Lipid Metabolic Changes and Mitochondrial Stress in Ethanol-Treated Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells: Initial Events Leading to Alcoholic Chronic Lung Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture Studies
2.3. Characterization of Immortalized Human AT2 Cells and Cytotoxicity of EtOH
2.4. Cytokines and Chemokines
2.5. Oxidative Stress
2.6. Mitochondrial Stress and Real-Time ATP Production Rate
2.7. Analysis of Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters (FAEEs) and Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC)
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
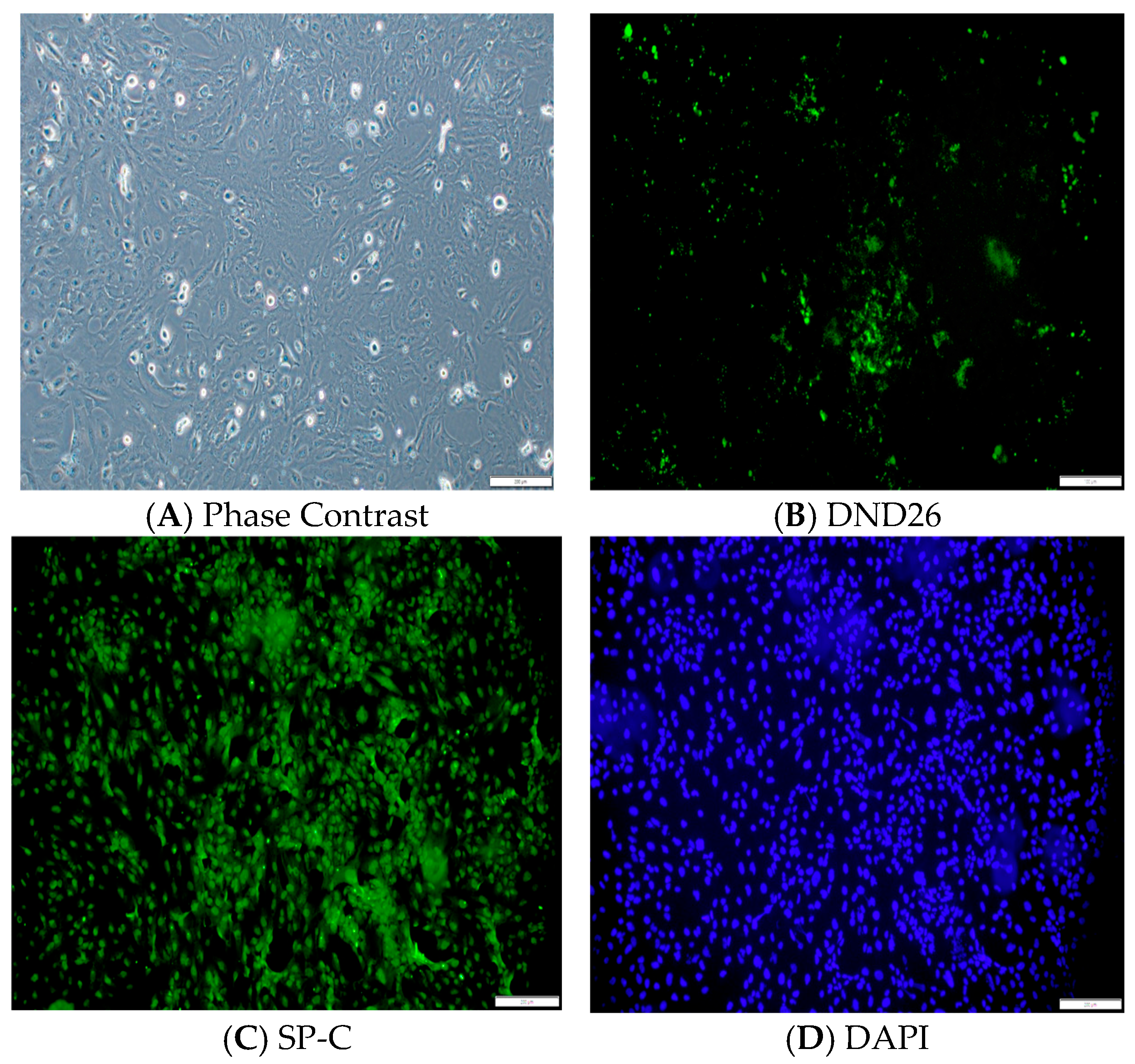
Phenotypic Characterization of Immortalized Human AT2 Cells
4. Concentration-Dependent Studies
4.1. Viability and Cytotoxicity
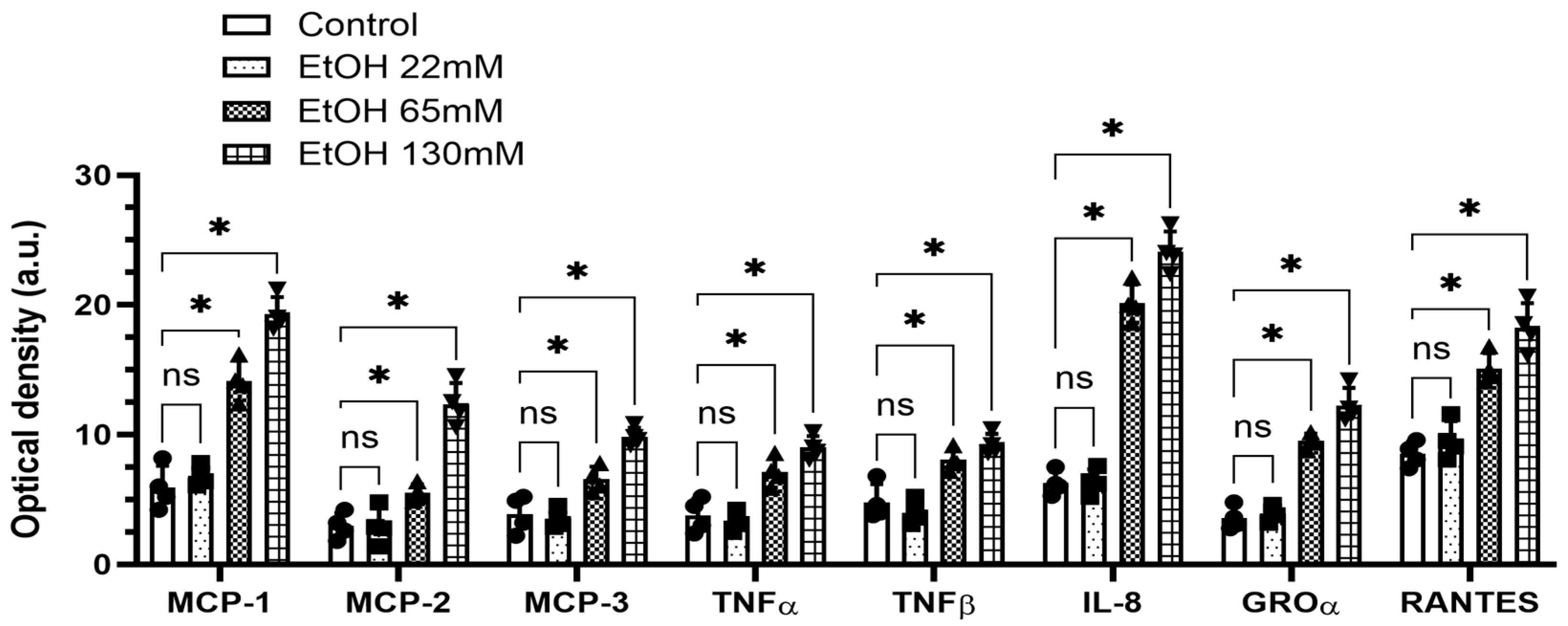
4.2. EtOH-Induced Secretion of Cytokines and Chemokines
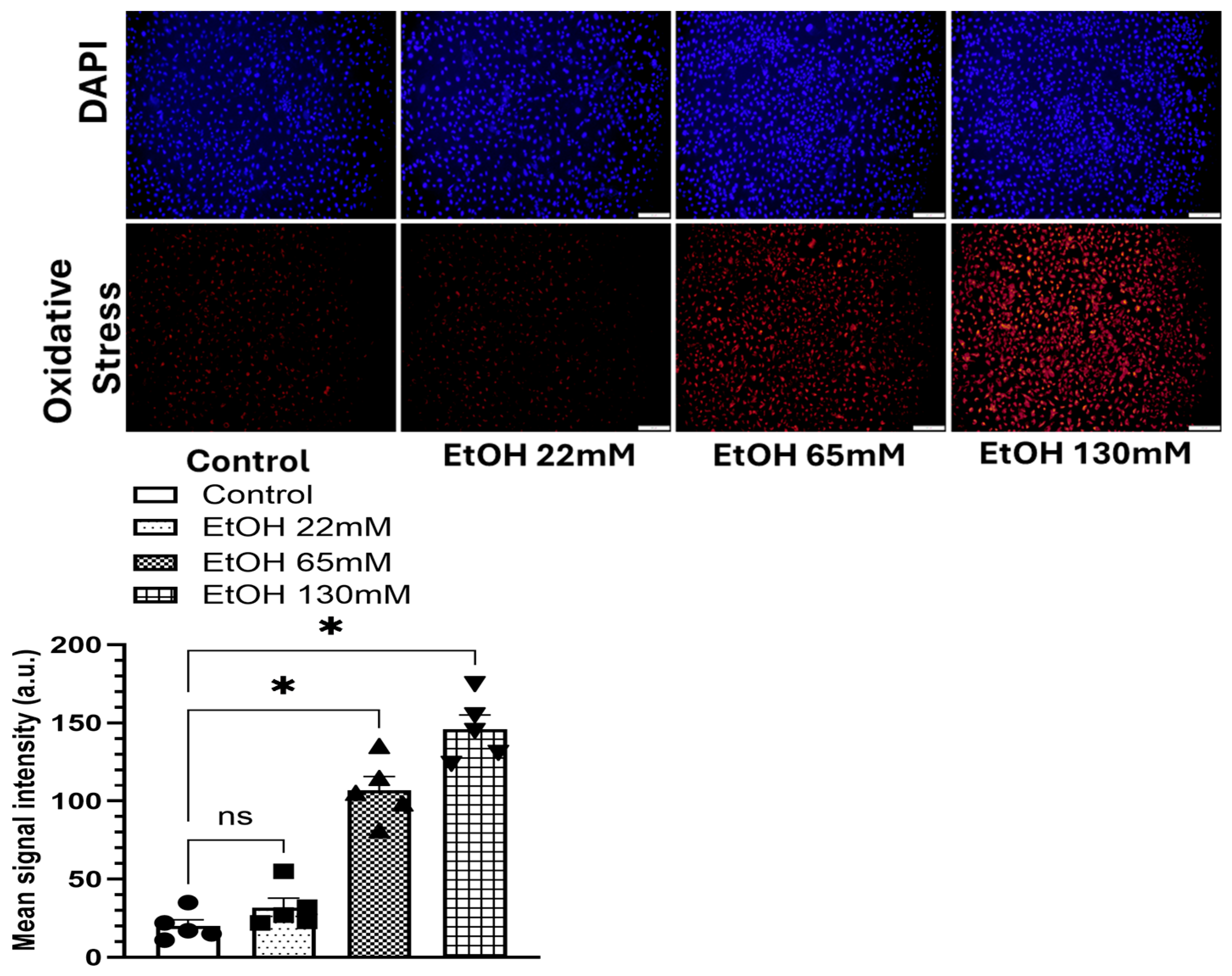
4.3. EtOH-Induced Oxidative Stress
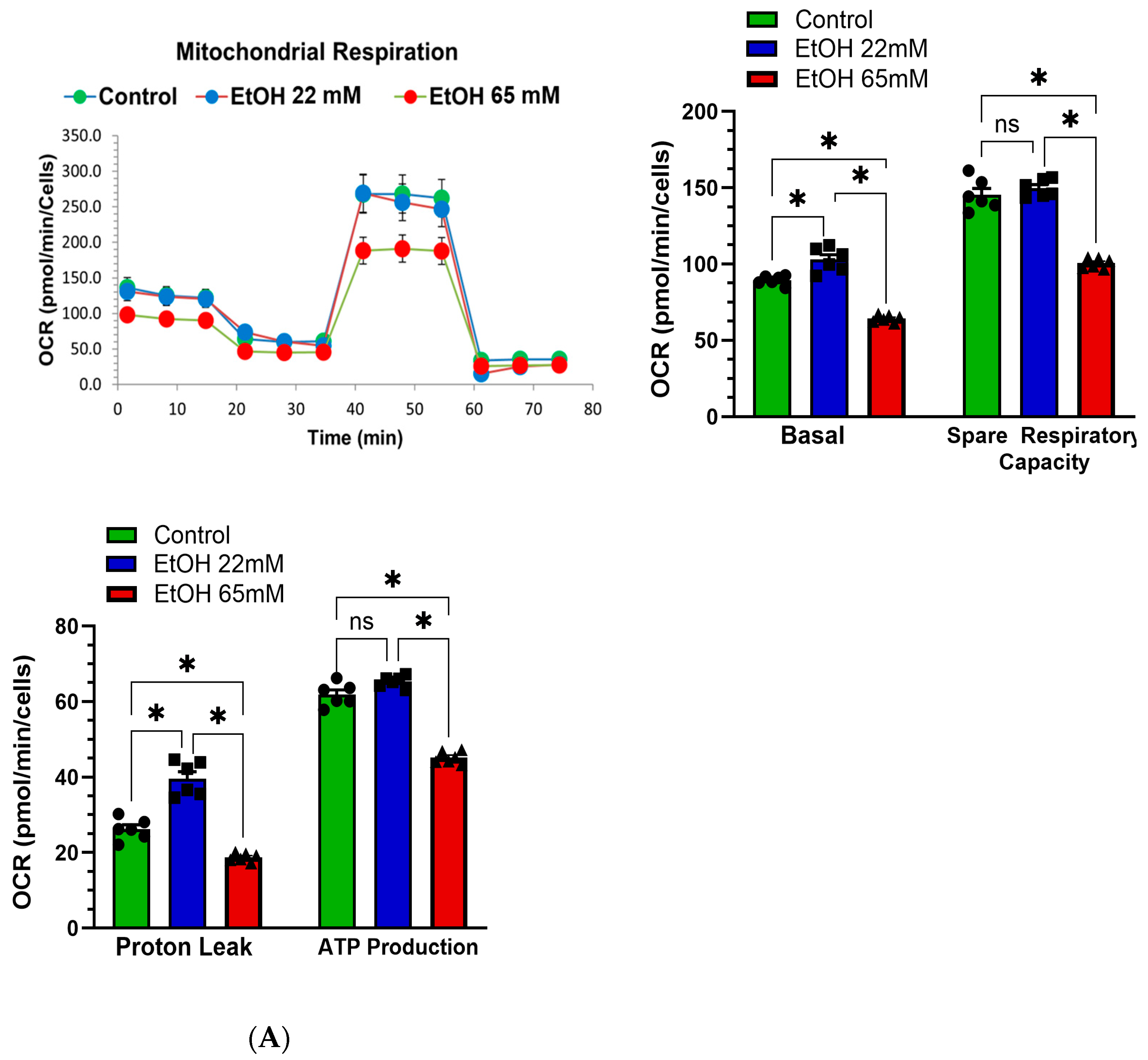
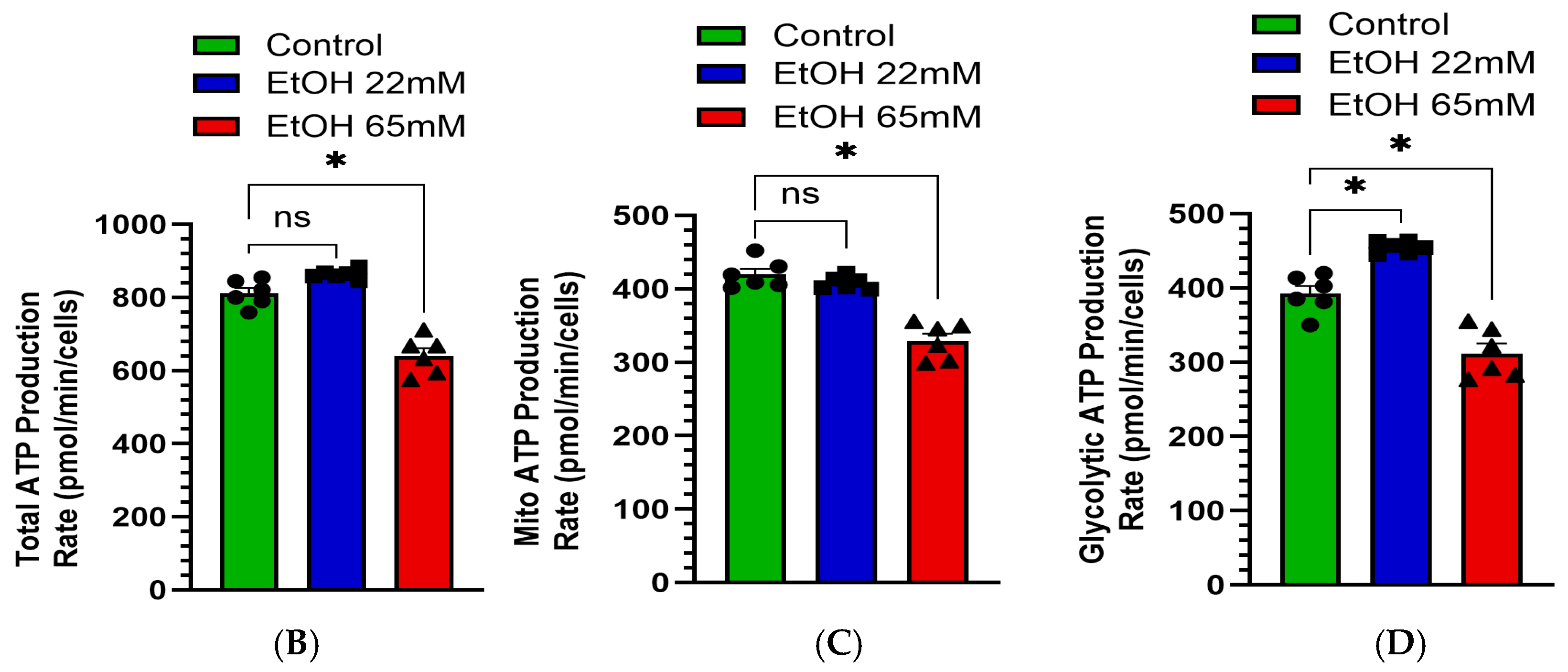
4.4. EtOH-Induced Mitochondrial Stress and Reduced Real-Time ATP Production Rate
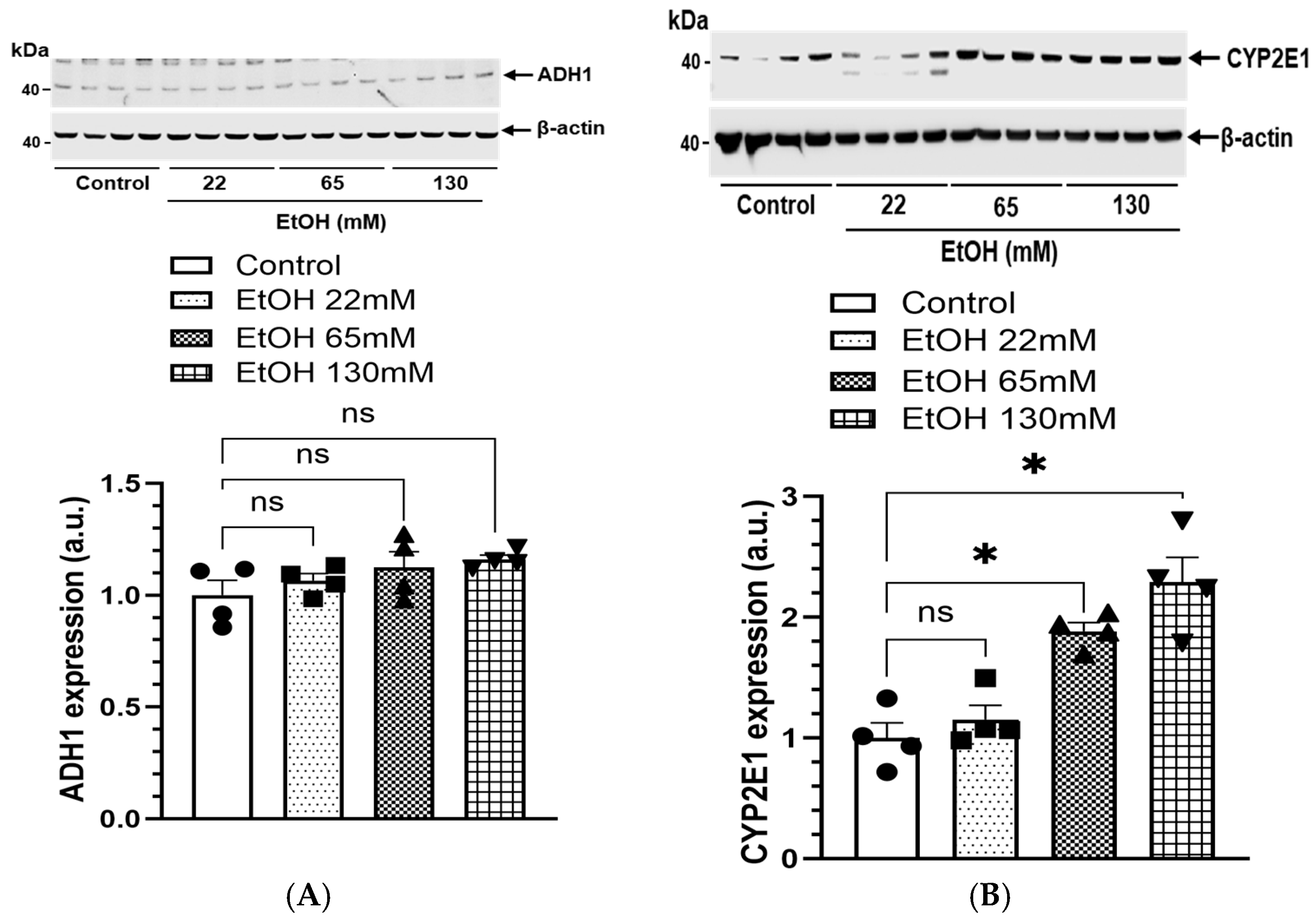
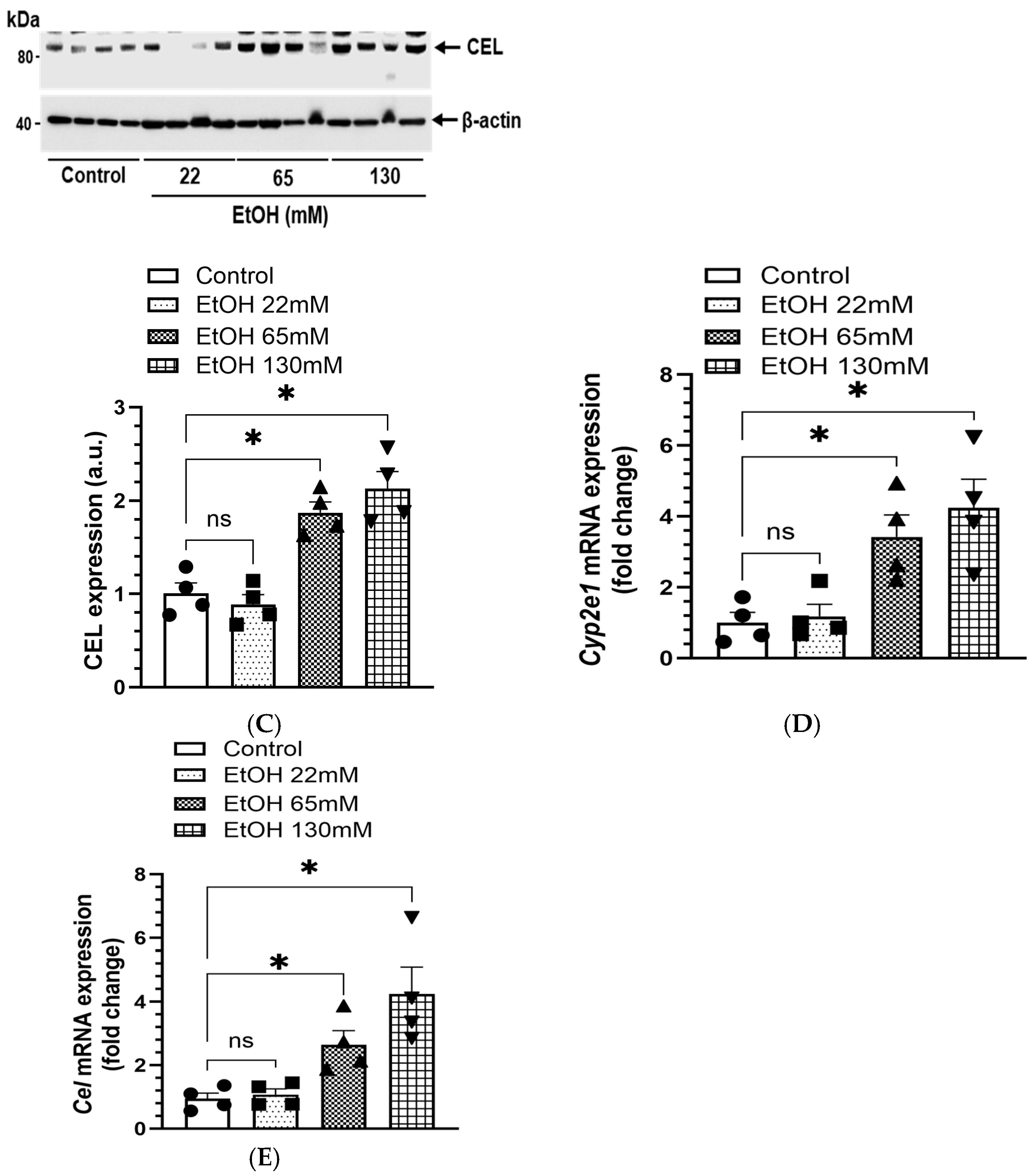
4.5. Expression of EtOH Metabolizing Proteins and Genes
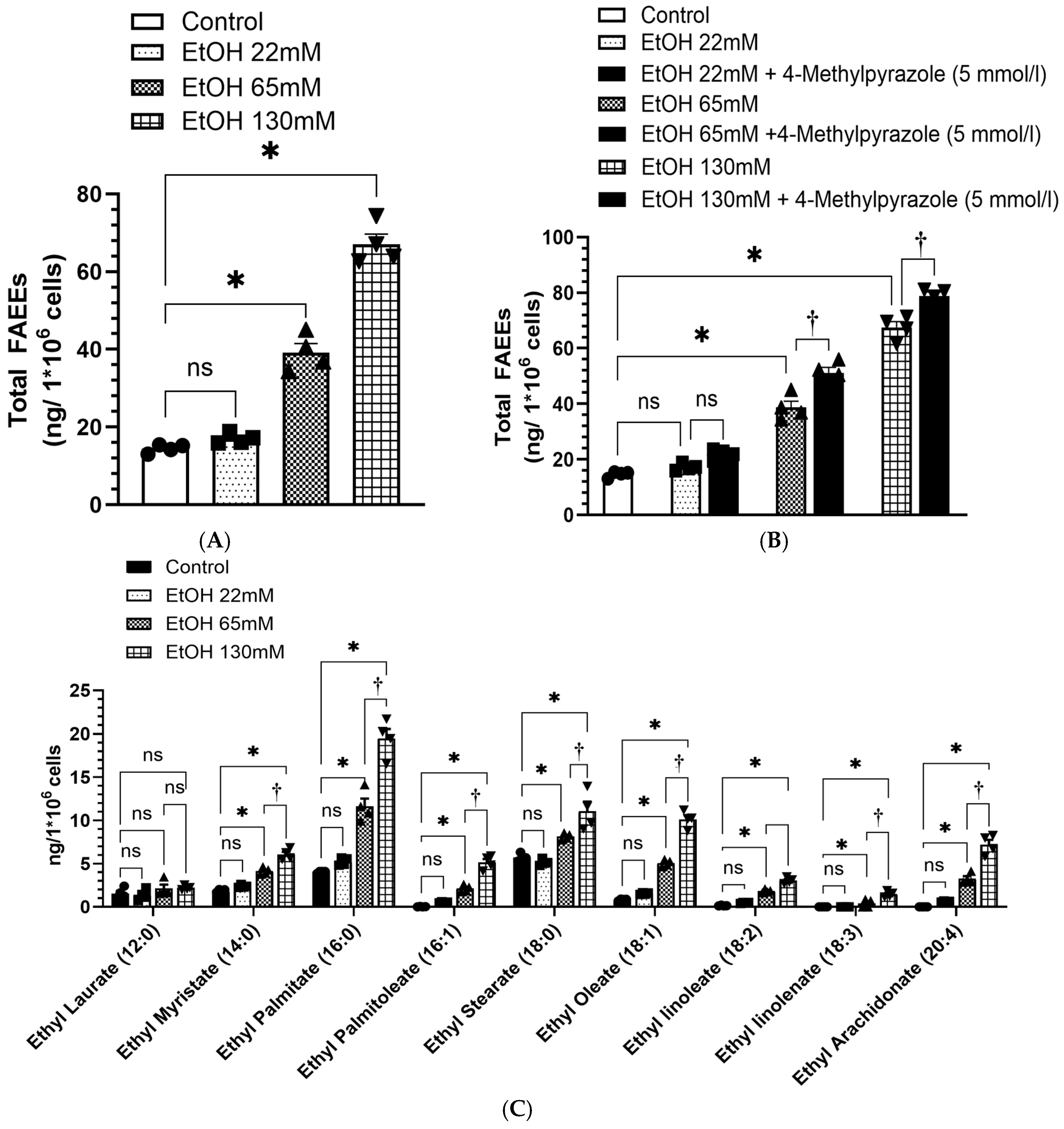
4.6. Increased Formation of FAEEs in AT2 Cells Treated with EtOH
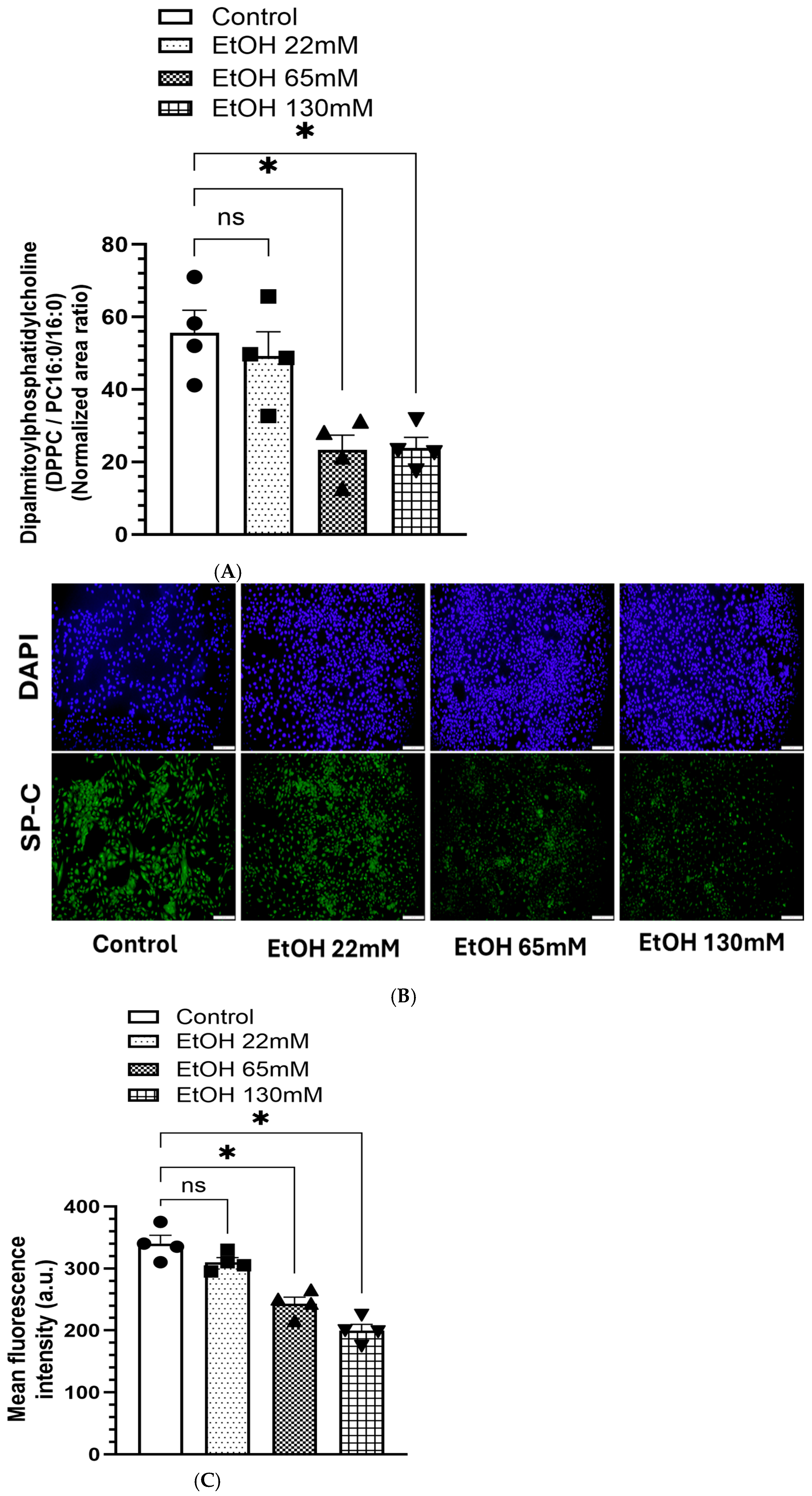
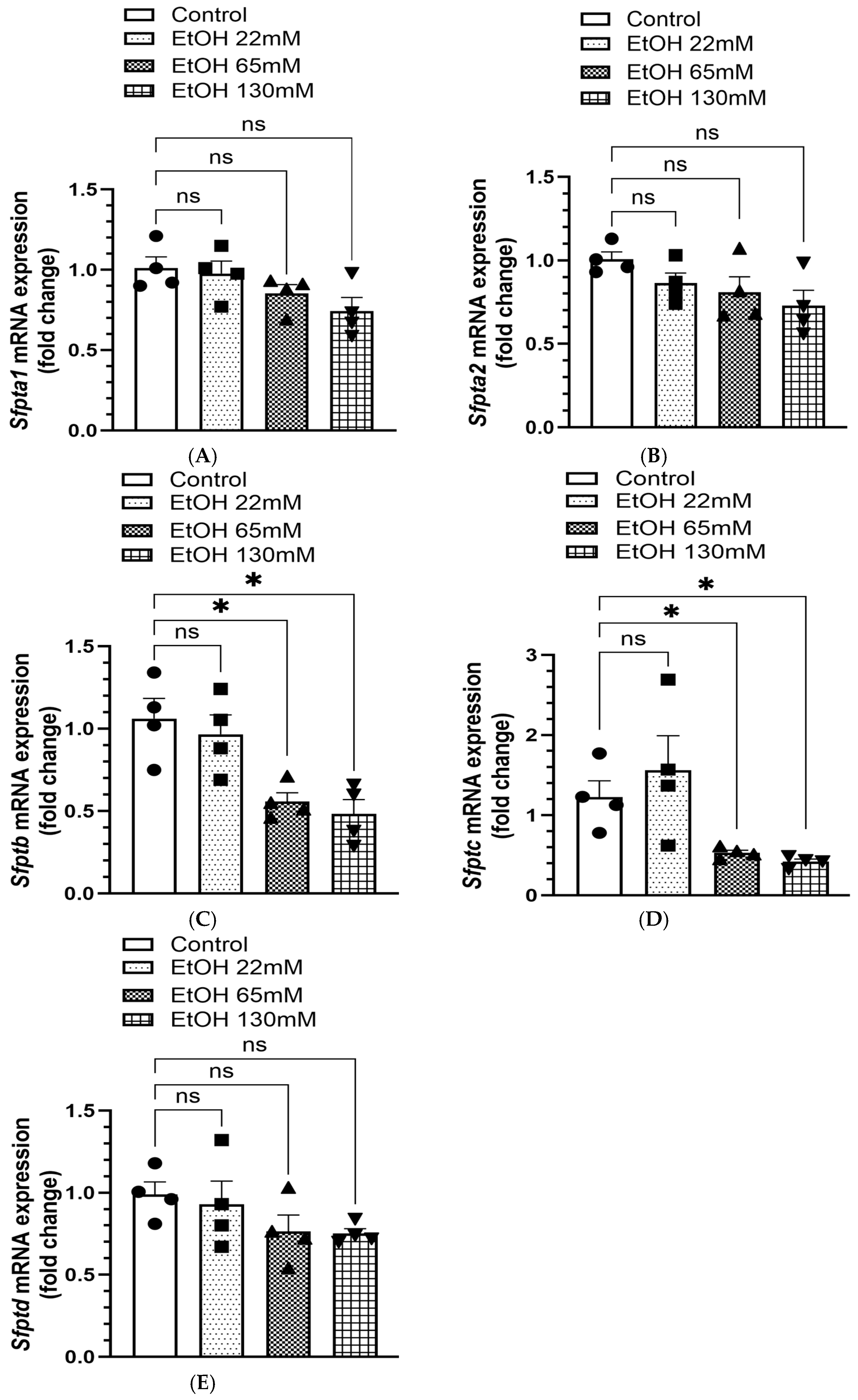
4.7. Reduced Levels of DPPC and Associated SPs in AT2 Cells Treated with EtOH
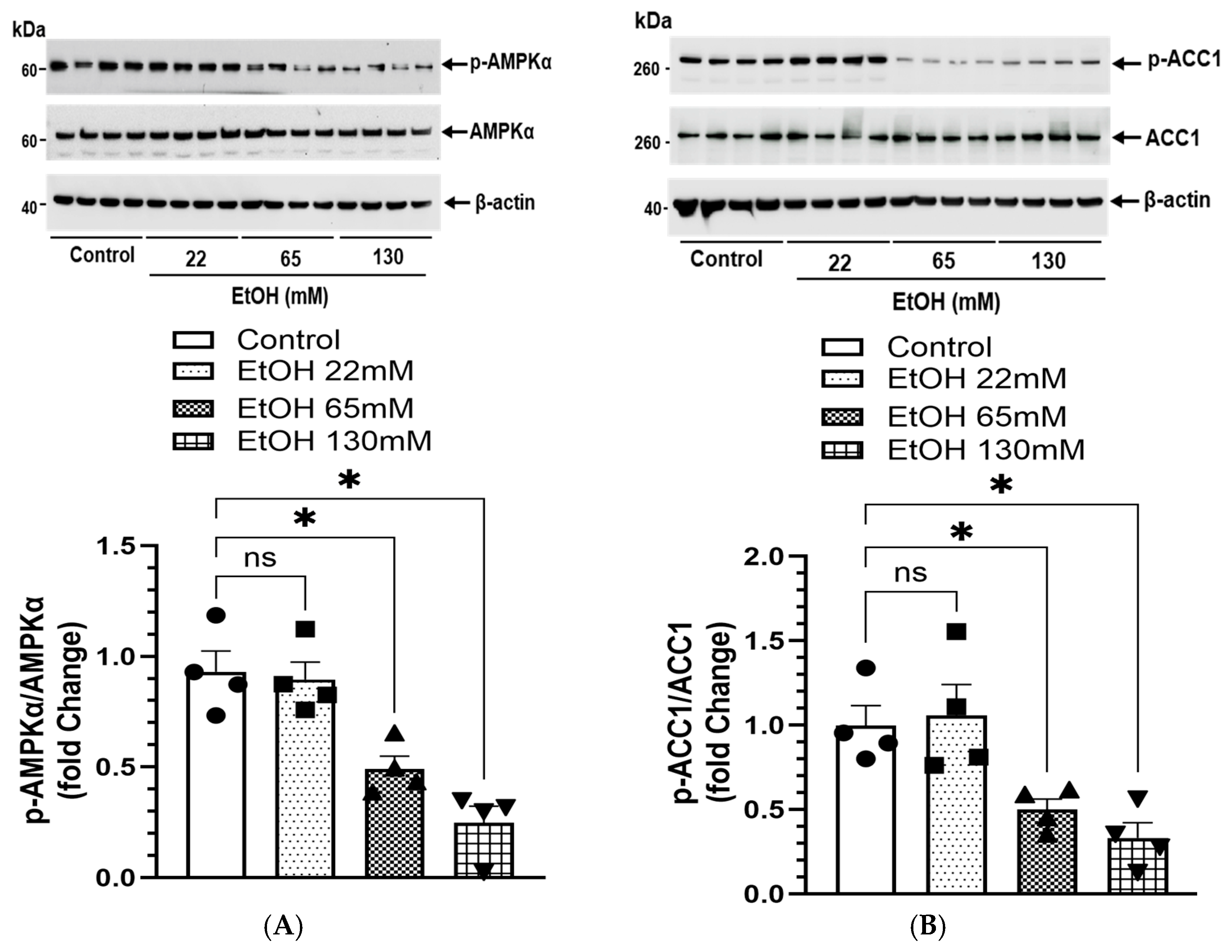
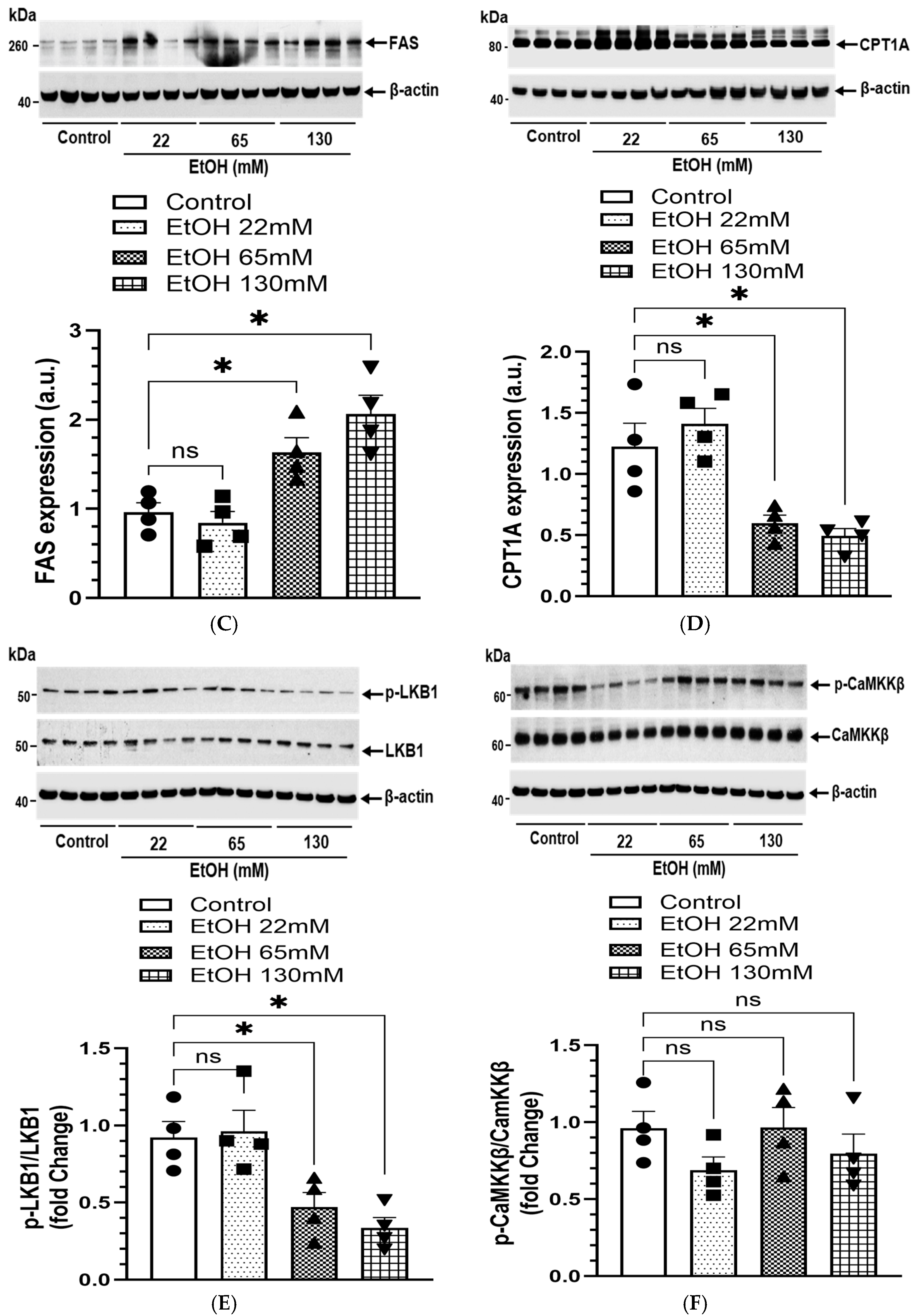
4.8. EtOH-Induced Changes in AMPKα Signaling and Lipogenesis
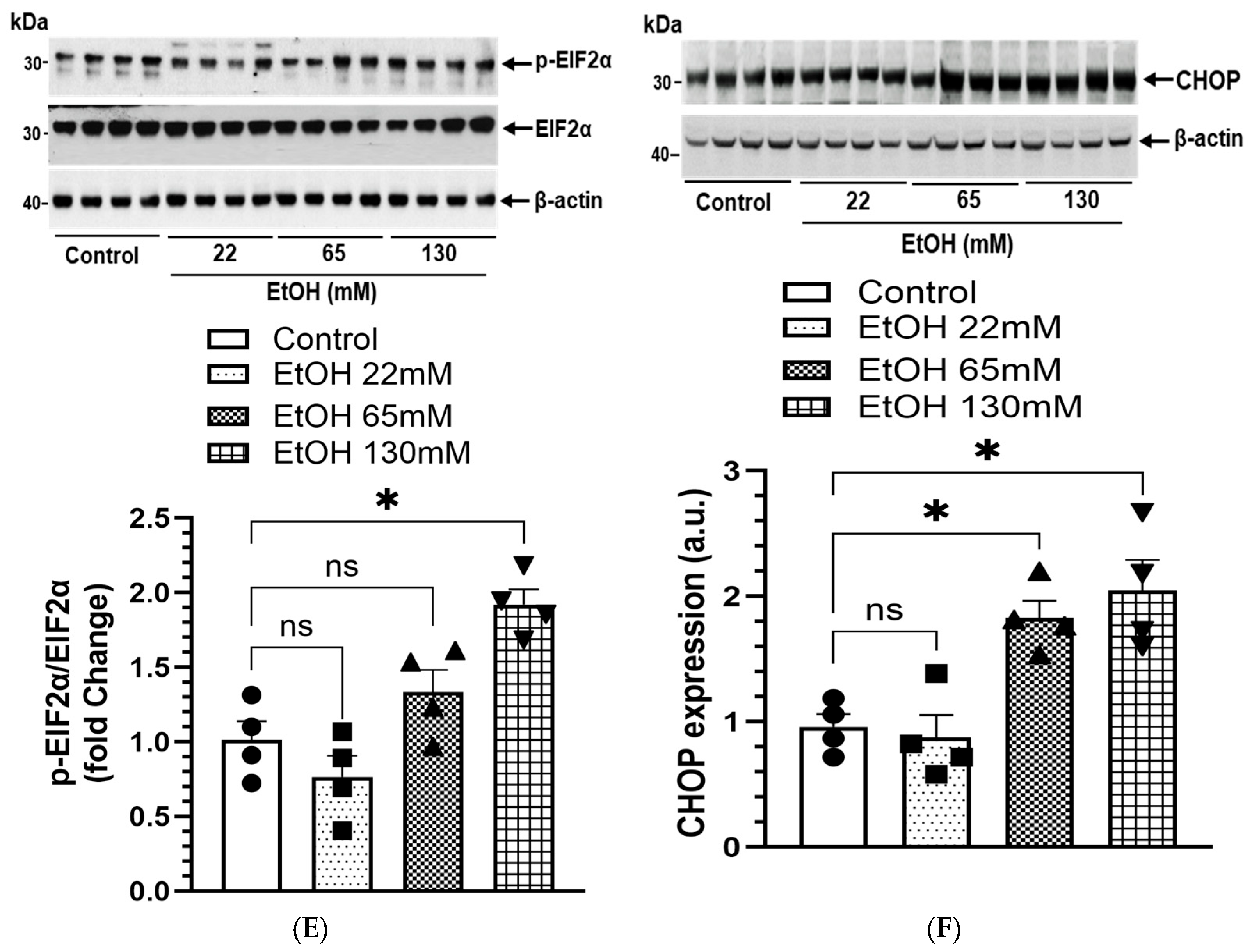
4.9. EtOH-Induced ER Stress
5. Time-Dependent Studies
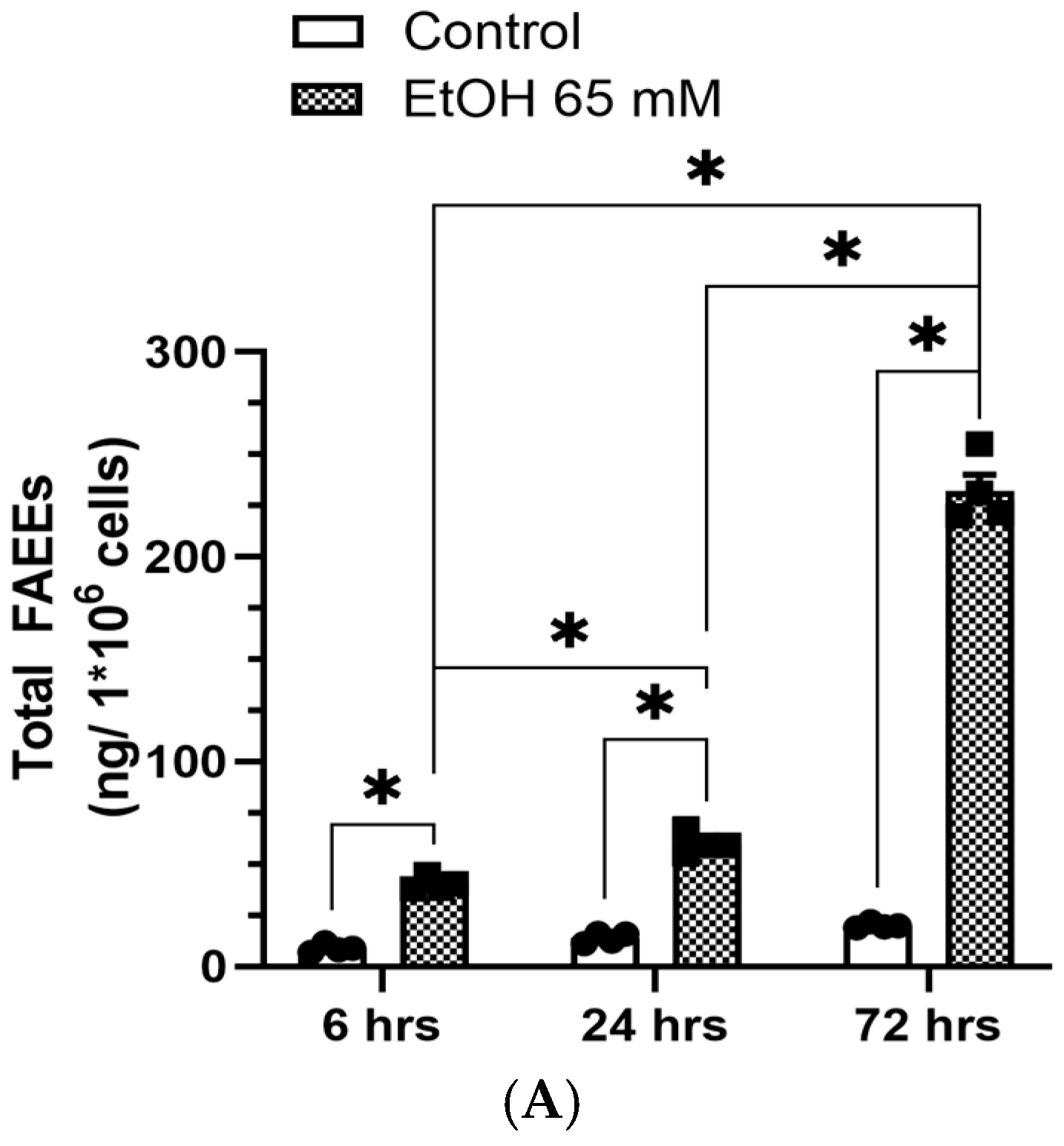
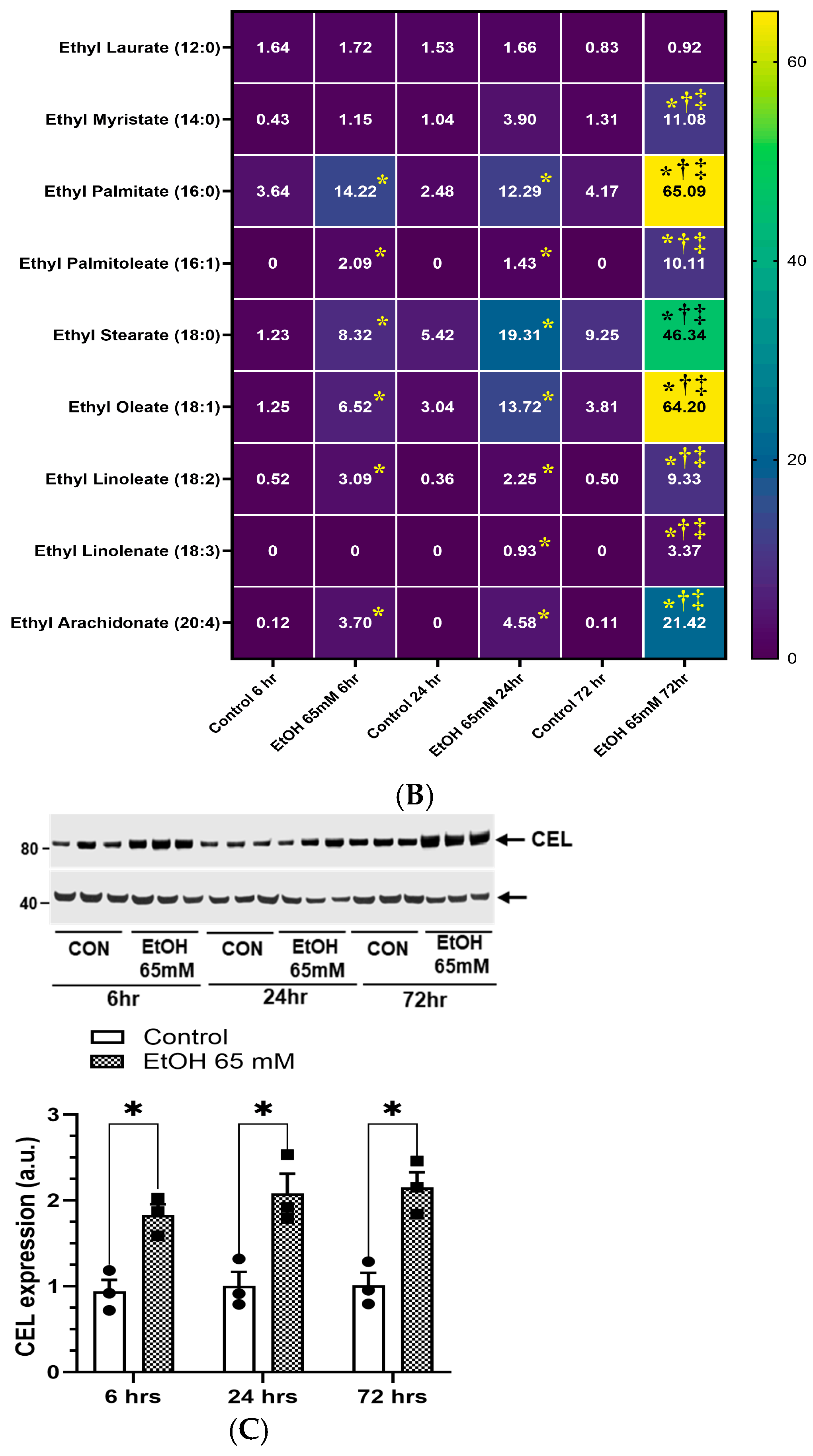
5.1. Increased Formation of FAEEs and Expression of CEL in AT2 Cells Treated with EtOH
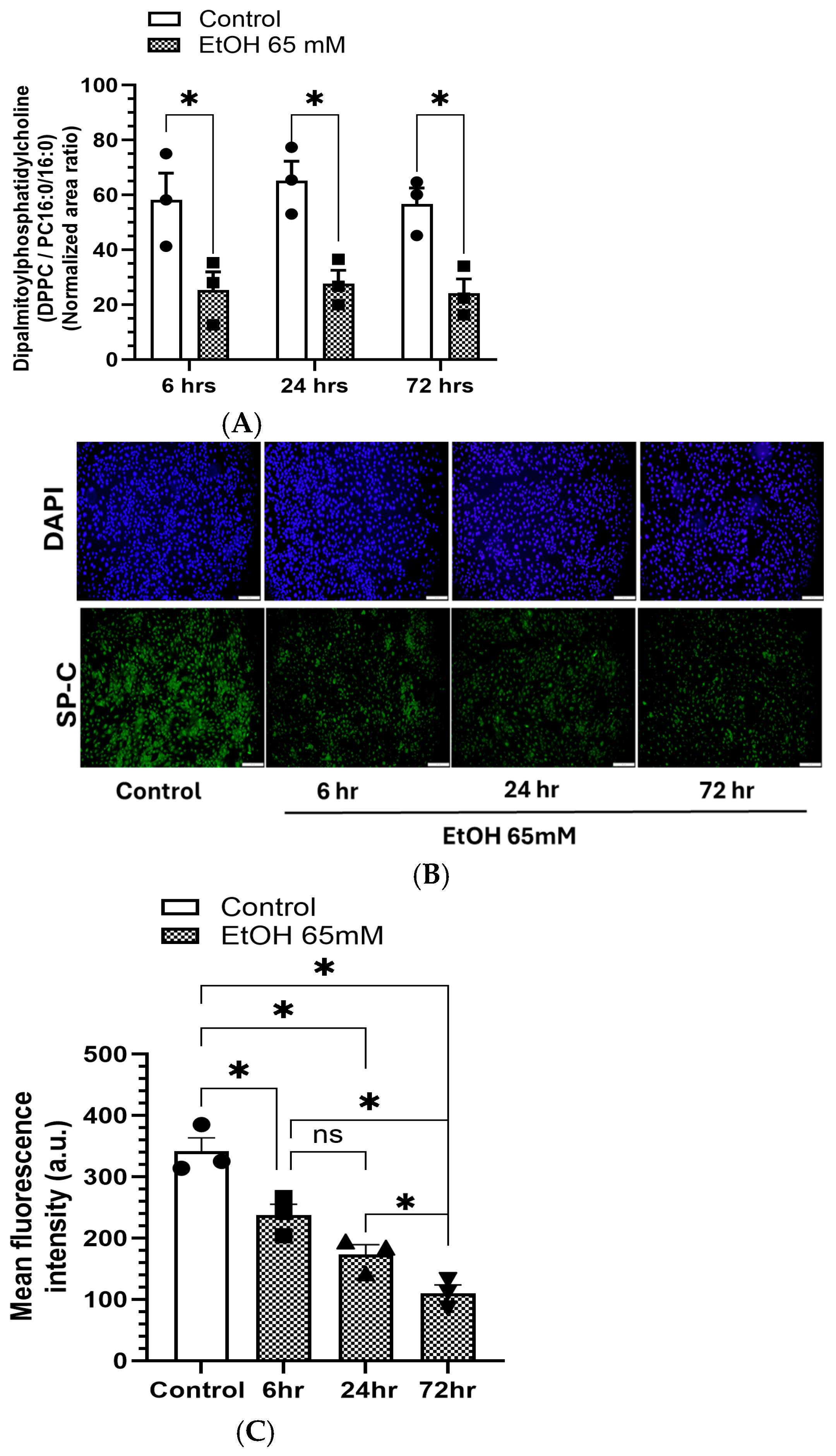
5.2. Reduced DPPC Levels and Expression of SP-C in AT2 Cells Treated with EtOH
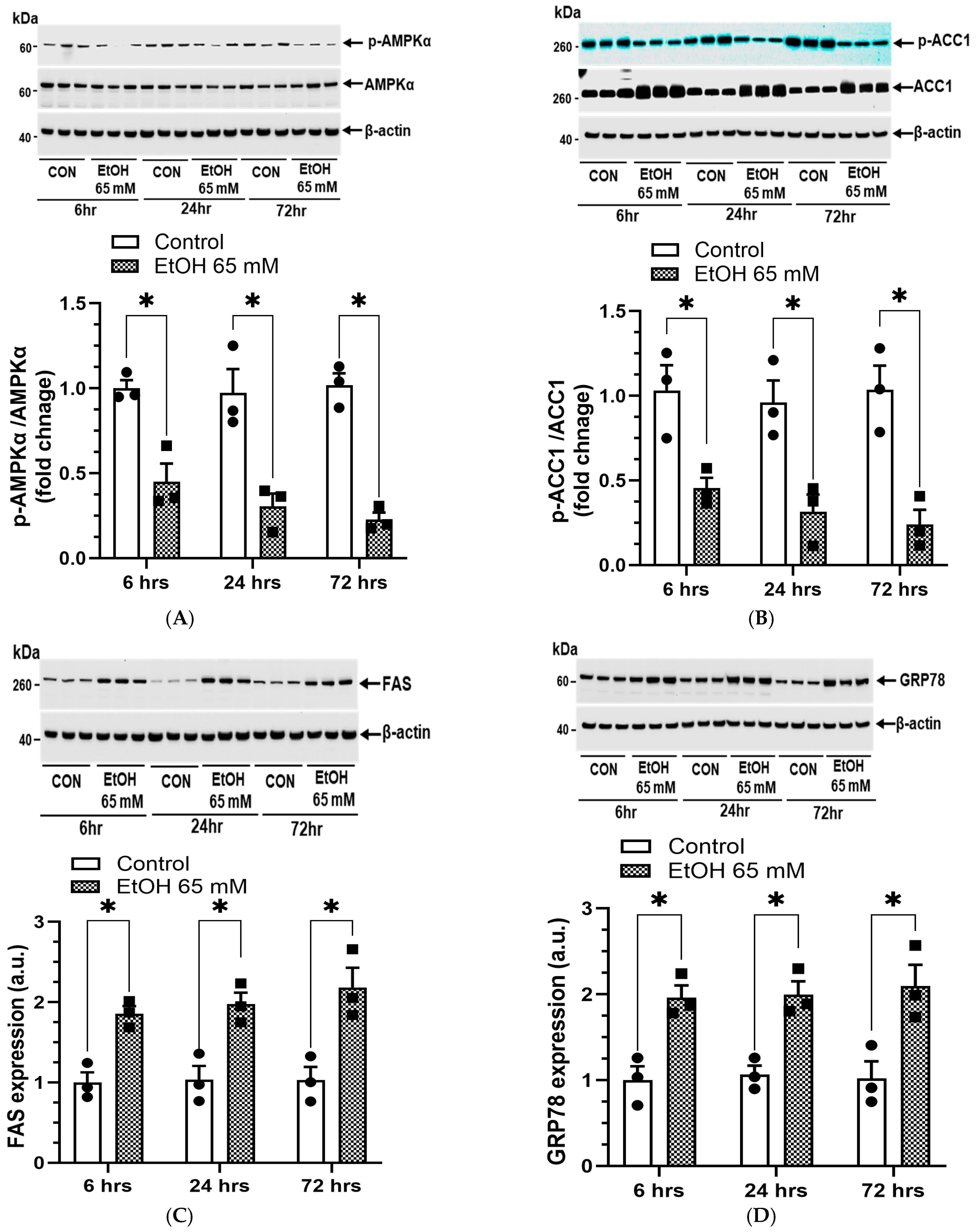
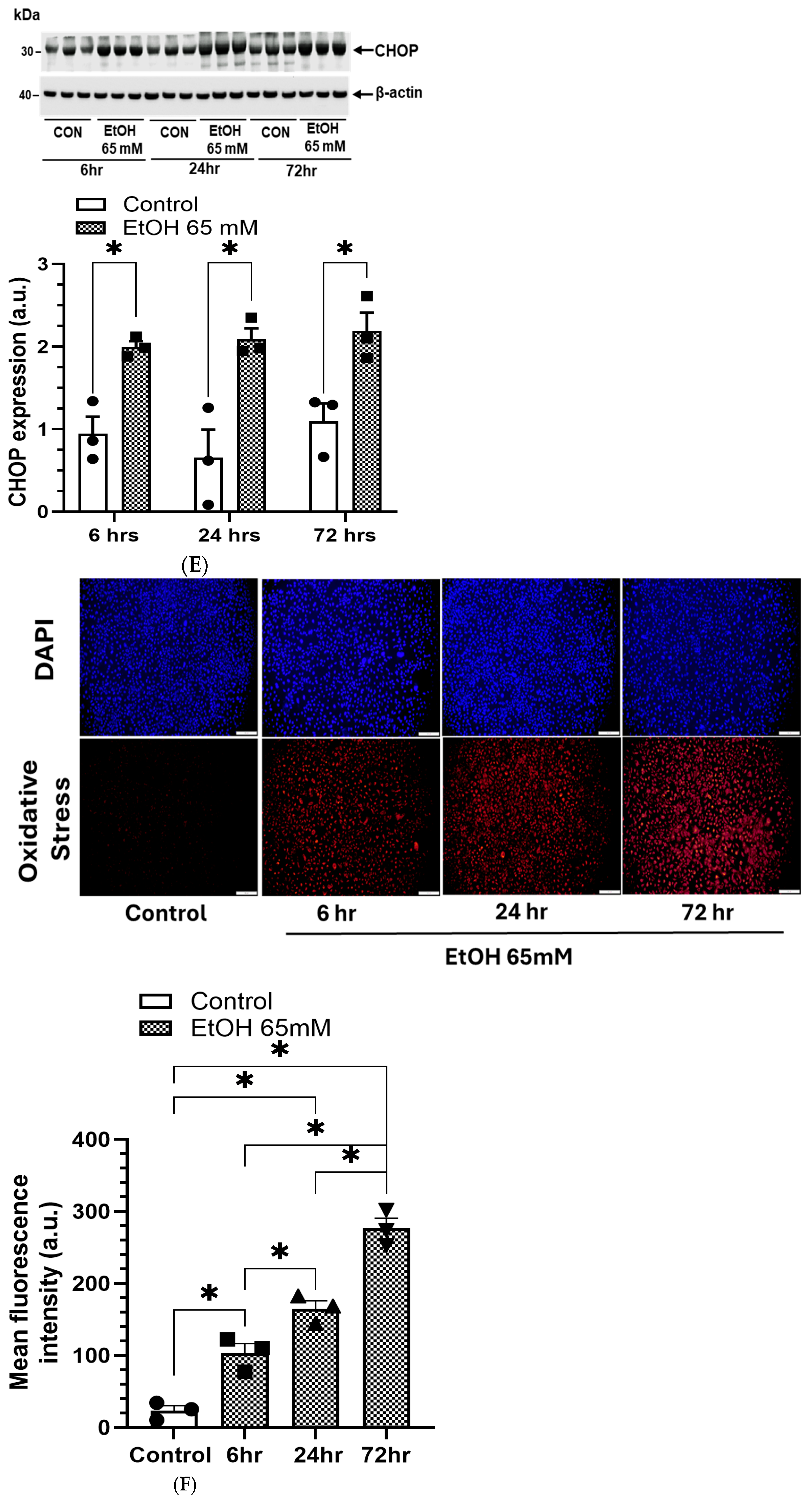
5.3. AMPKα/ER Stress Signaling and Oxidative Stress
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC1 | Acetyl CoA carboxylase 1 |
| ADH1 | Alcohol dehydrogenase 1 |
| AMPKα | AMP activated protein kinase α |
| ARLD | Alcohol-related lung disease |
| AT2 | Alveolar type 2 epithelial cells |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| AUD | Alcohol use disorder |
| BAC | Blood alcohol concentration |
| CEL | Carboxyl ester lipase |
| CPT1A | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A |
| CYP2E1 | Cytochrome P450 2E1 |
| DPPC | Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine |
| ECAR | Extracellular acidification rate |
| EIF2α | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| FAEEs | Fatty acid ethyl esters |
| GROα | Growth-Regulated Oncogene |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| IRE1α | Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| LKB1 | Liver kinase B1 |
