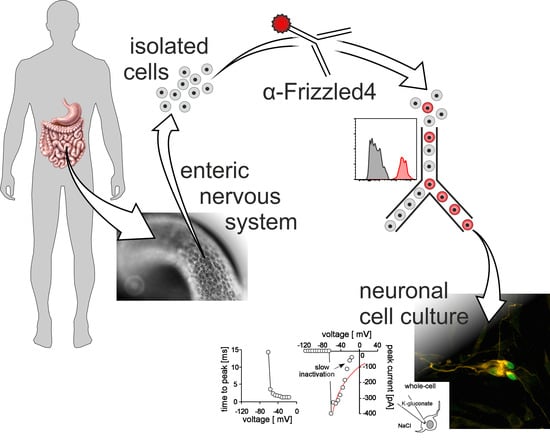
Wnt Receptor Frizzled-4 as a Marker for Isolation of Enteric Neural Progenitors in Human Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Specimen
2.2. Nomenclature: Enterosphere vs. Neurosphere
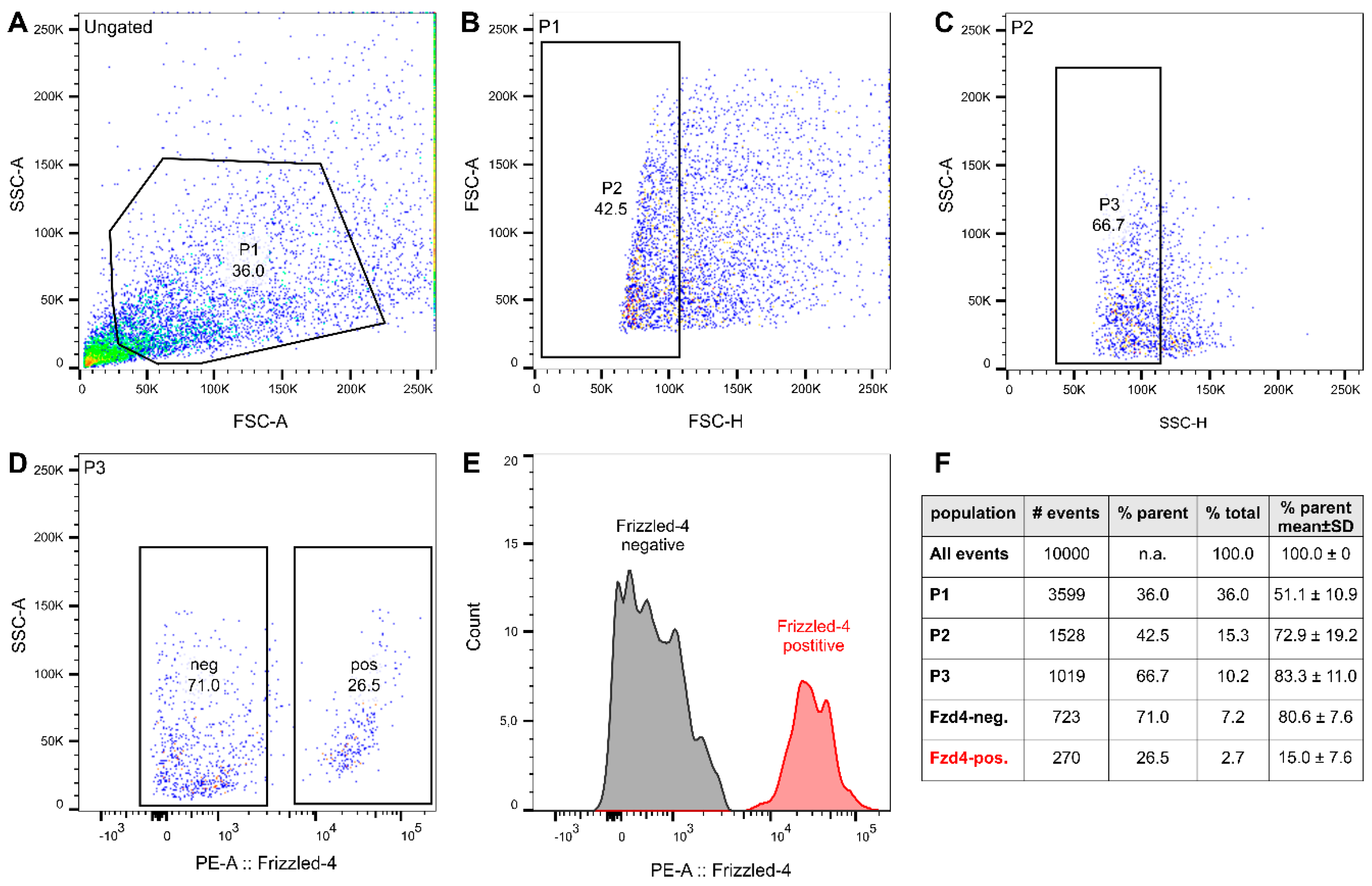
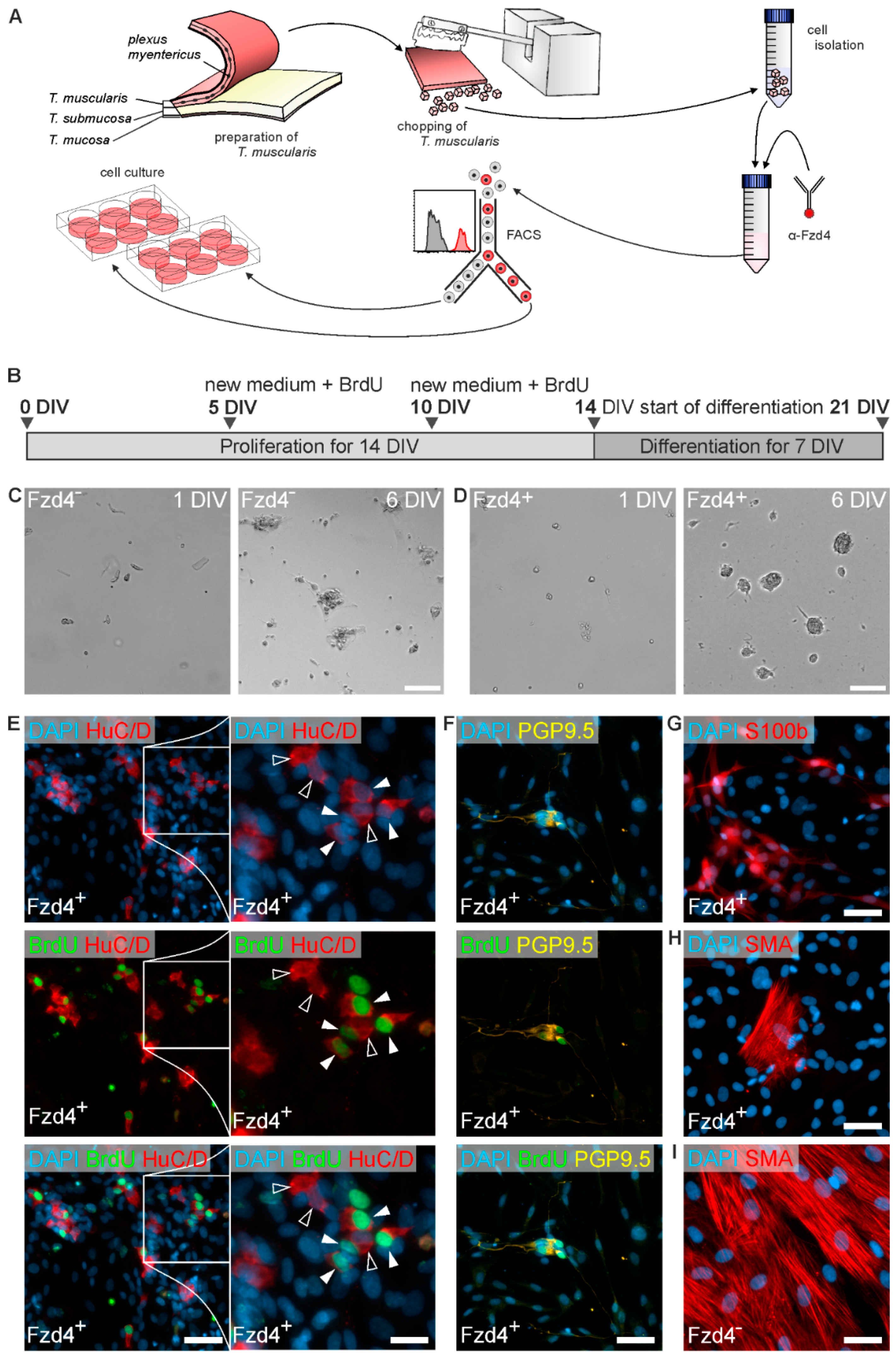
2.3. Isolation, FACS, and Culture of Enteric Neurospheres
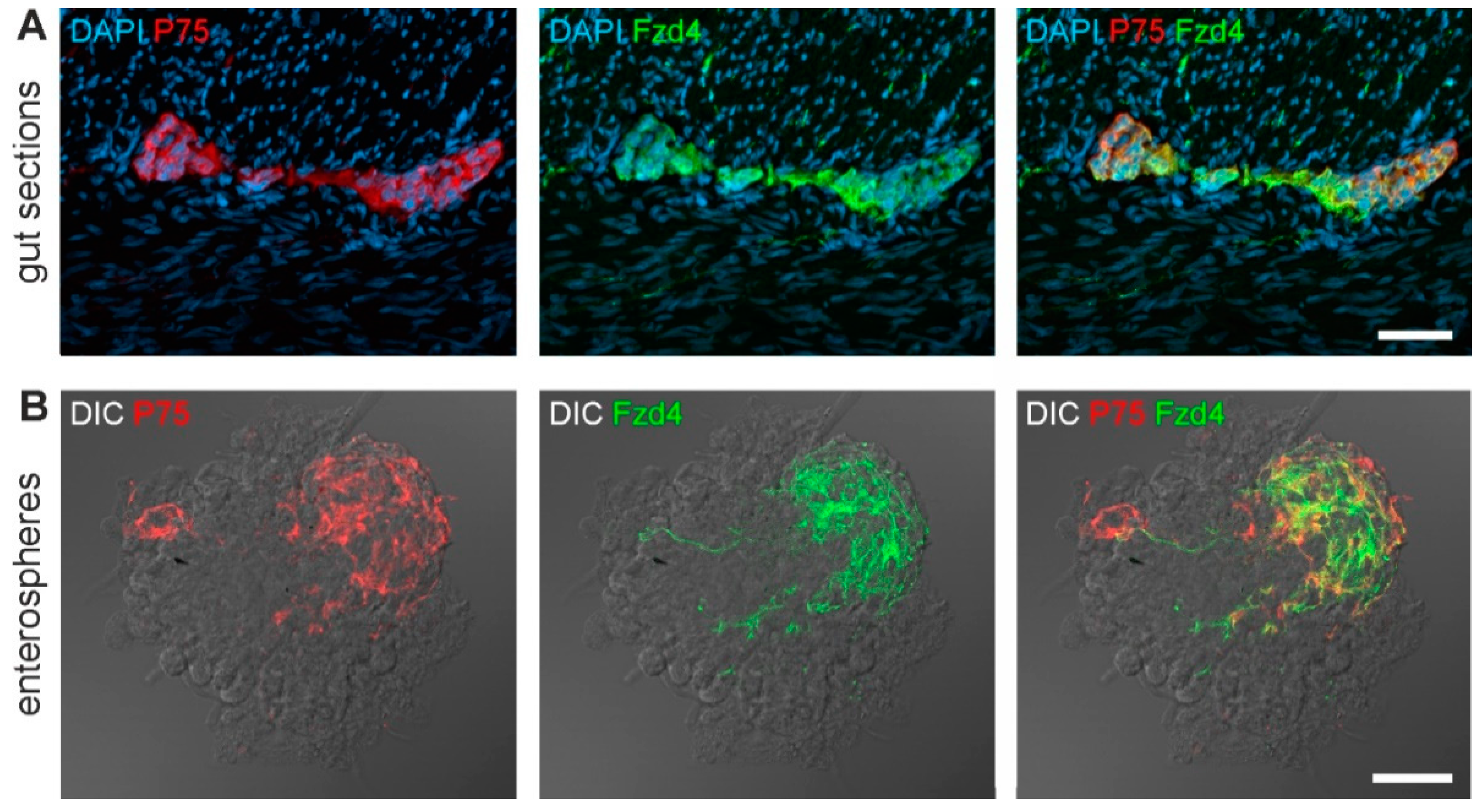
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
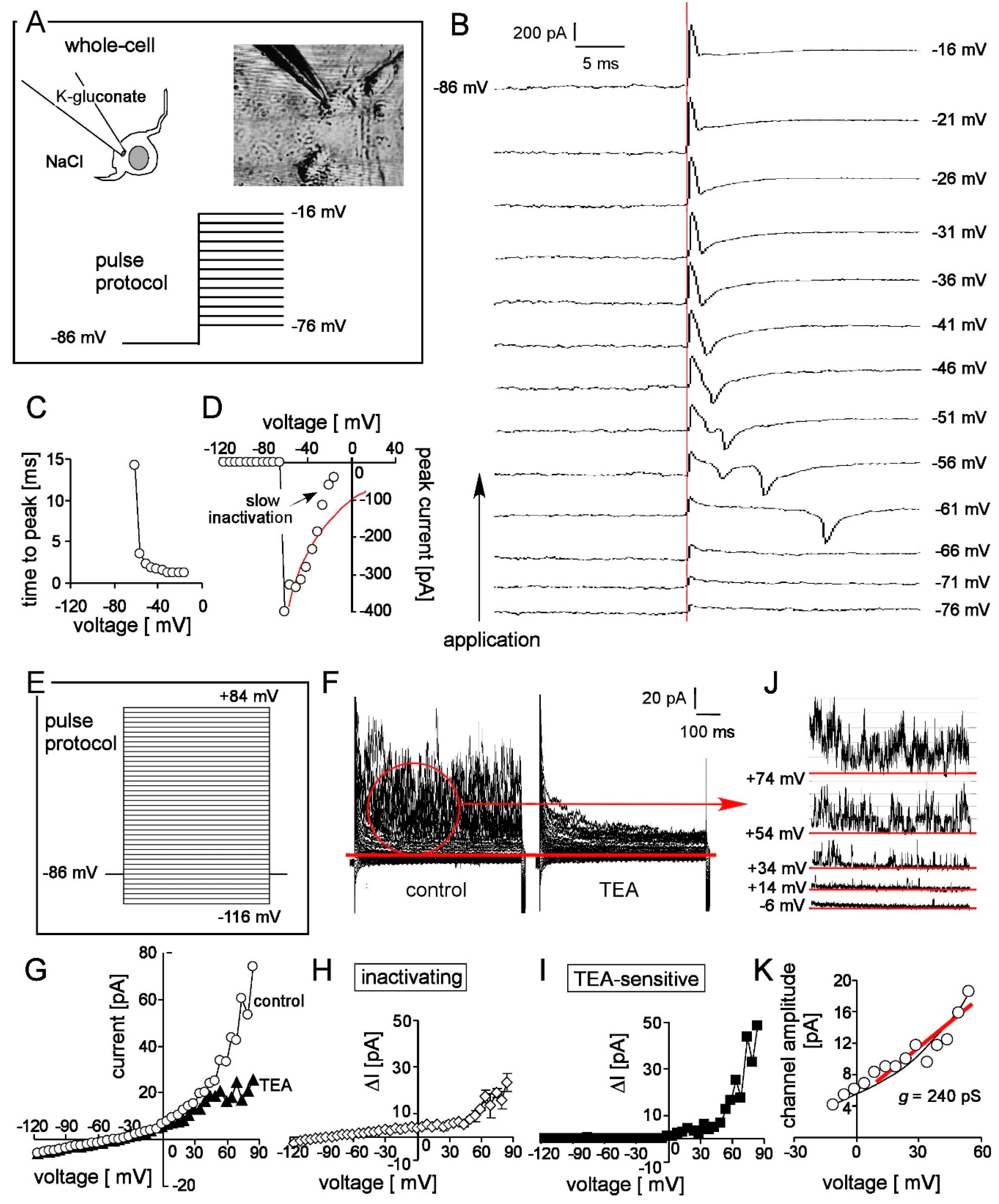
2.5. Patch-Clamp Recording
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Frizzled-4 Expression in Tunica Muscularis-Derived Enterospheres
3.2. FACS Isolation of Frizzled-4positive Cells
3.3. Frizzled-4positive Cells Give Rise to Neurospheres and New-Born Neurons
3.4. Patch-Clamp Reveals Nav and K Channels in Frizzled-4positive Sort
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furness, J.B. The Enteric Nervous System, 1st ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Malden, MA, USA; Oxford, UK; Carlton, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Walzer, N.; Hirano, I. Achalasia. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2008, 37, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, M.; Bernard, C.E.; Pasricha, P.J.; Lurken, M.S.; Faussone-Pellegrini, M.S.; Smyrk, T.C.; Parkman, H.P.; Abell, T.L.; Snape, W.J.; Hasler, W.L.; et al. Clinical-histological associations in gastroparesis: Results from the gastroparesis clinical research consortium. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermayr, F.; Hotta, R.; Enomoto, H.; Young, H.M. Development and developmental disorders of the enteric nervous system. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, A.J.; Goldstein, A.M.; Newgreen, D.F.; Stamp, L.; Schafer, K.H.; Metzger, M.; Hotta, R.; Young, H.M.; Andrews, P.W.; Thapar, N.; et al. White paper on guidelines concerning enteric nervous system stem cell therapy for enteric neuropathies. Dev. Biol. 2016, 417, 229–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamp, L.A. Cell therapy for gi motility disorders: Comparison of cell sources and proposed steps for treating hirschsprung disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G348–G354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, G.M.; Mosher, J.T.; Bixby, S.; Joseph, N.; Iwashita, T.; Morrison, S.J. Neural crest stem cells persist in the adult gut but undergo changes in self-renewal, neuronal subtype potential, and factor responsiveness. Neuron 2002, 35, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmann, H.M.; Zhang, Y.; Wronna, N.; Kraushaar, U.; Guenther, E.; Mohr, R.; Neckel, P.H.; Mack, A.; Fuchs, J.; Just, L.; et al. Isolation, expansion and transplantation of postnatal murine progenitor cells of the enteric nervous system. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondurand, N.; Natarajan, D.; Thapar, N.; Atkins, C.; Pachnis, V. Neuron and glia generating progenitors of the mammalian enteric nervous system isolated from foetal and postnatal gut cultures. Development 2003, 130, 6387–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, M.; Caldwell, C.; Barlow, A.J.; Burns, A.J.; Thapar, N. Enteric nervous system stem cells derived from human gut mucosa for the treatment of aganglionic gut disorders. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2214–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, M.; Bareiss, P.M.; Danker, T.; Wagner, S.; Hennenlotter, J.; Guenther, E.; Obermayr, F.; Stenzl, A.; Koenigsrainer, A.; Skutella, T.; et al. Expansion and differentiation of neural progenitors derived from the human adult enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heanue, T.A.; Pachnis, V. Prospective identification and isolation of enteric nervous system progenitors using sox2. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearn, C.J.; Murphy, M.; Newgreen, D. Gdnf and et-3 differentially modulate the numbers of avian enteric neural crest cells and enteric neurons in vitro. Dev. Biol. 1998, 197, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basch, M.L.; Garcia-Castro, M.I.; Bronner-Fraser, M. Molecular mechanisms of neural crest induction. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today 2004, 72, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishaba, Y.; Matsubara, D.; Niki, T. Heterogeneous expression of nestin in myofibroblasts of various human tissues. Pathol. Int. 2010, 60, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Wang, S.; Ye, B.; Du, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhu, P.; Fan, Z. Sox2 functions as a sequence-specific DNA sensor in neutrophils to initiate innate immunity against microbial infection. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, C.Y.; Nusse, R. The wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 781–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reya, T.; Clevers, H. Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 2005, 434, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusse, R. Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neckel, P.H.; Mohr, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hirt, B.; Just, L. Comparative microarray analysis of proliferating and differentiating murine ens progenitor cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 9695827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, R.; Neckel, P.; Zhang, Y.; Stachon, S.; Nothelfer, K.; Schaeferhoff, K.; Obermayr, F.; Bonin, M.; Just, L. Molecular and cell biological effects of 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine on progenitor cells of the enteric nervous system in vitro. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 11, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Liddo, R.; Bertalot, T.; Schuster, A.; Schrenk, S.; Tasso, A.; Zanusso, I.; Conconi, M.T.; Schafer, K.H. Anti-inflammatory activity of wnt signaling in enteric nervous system: In vitro preliminary evidences in rat primary cultures. J. Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollo, B.N.; Zhang, D.; Stamp, L.A.; Menheniott, T.R.; Stathopoulos, L.; Denham, M.; Dottori, M.; King, S.K.; Hutson, J.M.; Newgreen, D.F. Enteric neural cells from hirschsprung disease patients form ganglia in autologous aneuronal colon. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Seid, K.; Obermayr, F.; Just, L.; Neckel, P.H. Activation of wnt signaling increases numbers of enteric neurons derived from neonatal mouse and human progenitors cells. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nothelfer, K.; Obermayr, F.; Belz, N.; Reinartz, E.; Bareiss, P.M.; Buhring, H.J.; Beschorner, R.; Just, L. Expression of the wnt receptor frizzled-4 in the human enteric nervous system of infants. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 9076823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijksterhuis, J.P.; Baljinnyam, B.; Stanger, K.; Sercan, H.O.; Ji, Y.; Andres, O.; Rubin, J.S.; Hannoush, R.N.; Schulte, G. Systematic mapping of wnt-fzd protein interactions reveals functional selectivity by distinct wnt-fzd pairs. J. Biol Chem 2015, 290, 6789–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, E.; Natarajan, D.; Cooper, J.; Kronfli, R.; Cananzi, M.; Delalande, J.M.; McCann, C.; Burns, A.J.; Thapar, N. Enteric neurospheres are not specific to neural crest cultures: Implications for neural stem cell therapies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, D.J.; Bethell, G.S.; Shukla, R.; Kenny, S.E.; Edgar, D.H. Isolation of enteric nervous system progenitor cells from the aganglionic gut of patients with hirschsprung’s disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Jeon, H.Y.; Joo, K.M.; Kim, J.K.; Jin, J.