Hepatitis C Direct Acting Antivirals and Ribavirin Modify Lipid but not Glucose Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. HCV Treatment Response
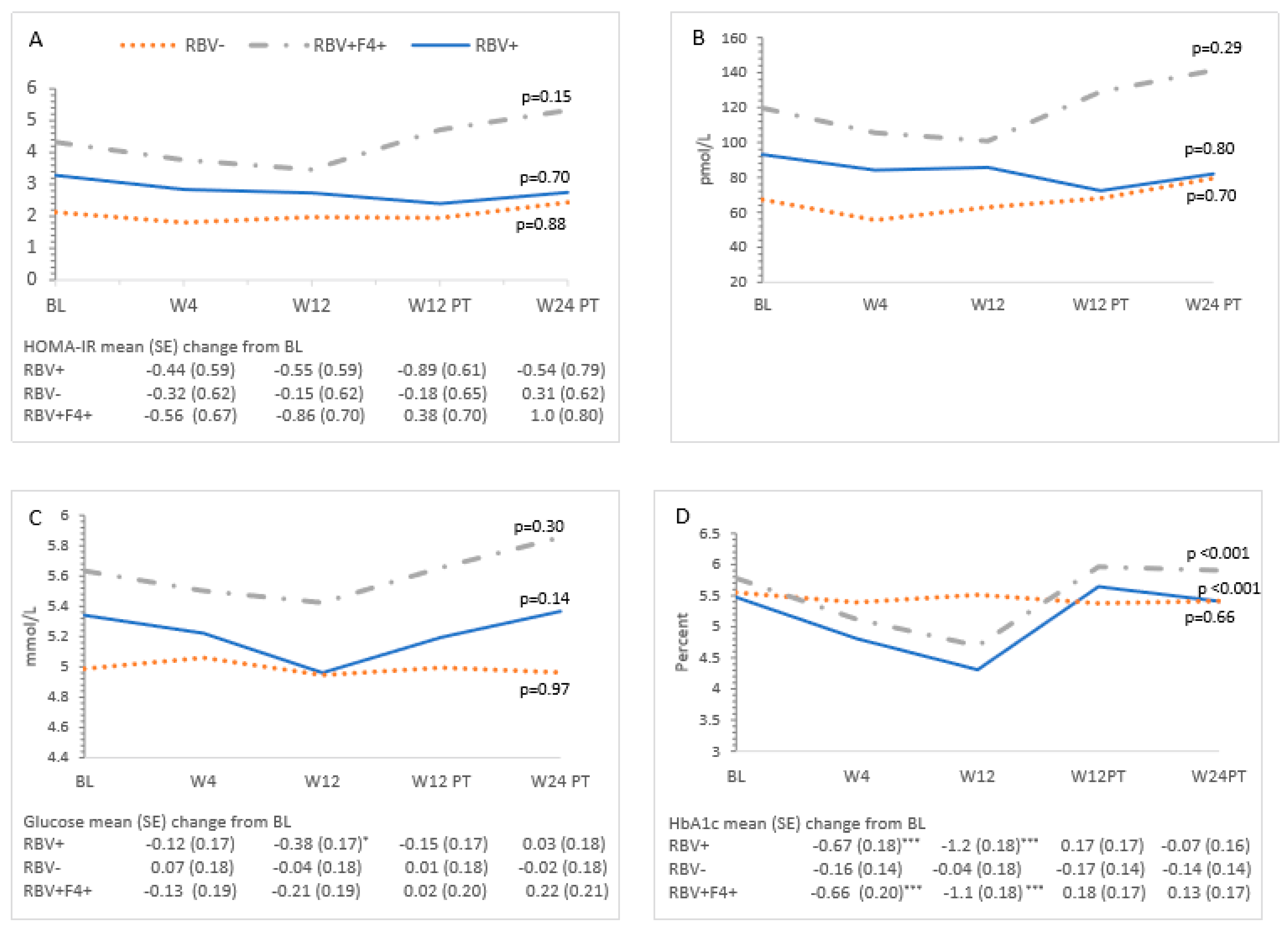
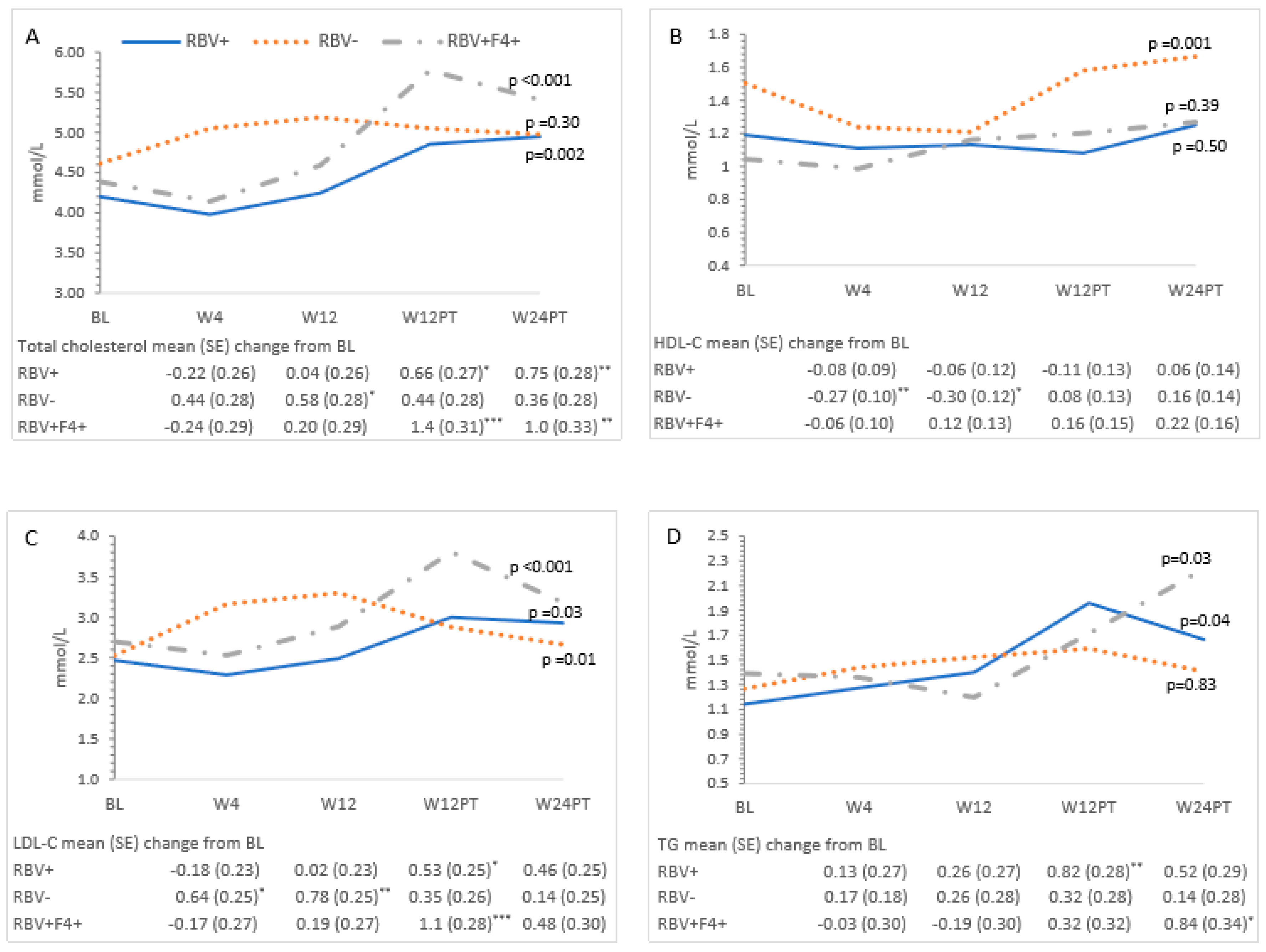
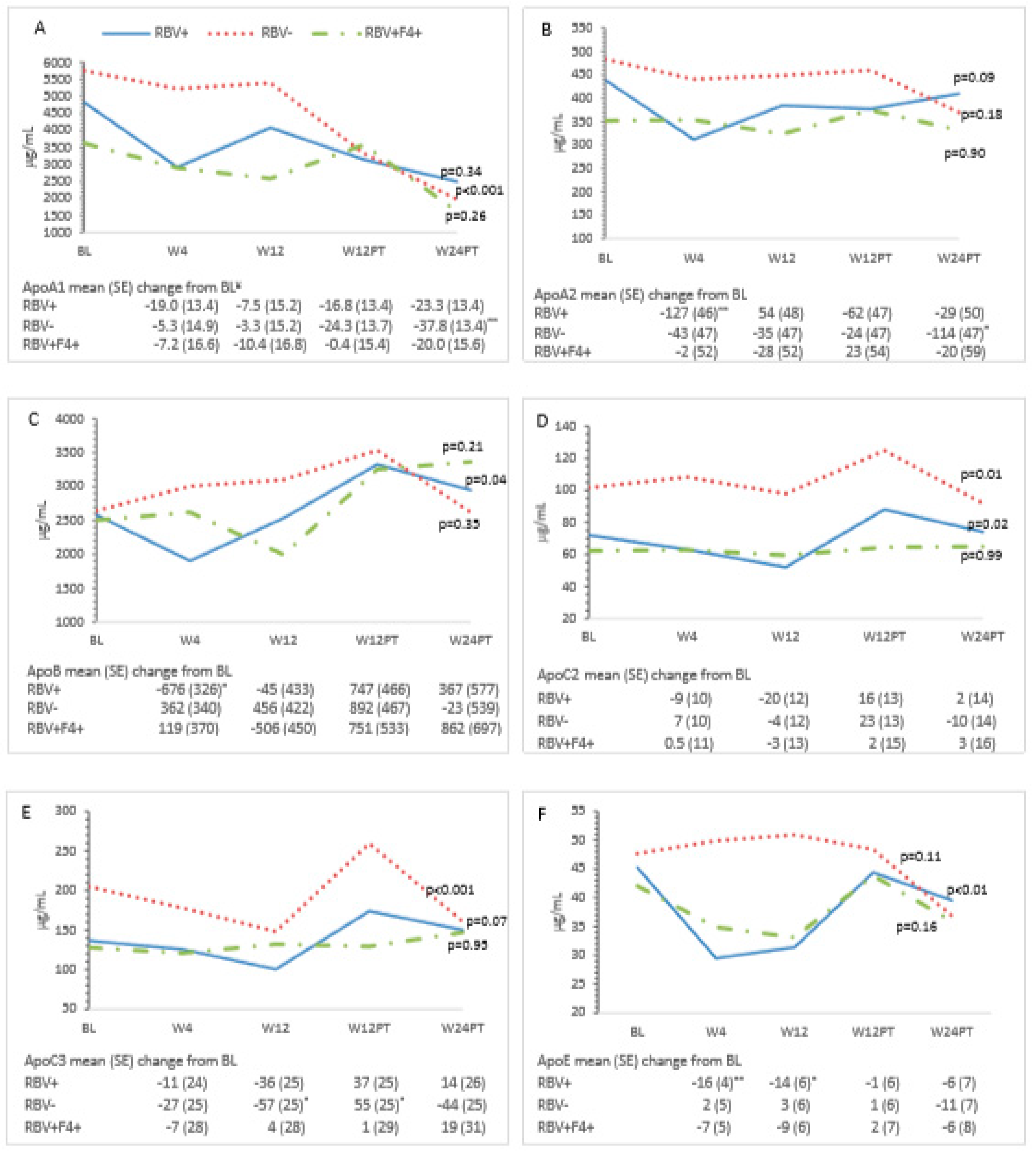
3.3. Metabolic Measures and HCV Treatment—All Patients
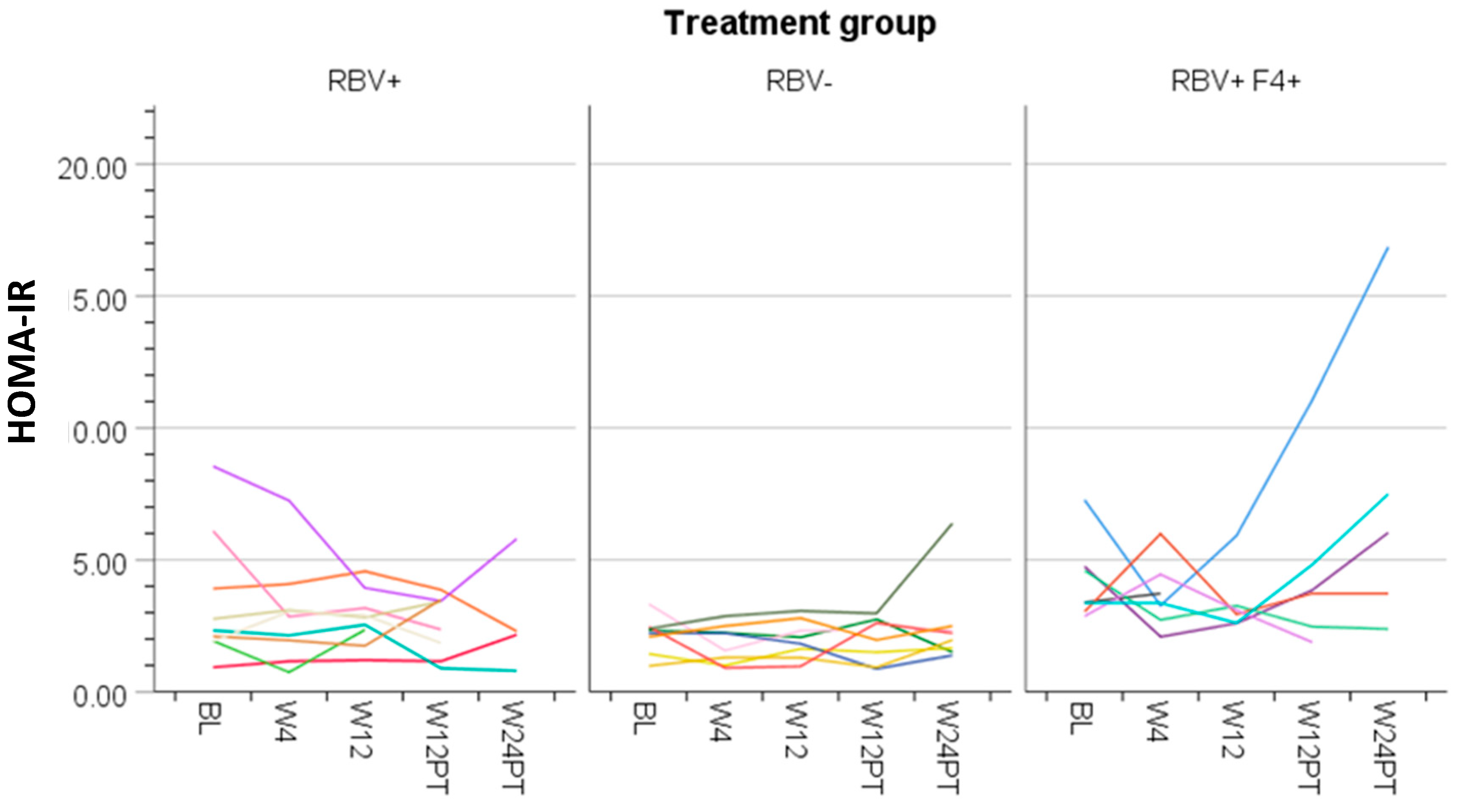
3.4. Ribavirin and Metabolic Measures
3.5. Cirrhosis and Metabolic Measures
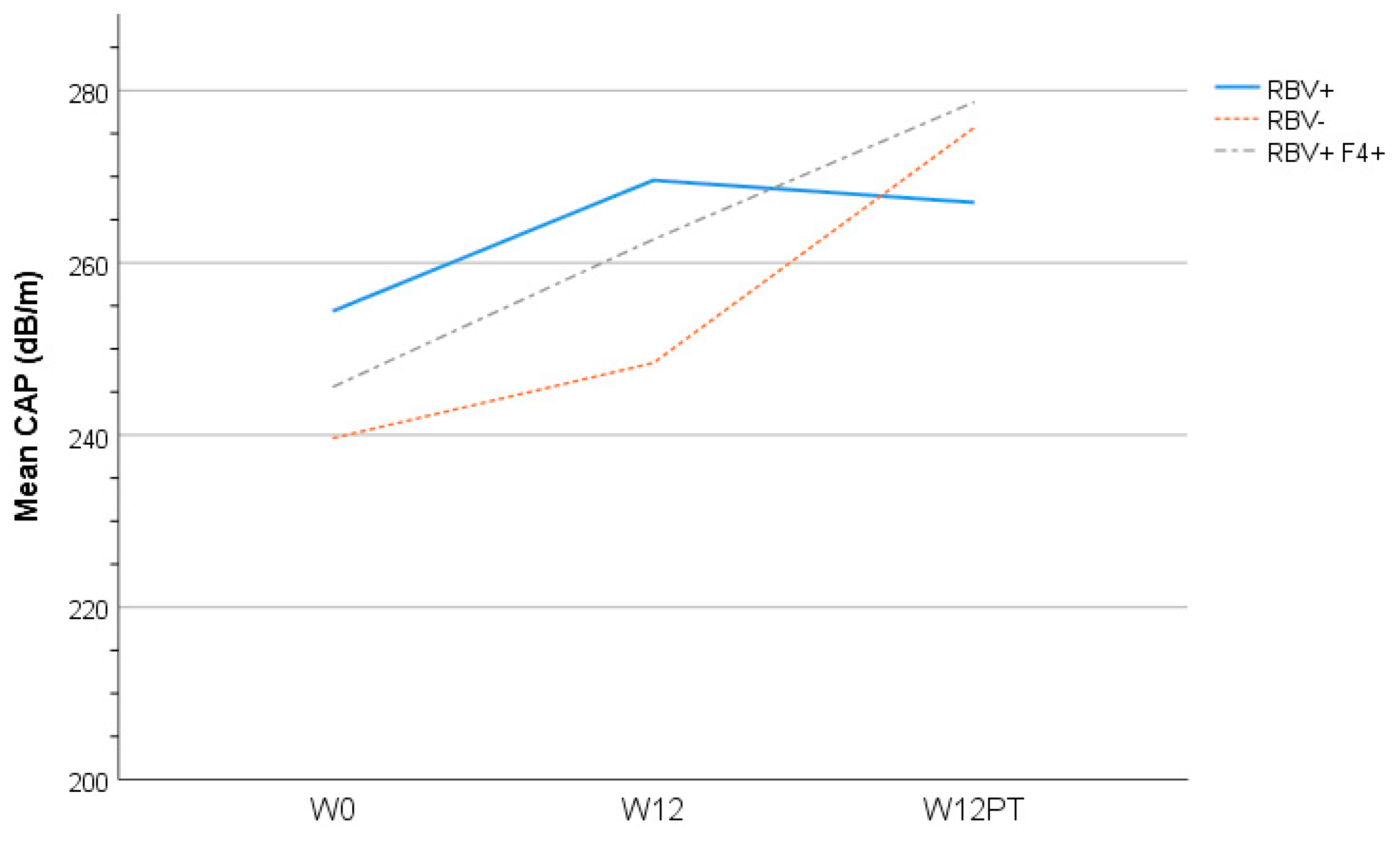
3.6. Liver Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| HCV | Hepatitis C |
| RBV | Ribavirin |
| PrOD | Paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir/dasabuvir |
| CAP | Controlled attenuation parameter |
| SVR | Sustained virologic response |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic model assessment—insulin resistance |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| VLDL | Very-low-density lipoprotein |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| DAA | Direct acting antivirals |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| REB | Research Ethics Board |
| kPa | Kilopascal |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| IFN | Interferon |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| LVP | Lipo-viral particles |
References
- Averhoff, F.M.; Glass, N.; Holtzman, D. Global burden of hepatitis C: Considerations for healthcare providers in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55 (Suppl. 1), S10–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.H.; Wang, J.H.; Hu, T.H.; Chen, C.H.; Chang, K.C.; Yen, Y.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Tsai, M.C.; Lu, S.N.; Lee, C.M. Insulin resistance is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 2265–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baid, S.; Cosimi, A.B.; Farrell, M.L.; Schoenfeld, D.A.; Feng, S.; Chung, R.T.; Tolkoff-Rubin, N.; Pascual, M. Posttransplant diabetes mellitus in liver transplant recipients: Risk factors, temporal relationship with hepatitis C virus allograft hepatitis, and impact on mortality. Transplantation 2001, 72, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taura, N.; Ichikawa, T.; Hamasaki, K.; Nakao, K.; Nishimura, D.; Goto, T.; Fukuta, M.; Kawashimo, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Kusumoto, K.; et al. Association between liver fibrosis and insulin sensitivity in chronic