The Anti-Myogenic Role of Tetranectin and Its Inhibition by Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Enhances Myogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Myogenic Differentiation
2.2. Preparation and Activity Assay of Recombinant TN Proteins
2.3. Determination of Fusion Index and Creatine Kinase Activity
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR for Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
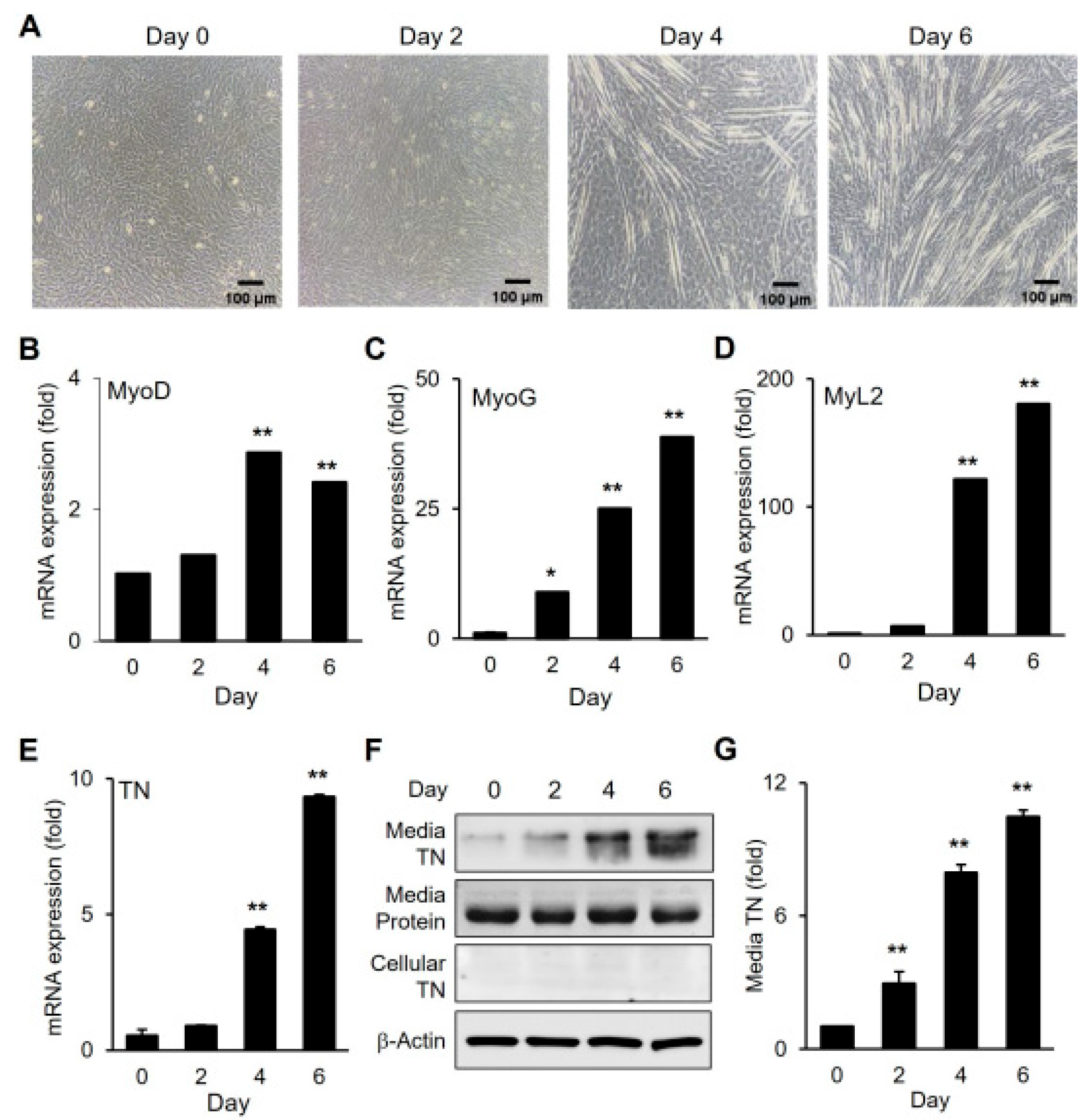
3.1. Upregulation of TN During Myogenic Differentiation and Its Secretion
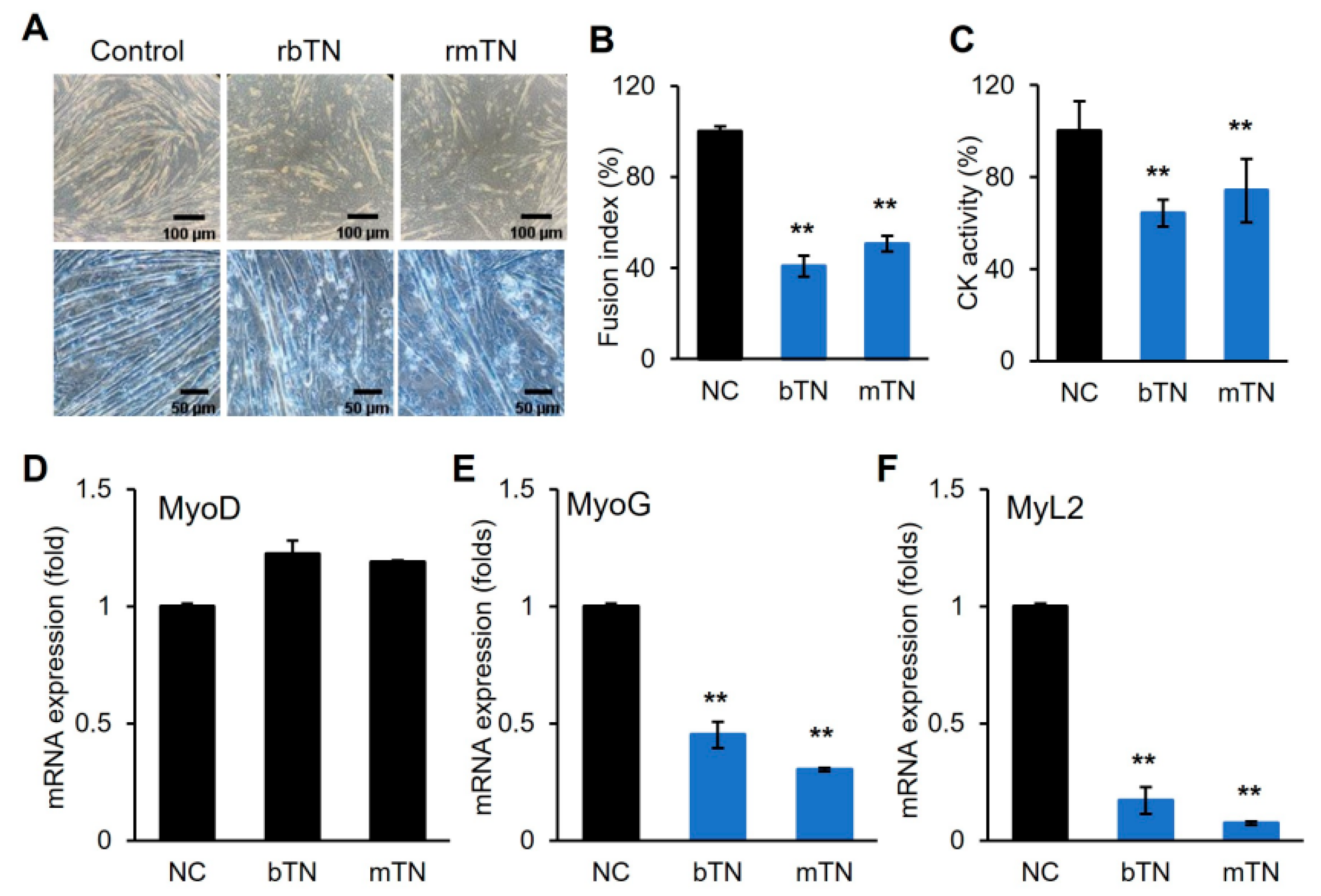
3.2. TN Suppresses Myogenic Differentiation
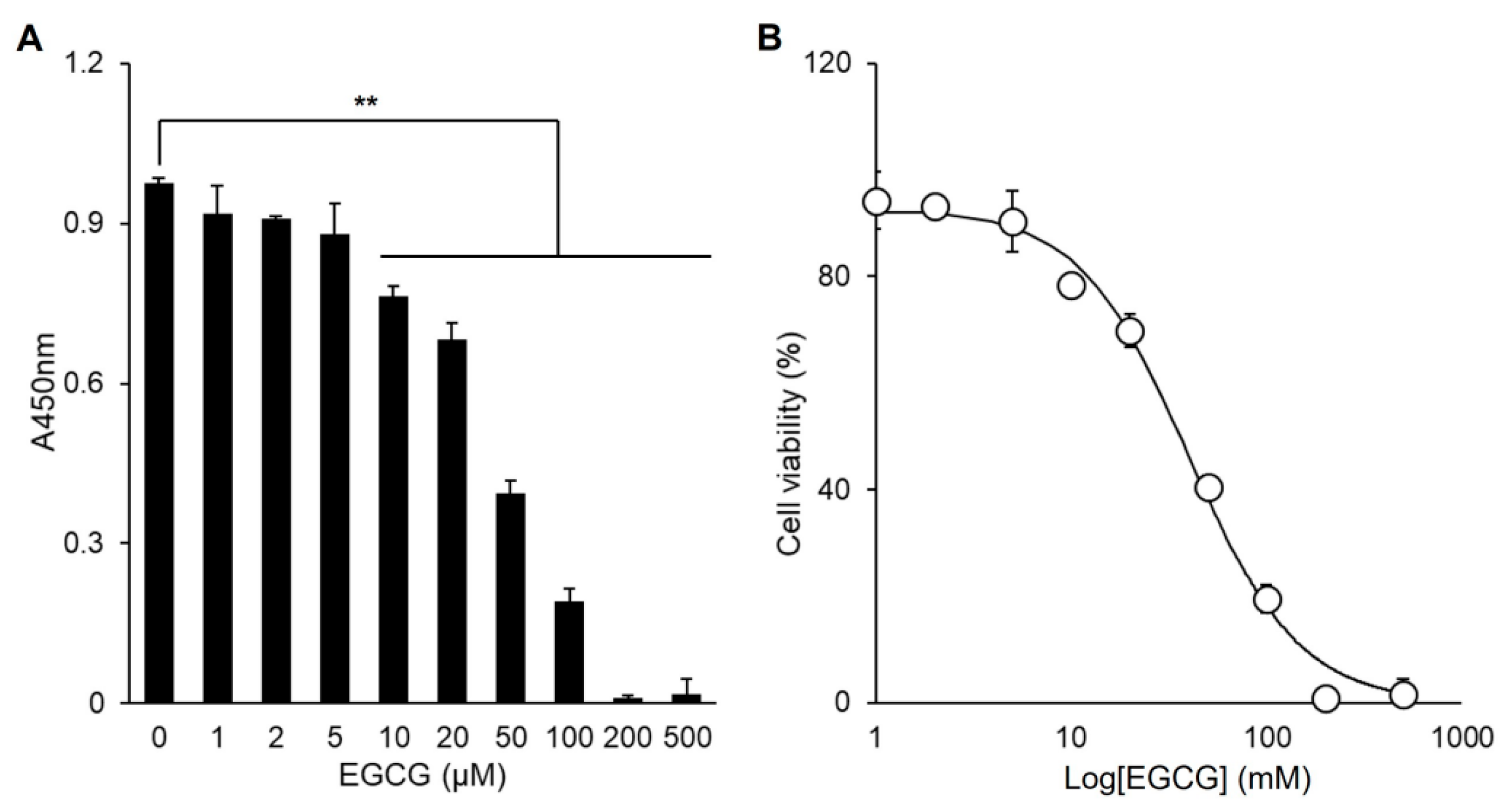
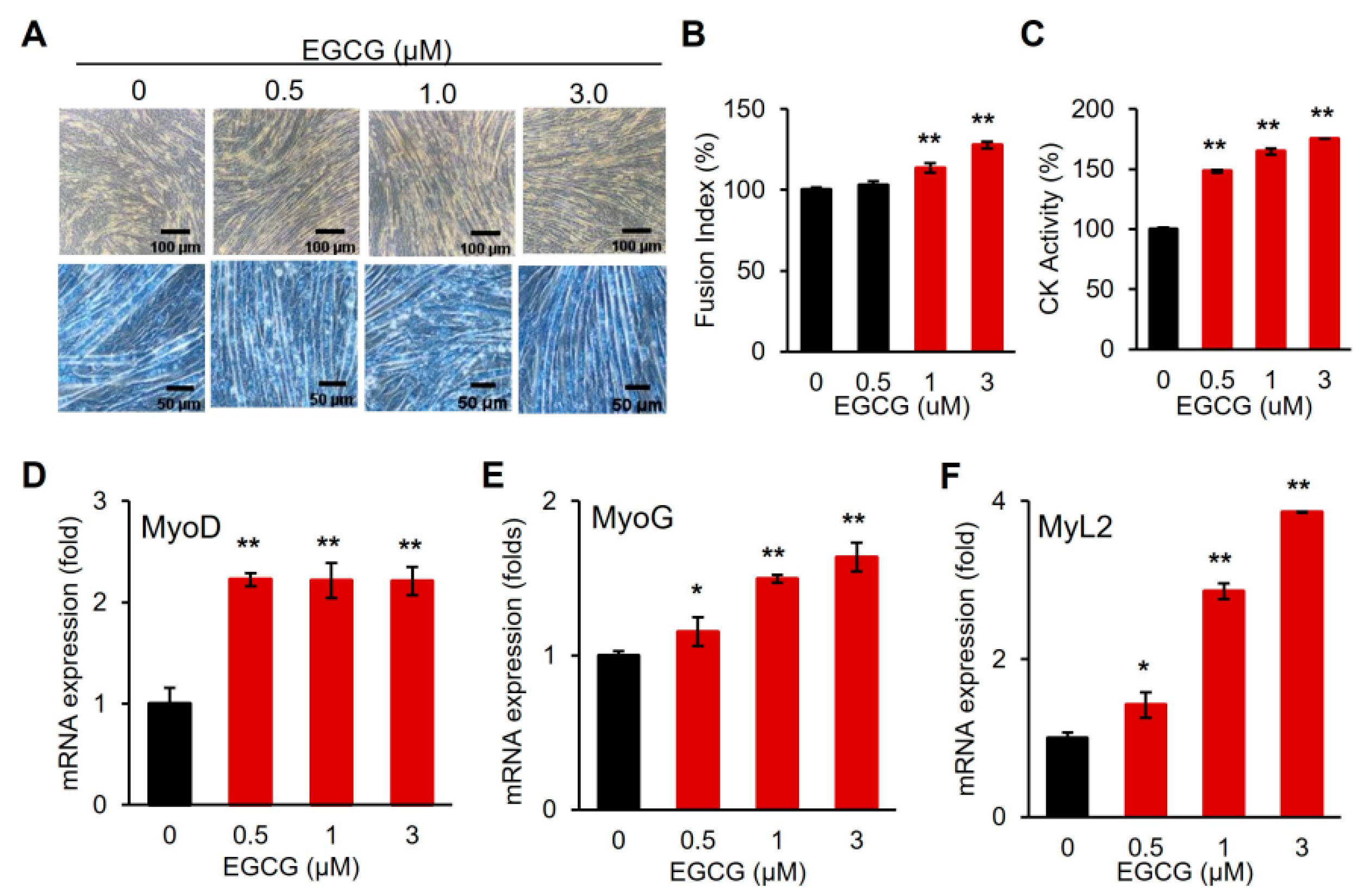
3.3. EGCG Promotes Myogenic Differentiation
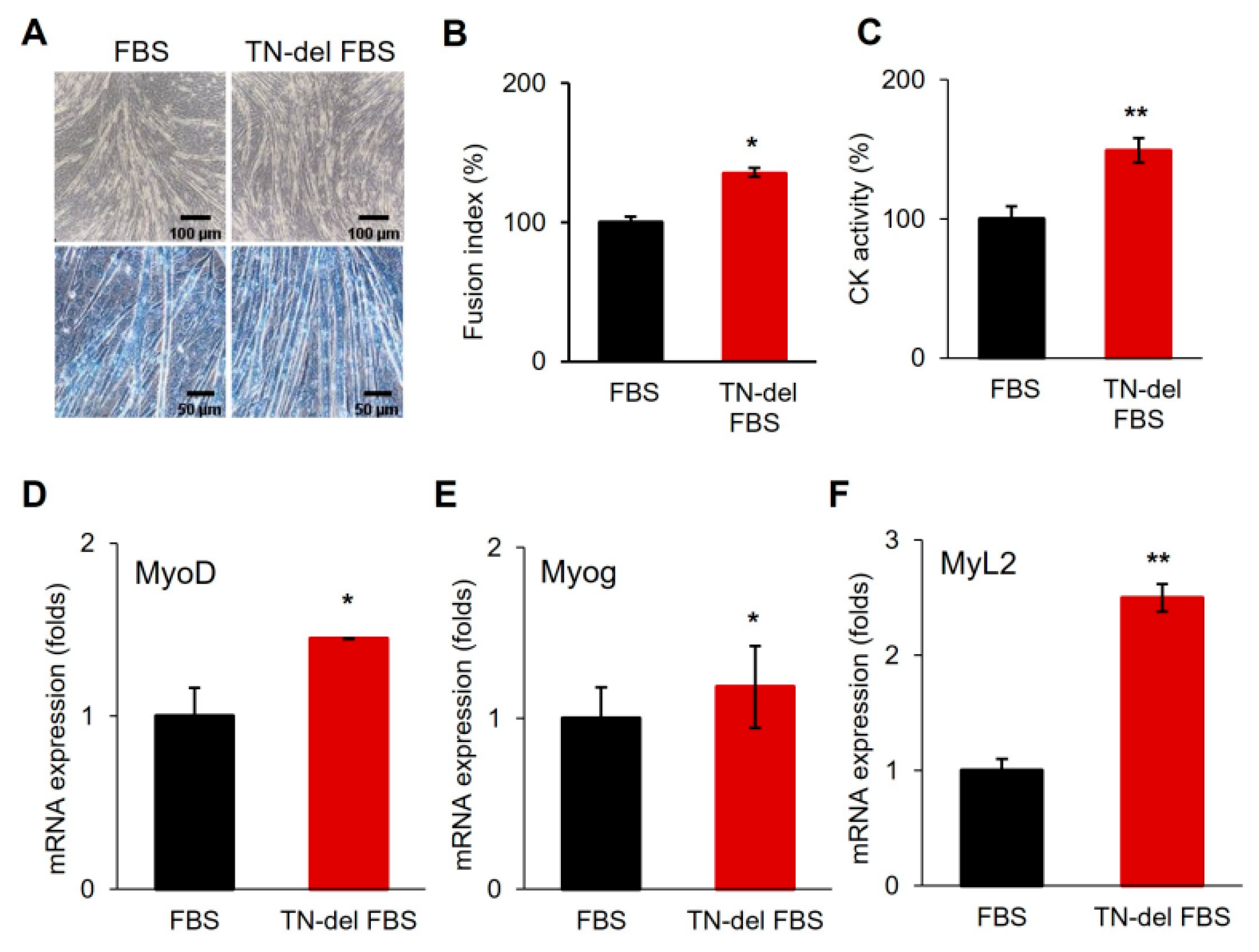
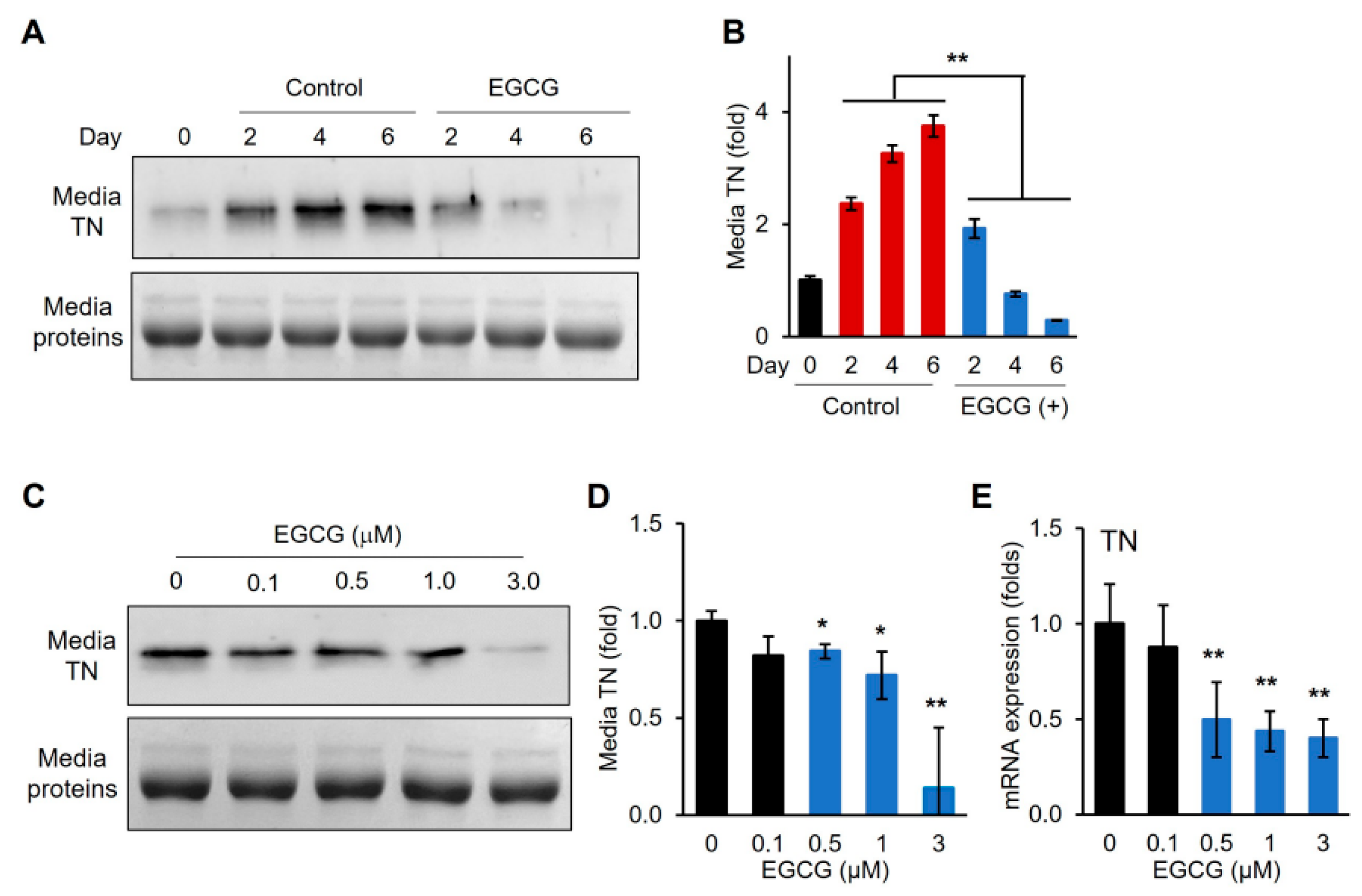
3.4. EGCG Removes TN from Differentiation Medium and Downregulates TN Gene Expression
