUND | |
| hsa-miR-206 (2.04 up) | JUND | |
| hsa-miR-520e (1.83 down) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-520d-3p (1.92 down) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-520c-3p (1.52 down) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-520b (1.70 down) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-520a-3p (1.50 down) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-372-3p (1.63 up) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-302e (2.18 down) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-302d-3p (1.84 down) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-302c-3p (2.48 down) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-302b-3p (1.66 down) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-302a-3p (1.58 down) | RELA | |
| hsa-miR-137 (2.54 up) | SRC | |
| M6 | hsa-miR-23c (1.56 up) | STX12 |
| hsa-miR-23b-3p (2.06 up) | STX12 | |
| hsa-miR-23a-3p (1.74 down) | STX12 | |
| hsa-miR-206 (2.04 up) | STX12 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dolcino, M.; Tinazzi, E.; Puccetti, A.; Lunardi, C. Long Non-Coding RNAs Target Pathogenetically Relevant Genes and Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells 2019, 8, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080816
Dolcino M, Tinazzi E, Puccetti A, Lunardi C. Long Non-Coding RNAs Target Pathogenetically Relevant Genes and Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells. 2019; 8(8):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080816
Chicago/Turabian StyleDolcino, Marzia, Elisa Tinazzi, Antonio Puccetti, and Claudio Lunardi. 2019. "Long Non-Coding RNAs Target Pathogenetically Relevant Genes and Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis" Cells 8, no. 8: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080816
APA StyleDolcino, M., Tinazzi, E., Puccetti, A., & Lunardi, C. (2019). Long Non-Coding RNAs Target Pathogenetically Relevant Genes and Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells, 8(8), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080816





