Imaging of Proteinopathies in the Brains of Parkinsonian Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
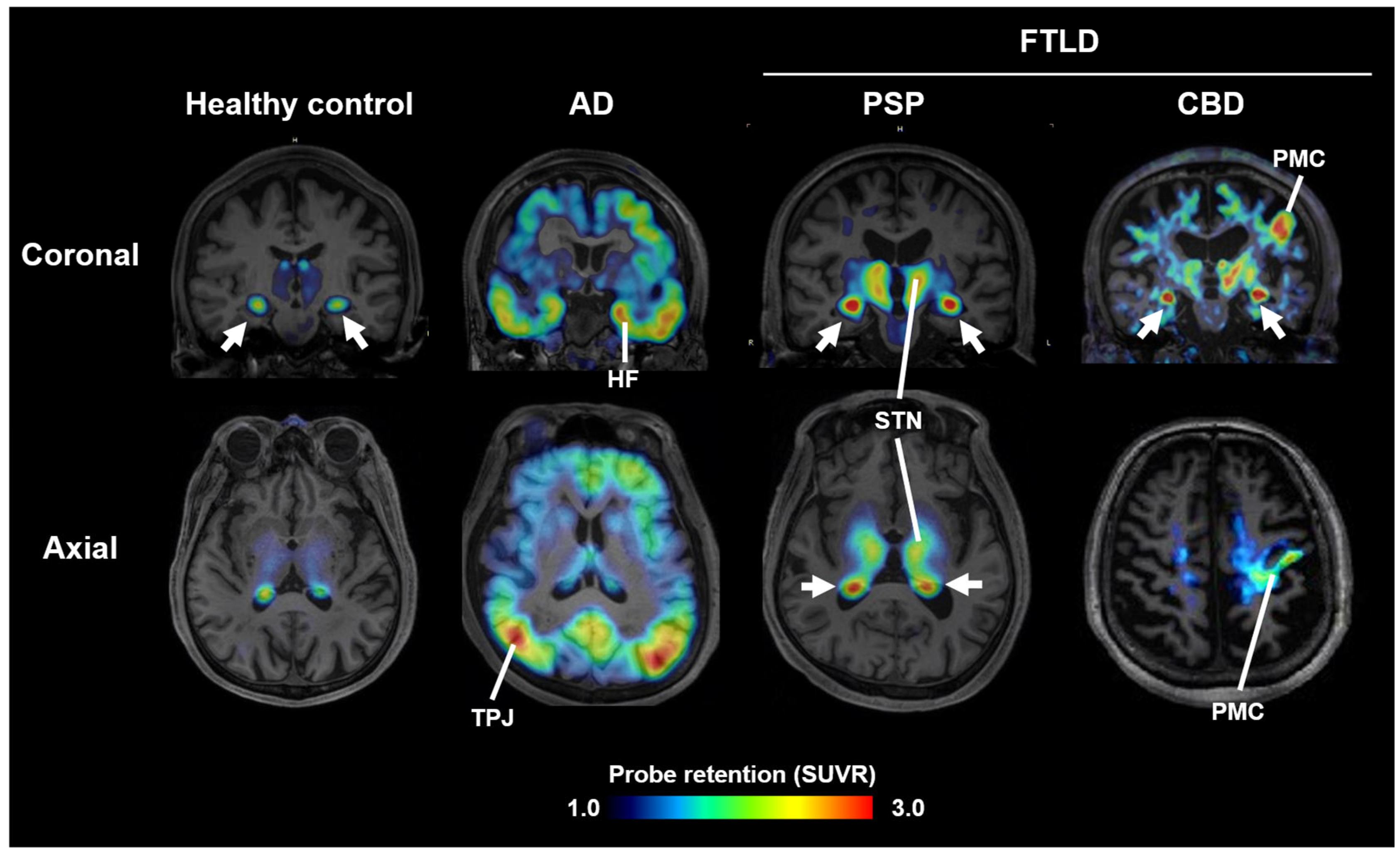
2. Imaging of Tau Pathology in Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
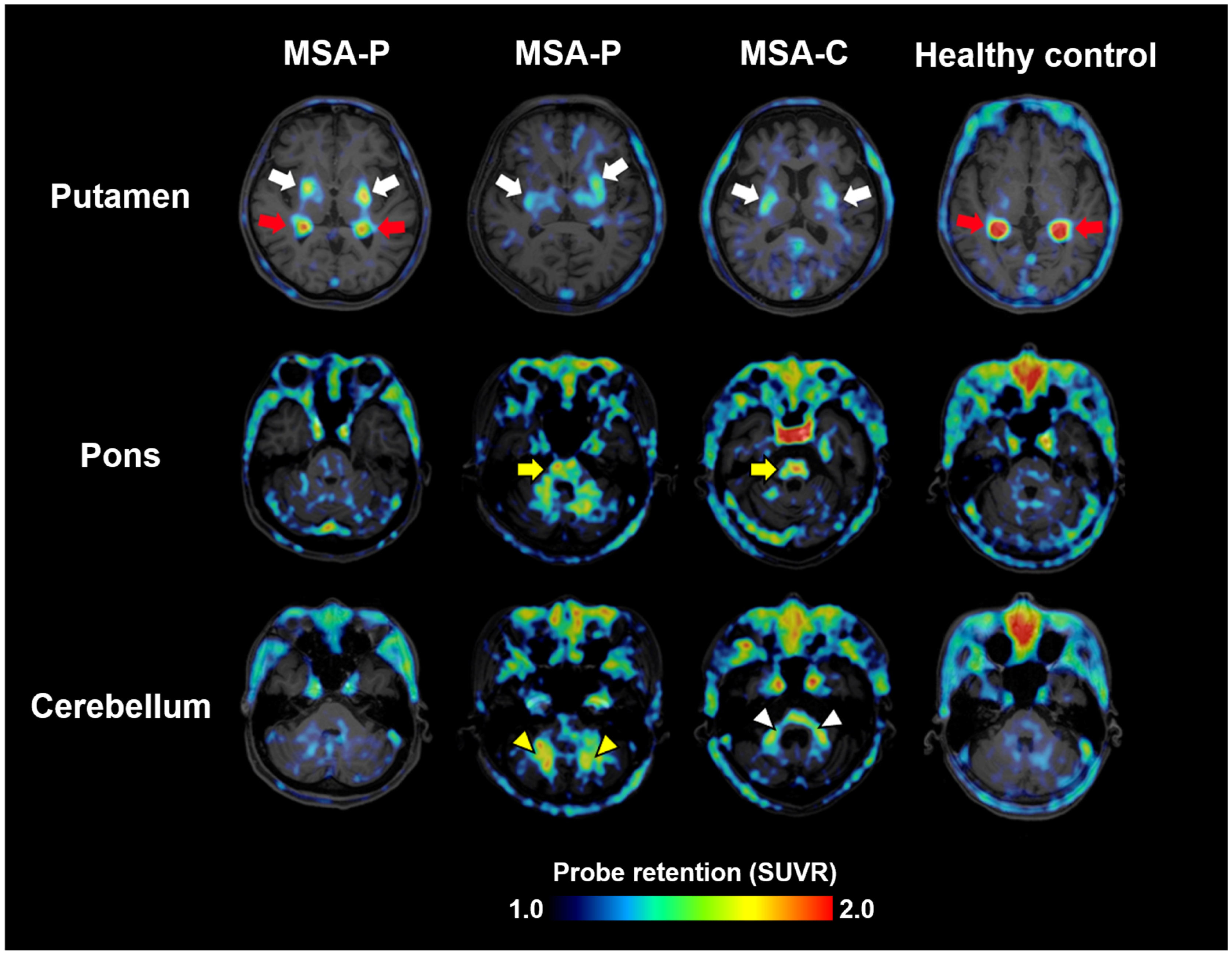
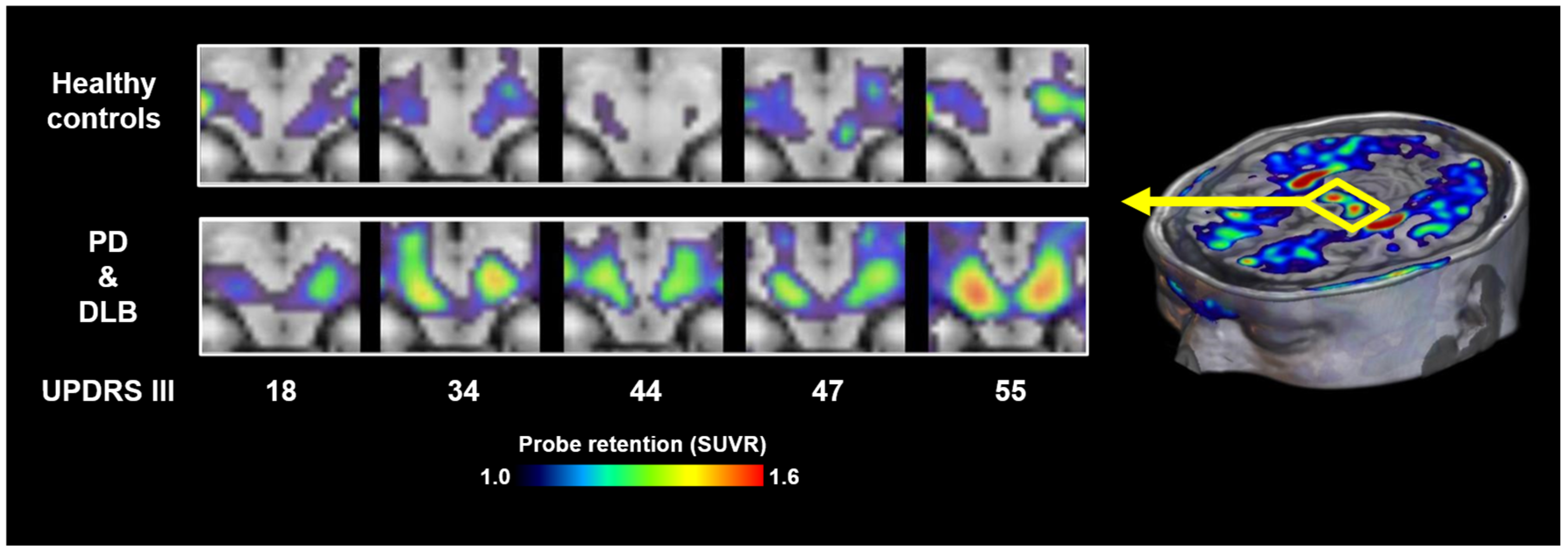
3. Imaging of α-Synuclein Pathology
4. Comparative Utility of Proteinopathy PET and Conventional Neuroimaging Modalities in Parkinsonian Syndromes
- (1)
- DAT SPECT
- (2)
- MIBG scintigraphy
- (3)
- FDG-PET
- (4)
- Volumetric MRI
- (5)
- DTI
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ | Amyloid-β |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| CBD | Corticobasal degeneration |
| Cryo-EM | Cryo-electron microscopy |
| DAT-SPECT | Dopamine transporter single-photon emission computed tomography |
| DLB | Dementia with Lewy bodies |
| DTI | Diffusion tensor imaging |
| FDG-PET | 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography |
| FTLD | Frontotemporal lobar degeneration |
| KD | Dissociation constant |
| MDS | Movement Disorders Society |
| MIBG | 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine |
| MSA | Multiple system atrophy |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| PHF | Paired helical filament |
| PSP | Progressive supranuclear palsy |
| QST | National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology |
| UPDRS | Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale |
References
- Higuchi, M.; Tagai, K.; Takahata, K.; Endo, H. Advances in PET imaging of protein aggregates associated with neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2025, 21, 506–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. The α-synucleinopathies: Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 920, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Cuina, M.; Meissner, W.G. Targeting α-synuclein or tau for treating neurodegenerative movement disorders. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 178, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemagne, V.L.; Doré, V.; Burnham, S.C.; Masters, C.L.; Rowe, C.C. Imaging tau and amyloid-β proteinopathies in Alzheimer disease and other conditions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahara, N.; Higuchi, M. Diagnostic and therapeutic targeting of pathological tau proteins in neurodegenerative disorders. FEBS Open Bio 2024, 14, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Murzin, A.G.; Falcon, B.; Kotecha, A.; van Beers, M.; Tarutani, A.; Kametani, F.; Garringer, H.J.; et al. Structure-based classification of tauopathies. Nature 2021, 598, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuzy, A.; Chiotis, K.; Lemoine, L.; Gillberg, P.G.; Almkvist, O.; Rodriguez-Vieitez, E.; Nordberg, A. Tau PET imaging in neurodegenerative tauopathies—Still a challenge. