Abstract
Liver fibrosis is a frequent pathological outcome of long-term liver diseases, arising from sustained damage to the liver. Two main types of liver damage can trigger fibrotic progression: hepatocellular injury, often caused by viral infections, alcohol, or metabolic disorders, and cholestatic injury, associated with impaired bile flow due to autoimmune or congenital conditions. Despite diverse etiologies, liver fibrosis exhibits conserved biological processes, including hepatocyte death, chronic inflammation, disruption of epithelial or endothelial barriers, and excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components. These coordinated events reflect the complex interplay among parenchymal damage, immune activation, and fibrogenic signaling pathways. If unresolved, fibrosis may progress to cirrhosis, liver failure, or hepatocellular carcinoma. In the pursuit of non-invasive biomarkers for early detection and monitoring of fibrosis, extracellular vesicles (EVs) have garnered significant attention. Among the diverse cargoes within EVs, microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as particularly promising due to their stability, disease-specific expression patterns, and involvement in fibrogenic signaling. This review explores the role of EV-associated miRNAs in liver fibrosis, highlighting key candidates implicated in hepatocellular and cholestatic injury and their clinical potential as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, with special focus on MAFLD/MASH, primary sclerosing cholangitis, primary biliary cholangitis, and biliary atresia as representatives.
1. Introduction
Liver fibrosis represents a common pathological outcome of various chronic liver diseases and develops as a consequence of sustained hepatic damage. It is characterized by aberrant deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, primarily type I and type III collagens, which eventually form fibrous tissue that distorts liver architecture and compromises function. Different hepatic cell types orchestrate collagen deposition, including activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs), and portal fibroblasts [1]. Liver fibrosis can be broadly classified into two categories: hepatocellular and cholestatic injuries [2]. Hepatocellular injury results from direct cellular damage due to external agents such as chronic viral infections (hepatitis B and C), excessive alcohol intake leading to alcoholic steatohepatitis (ASH), or from metabolic disturbances causing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), as well as from chronic immune-inflammatory responses such as autoimmune hepatitis [3,4]. On the other hand, cholestatic injury is caused by impaired bile secretion or flow, often linked to disorders such as primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), or congenital anomalies like biliary atresia [4]. These diseases are liver conditions involving damage to the bile ducts, marked by ongoing inflammation, impaired bile flow, and biliary fibrosis [5]. As these diseases advance, they can lead to cirrhosis, increased pressure in the portal vein, and eventual liver failure. Despite the multiple origins of liver injury, fibrosis progression follows a set of conserved mechanisms, including hepatocyte loss, persistent inflammatory signaling, breakdown of tissue barriers such as the sinusoidal endothelium or biliary epithelium, and ECM deposition [6]. These events reflect the complexity of hepatic fibrogenesis, which integrates a dynamic interplay between parenchymal injury, immune responses, and fibrogenic signaling pathways. If left unchecked, fibrosis can progress to cirrhosis, liver failure, or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Therefore, early detection, staging, and monitoring of fibrosis are critical for disease management and therapeutic intervention.
The current gold standard for assessing liver fibrosis is liver biopsy, despite the drawbacks of being invasive, subject to sampling errors, and unsuitable for serial monitoring [7]. In the race to search for biomarkers in recent years, extracellular vesicles (EVs), lipid bilayer-bound particles released by cells and found in all body fluids, have emerged as a promising non-invasive source of biomolecules for early detection of liver fibrosis [8,9,10]. EVs enclose microRNAs (miRNAs), which are small non-coding RNAs (typically 18–24 nt long) that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression and participate in homeostasis maintenance or disease promotion [11]. These EV-derived miRNAs hold particular promise due to their stability, disease specificity, and involvement in fibrogenic pathways. In this review, we examine EV-encapsulated miRNAs implicated in liver fibrogenesis and highlight their potential as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in both hepatocellular and cholestatic liver injury.
2. Extracellular Vesicle Isolation and Purification for Biomarker Search
EVs encompass a heterogeneous population of vesicles, mainly categorized as exosomes (30–150 nm) generated via the endosomal pathway, microvesicles (100–1000 nm) shed directly from the plasma membrane, and apoptotic bodies (>1000 nm) formed during programmed cell death. Surface markers on extracellular vesicles, including exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies, reflect their cellular origin and biogenesis pathways, offering valuable insight for distinguishing between vesicle subtypes and enabling their use in diagnostic and therapeutic applications. For instance, specific surface markers such as CD81, CD63, Alix, and Tsg101 on exosomes, Caspase 3 and histones on apoptotic bodies, and selectins, integrin, and CD40 on microvesicles can help differentiate EV subtypes [12,13,14]. Due to their pivotal role in mediating intercellular communication from donor to recipient cells, EVs are increasingly recognized as versatile agents in biomedical applications. These nanosized vesicles, secreted by nearly all cell types, carry a plethora of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids that provide a molecular snapshot of their cells of origin. For example, tumor-derived exosomes have been shown to transport oncogenic biomolecules that can influence the tumor microenvironment and promote metastasis [15]. This cargo-loading capacity positions EVs as promising vehicles for targeted drug delivery, allowing therapeutic molecules to be transported directly to specific tissues or cell types with high precision and reduced systemic toxicity [16,17]. Furthermore, because the molecular contents of EVs can mirror disease-specific changes, they are being actively explored as non-invasive biomarkers for conditions such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, liver failure, and cardiovascular disease [18,19,20,21]. These features collectively highlight the potential of EVs not only as diagnostic tools but also as platforms for novel therapeutic strategies.