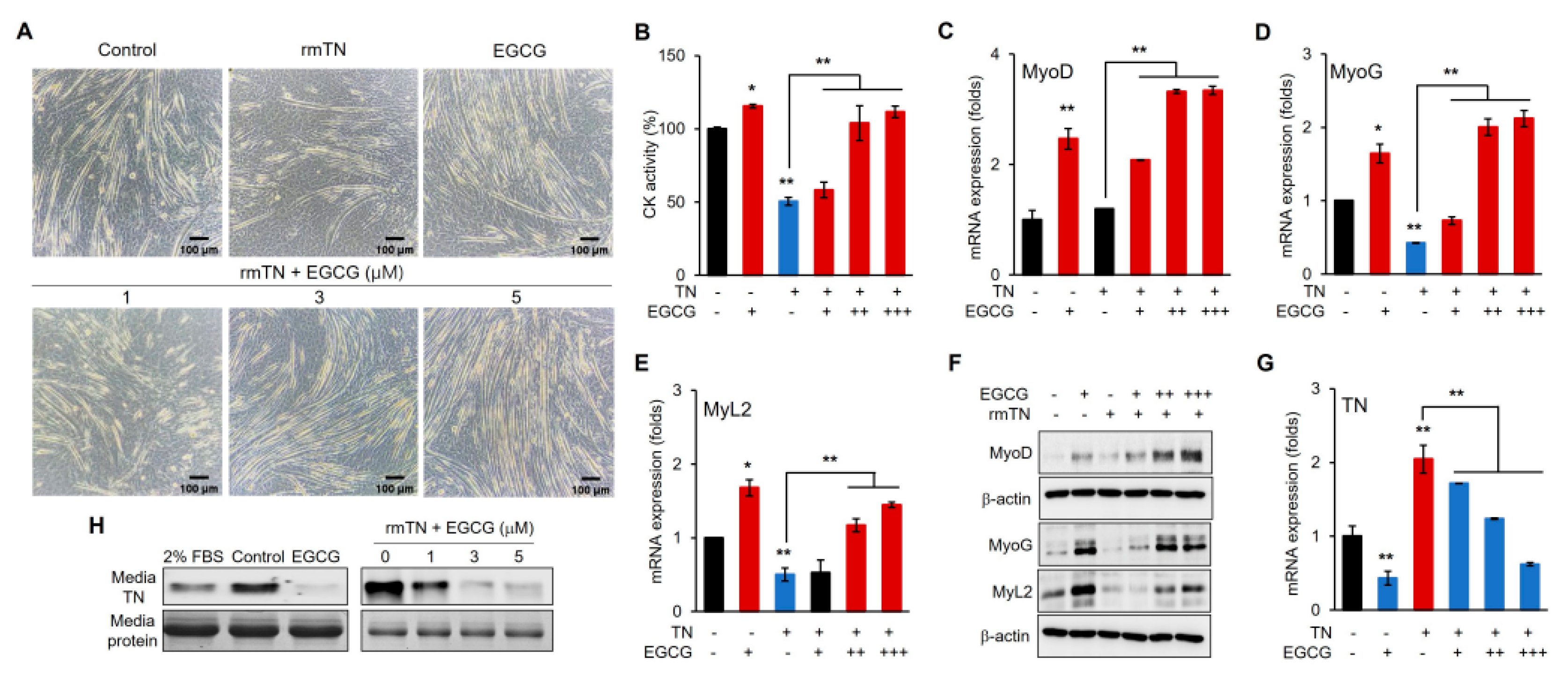
3.5. EGCG Promotes Myogenic Differentiation via the Inhibition of TN
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TN | Tetranectin |
| CK | Creatine kinase |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
| MyoD | Myoblast determination protein 1 |
| MyoG | Myogenin |
| MyL2 | Myosin regulatory light chain 2 |
| Plg | Plasminogen |
| TN-del-FBS | Tetranectin-depleted fetal bovine serum |
References
- Christensen, L.; Johansen, N.; Jensen, B.A.; Clemmensen, I. Immunohistochemical localization of a novel, human plasma protein, tetranectin, in human endocrine tissues. Histochemistry 1987, 87, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmensen, I.; Petersen, L.C.; Kluft, C. Purification and characterization of a novel, oligomeric, plasminogen kringle 4 binding protein from human plasma: Tetranectin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1986, 156, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogdall, C.K.; Christiansen, M.; Norgaard-Pedersen, B.; Bentzen, S.M.; Kronborg, O.; Clemmensen, I. Plasma tetranectin and colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 1995, 31, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogdall, C.K.; Christensen, L.; Clemmensen, I. Tetranectin, a plasma and tissue protein—A prognostic marker of breast and ovarian cancer. Ugeskr. Laeger 1994, 156, 6190–6195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Graversen, J.H.; Lorentsen, R.H.; Jacobsen, C.; Moestrup, S.K.; Sigurskjold, B.W.; Thogersen, H.C.; Etzerodt, M. The plasminogen binding site of the C-type lectin tetranectin is located in the carbohydrate recognition domain, and binding is sensitive to both calcium and lysine. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 29241–29246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogdall, C.K.; Soletormos, G.; Nielsen, D.; Norgaard-Pedersen, B.; Dombernowsky, P.; Clemmensen, I. Prognostic value of serum tetranectin in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Acta Oncol. 1993, 32, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, K.; Abe, Y.; Chikenji, T.; Kanaya, K.; Chiba, H.; Sasaki, K.; Dohke, T.; Wada, T.; Yamashita, T. Delayed fracture healing in tetranectin-deficient mice. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2013, 31, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wewer, U.M.; Iba, K.; Durkin, M.E.; Nielsen, F.C.; Loechel, F.; Gilpin, B.J.; Kuang, W.; Engvall, E.; Albrechtsen, R. Tetranectin is a novel marker for myogenesis during embryonic development, muscle regeneration, and muscle cell differentiation in vitro. Dev. Biol. 1998, 200, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, J.; Buer, J.; Pietschmann, T.; Steinmann, E. Anti-infective