| OCR | Oxygen consumption rate |
| PERK | Protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase |
| RANTES | Regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted |
| SP-C | Surfactant protein C |
| XBP1 | X-Box binding protein 1 |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
References
- Sacks, J.J.; Gonzales, K.R.; Bouchery, E.E.; Tomedi, L.E.; Brewer, R.D. 2010 National and State Costs of Excessive Alcohol Consumption. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 49, e73–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boé, D.M.; Vandivier, R.W.; Burnham, E.L.; Moss, M. Alcohol abuse and pulmonary disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaphalia, L.; Calhoun, W.J. Alcoholic lung injury: Metabolic, biochemical and immunological aspects. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 222, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.J.; Guidot, D.M. Alcohol and the Lung. Alcohol. Res. 2017, 38, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.B.; Johansen, M.O.; Riddersholm, S.J.; Weinreich, U.M. The association between alcohol consumption and pulmonary function: A scoping review. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2024, 33, 230233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results from the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (HHS Publication No. PEP23-07-01-006, NSDUH Series H-58). Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. 2023. Available online: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/report/2022-nsduh-annual-national-report (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Luján, M.; Gallego, M.; Belmonte, Y.; Fontanals, D.; Vallès, J.; Lisboa, T.; Rello, J. Influence of pneumococcal serotype group on outcome in adults with bacteraemic pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, K.L.; Samuelson, D.R.; Wyatt, T.A. Alcohol use disorder: A pre-existing condition for COVID-19? Alcohol 2021, 90, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, S.A.; Koval, M. Alcohol and the Alveolar Epithelium. In Alcohol Use Disorders and the Lung; Guidot, D.M., Mehta, A.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 14, pp. 83–101. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, L.G.; Beier, J.I.; Torres-Gonzales, E.; Schlueter, C.F.; Hudson, S.V.; Artis, A.; Warner, N.L.; Nguyen-Ho, C.T.; Dolin, C.E.; Ritzenthaler, J.D.; et al. Chronic + binge alcohol exposure promotes inflammation and alters airway mechanics in the lung. Alcohol 2019, 80, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simet, S.M.; Sisson, J.H. Alcohol’s Effects on Lung Health and Immunity. Alcohol Res. 2015, 37, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueblinvong, V.; Kerchberger, V.E.; Saghafi, R.; Mills, S.T.; Fan, X.; Guidot, D.M. Chronic Alcohol Ingestion Primes the Lung for Bleomycin-Induced Fibrosis in Mice. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueblinvong, V.; Tseng, V.; Smith, T.; Saghafi, R.; Mills, S.T.; Neujahr, D.C.; Guidot, D.M. TGF β 1 Mediates Alcohol--Induced Nrf2 Suppression in Lung Fibroblasts. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 2731–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteel, G.E. Liver-lung axes in alcohol-related liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, V.; Beier, J.; Ritzenthaler, J.; Roman, J.; Arteel, G. Potential Role of the Gut/Liver/Lung Axis in Alcohol-Induced Tissue Pathology. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 2477–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuutinen, H.; Lindros, K.O.; Salaspuro, M. Determinants of Blood Acetaldehyde Level during Ethanol Oxidation in Chronic Alcoholics. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1983, 7, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkawi, M. In vivo inhibition of liver alcohol dehydrogenase by ethanol administration. Life Sci. 1984, 35, 2353–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panés, J.; Soler, X.; Parés, A.; Caballería, J.; Farrés, J.; Rodés, J.; Parés, X. Influence of liver disease on hepatic alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases. Gastroenterology 1989, 97, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuclan, L.; Ehnert, S.; Ilkavets, I.; Weng, H.L.; Gaitantzi, H.; Tsukamoto, H.; Ueberham, E.; Meindl-Beinker, N.M.; Singer, M.V.; Breitkopf, K.; et al. TGF-beta enhances alcohol dependent hepatocyte damage via down-regulation of alcohol dehydrogenase I. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardesty, J.; Day, L.; Warner, J.; Warner, D.; Gritsenko, M.; Asghar, A.; Stolz, A.; Morgan, T.; McClain, C.; Jacobs, J.; et al. Hepatic Protein and Phosphoprotein Signatures of Alcohol-Associated Cirrhosis and Hepatitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2022, 192, 1066–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laposata, M. Fatty acid ethyl esters: Nonoxidative metabolites of ethanol. Addict. Biol. 1998, 3, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, L.G.; Sobel, B.E. Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by fatty acid ethyl esters, myocardial metabolites of ethanol. J. Clin. Investig. 1983, 72, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laposata, E.A.; Lange, L.G. Presence of nonoxidative ethanol metabolism in human organs commonly damaged by ethanol abuse. Science 1986, 231, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaphalia, B.S.; Ansari, G.A. Fatty acid ethyl esters and ethanol-induced pancreatitis. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2001, 47, OL173–OL179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manautou, J.E.; Carlson, G.P. Ethanol-induced fatty acid ethyl ester formation in vivo and in vitro in rat lung. Toxicology 1991, 70, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manautou, J.E.; Buss, N.J.; Carlson, G.P. Oxidative and non-oxidative metabolism of ethanol by the rabbit lung. Toxicol. Lett. 1992, 62, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaphalia, L.; Boroumand, N.; Hyunsu, J.; Kaphalia, B.S.; Calhoun, W.J. Ethanol metabolism, oxidative stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in the lungs of hepatic alcohol dehydrogenase deficient deer mice after chronic ethanol feeding. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 277, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaphalia, L.; Srinivasan, M.P.; Kakumanu, R.D.; Kaphalia, B.S.; Calhoun, W.J. Ethanol Exposure Impairs AMPK Signaling and Phagocytosis in Human Alveolar Macrophages: Role of Ethanol Metabolism. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 1682–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapo, J.D.; Barry, B.E.; Gehr, P.; Bachofen, M.; Weibel, E.R. Cell number and cell characteristics of the normal human lung. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1982, 126, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, T.J.; Colby, T.V.; Travis, W.D.; Tuder, R.M.; Reynolds, H.Y.; Brody, A.R.; Cardoso, W.V.; Crystal, R.G.; Drake, C.J.; Engelhardt, J.; et al. Resident cellular components of the human lung: Current knowledge and goals for research on cell phenotyping and function. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillot, L.; Nathan, N.; Tabary, O.; Thouvenin, G.; Le Rouzic, P.; Corvol, H.; Amselem, S.; Clement, A. Alveolar epithelial cells: Master regulators of lung homeostasis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, B.; Salton, F.; Braga, L.; Wade, B.; Confalonieri, P.; Volpe, M.C.; Baratella, E.; Maiocchi, S.; Confalonieri, M. The History and Mystery of Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells: Focus on Their Physiologic and Pathologic Role in Lung. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeligar, S.M.; Chen, M.M.; Kovacs, E.J.; Sisson, J.H.; Burnham, E.L.; Brown, L.A. Alcohol and lung injury and immunity. Alcohol 2016, 55, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaphalia, L.; Kalita, M.; Kaphalia, B.S.; Calhoun, W.J. Effects of acute ethanol exposure on cytokine production by primary airway smooth muscle cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 292, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaphalia, L.; Srinivasan, M.P.; Kaphalia, B.S.; Calhoun, W.J. Alcohol and its metabolites dysregulate cellular bioenergetics and induce oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in primary human bronchial epithelial cells. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 48, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G. AMP-activated protein kinase—An energy sensor that regulates all aspects of cell function. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1895–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, M.P.; Bhopale, K.K.; Amer, S.M.; Wan, J.; Kaphalia, L.; Ansari, G.S.; Kaphalia, B.S. Linking Dysregulated AMPK Signaling and ER Stress in Ethanol-Induced Liver Injury in Hepatic Alcohol Dehydrogenase Deficient Deer Mice. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beers, M.F.; Moodley, Y. When Is an Alveolar Type 2 Cell an Alveolar Type 2 Cell? A Conundrum for Lung Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, P.