2.1. Isolation and Purification of Extracellular Vesicles for Clinical Biomarker Applications
The clinical potential of EVs as biomarkers relies heavily on the ability to isolate and purify them effectively from complex biological fluids (biofluids) such as blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid. However, EV isolation presents substantial technical challenges due to their small size, heterogeneity, and the presence of contaminating proteins and lipoproteins in biofluids [22]. The efficiency of retrieving EVs from plasma varies based on the chosen isolation technique. Several methods have been developed, each with unique strengths and limitations, especially concerning yield, purity, scalability, and compatibility with downstream molecular analyses.
2.1.1. Differential Ultracentrifugation
Differential ultracentrifugation is one of the most widely used traditional methods for EV isolation from cell culture media or from body fluids such as serum. It involves sequential centrifugation steps at increasing speeds to remove cells, debris, and finally to pellet EVs [23]. With this procedure, EVs do not require particular pretreatment prior to their isolation. However, although effective, this method is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and often results in co-purification of protein aggregates or lipoproteins, hence reducing EV purity. The latter is an important consideration in clinical diagnostics [24].
2.1.2. Density Gradient Centrifugation
To improve purity and yield, density gradient centrifugation (e.g., sucrose gradients) can be employed after ultracentrifugation. This approach separates EVs based on their buoyant density, helping to discriminate between EV subtypes and contaminants [25]. However, density gradient centrifugation remains a low-throughput technique and is not easily automated, limiting its applicability in high-volume clinical settings. Moreover, EV functionality may be impaired due to the excessive force applied during ultracentrifugation. Contemporary precipitation-based approaches have emerged as substitutes for ultracentrifugation, offering advantages such as minimal input volume requirements from human biofluids and compatibility with high-throughput workflows. However, isolating EVs from plasma remains particularly challenging due to the inherent viscosity and high protein content of plasma, which adversely affect the purity achievable through ultracentrifugation techniques [26]. More recently, a streamlined method utilizing a single-step size-exclusion chromatography (SEC, described below) process has been introduced for isolating EVs directly from human plasma.
2.1.3. Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
SEC separates EVs from other particles based on hydrodynamic properties and size. It is a gentle, reproducible, and scalable method that preserves EV integrity and is especially compatible with clinical applications [27]. Lobb et al. compared different isolation methods for retrieving EVs from plasma and demonstrated that ultrafiltration coupled with SEC had superior efficiency in terms of purity compared to other precipitation methods, such as ultracentrifugation or charge-based precipitation, for isolating EVs from human plasma. This was confirmed recently in another study showing the reproducibility, simplicity, and purity of SEC-based separation of EVs in the clinical setting from 1 mL of plasma, and its suitability in the clinical setting [28]. Despite its utility, SEC may result in the co-elution of particles with comparable dimensions, like protein clusters or lipoproteins, and typically necessitates additional concentration procedures.
2.1.4. Polymer-Based Precipitation
Water-excluding polymer-based precipitation methods (e.g., using polyethylene glycol and PEG) offer a simple, rapid, and scalable solution to isolate EVs from various fluids [29]. Exosome precipitation kits also provide higher EV yields of miRNAs and mRNAs for high-throughput molecular analyses [30]. These kits are widely used in clinical research due to ease of use [31]. However, they typically yield low-purity preparations with significant contamination from soluble proteins, which can hinder tissue-derived biomarker discovery [32].
2.1.5. Immunoaffinity Capture
Immunoaffinity-based methods use antibodies against specific EV surface markers (e.g., CD63, CD9, and CD81) to selectively capture vesicles of interest. For instance, the use of anti-CD81 VHH ligand-based immunoaffinity chromatography methods allows for the direct capture of EVs from cell culture supernatant, showing strong potential in enriching disease-specific EV populations with high specificity [33,34]. However, the high cost, limited scalability, and dependence on well-defined surface markers restrict its general application.
2.1.6. Microfluidic and Lab-on-a-Chip Technologies
Advancements in microfluidic platforms, commonly known as lab-on-a-chip systems, have paved the way for streamlined EV capture, refinement, and characterization in compact, efficient formats suitable for clinical applications [35]. These microscale devices replicate conventional isolation methods by precisely directing fluid behavior within confined channels. Among their key advantages are rapid processing times, reduced consumption of biological material and reagents, multiplexing capabilities, and compatibility with automated high-throughput protocols. By integrating diverse separation mechanisms such as antibody-based targeting, electric field-driven sorting, and membrane-based sieving, these tools enable high-purity EV isolation from limited sample inputs. Despite their potential, many of these technologies remain in the developmental phase or are undergoing preliminary clinical validation.
Identifying the most effective method for isolating EVs remains a major hurdle in their clinical application. When evaluating these approaches, the ideal protocol would be straightforward, cost-effective, avoid reliance on complex or high-end instrumentation, deliver results quickly, and be capable of processing large sample volumes efficiently [36]. The effectiveness of any EV isolation technique hinges on how well it performs with human clinical specimens, especially when EVs are being investigated as potential new biomarkers. All these procedures, applied individually, produce different yields of EVs with different grades of purity. Integrating multiple enrichment techniques can improve the purity of EVs, thereby strengthening the accuracy and validity of subsequent experimental analyses, which may help in finding the right combination for a cost-effective procedure for the clinical setting. For instance, merging PEG-based precipitation with ultrafiltration can provide highly pure small EVs nearly void of non-vesicular particles or artifacts [37].