hepatitis C patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2752–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.A.; Xiaoqiang, W.; Budoff, M.; Leaf, D.; Kuller, L.H.; Justice, A.C. Hepatitis C virus infection and the risk of coronary disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasso, A.; Malfatti, F.; De Leo, P.; Martines, H.; Fabris, P.; Toscanini, F.; Anselmo, M.; Menardo, G. Insulin resistance predicts rapid virological response in non-diabetic, non-cirrhotic genotype 1 HCV patients treated with peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poustchi, H.; Negro, F.; Hui, J.; Cua, I.H.; Brandt, L.R.; Kench, J.G.; George, J. Insulin resistance and response to therapy in patients infected with chronic hepatitis C virus genotypes 2 and 3. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandman, D.; Bacchetti, P.; Ayala, C.E.; Maher, J.J.; Khalili, M. Impact of insulin resistance on HCV treatment response and impact of HCV treatment on insulin sensitivity using direct measurements of insulin action. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, Y.N.; Jeong, S.W.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, B.S. The impact of pegylated interferon and ribavirin combination treatment on lipid metabolism and insulin resistance in chronic hepatitis C patients. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2014, 20, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simo, R.; Lecube, A.; Genesca, J.; Esteban, J.I.; Hernandez, C. Sustained virological response correlates with reduction in the incidence of glucose abnormalities in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2462–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serfaty, L.; Forns, X.; Goeser, T.; Ferenci, P.; Nevens, F.; Carosi, G.; Drenth, J.P.; Lonjon-Domanec, I.; DeMasi, R.; Picchio, G.; et al. Insulin resistance and response to telaprevir plus peginterferon alpha and ribavirin in treatment-naive patients infected with HCV genotype 1. Gut 2012, 61, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felmlee, D.J.; Hafirassou, M.L.; Lefevre, M.; Baumert, T.F.; Schuster, C. Hepatitis C virus, cholesterol and lipoproteins—impact for the viral life cycle and pathogenesis of liver disease. Viruses 2013, 5, 1292–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnello, V.; Abel, G.; Elfahal, M.; Knight, G.B.; Zhang, Q.X. Hepatitis C virus and other flaviviridae viruses enter cells via low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12766–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.Y.; Chuang, W.L.; Ho, C.K.