Current Status of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Therapies in Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Biochemical Structure of the Receptor
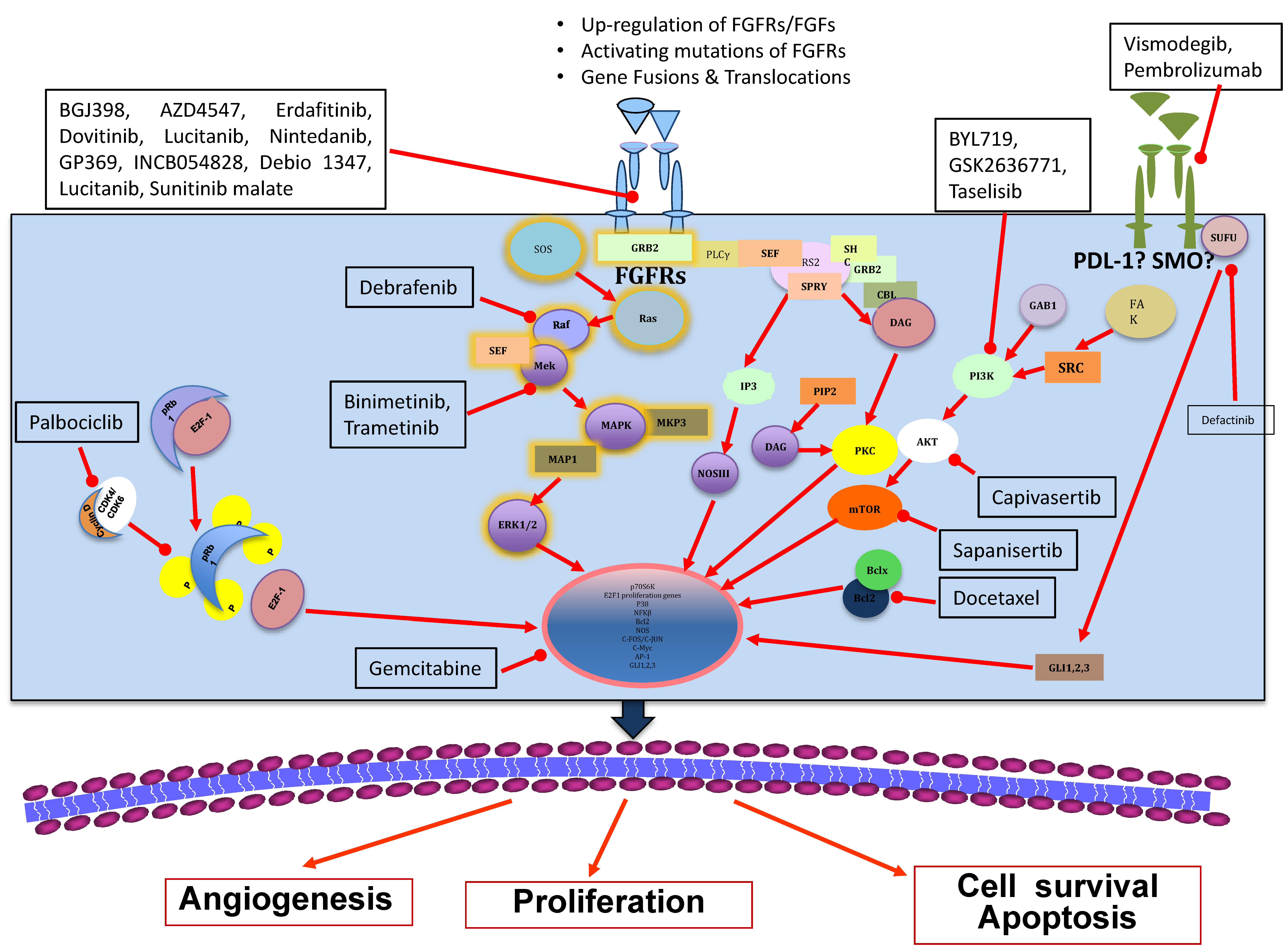
1.2. FGFR Signalling
1.3. The Control of FGFR Signalling
2. FGFRs as Oncogenic Drivers
3. FGFR Genetic Alterations in Breast Cancer
3.1. Amplification of FGFRs
3.2. FGFRs Activating Mutations
3.3. Gene Fusions of FGFRs
4. Anti-FGFR Therapies
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | Breast Cancer |
| FGF | Fibroblast Growth Factor |
| FGFR | Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor |
| VEGFR | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| HPSGs | heparan sulfate proteoglycans |
| EC | N-terminal extracellular |
| TM | transmembrane |
| IC | intracellular |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide-3-kinase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PKC | activates protein kinase C |
| 4-OHT | 4-hydroxytamoxifen |
| TICs | maintaining tumor-initiating cells |
| GWAS | Genome-Wide-Association-Studies |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. Fibroblast growth factors. Genome Biol. 2001, 2, REVIEWS3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswarakumar, V.P.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, J. Cellular signaling by fibroblast growth factor receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, R.; Borea, R.; Coelho, A.; Khan, S.; Araújo, A.; Reclusa, P.; Franchina, T.; Van Der Steen, N.; Van Dam, P.; Ferri, J.; et al. FGFR a promising druggable target in cancer: Molecular biology and new drugs. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2017, 113, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belov, A.A.; Mohammadi, M. Molecular mechanisms of fibroblast growth factor signaling in physiology and pathology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a015958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babina, I.S.; Turner, N.C. Advances and challenges in targeting FGFR signalling in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Zhou, F.; Kuo, A.; Leder, P. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is a negative regulator of bone growth. Cell 1996, 84, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presta, M.; Chiodelli, P.; Giacomini, A.; Rusnati, M.; Ronca, R. Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) in cancer: FGF traps as a new therapeutic approach. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 179, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, F.; Cortés, J. Rationale for targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 150, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turner, N.; Grose, R. Fibroblast growth factor signalling: From development to cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Xu, J.; Colvin, J.S.; McEwen, D.G.; MacArthur, C.A.; Coulier, F.; Gao, G.; Goldfarb, M. Receptor specificity of the fibroblast growth factor family. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 15292–15297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linggi, B.; Carpenter, G. ErbB receptors: New insights on mechanisms and biology. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knights, V.; Cook, S.J. De-regulated FGF receptors as therapeutic targets in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 125, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, S.-G. Isoforms of Receptors of Fibroblast Growth Factors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; Williams, L.T. Structural and functional diversity in the FGF receptor multigene family. Adv. Cancer Res. 1993, 60, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goetz, R.; Mohammadi, M. Exploring mechanisms of FGF signalling through the lens of structural biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dienstmann, R.; Rodon, J.; Prat, A.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Adamo, B.; Felip, E.; Cortes, J.; Iafrate, A.J.; Nuciforo, P.; Tabernero, J. Genomic aberrations in the FGFR pathway: Opportunities for targeted therapies in solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2014, 25, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, Y.; Grose, R.P. Dysregulated FGF signalling in neoplastic disorders. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 53, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M.; Nakagama, H. FGF Receptors: Cancer Biology and Therapeutics. Med. Res. Rev. 2014, 34, 280–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, B.C.; Engels, M.; Annala, M.; Zhang, W. Emergence of FGFR family gene fusions as therapeutic targets in a wide spectrum of solid tumours. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlessinger, J. Common and distinct elements in cellular signaling via EGF and FGF receptors. Science 2004, 306, 1506–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flippot, R.; Kone, M.; Magné, N.; Vignot, S. La signalisation FGF/FGFR: Implication dans l’oncogenèse et perspectives thérapeutiques. Bull. Cancer 2015, 102, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Dikic, I.; Sorokin, A.; Burgess, W.H.; Jaye, M.; Schlessinger, J. Identification of six novel autophosphorylation sites on fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 and elucidation of their importance in receptor activation and signal transduction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashiro, M.; Matsuoka, T. Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling as therapeutic targets in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiong, K.H.; Mah, L.Y.; Leong, C.-O. Functional roles of fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) signaling in human cancers. Apoptosis 2013, 18, 1447–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chell, V.; Balmanno, K.; Little, A.S.; Wilson, M.; Andrews, S.; Blockley, L.; Hampson, M.; Gavine, P.R.; Cook, S.J. Tumour cell responses to new fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and identification of a gatekeeper mutation in FGFR3 as a mechanism of acquired resistance. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3059–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M. FGFR inhibitors: Effects on cancer cells, tumor microenvironment and whole-body homeostasis (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Xiao, J.; McKeehan, W.L.; Wang, F. Fibroblast growth factors, old kids on the new block. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 53, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hierro, C.; Rodon, J.; Tabernero, J. Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) Receptor/FGF Inhibitors: Novel Targets and Strategies for Optimization of Response of Solid Tumors. Semin. Oncol. 2015, 42, 801–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesche, J.; Haglund, K.; Haugsten, E.M. Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in cancer. Biochem. J. 2011, 437, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giacomini, A.; Chiodelli, P.; Matarazzo, S.; Rusnati, M.; Presta, M.; Ronca, R. Blocking the FGF/FGFR system as a “two-compartment” antiangiogenic/antitumor approach in cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 107, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallinan, N.; Finn, S.; Cuffe, S.; Rafee, S.; O’Byrne, K.; Gately, K. Targeting the fibroblast growth factor receptor family in cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 46, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Rudert, W.A.; Loutaev, I.; Roginskaya, V.; Corey, S.J. Repression of c-Cbl leads to enhanced G-CSF Jak-STAT signaling without increased cell proliferation. Oncogene 2002, 21, 5346–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kovalenko, D.; Yang, X.; Nadeau, R.J.; Harkins, L.K.; Friesel, R. Sef inhibits fibroblast growth factor signaling by inhibiting FGFR1 tyrosine phosphorylation and subsequent ERK activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 14087–14091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torii, S.; Kusakabe, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Maekawa, M.; Nishida, E. Sef Is a Spatial Regulator for Ras/MAP Kinase Signaling. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stauber, D.J.; DiGabriele, A.D.; Hendrickson, W.A. Structural interactions of fibroblast growth factor receptor with its ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalinina, J.; Dutta, K.; Ilghari, D.; Beenken, A.; Goetz, R.; Eliseenkova, A.V.; Cowburn, D.; Mohammadi, M. The Alternatively Spliced Acid Box Region Plays a Key Role in FGF Receptor Autoinhibition. Structure 2012, 20, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herbert, C.; Lassalle, G.; Alcouffe, C.; Bono, F. Approaches targeting the FGF–FGFR system: A review of the recent patent literature and associated advanced therapeutic agents. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2014, 3, 585–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, Y.; Ferrara, N. Tumor and stromal pathways mediating refractoriness/resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, A.E.; Gould, C.R.; Grose, R.P. FGFR signalling in women’s cancers. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2832–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasorella, A.; Sanson, M.; Iavarone, A. FGFR-TACC gene fusions in human glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 19, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touat, M.; Ileana, E.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Andre, F.; Soria, J.-C. Targeting FGFR Signaling in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2684–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saichaemchan, S.; Ariyawutyakorn, W.; Varella-Garcia, M. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors: From the Oncogenic Pathway to Targeted Therapy. Curr. Mol. Med. 2016, 16, 40–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M. Therapeutics Targeting FGF Signaling Network in Human Diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1081–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarabipour, S.; Hristova, K. Mechanism of FGF receptor dimerization and activation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Therapeutic uses of FGFs. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 53, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, A.N.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Jang, M.H.; Lee, H.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.Y. Tumour-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes as an independent predictive factor for pathological complete response to primary systemic therapy in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, L.; Su, X.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.; Tang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Liu, K.; Zhou, M.; et al. FGFR2 gene amplification in gastric cancer predicts sensitivity to the selective FGFR inhibitor AZD4547. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2572–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.; Pearson, A.; Sharpe, R.; Lambros, M.; Geyer, F.; Lopez-Garcia, M.A.; Natrajan, R.; Marchio, C.; Iorns, E.; Mackay, A.; et al. FGFR1 amplification drives endocrine therapy resistance and is a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronca, R.; Giacomini, A.; Rusnati, M.; Presta, M. The potential of fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling as a therapeutic target in tumor angiogenesis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.B.V.S.; Narasu, L.; Gundla, R.; Dayam, R.; JARP, S. Fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelleher, F.C.; O’Sullivan, H.; Smyth, E.; McDermott, R.; Viterbo, A. Fibroblast growth factor receptors, developmental corruption and malignant disease. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2198–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helsten, T.; Schwaederle, M.; Kurzrock, R. Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling in hereditary and neoplastic disease: Biologic and clinical implications. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsten, T.; Elkin, S.; Arthur, E.; Tomson, B.N.; Carter, J.; Kurzrock, R. The FGFR Landscape in Cancer: Analysis of 4,853 Tumors by Next-Generation Sequencing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, E.P.; Fearon, A.E.; Grose, R.P. Careless talk costs lives: Fibroblast growth factor receptor signalling and the consequences of pathway malfunction. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzle, C.; Sutterlüty, H.; Grusch, M.