2.2. EV Quality Testing
Quality testing of EVs is crucial, since EVs are highly heterogeneous, and their quality can significantly affect the reliability of results. Quality testing involves a multifaceted approach that combines physical, biochemical, and functional assessments to ensure the suitability of EV preparations for different applications. The MISEV guidelines were recently updated and can help researchers in standardizing the different techniques used to characterize EV preparations in order to obtain comparable results among different laboratories [38]. Dynamic light scattering and nanoparticle tracking analyses are commonly used to determine EV size and concentration. Transmission electron microscopy is used to assess the integrity of EV membranes. Assessing zeta potential, a measure of the surface charge of EVs, can confirm the integrity of EVs. EVs are negatively charged in biofluids and zeta potential effects EV stability, aggregation, and interaction with target cells. Specific proteins, such as tetraspanins (CD63, CD9, and CD81), can serve as markers to identify EVs, and different techniques, such as ELISA, flow cytometry, and western blotting, are commonly used to detect these markers.
2.3. EV Composition
EVs carry nucleic acids, proteins and lipids, which can influence the behavior of recipient cells and hold potential as diagnostic biomarkers or as vehicles for drug delivery [14]. Among nucleic acids, RNA is the most abundant and is predominantly short in size (less than 200 nucleotides (nt) long) [39,40]. Sequencing of total RNA from serum-derived EVs showed that miRNAs and transfer RNA constitute around 15% of all RNA species contained inside these nanoparticles [41]. The presence of long transcripts (more than 200 nt long) as well as coding and non-coding RNAs have also been reported in EVs [40,41]. Interestingly, some RNAs, especially miRNAs were enriched in the released EVs, in comparison with the cells of origin [42,43,44]. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are also abundant in circulating EVs. RNA-seq analyses indicated that they are enriched in EVs compared to the cells of origin; more than 1000 circRNAs were identified in human serum exosomes [45]. EVs can transport DNA ranging in size from 100 base pairs (bp) to 2.5 kilobase pairs (kB) [46,47,48]. EV-DNA reflects parental cell genomic DNA, as cancer-related mutations in genes such as BRAF, EGFR, KRAS, and TP53 have been identified in DNA from EVs derived from melanoma and pancreatic cancer cells [48,49].
The protein composition of EVs is influenced by both the cell of origin and the mechanism of vesicle formation. Exosomes originate from the endosomal compartment and are enriched in major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC class II) and tetraspanins, and in the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) that constitutes a group of proteins indispensable for the formation of multivesicular bodies [50,51,52]. The ESCRT pathway requires accessory proteins, such as Alix and tumor susceptibility gene protein 101 [52]. Owing to their plasma membrane origin, MVs are enriched in a different set of proteins, such as integrins, glycoprotein Ib, and P-selectin [50]. EV proteins can be grouped in functional classes. For example, nucleic acid binding is the most common function among proteins present in EVs, together with catalytic activity [53,54]. Moreover, in EVs, transcription factors, receptors, enzymes, and functional metalloproteases that can induce phenotypic changes in recipient cells can be found [55].
The lipid bilayer of EVs resembles that of the plasma membrane. Exosomes are enriched in gangliosides, sphingomyelin, and desaturated lipids, and phosphatidylcholine and diacylglycerol proportions are lower than in their cells of origin [56]. An increased presence of cholesterol in exosomes compared with the membranes of cells of origin has been reported [57].
During EV biogenesis and secretion, factors such as membrane composition, surface proteins, and cellular origin shape the biomolecular corona, the dynamic layer of proteins and other biomolecules that adsorb onto the EV surface [58]. Once released, EVs encounter diverse extracellular environments that can alter or reshape this corona, influencing their stability, uptake, and functionality. The biomolecular corona of EVs constitutes a dynamic and functionally significant layer that plays a central role in mediating EV interactions with recipient cells. During EV biogenesis within the cell, a subset of proteins associates with the vesicle surface, forming a nascent corona. Following secretion, this corona evolves as additional proteins and biomolecules from the extracellular environment bind to the EV surface, giving rise to what is commonly referred to as the protein corona [58]. Emerging evidence indicates that the EV corona is not limited to proteins alone but also encompasses other classes of biomolecules, including lipids, RNA, and even DNA. This expanded composition forms what is increasingly recognized as the EV biomolecular corona. Pathological conditions are often accompanied by changes in cellular physiology, which are reflected in the composition of secreted EVs, both in their internal cargo and surface-associated molecules. These disease-specific alterations in the EV biomolecular corona present a valuable opportunity for biomarker discovery. Given its accessibility and responsiveness to pathophysiological states, the EV biomolecular corona holds significant promise as a diagnostic tool, particularly for the early detection of diseases [59].