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Huang, J.F.; Lee, L.P.; Hou, N.J.; Lin, Z.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Hsieh, M.Y.; et al. Associations between hepatitis C viremia and low serum triglyceride and cholesterol levels: A community-based study. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, J.M.; Benichou, M.; Duvillard, L.; Jooste, V.; Bour, J.B.; Minello, A.; Verges, B.; Brun, J.M.; Gambert, P.; Hillon, P. Hepatitis C virus-associated hypobetalipoproteinemia is correlated with plasma viral load, steatosis, and liver fibrosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siagris, D.; Christofidou, M.; Theocharis, G.J.; Pagoni, N.; Papadimitriou, C.; Lekkou, A.; Thomopoulos, K.; Starakis, I.; Tsamandas, A.C.; Labropoulou-Karatza, C. Serum lipid pattern in chronic hepatitis C: Histological and virological correlations. J. Viral. Hepat. 2006, 13, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, M.; Milionis, H.; Filis, S.; Baltayiannis, G.; Christou, L.; Elisaf, M.; Tsianos, E. Baseline cholesterol is associated with the response to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, K.E.; Kane, E.; Munroe, C.; Barlow, L.L.; Zheng, H.; Chung, R.T. Hepatitis C virus infection and its clearance alter circulating lipids: Implications for long-term follow-up. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, S.; Saito, H.; Ebinuma, H.; Ojiro, K.; Yamagishi, Y.; Kumagai, N.; Inagaki, Y.; Masuda, T.; Nishida, J.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Treatment of hepatitis C virus with peg-interferon and ribavirin combination therapy significantly affects lipid metabolism. Hepatol. Res. 2009, 39, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afdhal, N.; Zeuzem, S.; Kwo, P.; Chojkier, M.; Gitlin, N.; Puoti, M.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zarski, J.P.; Agarwal, K.; Buggisch, P.; et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for untreated HCV genotype 1 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.J.; Jacobson, I.M.; Hezode, C.; Asselah, T.; Ruane, P.J.; Gruener, N.; Abergel, A.; Mangia, A.; Lai, C.L.; Chan, H.L.; et al. Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir for HCV Genotype 1, 2, 4, 5, and 6 Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2599–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.J.; Kowdley, K.V.; Coakley, E.; Sigal, S.; Nelson, D.R.; Crawford, D.; Weiland, O.; Aguilar, H.; Xiong, J.; Pilot-Matias, T.; et al. Treatment of HCV with ABT-450/r-ombitasvir and dasabuvir with ribavirin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moucari, R.; Forestier, N.; Larrey, D.; Guyader, D.; Couzigou, P.; Benhamou, Y.; Voitot, H.; Vidaud, M.; Seiwert, S.; Bradford, B.; et al. Danoprevir, an HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor, improves insulin sensitivity in patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2010, 59, 1694–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, E.G.; Lee, Y.J.; Osinusi, A.; Sims, Z.; Qin, J.; Sturdevant, D.; McHutchison, J.; Subramanian, M.; Sampson, M.; Naggie, S.; et al. Effect of sofosbuvir and ribavirin treatment on peripheral and hepatic lipid metabolism in chronic hepatitis C virus, genotype 1-infected patients. Hepatology 2015, 61, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, A.L.; Junga, Z.; Singla, M.B.; Sjogren, M.; Torres, D. Hepatitis C eradication with sofosbuvir leads to significant metabolic changes. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.; Kottilil, S.; Wilson, E. Use of Ribavirin for Hepatitis C Treatment in the Modern Direct-acting Antiviral Era. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, M.W.; Rollet, K.; Moodie, E.E.; Walmsley, S.; Cox, J.; Potter, M.; Cooper, C.; Pick, N.; Saeed, S.; Klein, M.B.; et al. Insulin resistance is associated with progression to hepatic fibrosis in a cohort of HIV/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients. Aids 2012, 26, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucidarme, D.; Foucher, J.; Le Bail, B.; Vergniol, J.; Castera, L.; Duburque, C.; Forzy, G.; Filoche, B.; Couzigou, P.; de Ledinghen, V. Factors of accuracy of transient elastography (fibroscan) for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.W.; Sun, L.J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Kang, P.; Yan, B.Z. The effect of metformin on the efficacy of antiviral therapy in patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C and insulin resistance. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, e436–e441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.E.; Wreghitt, T.; Palmer, C.R.; Alexander, G.J. Evidence for a link between hepatitis C virus infection and diabetes mellitus in a cirrhotic population. J. Hepatol. 1994, 21, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.F.; Dai, C.Y.; Hwang, S.J.; Ho, C.K.; Hsiao, P.J.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Lee, L.P.; Lin, Z.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Hsieh, M.Y.; et al. Hepatitis C viremia increases the association with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a hepatitis B and C endemic area: An epidemiological link with virological implication. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Yoshida, T.; Harada, M.; Hisamoto, T.; Nagao, Y.; Ide, T.; Taniguchi, E.; Kumemura, H.; Hanada, S.; Maeyama, M.; et al. Hepatitis C virus down-regulates insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 through up-regulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.L.; Ratziu, V.; El-Serag, H.B. Hepatitis C infection and risk of diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio Blanco, C.; Gentile, S.; Marmo, R.; Carbone, L.; Coltorti, M. Alterations of glucose metabolism in chronic liver disease. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1990, 8, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.J.; Pirlich, M.; Balks, H.J.; Selberg, O. Glucose intolerance in liver cirrhosis: Role of hepatic and non-hepatic influences. Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1994, 32, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Franceschi, L.; Fattovich, G.; Turrini, F.; Ayi, K.; Brugnara, C.; Manzato, F.; Noventa, F.; Stanzial, A.M.; Solero, P.; Corrocher, R. Hemolytic anemia induced by ribavirin therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: Role of membrane oxidative damage. Hepatology 2000, 31, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, M. Artificially low HbA1c associated with treatment with ribavirin. BMJ 2008, 336, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hum, J.; Jou, J.H.; Green, P.K.; Berry, K.; Lundblad, J.; Hettinger, B.D.; Chang, M.; Ioannou, G.N. Improvement in Glycemic Control of Type 2 Diabetes After Successful Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, P.; Tieghi, T.; d’Ettorre, G.; Lichtner, M.; Marocco, R.; Mezzaroma, I.; Passavanti, G.; Vittozzi, P.; Mastroianni, C.M.; Vullo, V. Rapid decline of fasting glucose in HCV diabetic patients treated with direct-acting antiviral agents. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 462e1-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, T.; Ono, C.; Puig-Basagoiti, F.; Matsuura, Y. Roles of Lipoproteins and Apolipoproteins in Particle Formation of Hepatitis C Virus. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouchet, E.; Baumert, T.F.; Schuster, C. Hepatitis C virus-apolipoprotein interactions: Molecular mechanisms and clinical impact. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2017, 14, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Cun, W.; Wu, X.; Shi, Q.; Tang, H.; Luo, G. Hepatitis C virus attachment mediated by apolipoprotein E binding to cell surface heparan sulfate. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7256–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Luo, G. Apolipoprotein E but not B is required for the formation of infectious hepatitis C virus particles. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12680–12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, D.M.; Huang, H.; Ye, J.; Gale, M., Jr. Apolipoprotein E on hepatitis C virion facilitates infection through interaction with low-density lipoprotein receptor. Virology 2009, 394, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chi, X.; Zhao, F.; Guo, J.; Ma, P.; Zhong, J.; Niu, J.; Pan, X.; Long, G. Neglected but Important Role of Apolipoprotein E Exchange in Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9632–9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancone, C.; Steindler, C.; Santangelo, L.; Simonte, G.; Vlassi, C.; Longo, M.A.; D’Offizi, G.; Di Giacomo, C.; Pucillo, L.P.; Amicone, L.; et al. Hepatitis C virus production requires apolipoprotein A-I and affects its association with nascent low-density lipoproteins. Gut 2011, 60, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icard, V.; Diaz, O.; Scholtes, C.; Perrin-Cocon, L.; Ramiere, C.; Bartenschlager, R.; Penin, F.; Lotteau, V.; Andre, P. Secretion of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoproteins depends on assembly of apolipoprotein B positive lipoproteins. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serfaty, L.; Andreani, T.; Giral, P.; Carbonell, N.; Chazouilleres, O.; Poupon, R. Hepatitis C virus induced hypobetalipoproteinemia: A possible mechanism for steatosis in chronic hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, P.; Walic, M.; Meuleman, P.; Roohvand, F.; Huby, T.; Le Goff, W.