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, B.G.; Beck, S.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.K.; et al. Frizzled 4 regulates stemness and invasiveness of migrating glioma cells established by serial intracranial transplantation. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3066–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.H.; Hsieh, F.L.; Zebisch, M.; Harlos, K.; Elegheert, J.; Jones, E.Y. Structure and functional properties of norrin mimic wnt for signalling with frizzled4, lrp5/6, and proteoglycan. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, R.; Hackl, S.; Seibuchner, T.; Tamm, E.R.; Ohlmann, A. Norrin mediates neuroprotective effects on retinal ganglion cells via activation of the wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and the induction of neuroprotective growth factors in muller cells. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 5998–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rattner, A.; Zhou, Y.; Williams, J.; Smallwood, P.M.; Nathans, J. Norrin/frizzled4 signaling in retinal vascular development and blood brain barrier plasticity. Cell 2012, 151, 1332–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudy, B. Slow inactivation of the sodium conductance in squid giant axons. Pronase resistance. J. Physiol. 1978, 283, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vydyanathan, A.; Wu, Z.Z.; Chen, S.R.; Pan, H.L. A-type voltage-gated k+ currents influence firing properties of isolectin b4-positive but not isolectin b4-negative primary sensory neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 93, 3401–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, P.; Faber, E.S. Channels underlying neuronal calcium-activated potassium currents. