Formyl Peptide Receptors 1 and 2: Essential for Immunomodulation of Crotoxin in Human Macrophages, Unrelated to Cellular Entry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CTX Purification
2.2. THP-1 Cell Culture
2.3. Induction of Cell Differentiation
2.4. Toxin Labeling Assay
2.5. FPR1 SiRNA Transfection in THP-1 Cells
2.6. Assay Protocols and Pharmacological Treatments
2.6.1. CTX Treatment
2.6.2. fMLP Treatment
2.6.3. Boc-2 Treatment
2.7. Fluorescence Assay of THP-1 Cells Incubated with FITC-CTX
2.8. Evaluation of Functional Assays
2.8.1. Measurement of Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Production
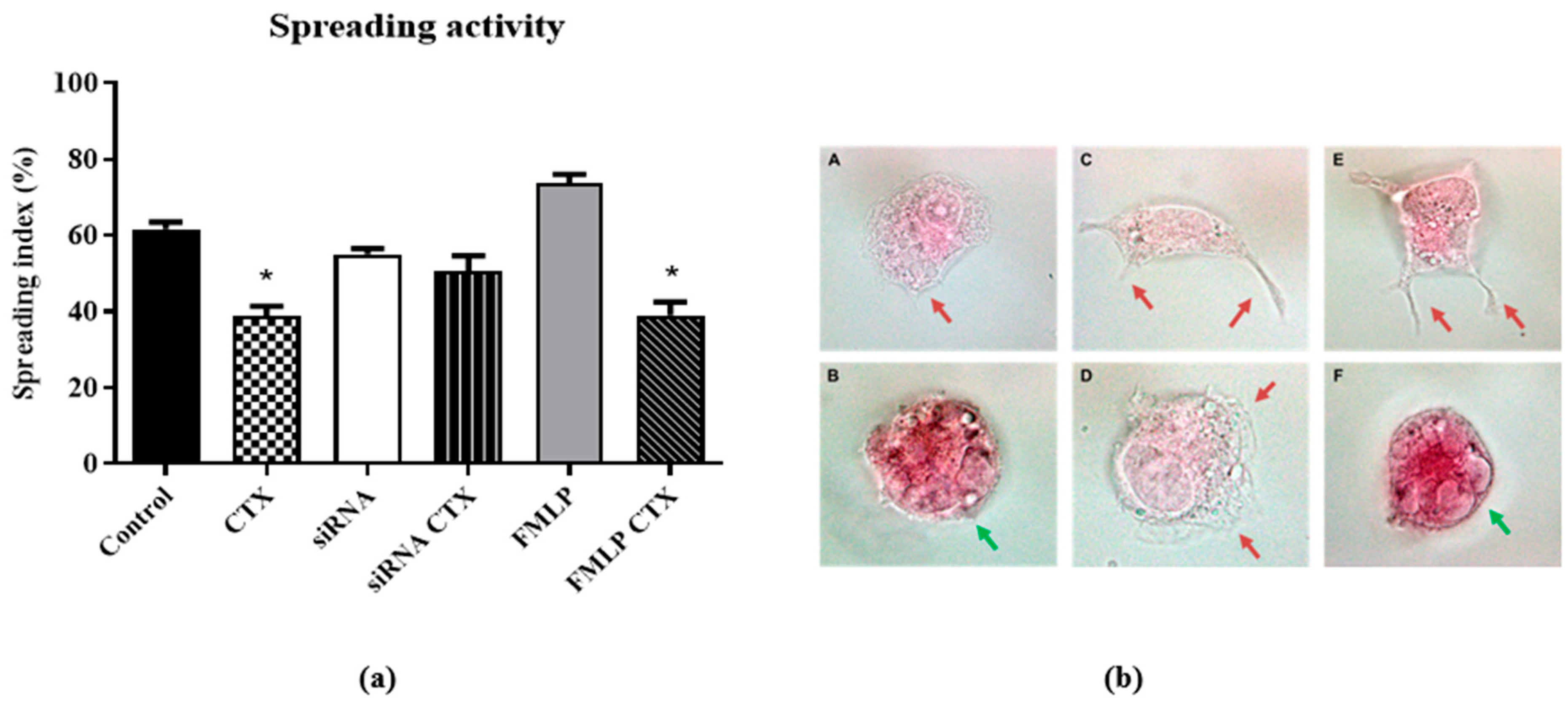
2.8.2. Macrophage Spreading Capacity
2.8.3. Phagocytosis Assay
2.9. Expression of Formyl Peptide Receptors and Signaling Pathway
2.10. In Silico Study
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differentiation of TPH-1 Cells into Macrophages
3.2. Effectiveness of FPR1 Silencing in Differentiated and Undifferentiated THP-1 Cells
3.3. Evaluation of Functions of THP-1-Differentiated Macrophages
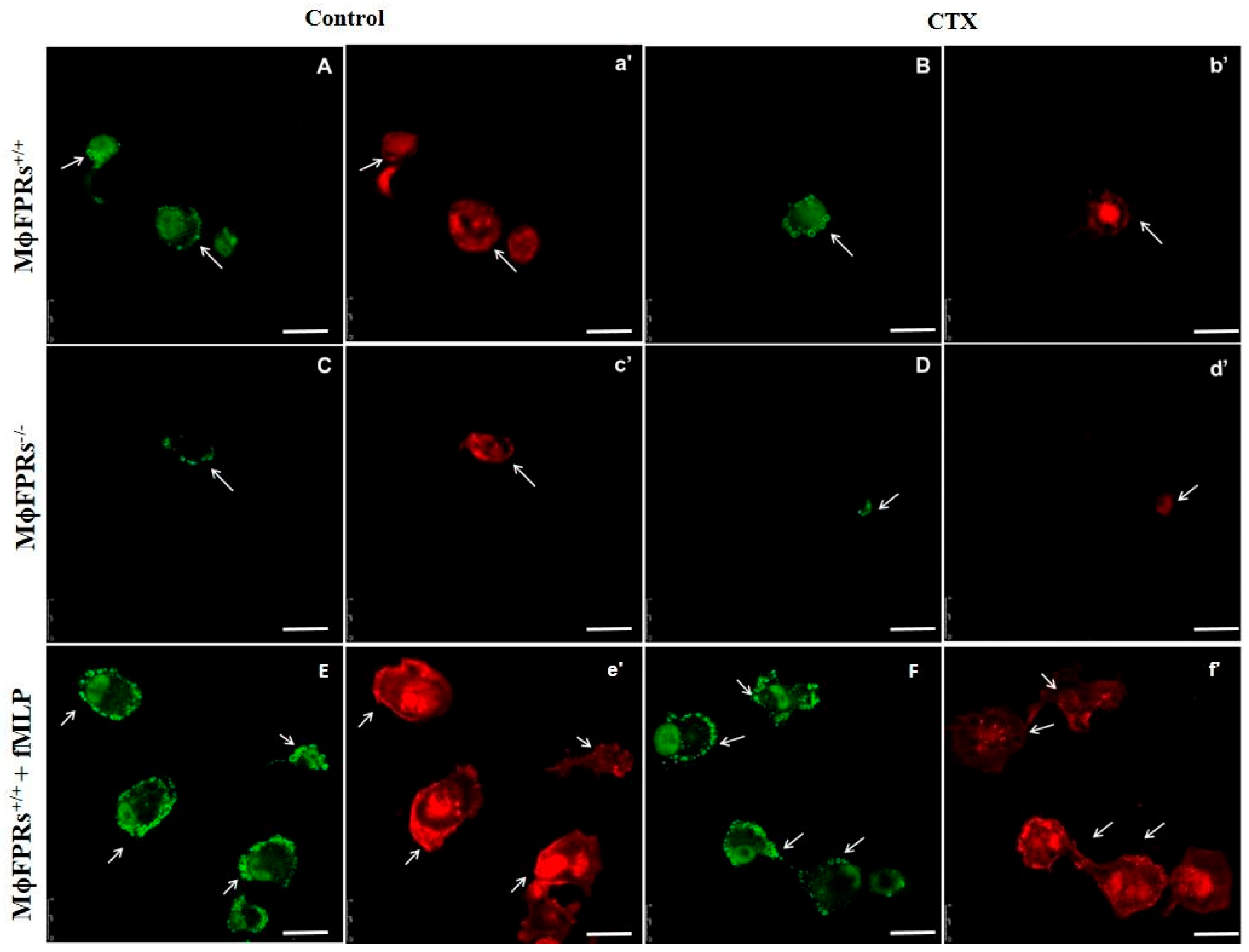
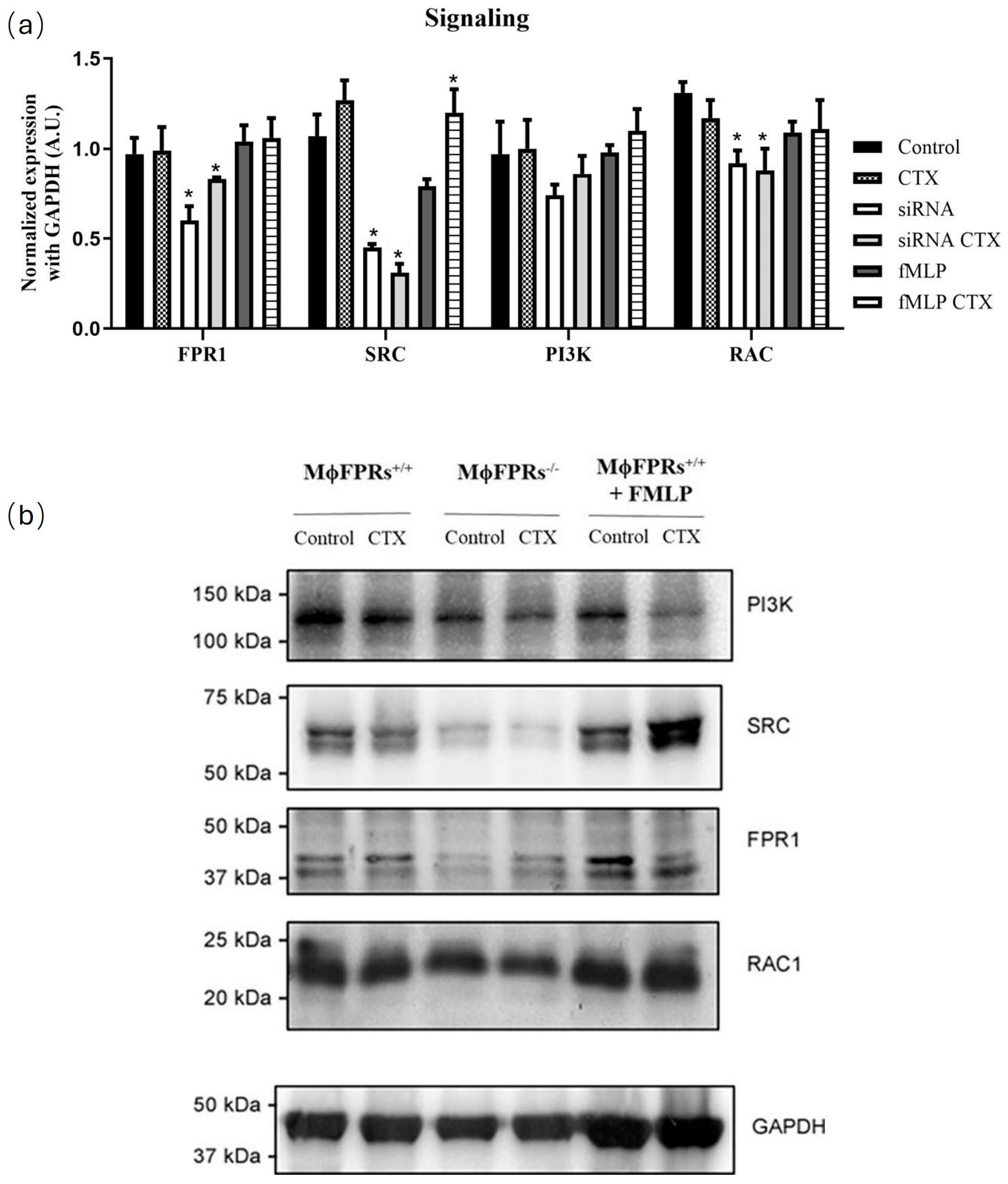
3.4. Formyl Peptide Receptor Expression and Activation
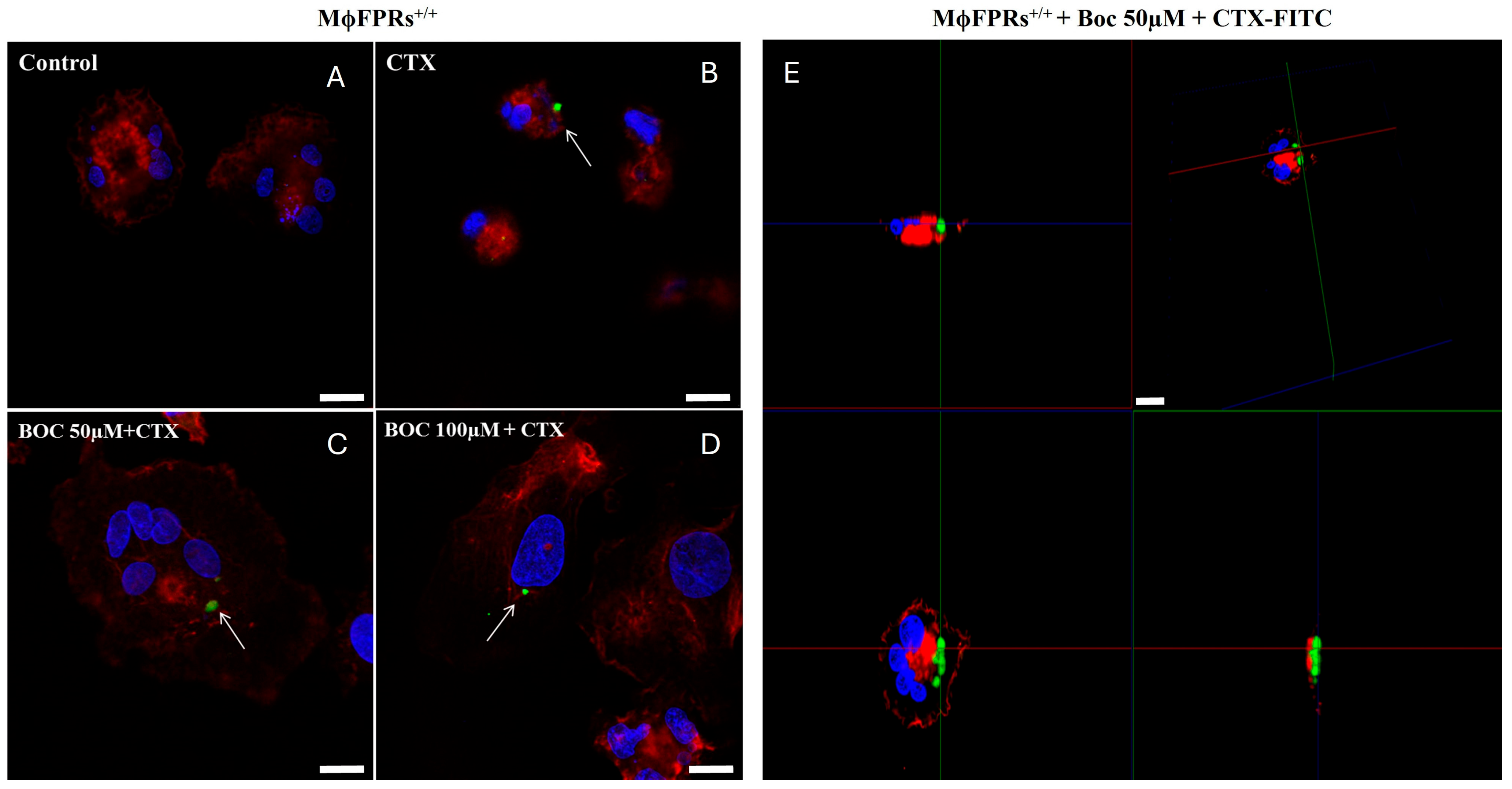
3.5. Membrane Permeability Experiment—Fluorescent Marking-CTX
3.6. Analysis of DrugBank and TTD Database
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bailey, P.; Wilce, J. Venom as a Source of Useful Biologically Active Molecules. Emerg. Med. 2001, 13, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Garcia, M.L. Therapeutic Potential of Venom Peptides. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, Y.; Picolo, G. Animal Toxins as Analgesics—An Overview. Drug News Perspect. 2006, 19, 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Brazil, V. Do Emprego Da Peçonha Em Terapêutica. Ann. Paul. Med. Cir. 1950, 60, 398–408. [Google Scholar]