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Fu, W.; He, W.; Liu, X.; Slutsky, A.S.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Human alveolar epithelial type II cells in primary culture. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaphalia, B.S.; Cai, P.; Khan, M.F.; Okorodudu, A.O.; Ansari, G.A. Fatty acid ethyl esters: Markers of alcohol abuse and alcoholism. Alcohol 2004, 34, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negussie, Y.; Geller, A.; Teutsch, S.M. Getting to Zero Alcohol-Impaired Driving Fatalities: A Comprehensive Approach to a Persistent Problem; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Velden, J.L.; Bertoncello, I.; McQualter, J.L. LysoTracker is a marker of differentiated alveolar type II cells. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, R.; Muire, P.J.; Xi, N.M.; Ji, H.L. Surfactant Protein-C Regulates Alveolar Type 2 Epithelial Cell Lineages via the CD74 Receptor. J. Respir. Biol. Transl. Med. 2024, 1, 10017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzeniewski, C.; Callewaert, D.M. An enzyme-release assay for natural cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 64, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, T.; Lohmann-Matthes, M.L. A quick and simple method for the quantitation of lactate dehydrogenase release in measurements of cellular cytotoxicity and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity. J. Immunol. Methods 1988, 115, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.P.; Bhopale, K.K.; Caracheo, A.A.; Amer, S.M.; Khan, S.; Kaphalia, L.; Loganathan, G.; Balamurugan, A.N.; Kaphalia, B.S. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase attenuates ethanol-induced ER/oxidative stress and lipid phenotype in human pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.P.; Bhopale, K.K.; Caracheo, A.A.; Kaphalia, L.; Loganathan, G.; Balamurugan, A.N.; Rastellini, C.; Kaphalia, B.S. Differential cytotoxicity, ER/oxidative stress, dysregulated AMPKα signaling, and mitochondrial stress by ethanol and its metabolites in human pancreatic acinar cells. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 45, 961–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Kota, S.; Bhopale, K.; Caracheo, A.; Kaphalia, L.; Linares, J.; Romsdahl, T.; Russell, W.; Popov, V.; Boor, P.; et al. Dysregulated hepatic alcohol metabolism: A key factor involved in the pathogenesis of alcohol-associated liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2025, 328, G289–G308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidot, D.M.; Hart, C.M. Alcohol abuse and acute lung injury: Epidemiology and pathophysiology of a recently recognized association. J. Investig. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Fed. Clin. Res. 2005, 53, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlastala, M.P.; Anderson, J.C. The impact of breathing pattern and lung size on the alcohol breath test. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 35, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlastala, M.P.; Anderson, J.C. Alcohol breath test: Gas exchange issues. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 121, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.B. Effect of alcohol on cellular membranes. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1986, 15, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simet, S.M.; Wyatt, T.A.; DeVasure, J.; Yanov, D.; Allen-Gipson, D.; Sisson, J.H. Alcohol increases the permeability of airway epithelial tight junctions in Beas-2B and NHBE cells. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, E.L.; Kovacs, E.J.; Davis, C.S. Pulmonary cytokine composition differs in the setting of alcohol use disorders and cigarette smoking. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L873–L882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghapour, M.; Remels, A.H.V.; Pouwels, S.D.; Bruder, D.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Cloonan, S.M.; Heijink, I.H. Mitochondria: At the crossroads of regulating lung epithelial cell function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L149–L164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davigo, M.; Van Schooten, F.J.; Wijnhoven, B.; Drittij, M.J.; Dubois, L.; Opperhuizen, A.; Talhout, R.; Remels, A.H.V. Alterations in the molecular regulation of mitochondrial metabolism in human alveolar epithelial cells in response to cigarette- and heated tobacco product emissions. Toxicol. Lett. 2024, 401, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Cederbaum, A.I. Alcohol, oxidative stress, and free radical damage. Alcohol Res. Health 2003, 27, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Zhai, Q.; Shi, X. Alcohol-induced oxidative stress and cell responses. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21 (Suppl. 3), S26–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, J.B.; Cahill, A.; Pastorino, J.G. Alcohol and mitochondria: A dysfunctional relationship. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 2049–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Harris, F.L.; Brown, L.A. Alcohol induced mitochondrial oxidative stress and alveolar macrophage dysfunction. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 371593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekala, N.; Trivedi, J.; Bhoj, P.; Togre, N.; Rom, S.; Sriram, U.; Persidsky, Y. Alcohol and e-cigarette damage alveolar-epithelial barrier by activation of P2X7r and provoke brain endothelial injury via extracellular vesicles. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; Molina, P.E. Cellular Bioenergetics: Experimental Evidence for Alcohol-induced Adaptations. Function 2022, 3, zqac039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y. Mitochondrial dynamics in health and disease: Mechanisms and potential targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.C. Fusion and fission: Interlinked processes critical for mitochondrial health. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2012, 46, 265–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.S.; Fan, X.; Guidot, D.M. Alcohol causes alveolar epithelial oxidative stress by inhibiting the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikot, R.T.; Bedi, B.; Li, J.; Yeligar, S.M. Alcohol-induced mitochondrial DNA damage promotes injurious crosstalk between alveolar epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages. Alcohol 2019, 80, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alli, A.A.; Brewer, E.M.; Montgomery, D.S.; Ghant, M.S.; Eaton, D.C.; Brown, L.A.; Helms, M.N. Chronic ethanol exposure alters the lung proteome and leads to mitochondrial dysfunction in alveolar type 2 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L1026–L1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Lipid metabolism reprogramming in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Luo, G.; Ding, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, N.; Geng, Q. The role of fatty acid metabolism in acute lung injury: A special focus on immunometabolism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Mallampalli, R.K. The Role of Surfactant in Lung Disease and Host Defense against Pulmonary Infections. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, M.; Burnham, E.L. Chronic alcohol abuse, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and multiple organ dysfunction. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, S207–S212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisson, J.H. Alcohol and airways function in health and disease. Alcohol 2007, 41, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Capote, K.; Manzanares, D.; Haines, T.; Possmayer, F. Reactive oxygen species inactivation of surfactant involves structural and functional alterations to surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 2808–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.K.; Cismowski, M.J. Oxidative Stress in the Lung—The Essential Paradox. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, W.; Gao, Y. Understanding the impact of ER stress on lung physiology. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1466997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, N.; Hamada, H.; Kashio, M.; Jin, H.; Toyama, Y.; Kimura, K.; Iida, M.; Goto, S.; Saisho, H.; Toshimori, K.; et al. Aberrant quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum impairs the biosynthesis of pulmonary surfactant in mice expressing mutant BiP. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinak, S.J.; Ron, D. The unfolded protein response in lung disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2010, 7, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.C.; Guidot, D.M. The alcoholic lung: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and potential therapies. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2007, 292, L813–L823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Boggaram, V. Proteasome dysfunction inhibits surfactant protein gene expression in lung epithelial cells: Mechanism of inhibition of SP-B gene expression. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2007, 292, L74–L84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguin, F.; Moss, I.; Brown, L.A.; Guidot, D.M. Chronic ethanol ingestion impairs alveolar type II cell glutathione homeostasis and function and predisposes to endotoxin-mediated acute edematous lung injury in rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, A.; Han, Y.; Yan, H.; Sangwan, N.; Cresci, G.A.M. The Gut-Lung Axis During Ethanol Exposure and a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Bacterial Challenge. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Hsu, C.L. Alcohol Use Disorder and the Gut-Brain Axis: A Narrative Review of the Role of Gut Microbiota and Implications for Treatment. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, G.R.; Carling, D. AMP-activated protein kinase: The current landscape for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 527–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Booth, D.M.; Cane, M.C.; Chvanov, M.; Javed, M.A.; Elliott, V.L.; Armstrong, J.A.; Dingsdale, H.; Cash, N.; Li, Y.; et al. Fatty acid ethyl ester synthase inhibition ameliorates ethanol-induced Ca2+-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction and acute pancreatitis. Gut 2014, 63, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Cel | TCGTGGAAGGCGTCAATAAG | CAGGATGTGGCTGAGGATTT |
| Cyp2e1 | CTCGTGCTCTTGCCCTATTT | TGCTGACGGCGTTCTTTATC |
| SfptA1 | GGCTATTGACTGAGCACCTATC | GGTCCCGTGACATTGTGTAA |
| SfptA2 | GAGAGATGGTGTCAAAGGAGAC | TCCAGGCAGCCCATTATTC |
| SfptB | TACTCACTGGGATGAGGTTAGG | GGACACTTCCAGGCATTTCA |
| SfptC | GCACCTGAAACGCCTTCTTATC | TGCTCATCTCCAGAACCATCTC |
| SfptD | GGCTACCTGGAAGCAGAAAT | CTCCACTGAGCTACACATGAC |
| Rplpo | GGAGAAACTGCTGCCTCATATC | CAGCAGCTGGCACCTTATT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srinivasan, M.; Kaphalia, B.S. Lipid Metabolic Changes and Mitochondrial Stress in Ethanol-Treated Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells: Initial Events Leading to Alcoholic Chronic Lung Disease. Cells 2025, 14, 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221817
Srinivasan M, Kaphalia BS. Lipid Metabolic Changes and Mitochondrial Stress in Ethanol-Treated Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells: Initial Events Leading to Alcoholic Chronic Lung Disease. Cells. 2025; 14(22):1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221817
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrinivasan, Mukund, and Bhupendra S. Kaphalia. 2025. "Lipid Metabolic Changes and Mitochondrial Stress in Ethanol-Treated Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells: Initial Events Leading to Alcoholic Chronic Lung Disease" Cells 14, no. 22: 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221817
APA StyleSrinivasan, M., & Kaphalia, B. S. (2025). Lipid Metabolic Changes and Mitochondrial Stress in Ethanol-Treated Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells: Initial Events Leading to Alcoholic Chronic Lung Disease. Cells, 14(22), 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14221817