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Berger, W.; Marian, B. Targeting fibroblast-growth-factor-receptor-dependent signaling for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greulich, H.; Pollock, P.M. Targeting mutant fibroblast growth factor receptors in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adnane, J.; Gaudray, P.; Dionne, C.A.; Crumley, G.; Jaye, M.; Schlessinger, J.; Jeanteur, P.; Birnbaum, D.; Theillet, C. BEK and FLG, two receptors to members of the FGF family, are amplified in subsets of human breast cancers. Oncogene 1991, 6, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dey, N.; Williams, C.; Leyland-Jones, B.; De, P. Mutation matters in precision medicine: A future to believe in. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 55, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, F.; Sun, H.; Deng, C.-X.; Shao, F.; Sun, H.; Deng, C.-X.; Shao, F.; Sun, H.; Deng, C.-X. Potential therapeutic targets of triple-negative breast cancer based on its intrinsic subtype. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73329–73344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elbauomy Elsheikh, S.; Green, A.R.; Lambros, M.B.; Turner, N.C.; Grainge, M.J.; Powe, D.; Ellis, I.O.; Reis-Filho, J.S. FGFR1 amplification in breast carcinomas: A chromogenic in situ hybridisation analysis. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, R23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massard, C.; Michiels, S.; Ferté, C.; Le Deley, M.-C.; Lacroix, L.; Hollebecque, A.; Verlingue, L.; Ileana, E.; Rosellini, S.; Ammari, S.; et al. High-Throughput Genomics and Clinical Outcome in Hard-to-Treat Advanced Cancers: Results of the MOSCATO 01 Trial. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, F.; Bachelot, T.; Commo, F.; Campone, M.; Arnedos, M.; Dieras, V.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Lacroix, L.; Cohen, P.; Gentien, D.; et al. Comparative genomic hybridisation array and DNA sequencing to direct treatment of metastatic breast cancer: A multicentre, prospective trial (SAFIR01/UNICANCER). Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, E.; Brunelli, M.; Bogina, G.; Caliò, A.; Manfrin, E.; Nottegar, A.; Vergine, M.; Molino, A.; Bria, E.; Massari, F.; et al. FGFR-1 amplification in metastatic lymph-nodal and haematogenous lobular breast carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reis-Filho, J.S.; Simpson, P.T.; Turner, N.C.; Lambros, M.B.; Jones, C.; Mackay, A.; Grigoriadis, A.; Sarrio, D.; Savage, K.; Dexter, T.; et al. FGFR1 Emerges as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Lobular Breast Carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6652–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Courjal, F.; Cuny, M.; Simony-Lafontaine, J.; Louason, G.; Speiser, P.; Zeillinger, R.; Rodriguez, C.; Theillet, C. Mapping of DNA amplifications at 15 chromosomal localizations in 1875 breast tumors: Definition of phenotypic groups. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4360–4367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andre, F.; Bachelot, T.; Campone, M.; Dalenc, F.; Perez-Garcia, J.M.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Turner, N.; Rugo, H.; Smith, J.W.; Deudon, S.; et al. Targeting FGFR with Dovitinib (TKI258): Preclinical and Clinical Data in Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3693–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Dubrovska, A.; Salamone, R.J.; Walker, J.R.; Grandinetti, K.B.; Bonamy, G.M.C.; Orth, A.P.; Elliott, J.; Porta, D.G.; Garcia-Echeverria, C.; et al. FGFR2 promotes breast tumorigenicity through maintenance of breast tumor-initiating cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e51671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guagnano, V.; Kauffmann, A.; Wohrle, S.; Stamm, C.; Ito, M.; Barys, L.; Pornon, A.; Yao, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. FGFR Genetic Alterations Predict for Sensitivity to NVP-BGJ398, a Selective Pan-FGFR Inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.-M.; Su, F.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Khazanov, N.; Ateeq, B.; Cao, X.; Lonigro, R.J.; Vats, P.; Wang, R.; Lin, S.-F.; et al. Identification of targetable FGFR gene fusions in diverse cancers. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, K.C.; Robertson, S.C.; Kanemitsu, M.Y.; Meyer, A.N.; Tynan, J.A.; Donoghue, D.J. Transformation and Stat activation by derivatives of FGFR1, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Oncogene 2000, 19, 3309–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, E.D.; Furdui, C.M.; Anderson, K.S.; Schlessinger, J. The Precise Sequence of FGF Receptor Autophosphorylation Is Kinetically Driven and Is Disrupted by Oncogenic Mutations. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandith, A.A.; Shah, Z.A.; Siddiqi, M.A. Oncogenic role of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 in tumorigenesis of urinary bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2013, 31, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Guo, W.; Shen, J.K.; Mankin, H.J.; Hornicek, F.J.; Duan, Z. Rhabdomyosarcoma: Advances in Molecular and Cellular Biology. Sarcoma 2015, 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Easton, D.F.; Pooley, K.A.; Dunning, A.M.; Pharoah, P.D.P.; Thompson, D.; Ballinger, D.G.; Struewing, J.P.; Morrison, J.; Field, H.; Luben, R.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies novel breast cancer susceptibility loci. Nature 2007, 447, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stacey, S.N.; Manolescu, A.; Sulem, P.; Thorlacius, S.; Gudjonsson, S.A.; Jonsson, G.F.; Jakobsdottir, M.; Bergthorsson, J.T.; Gudmundsson, J.; Aben, K.K.; et al. Common variants on chromosome 5p12 confer susceptibility to estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.B.; Maia, A.-T.; O’Reilly, M.; Teschendorff, A.E.; Chin, S.-F.; Caldas, C.; Ponder, B.A.J. Allele-specific up-regulation of FGFR2 increases susceptibility to breast cancer. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.J.; Kraft, P.; Jacobs, K.B.; Cox, D.G.; Yeager, M.; Hankinson, S.E.; Wacholder, S.; Wang, Z.; Welch, R.; Hutchinson, A.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies alleles in FGFR2 associated with risk of sporadic postmenopausal breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Penault-Llorca, F.; Bertucci, F.; Adélaïde, J.; Parc, P.; Coulier, F.; Jacquemier, J.; Birnbaum, D.; DeLapeyrière, O. Expression of FGF and FGF receptor genes in human breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 61, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.N.; Meyer, A.N.; Siari, A.; Campos, A.R.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Donoghue, D.J. Oncogenic Gene Fusion FGFR3-TACC3 Is Regulated by Tyrosine Phosphorylation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stransky, N.; Cerami, E.; Schalm, S.; Kim, J.L.; Lengauer, C. The landscape of kinase fusions in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedussi, F.; Bottini, A.; Memo, M.; Fox, S.B.; Sigala, S.; Generali, D. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor in breast cancer: A promise or a pitfall? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Garcia, J.; Muñoz-Couselo, E.; Soberino, J.; Racca, F.; Cortes, J. Targeting FGFR pathway in breast cancer. Breast 2018, 37, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahores, A.; May, M.; Sequeira, G.; Fuentes, C.; Jacobsen, B.; Lanari, C.; Lamb, C.A. Targeting FGFR with BGJ398 in breast cancer: Effect on tumor growth and metastasis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Frezzetti, D.; Gallo, M.; Normanno, N. FGFR-targeted therapeutics for the treatment of breast cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 26, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, A.; Meetze, K.; Vo, N.Y.; Kollipara, S.; Mazsa, E.K.; Winston, W.M.; Weiler, S.; Poling, L.L.; Chen, T.; Ismail, N.S.; et al. GP369, an FGFR2-IIIb-Specific Antibody, Exhibits Potent Antitumor Activity against Human Cancers Driven by Activated FGFR2 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7630–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharpe, R.; Pearson, A.; Herrera-Abreu, M.T.; Johnson, D.; Mackay, A.; Welti, J.C.; Natrajan, R.; Reynolds, A.R.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Ashworth, A.; et al. FGFR signaling promotes the growth of triple-negative and basal-like breast cancer cell lines both in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5275–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Patnaik, A.; Wilson, K.; Thayer, S.; Zanghi, J.; Gemo, A.T.; Kavanaugh, W.M.; Keer, H.N.; LoRusso, P.M. A phase I, first in human study of FP-1039 (GSK3052230), a novel FGF ligand trap, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semrad, T.J.; Kim, E.J.; Tanaka, M.S.; Sands, J.; Roberts, C.; Burich, R.A.; Li, Y.; Gandara, D.R.; Lara, P.; Mack, P.C. Phase II study of dovitinib in patients progressing on anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2017, 10, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Issa, A.; Gill, J.W.; Heideman, M.R.; Sahin, O.; Wiemann, S.; Dey, J.H.; Hynes, N.E. Combinatorial targeting of FGF and ErbB receptors blocks growth and metastatic spread of breast cancer models. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Trial Identifier | Study Design | Intervention/s | Setting | Primary Endpoint | Phase | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03238196 | 32 Participants, Non-Randomized, Open label | Fulvestrant + palbociclib + erdafitinib as an escalation (Arm A: 4–8 mg once daily for erdafitinib, 125 mg once every 21 days followed by 1 week of rest (without taking the drug) and 500 mg once daily for erdafitinib) or the same combination of drugs as an expansion (Arm A: 4–8 mg once daily for erdafitinib, 125 mg once every 21 days followed by 1 week of rest (without taking the drug) and 500 mg once daily for erdafitinib). | Second line | Safety and Tolerability | 1 | Recruiting |
| NCT02465060 | 6452 participants, Non-Randomized, Parallel assignment, Open Label | Adavosertib, afatinib, binimetinib, capivasertib, crizotinib, dabrafenib, dasatinib, defactinib, AZD4547, larotrectinib, nivolumab, osimertinib, palbociclib, pertuzumab, GSK2636771, sapanisertib, sunitinib malate, taselisib, trametinib, trastuzumab, trastuzumab emtansine, vismodegib | Second line | OR | 2 | Recruiting |
| NCT02202746 | 178 participants, Parallel Assignment, Open label | Lucitanib in patients with FGFR1-amplified or 11q-amplified (Arm A: 10 mg once daily), and in patients with FGFR1- non amplified and 11q non-amplified (Arm B: 10 mg once daily) | Second Line | PFS | 2 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT01004224 | 208 participants, Single group assignment, Non-Randomized, Open label | BGJ398 (dose escalation) | Second line | MTD | 1 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT01791985 | 56 participants, Single group assignment, Open label | Anastrazole (1 mg daily), letrozole (2.5 mg once daily) and AZD4547 (80 mg twice daily) | Second line | Safety and Tolerability | 1 & 2 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT02619162 | 22 participants, Single group assignment, Open label | Letrozole (2.5 mg) with nintedanib (100–150 mg) | Second line | DLT | 1 | Recruiting |
| NCT03344536 | 55 participants, Single group assignment, Open label | Fulvestrant (500 mg 1, 15, 29 and every 28 days (+/− 3 days) thereafter) and Debio 1347 (dose escalation, administered once daily). | Second line maximum for phase II; phase I could have received more than one prior treatment | DLT | 1 & 2 | Recruiting |
| NCT02393248 | 280 participants, Single group assignment, Open label | Combination therapy: Gemcitabine + Cisplatin + INCB054828; Pembrolizumab + INCB054828; Docetaxel + INCB054828; Trastuzumab + INCB054828. | Second line | MTD | 1 & 2 | Recruiting |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobhani, N.; Ianza, A.; D’Angelo, A.; Roviello, G.; Giudici, F.; Bortul, M.; Zanconati, F.; Bottin, C.; Generali, D. Current Status of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Therapies in Breast Cancer. Cells 2018, 7, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070076
Sobhani N, Ianza A, D’Angelo A, Roviello G, Giudici F, Bortul M, Zanconati F, Bottin C, Generali D. Current Status of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Therapies in Breast Cancer. Cells. 2018; 7(7):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070076
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobhani, Navid, Anna Ianza, Alberto D’Angelo, Giandomenico Roviello, Fabiola Giudici, Marina Bortul, Fabrizio Zanconati, Cristina Bottin, and Daniele Generali. 2018. "Current Status of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Therapies in Breast Cancer" Cells 7, no. 7: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070076
APA StyleSobhani, N., Ianza, A., D’Angelo, A., Roviello, G., Giudici, F., Bortul, M., Zanconati, F., Bottin, C., & Generali, D. (2018). Current Status of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Therapies in Breast Cancer. Cells, 7(7), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070076