- Amorim, M.d.F.; Mello, R.F.; Saliba, F. Envenenamento Botrópico e Crotálico. Mem. Inst. Butantan 1951, 23, 63–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bercovici, D.; Chudziniski, A.M.; Dias, W.d.O.; Esteves, M.I.; Hirachi, E.; Oishi, N.; Picarelli, Z.; Rocha, M.C.; Ueda, C.M.P.M.; Yamanouye, N.; et al. A Systematic Fractionation of Crotalus durissus Terrificus Venom. Mem. Inst. Butantan 1987, 49, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, G.; Grothusen, J.; Zepeda, H.; Schwartzman, R.J. Gyroxin, a Toxin from the Venom of Crotalus durissus Terrificus, Is a Thrombin-like Enzyme. Toxicon 1988, 26, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotta, K.H.; Fraenkel-Conrat, H. Estudos Químicos Sobre Os Venenos Ofídicos. 4. Purificação e Cristalização Do Veneno Da Cobra Cascavel. Mem. Inst. Butantan 1938, 12, 505–513. [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel-Conrat, H.; Singer, B. Fractionation and Composition of Crotoxin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1956, 60, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cura, J.E.; Blanzaco, D.P.; Brisson, C.; Cura, M.A.; Cabrol, R.; Larrateguy, L.; Mendez, C.; Sechi, J.C.; Silveira, J.S.; Theiller, E.; et al. Phase I and Pharmacokinetics Study of Crotoxin (Cytotoxic PLA(2), NSC-624244) in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, S.C.; Hyslop, S.; Fontes, M.R.M.; Prado-Franceschi, J.; Zambelli, V.O.; Magro, A.J.; Brigatte, P.; Gutierrez, V.P.; Cury, Y. Crotoxin: Novel Activities for a Classic β-Neurotoxin. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartim, M.A.; Menaldo, D.L.; Sampaio, S.V. Immunotherapeutic Potential of Crotoxin: Anti-Inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Properties. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 24, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigatte, P.; Faiad, O.J.; Ferreira Nocelli, R.C.; Landgraf, R.G.; Palma, M.S.; Cury, Y.; Curi, R.; Sampaio, S.C. Walker 256 Tumor Growth Suppression by Crotoxin Involves Formyl Peptide Receptors and Lipoxin A4. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 2457532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, C.S.; Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Câmara, N.O.S.; Jacysyn, J.F.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L. Crotoxin from Crotalus durissus Terrificus Is Able to Down-Modulate the Acute Intestinal Inflammation in Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, E.E.; Pimenta, L.A.; de Almeida, M.E.S.; Zambelli, V.O.; dos Santos, M.F.; Sampaio, S.C. Crotoxin Inhibits Endothelial Cell Functions in Two- and Three-Dimensional Tumor Microenvironment. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 713332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.S.; Faiad, O.J.; Landgraf, R.G.; Ferreira, A.K.; Brigatte, P.; Curi, R.; Cury, Y.; Sampaio, S.C. Involvement of Formyl Peptide Receptors in the Stimulatory Effect of Crotoxin on Macrophages Co-Cultivated with Tumour Cells. Toxicon 2013, 74, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araújo Pimenta, L.; de Almeida, M.E.S.; Bretones, M.L.; Cirillo, M.C.; Curi, R.; Sampaio, S.C. Crotoxin Promotes Macrophage Reprogramming towards an Antiangiogenic Phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, C.; Gong, W.; Yoshimura, T.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.M. Cell Surface Receptor FPR2 Promotes Antitumor Host Defense by Limiting M2 Polarization of Macrophages. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Bao, Z.; Gong, W.; Tang, P.; Yoshimura, T.; Wang, J.M. Regulation of Inflammation by Members of the Formyl-Peptide Receptor Family. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 85, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Santos, A.; Dos-Santos, E.C.