3. Intercellular Communication via EVs in Liver Fibrosis
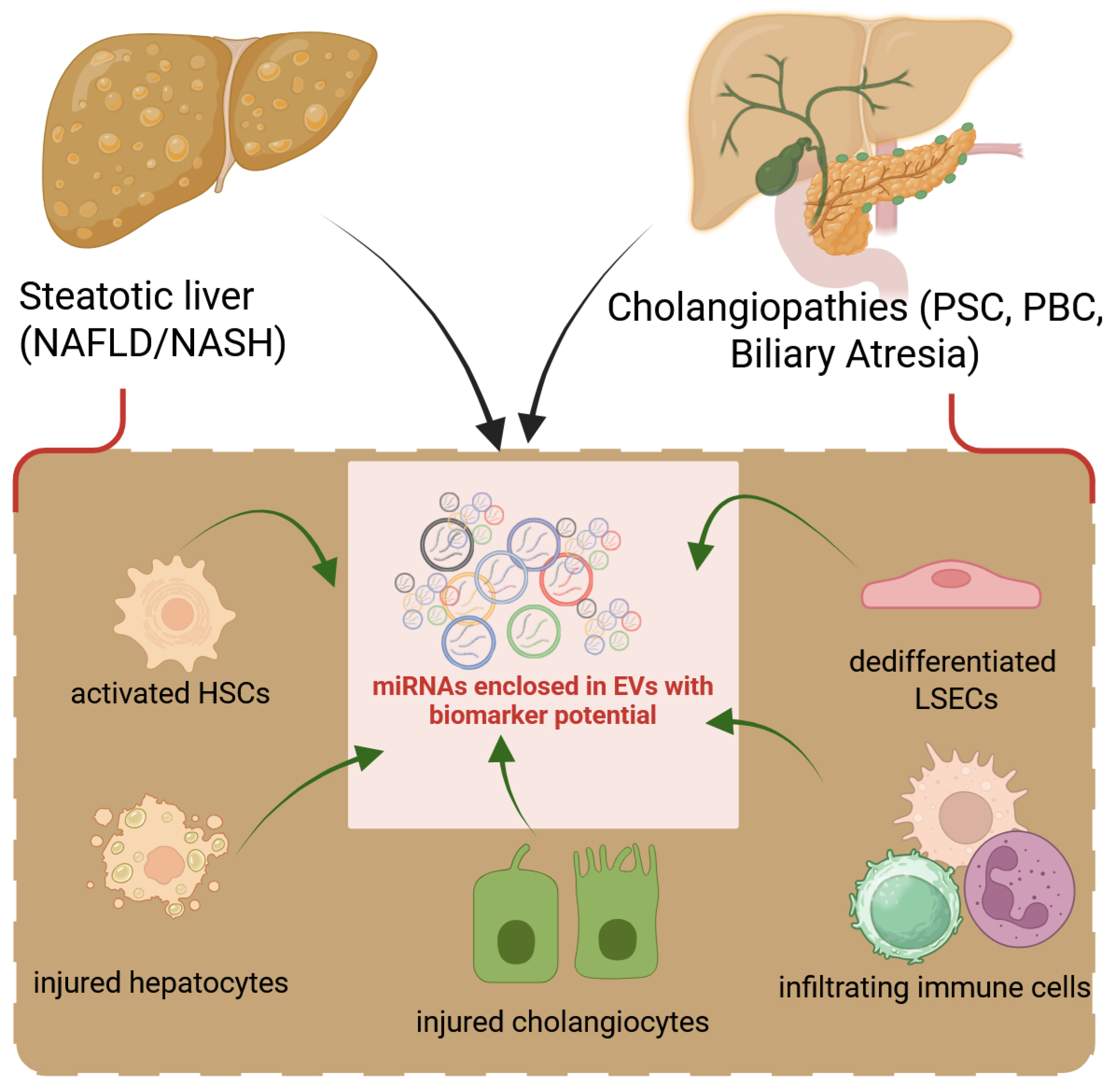
Persistent hepatocyte damage leads to inflammation, activation of fibrogenic pathways, and excessive ECM deposition, which gradually distorts liver architecture and impairs function. Liver fibrosis arises from a complex interplay among various cellular and molecular components, beginning with hepatic injury and progressing to irreversible ECM deposition. Signaling between hepatocytes, HSCs, Kupffer cells, LSECs, and immune cells plays a central role in the initiation and perpetuation of fibrogenesis (Figure 1).
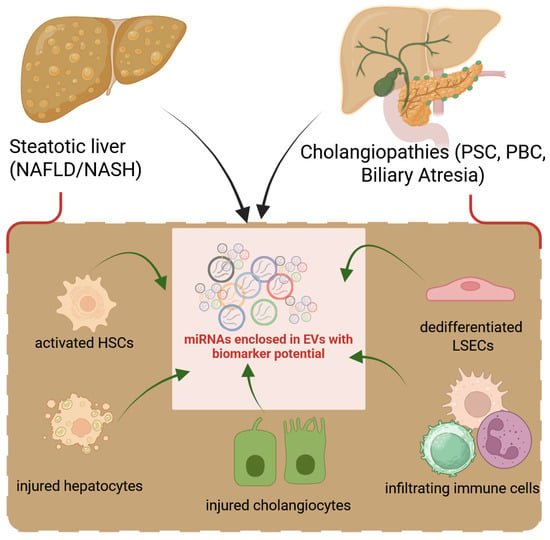
Figure 1.
Liver cells release EVs to perpetuate fibrotic signals. Following damage to hepatocytes (hepatocellular) or cholangiocytes (biliary), all hepatic cell types react by releasing growth factors, cytokines, or EVs into the secretome, which lead to the dedifferentiation of LSECs followed by activation of HSCs or fibroblasts and dysregulated production of ECM. Infiltrating inflammatory cells also contribute to liver fibrosis with their load of secreted factors.
The liver, as a central metabolic organ, constantly communicates with other tissues via secreted molecules, including EVs. The resident liver cells’ secretome, which is its repertoire of bioactive factors, exerts a profound influence on liver fibrogenesis (Table 1).

Table 1.
Endogenous liver cell secretomes influences on fibrogenesis (including insights from preclinical models). Some examples of biomolecules released by hepatic cell types are shown. NO—nitric oxide; CCL2—C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; TNF-α—tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TGF-β—transforming growth factor-beta; PDGF—platelet-derived growth factor; DAMP: damage-associated molecular pattern; MASP1—mannan-binding lectin serine protease 1; OPN—osteopontin; TGF-α—transforming growth factor-α; FGF—fibroblast growth factor. ↑ and ↓ represent increased or decreased, respectively.