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1112–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, M.; Shimada, H.; Suhara, T.; Shinotoh, H.; Ji, B.; Maeda, J.; Zhang, M.R.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.; Ono, M.; et al. Imaging of tau pathology in a tauopathy mouse model and in Alzheimer patients compared to normal controls. Neuron 2013, 79, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagai, K.; Ono, M.; Kubota, M.; Kitamura, S.; Takahata, K.; Seki, C.; Takado, Y.; Shinotoh, H.; Sano, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. In vivo imaging of tau pathologies in Alzheimer’s and non-Alzheimer’s disease tauopathies. Neuron 2021, 109, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, F.T.; Li, M.; Lu, J.Y.; Sun, Y.M.; Liang, X.; Bao, W.; Chen, Q.S.; Li, X.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; et al. Clinical utility of 18F-APN-1607 tau PET imaging in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2314–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, H.; Tagai, K.; Ono, M.; Ikoma, Y.; Oyama, A.; Matsuoka, K.; Kokubo, N.; Hirata, K.; Sano, Y.; Oya, M.; et al. A machine learning-based approach to discrimination of tauopathies using [18F]PM-PBB3 PET images. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 2236–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Murzin, A.G.; Falcon, B.; Epstein, A.; Machin, J.; Tempest, P.; Newell, K.L.; Vidal, R.; Garringer, H.J.; Sahara, N.; et al. Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer’s disease with PET ligand APN-1607. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, G.E.; Chalkley, M.J.; Tan, S.K.; Tse, E.; Lee, J.; Prusiner, S.B.; Paras, N.A.; DeGrado, W.F.; Southworth, D.R. Stacked binding of a PET ligand to Alzheimer’s tau paired helical filaments. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunach, P.; Vaquer-Alicea, J.; Smith, M.S.; Monistrol, J.; Hopewell, R.; Moquin, L.; Therriault, J.; Tissot, C.; Rahmouni, N.; Massarweh, G.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of Alzheimer’s disease tau filaments with PET ligand MK-6240. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, S.; Ono, M.; Sahara, N.; Dickson, D.W. Fluorescence and autoradiographic evaluation of tau PET ligand PBB3 to α-synuclein pathology. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.T.; Li, X.Y.; Lu, J.Y.; Wu, P.; Li, L.; Liang, X.N.; Ju, Z.Z.; Jiao, F.Y.; Chen, M.J.; Ge, J.J.; et al. 18F-Florzolotau tau positron emission tomography imaging in patients with multiple system atrophy-parkinsonian subtype. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Ono, M.; Takado, Y.; Matsuoka, K.; Takahashi, M.; Tagai, K.; Kataoka, Y.; Hirata, K.; Takahata, K.; Seki, C.; et al. Imaging α-synuclein pathologies in animal models and patients with Parkinson’s and related diseases. Neuron 2024, 112, 2540–2557.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Ono, M.; Takado, Y.; Hirata, K.; Endo, H.; Ohfusa, T.; Kojima, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Onishi, T.; Orihara, A.; et al. High-contrast imaging of α-synuclein pathologies in living patients with multiple system atrophy. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 2159–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Capotosti, F.; Schain, M.; Ohlsson, T.; Vokali, E.; Molette, J.; Touilloux, T.; Hliva, V.; Dimitrakopoulos, I.K.; Puschmann, A.; et al. The α-synuclein PET tracer [18F]ACI-12589 distinguishes multiple system atrophy from other neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Tao, Y.; Xia, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhao, Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Xia, W.; Zhang, M.; et al. Development of an α-synuclein positron emission tomography tracer for imaging synucleinopathies. Cell 2023, 186, 3350–3367.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, R.S.; Buss, S.; Schmidt, F.; Ryazanov, S.; Leonov, A.; Kuebler, L.; Bleher, D.; Papadopoulos, I.; Roeben, B.; Schmidt, F.; et al. [11C]MODAG 005—A novel PET tracer targeting alpha-synuclein aggregates in the brain. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, A.; Takeda, A.; Okamura, N.; Tashiro, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Furumoto, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Sugeno, N.; Baba, T.; Miki, Y.; et al. In vivo visualization of alpha-synuclein deposition by carbon-11-labelled 2-[2-(2-dimethylaminothiazol-5-yl)ethenyl]-6-[2-(fluoro)ethoxy]benzoxazole positron emission tomography in multiple system atrophy. Brain 2010, 133, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josephson, L.; Stratman, N.; Liu, Y.; Qian, F.; Liang, S.H.; Vasdev, N.; Patel, S. The Binding of BF-227-Like Benzoxazoles to Human α-Synuclein and Amyloid β Peptide Fibrils. Mol. Imaging 2018, 17, 1536012118796297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papathanasiou, N.D.; Boutsiadis, A.; Dickson, J.; Bomanji, J. B. Diagnostic accuracy of 123I-FP-CIT (DaTSCAN) in dementia with Lewy bodies: A meta-analysis of published studies. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, G.; Giannoni, S.; Bellini, G.; Siciliano, G.; Ceravolo, R. Dopamine Transporter Imaging, Current Status of a Potential Biomarker: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvan, I.; Bhatia, K.P.; Burn, D.J.; Goetz, C.G.; Lang, A.E.; McKeith, I.; Quinn, N.; Sethi, K.D.; Shults, C.; Wenning, G.K.; et al. Movement Disorders Society Scientific Issues Committee report: SIC Task Force appraisal of clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinsonian disorders. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 467–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibyl, J.P.; Kuo, P. What Is the Role of Dopamine Transporter Imaging in Parkinson Prevention Clinical Trials? Neurology 2022, 99 (Suppl. 1), 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffen, W.; Mair, A.; Unterrainer, J.; Trinka, E.; Ladurner, G. Measuring the progression of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease with [123I]-β-CIT SPECT. J. Neural Transm. 2000, 107, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, Y.; Tagai, K.; Goto, R.; Matsuoka, K.; Hirata, K.; Takahata, K.; Oya, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Kurose, S.; Ichihashi, M.; et al. Imaging-based Topographic Association and Dissociation between Tau Pathology and Atrophy Correlated with Impairments of Key Motor Domains in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. medRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimo, S.; Ozawa, E.; Nakade, S.; Sugimoto, T.; Mizusawa, H. 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine myocardial scintigraphy in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 67, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, J. Diagnostic and pathophysiological impact of myocardial MIBG scintigraphy in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2010, 2010, 295346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treglia, G.; Stefanelli, A.; Cason, E.; Cocciolillo, F.; Di Giuda, D.; Giordano, A. MIBG scintigraphy in differential diagnosis of Parkinsonism: A meta-analysis of published studies. Clin. Auton. Res. 2012, 22, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidelberg, D. Metabolic brain networks in neurodegenerative disorders: A functional imaging approach. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Wu, P.; Zuo, C. The metabolic brain network in patients with Parkinson’s disease based on 18F-FDG PET imaging: Evaluation of neuronal injury and regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2014, 9, 763–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Katsifis, A.; Villemagne, V.L.; Best, R.; Jones, G.; Saling, M.; Bradshaw, J.; Merory, J.; Woodward, M.; Hopwood, M.; et al. The 18F-FDG PET cingulate island sign and comparison to 123I-beta-CIT SPECT for diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, B.; Krismer, F.; De Marzi, R.; Seppi, K. Magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 915–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, U.; Compagnone, J.; Aviv, R.I.; Strafella, A.P.; Black, S.E.; Lang, A.E.; Masellis, M. Imaging biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease and Parkinsonian syndromes: Current and emerging concepts. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekhlef, F.; Ballan, G.; Macia, F.; Delmer, O.; Sourgen, C.; Tison, F. Routine MRI for the differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease, MSA, PSP, and CBD. J. Neural Transm. 2003, 110, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillancourt, D.E.; Spraker, M.B.; Prodoehl, J.; Abraham, I.; Corcos, D.M.; Zhou, X.J.; Comella, C.L.; Little, D.M. High-resolution diffusion tensor imaging in the substantia nigra of de novo Parkinson disease. Neurology 2009, 72, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loane, C.; Politis, M.; Kefalopoulou, Z.; Valle-Guzman, N.; Paul, G.; Widner, H.; Foltynie, T.; Barker, R.A.; Piccini, P. Aberrant nigral diffusion in Parkinson’s disease: A longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging study. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamino, M.; Keeling, M.; Mishra, R.; Stokes, A.; Walsh, R. Assessing white matter pathology in early-stage Parkinson disease: A systematic and critical review of dMRI studies. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Galvan, P.; Przybelski, S.A.; Lesnick, T.G.; Murray, M.E.; Nguyen, A.; Reichard, R.R.; Dickson, D.W.; Ono, D.; Senjem, M.L.; Schwarz, C.G.; et al. Substantia Nigra Iron Deposition in Lewy Body Disease: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Neuropathology Study. Mov. Disord. 2025, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindlbeck, K.A.; Gupta, D.K.; Tang, C.C.; O’Shea, S.A.; Poston, K.L.; Choi, Y.Y.; Dhawan, V.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Fahn, S.; Eidelberg, D. Neuropathological correlation supports automated image-based differential diagnosis in parkinsonism. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3522–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perju-Dumbrava, L.D.; Kovacs, G.G.; Pirker, S.; Jellinger, K.; Hoffmann, M.; Asenbaum, S.; Pirker, W. Dopamine transporter imaging in autopsy-confirmed Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colloby, S.J.; McParland, S.; O’Brien, J.T.; Attems, J. Neuropathological correlates of dopaminergic imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body dementias. Brain 2012, 135 Pt 9, 2798–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.J.; Attems, J.; Colloby, S.J.; O’Brien, J.T.; McKeith, I.; Walker, R.; Lee, L.; Burn, D.; Lett, D.J.; Walker, Z. Autopsy validation of 123I-FP-CIT dopaminergic neuroimaging for the diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 2017, 88, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Araki, N.; Takeda, T.; Takado, Y.; Tagai, K.; Matsuoka, K.; Seki, C.; Takahata, K.; Sahara, N.; Shinotoh, H.; et al. Correlation of 18F-PM-PBB3 (18F-florzolotau) Tau PET Imaging with Postmortem Neuropathological Findings in A Case with Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Neurology 2023, 100 (Suppl. 2), 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Kubota, M.; Kurose, S.; Tagai, K.; Endo, H.; Onaya, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sahara, N.; Ohgidani, M.; Haga, C.; et al. Neuropathological correlations of 18F-florzolotau PET in a case with Pick’s disease. EJNMMI Res. 2025, 15, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglinger, G.U.; Adler, C.H.; Berg, D.; Klein, C.; Outeiro, T.F.; Poewe, W.; Postuma, R.; Stoessl, A.J.; Lang, A.E. A biological classification of Parkinson’s disease: The SynNeurGe research diagnostic criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simuni, T.; Chahine, L.M.; Poston, K.; Brumm, M.; Buracchio, T.; Campbell, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Coffey, C.; Concha-Marambio, L.; Dam, T.; et al. A biological definition of neuronal α-synuclein disease: Towards an integrated staging system for research. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVos, S.L.; Miller, R.L.; Schoch, K.M.; Holmes, B.B.; Kebodeaux, C.S.; Wegener, A.J.; Chen, G.; Shen, T.; Tran, H.; Nichols, B.; et al. Tau reduction prevents neuronal loss and reverses pathological tau deposition and seeding in mice with tauopathy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaag0481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, G.; Takahashi, M.; Tashima, H.; Iwao, Y.; Yoshida, E.; Wakizaka, H.; Kumagai, M.; Yamashita, T.; Yamaya, T. Performance evaluation of VRAIN: A brain-dedicated PET with a hemispherical detector arrangement. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 225011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, P.; Lashuel, H.A. Opportunities and challenges of alpha-synuclein as a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuzumi, A.; Hatano, T.; Matsumoto, G.; Nojiri, S.; Ueno, S.-I.; Imamichi-Tatano, Y.; Kimura, H.; Kakuta, S.; Kondo, A.; Fukuhara, T.; et al. Propagative α-synuclein seeds as serum biomarkers for synucleinopathies. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacson, J.R.; Freeman, R.; Gibbons, C.H. Clinical utility of synuclein skin biopsy in the diagnosis and evaluation of synucleinopathies. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1510796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkinderen, P.; Cossais, F.; de Guilhem de Lataillade, A.; Leclair-Visonneau, L.; Neunlist, M.; Paillusson, S.; De Giorgio, R. Gastrointestinal mucosal biopsies in Parkinson’s disease: Beyond alpha-synuclein detection. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Affinity | Brain PK | Off-Target Binding | Cross-Reactivity with Tau | Development Stage | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1/2 | BKG @ 60 min | Affinity | In Vivo Binding | |||||
| 18F-C05-05 | IC50 = 1.5 nM | ~40 min | ~35% | TMEM106B | IC50 = 12.9 nM | PSP | eIND for PD, DLB, MSA | [17] |
| 18F-SPAL-T-06 | KD = 2.5 nM | ~20 min | ~25% | TMEM106B | N/A | N/A | eIND for MSA | [18] |
| 18F-ACI-12589 | KD = 17–30 nM | ~20 min | ~30% | N/A | AD(, PSP) | eIND for MSA | [19] | |
| 11C-MODAG-005 | KD = 0.2 nM | ~35 min | ~45% | KD = 7.1 nM | eIND for MSA | [21] | ||
| * 11C-BF-227 | KD = 46.0 nM | ~40 min | ~45% | Aβ KD = 15.7 nM | AD Aβ | (MSA) | [22,23] | |
| ** 11C-PBB3 | IC50 = 58.8 nM | ~20 min | ~35% | TMEM106B | IC50 = 8.6 nM | AD, PSP | (MSA) | [8,17] |
| Disired ligand | KD < 0.2 nM | 20–30 min | <25% | KD > 50 nM | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Higuchi, M. Imaging of Proteinopathies in the Brains of Parkinsonian Disorders. Cells 2025, 14, 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181418
Higuchi M. Imaging of Proteinopathies in the Brains of Parkinsonian Disorders. Cells. 2025; 14(18):1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181418
Chicago/Turabian StyleHiguchi, Makoto. 2025. "Imaging of Proteinopathies in the Brains of Parkinsonian Disorders" Cells 14, no. 18: 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181418
APA StyleHiguchi, M. (2025). Imaging of Proteinopathies in the Brains of Parkinsonian Disorders. Cells, 14(18), 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181418






