Engineering Liver-Specific Promoters: A Comprehensive Review of Design, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications in Gene Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Liver as a Target for Gene Therapy
2.1. Vector Size Limitations
2.2. Low Hepatocyte Proliferation Rate—An Advantage and an Obstacle for Vectors
2.3. Immune System Barriers to Liver-Directed Gene Therapy
2.4. Liver Immune Privilege in Gene Therapy
- Non-parenchymal liver cells (including stellate cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells) produce a large number of immunosuppressive anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10, TGF-beta [41];
- Liver natural killer cells express a negative T-lymphocyte costimulatory–the programmed cell death ligand (PD-L1) [42];
- Hepatocytes themselves also contribute to immune tolerance by producing PD-L1 [43].
3. Liver Gene Expression Regulation
3.1. Genomic Regulatory Elements
3.2. Liver-Enriched Transcription Factors
4. Safety Advantages of Liver-Specific over Ubiquitous Promoters
5. Promoters Based on Human SERPINA1 Gene
6. Promoters Based on TTR Gene
7. Promoters Based on Albumin (Alb) Gene
8. Promoters Based on AFP Gene
9. Promoters Based on TBG Gene
10. Synthetic Promoters
11. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobs, F.; Gordts, S.; Muthuramu, I.; De Geest, B. The Liver as a Target Organ for Gene Therapy: State of the Art, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 1372–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, S.; Green, A.; Preece, M.A.; Burton, H. The Incidence of Inherited Metabolic Disorders in the West Midlands, UK. Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuecos, M.A.; Lagor, W.R. Liver Directed Adeno-associated Viral Vectors to Treat Metabolic Disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2024, 47, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravalli, R.N.; Belcher, J.D.; Steer, C.J. Liver-targeted Gene Therapy: Approaches and Challenges. Liver Transplant. 2015, 21, 718–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebert, R.C.; Rakela, J. Cellular Therapy for Liver Disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Li, H. Analysis of Clinical Trials of New Drugs for Liver Diseases in China. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 3181–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadori, G.; Saile, B.; Ramadori, G.; Saile, B. Mesenchymal Cells in the Liver—One Cell Type or Two? Liver 2002, 22, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, H.; Nakamura, M.; Komori, A.; Migita, K.; Shimoda, S. Liver Architecture, Cell Function, and Disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2009, 31, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, R.W.; Kaczmarek, R.; High, K.A. Gene Therapy for Hemophilia—From Basic Science to First Approvals of “One-and-Done” Therapies. Mol. Ther. 2025, 33, 2015–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Ferry, N. Liver Gene Therapy: Advances and Hurdles. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, S76–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, J.; Abriss, B.; Van De Leur, E.; Weiskirchen, S.; Gressner, A.M.; Weiskirchen, R. Comparative Analysis of Adenoviral Transgene Delivery via Tail or Portal Vein into Rat Liver. Arch. Virol. 2004, 149, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, A.; Schlachterman, A.; Cooper, M.; Merricks, E.P.; Raymer, R.A.; Bellinger, D.A.; Herzog, R.W.; Nichols, T.C. Portal Vein Delivery of Viral Vectors for Gene Therapy for Hemophilia. In Gene Correction; Storici, F., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 1114, pp. 413–426. ISBN 978-1-62703-760-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sands, M.S. AAV-Mediated Liver-Directed Gene Therapy. In Adeno-Associated Virus; Snyder, R.O., Moullier, P., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 807, pp. 141–157. ISBN 978-1-61779-369-1. [Google Scholar]
- Braet, F.; Wisse, E. Structural and Functional Aspects of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell Fenestrae: A Review. Comp. Hepatol. 2002, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, A.; Le Couteur, D.G.; Fraser, R.; Bowen, D.G.; McCaughan, G.W.; Bertolino, P. T Lymphocytes Interact with Hepatocytes through Fenestrations in Murine Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeys, J.; Lievens, J.; Wisse, E.; Jacobs, F.; Duimel, H.; Collen, D.; Frederik, P.; De Geest, B. Species Differences in Transgene DNA Uptake in Hepatocytes after Adenoviral Transfer Correlate with the Size of Endothelial Fenestrae. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, N.L.; Swaffield, M.N. The Rate of Incorporation of Labeled Thymidine Into the Deoxyribonucleic Acid of Regenerating Rat Liver in Relation to the Amount of Liver Excised. Cancer Res. 1964, 24, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Rozga, J. Hepatocyte Proliferation in Health and in Liver Failure. Med. Sci. Monit. 2002, 8, RA32–RA38. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Haskins, M.E.; Melniczek, J.R.; Gao, C.; Weil, M.A.; O’Malley, T.M.; O’Donnell, P.A.; Mazrier, H.; Ellinwood, N.M.; Zweigle, J.; et al. Transduction of Hepatocytes after Neonatal Delivery of a Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus Based Retroviral Vector Results in Long-Term Expression of β-Glucuronidase in Mucopolysaccharidosis VII Dogs. Mol. Ther. 2002, 5, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, S.C.; Dane, A.P.; Spinoulas, A.; Alexander, I.E. Gene Delivery to the Juvenile Mouse Liver Using AAV2/8 Vectors. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arii, S.; Imamura, M. Physiological Role of Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells and Kupffer Cells and Their Implication in the Pathogenesis of Liver Injury. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Surg. 2000, 7, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, G.; Worgall, S.; Van Rooijen, N.; Song, W.R.; Harvey, B.G.; Crystal, R.G. Enhancement of in Vivo Adenovirus-Mediated Gene Transfer and Expression by Prior Depletion of Tissue Macrophages in the Target Organ. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, Z.; Leborgne, C.; Barbon, E.; Masat, E.; Ronzitti, G.; Van Wittenberghe, L.; Vignaud, A.; Collaud, F.; Charles, S.; Simon Sola, M.; et al. Influence of Pre-Existing Anti-Capsid Neutralizing and Binding Antibodies on AAV Vector Transduction. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2018, 9, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingozzi, F.; Maus, M.V.; Hui, D.J.; Sabatino, D.E.; Murphy, S.L.; Rasko, J.E.J.; Ragni, M.V.; Manno, C.S.; Sommer, J.; Jiang, H.; et al. CD8+ T-Cell Responses to Adeno-Associated Virus Capsid in Humans. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttner, N.A.; Girod, A.; Perabo, L.; Edbauer, D.; Kleinschmidt, J.A.; Büning, H.; Hallek, M. Genetic Modifications of the Adeno-Associated Virus Type 2 Capsid Reduce the Affinity and the Neutralizing Effects of Human Serum Antibodies. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mével, M.; Bouzelha, M.; Leray, A.; Pacouret, S.; Guilbaud, M.; Penaud-Budloo, M.; Alvarez-Dorta, D.; Dubreil, L.; Gouin, S.G.; Combal, J.P.; et al. Chemical Modification of the Adeno-Associated Virus Capsid to Improve Gene Delivery. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Leng, M.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; He, S.; Qiao, W.; Xiao, L.; Xiao, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhou, L.; et al. The Combination of rAAV Pseudo-Lipid Nanoparticle and Triamcinolone Acetonide Enables Multi-Administration to Liver. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2025, 33, 101399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Yang, C.-H.; Zhao, K.; Sun, Y.-L.; Rao, Z.-Y.; Qu, W.-Q.; Zhang, S.-M.; Jin, X.-K.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.-Z. Biomimetic Artificial Enveloped Viral Vectors: Overcoming Immune Barriers for Re-Administration and Long-Term Gene Therapy. Cell Biomater. 2025, 1, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, E.; Nicklin, S.; Baker, A.; White, S. Promoters and Control Elements: Designing Expression Cassettes for Gene Therapy. Curr. Gene Ther. 2004, 4, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.-J.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Nayal, M.; He, Z.; White, J.; Lebel-Hagan, D.; Wilson, J.M. Effects of Self-Complementarity, Codon Optimization, Transgene, and Dose on Liver Transduction with AAV8. Hum. Gene Ther. Methods 2016, 27, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, I.; De Stefano, V.; Mannucci, P.M. Inherited Risk Factors for Venous Thromboembolism. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, R.W.; Mount, J.D.; Arruda, V.R.; High, K.A.; Lothrop, C.D. Muscle-Directed Gene Transfer and Transient Immune Suppression Result in Sustained Partial Correction of Canine Hemophilia B Caused by a Null Mutation. Mol. Ther. 2001, 4, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, R.W.; Yang, E.Y.; Couto, L.B.; Hagstrom, J.N.; Elwell, D.; Fields, P.A.; Burton, M.; Bellinger, D.A.; Read, M.S.; Brinkhous, K.M.; et al. Long-Term Correction of Canine Hemophilia B by Gene Transfer of Blood Coagulation Factor IX Mediated by Adeno-Associated Viral Vector. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, S.; Handyside, B.; Sihn, C.-R.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Xie, L.; Murphy, R.; Galicia, N.; Yates, B.; Minto, W.C.; et al. Induction of ER Stress by an AAV5 BDD FVIII Construct Is Dependent on the Strength of the Hepatic-Specific Promoter. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 18, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.P.; Hoffman, B.E.; Terhorst, C.; De Jong, Y.P.; Herzog, R.W. The Balance between CD8+ T Cell-Mediated Clearance of AAV-Encoded Antigen in the Liver and Tolerance Is Dependent on the Vector Dose. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basner-Tschakarjan, E.; Mingozzi, F. Cell-Mediated Immunity to AAV Vectors, Evolving Concepts and Potential Solutions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederkorn, J.Y. See No Evil, Hear No Evil, Do No Evil: The Lessons of Immune Privilege. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, J.V.; Xu, H.; Lambe, T.; Cornall, R. Immune Privilege or Privileged Immunity? Mucosal Immunol. 2008, 1, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispe, I.N.; Giannandrea, M.; Klein, I.; John, B.; Sampson, B.; Wuensch, S. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Liver Tolerance. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 213, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, D.M.; Hickman, R.; Uys, C.J.; Saunders, S.; Terblanche, J. The Natural History of Liver Allo- and Autotransplantation in the Pig. Br. J. Surg. 1971, 58, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiegs, G.; Lohse, A.W. Immune Tolerance: What Is Unique about the Liver. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, H.; Li, K.; Qu, K.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Ye, L.; Dong, Z.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; et al. Liver-Resident NK Cells Control Antiviral Activity of Hepatic T Cells via the PD-1-PD-L1 Axis. Immunity 2019, 50, 403–417.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Wherry, E.J.; Ahmed, R.; Freeman, G.J. The Function of Programmed Cell Death 1 and Its Ligands in Regulating Autoimmunity and Infection. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, B.E.; Martino, A.T.; Sack, B.K.; Cao, O.; Liao, G.; Terhorst, C.; Herzog, R.W. Nonredundant Roles of IL-10 and TGF-β in Suppression of Immune Responses to Hepatic AAV-Factor IX Gene Transfer. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, O.; Dobrzynski, E.; Wang, L.; Nayak, S.; Mingle, B.; Terhorst, C.; Herzog, R.W. Induction and Role of Regulatory CD4+CD25+ T Cells in Tolerance to the Transgene Product Following Hepatic in Vivo Gene Transfer. Blood 2007, 110, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, P.A.; Arruda, V.R.; Armstrong, E.; Chu, K.; Mingozzi, F.; Hagstrom, J.N.; Herzog, R.W.; High, K.A. Risk and Prevention of Anti-Factor IX Formation in AAV-Mediated Gene Transfer in the Context of a Large Deletion of F9. Mol. Ther. 2001, 4, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, J.D.; Herzog, R.W.; Tillson, D.M.; Goodman, S.A.; Robinson, N.; McCleland, M.L.; Bellinger, D.; Nichols, T.C.; Arruda, V.R.; Lothrop, C.D.; et al. Sustained Phenotypic Correction of Hemophilia B Dogs with a Factor IX Null Mutation by Liver-Directed Gene Therapy. Blood 2002, 99, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markusic, D.M.; Hoffman, B.E.; Perrin, G.Q.; Nayak, S.; Wang, X.; LoDuca, P.A.; High, K.A.; Herzog, R.W. Effective Gene Therapy for Haemophilic Mice with Pathogenic Factor IX Antibodies. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1698–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Tian, Z. Liver-Mediated Adaptive Immune Tolerance. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoDuca, P.; Hoffman, B.; Herzog, R. Hepatic Gene Transfer as a Means of Tolerance Induction to Transgene Products. Curr. Gene Ther. 2009, 9, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, J.D.; Ozelo, M.C.; Sabatino, D.E.; Franck, H.W.G.; Merricks, E.P.; Crudele, J.M.; Zhou, S.; Kazazian, H.H.; Lillicrap, D.; Nichols, T.C.; et al. Eradication of Neutralizing Antibodies to Factor VIII in Canine Hemophilia A after Liver Gene Therapy. Blood 2010, 116, 5842–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, G.; Park, Y.-S.; Ozelo, M.C.; Chou, S.-C.; Li, M.; Imtiaz, U.; Chavele, K.-M. European Association for Haemophilia and Allied Disorders (EAHAD) 2024 SLAM Session 6. Available online: https://medical.biomarin.com/en-us/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2024/02/EAHAD-2024-GENEr8-INH.pdf?v=1.1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Kaczmarek, R.; Samelson-Jones, B.J.; Herzog, R.W. Immune Tolerance Induction by Hepatic Gene Transfer: First-in-Human Evidence. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberle, V.; Stark, A. Eukaryotic Core Promoters and the Functional Basis of Transcription Initiation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Garcia, C.M.; Finer, J.J. Identification and Validation of Promoters and Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements. Plant Sci. 2014, 217–218, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beagrie, R.A.; Scialdone, A.; Schueler, M.; Kraemer, D.C.A.; Chotalia, M.; Xie, S.Q.; Barbieri, M.; De Santiago, I.; Lavitas, L.