Input from mice models and clinical samples has demonstrated the utility of EVs as a biomarker source in the context of liver fibrosis. EVs secreted from any cell type of the injured liver can participate in damage perpetuation. Thus, identifying EVs carrying loads of fibrotic indicators could facilitate early diagnosis and serve as a valuable diagnostic marker. The EV contents vary according to disease etiology, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
EVs released by the different hepatic cell types and examples of their roles in fibrogenesis.
Recent studies have reported that specific subpopulations of EVs are released by organelles, for instance by mitochondria, and are enriched with mitochondrial components, which can influence the phenotype and metabolic state of recipient cells [70,71]. The mitochondrial content of EVs appears to vary under pathological conditions. For instance, in a murine model fed an ethanol-enriched diet, plasma levels of hepatocyte-derived EVs containing mitochondrial components were elevated and this was suggested to contribute to liver injury by promoting inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress [72]. Similarly, EVs isolated from in vitro ethanol-treated human or murine hepatocytes exhibited increased levels of mitochondrial RNA. These EVs induced IL-1β expression in Kupffer cells, thereby promoting inflammation through the activation of a specific T lymphocyte subpopulation [73]. Collectively, this evidence suggests that alterations in the quantity or composition of circulating EVs enriched in mitochondrial components could serve as potential biomarkers for pathological conditions, particularly in alcoholic liver disease.
3.1. Biofluids with Biomarker Utility for Liver Fibrosis
Biofluids, such as serum, bile, and urine, are rich in biomarkers for detecting liver fibrosis and these fall into several categories: proteins, metabolites, nucleic acids, and lipids, as well as EVs. The latter reflect the molecular state of the cells of origin and are detectable in several biofluids, notably serum, bile, and urine. Each fluid offers unique insights into liver pathophysiology, disease biomarkers, and therapeutic monitoring.
3.1.1. Blood
Serum and plasma are the most commonly used biofluids for assessing liver fibrosis due to their accessibility and the abundance of potential biomarkers. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) are routinely measured enzymes that indicate liver injury, although they do not correlate specifically with the stage of fibrosis. Elevated levels of gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) are more suggestive of cholestasis and advanced fibrotic changes [74,75]. Components of ECM can also be detected in serum and serve as direct indicators of fibrogenesis [76]. For example, hyaluronic acid (HA), a marker of ECM remodeling, increases in circulation with the progression of fibrosis. Similarly, procollagen III N-terminal peptide (PIIINP), a precursor of collagen type III, correlates well with fibrosis severity in infantile cholestasis [77]. Another notable marker is cytokeratin-18 (CK-18), which reflects hepatocyte apoptosis and is particularly elevated in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH)-related fibrosis [78]. In addition to proteins, serum contains circulating non–EV-bound microRNAs, such as miR-122 and miR-34a. In an effort to distinguish between non-hepatitis B- and non-hepatitis C-related HCC and NAFLD patients or healthy controls, Boonkaew et al. analysed plasma EV miRNA profiles. The results pointed to five EV miRNAs comprising miR-19-3p, miR-16-5p, miR-223-3p, miR-30d-5p, and miR-451a as elevated in the HCC group compared to controls, with EV miR-19-3p being revealed as the best diagnostic predictor of Alfa-fetoprotein-negative and early HCC [79]. On the other hand, EV miR-223-3p was statistically significantly higher in NAFLD patients with respect to controls, suggesting its potential as a biomarker for this pathology.
3.1.2. Bile
Bile is a complex fluid secreted by the liver, and is a viable and promising source of biomarkers for liver and biliary tract cancers because of its proximity to the disease site [80]. Human bile contains inorganic electrolytes, lipids (bile acids, phospholipids, and cholesterol), bilirubin, and proteins, and is abundant in EVs that can be isolated and characterized using standard protocols, typically yielding vesicles of ~30–200 nm in size [81,82].Bile-derived EVs have been reported to contain higher amounts of Claudin 3 protein in Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cohorts compared to biliary stone disease patients, showing potential as a diagnostic marker for CCA [83]. Moreover, bile offers a rich, disease-relevant EV miRNA milieu that surpasses serum in biomarker concentration and specificity, making EV-derived miRNAs particularly useful for detecting cholestatic and biliary tract diseases. For instance, significantly higher levels of bile exosomal miR-200 family members (including miR-200a-3p and miR-200c-3p) have been found in patients with CCA compared to those with benign diseases, such as biliary stone disease [84]. Moreover, pairing the bile EV miRNAs miR-200a-3p/-200c-3p with serum CA19-9 greatly enhanced diagnostic performance. Bile EV analysis on larger human cohorts during ERCP has identified miR-451a and miR-3619-3p as robust biomolecules for distinguishing biliary tract cancers from non-malignant controls [85]. Notably, higher expression of miR-3619-3p was also linked to a worse prognosis in patients with biliary tract cancers. Technically, accurate quantification of bile EV miRNAs requires rigorous normalization procedures, like the inclusion of synthetic spike-in controls such as Cel-miR-39, in order to mitigate variability introduced during RNA extraction [86].