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 66, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.T.; Kuan, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Hen, R.; Gershon, M.D. 5-ht4 receptor-mediated neuroprotection and neurogenesis in the enteric nervous system of adult mice. J. Neurosci 2009, 29, 9683–9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeown, S.J.; Mohsenipour, M.; Bergner, A.J.; Young, H.M.; Stamp, L.A. Exposure to gdnf enhances the ability of enteric neural progenitors to generate an enteric nervous system. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Vohra, B.P.; Wind, D.; Heuckeroth, R.O. Bmp signaling regulates murine enteric nervous system precursor migration, neurite fasciculation, and patterning via altered ncam1 polysialic acid addition. Dev. Biol. PLoS 2006, 299, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neckel, P.H.; Scharr, M.; Seid, K.; Nothelfer, K.; Fuchs, J.; Obermayr, F.; Hirt, B.; Huber, S.M.; Just, L. Wnt Receptor Frizzled-4 as a Marker for Isolation of Enteric Neural Progenitors in Human Children. Cells 2019, 8, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080792
Neckel PH, Scharr M, Seid K, Nothelfer K, Fuchs J, Obermayr F, Hirt B, Huber SM, Just L. Wnt Receptor Frizzled-4 as a Marker for Isolation of Enteric Neural Progenitors in Human Children. Cells. 2019; 8(8):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080792
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeckel, Peter H., Melanie Scharr, Karin Seid, Katharina Nothelfer, Jörg Fuchs, Florian Obermayr, Bernhard Hirt, Stephan M. Huber, and Lothar Just. 2019. "Wnt Receptor Frizzled-4 as a Marker for Isolation of Enteric Neural Progenitors in Human Children" Cells 8, no. 8: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080792
APA StyleNeckel, P. H., Scharr, M., Seid, K., Nothelfer, K., Fuchs, J., Obermayr, F., Hirt, B., Huber, S. M., & Just, L. (2019). Wnt Receptor Frizzled-4 as a Marker for Isolation of Enteric Neural Progenitors in Human Children. Cells, 8(8), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080792