properties of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a component of green tea. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, Q.Y.; Thanikachalam, P.V.; Ramamurthy, S. Molecular understanding of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 210, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokra, D.; Joskova, M.; Mokry, J. Therapeutic effects of green tea polyphenol (‒)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) in relation to molecular pathways controlling inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meador, B.; Mirza, K.; Tian, M.; Skelding, M.; Reaves, L.; Edens, N.; Tisdale, M.; Pereira, S. The green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCg) attenuates skeletal muscle atrophy in a rat model of sarcopenia. J. Frailty Aging 2015, 4, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.-T.; Chang, T.-W.; Lee, M.-S.; Lin, J.-K. Suppression of free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance by phytopolyphenols in C2C12 mouse skeletal muscle cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Lee, W.-J. Effects of dietary polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the differentiation of mouse C2C12 myoblasts. J. Life Sci. 2007, 17, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Ryu, Y.; Rahman, S.; Kim, J. Adipogenic function of mouse tetranectin and identification of its functional domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 519, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iram, S.; Rahman, S.; Ali, S.; Kim, J. Tetranectin targeting by epigallocatechin gallate suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, B.; Depreux, F.; Geay, Y. Muscle differentiation of normal and double-muscled bovine foetal myoblasts in primary culture. Basic Appl. Myol. BAM 1998, 8, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Price, F.; Rudnicki, M.A. Satellite cells and the muscle stem cell niche. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 23–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, K.; Glezeva, N.; Collier, P.; O’Reilly, J.; O’Connell, E.; Tea, I.; Russell-Hallinan, A.; Tonry, C.; Pennington, S.; Gallagher, J.; et al. Tetranectin, a potential novel diagnostic biomarker of heart failure, is expressed within the myocardium and associates with cardiac fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Si, A.; Chen, Y. CLEC3B protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes from apoptosis caused by hypoxia via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, e9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akash, A.; Kim, J. The Anti-Myogenic Role of Tetranectin and Its Inhibition by Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Enhances Myogenesis. Cells 2025, 14, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151160
Akash A, Kim J. The Anti-Myogenic Role of Tetranectin and Its Inhibition by Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Enhances Myogenesis. Cells. 2025; 14(15):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151160
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkash, Amar, and Jihoe Kim. 2025. "The Anti-Myogenic Role of Tetranectin and Its Inhibition by Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Enhances Myogenesis" Cells 14, no. 15: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151160
APA StyleAkash, A., & Kim, J. (2025). The Anti-Myogenic Role of Tetranectin and Its Inhibition by Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Enhances Myogenesis. Cells, 14(15), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151160