3.1.3. Urine
Urine is a valuable, accessible and non-invasive biofluid, which is rich in EVs. Urinary EVs can be purified by methods such as SEC or precipitation, and they contain stable, vesicle-encapsulated miRNAs derived from the urogenital tract and also from various tissues. Although urinary EV miRNA levels may be lower than those in serum due to renal filtration, disease-specific signatures have been detected in liver pathology contexts. Lipidomic profiling of urinary EVs from NAFLD and NASH patients revealed four lipid molecules (free fatty acid (18:0), lysophosphatidylcholine (22:6/0:0), free fatty acid (18:1), and phosphatidylinositol (16:0/18:1), capable of high discrimination of NALFD cohorts that progress to NASH [87]. Moreover, in CCA, specific EV transcripts reflecting tumor tissue were detected in urine, despite the fact that the overall number of potential biomarkers in urine may be lower than in serum, a result of renal filtration processes [88]. In non-viral hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), plasma EV miR-19-3p showed strong diagnostic accuracy, showing excellent detection capability for early-stage and AFP-negative HCC [79].
Due to their accessibility in the clinic, these biofluids are regarded as ideal sources of EVs for biomarker discovery and analysis. Differences exist between EVs derived from biofluids and those isolated directly from tissues. In fact, growing evidence indicates that tissue-derived EVs contain a richer repertoire of biological information and more precisely reflect changes in the tissue microenvironment compared to EVs derived from cultured cells or biofluids [89]. Tissue-derived EVs are usually found at significantly lower concentrations than EVs derived from circulating blood components. Consequently, molecular analysis of tissue-derived EVs in biofluids necessitates stringent pre-analytical handling and highly reproducible analytical methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable data acquisition (https://www.biomedcentral.com/collections/EVPCLIP; accessed on 1 July 2025). The origin of tissue-derived EVs is more well-defined, allowing for more precise tracking using electron microscopy. However, their isolation typically requires tissue explants or biopsies, which are inherently invasive procedures. For example, to isolate liver-derived EVs, whole livers were harvested from carbon tetrachloride-treated mice [90]. Therefore, at present, EVs derived from biofluids remain the most practical and minimally invasive option for biomarker discovery in disease diagnostics.
4. EV-Derived miRNAs as Biomarkers for Liver Fibrosis
4.1. NAFLD/NASH
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), recently renamed metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), is the most common chronic liver disease in Western countries and affects about a quarter of the world’s adult population [91,92]. MASLD encompasses several pathological conditions, from steatosis to liver inflammation and fibrosis (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), now known as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH)), which can progress to cirrhosis and carcinoma [91]. Recently published studies have investigated the use of EVs as a non-invasive tool for NAFLD/MASLD and NASH/MASH diagnosis and staging.
Higher levels of circulating EVs were found in the plasma of mice and humans with chronic liver diseases compared to healthy controls [93,94,95]. The correlation between circulating EV levels and disease severity has been demonstrated in various mouse models of NAFLD and NASH [96]. For example, the number of circulating EVs increased with the progression of NAFLD and correlated with liver fibrosis in diet-induced NAFLD in mice. Circulating EVs in the NASH mouse model were enriched with miR-122 and miR-192, two miRNAs typically expressed in hepatocytes [97,98]. In the sera of NAFLD patients, EV–associated miR-122 and miR-192 were described as candidate biomarkers of NASH progression [99,100]. In addition, the expression of EV-derived miR135a-3p was found to be lower in the serum of patients with NAFLD compared to healthy controls, and ROC analysis suggested that this EV-derived miRNA may be a sensitive biological marker for the diagnosis of NAFLD [101]. A recent publication reported that miR-122 and miR-128 were upregulated, while miR-200, miR-298, and miR-342 were downregulated in EVs isolated by ultracentrifugation from plasma samples of patients with NAFLD and NASH compared to normal controls [102]. Similarly, EVs isolated from serum using a commercially available isolation kit contained specific miRNAs that correlated with inflammation, steatosis, ballooning, and NASH scores [103].
The selective isolation of circulating EVs derived from hepatocytes represents an opportunity to improve the use of EV-derived miRNAs as biomarkers for liver disease. Liver-derived EVs can be isolated by immunoprecipitation with anti-sialoglycoprotein receptor 1. The EVs isolated from NASH patients’ livers showed enrichment of several miRNAs (miR-122, miR192, and miR-128-3p) compared to those obtained from NAFLD patients and healthy controls, suggesting that these EV miRNAs are significantly associated with liver disease severity [104]. This study emphasizes the possibility of isolating liver-specific EVs to identify biomarkers for NAFLD that reliably distinguish patients with NAFLD and NASH.
The various techniques commonly used for the purification of EVs, such as ultracentrifugation and selective selection by immunoprecipitation, are time-consuming, work-intensive, and costly, which limits their applicability in the clinical setting. An innovative approach of capturing EVs from serum using wheat germ agglutinin-coupled magnetic beads and real-time quantitative PCR to analyze EV miRNAs, showed that miR-574-3p, miR-542-3p, and miR-200a were significantly elevated in patients with MASLD [105]. These miRNAs are involved in various processes associated with the development of liver fibrosis and chronic liver disease. For example, miR-574-5p was found to be upregulated in serum EVs and positively correlated with collagen deposition and alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression in liver tissue during fibrosis [106]. Furthermore, miR-542-3p and 200a-3p were significantly upregulated in liver fibrosis and promoted the activation of HSCs [107,108]. These results suggest that EV miR-574-3p, miR-542-3p, and miR-200a-3p may play a role in the occurrence and progression of MASLD and could be used as diagnostic markers.
