The Role of Phosphatases in Nuclear Envelope Disassembly and Reassembly and Their Relevance to Pathologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
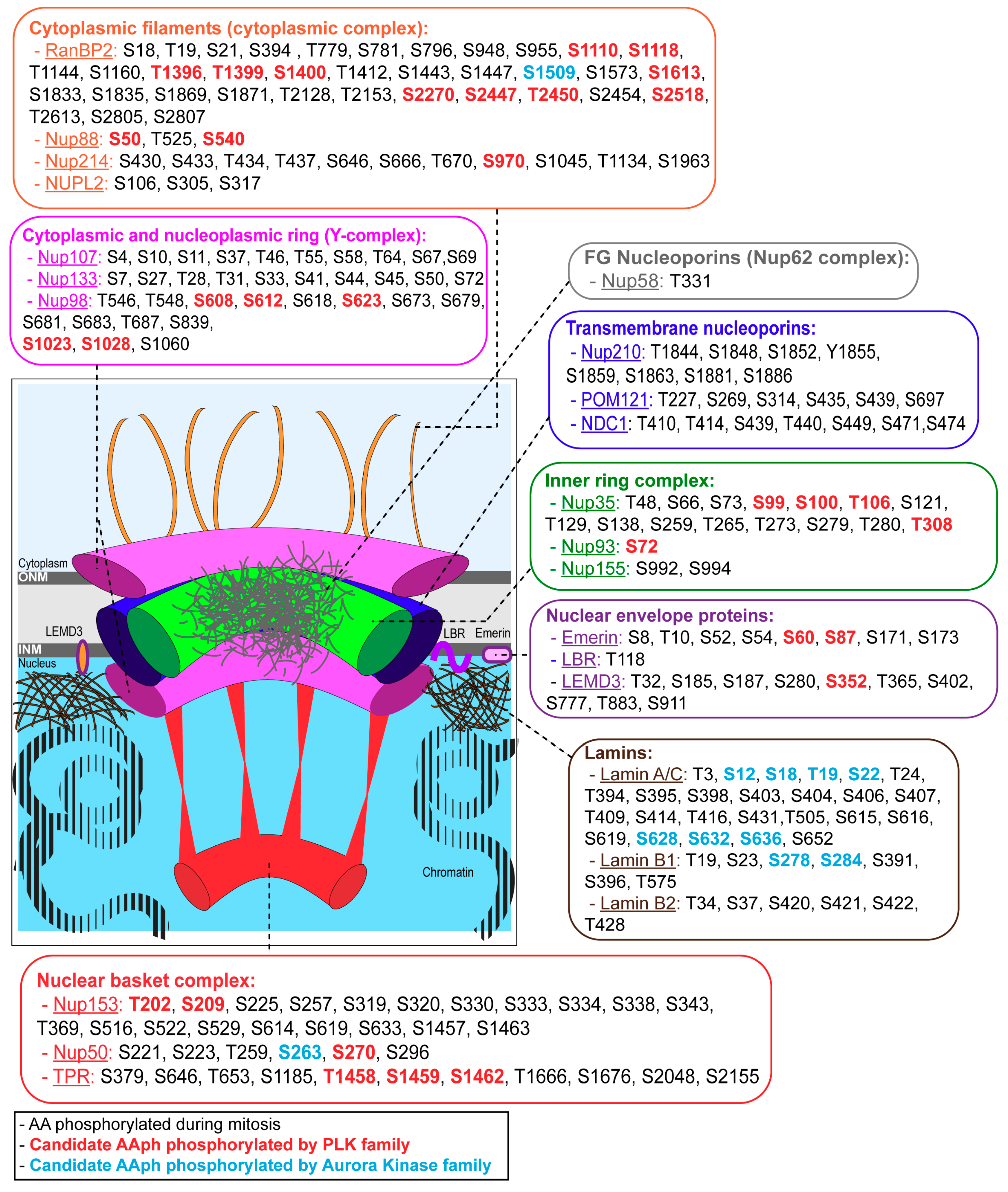
2. Nuclear Envelope Structure and Composition
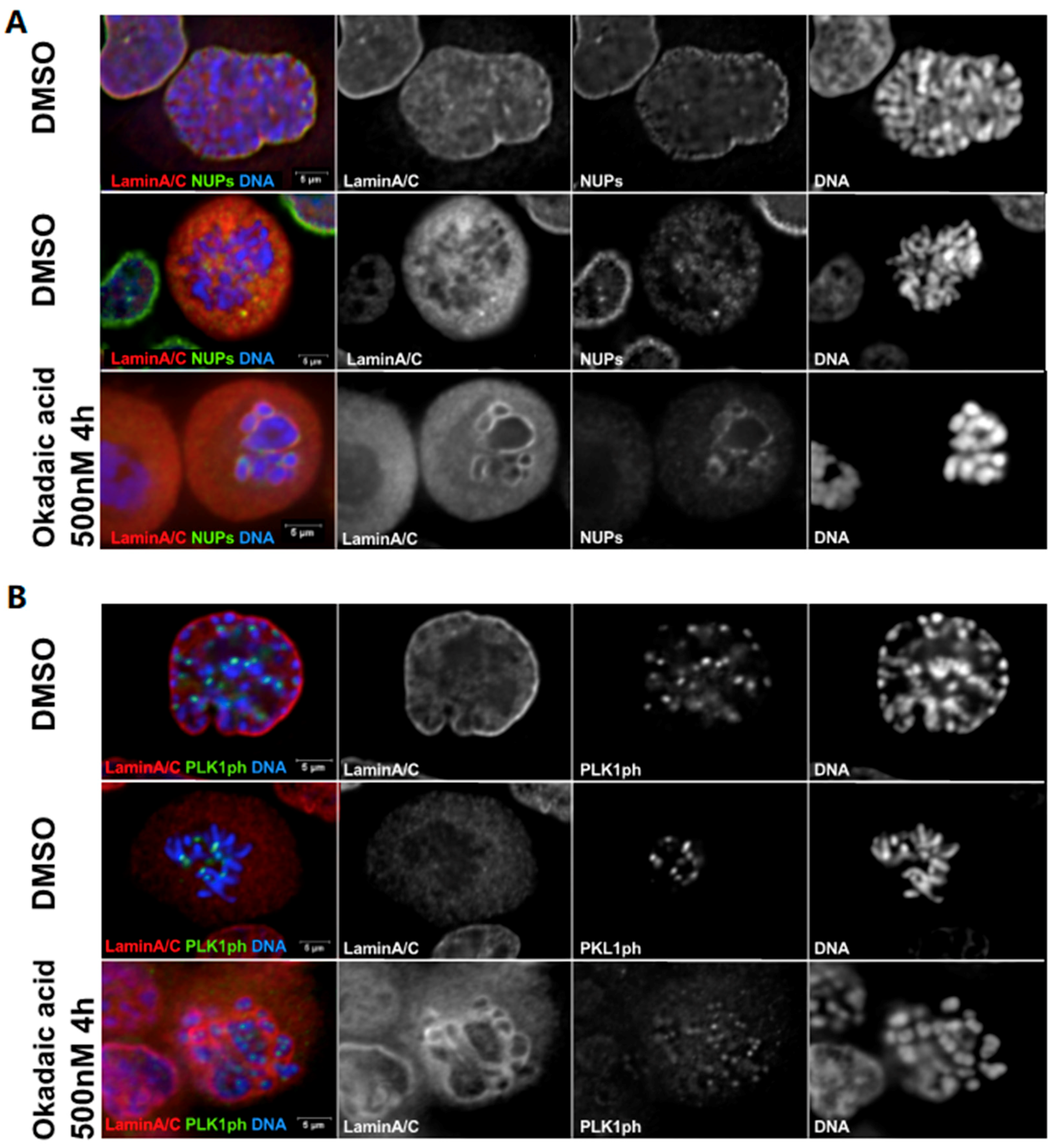
3. Nuclear Envelope Disassembly
4. Nuclear Envelope Reassembly
4.1. Lamina Re-Assembly
4.2. NPC Re-Assembly
4.3. Membrane Re-Assembly
5. Potential for Disease
6. Conclusion and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egli, D.; Birkhoff, G.; Eggan, K. Mediators of reprogramming: Transcription factors and transitions through mitosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagnarelli, P.; Ribeiro, S.; Sennels, L.; Sanchez-Pulido, L.; de, L.A.; Verheyen, T.; Kelly, D.A.; Ponting, C.P.; Rappsilber, J.; Earnshaw, W.C. Repo-Man coordinates chromosomal reorganization with nuclear envelope reassembly during mitotic exit. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerace, L.; Burke, B. Functional Organization of the Nuclear Envelope. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1988, 4, 335–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichelt, R.; Holzenburg, A.; Buhle, E.L.; Jarnik, M.; Engel, A.; Aebi, U. Correlation between structure and mass distribution of the nuclear pore complex and of distinct pore complex components. J. Cell Biol. 1990, 110, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strambio-De-Castillia, C.; Niepel, M.; Rout, M.P. The nuclear pore complex: Bridging nuclear transport and gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, S.; Osmani, S.A. Poring over chromosomes: Mitotic nuclear pore complex segregation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2019, 58, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronshaw, J.M.; Krutchinsky, A.N.; Zhang, W.; Chait, B.T.; Matunis, M.J. Proteomic analysis of the mammalian nuclear pore complex. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 158, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.; Hurt, E. The nuclear pore complex: Understanding its function through structural insight. Nat. Reviews. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechat, T.; Pfleghaar, K.; Sengupta, K.; Shimi, T.; Shumaker, D.K.; Solimando, L.; Goldman, R.D. Nuclear lamins: Major factors in the structural organization and function of the nucleus and chromatin. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 832–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, R.; Gruenbaum, Y.; Medalia, O. Nuclear Lamins: Thin Filaments with Major Functions. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurzenberger, C.; Gerlich, D.W. Phosphatases: Providing safe passage through mitotic exit. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castilho, P.V.; Williams, B.C.; Mochida, S.; Zhao, Y.; Goldberg, M.L. The M Phase Kinase Greatwall (Gwl) Promotes Inactivation of PP2A/B55δ, a Phosphatase Directed Against CDK Phosphosites. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 4777–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, A.; Vigneron, S.; Brioudes, E.; Labbé, J.