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Pecheur, E.I.; Budkowska, A. Lipoprotein lipase inhibits hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection by blocking virus cell entry. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, N.; Sugita, T.; Aida, Y.; Itagaki, M.; Ishiguro, H.; Sutoh, S.; Abe, H.; Tsubota, A.; Matsushima, M.; Aizawa, Y. Assessment of the features of serum apolipoprotein profiles in chronic HCV infection: Difference between HCV genotypes 1b and 2. Hepatol. Int. 2014, 8, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Lee, J.C.; Wang, S.W.; Cheng, P.N.; Wu, I.C.; Chang, T.T.; Lai, M.D.; Shieh, D.B.; Young, K.C. Very low-density lipoprotein/lipo-viro particles reverse lipoprotein lipase-mediated inhibition of hepatitis C virus infection via apolipoprotein C-III. Gut 2013, 62, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 24) | RBV+ (n = 9) | RBV− (n = 8) | RBV+F4+ (n = 7) | p-Value ** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Age * | 54 (11.6) | - | 53 (9.9) | - | 51 (12.7) | - | 59 (12.2) | - | 0.36 |
| Male | 17 | 71 | 7 | 79 | 5 | 63 | 5 | 71 | 0.79 |
| Genotype | |||||||||
| 1a | 13 | 54 | 9 | 100 | - | 4 | 57 | <0.001 | |
| 1b | 11 | 46 | - | - | 8 | 100 | 3 | 43 | |
| Race | |||||||||
| White | 19 | 79 | 9 | 100 | 4 | 50 | 6 | 86 | 0.02 |
| Indigenous | 4 | 17 | - | - | 4 | 50 | - | - | |
| South East Asian | 1 | 4 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 14 | |
| Years infected * | 31 (11.3) | - | 33 (12.1) | - | 30 (7.9) | - | 31 (16.3) | - | 0.91 |
| History HCV treatment | 4 | 17 | 2 | 22 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 14 | 0.85 |
| Fibrosis score * (kPa) | 9.7 (6.6) | - | 6.9 (2.5) | - | 5.9 (2.0) | - | 18.3 (6.3) | - | <0.001 |
| F0-F1 | 12 | 50 | 6 | 67 | 6 | 75 | - | - | <0.001 |
| F2 | 3 | 13 | 1 | 11 | 2 | 25 | - | - | |
| F3 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 22 | - | - | - | - | |
| F4 | 7 | 29 | - | - | - | - | 8 | 100 | |
| Controlled Attenuation Parameter (CAP) score * | 246 (69.1) | - | 254 (78.4) | - | 240 (71.9) | 242 (64.2) | 0.91 | ||
| Metabolic Parameter | Estimated Mean (95% CI) * | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 4 | Week 12 | 12 Weeks Post-Treatment | 24 Weeks Post-Treatment | ||
| HOMA-IR | 3.2 (2.6–3.9) | 2.8 (2.2–3.4) | 2.7 (2.1–3.4) | 3.0 (2.3–3.7) | 3.5 (2.7–4.3) | 0.32 |