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Lima, C.; Cardoso, D.F.; Mota, I. A Comparative Study of Biological Activities of Crotoxin and CB Fraction of Venoms from Crotalus durissus Terrificus, Crotalus durissus Cascavella and Crotalus durissus Collilineatus. Toxicon 2004, 43, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knittel, P.S.; Long, P.F.; Brammall, L.; Marques, A.C.; Almeida, M.T.; Padilla, G.; Moura-Da-Silva, A.M. Characterising the Enzymatic Profile of Crude Tentacle Extracts from the South Atlantic Jellyfish Olindias sambaquiensis (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). Toxicon 2016, 119, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curi, R.; Perez, C.M. Como Cultivar Células; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya, S.; Yamabe, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Konno, T.; Tada, K. Establishment and Characterization of a Human Acute Monocytic Leukemia Cell Line (THP-1). Int. J. Cancer 1980, 26, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohro, T.; Tanaka, T.; Murakami, T.; Wada, Y.; Aburatani, H.; Hamakubo, T.; Kodama, T. A Comparison of Differences in the Gene Expression Profiles of Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate Differentiated THP-1 Cells and Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophage. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2004, 11, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigneault, M.; Preston, J.A.; Marriott, H.M.; Whyte, M.K.B.; Dockrell, D.H. The Identification of Markers of Macrophage Differentiation in PMA-Stimulated THP-1 Cells and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambiaghi, T.D. Estudo do Controle Traducional de PPARβ Durante o Processo de Diferenciação de Macrófagos. Doctoral Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.K.; Jung, H.S.; Yang, H.I.; Yoo, M.C.; Kim, C.; Kim, K.S. Optimized THP-1 Differentiation Is Required for the Detection of Responses to Weak Stimuli. Inflamm. Res. 2007, 56, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigoni, M.; Paoli, M.; Milanesi, E.; Caccin, P.; Rasola, A.; Bernardi, P.; Montecucco, C. Snake Phospholipase A2 Neurotoxins Enter Neurons, Bind Specifically to Mitochondria, and Open Their Transition Pores. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34013–34020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, S.C.; Brigatte, P.; Sousa-E-Silva, M.C.C.; Dos-Santos, E.C.; Rangel-Santos, A.C.; Curi, R.; Cury, Y. Contribution of Crotoxin for the Inhibitory Effect of Crotalus durissus Terrificus Snake Venom on Macrophage Function. Toxicon 2003, 41, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pick, E.; Mizel, D. Rapid Microassays for the Measurement of Superoxide and Hydrogen Peroxide Production by Macrophages in Culture Using an Automatic Enzyme Immunoassay Reader. J. Immunol. Methods 1981, 46, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A Major Update to the DrugBank Database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Yu, C.Y.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, P.; Tang, J.; Yang, Q.; Fu, T.; Zhang, X.; Cui, X.; Tu, G.; et al. Therapeutic Target Database Update 2018: Enriched Resource for Facilitating Bench-to-Clinic Research of Targeted Therapeutics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1121–D1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.Q.; Ye, R.D. The Formyl Peptide Receptors: Diversity of Ligands and Mechanism for Recognition. Molecules 2017, 22, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Han, J.; Jung, Y. Formyl Peptide Receptor 2 Is an Emerging Modulator of Inflammation in the Liver. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, Z.W.; Yang, Y.; Yu, C.M.; Gu, D.D.; Deng, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, A.P.; Luo, W.Z. Liposomes Formulated with FMLP-Modified Cholesterol for Enhancing Drug Concentration at Inflammatory Sites. J. Drug Target. 2014, 22, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardini, S.; Dalli, J.; Fineschi, S.; Perretti, M.; Lungarella, G.; Lucattelli, M. Genetic Ablation of the Fpr1 Gene Confers Protection from Smoking-Induced Lung Emphysema in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migeotte, I.; Communi, D.; Parmentier, M. Formyl Peptide Receptors: A Promiscuous Subfamily of G Protein-Coupled Receptors Controlling Immune Responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshart, H.; Heinzelmann, M. THP-1 Cells as a Model for Human Monocytes. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanput, W.; Mes, J.J.; Wichers, H.J. THP-1 Cell Line: An in Vitro Cell Model for Immune Modulation Approach. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Goto, Y.; Okumura, H.; Nakae, S.; Konno, T.; Tada, K. Induction of Maturation in Cultured Human Monocytic Leukemia Cells by a Phorbol Diester. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Sun, J.; Benet, Z.L.; Wang, Z.; Al-Khodor, S.; John, S.P.; Lin, B.; Sung, M.H.; Fraser, I.D.C. Development of a Cell System for SiRNA Screening of Pathogen Responses in Human and Mouse Macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeß, M.B.; Wittig, B.; Lorkowski, S. Highly Efficient Transfection of Human THP-1 Macrophages by Nucleofection. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 91, e51960. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weiß, E.; Kretschmer, D. Formyl-Peptide Receptors in Infection, Inflammation, and Cancer. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Van Keymeulen, A.; Herzmark, P.; Straight, A.; Kelly, K.; Takuwa, Y.; Sugimoto, N.; Mitchison, T.; Bourne, H.R. Divergent Signals and Cytoskeletal Assemblies Regulate Self-Organizing Polarity in Neutrophils. Cell 2003, 114, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.F.; Yang, S.C.; Hwang, T.L. Formyl Peptide Receptor Modulators: A Patent Review and Potential Applications for Inflammatory Diseases (2012–2015). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 1139–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, F.S.; Johndrow, J.E.; Esper, L.; Dias, A.; Bafica, A.; Serhan, C.N.; Aliberti, J. Anti-Inflammatory Actions of Lipoxin A4 and Aspirin-Triggered Lipoxin Are SOCS-2 Dependent. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenfeldt, A.L.; Karlsson, J.; Wennerås, C.; Bylund, J.; Fu, H.; Dahlgren, C. Cyclosporin H, Boc-MLF and Boc-FLFLF Are Antagonists That Preferentially Inhibit Activity Triggered through the Formyl Peptide Receptor. Inflammation 2007, 30, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araújo Pimenta, L.; Duarte, E.L.; Muniz, G.S.V.; Pasqualoto, K.F.M.; de Mattos Fontes, M.R.; Lamy, M.T.; Sampaio, S.C. Correlating Biological Activity to Thermo-Structural Analysis of the Interaction of CTX with Synthetic Models of Macrophage Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pimenta, L.d.A.; Kato, E.E.; Sobral, A.C.M.; Duarte, E.L.; Lamy, M.T.M.; Pasqualoto, K.F.M.; Sampaio, S.C. Formyl Peptide Receptors 1 and 2: Essential for Immunomodulation of Crotoxin in Human Macrophages, Unrelated to Cellular Entry. Cells 2025, 14, 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151159
Pimenta LdA, Kato EE, Sobral ACM, Duarte EL, Lamy MTM, Pasqualoto KFM, Sampaio SC. Formyl Peptide Receptors 1 and 2: Essential for Immunomodulation of Crotoxin in Human Macrophages, Unrelated to Cellular Entry. Cells. 2025; 14(15):1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151159
Chicago/Turabian StylePimenta, Luciana de Araújo, Ellen Emi Kato, Ana Claudia Martins Sobral, Evandro Luiz Duarte, Maria Teresa Moura Lamy, Kerly Fernanda Mesquita Pasqualoto, and Sandra Coccuzzo Sampaio. 2025. "Formyl Peptide Receptors 1 and 2: Essential for Immunomodulation of Crotoxin in Human Macrophages, Unrelated to Cellular Entry" Cells 14, no. 15: 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151159
APA StylePimenta, L. d. A., Kato, E. E., Sobral, A. C. M., Duarte, E. L., Lamy, M. T. M., Pasqualoto, K. F. M., & Sampaio, S. C. (2025). Formyl Peptide Receptors 1 and 2: Essential for Immunomodulation of Crotoxin in Human Macrophages, Unrelated to Cellular Entry. Cells, 14(15), 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151159