4.2. Cholestatic Injury-Related Liver Fibrosis
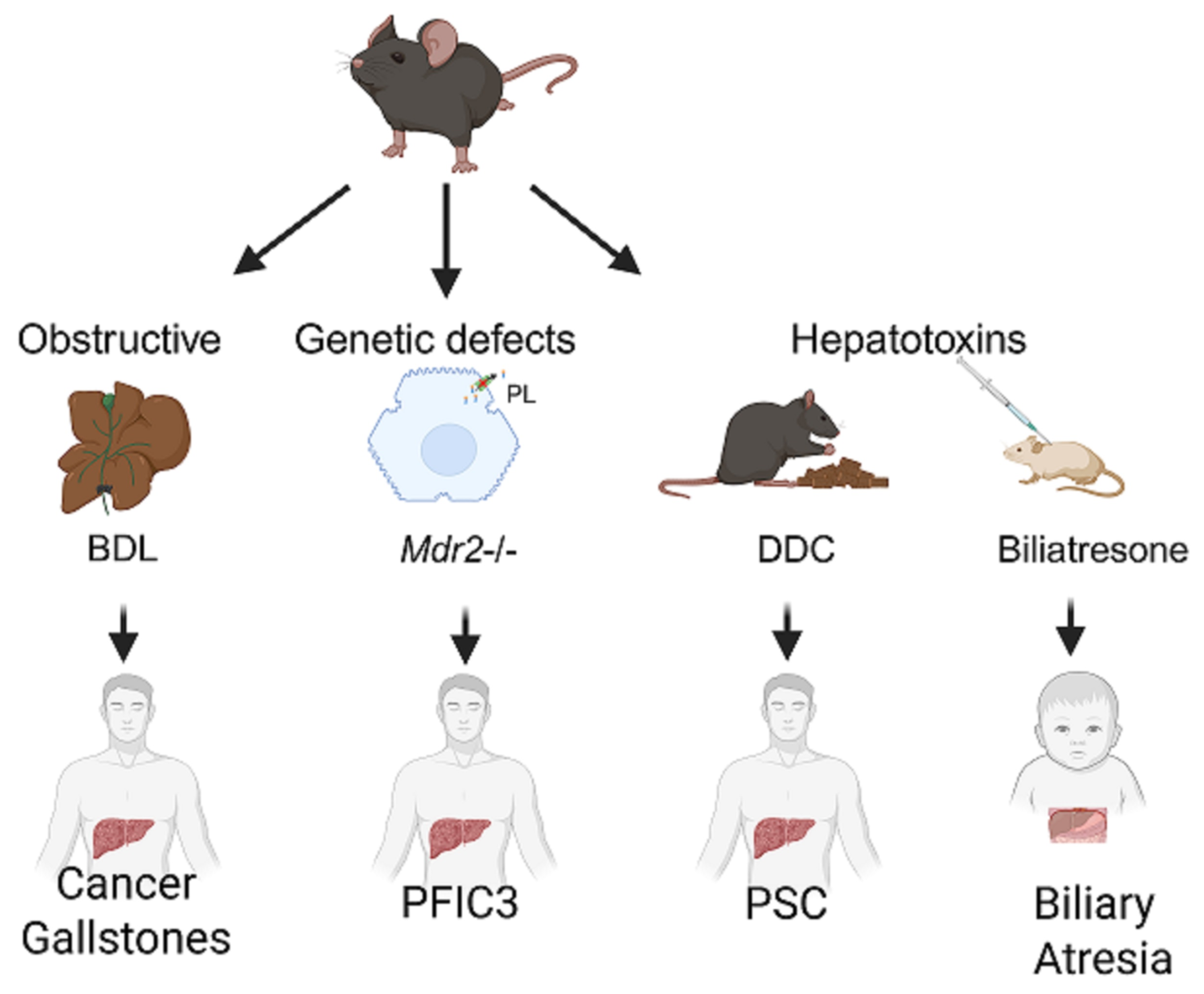
Very few studies have been performed on the potential use of EV miRNAs as biomarkers for human cholangiopathies. Valuable insights regarding the potential of EV miRNAs as biomarkers for biliary tract diseases have come from preclinical studies. Several mouse models for cholestatic injuries have been developed for biomarker discovery for human biliary tract diseases (Figure 2).
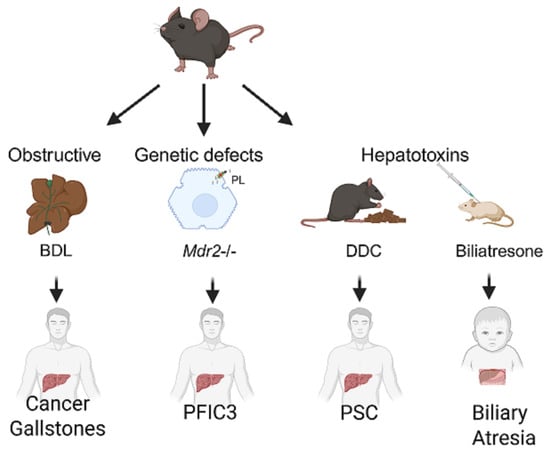
Figure 2.
Mouse models of human biliary tract diseases. Representative models of biliary damage caused by bile duct obstruction, genetic defects, or exposure to hepatotoxins are shown, with clinical translatability regarding cancer and gallstones, progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 (PFIC3), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and biliary atresia, respectively, in humans. BDL—bile duct ligation; Mdr2—multidrug resistance 2 (Abcb4); DDC—3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4 dihydrocollidine.