| Insulin | 93 (76–111) | 82 (65–99) | 83 (66–101) | 90 (72–108) | 101 (80–122) | 0.42 |
| Glucose | 5.3 (5.1–5.5) | 5.3 (5.1–5.4) | 5.1 (4.9–5.3) | 5.3 (5.1–5.5) | 5.4 (5.2–5.6) | 0.11 |
| HbA1c * | 5.6 (5.4–5.8) | 5.1 (4.9–5.3) | 4.8 (4.6–5.0) | 5.7 (5.5–5.8) | 5.6 (5.4–5.8) | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol | 4.4 (4.1–4.7) | 4.4 (4.1–4.7) | 4.7 (4.4–5.0) | 5.2 (4.9–5.5) | 5.1 (4.8–5.4) | <0.001 |
| HDL-C | 1.2 (1.1–1.4) | 1.1 (0.92–1.3) | 1.2 (0.98–1.4) | 1.3 (1.1–1.5) | 1.4 (1.2–1.6) | 0.01 |
| LDL-C | 2.6 (2.3–2.8) | 2.7 (2.4–2.9) | 2.9 (2.6–3.2) | 3.2 (2.9–3.5) | 2.9 (2.6–3.2) | <0.001 |
| TG | 1.3 (0.96–1.6) | 1.4 (1.0–1.7) | 1.4 (1.1–1.7) | 1.8 (1.4–2.1) | 1.8 (1.4–2.1) | 0.01 |
| apoA1 | 4647 (3290–6566) | 3534 (2685–4654) | 3842 (2889–5111) | 3343 (2775–4026) | 1997 (1436–2777) | 0.002 |
| apoA2 | 421 (376–471) | 365 (321–415) | 382 (337–433) | 402 (356–453) | 369 (321–424) | 0.27 |
| apoB | 2575 (2329–2846) | 2466 (2180–2790) | 2503 (2101–2983) | 3370 (2902–3913) | 2962 (2396–3662) | 0.03 |
| apoC2 | 79 (67–90) | 78 (67–89) | 70 (58–81) | 93 (81–104) | 77 (65–90) | 0.004 |
| apoC3 | 153 (128–183) | 139 (115–169) | 125 (101–156) | 180 (152–213) | 153 (127–184) | 0.02 |
| apoE | 45 (39–51) | 38 (32–44) | 39 (33–44) | 46 (40–51) | 37 (31–44) | 0.003 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doyle, M.-A.; Galanakis, C.; Mulvihill, E.; Crawley, A.; Cooper, C.L. Hepatitis C Direct Acting Antivirals and Ribavirin Modify Lipid but not Glucose Parameters. Cells 2019, 8, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030252
Doyle M-A, Galanakis C, Mulvihill E, Crawley A, Cooper CL. Hepatitis C Direct Acting Antivirals and Ribavirin Modify Lipid but not Glucose Parameters. Cells. 2019; 8(3):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030252
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoyle, Mary-Anne, Chrissi Galanakis, Erin Mulvihill, Angela Crawley, and Curtis L. Cooper. 2019. "Hepatitis C Direct Acting Antivirals and Ribavirin Modify Lipid but not Glucose Parameters" Cells 8, no. 3: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030252
APA StyleDoyle, M.-A., Galanakis, C., Mulvihill, E., Crawley, A., & Cooper, C. L. (2019). Hepatitis C Direct Acting Antivirals and Ribavirin Modify Lipid but not Glucose Parameters. Cells, 8(3), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030252