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A. Loss of human Greatwall results in G2 arrest and multiple mitotic defects due to deregulation of the cyclin B-Cdc2/PP2A balance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorca, T.; Castro, A. The Greatwall kinase: A new pathway in the control of the cell cycle. Oncogene 2012, 32, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohadwala, M.; da Cruz e Silva, E.F.; Hall, F.L.; Williams, R.T.; Carbonaro-Hall, D.; Nairn, A.C.; Greengard, P.; Berndt, N. Phosphorylation and inactivation of protein phosphatase 1 by cyclin-dependent kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochida, S.; Ikeo, S.; Gannon, J.; Hunt, T. Regulated activity of PP2A-B55δ is crucial for controlling entry into and exit from mitosis in Xenopus egg extracts. Embo J. 2009, 28, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, Y.; Greengard, P.; Nairn, A.C. Cell Cycle-Dependent Phosphorylation of Mammalian Protein Phosphatase 1 by cdc2 Kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2168–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grallert, A.; Boke, E.; Hagting, A.; Hodgson, B.; Connolly, Y.; Griffiths, J.R.; Smith, D.L.; Pines, J.; Hagan, I.M. A PP1-PP2A phosphatase relay controls mitotic progression. Nature 2015, 517, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurell, E.; Beck, K.; Krupina, K.; Theerthagiri, G.; Bodenmiller, B.; Horvath, P.; Aebersold, R.; Antonin, W.; Kutay, U. Phosphorylation of Nup98 by Multiple Kinases Is Crucial for NPC Disassembly during Mitotic Entry. Cell 2011, 144, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, M.I.; Köhler, M.; Boersema, P.; Weberruss, M.; Wandke, C.; Marino, J.; Ashiono, C.; Picotti, P.; Antonin, W.; Kutay, U. Mitotic Disassembly of Nuclear Pore Complexes Involves CDK1- and PLK1-Mediated Phosphorylation of Key Interconnecting Nucleoporins. Dev. Cell 2017, 43, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dephoure, N.; Zhou, C.; Villén, J.; Beausoleil, S.A.; Bakalarski, C.E.; Elledge, S.J.; Gygi, S.P. A quantitative atlas of mitotic phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10762–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.V.; Vermeulen, M.; Santamaria, A.; Kumar, C.; Miller, M.L.; Jensen, L.J.; Gnad, F.; Cox, J.; Jensen, T.S.; Nigg, E.A.; et al. Quantitative Phosphoproteomics Reveals Widespread Full Phosphorylation Site Occupancy During Mitosis. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettenbach, A.N.; Schweppe, D.K.; Faherty, B.K.; Pechenick, D.; Pletnev, A.A.; Gerber, S.A. Quantitative phosphoproteomics identifies substrates and functional modules of Aurora and Polo-like kinase activities in mitotic cells. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, rs5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurell, E.; Kutay, U. Dismantling the NPC permeability barrier at the onset of mitosis. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 2243–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Martino, L.; Morchoisne-Bolhy, S.; Cheerambathur, D.K.; Van Hove, L.; Dumont, J.; Joly, N.; Desai, A.; Doye, V.; Pintard, L. Channel Nucleoporins Recruit PLK-1 to Nuclear Pore Complexes to Direct Nuclear Envelope Breakdown in C. elegans. Dev. Cell 2017, 43, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro, I.J.; Gil, R.S.; Ligammari, L.; Di Giacinto, M.L.; Vagnarelli, P. CDK1 and PLK1 coordinate the disassembly and reassembly of the nuclear envelope in vertebrate