-M.; Branco, M.R.; et al. Complex Multi-Enhancer Contacts Captured by Genome Architecture Mapping. Nature 2017, 543, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, A.G.; Baldi, P.; Chauvin, Y.; Brunak, S. The Biology of Eukaryotic Promoter Prediction—A Review. Comput. Chem. 1999, 23, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemyev, V.; Gubaeva, A.; Paremskaia, A.I.; Dzhioeva, A.A.; Deviatkin, A.; Feoktistova, S.G.; Mityaeva, O.; Volchkov, P.Y. Synthetic Promoters in Gene Therapy: Design Approaches, Features and Applications. Cells 2024, 13, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassler, J.S.; Gussin, G.N. [1] Promoters and Basal Transcription Machinery in Eubacteria and Eukaryotes: Concepts, Definitions, and Analogies. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 273, pp. 3–29. ISBN 978-0-12-182174-6. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, S.K.; Rivera-Soto, R.; Gray, S.J. Viral Expression Cassette Elements to Enhance Transgene Target Specificity and Expression in Gene Therapy. Discov. Med. 2015, 19, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gingrich, J.R.; Roder, J. Inducible Gene Expression in the Nervous System of Transgenic Mice. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1998, 21, 377–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlyueva, D.; Stampfel, G.; Stark, A. Transcriptional Enhancers: From Properties to Genome-Wide Predictions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitz, F. Gene Regulation at a Distance: From Remote Enhancers to 3D Regulatory Ensembles. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 57, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calo, E.; Wysocka, J. Modification of Enhancer Chromatin: What, How, and Why? Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huminiecki, Ł.; Horbańczuk, J. Can We Predict Gene Expression by Understanding Proximal Promoter Architecture? Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 530–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natoli, G.; Andrau, J.-C. Noncoding Transcription at Enhancers: General Principles and Functional Models. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2012, 46, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.K.; Prescott, S.L.; Wysocka, J. Ever-Changing Landscapes: Transcriptional Enhancers in Development and Evolution. Cell 2016, 167, 1170–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Huang, C.; Tong, C.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Shao, C.; et al. Regulation of Essential Hepatocyte Functions and Identity by Super-Enhancers in Health and Disease. bioRxiv 2025. bioRxiv:2025.06.04.657826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, B.; Zhu, Z.; Yi, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, G. A Constitutive Super-Enhancer: Homologous Region 3 of Bombyx Mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 318, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, W.A.; Orlando, D.A.; Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Kagey, M.H.; Rahl, P.B.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Master Transcription Factors and Mediator Establish Super-Enhancers at Key Cell Identity Genes. Cell 2013, 153, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutourina, J. Transcription Regulation by the Mediator Complex. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, B.L.; Taatjes, D.J. The Mediator Complex: A Central Integrator of Transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabari, B.R.; Dall’Agnese, A.; Boija, A.; Klein, I.A.; Coffey, E.L.; Shrinivas, K.; Abraham, B.J.; Hannett, N.M.; Zamudio, A.V.; Manteiga, J.C.; et al. Coactivator Condensation at Super-Enhancers Links Phase Separation and Gene Control. Science 2018, 361, eaar3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Yang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y. Super-Enhancer Function and Its Application in Cancer Targeted Therapy. npj Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preissl, S.; Fang, R.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Raviram, R.; Gorkin, D.U.; Zhang, Y.; Sos, B.C.; Afzal, V.; Dickel, D.E.; et al. Single-Nucleus Analysis of Accessible Chromatin in Developing Mouse Forebrain Reveals Cell-Type-Specific Transcriptional Regulation. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.Y.; Willi, M.; Yoo, K.H.; Zeng, X.; Wang, C.; Metser, G.; Hennighausen, L. Hierarchy within the Mammary STAT5-Driven Wap Super-Enhancer. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.I.; Young, R.A.; Sharp, P.A. Super-Enhancer-Mediated RNA Processing Revealed by Integrative MicroRNA Network Analysis. Cell 2017, 168, 1000–1014.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeva, V. Analysis of Genomic Sequence Motifs for Deciphering Transcription Factor Binding and Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotic Cells. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Meng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chang, W. Coordination of FOXA2 and SIRT6 Suppresses the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression through ZEB2 Inhibition. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfrum, C.; Stoffel, M. Coactivation of Foxa2 through Pgc-1β Promotes Liver Fatty Acid Oxidation and Triglyceride/VLDL Secretion. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.-R.; Feng, H.; Huang, F.; Zhu, I.; Portillo-Ledesma, S.; Shi, D.; Zaret, K.S.; Schlick, T.; Landsman, D.; Wang, Q.; et al. Structural Insights into the Cooperative Nucleosome Recognition and Chromatin Opening by FOXA1 and GATA4. Mol. Cell 2024, 84, 3061–3079.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.L.; Loell, K.J.; Cohen, B.A. A Test of the Pioneer Factor Hypothesis Using Ectopic Liver Gene Activation. Elife 2022, 11, e73358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odom, D.T.; Zizlsperger, N.; Gordon, D.B.; Bell, G.W.; Rinaldi, N.J.; Murray, H.L.; Volkert, T.L.; Schreiber, J.; Rolfe, P.A.; Gifford, D.K.; et al. Control of Pancreas and Liver Gene Expression by HNF Transcription Factors. Science 2004, 303, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Park, K.; Cullum, R.; Fuglerud, B.M.; Khoshnoodi, M.; Drissler, S.; Stephan, T.L.; Lotto, J.; Kim, D.; Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. HNF4A Guides the MLL4 Complex to Establish and Maintain H3K4me1 at Gene Regulatory Elements. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.Z.; Yun, J. Increased Expression of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 Alpha Transcribed by Promoter 2 Indicates a Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Wilson, E.R.; Larsen, S.N.; Orellana, W.A.; Hall, M.A.; Stubben, C.; Kabir, A.H.; Affolter, K.; Moffitt, R.A.; Zhang, X.; et al. Differential Control of Growth and Identity by HNF4α Isoforms in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2025, 23, 936–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Huang, P.; Potluri, N.; Wu, D.; Kim, Y.; Rastinejad, F. Multidomain Integration in the Structure of the HNF-4α Nuclear Receptor Complex. Nature 2013, 495, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, É.; Babeu, J.-P.; Simoneau, J.; Raisch, J.; Lavergne, L.; Lévesque, D.; Jolibois, É.; Avino, M.; Scott, M.S.; Boudreau, F.; et al. Human Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4-α Encodes Isoforms with Distinct Transcriptional Functions. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 808–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-C.; Stafford, J.M.; Granner, D.K. SRC-1 and GRIP1 Coactivate Transcription with Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 30847–30850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouketsu, T.; Monma, R.; Miyairi, Y.; Sawatsubashi, S.; Shima, H.; Igarashi, K.; Sugawara, A.; Yokoyama, A. IRF2BP2 Is a Novel HNF4α Co-Repressor: Its Role in Gluconeogenic Gene Regulation via Biochemically Labile Interaction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 615, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedumaran, B.; Hong, S.; Xie, Y.-B.; Kim, Y.-H.; Seo, W.-Y.; Lee, M.-W.; Lee, C.H.; Koo, S.-H.; Choi, H.-S. DAX-1 Acts as a Novel Corepressor of Orphan Nuclear Receptor HNF4α and Negatively Regulates Gluconeogenic Enzyme Gene Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27511–27523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Duffy, T.; Hirota, T.; Kay, S.A. Nuclear Receptor HNF4A Transrepresses CLOCK: BMAL1 and Modulates Tissue-Specific Circadian Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E12305–E12312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Qu, H.; Jia, Z.; Kay, S.A. HNF4A Defines Tissue-Specific Circadian Rhythms by Beaconing BMAL1::CLOCK Chromatin Binding and Shaping the Rhythmic Chromatin Landscape. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, D.B.; Hansen, L.P.; Graves, M.K.; Conley, P.B.; Crabtree, G.R. HNF-1 Alpha and HNF-1 Beta (vHNF-1) Share Dimerization and Homeo Domains, but Not Activation Domains, and Form Heterodimers in Vitro. Genes Dev. 1991, 5, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.K.; Párrizas, M.; Jensen, M.L.; Pruhova, S.; Ek, J.; Boj, S.F.; Johansen, A.; Maestro, M.A.; Rivera, F.; Eiberg, H.; et al. Genetic Evidence That HNF-1α–Dependent Transcriptional Control of HNF-4α Is Essential for Human Pancreatic β Cell Function. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Teeli, A.S.; Winiarczyk, D.; Taguchi, M.; Sakuraba, S.; Kono, H.; Leszczyński, P.; Pierzchała, M.; Taniguchi, H. HNF1A POU Domain Mutations Found in Japanese Liver Cancer Patients Cause Downregulation of HNF4A Promoter Activity with Possible Disruption in Transcription Networks. Genes 2022, 13, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Huang, X.; Han, X.; Ji, L. Loss of HNF1α Function Contributes to Hepatocyte Proliferation and Abnormal Cholesterol Metabolism via Downregulating miR-122: A Novel Mechanism of MODY3. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Xu, J.; Wei, G.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Wang, G.; Li, F.; Jiang, F. HNF1 α Controls Liver Lipid Metabolism and Insulin Resistance via Negatively Regulating the SOCS-3-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 5483946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, L.; Guo, H.; Fan, X.; Liu, T.; Xu, C.; He, Z.; Song, Y.; Gao, L.; Shao, S.; et al. Dominant-Negative HNF1α Mutant Promotes Liver Steatosis and Inflammation by Regulating Hepatic Complement Factor D. iScience 2023, 26, 108018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto-Barbosa, R.; Reis, A.F.; Giuffrida, F.M.A. Update on Clinical Screening of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY). Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Deng, X.; Huang, Z.-W.; Wei, J.; Ding, C.-H.; Feng, R.-X.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Y.-X.; Ding, J.; Qiu, L.; et al. An HNF1α-Regulated Feedback Circuit Modulates Hepatic Fibrogenesis via the Crosstalk between Hepatocytes and Hepatic Stellate Cells. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 930–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, T.G.; De Oliveira, A.G.; Vecina, J.F.; Marin, R.M.; Franco, E.S.; Abdalla Saad, M.J.; De Sousa Maia, M.B. Parkinsonia aculeata (Caesalpineaceae) Improves High-Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance in Mice through the Enhancement of Insulin Signaling and Mitochondrial Biogenesis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 183, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Wang, M.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, J.-W.; Tong, X.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Prox1a Promotes Liver Growth and Differentiation by Repressing Cdx1b Expression and Intestinal Fate Transition in Zebrafish. J. Genet. Genom. 2025, 52, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudas, J.; Elmaouhoub, A.; Mansuroglu, T.; Batusic, D.; Tron, K.; Saile, B.; Papoutsi, M.; Pieler, T.; Wilting, J.; Ramadori, G. Prospero-Related Homeobox 1 (Prox1) Is a Stable Hepatocyte Marker during Liver Development, Injury and Regeneration, and Is Absent from “Oval Cells”. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 126, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F. LYVE1 and PROX1 in the Reconstruction of Hepatic Sinusoids after Partial Hepatectomy in Mice. Folia Morphol. 2017, 76, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.; Kamal, A.; Gomez Ramos, B.; Adrian Segarra, J.M.; Ibarra, I.L.; Dignas, L.; Kindinger, T.; Volz, K.; Rahbari, M.; Rahbari, N.; et al. Active Repression of Cell Fate Plasticity by PROX1 Safeguards Hepatocyte Identity and Prevents Liver Tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2025, 57, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.W.; Ma, S. PROX1: A Key Regulator of Hepatocyte Identity and Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2025, 85, 1957–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoutsi, M.; Dudas, J.; Becker, J.; Tripodi, M.; Opitz, L.; Ramadori, G.; Wilting, J. Gene Regulation by Homeobox Transcription Factor Prox1 in Murine Hepatoblasts. Cell Tissue Res. 2007, 330, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.-H.; Li, T.; Chiang, J.Y.L. A Prospero-Related Homeodomain Protein Is a Novel Co-Regulator of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α That Regulates the Cholesterol 7α-Hydroxylase Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10081–10088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ou, C.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, M.; Liang, K.; Peng, Q.; Gao, Y. The Effect of FOXA3 Overexpression on Hepatocyte Differentiation and Liver Regeneration in a Fah cKO Mouse Model. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, L.; Guo, M.; Wang, D.; Meng, M.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Characterisation of Forkhead Box Protein A3 as a Key Transcription Factor for Hepatocyte Regeneration. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.Y.; Dama, G.; Liu, Y.L.; Guo, W.Y.; Lin, J.T. Combinational Overexpression of Foxa3 and Hnf4a Enhance the Proliferation and Prolong the Functional Maintenance of Primary Hepatocytes. Mol. Biol. 2023, 57, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereghini, S. Liver-Enriched Transcription Factors and Hepatocyte Differentiation. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; White, P.; Tuteja, G.; Rubins, N.; Sackett, S.; Kaestner, K.H. Foxa1 and Foxa2 Regulate Bile Duct Development in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomofuji, K.; Kondo, J.; Onuma, K.; Coppo, R.; Horie, H.; Oyama, K.; Miyoshi, E.; Fukumitsu, K.; Ishii, T.; Hatano, E.; et al. Hepatocyte Differentiation from Mouse Liver Ductal Organoids by Transducing 4 Liver-Specific Transcription Factors. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, I.; Moeller, M.M.; Guiggey, D.; Chiang, A.; Maloy, M.; Ogoke, O.; Groth, T.; Mon, T.; Meamardoost, S.; Liu, X.; et al. FOXA1/2 Depletion Drives Global Reprogramming of Differentiation State and Metabolism in a Human Liver Cell Line and Inhibits Differentiation of Human Stem Cell-derived Hepatic Progenitor Cells. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Gao, W.; Ma, S.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; An, F.; Qi, J.; Yang, Z. Role of HNF6 in Liver Homeostasis and Pathophysiology. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyaguchi, D.; Yao, M.; Watanabe, N.; Nishihira, J.; Tanaka, I. DNA Recognition Mechanism of the ONECUT Homeodomain of Transcription Factor HNF-6. Structure 2007, 15, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, H. Advances in the Relationship between AP-1 and Tumorigenesis, Development and Therapy Resistance. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, J.I.; Crissey, M.A.S.; Leu, J.P.; Ciliberto, G.; Taub, R. Interleukin-6-Induced STAT3 and AP-1 Amplify Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 1-Mediated Transactivation of Hepatic Genes, an Adaptive Response to Liver Injury. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, S.; Korbelik, M. Upregulation of Genes for C-Reactive Protein and Related Pentraxin/Complement Proteins in Photodynamic Therapy-Treated Human Tumor Cells: Enrolment of PI3K/Akt and AP-1. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelins’ka, A.M.; Akimov, O.Y.; Kostenko, V.O. Role of AP-1 Transcriptional Factor in Development of Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress in Periodontal Tissues during Systemic Inflammatory Response. Ukr. Biochem. J. 2019, 91, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Gao, X.; Deng, H. AP-1 Is a Regulatory Transcription Factor of Inflammaging in the Murine Kidney and Liver. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakiri, L.; Hasenfuss, S.C.; Wagner, E.F. A FATal AP-1 Dimer Switch in Hepatosteatosis. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1218–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, C.; Vennegeerts, T.; Beuers, U.; Rust, C. The Human Transcription Factor AP-1 Is a Mediator of Bile Acid-Induced Liver Cell Apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaulian, E.; Karin, M. AP-1 in Cell Proliferation and Survival. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2390–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Muck, J.S.; Ustyantsev, K.; Kortman, G.; Hartung, J.; Berezikov, E.; Calkhoven, C.F. Enhanced C/EBPα Function Extends Healthspan and Lifespan in the African Turquoise Killifish. Aging Cell 2025, 24, e70211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolosano, E.; Altruda, F. Hemopexin: Structure, Function, and Regulation. DNA Cell Biol. 2002, 21, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischoulon, D.; Rana, B.; Bucher, N.L.R.; Farmer, S.R. Growth-Dependent Inhibition of CCAAT Enhancer-Binding Protein (C/EPBα) Gene Expression during Hepatocyte Proliferation in the Regenerating Liver and in Culture. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1992, 12, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-C.; Jeong, W.-J.; Seo, S.H.; Choi, K.-Y. WDR76 Mediates Obesity and Hepatic Steatosis via HRas Destabilization. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Cao, J.; Meng, S.; Ma, A.; Radovick, S.; Wondisford, F.E. Activation of Basal Gluconeogenesis by Coactivator P300 Maintains Hepatic Glycogen Storage. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.; Lu, S.; Su, Y.; Ding, D.; Tao, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. C/EBP-α Induces Autophagy by Binding to Beclin1 through Its Own Acetylation Modification in Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 405, 112721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramji, D.P.; Vitelli, A.; Tronche, F.; Cortese, R.; Ciliberto, G. The Two C/EBP Isoforms, IL6DBP/NFIL6 and CEBP6δ/NFIL63, Are Induced by IL6β to Promote Acute Phase Gene Transcription via Different Mechanisms. Nucl. Acids Res. 1993, 21, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ge, Y.; Chai, Y.; Kou, C.; Sun, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. THSR Mediated MiR374b Targeting C/EBP β/FOXO1 to Accelerate Thyroid Stimulating Hormone-Induced Hepatic Steatosis. Hepatic Med. Évid. Res. 2024, 16, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Wysocka, J. Deciphering the Multi-Scale, Quantitative Cis-Regulatory Code. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, E.; Messerle, M. Development of a Cytomegalovirus Vector for Somatic Gene Therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000, 25, S80–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arad, U.; Zeira, E.; El-Latif, M.A.; Mukherjee, S.; Mitchell, L.; Pappo, O.; Galun, E.; Oppenheim, A. Liver-Targeted Gene Therapy by SV40-Based Vectors Using the Hydrodynamic Injection Method. Hum. Gene Ther. 2005, 16, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, K.N.; Maneval, D.C.; Menzel, P.; Harris, M.P.; Sutjipto, S.; Vaillancourt, M.-T.; Huang, W.-M.; Johnson, D.E.; Anderson, S.C.; Wen, S.F.; et al. Development and Characterization of Recombinant Adenoviruses Encoding Human P53 for Gene Therapy of Cancer. Hum. Gene Ther. 1994, 5, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettinger, S.D.; Kennedy, S.C.; Wu, X.; Saylors, R.L.; Hafenrichter, D.G.; Flye, M.W.; Ponder, K.P. Liver-Directed Gene Therapy: Quantitative Evaluationof Promoter Elements by Using in Vivo Retroviral Transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, D.A.; Shutova, M.V.; Johnston, N.R.; Smith, O.P.; Fedorin, V.V.; Kukushkin, Y.S.; Van Der Loo, J.C.M.; Johnstone, E.C. The Clinical Landscape for AAV Gene Therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.G.; Barajas, M.; Razquin, N.; Berraondo, P.; Rodrigo, M.; Wu, C.; Qian, C.; Fortes, P.; Prieto, J. In Vitro and in Vivo Comparative Study of Chimeric Liver-Specific Promoters. Mol. Ther. 2003, 7, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Ding, Y.; Pahud, D.R.; Chang, E.; Imperiale, M.J.; Bromberg, J.S. Promoter Attenuation in Gene Therapy: Interferon-γ and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibit Transgene Expression. Hum. Gene Ther. 1997, 8, 2019–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, H.; Herzog, R.W.; Hagstrom, J.N.; Walter, J.; Kung, S.-H.; Yang, E.Y.; Tai, S.J.; Iwaki, Y.; Kurtzman, G.J.; Fisher, K.J.; et al. Adeno-Associated Viral Vector-Mediated Gene Transfer of Human Blood Coagulation Factor IX Into Mouse Liver. Blood 1998, 91, 4600–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannell, D.; Ellis, J. Silencing of Gene Expression: Implications for Design of Retrovirus Vectors. Rev. Med. Virol. 2001, 11, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaji, S.Y.; Ngai, S.C.; Abdullah, S. Silencing of Transgene Expression in Mammalian Cells by DNA Methylation and Histone Modifications in Gene Therapy Perspective. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2019, 35, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D. Epigenetic Modification Enzymes: Catalytic Mechanisms and Inhibitors. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2013, 3, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, D.; Hensel, J.; Higgs, J.; Grover, R.; Kaza, N.; Ponnazhagan, S. Effects of Cellular Methylation on Transgene Expression and Site-Specific Integration of Adeno-Associated Virus. Genes 2017, 8, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, B.K.; Herzog, R.W. Evading the Immune Response upon in Vivo Gene Therapy with Viral Vectors. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2009, 11, 493–503. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Yan, H.; Ou, H. Human Thyroxine Binding Globulin (TBG) Promoter Directs Efficient and Sustaining Transgene Expression in Liver-Specific Pattern. Gene 2012, 506, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.; Domenger, C.; Choksi, P.; Krämer, C.; Baumgartl, C.; Maiakovska, O.; Kim, J.-J.; Weinmann, J.; Huber, G.; Schmidt, F.; et al. Identification of a Robust Promoter in Mouse and Human Hepatocytes by in Vivo Biopanning of a Barcoded AAV Library. Mol. Ther. 2025, 33, 3881–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, O.; Collantes, M.; Gazquez, C.; Moreno, D.; Hernandez-Alcoceba, R.; Barberia, M.; Ecay, M.; Tamarit, B.; Douar, A.; Ferrer, V.; et al. High Value of 64Cu as a Tool to Evaluate the Restoration of Physiological Copper Excretion after Gene Therapy in Wilson’s Disease. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 26, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, T.S.; Torres, E.V. Pharmaceutical Compositions Containing Adeno-Associated Viral Vector. U.S. Patent 18/551,038, 19 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Aldabe, R.; Lantero, A.; Aseguinolaza, G.G. Gene Therapy Vectors Comprising s/Mar Sequences. 2019. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2019219649A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- D’Avola, D.; López-Franco, E.; Sangro, B.; Pañeda, A.; Grossios, N.; Gil-Farina, I.; Benito, A.; Twisk, J.; Paz, M.; Ruiz, J.; et al. Phase I Open Label Liver-Directed Gene Therapy Clinical Trial for Acute Intermittent Porphyria. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, M.S.R.; Petry, H.; Twisk, J.; Deventer, S.J.H.V.; Ruiz, E.C.S.; Ramirez, A.T. Alanine-Glyoxylate Aminotransferase Therapeutics. 2010. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2010087709A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Romá, A.F.; Aseguinolaza, G.G.; Pena, M.S.R.; Rodriguez, M.A.P.; Twisk, J.; Valtueña, J.M.P.; Petry, H.; Deventer, S.J.H.V. Porphobilinogen Deaminase Gene Therapy. 2010. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2010036118A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- George, L.A.; Sullivan, S.K.; Giermasz, A.; Rasko, J.E.J.; Samelson-Jones, B.J.; Ducore, J.; Cuker, A.; Sullivan, L.M.; Majumdar, S.; Teitel, J.; et al. Hemophilia B Gene Therapy with a High-Specific-Activity Factor IX Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wilson, J.M. Gene Therapy for Treating Hemophilia b. 2017. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US11191847B2 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- BioMarin Corporate. U.S. FDA Placed a Clinical Hold on BMN 307 Phearless Phase 1/2 Gene Therapy Study in Adults with PKU Based on Interim Pre-Clinical Study Findings—BioMarin Corporate. Available online: https://www.biomarin.com/news/press-releases/u-s-fda-placed-a-clinical-hold-on-bmn-307-phearless-phase-1-2-gene-therapy-study-in-adults-with-pku-based-on-interim-pre-clinical-study-findings/ (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Wright, J.B.; Sookiasian, D.L.; Martin, T.B.S.; Francone, O.; Seymour, A.B. Adeno-Associated Virus Compositions for Restoring Pah Gene Function and Methods of Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 12,076,420, 3 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, L. Optimized PAH gene and Expression Cassette and Use Thereof. 2024. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2024094044A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Yasuda, M.; Huston, M.W.; Pagant, S.; Gan, L.; Martin, S.S.; Sproul, S.; Richards, D.; Ballaron, S.; Hettini, K.; Ledeboer, A.; et al. AAV2/6 Gene Therapy in a Murine Model of Fabry Disease Results in Supraphysiological Enzyme Activity and Effective Substrate Reduction. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 18, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.E.; Lorget, F.; Prawdzik, G.; Falaleeva, M.; Cao, L.; Falese, L.; Huston, M.W.; Hettini, K.; Lu, Y.; Ledeboer, A. A 3-Month Gene Therapy Single-Dose IV Administration Pharmacology and Safety Study with ST-920 (Isaralgagene Civaparvovec) for Fabry Disease in Mice. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2024, 141, 107963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passalacqua, C.; Huston, M.; Souberbielle, B. Methods for Use of Viral Vector Constructs for the Treatment of Fabry Disease. U.S. Patent 18/707,085, 8 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- D’Antiga, L.; Beuers, U.; Ronzitti, G.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Baumann, U.; Di Giorgio, A.; Aronson, S.; Hubert, A.; Romano, R.; Junge, N.; et al. Gene Therapy in Patients with the Crigler–Najjar Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingozzi, F.; Colella, P. Hybrid Regulatory Elements. 2019. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2019154939A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Bella, T.L.; Ronzitti, G.; Siauve, J. Hybrid Aav Vector Enhancing Transgene Expression in the Liver. 2024. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2024079249A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Anguela, X.; Armour, S.; Nordin, J. Codon-Optimized Acid Alpha-Glucosidase Expression Cassettes and Methods of Using Same. U.S. Patent 12,084,693, 10 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Vanglusagene Ensiparvovec. Available online: https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/ui/substances/Y47XZ2EW2J (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Comper, F.; Miranda, C.J.; Liou, B.; Dodev, T.; Jeyakumar, J.M.; Canavese, M.; Cocita, C.; Khoshrou, K.; Tiscornia, G.; Chisari, E.; et al. FLT201, a Novel Liver-Directed AAV Gene Therapy Candidate for Gaucher Disease Type 1. Mol. Ther. 2025, 33, 3789–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipe, S.W.; Leebeek, F.W.G.; Recht, M.; Key, N.S.; Castaman, G.; Miesbach, W.; Lattimore, S.; Peerlinck, K.; Van Der Valk, P.; Coppens, M.; et al. Gene Therapy with Etranacogene Dezaparvovec for Hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubelski, J.; Plessis, D.J.F.D.; Liu, Y.P.; Brake, O.T.; Gonzalez, J.M.I.; Fraser, R.; Roberts, M. Liver-Specific Viral Promoters and Methods of Using the Same. U.S. Patent 12,319,924, 3 June 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Reiss, U.M.; Davidoff, A.M.; Tuddenham, E.G.D.; Chowdary, P.; McIntosh, J.H.; Riddell, A.; Pie, A.; Batty, P.; Calvert, J.C.M.; Mangles, S.; et al. Stable Therapeutic Transgenic FIX Levels for More Than 10 Years in Subjects with Severe Hemophilia B Who Received scAAV2/8-LP1-Hfixco Adeno-Associated Virus Gene Therapy. Blood 2023, 142, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathwani, A.C.; Gray, J.T.; Ng, C.Y.C.; Zhou, J.; Spence, Y.; Waddington, S.N.; Tuddenham, E.G.D.; Kemball-Cook, G.; McIntosh, J.; Boon-Spijker, M.; et al. Self-Complementary Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors Containing a Novel Liver-Specific Human Factor IX Expression Cassette Enable Highly Efficient Transduction of Murine and Nonhuman Primate Liver. Blood 2006, 107, 2653–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathwani, A.C.; Reiss, U.M.; Tuddenham, E.G.D.; Rosales, C.; Chowdary, P.; McIntosh, J.; Della Peruta, M.; Lheriteau, E.; Patel, N.; Raj, D.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Factor IX Gene Therapy in Hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1994–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, U.M.; Davidoff, A.M.; Tuddenham, E.G.D.; Chowdary, P.; McIntosh, J.; Muczynski, V.; Journou, M.; Simini, G.; Ireland, L.; Mohamed, S.; et al. Sustained Clinical Benefit of AAV Gene Therapy in Severe Hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.S.; Rubin, H.; Wang, M.; Faulkner, D.; Sengooba, A.; Dollive, S.N.; Avila, N.; Ellsworth, J.L.; Lamppu, D.; Lobikin, M.; et al. Sustained Correction of a Murine Model of Phenylketonuria Following a Single Intravenous Administration of AAVHSC15-PAH. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iles-Somaratne, J.N.; Cohn, G.M.; Glyman, S.A.; Tzianabos, A.O. Improved Gene Therapy Methods 2022. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2022099301A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Shioshita, G. P008: pheEDIT: A Phase 1, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Safety and Efficacy Gene Editing Study Evaluating HMI-103 in Adults with Classical PKU. Genet. Med. Open 2023, 1, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdary, P.; Reiss, U.M.; Tuddenham, E.G.D.; Batty, P.; McIntosh, J.H.; Radulescu, V.C.; Chang, E.; Laffan, M.A.; Riddell, A.; Calvert, J.C.M.; et al. GO-8: Stable Expression of Factor VIII over 5 Years Following Adeno-Associated Gene Transfer in Subjects with Hemophilia a Using a Novel Human Factor VIII Variant. Blood 2023, 142, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathwani, A.; Ward, N.; Thrasher, A.; Tuddenham, E.; Mcvey, J.; Gray, J.; Davidoff, A. Codon-Optimized Factor vi i i Variants and Synthetic Liver-Specific Promoter. 2011. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US9393323B2 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Rangarajan, S.; Walsh, L.; Lester, W.; Perry, D.; Madan, B.; Laffan, M.; Yu, H.; Vettermann, C.; Pierce, G.F.; Wong, W.Y.; et al. AAV5–Factor VIII Gene Transfer in Severe Hemophilia A. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, J.; Lenting, P.J.; Rosales, C.; Lee, D.; Rabbanian, S.; Raj, D.; Patel, N.; Tuddenham, E.G.D.; Christophe, O.D.; McVey, J.H.; et al. Therapeutic Levels of FVIII Following a Single Peripheral Vein Administration of rAAV Vector Encoding a Novel Human Factor VIII Variant. Blood 2013, 121, 3335–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettermann, C. Methods of Treating Anti-Aav Seropositive Hemophilia Patients. 2024. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2024238591A2 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Chowdary, P.; Shapiro, S.; Makris, M.; Evans, G.; Boyce, S.; Talks, K.; Dolan, G.; Reiss, U.; Phillips, M.; Riddell, A.; et al. Phase 1–2 Trial of AAVS3 Gene Therapy in Patients with Hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyvandi, F.; Garagiola, I. Clinical Advances in Gene Therapy Updates on Clinical Trials of Gene Therapy in Haemophilia. Haemophilia 2019, 25, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, A.; Corbau, R. Transcription Regulatory Elements. 2021. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2021084277A2 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Jeyakumar, J.M.; Kia, A.; Tam, L.C.S.; McIntosh, J.; Spiewak, J.; Mills, K.; Heywood, W.; Chisari, E.; Castaldo, N.; Verhoef, D.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of FLT190, a Liver-Directed AAV Gene Therapy for Fabry Disease. Gene Ther. 2023, 30, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Zhang, B.; Ye, J.; Xiao, L.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y. Engineered Human Fviii with Enhanced Secretion Ability and Clotting Activity. U.S. Patent 17/774,450, 1 August 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Yang, L. Engineered Liver-Specific Core Promoters and Their Applications. 2024. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2024230802A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Cao, Q.; Wen, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L. Coagulation factor fviii protein variant, expression vector and use 2024. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2024255448A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Anguela, X. Factor Viii (Fviii) Gene Therapy Methods. U.S. Patent 18/803,700, 6 March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Elkouby, L.; Armour, S.M.; Toso, R.; DiPietro, M.; Davidson, R.J.; Nguyen, G.N.; Willet, M.; Kutza, S.; Silverberg, J.; Frick, J.; et al. Preclinical Assessment of an Optimized AAV-FVIII Vector in Mice and Non-Human Primates for the Treatment of Hemophilia A. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 24, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguela, X.; Shen, S.H. Cpg Reduced Factor Viii Variants, Compositions and Methods and Uses for Treatment of Hemostasis Disorders. U.S. Patent 11,168,124, 9 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Konkle, B.A.; Walsh, C.E.; Escobar, M.A.; Josephson, N.C.; Young, G.; Von Drygalski, A.; McPhee, S.W.J.; Samulski, R.J.; Bilic, I.; De La Rosa, M.; et al. BAX 335 Hemophilia B Gene Therapy Clinical Trial Results: Potential Impact of CpG Sequences on Gene Expression. Blood 2021, 137, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horling, F.; Lengler, J.; Falkner, F.; Rottensteiner, H.; Scheiflinger, F. Viral Vectors Encoding Recombinant Fix with Increased Expression for Gene Therapy of Hemophilia b. U.S. Patent 10,842,853, 24 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lengler, J.; Weiller, M.; Horling, F.; Mayrhofer, J.; Schuster, M.; Falkner, F.G.; Gil-Farina, I.; Klugmann, M.; Scheiflinger, F.; Hoellriegl, W.; et al. Preclinical Development of TAK-754, a High-Performance AAV8-Based Vector Expressing Coagulation Factor VIII. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2025, 33, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkner, F.-G.; Horling, F.; Lengler, J.; Rottensteiner, H.; Scheiflinger, F. Viral Vectors Encoding Recombinant Fviii Variants with Increased Expression for Gene Therapy of Hemophilia a. U.S. Patent 10,189,888, 29 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rottensteiner, H.; Hoellriegl, W. Gene Therapy of Hemophilia a Using Viral Vectors Encoding Recombinant Fviii Variants with Increased Expression. 2021. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2021119357A2/en (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Zozulya, N.; Ptushkin, V.; Davydkin, I.; Ivanov, V.; Korobkin, A.; Zorenko, V.; Uss, A.; Fatenkova, E.; Yudina, N.; Linkova, Y.; et al. Arvenacogene Sanparvovec, A Novel Option for Hemophilia B Gene Therapy: First-in-Human Findings. Available online: https://library.ehaweb.org/eha/2025/eha2025-congress/4161329/nadezhda.zozulya.arvenacogene.sanparvovec.a.novel.option.for.hemophilia.b.gene.html?f=menu%3D6%2Abrowseby%3D8%2Asortby%3D2%2Amedia%3D3%2Ace_id%3D2882%2Aot_id%3D31584%2Amarker%3D5844%2Afeatured%3D19595 (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Prokofyev, A.V.; Gershovich, P.M.; Strelkova, A.N.; Spirina, N.A.; Shugaeva, T.E.; Morozov, D.V. Codon-Optimized Nucleic Acid Encoding the Fix Protein. U.S. Patent 18/280,338, 7 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Pipe, S.W.; Arruda, V.R.; Lange, C.; Kitchen, S.; Eichler, H.; Wadsworth, S. Characteristics of BAY 2599023 in the Current Treatment Landscape ofHemophilia A Gene Therapy. Curr. Gene Ther. 2023, 23, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greig, J.A.; Wang, Q.; Reicherter, A.L.; Chen, S.-J.; Hanlon, A.L.; Tipper, C.H.; Clark, K.R.; Wadsworth, S.; Wang, L.; Wilson, J.M. Characterization of Adeno-Associated Viral Vector-Mediated Human Factor VIII Gene Therapy in Hemophilia A Mice. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wilson, J.M.; Sidrane, J.A. Gene Therapy for Treating Hemophilia a. 2017. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2017180857A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Cataldo, J.; Allen, J.; Sankoh, S.; Weiss, K.; Askari, F. eP140: A Novel, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Seamless Phase 1/2/3 AAV9 Gene Therapy Study for Wilson Disease. Genet. Med. 2022, 24, S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, C.; Wadsworth, S. Gene Therapy Constructs for Treating Wilson Disease. U.S. Patent 12,338,450, 24 June 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Nambiar, B.; Cornell Sookdeo, C.; Berthelette, P.; Jackson, R.; Piraino, S.; Burnham, B.; Nass, S.; Souza, D.; O’Riordan, C.R.; Vincent, K.A.; et al. Characteristics of Minimally Oversized Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors Encoding Human Factor VIII Generated Using Producer Cell Lines and Triple Transfection. Hum. Gene Ther. Methods 2017, 28, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyostio-Moore, S.; Manavalan, P. Generation of Improved Human Pah for Treatment of Severe Pku by Liver-Directed Gene Replacement Therapy. 2020. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2020077250A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Leavitt, A.D.; Konkle, B.A.; Stine, K.C.; Visweshwar, N.; Harrington, T.J.; Giermasz, A.; Arkin, S.; Fang, A.; Plonski, F.; Yver, A.; et al. Giroctocogene Fitelparvovec Gene Therapy for Severe Hemophilia A: 104-Week Analysis of the Phase 1/2 Alta Study. Blood 2024, 143, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, B.E. Liver-Specific Constructs, Factor Viii Expression Cassettes and Methods of Use Thereof. 2017. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2017074526A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Conner, J.E.; Crawford, L.A.; Damitz, R.; Davis, B.M.; Hodge, C.M.; Kimmel, M.L., II; Willard, T.Q.; Ramsey, P.; Thorne, D.J.; Young, A.L. Improved Pharmaceutical Compositions Containing Adeno-Associated Viral Vector. U.S. Patent 18/258,027, 29 February 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Weiller, M.; Wang, H.; Coulibaly, S.; Schuster, M.; Rottensteiner, H.; Sun, K.; Chuah, M.K.; Vandendriessche, T.; Scheiflinger, F.; Höllriegl, W. Evaluation of the Human Factor IX Gene Therapy Vector TAK-748 in Hemophilia: Results from Non-Clinical Studies in Factor IX Knockout Mice and Rhesus Monkeys. Blood 2019, 134, 4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Jiabao, H.; Wei, L.; Shin-Shay, T.; Bin, L.; Xi, Z.; Zhao, X.P. Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Vector and Method for Treating or Preventing Hemophilia b. 2023. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2023280323A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Brown, H.C.; Zakas, P.M.; George, S.N.; Parker, E.T.; Spencer, H.T.; Doering, C.B. Target-Cell-Directed Bioengineering Approaches for Gene Therapy of Hemophilia A. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2018, 9, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doering, C.B.; Spencer, T.H.; Brown, H.C. Recombinant Promoters and Vectors for Protein Expression in Liver and Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 10,058,624, 28 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, H. Nucleic Acid and Amino Acid Sequences Encoding High-Level Expressor Factor Viii Polypeptides and Methods of Use. 2022. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2022165390A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Yu, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Rao, Y. Isolated Nucleic Acid Molecule and Use Thereof. 2023. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2023078220A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Yu, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, E.; Dai, X.; Rao, Y. Isolated Nucleic Acid Molecule and Application Thereof. U.S. Patent 17/788,713, 5 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Ferla, R.; Ginocchio, V.M.; Rossi, A.; Fecarotta, S.; Romano, R.; Parenti, G.; Yildiz, Y.; Zancan, S.; Pecorella, V.; et al. Liver-Directed Adeno-Associated Virus–Mediated Gene Therapy for Mucopolysaccharidosis Type VI. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2200052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auricchio, A.; Alliegro, M.; Ferla, R. Combined Therapy for Mucopolysaccharidosis Type vi (Maroteaux-Lamy-Syndrome). 2018. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2018046737A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Rosenberg, M. First Patient Dosed with Gene Therapy in Phase 1/2 Study of ACTUS-101 in Patients with Pompe Disease. AskBio 2019. Available online: https://www.askbio.com/first-patient-dosed-with-gene-therapy-in-phase-1-2-study-of-actus-101-in-patients-with-pompe-disease/ (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Hopkins, S.; Smith, E.C. Therapeutic Adeno-Associated Virus for Treating Pompe Disease with Long Term Cessation of Gaa Enzyme Replacement Therapy. U.S. Patent 18/840,822, 22 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Pipe, S.; Poma, A.; Rajasekhar, A.; Everington, T.; Sankoh, S.; Allen, J.; Cataldo, J.; Crombez, E. Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: Results from the Phase 1/2 101HEMB01/02 Studies. Blood Adv. 2025, 9, 2980–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wilson, J.M. Compositions Useful in Treatment of Otc Deficency. U.S. Patent 9,890,365, 13 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Warzecha, C.C.; Kistner, A.; Chichester, J.A.; Bell, P.; Buza, E.L.; He, Z.; Pampena, M.B.; Couthouis, J.; Sethi, S.; et al. Prednisolone Reduces the Interferon Response to AAV in Cynomolgus Macaques and May Increase Liver Gene Expression. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 24, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bell, P.; Morizono, H.; He, Z.; Pumbo, E.; Yu, H.; White, J.; Batshaw, M.L.; Wilson, J.M. AAV Gene Therapy Corrects OTC Deficiency and Prevents Liver Fibrosis in Aged OTC-Knock out Heterozygous Mice. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 120, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Morizono, H.; Bell, P.; Jones, D.; Lin, J.; McMenamin, D.; Yu, H.; Batshaw, M.L.; Wilson, J.M. Sustained Correction of OTC Deficiency in Spfash Mice Using Optimized Self-Complementary AAV2/8 Vectors. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li, D.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, T.; Yuan, L.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Jiang, W.; Wu, X.; et al. Improved Human Coagulation Factor Viii Gene Expression Cassette and Use Thereof. 2024. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2024060463A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Xue, F.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, F.; Tang, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Chi, Y.; Zheng, J.; et al. Safety and Activity of an Engineered, Liver-Tropic Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Expressing a Hyperactive Padua Factor IX Administered with Prophylactic Glucocorticoids in Patients with Haemophilia B: A Single-Centre, Single-Arm, Phase 1, Pilot Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2022, 9, e504–e513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, D.A.; Derks, T.G.; Rodriguez-Buritica, D.F.; Ahmad, A.; Couce, M.; Mitchell, J.J.; Riba-Wolman, R.; Mount, M.; Sallago, J.B.; Ross, K.M.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of DTX401, an AAV8-Mediated Liver-Directed Gene Therapy, in Adults with Glycogen Storage Disease Type I a (GSDIa). J. Inher Metab. Disea 2025, 48, e70014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipper, C.; Clark, K.R.; Wadsworth, S. Methods and Compositions for Treating Glycogen Storage Diseases. 2020. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2020132115A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Liefhebber, J.M.P.; Brasser, G.; Spronck, E.A.; Ottenhoff, R.; Paerels, L.; Ferraz, M.J.; Schwarz, L.K.; Efthymiopoulou, N.; Kuo, C.-L.; Montenegro-Miranda, P.S.; et al. Preclinical Efficacy and Safety of Adeno-Associated Virus 5 Alpha-Galactosidase: A Gene Therapy for Fabry Disease. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2024, 32, 101375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janciauskiene, S.; Welte, T. Well-Known and Less Well-Known Functions of Alpha-1 Antitrypsin. Its Role in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Other Disease Developments. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, S280–S288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamala, N.; Martínez, M.T.; Lara, B.; Pérez, L.; Vázquez, I.; Jimenez, A.; Barquín, M.; Ferrarotti, I.; Blanco, I.; Janciauskiene, S.; et al. Alternative Transcripts of the SERPINA1 Gene in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.; Chappell, S.; Guetta-Baranés, T.; Morley, S.; Kalsheker, N. The Alpha-1-Antitrypsin Gene Promoter in Human A549 Lung Derived Cells, and a Novel Transcription Initiation Site. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.L.; Chandra, T.; Woo, S.L.C.; Davie, E.W.; Kurachi, K. Complete Sequence of the cDNA for Human. Alpha. 1-Antitrypsin and the Gene for the S Variant. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 4828–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciliberto, G.; Dente, L.; Cortese, R. Cell-Specific Expression of a Transfected Human A1-Antitrypsin Gene. Cell 1985, 41, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, V.; Ciliberto, G.; Hardon, E.; Paonessa, G.; Palla, F.; Lundberg, L.; Cortese, R. Cis- and Trans-Acting Elements Responsible for the Cell-Specific Expression of the Human Alpha 1-Antitrypsin Gene. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, K.; Scobie, G.; Marsters, P.; Kalsheker, N.A. Mutation in an A1-Antitrypsin Enhancer Results in an Interleukin-6 Deficient Acute-Phase Response Due to Loss of Cooperativity between Transcription Factors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 1997, 1362, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.; Kalsheker, N.A. Regulation of the Serine Proteinase Inhibitor (SERPIN) Gene A1-Antitrypsin: A Paradigm for Other SERPINs. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, M.K.; Petrus, I.; De Bleser, P.; Le Guiner, C.; Gernoux, G.; Adjali, O.; Nair, N.; Willems, J.; Evens, H.; Rincon, M.Y.; et al. Liver-Specific Transcriptional Modules Identified by Genome-Wide In Silico Analysis Enable Efficient Gene Therapy in Mice and Non-Human Primates. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadani, U.; Costa, R.H. The Transcriptional Activator Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 6 Regulates Liver Gene Expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 6273–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.H.; Grayson, D.R.; Darnell, A.E. Multiple Hepatocyte-Enriched Nuclear Factors Function in the Regulation of Transthyretin and A1-Antitrypsin Genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1989, 9, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, K.P.; Dunbar, R.P.; Wilson, D.R.; Darlington, G.J.; Woo, S.L.C. Evaluation of Relative Promoter Strength in Primary Hepatocytes Using Optimized Lipofection. Hum. Gene Ther. 1991, 2, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafenrichter, D.; Wu, X.; Rettinger, S.; Kennedy, S.; Flye, M.; Ponder, K. Quantitative Evaluation of Liver-Specific Promoters from Retroviral Vectors after in Vivo Transduction of Hepatocytes. Blood 1994, 84, 3394–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Liang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Du, J.; Zhan, L. Evaluation of Hepatitis B Virus Promoters for Sustained Transgene Expression in Mice by Bioluminescence Imaging. Virus Res. 2010, 149, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Mendioroz, I.; Sampedro, A.; Alegre, M.; Enríquez De Salamanca, R.; Berraondo, P.; Fontanellas, A. An Inducible Promoter Responsive to Different Porphyrinogenic Stimuli Improves Gene Therapy Vectors for Acute Intermittent Porphyria. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Mendioroz, I.; Sampedro, A.; Serna, N.; De Salamanca, R.E.; Sanz-Parra, A.; Corrales, F.; Berraondo, P.; Millet, O.; Fontanellas, A. Bioengineered PBGD Variant Improves the Therapeutic Index of Gene Therapy Vectors for Acute Intermittent Porphyria. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3688–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.-J.; Allan, C.; Grehan, S.; Tse, E.; Moran, C.; Taylor, J.M. Duplicated Downstream Enhancers Control Expression of the Human Apolipoprotein E Gene in Macrophages and Adipose Tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 31567–31572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.P.; Lin, A.; Bloom, J.S.; Khan, A.H.; Park, C.C.; Smith, D.J. Screening Reveals Conserved and Nonconserved Transcriptional Regulatory Elements Including an E3/E4 Allele-Dependent APOE Coding Region Enhancer. Genomics 2008, 92, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.; Walker, D.; Taylor, S.; Allan, C.; Chin, P.; Fan, J.; Taylor, J. Structure of the Hepatic Control Region of the Human Apolipoprotein E/C-I Gene Locus. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 22577–22585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shachter, N.; Zhu, Y.; Walsh, A.; Breslow, J.; Smith, J. Localization of a Liver-Specific Enhancer in the Apolipoprotein E/C-I/C-II Gene Locus. J. Lipid Res. 1993, 34, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, C.M.; Taylor, S.; Taylor, J.M. Two Hepatic Enhancers, HCR.1 and HCR.2, Coordinate the Liver Expression of the Entire Human Apolipoprotein E/C-I/C-IV/C-II Gene Cluster. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29113–29119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, T.; Huber, R.M.; Bowling, W.; Pearline, R.; Kennedy, S.C.; Flye, M.W.; Ponder, K.P. Liver-Directed Gene Therapy: A Retroviral Vector with a Complete LTR and the ApoE Enhancer-α1-Antitrypsin Promoter Dramatically Increases Expression of Human α1-Antitrypsin In Vivo. Hum. Gene Ther. 1996, 7, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Linthout, S.; Collen, D.; De Geest, B. Effect of Promoters and Enhancers on Expression, Transgene DNA Persistence, and Hepatotoxicity After Adenoviral Gene Transfer of Human Apolipoprotein A-I. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, F.; Snoeys, J.; Feng, Y.; Van Craeyveld, E.; Lievens, J.; Armentano, D.; Cheng, S.H.; De Geest, B. Direct Comparison of Hepatocyte-Specific Expression Cassettes Following Adenoviral and Nonviral Hydrodynamic Gene Transfer. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.; Okuyama, T.; Cai, S.-R.; Kennedy, S.C.; Bowling, W.M.; Flye, M.W.; Ponder, K.P. Therapeutic Levels of Functional Human Factor X in Rats After Retroviral-Mediated Hepatic Gene Therapy. Blood 1997, 89, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geest, B.R.; Van Linthout, S.A.; Collen, D. Humoral Immune Response in Mice against a Circulating Antigen Induced by Adenoviral Transfer Is Strictly Dependent on Expression in Antigen-Presenting Cells. Blood 2003, 101, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingozzi, F.; Liu, Y.-L.; Dobrzynski, E.; Kaufhold, A.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Arruda, V.R.; High, K.A.; Herzog, R.W. Induction of Immune Tolerance to Coagulation Factor IX Antigen by in Vivo Hepatic Gene Transfer. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.H.; Ohashi, K.; Patijn, G.A.; Meuse, L.; Ye, X.; Thompson, A.R.; Kay, M.A. Inclusion of the Hepatic Locus Control Region, an Intron, and Untranslated Region Increases and Stabilizes Hepatic Factor IX Gene Expression in Vivo but Not in Vitro. Mol. Ther. 2000, 1, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, C.S.; Pierce, G.F.; Arruda, V.R.; Glader, B.; Ragni, M.; Rasko, J.J.E.; Ozelo, M.C.; Hoots, K.; Blatt, P.; Konkle, B.; et al. Successful Transduction of Liver in Hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and Limitations Imposed by the Host Immune Response. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.; Nayak, S.; Hoffman, B.E.; Terhorst, C.; Cao, O.; Herzog, R.W. Improved Induction of Immune Tolerance to Factor IX by Hepatic AAV-8 Gene Transfer. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandendriessche, T.; Thorrez, L.; Acosta-Sanchez, A.; Petrus, I.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; De Waele, L.; Iwasaki, Y.; Gillijns, V.; Wilson, J.M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Adeno-associated Viral Vectors Based on Serotype 8 and 9 vs. Lentiviral Vectors for Hemophilia B Gene Therapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidoff, A.M.; Gray, J.T.; Ng, C.Y.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Spence, Y.; Bakar, Y.; Nathwani, A.C. Comparison of the Ability of Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors Pseudotyped with Serotype 2, 5, and 8 Capsid Proteins to Mediate Efficient Transduction of the Liver in Murine and Nonhuman Primate Models. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, T.; Yin, C.; Yin, F.; Van Dyke, T.; Samulski, R.J.; Monahan, P.E. Optimization of Self-Complementary AAV Vectors for Liver-Directed Expression Results in Sustained Correction of Hemophilia B at Low Vector Dose. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.; Jérôme, V.; Müller, R. Chimeric Transcriptional Control Units for Improved Liver-Specific Transgene Expression. Gene 2003, 322, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulk, N.K.; Pekrun, K.; Zhu, E.; Nygaard, S.; Li, B.; Xu, J.; Chu, K.; Leborgne, C.; Dane, A.P.; Haft, A.; et al. Bioengineered AAV Capsids with Combined High Human Liver Transduction In Vivo and Unique Humoral Seroreactivity. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dane, A.P.; Cunningham, S.C.; Graf, N.S.; Alexander, I.E. Sexually Dimorphic Patterns of Episomal rAAV Genome Persistence in the Adult Mouse Liver and Correlation With Hepatocellular Proliferation. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanes-Creus, M.; Westhaus, A.; Navarro, R.G.; Baltazar, G.; Zhu, E.; Amaya, A.K.; Liao, S.H.Y.; Scott, S.; Sallard, E.; Dilworth, K.L.; et al. Attenuation of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan Binding Enhances In Vivo Transduction of Human Primary Hepatocytes with AAV2. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 1139–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanes-Creus, M.; Navarro, R.G.; Zhu, E.; Baltazar, G.; Liao, S.H.Y.; Drouyer, M.; Amaya, A.K.; Scott, S.; Nguyen, L.H.; Westhaus, A.; et al. Novel Human Liver-Tropic AAV Variants Define Transferable Domains That Markedly Enhance the Human Tropism of AAV7 and AAV8. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 24, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, S.C.; Spinoulas, A.; Carpenter, K.H.; Wilcken, B.; Kuchel, P.W.; Alexander, I.E. AAV2/8-Mediated Correction of OTC Deficiency Is Robust in Adult but Not Neonatal Spfash Mice. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, S.C.; Siew, S.M.; Hallwirth, C.V.; Bolitho, C.; Sasaki, N.; Garg, G.; Michael, I.P.; Hetherington, N.A.; Carpenter, K.; De Alencastro, G.; et al. Modeling Correction of Severe Urea Cycle Defects in the Growing Murine Liver Using a Hybrid Recombinant Adeno-associated Virus/piggyBac Transposase Gene Delivery System. Hepatology 2015, 62, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginn, S.L.; Amaya, A.K.; Liao, S.H.Y.; Zhu, E.; Cunningham, S.C.; Lee, M.; Hallwirth, C.V.; Logan, G.J.; Tay, S.S.; Cesare, A.J.; et al. Efficient in Vivo Editing of OTC-Deficient Patient-Derived Primary Human Hepatocytes. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouet, P.; Raguenez, G.; Tronche, F.; Yaniv, M.; N’Guyen, C.; Salier, J.P. A Potent Enhancer Made of Clustered Liver-Specific Elements in the Transcription Control Sequences of Human Alpha 1-Microglobulin/Bikunin Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 20765–20773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEachern, K.A.; Nietupski, J.B.; Chuang, W.; Armentano, D.; Johnson, J.; Hutto, E.; Grabowski, G.A.; Cheng, S.H.; Marshall, J. AAV8-mediated Expression of Glucocerebrosidase Ameliorates the Storage Pathology in the Visceral Organs of a Mouse Model of Gaucher Disease. J. Gene Med. 2006, 8, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Craeyveld, E.; Gordts, S.C.; Nefyodova, E.; Jacobs, F.; De Geest, B. Regression and Stabilization of Advanced Murine Atherosclerotic Lesions: A Comparison of LDL Lowering and HDL Raising Gene Transfer Strategies. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatino, D.E.; Lange, A.M.; Altynova, E.S.; Sarkar, R.; Zhou, S.; Merricks, E.P.; Franck, H.G.; Nichols, T.C.; Arruda, V.R.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr. Efficacy and Safety of Long-Term Prophylaxis in Severe Hemophilia A Dogs Following Liver Gene Therapy Using AAV Vectors. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.N.; George, L.A.; Siner, J.I.; Davidson, R.J.; Zander, C.B.; Zheng, X.L.; Arruda, V.R.; Camire, R.M.; Sabatino, D.E. Novel Factor VIII Variants with a Modified Furin Cleavage Site Improve the Efficacy of Gene Therapy for Hemophilia A. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siner, J.I.; Iacobelli, N.P.; Sabatino, D.E.; Ivanciu, L.; Zhou, S.; Poncz, M.; Camire, R.M.; Arruda, V.R. Minimal Modification in the Factor VIII B-Domain Sequence Ameliorates the Murine Hemophilia A Phenotype. Blood 2013, 121, 4396–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.C.; Doering, C.B.; Herzog, R.W.; Ling, C.; Markusic, D.M.; Spencer, H.T.; Srivastava, A.; Srivastava, A. Development of a Clinical Candidate AAV3 Vector for Gene Therapy of Hemophilia B. Hum. Gene Ther. 2020, 31, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, H.; Carlisle, R.C. Progress in Gene Therapy for Hereditary Tyrosinemia Type 1. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homology Medicines, Inc. Homology Medicines Announces Plan to Evaluate Strategic Options for the Company and Its Genetic Medicines Programs, Including HMI-103 Gene Editing Candidate for PKU. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2023/07/27/2712687/0/en/Homology-Medicines-Announces-Plan-to-Evaluate-Strategic-Options-for-the-Company-and-its-Genetic-Medicines-Programs-including-HMI-103-Gene-Editing-Candidate-for-PKU.html (accessed on 10 December 2025).
- Nathwani, A.; Raj, D. Fabry Disease Gene Therapy. U.S. Patent 11,103,596, 31 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Yang, L. Engineered Liver-Specific Enhancers and Their Applications. U.S. Patent 18/919,331, 17 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Burke, P.A. Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor-4α Interacts with Other Hepatocyte Nuclear Factors in Regulating Transthyretin Gene Expression. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 4066–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, C.; Minniti, M.; Susini, V.; Caponi, L.; Panichella, G.; Castiglione, V.; Aimo, A.; Emdin, M.; Vergaro, G.; Franzini, M. The Journey of Human Transthyretin: Synthesis, Structure Stability, and Catabolism. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.H.; Lai, E.; Darnell, J.E. Transcriptional Control of the Mouse Prealbumin (Transthyretin) Gene: Both Promoter Sequences and a Distinct Enhancer Are Cell Specific. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1986, 6, 4697–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Costa, R.H.; Darnell, J.E.; Chen, J.D.; Van Dyke, T.A. Distinct Positive and Negative Elements Control the Limited Hepatocyte and Choroid Plexus Expression of Transthyretin in Transgenic Mice. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoag, H.; Gore, J.; Barry, D.; Mueller, C.R. Gene Therapy Expression Vectors Based on the Clotting Factor IX Promoter. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhuri, M.; Levy, D.I.; Schulz, M.; McCarty, D.; Gao, G. Durability of Transgene Expression after rAAV Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1364–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, J.; Álvarez Román, M.T.; Ayash-Rashkovsky, M.; Diogo, D.; Kenniston, J.; Lopez-Jaime, F.; Maggiore, C.; Mingot-Castellano, M.; Rajavel, K.; Rauch, A.; et al. A Phase 1/2 Safety and Efficacy Study of TAK-754 Gene Therapy: The Challenge of Achieving Durable Factor VIII Expression in Haemophilia A Clinical Trials. Haemophilia 2025, 31, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigna, E.; Amendola, M.; Benedicenti, F.; Simmons, A.D.; Follenzi, A.; Naldini, L. Efficient Tet-Dependent Expression of Human Factor IX in Vivo by a New Self-Regulating Lentiviral Vector. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantore, A.; Ranzani, M.; Bartholomae, C.C.; Volpin, M.; Valle, P.D.; Sanvito, F.; Sergi, L.S.; Gallina, P.; Benedicenti, F.; Bellinger, D.; et al. Liver-Directed Lentiviral Gene Therapy in a Dog Model of Hemophilia B. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 277ra28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Lillicrap, D.; Patarroyo-White, S.; Liu, T.; Qian, X.; Scallan, C.D.; Powell, S.; Keller, T.; McMurray, M.; Labelle, A.; et al. Multiyear Therapeutic Benefit of AAV Serotypes 2, 6, and 8 Delivering Factor VIII to Hemophilia A Mice and Dogs. Blood 2006, 108, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallan, C.D.; Lillicrap, D.; Jiang, H.; Qian, X.; Patarroyo-White, S.L.; Parker, A.E.; Liu, T.; Vargas, J.; Nagy, D.; Powell, S.K.; et al. Sustained Phenotypic Correction of Canine Hemophilia A Using an Adeno-Associated Viral Vector. Blood 2003, 102, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.H.; Grayson, D.R. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor (HNF) Binding Sites in the Mouse Transthyretin (TTR) Promoter Reveal Synergistic Interactions with Its Enhancer Region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 4139–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croteau, S.E.; Eyster, M.E.; Tran, H.; Ragni, M.V.; Samelson-Jones, B.J.; George, L.; Sullivan, S.; Rasko, J.E.J.; Moormeier, J.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; et al. Long-Term Durable FVIII Expression with Improvements in Bleeding Rates Following AAV-Mediated FVIII Gene Transfer for Hemophilia A: Multiyear Follow-up on the Phase I/II Trial of SPK-8011. Blood 2022, 140, 1899–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.N.; Lindgren, J.R.; Seleme, M.C.; Kafle, S.; Zander, C.B.; Zheng, X.L.; Sabatino, D.E. Altered Cleavage of Human Factor VIII at the B-Domain and Acidic Region 3 Interface Enhances Expression after Gene Therapy in Hemophilia A Mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 2101–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, K.; Wakasugi, S.; Maeda, S.; Inomoto, T.; Iwanaga, T.; Uehira, M.; Araki, K.; Miyazaki, J.; Shimada, K. Tissue-specific and Developmental Expression of Human Transthyretin Gene in Transgenic Mice. Dev. Genet. 1987, 8, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greig, J.A.; Nordin, J.M.L.; White, J.W.; Wang, Q.; Bote, E.; Goode, T.; Calcedo, R.; Wadsworth, S.; Wang, L.; Wilson, J.M. Optimized Adeno-Associated Viral-Mediated Human Factor VIII Gene Therapy in Cynomolgus Macaques. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipe, S.W.; Sheehan, J.P.; Coppens, M.; Eichler, H.; Linardi, C.; Wiegmann, S.; Hay, C.R.; Lissitchkov, T. First-in-Human Dose-Finding Study of AAVhu37 Vector-Based Gene Therapy: BAY 2599023 Has Stable and Sustained Expression of FVIII over 2 Years. Blood 2021, 138, 3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyostio-Moore, S.; Berthelette, P.; Piraino, S.; Sookdeo, C.; Nambiar, B.; Jackson, R.; Burnham, B.; O’Riordan, C.R.; Cheng, S.H.; Armentano, D. The Impact of Minimally Oversized Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors Encoding Human Factor VIII on Vector Potency in Vivo. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 3, 16006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.P.; Xie, J.; Hu, S.; Ko, J.; Huang, Q.; Brown, H.C.; Srivastava, A.; Markusic, D.M.; Doering, C.B.; Spencer, H.T.; et al. Coagulation Factor IX Gene Transfer to Non-Human Primates Using Engineered AAV3 Capsid and Hepatic Optimized Expression Cassette. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 23, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, C.W.; Knight, K.A.; Brown, H.C.; George, S.N.; Denning, G.; Branella, G.M.; Childers, K.C.; Spiegel, P.C.; Spencer, H.T.; Doering, C.B. Humanization and Functional Characterization of Enhanced Coagulation Factor IX Variants Identified through Ancestral Sequence Reconstruction. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 22, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, K.A.; Coyle, C.W.; Radford, C.E.; Parker, E.T.; Fedanov, A.; Shields, J.M.; Szlam, F.; Purchel, A.; Chen, M.; Denning, G.; et al. Identification of Coagulation Factor IX Variants with Enhanced Activity through Ancestral Sequence Reconstruction. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3333–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Wang, M.; Wheeler, A.P.; Croteau, S.E. 2025 Clinical Trials Update on Hemophilia VWD, and Rare Inherited Bleeding Disorders. Am. J. Hematol. 2025, 100, 666–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuah, M.; Vandendriessche, T. Optimized Liver-Specific Expression Systems for Fviii and Fix 2016. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2016146757A1 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Mazzaferro, E.M.; Edwards, T. Update on Albumin Therapy in Critical Illness. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 50, 1289–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereghini, S.; Raymondjean, M.; Carranca, A.G.; Herbomel, P.; Yaniv, M. Factors Involved in Control of Tissue-Specific Expression of Albumin Gene. Cell 1987, 50, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Shi, Y.; Bu, H.; Bao, J.; Xie, M. Construction of a General Albumin Promoter Reporter System for Real-Time Monitoring of the Differentiation Status of Functional Hepatocytes from Stem Cells in Mouse, Rat and Human. Biomed. Rep. 2017, 6, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanrell, L.; Di Scala, M.; Blanco, L.; Otano, I.; Gil-Farina, I.; Baldim, V.; Paneda, A.; Berraondo, P.; Beattie, S.G.; Chtarto, A.; et al. Development of a Liver-Specific Tet-On Inducible System for AAV Vectors and Its Application in the Treatment of Liver Cancer. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmatz, P.; Prada, C.E.; Burton, B.K.; Lau, H.; Kessler, C.M.; Cao, L.; Falaleeva, M.; Villegas, A.G.; Zeitler, J.; Meyer, K.; et al. First-in-Human in Vivo Genome Editing via AAV-Zinc-Finger Nucleases for Mucopolysaccharidosis I/II and Hemophilia B. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3587–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenzer, J.; Prada, C.E.; Burton, B.; Lau, H.A.; Ficicioglu, C.; Foo, C.W.P.; Vaidya, S.A.; Whitley, C.B.; Harmatz, P. CHAMPIONS: A Phase 1/2 Clinical Trial with Dose Escalation of SB-913 ZFN-Mediated in Vivo Human Genome Editing for Treatment of MPS II (Hunter Syndrome). Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 126, S104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmatz, P.; Lau, H.A.; Heldermon, C.; Leslie, N.; Foo, C.W.P.; Vaidya, S.A.; Whitley, C.B. EMPOWERS: A Phase 1/2 Clinical Trial of SB-318 ZFN-Mediated in Vivo Human Genome Editing for Treatment of MPS I (Hurler Syndrome). Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 126, S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbomel, P.; Rollier, A.; Tronche, F.; Ott, M.-O.; Yaniv, M.; Weiss, M.C. The Rat Albumin Promoter Is Composed of Six Distinct Positive Elements within 130 Nucleotides. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1989, 9, 4750–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, S.C.; Cereghini, S.; Rollier, A.; Gannon, F. Isolation and Functional Analysis of the Promoter of the Bovine Serum Albumin Gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorpp, M.; Kugler, W.; Wagner, U.; Ryffel, G.U. Hepatocyte-Specific Promoter Element HP1 of the Xenopus Albumin Gene Interacts with Transcriptional Factors of Mammalian Hepatocytes. J. Mol. Biol. 1988, 202, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorachek, W.R.; Steppan, C.M.; Lima, M.; Black, H.; Bhattacharya, R.; Wen, P.; Kajiyama, Y.; Locker, J. Distant Enhancers Stimulate the Albumin Promoter through Complex Proximal Binding Sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 29031–29041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorski, K.; Carneiro, M.; Schibler, U. Tissue-Specific in Vitro Transcription from the Mouse Albumin Promoter. Cell 1986, 47, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Reppen, T.; Wolff, J.A.; Herweijer, H. Sustained Liver-specific Transgene Expression from the Albumin Promoter in Mice Following Hydrodynamic Plasmid DNA Delivery. J. Gene Med. 2008, 10, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Friedman, N.; Darnell, J.E.; Babiss, L.E. Positive and Negative Regulatory Elements in the Mouse Albumin Enhancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 1553–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Kan, K.; Sticht, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Shao, C.; Munker, S.; Niess, H.; Wang, S.; et al. A Hierarchical Regulatory Network Ensures Stable Albumin Transcription under Various Pathophysiological Conditions. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1673–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, D. Transcription Factor Binding Site in Promoter Determines the Pattern of Plasmid-Based Transgene Expression In Vivo. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkert, C.A.; Ornitz, D.M.; Brinster, R.L.; Palmiter, R.D. An Albumin Enhancer Located 10 Kb Upstream Functions along with Its Promoter to Direct Efficient, Liver-Specific Expression in Transgenic Mice. Genes Dev. 1987, 1, 268–276. 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Berta, S.C.; Lu, M.M.; Moscioni, A.D.; Tazelaar, J.; Wilson, J.M. Adeno-Associated Virus as a Vector for Liver-Directed Gene Therapy. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 10222–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.M.; Camper, S.A.; Tilghman, S.M.; Miller, T.; Georgoff, I.; Serra, R.; Isom, H.C. Functional Analyses of Albumin Expression in a Series of Hepatocyte Cell Lines and in Primary Hepatocytes. Cell Growth Differ. 1992, 3, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Connelly, S.; Smith, T.A.G.; Dhir, G.; Gardner, J.M.; Mehaffey, M.G.; Zaret, K.S.; McClelland, A.; Kaleko, M. In Vivo Gene Delivery and Expression of Physiological Levels of Functional Human Factor VIII in Mice. Hum. Gene Ther. 1995, 6, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaret, K.S.; DiPersio, C.M.; Jackson, D.A.; Montigny, W.J.; Weinstat, D.L. Conditional Enhancement of Liver-Specific Gene Transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 9076–9080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, S.; Andrews, J.L.; Gallo, A.M.; Kayda, D.B.; Qian, J.; Hoyer, L.; Kadan, M.J.; Gorziglia, M.I.; Trapnell, B.C.; McClelland, A.; et al. Sustained Phenotypic Correction of Murine Hemophilia A by In Vivo Gene Therapy. Blood 1998, 91, 3273–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafenrichter, D.G.; Ponder, K.P.; Rettinger, S.D.; Kennedy, S.C.; Wu, X.; Saylors, R.S.; Flye, M.W. Liver-Directed Gene Therapy: Evaluation of Liver Specific Promoter Elements. J. Surg. Res. 1994, 56, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, S.; Gardner, J.; Lyons, R.; McClelland, A.; Kaleko, M. Sustained Expression of Therapeutic Levels of Human Factor VIII in Mice. Blood 1996, 87, 4671–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nietupski, J.B.; Hurlbut, G.D.; Ziegler, R.J.; Chu, Q.; Hodges, B.L.; Ashe, K.M.; Bree, M.; Cheng, S.H.; Gregory, R.J.; Marshall, J.; et al. Systemic Administration of AAV8-α-Galactosidase A Induces Humoral Tolerance in Nonhuman Primates Despite Low Hepatic Expression. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1999–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, R.J.; Cherry, M.; Barbon, C.M.; Li, C.; Bercury, S.D.; Armentano, D.; Desnick, R.J.; Cheng, S.H. Correction of the Biochemical and Functional Deficits in Fabry Mice Following AAV8–Mediated Hepatic Expression of α-Galactosidase A. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlbut, G.D.; Ziegler, R.J.; Nietupski, J.B.; Foley, J.W.; Woodworth, L.A.; Meyers, E.; Bercury, S.D.; Pande, N.N.; Souza, D.W.; Bree, M.P.; et al. Preexisting Immunity and Low Expression in Primates Highlight Translational Challenges for Liver-Directed AAV8-Mediated Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1983–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, R.J.; Lonning, S.M.; Armentano, D.; Li, C.; Souza, D.W.; Cherry, M.; Ford, C.; Barbon, C.M.; Desnick, R.J.; Gao, G.; et al. AAV2 Vector Harboring a Liver-Restricted Promoter Facilitates Sustained Expression of Therapeutic Levels of α-Galactosidase A and the Induction of Immune Tolerance in Fabry Mice. Mol. Ther. 2004, 9, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryffel, G.U.; Kugler, W.; Wagner, U.; Kaling, M. Liver Cell Specific Gene Transcription in Vitro: The Promoter Elements HP1 and TATA Box Are Necessary and Sufficient to Generate a Liver-Specific Promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzi, A.; Forni, D.; Cagliani, R.; Pozzoli, U.; Vertemara, J.; Bresolin, N.; Sironi, M. Albuminoid Genes: Evolving at the Interface of Dispensability and Selection. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 2983–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, R.E.; Krumlauf, R.; Camper, S.A.; Brinster, R.L.; Tilghman, S.M. Diversity of Alpha-Fetoprotein Gene Expression in Mice Is Generated by a Combination of Separate Enhancer Elements. Science 1987, 235, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, V.; Silengo, L.; Altruda, F.; Cortese, R. The Analysis of the Human Hemopexin Promoter Defines a New Class of Liver-Specific Genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 9351–9365. [Google Scholar]
- Kanai, F.; Lan, K.H.; Shiratori, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ohashi, M.; Okudaira, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Wakimoto, H.; Hamada, H.; Nakabayashi, H.; et al. In Vivo Gene Therapy for Alpha-Fetoprotein-Producing Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Adenovirus-Mediated Transfer of Cytosine Deaminase Gene. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Pin, R.H.; Reinblatt, M.; Fong, Y. Utilizing α-Fetoprotein Expression to Enhance Oncolytic Viral Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucdal, M.; Yazarkan, Y.; Sonmez, G.; Celtikci, B.; Balaban, Y. Alpha-Fetoprotein: A Multifaceted Player in Cancer Biology. Euroasian J. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2025, 15, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbout, R.; Ingram, R.; Tilghman, S.M. Multiple Regulatory Elements in the Intergenic Region Between the α-Fetoprotein and Albumin Genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1986, 6, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarevich, N.L. Molecular Mechanisms of Alpha-Fetoprotein Gene Expression. Biochemistry 2000, 65, 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, Y.; Mori, Y.; Janssen, O.E.; Sunthornthepvarakul, T.; Weiss, R.E.; Takeda, K.; Weinberg, M.; Seo, H.; Bell, G.I.; Refetoff, S. Human Thyroxine-Binding Globulin Gene: Complete Sequence and Transcriptional Regulation. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993, 7, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.-P.; Alvira, M.R.; Wang, L.; Calcedo, R.; Johnston, J.; Wilson, J.M. Novel Adeno-Associated Viruses from Rhesus Monkeys as Vectors for Human Gene Therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11854–11859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Takabe, K.; Bidlingmaier, S.M.; Ill, C.R.; Verma, I.M. Sustained Correction of Bleeding Disorder in Hemophilia B Mice by Gene Therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3906–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ill, C.R.; Yang, C.Q.; Bidlingmaier, S.M.; Gonzales, J.N.; Burns, D.S.; Bartholomew, R.M.; Scuderi, P. Optimization of the Human Factor VIII Complementary DNA Expression Plasmid for Gene Therapy of Hemophilia A. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1997, 8 (Suppl. 2), S23–S30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Calcedo, R.; Nichols, T.C.; Bellinger, D.A.; Dillow, A.; Verma, I.M.; Wilson, J.M. Sustained Correction of Disease in Naive and AAV2-Pretreated Hemophilia B Dogs: AAV2/8-Mediated, Liver-Directed Gene Therapy. Blood 2005, 105, 3079–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Nichols, T.C.; Read, M.S.; Bellinger, D.A.; Verma, I.M. Sustained Expression of Therapeutic Level of Factor IX in Hemophilia B Dogs by AAV-Mediated Gene Therapy in Liver. Mol. Ther. 2000, 1, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.; Tetreault, R.; Gao, G.; Wang, L.; Bell, P.; Chandler, R.; Wilson, J.M.; Kazazian, H.H. Total Correction of Hemophilia A Mice with Canine FVIII Using an AAV 8 Serotype. Blood 2004, 103, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Huang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, L.; Ma, F. Accelerating Promoter Identification and Design by Deep Learning. Trends Biotechnol. 2025, 43, 3071–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.; Lim, S.; Kim, S. Enhancer Prediction with Histone Modification Marks Using a Hybrid Neural Network Model. Methods 2019, 166, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo González-Blas, C.; Matetovici, I.; Hillen, H.; Taskiran, I.I.; Vandepoel, R.; Christiaens, V.; Sansores-García, L.; Verboven, E.; Hulselmans, G.; Poovathingal, S.; et al. Single-Cell Spatial Multi-Omics and Deep Learning Dissect Enhancer-Driven Gene Regulatory Networks in Liver Zonation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2024, 26, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosai, S.J.; Castro, R.I.; Fuentes, N.; Butts, J.C.; Mouri, K.; Alasoadura, M.; Kales, S.; Nguyen, T.T.L.; Noche, R.R.; Rao, A.S.; et al. Machine-Guided Design of Cell-Type-Targeting Cis-Regulatory Elements. Nature 2024, 634, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.A.G.; Mehaffey, M.G.; Kayda, D.B.; Saunders, J.M.; Yei, S.; Trapnell, B.C.; McClelland, A.; Kaleko, M. Adenovirus Mediated Expression of Therapeutic Plasma Levels of Human Factor IX in Mice. Nat. Genet. 1993, 5, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, S.-H.; Nathan Hagstrom, J.; Cass, D.; Jen Tai, S.; Lin, H.-F.; Stafford, D.W.; High, K.A. Human Factor IX Corrects the Bleeding Diathesis of Mice With Hemophilia B. Blood 1998, 91, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geest, B.D.; Linthout, S.V.; Lox, M.; Collen, D.; Holvoet, P. Sustained Expression of Human Apolipoprotein A-I after Adenoviral Gene Transfer in C57BL/6 Mice: Role of Apolipoprotein A-I Promoter, Apolipoprotein A-I Introns, and Human Apolipoprotein E Enhancer. Hum. Gene Ther. 2000, 11, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrhardt, A.; Kay, M.A. A New Adenoviral Helper–Dependent Vector Results in Long-Term Therapeutic Levels of Human Coagulation Factor IX at Low Doses in Vivo. Blood 2002, 99, 3923–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geest, B.; Van Linthout, S.; Collen, D. Sustained Expression of Human Apo A-I Following Adenoviral Gene Transfer in Mice. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, S.; Gardner, J.M.; McClelland, A.; Kaleko, M. High-Level Tissue-Specific Expression of Functional Human Factor VIII in Mice. Hum. Gene Ther. 1996, 7, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, L.; Morral, N.; Zhou, H.; Garcia, R.; Parks, R.J.; Kochanek, S.; Graham, F.L.; Lee, B.; Beaudet, A.L. Use of a Liver-Specific Promoter Reduces Immune Response to the Transgene in Adenoviral Vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, R.O.; Miao, C.H.; Patijn, G.A.; Spratt, S.K.; Danos, O.; Nagy, D.; Gown, A.M.; Winther, B.; Meuse, L.; Cohen, L.K.; et al. Persistent and Therapeutic Concentrations of Human Factor IX in Mice after Hepatic Gene Transfer of Recombinant AAV Vectors. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, R.O.; Miao, C.; Meuse, L.; Tubb, J.; Donahue, B.A.; Lin, H.-F.; Stafford, D.W.; Patel, S.; Thompson, A.R.; Nichols, T.; et al. Correction of Hemophilia B in Canine and Murine Models Using Recombinant Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.; Mao, L.; Bruce, A.T.; Walsh, C.E. Sustained Expression of Human Factor VIII in Mice Using a Parvovirus-Based Vector. Blood 2000, 95, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, V.R.; Samelson-Jones, B.J. Gene Therapy for Immune Tolerance Induction in Hemophilia with Inhibitors. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, H.; Franco, L.M.; Brown, T.; Bird, A.; Schneider, A.; Koeberl, D.D. Correction of Glycogen Storage Disease Type II by an Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Containing a Muscle-Specific Promoter. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggers, M.; Vannoy, C.H.; Huang, J.; Purushothaman, P.; Brassard, J.; Fonck, C.; Meng, H.; Prom, M.J.; Lawlor, M.W.; Cunningham, J.; et al. Muscle-directed Gene Therapy Corrects Pompe Disease and Uncovers Species-specific GAA Immunogenicity. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e13968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, M.; Liberati, C.; Smith, B.K.; Lawson, L.A.; Tuna, I.S.; Conlon, T.J.; Coleman, K.E.; Islam, S.; Herzog, R.W.; Fuller, D.D.; et al. Safety of Intradiaphragmatic Delivery of Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Alpha-Glucosidase (rAAV1-CMV-hGAA) Gene Therapy in Children Affected by Pompe Disease. Hum. Gene Ther. Clin. Dev. 2017, 28, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colella, P.; Sellier, P.; Costa Verdera, H.; Puzzo, F.; Van Wittenberghe, L.; Guerchet, N.; Daniele, N.; Gjata, B.; Marmier, S.; Charles, S.; et al. AAV Gene Transfer with Tandem Promoter Design Prevents Anti-Transgene Immunity and Provides Persistent Efficacy in Neonate Pompe Mice. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2019, 12, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellier, P.; Vidal, P.; Bertin, B.; Gicquel, E.; Bertil-Froidevaux, E.; Georger, C.; Van Wittenberghe, L.; Miranda, A.; Daniele, N.; Richard, I.; et al. Muscle-specific, Liver-detargeted Adeno-Associated Virus Gene Therapy Rescues Pompe Phenotype in Adult and Neonate Gaa−/− Mice. J. Inher Metab. Disea 2024, 47, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Álvarez, J.V.; Nidhi, F.N.U.; Benincore-Florez, E.; Tomatsu, S. Evaluation of AAV Vectors with Tissue-Specific or Ubiquitous Promoters in a Mouse Model of Mucopolysaccharidosis Type IVA. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2025, 33, 101447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baruteau, J.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Gissen, P. Liver-directed Gene Therapy for Inherited Metabolic Diseases. J. Inher Metab. Disea 2024, 47, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crudele, J.M.; Finn, J.D.; Siner, J.I.; Martin, N.B.; Niemeyer, G.P.; Zhou, S.; Mingozzi, F.; Lothrop, C.D.; Arruda, V.R. AAV Liver Expression of FIX-Padua Prevents and Eradicates FIX Inhibitor without Increasing Thrombogenicity in Hemophilia B Dogs and Mice. Blood 2015, 125, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Nawab, S.; Xia, M.; Ma, X.; Huo, Y. Context-dependency of Synthetic Minimal Promoters in Driving Gene Expression: A Case Study. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaysen, G.A.; Dubin, J.A.; Müller, H.-G.; Mitch, W.E.; Rosales, L.M.; Levin, N.W. The Hemo Study Group Relationships among Inflammation Nutrition and Physiologic Mechanisms Establishing Albumin Levels in Hemodialysis Patients. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, D.; Levitt, M. Human Serum Albumin Homeostasis: A New Look at the Roles of Synthesis, Catabolism, Renal and Gastrointestinal Excretion, and the Clinical Value of Serum Albumin Measurements. IJGM 2016, 9, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahm, A.M.; Owens, W.S.; Himes, S.R.; Fallon, B.S.; Rondem, K.E.; Gormick, A.N.; Bloom, J.S.; Kosuri, S.; Chan, H.; English, J.G. A Massively Parallel Reporter Assay Library to Screen Short Synthetic Promoters in Mammalian Cells. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degner, K.N.; Bell, J.L.; Jones, S.D.; Won, H. Just a SNP Away: The Future of in Vivo Massively Parallel Reporter Assay. Cell Insight 2025, 4, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, F.; Ahituv, N. Decoding Enhancers Using Massively Parallel Reporter Assays. Genomics 2015, 106, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, M.; Messing, A. Regulation of GFAP Expression. ASN Neuro 2021, 13, 1759091420981206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Chan, E.M.; Edenberg, H.J. Tissue-Specific Regulatory Elements in the Human Alcohol Dehydrogenase 6 Gene. DNA Cell Biol. 2000, 19, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorgia, P.; Zannis, V.I.; Kardassis, D. A Short Proximal Promoter and the Distal Hepatic Control Region-1 (HCR-1) Contribute to the Liver Specificity of the Human Apolipoprotein C-II Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 4188–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falquerho, L.; Paquereau, L.; Vilarem, M.J.; Galas, S.; Patey, G.; Le Cam, A. Functional Characterization of the Promoter of Pp63, a Gene Encoding a Natural Inhibitor of the Insulin Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaulont, S.; Puzenat, N.; Kahn, A.; Raymondjean, M. Analysis by Cell-Free Transcription of the Liver-Specific Pyruvate Kinase Gene Promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1989, 9, 4409–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregori, C.; Porteu, A.; Lopez, S.; Kahn, A.; Pichard, A.-L. Characterization of the Aldolase B Intronic Enhancer. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 25237–25243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero, S.; Cortese, R. The Human Haptoglobin Gene Promoter: Interleukin-6-Responsive Elements Interact with a DNA-Binding Protein Induced by Interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagae, Y.; Muller-Eberhard, U. Identification of an Interleukin-6 Responsive Element and Characterization of the Proximal Promoter Region of the Rat Hemopexin Gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 185, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquereau, L.; Vilarem, M.J.; Rossi, V.; Rouayrenc, J.F.; Le Cam, A. Regulation of Two Rat Serine-protease Inhibitor Gene Promoters by Somatotropin and Glucocorticoids: Study with Intact Hepatocytes and Cell-free Systems. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 209, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, R.J.; Neerman-Arbez, M. Fibrinogen Gene Regulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 108, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-H.; Harris, J.E.; Davie, E.W.; Chung, D.W. Characterization of the 5′-Flanking Region of the Gene for the α Chain of Human Fibrinogen. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 28342–28349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmon, J.; Laurent, M.; Courtois, G. The Human β Fibrinogen Promoter Contains a Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 1-Dependent Interleukin-6-Responsive Element. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toniatti, C.; Demartis, A.; Monaci, P.; Nicosia, A.; Ciliberto, G. Synergistic Trans-Activation of the Human C-Reactive Protein Promoter by Transcription Factor HNF-1 Binding at Two Distinct Sites. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 4467–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, T.S.; Denning, G.; Stowell, S.R.; Spencer, H.T.; Doering, C.B. Pharmacokinetic Analysis Identifies a Factor VIII Immunogenicity Threshold after AAV Gene Therapy in Hemophilia A Mice. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 2628–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, J.S.S.; Yamada, K.; Bertolini, T.B.; Syed, F.; Kumar, S.R.P.; Li, X.; Arisa, S.; Piñeros, A.R.; Tapia, A.; Rogers, C.A.; et al. IL-15 Blockade and Rapamycin Rescue Multifactorial Loss of Factor VIII from AAV-Transduced Hepatocytes in Hemophilia A Mice. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3552–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handyside, B.; Ismail, A.M.; Zhang, L.; Yates, B.; Xie, L.; Sihn, C.-R.; Murphy, R.; Bouwman, T.; Kim, C.K.; De Angelis, R.; et al. Vector Genome Loss and Epigenetic Modifications Mediate Decline in Transgene Expression of AAV5 Vectors Produced in Mammalian and Insect Cells. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3570–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazloum, A.; Feoktistova, S.G.; Gubaeva, A.; Alsalloum, A.; Mityaeva, O.N.; Kim, A.; Bodunova, N.A.; Woroncow, M.V.; Volchkov, P.Y. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young 10 (MODY10): A Comprehensive Review of Genetics, Clinical Features, and Therapeutic Advances. IJMS 2025, 26, 8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
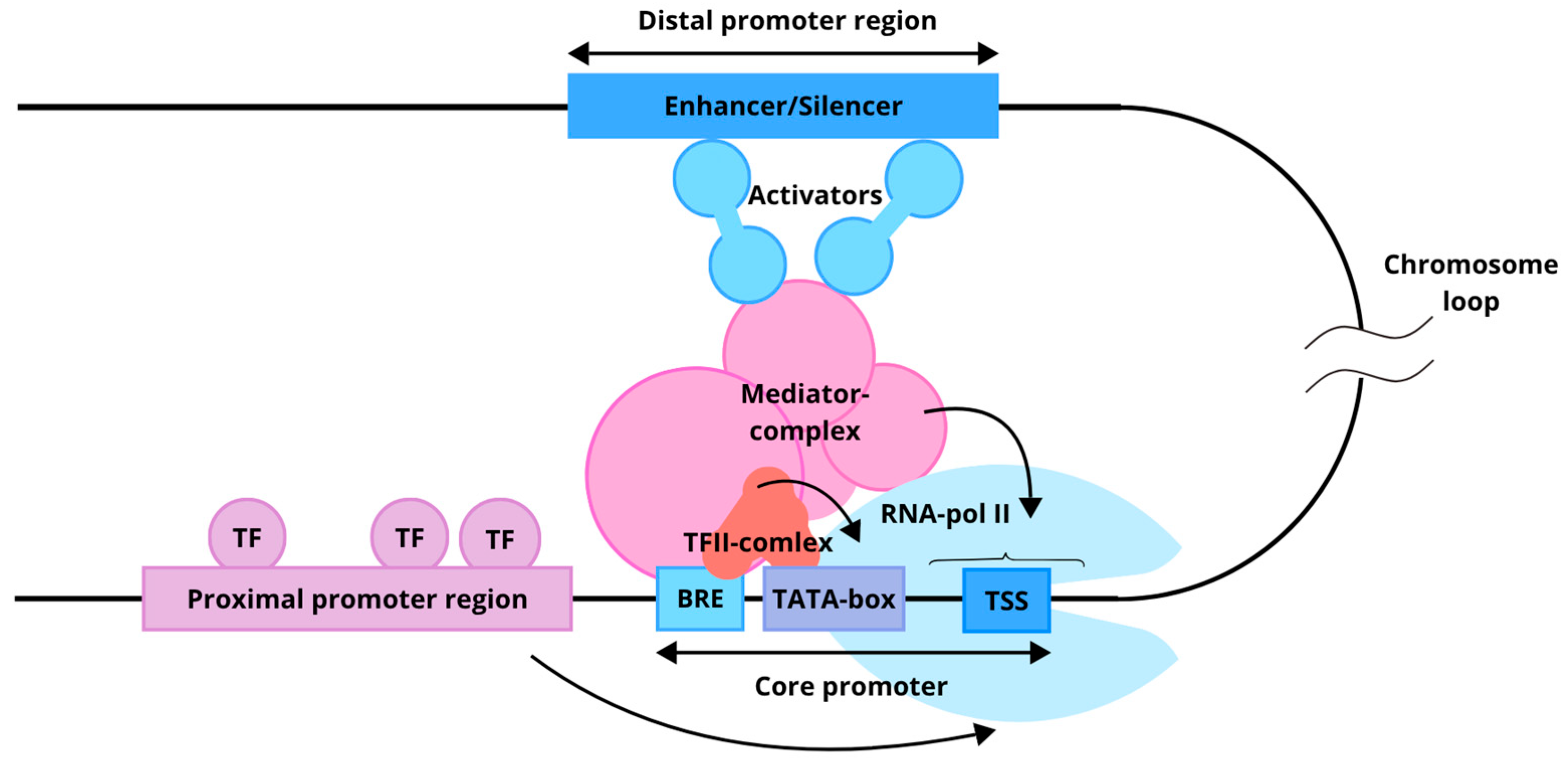
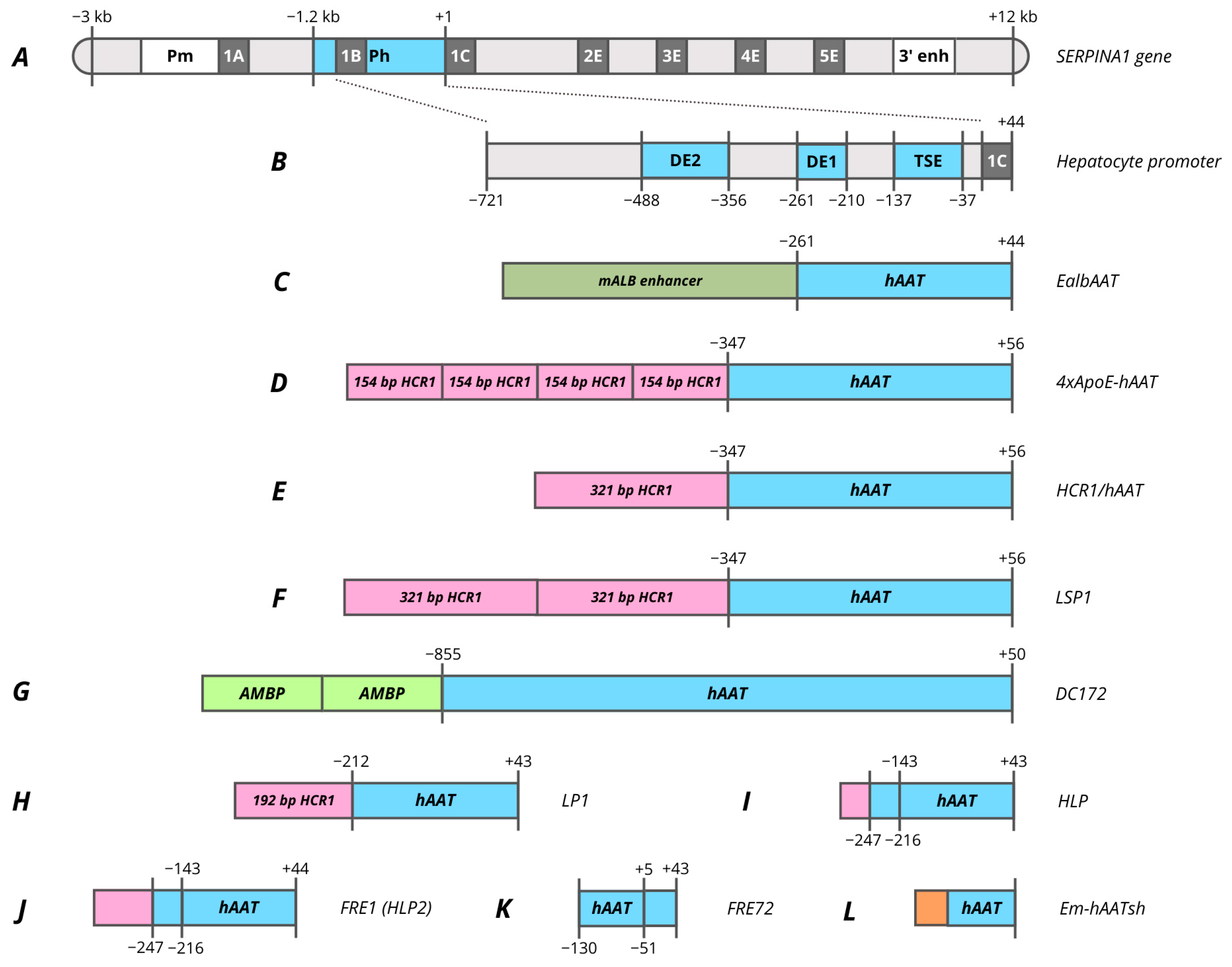
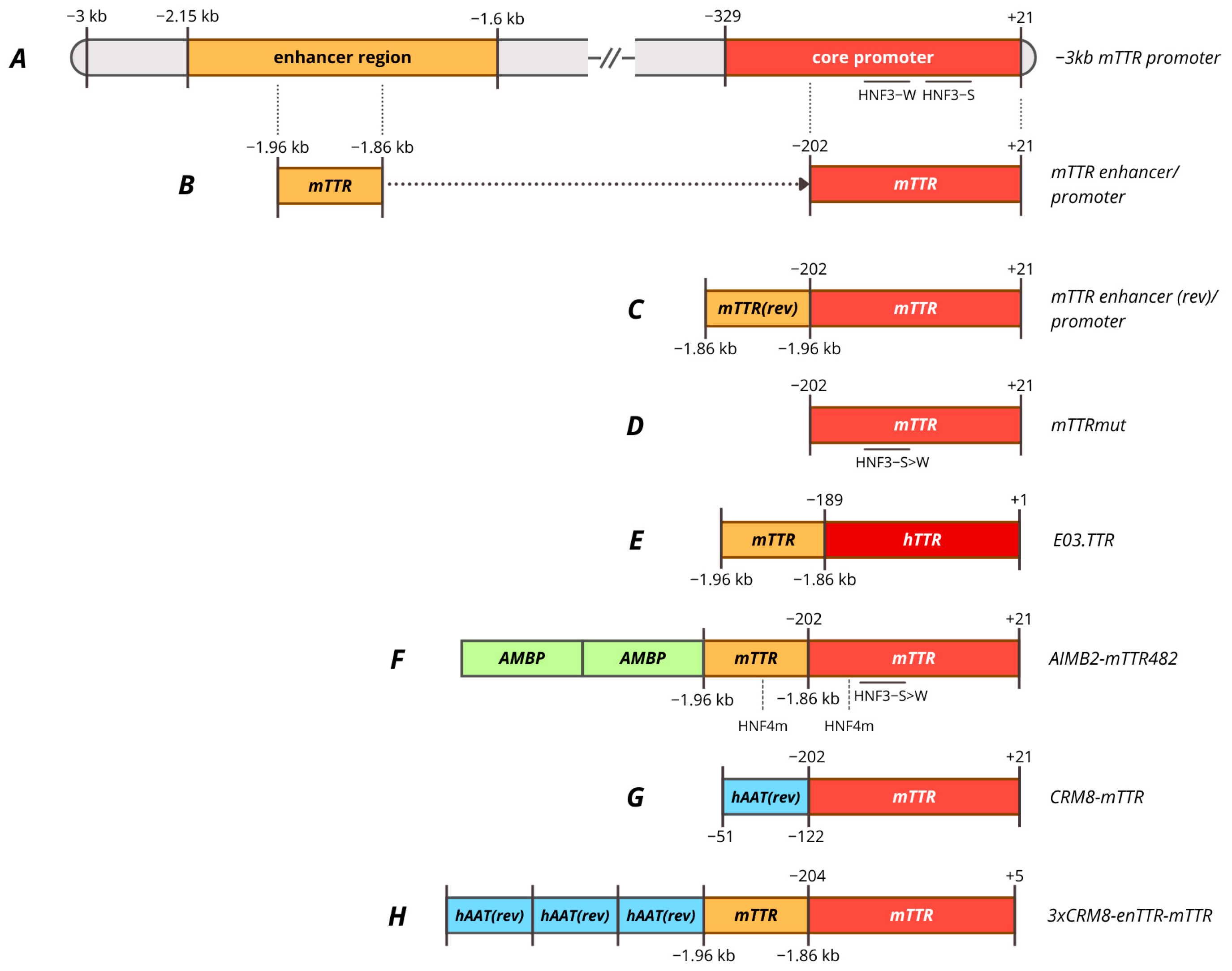
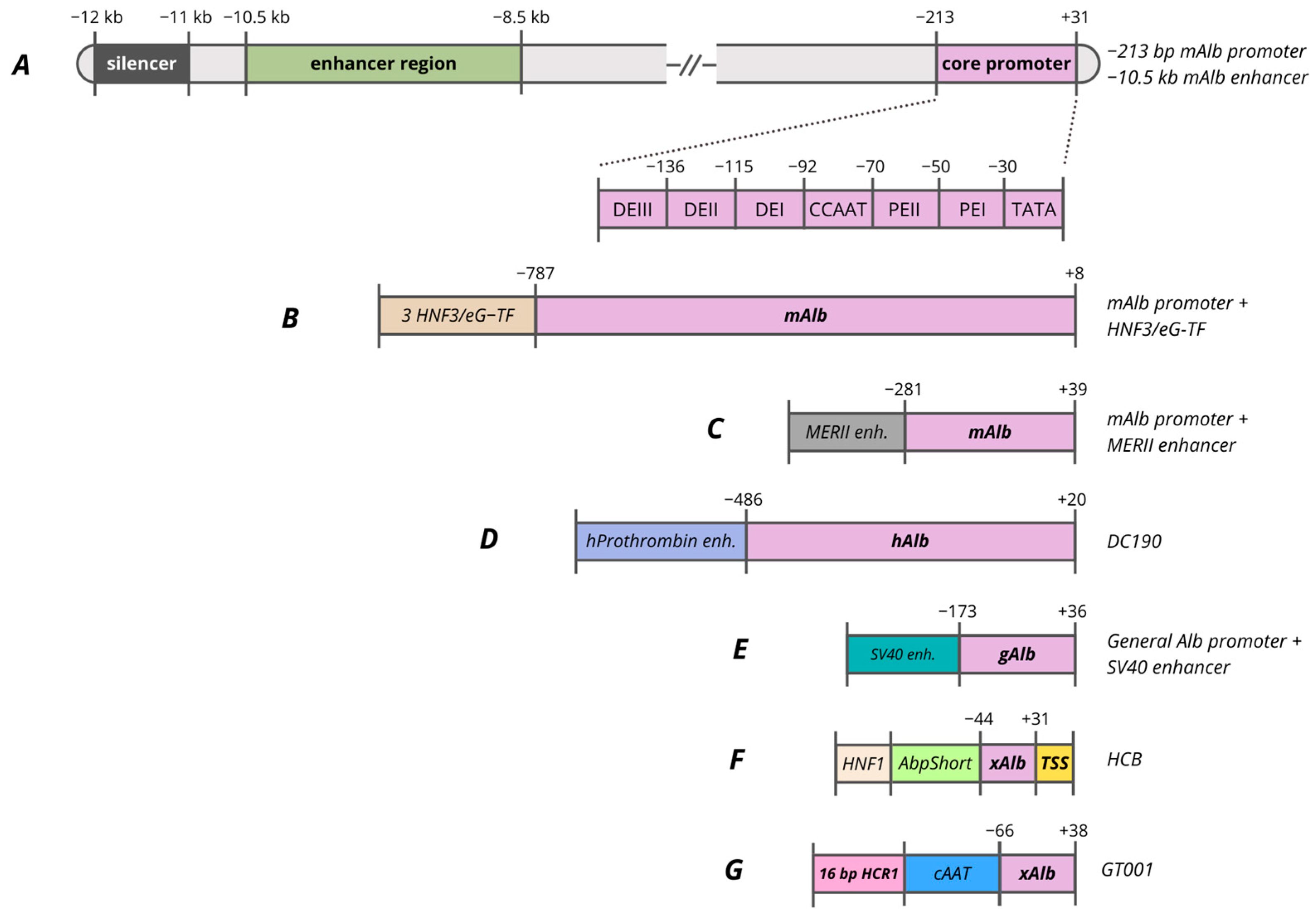
| Promoter | Gene of Origin | Length, bp | Features | Disease | Gene Therapy | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hAAT | Human AAT | 305 | −264/+41 hAAT promoter | Wilson disease | VTX801 | [151,152,153] |
| EalbAAT | Human AAT, murine Alb | 673 | −264/+20 hAAT promoter with 376 bp mAlb enhancer | AIP (acute intermittent porphyria) | rAAV2/5-PBGD | [154,155,156] |
| ApoE/HCR1-hAAT | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 727 | −355/+42 hAAT promoter with 321 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Hemophilia B | Beqvez (fidanacogene elaparvovec, SPK-9001) | [157,158] |
| ApoE/HCR1-hAAT | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 732 | −353/+50 hAAT promoter with 321 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Phenylketonuria (PKU) | BMN 307 | [159,160] |
| ApoE/HCR1-hAAT | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 725 | −355/+43 hAAT promoter with 321 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Phenylketonuria (PKU) | NGGT002 | [161] |
| ApoE/HCR1-hAAT | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 723 | −355/+38 hAAT promoter with 321 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Fabry Disease | ST-920 | [162,163,164] |
| ApoE/HCR1-hAAT | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 727 | −355/+42 hAAT promoter with 321 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Crigler-Najjar syndrome | GNT0003 | [165,166,167] |
| ApoE/HCR1-hAAT | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 732 | −355/+42 hAAT promoter with 326 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Pompe disease | SPK-3006 (vanglusagene ensiparvovec) | [168,169] |
| FRE76 | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 728 | −347/+43 hAAT promoter with 321 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer Same as ApoE/HCR1-hAAT | Gaucher disease type 1 | FLT201 | [170] |
| LP1 | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 448 | −212/+43 hAAT promoter with 192 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Hemophilia B | Hemgenix (AMT-061, CSL222, etranacogene dezaparvovec) | [171,172] |
| LP1 | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 448 | −212/+43 hAAT promoter with 192 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Hemophilia B | scAAV2/8-LP1-hFIXco | [173,174,175,176] |
| LP1 | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 448 | −212/+43 hAAT promoter with 192 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Phenylketonuria (PKU) | HMI-102 | [177,178] |
| LP1 | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 448 | −212/+43 hAAT promoter with 192 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Phenylketonuria (PKU) | HMI-103 | [160,179] |
| HLP | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 252 | −247/−216 and −143/+43 hAAT promoter with 34 bp ApoE/HCR1 | Hemophilia A | AAV-HLP-hFVIII-V3 (GO-8) | [180,181] |
| HLP | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 252 | −247/−216 and −143/+43 hAAT promoter with 34 bp ApoE/HCR1 | Hemophilia A | Roctavian (valoctocogene roxaparvovec, BMN 270) | [182,183,184] |
| FRE1 (HLP2) | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 335 | −247/−216 and −143/+43 hAAT promoter with 117 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Hemophilia B | FLT180a (verbrinacogene setparvovec) | [185,186,187] |
| FRE1 (HLP2) | Human ApoE/HCR1 and AAT | 335 | −247/−216 and −143/+43 hAAT promoter with 117 bp ApoE/HCR1 enhancer | Fabry disease | FLT190 | [187,188] |
| Em-hAATsh | Human AAT, synthetic enhancer | 139 | Shorten −133/+51 hAAT promoter divided on 4 parts with synthetic enhancer composed of hepatocyte TF binding sites | Hemophilia A | ZS802 | [189,190] |
| mTTR mut | Murine TTR | 223 | −138/−135 gact>tgtg mutant mTTR promoter | Hemophilia A | NGGT003 | [191] |
| mTTR mut | Murine TTR | 223 | −138/−135 gact>tgtg mutant mTTR promoter | Hemophilia A | SPK-8011 (dirloctocogene samoparvovec) | [192,193,194] |
| mTTR enhancer/promoter | Murine TTR | 330 | −204/+5 mTTR promoter with 100 bp mTTR enhancer in antisense orientation | Hemophilia B | AskBio009 (BAX 335) | [195,196] |
| mTTR enhancer/promoter | Murine TTR | 330 | −204/+5 mTTR promoter with 100 bp mTTR enhancer in antisense orientation | Hemophilia A | TAK-754 (BAX 888) | [197,198,199] |
| mTTR enhancer/promoter | Murine TTR | 372 | −202/+27 mTTR promoter with modified mTTR enhancer in antisense orientation Shorten ET promoter | Hemophilia B | ANB-002 | [200,201] |
| E03.TTR | Murine and human TTR | 296 | −189/+1 hTTR promoter with 100 bp mTTR enhancer | Hemophilia A | DTX201 (BAY2599023) | [202,203,204] |
| E03.TTR | Murine and human TTR | 290 | −189/+1 hTTR promoter with 100 bp mTTR enhancer | Wilson disease | UX701 | [205,206] |
| AlMB2-mTTR482 | Murine TTR, human AMBP | 671 | −203/+21 mTTR modified promoter with modified 92 bp mTTR enhancer and 2 copies of modified 162 bp hAMBP enhancer | Phenylketonuria (PKU) | SAR444836 | [207,208] |
| CRMSBS2-mTTR | Murine TTR, human AAT | 307 | −202/+21 mTTR promoter with modified −122/−51 hAAT in antisense orientation | Hemophilia A | PF-07055480, formerly SB-525 (giroctocogene fitelparvovec) | [209,210,211] |
| 3xCRM8-enTTR-mTTR | Murine TTR, human AAT | 548 | −204/+5 mTTR promoter with 100 bp mTTR enhancer and 3 copies of CRM8 (−122/−51 hAAT in antisense orientation) | Hemophilia B | TAK-748 (SHP648) | [196,212] |
| 3xCRM8-enTTR-mTTR | Murine TTR, human AAT | 520 | −202/+1 mTTR core promoter with 100 bp mTTR enhancer and 3 copies of CRM8 (−122/−51 hAAT in antisense orientation) | Hemophilia B | VGB-R04 | [213] |
| HCB | Xenopus laevis Alb, human AMBP | 146 | −67/−26 xAlb promoter (SynO region) with AbpShort (region of human AMBP shortened to 56 bp), and predicted conservative TSS | Hemophilia A | ASC618 | [214,215,216] |
| GT001 (vector title) | Xenopus laevis Alb, canine AAT, human ApoE/HCR1 | 266 | 16 bpHCR1 enhancer with modified canine AAT and −66/+38 Xenopus laevis Alb | Hemophilia A | GS1191-0445 | [217,218] |
| LSP | Human TBG and AMBP | 698 | −474/+3 TBG with 2 copies of 101 bp AMBP enhancer | MPS VI (Mucopolysaccharidosis Type VI) | AAV2/8.TBG.hARSB | [219,220] |
| LSP | Human TBG and AMBP | 747 | −475/+4 TBG promoter with 2 copies of modified 98 bp AMBP enhancer with 3 point mutations | Pompe disease | ACTUS-101 | [221,222] |
| LSP | Human TBG and AMBP | 734 | −475/+4 TBG promoter with 2 copies of 98 bp AMBP enhancer with 3 point mutations | Hemophilia B | DTX101 | [158,223] |
| LSP * | Human TBG and AMBP | 698 | −474/+3 TBG promoter with 2 copies of 101 bp AMBP enhancer | Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency | DTX301 | [224,225,226,227] |
| LXP2.1 | Completely synthetic | 188 | Consists of hepatocyte TF binding sites | Hemophilia A | BBM-H803 (BBM 002) | [228] |
| LXP2.1 | Completely synthetic | 188 | Consists of hepatocyte TF binding sites | Hemophilia B | BBM-H901 | [229] |
| G6PC1 | Human G6PC1 | 2864 | −2786/+78 hG6PC1 native promoter | Glycogen storage disease type I (GSDIa) | DTX401 | [230,231] |
| C7 | NS | NS | NS | Fabry Disease | AMT-191 | [232] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Artemyev, V.; Paremskaia, A.I.; Dzhioeva, A.A.; Mishina, D.; Bogdanov, V.; Krupinova, J.; Mazloum, A.; Feoktistova, S.G.; Mityaeva, O.N.; Volchkov, P.Y. Engineering Liver-Specific Promoters: A Comprehensive Review of Design, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications in Gene Therapy. Cells 2026, 15, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells15010014
Artemyev V, Paremskaia AI, Dzhioeva AA, Mishina D, Bogdanov V, Krupinova J, Mazloum A, Feoktistova SG, Mityaeva ON, Volchkov PY. Engineering Liver-Specific Promoters: A Comprehensive Review of Design, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications in Gene Therapy. Cells. 2026; 15(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells15010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleArtemyev, Valentin, Anastasiia Iu. Paremskaia, Amina A. Dzhioeva, Daria Mishina, Viktor Bogdanov, Julia Krupinova, Ali Mazloum, Sofya G. Feoktistova, Olga N. Mityaeva, and Pavel Yu. Volchkov. 2026. "Engineering Liver-Specific Promoters: A Comprehensive Review of Design, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications in Gene Therapy" Cells 15, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells15010014
APA StyleArtemyev, V., Paremskaia, A. I., Dzhioeva, A. A., Mishina, D., Bogdanov, V., Krupinova, J., Mazloum, A., Feoktistova, S. G., Mityaeva, O. N., & Volchkov, P. Y. (2026). Engineering Liver-Specific Promoters: A Comprehensive Review of Design, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications in Gene Therapy. Cells, 15(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells15010014


.png)