mitosis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7763–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, M.; Nakagawa, J.; Doree, M.; Labbe, J.C.; Nigg, E.A. In Vitro Disassemblyof of the Nuclear Lamina and M Phase-Specific Phosphorylation of Lamins by cdc2 Kinase. Cell 1990, 61, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald, R.; McKeon, F. Mutations of phosphorylation sites in lamin A that prevent nuclear lamina disassembly in mitosis. Cell 1990, 61, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collas, P.; Thompson, L.; Fields, A.P.; Poccia, D.L.; Courvalin, J. Protein Kinase C-mediated Interphase Lamin B Phosphorylation and Solubilization. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21274–21280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, V.L.; Hocevar, B.A.; Thompson, L.; Stratton, C.A.; Burns, D.J.; Fields, A.P. Identification of Nuclear BII Protein Kinase C as a Mitotic Lamin Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 19074–19080. [Google Scholar]
- Gorjanacz, M.; Klerkx, E.P.F.; Galy, V.; Santarella, R.; Lopez-Iglesias, C.; Askjaer, P.; Mattaj, I.W. Caenorhabditis elegans BAF-1 and its kinase VRK-1 participate directly in post-mitotic nuclear envelope assembly. Embo J. 2007, 26, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champion, L.; Pawar, S.; Luithle, N.; Ungricht, R.; Kutay, U. Dissociation of membrane–chromatin contacts is required for proper chromosome segregation in mitosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2019, 30, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Álvarez, A.; Cooper, J.P. Chromosomes Orchestrate Their Own Liberation: Nuclear Envelope Disassembly. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 27, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeev, O.; Cizmecioglu, O.; Settele, F.; Kempf, T.; Hoffmann, I. Cdc25 Phosphatases Are Required for Timely Assembly of CDK1-Cyclin B at the G2/M Transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16978–16990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, R.; Eguchi-Kasai, K.; Hayata, I. Phosphatase Inhibitors and Premature Chromosome Condensation in Human Peripheral Lymphocytes at Different Cell-Cycle Phases. Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 1999, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornforth, M.N.; Bedford, J.S. High-resolution measurement of breaks in prematurely condensed chromosomes by differential staining. Chromosoma 1983, 88, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srebniak, M.I.; Trapp, G.G.; Wawrzkiewicz, A.K.; Kaźmierczak, W.; Wiczkowski, A.K. The Usefulness of Calyculin A for Cytogenetic Prenatal Diagnosis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2005, 53, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, S.; Pines, J. The biochemistry of mitosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a015776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelens, L.; Qian, J.; Bollen, M.; Saurin, A.T. The Importance of Kinase–Phosphatase Integration: Lessons from Mitosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimborn, M.; Bell, S.M.; Felix, C.; Rashid, Y.; Jafri, H.; Griffiths, P.D.; Neumann, L.M.; Krebs, A.; Reis, A.; Sperling, K.; et al. Mutations in microcephalin cause aberrant regulation of chromosome condensation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 75, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platani, M.; Santarella-Mellwig, R.; Posch, M.; Walczak, R.; Swedlow, J.R.; Mattaj, I.W. The Nup107-160 nucleoporin complex promotes mitotic events via control of the localization state of the chromosome passenger complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 5260–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salina, D.; Enarson, P.; Rattner, J.B.; Burke, B. Nup358 integrates nuclear envelope breakdown with kinetochore assembly. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belgareh, N.; Rabut, G.; Baï, S.W.; van Overbeek, M.; Beaudouin, J.; Daigle, N.; Zatsepina, O.V.; Pasteau, F.; Labas, V.; Fromont-Racine, M.; et al. An evolutionarily conserved NPC subcomplex, which redistributes in part to kinetochores in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lee, K.K.; Segura-Totten, M.; Neufeld, E.; Wilson, K.L.; Gruenbaum, Y. MAN1 and emerin have overlapping function(s) essential for chromosome segregation and cell division in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatel, G.; Fahrenkrog, B. Nucleoporins: Leaving the nuclear pore complex for a successful mitosis. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, R.A.; Gudise, S.; Hallberg, E. Microtubule-associated nuclear envelope proteins in interphase and mitosis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hezwani, M.; Fahrenkrog, B. The functional versatility of the nuclear pore complex proteins. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 68, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Magistris, P.; Antonin, W. The Dynamic Nature of the Nuclear Envelope. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.W.; Solomon, M.J.; Kirschner, M.W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature 1989, 339, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoufias, D.A.; Indorato, R.; Lacroix, F.; Panopoulos, A.; Margolis, R.L. Mitosis persists in the absence of Cdk1 activity when proteolysis or protein phosphatase activity is suppressed. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungricht, R.; Kutay, U. Mechanisms and functions of nuclear envelope remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, R.L.; Martins, S.B.; Taskén, K.; Collas, P. Recruitment of protein phosphatase 1 to the nuclear envelope by A-kinase anchoring protein AKAP149 is a prerequisite for nuclear lamina assembly. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, O.; Matos, I.; Pereira, A.J.; Aguiar, P.; Lampson, M.A.; Maiato, H. Feedback control of chromosome separation by a midzone Aurora B gradient. Science 2014, 345, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriuchi, T.; Kuroda, M.; Kusumoto, F.; Osumi, T.; Hirose, F. Lamin A reassembly at the end of mitosis is regulated by its SUMO-interacting motif. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 342, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hached, K.; Goguet, P.; Charrasse, S.; Vigneron, S.; Sacristan, M.P.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A. ENSA and ARPP19 differentially control cell cycle progression and development. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasala, B.A.; Ramos, C.; Harel, A.; Forbes, D.J. Capture of AT-rich chromatin by ELYS recruits POM121 and NDC1 to initiate nuclear pore assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3982–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Shi, Y. Structure of a Protein Phosphatase 2A Holoenzyme: Insights into B55-Mediated Tau Dephosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galy, V.; Askjaer, P.; Franz, C.; López-Iglesias, C.; Mattaj, I.W. MEL-28, a Novel Nuclear-Envelope and Kinetochore Protein Essential for Zygotic Nuclear-Envelope Assembly in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasala, B.A.; Orjalo, A.V.; Shen, Z.; Briggs, S.; Forbes, D.J. ELYS is a dual nucleoporin/kinetochore protein required for nuclear pore assembly and proper cell division. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17801–17806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.G.; Piano, F. MEL-28 Is Downstream of the Ran Cycle and Is Required for Nuclear-Envelope Function and Chromatin Maintenance. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, C.; Walczak, R.; Yavuz, S.; Santarella, R.; Gentzel, M.; Askjaer, P.; Galy, V.; Hetzer, M.; Mattaj, I.W.; Antonin, W. MEL-28/ELYS is required for the recruitment of nucleoporins to chromatin and postmitotic nuclear pore complex assembly. Embo Rep. 2007, 8, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattersley, N.; Cheerambathur, D.; Moyle, M.; Stefanutti, M.; Richardson, A.; Lee, K.; Dumont, J.; Oegema, K.; Desai, A. A Nucleoporin Docks Protein Phosphatase 1 to Direct Meiotic Chromosome Segregation and Nuclear Assembly. Dev. Cell 2016, 38, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clever, M.; Funakoshi, T.; Mimura, Y.; Takagi, M.; Imamoto, N. The nucleoporin ELYS/Mel28 regulates nuclear envelope subdomain formation in HeLa cells. Nucleus 2012, 3, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinkle-Mulcahy, L.; Andersen, J.; Lam, Y.W.; Moorhead, G.; Mann, M.; Lamond, A.I. Repo-Man recruits PP1γ to chromatin and is essential for cell viability. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, B.; Lorenz, M.; Moreno-Andrés, D.; Bodenhöfer, M.; De Magistris, P.; Astrinidis, S.; Schooley, A.; Flötenmeyer, M.; Leptihn, S.; Antonin, W. Nup153 Recruits the Nup107-160 Complex to the Inner Nuclear Membrane for Interphasic Nuclear Pore Complex Assembly. Dev. Cell 2015, 33, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cundell, M.J.; Hutter, L.H.; Nunes Bastos, R.; Poser, E.; Holder, J.; Mohammed, S.; Novak, B.; Barr, F.A. A PP2A-B55 recognition signal controls substrate dephosphorylation kinetics during mitotic exit. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 214, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, I.J.; Budzak, J.; Di Giacinto, M.L.; Ligammari, L.; Gokhan, E.; Spanos, C.; Moralli, D.; Richardson, C.; de Las Heras, J.I.; Salatino, S.; et al. Repo-Man/PP1 regulates heterochromatin formation in interphase. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asencio, C.; Davidson, I.; Santarella-Mellwig, R.; Ly-Hartig, T.; Mall, M.; Wallenfang, M.; Mattaj, I.; Gorjánácz, M. Coordination of Kinase and Phosphatase Activities by Lem4 Enables Nuclear Envelope Reassembly during Mitosis. Cell 2012, 150, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.J.; Wiebe, M.S.; Traktman, P. The Vaccinia-related Kinases Phosphorylate the N′ Terminus of BAF, Regulating Its Interaction with DNA and Its Retention in the Nucleus. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 2451–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samwer, M.; Schneider, M.W.G.; Hoefler, R.; Schmalhorst, P.S.; Jude, J.G.; Zuber, J.; Gerlich, D.W. DNA Cross-Bridging Shapes a Single Nucleus from a Set of Mitotic Chromosomes. Cell 2017, 170, 972.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, T.; Kojidani, T.; Koujin, T.; Shimi, T.; Osakada, H.; Mori, C.; Yamamoto, A.; Hiraoka, Y. Live cell imaging and electron microscopy reveal dynamic processes of BAF-directed nuclear envelope assembly. J. Cell. Sci. 2008, 121, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Semenova, E.; Maric, D.; Craigie, R. Dephosphorylation of barrier-to-autointegration factor by protein phosphatase 4 and its role in cell mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.J.; Hetzer, M.W. Nuclear envelope formation by chromatin-mediated reorganization of the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Ladinsky, M.S.; Kirchhausen, T. Formation of the postmitotic nuclear envelope from extended ER cisternae precedes nuclear pore assembly. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmos, Y.; Hodgson, L.; Mantell, J.; Verkade, P.; Carlton, J.G. ESCRT-III controls nuclear envelope reformation. Nature 2015, 522, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmos, Y.; Carlton, J.G. The ESCRT machinery: New roles at new holes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scourfield, E.J.; Martin-Serrano, J. Growing functions of the ESCRT machinery in cell biology and viral replication. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietri, M.; Schink, K.O.; Campsteijn, C.; Wegner, C.S.; Schultz, S.W.; Christ, L.; Thoresen, S.B.; Brech, A.; Raiborg, C.; Stenmark, H. Spastin and ESCRT-III coordinate mitotic spindle disassembly and nuclear envelope sealing. Nature 2015, 522, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; LaJoie, D.; Chen, O.S.; von Appen, A.; Ladinsky, M.S.; Redd, M.J.; Nikolova, L.; Bjorkman, P.J.; Sundquist, W.I.; Ullman, K.S.; et al. LEM2 recruits CHMP7 for ESCRT-mediated nuclear envelope closure in fission yeast and human cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, Y.; Perdrix-Rosell, A.; Carlton, J.G. Membrane Binding by CHMP7 Coordinates ESCRT-III-Dependent Nuclear Envelope Reformation. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2635–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, J.; Frost, A.; Sundquist, W.I. Structures, Functions, and Dynamics of ESCRT-III/Vps4 Membrane Remodeling and Fission Complexes. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 34, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimini, D.; Howell, B.; Maddox, P.; Khodjakov, A.; Degrassi, F.; Salmon, E.D. Merotelic Kinetochore Orientation Is a Major Mechanism of Aneuploidy in Mitotic Mammalian Tissue Cells. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Kwon, M.; Mannino, M.; Yang, N.; Renda, F.; Khodjakov, A.; Pellman, D. Nuclear envelope assembly defects link mitotic errors to chromothripsis. Nature 2018, 561, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatch, E.M.; Fischer, A.H.; Deerinck, T.J.; Hetzer, M.W. Catastrophic nuclear envelope collapse in cancer cell micronuclei. Cell 2013, 154, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luijten, M.N.H.; Lee, J.X.T.; Crasta, K.C. Mutational game changer: Chromothripsis and its emerging relevance to cancer. Mutat. Res./Rev. Mutat. Res. 2018, 777, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crasta, K.; Ganem, N.J.; Dagher, R.; Lantermann, A.B.; Ivanova, E.V.; Pan, Y.; Nezi, L.; Protopopov, A.; Chowdhury, D.; Pellman, D. DNA breaks and chromosome pulverization from errors in mitosis. Nature 2012, 482, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatch, E.; Hetzer, M. Linking Micronuclei to Chromosome Fragmentation. Cell 2015, 161, 1502–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loïodice, I.; Alves, A.; Rabut, G.; Van Overbeek, M.; Ellenberg, J.; Sibarita, J.; Doye, V. The entire Nup107-160 complex, including three new members, is targeted as one entity to kinetochores in mitosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 3333–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güttinger, S.; Laurell, E.; Kutay, U. Orchestrating nuclear envelope disassembly and reassembly during mitosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Ikram, S.; Bibi, N.; Mir, A. Hutchinson–Gilford Progeria Syndrome: A Premature Aging Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 4417–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekarowicz, K.; Machowska, M.; Dzianisava, V.; Rzepecki, R. Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome-Current Status and Prospects for Gene Therapy Treatment. Cells 2019, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Abbas, A.; Irianto, J.; Ivanovska, I.L.; Xia, Y.; Tewari, M.; Discher, D.E. Progerin phosphorylation in interphase is lower and less mechanosensitive than lamin-A,C in iPS-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Nucleus 2018, 9, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.; Multani, P.S.; Sun, K.; Vincent, F.; de Pablo, Y.; Ghosh, S.; Gupta, R.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.; Smith, M.A.; et al. Nuclear envelope dispersion triggered by deregulated Cdk5 precedes neuronal death. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torvaldson, E.; Kochin, V.; Eriksson, J.E. Phosphorylation of lamins determine their structural properties and signaling functions. Nucleus 2015, 6, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huguet, F.; Flynn, S.; Vagnarelli, P. The Role of Phosphatases in Nuclear Envelope Disassembly and Reassembly and Their Relevance to Pathologies. Cells 2019, 8, 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070687
Huguet F, Flynn S, Vagnarelli P. The Role of Phosphatases in Nuclear Envelope Disassembly and Reassembly and Their Relevance to Pathologies. Cells. 2019; 8(7):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070687
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuguet, Florentin, Shane Flynn, and Paola Vagnarelli. 2019. "The Role of Phosphatases in Nuclear Envelope Disassembly and Reassembly and Their Relevance to Pathologies" Cells 8, no. 7: 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070687
APA StyleHuguet, F., Flynn, S., & Vagnarelli, P. (2019). The Role of Phosphatases in Nuclear Envelope Disassembly and Reassembly and Their Relevance to Pathologies. Cells, 8(7), 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070687