For instance, by inducing biliary injury in mice through obstruction (bile duct ligation (BDL)) or diet (3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine, DDC), and by using genetic models (Mdr2-/- mice), we have shown that circulating EV miRNAs such as miR-122-5p, miR-192-5p, and miR-29a-3p closely mirror disease progression following different causes of biliary injury, and can distinguish stages of liver fibrosis [8].
4.2.1. PSC
PSC, a chronic cholestatic disorder with genetic and environmental etiologies, affects bile ducts both at the intrahepatic and extrahepatic levels. EV miRNAs are emerging as promising non-invasive biomarkers for cholangiopathies, but only few data are available for PSC, a chronic cholestatic liver disease with limited diagnostic and prognostic tools. Specific EV miRNAs have shown altered expression profiles in PSC patients compared to healthy controls and those with other liver diseases. Notably, miR-122-5p and miR-192-5p, both liver-enriched miRNAs, were consistently and significantly upregulated in EVs isolated from PSC patients versus healthy controls, reflecting hepatocyte or cholangiocyte injury and serving as markers of disease activity [109]. Additionally, miR-4645-3p, recently identified through miRNA sequencing, exhibits approximately fourfold higher expression in PSC-derived EVs, with its levels correlating closely with miR-122-5p and miR-192-5p, thereby enhancing diagnostic specificity [109]. These EV miRNA signatures not only distinguish PSC from healthy states but also show potential to differentiate PSC from other cholestatic disorders such as PBC or overlap syndromes. More clinical studies should be undertaken to increase the repertoire of EV miRNAs to increase their potential for early diagnosis, risk stratification, and monitoring therapeutic response in PSC.
4.2.2. PBC
PBC is a chronic disorder, characterized by bile retention in the liver. Although its exact cause is unknown, the condition is believed to result from immune-mediated damage to intrahepatic bile ducts. Without treatment, the disease can advance to liver scarring, cirrhosis, and eventually liver failure, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis. Tomiyama et al. investigated the role of plasma-derived EV (exosomes) miRNAs in PBC and identified several upregulated and downregulated miRNAs, with miR-451a and miR-642a-3p being the most significantly upregulated in patients compared to healthy controls [110]. These miRNAs were shown to modulate the expression of co-stimulatory molecules, specifically CD86 and CD80, on antigen-presenting cells such as monocytes in vitro. The regulatory effect suggested a potential link between circulating EV miRNAs and immune dysregulation in PBC. These findings highlight the possibility that EV-associated miR-451a and miR-642a-3p are not only reflective of disease activity but may also contribute to its pathogenesis, underscoring their promise as non-invasive biomarkers for early detection or monitoring of disease progression.
4.2.3. Biliary Atresia
In biliary atresia, the intra- and extra-hepatic bile ducts are progressively destroyed in infants, making this disease the most common cause of pediatric cholangiopathy-associated liver transplantation. Early diagnosis is essential for an appropriate treatment. Albeit EV-associated miRNAs have shown promise as early, non-invasive biomarkers for cholangiopathies, to our knowledge, not much work has been performed regarding biliary atresia. Studies have been restricted to non-EV-enclosed miRNA profiling in serum. Notably, employing a microfluidic array platform, elevated levels of miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-429 have been observed in BA patients when compared to individuals with other types of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia (validated in n = 24 infants, in each group) [111]. Another study, using miRNA expression profiling by microarray analysis, revealed that miR-4429 was downregulated and miR-4689 was upregulated in serum, both showing potential utility in distinguishing BA (validated in n = 45 biliary atresia infants and n = 30 non-BA neonatal cholestatic controls) [112].
5. Clinical Utility of EV-Derived miRNAs in Liver Fibrosis
As described above, the evaluation of circulating EV miRNA contents has emerged as a promising area for discovering new biomarkers in chronic liver disease onset and progression. Development of EV miRNA-based biosensors and liquid biopsy platforms could facilitate non-invasive, real-time assessment of liver health. Panels of EV miRNAs (for instance, miRNA-122-5p and miRNA-409-3p,) may improve sensitivity and specificity when combined with serum markers (e.g., ALT and AST) or scores like aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio (APRI) and Fibrosis-4 (Fib-4) [113]. Elevated levels of certain EV miRNAs (e.g., miR-199a-5p and miR-21) are associated with worse clinical outcomes and may predict fibrosis progression or risk of cirrhosis, indicating the utility of EV miRNAs as prognostic indicators. EV miRNAs can also help in response to therapy monitoring, especially in this era of new anti-fibrotic drug design and testing. Changes in circulating EV miRNA levels can reflect treatment response to antifibrotic drugs or lifestyle interventions in MAFLD/MASH and viral hepatitis.
Although a growing body of evidence indicates the feasibility of adopting EV miRNAs as markers of specific liver diseases or for the staging of pathological conditions, there are currently no ongoing clinical trials for EV miRNA large-scale applications as screening or monitoring for liver disease progression. Encouraging results have been recently published showing a comprehensive analysis of plasma EV-associated miRNAs in patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) with and without liver disease, in comparison with non-AATD controls [114]. The objective was to identify miRNAs that could offer insights into liver disease status associated with AATD and help in recognizing individuals with AATD who are at risk of developing hepatic complications. AATD is a rare inherited disorder caused by a point mutation in the SERPINA1 gene, leading to misfolding and polymerization of alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) within hepatocytes, which can contribute to liver pathology. Moreover, the low level of AAT in plasma patients induces lung inflammation. Oshins et al. identified six circulating EV miRNAs (let-7a-5p, let-7f-5p, miR-15b-5p, miR-223-3p, miR-23a-3p, and miR-374a-3p) as potential molecular signatures for the detection of AATD liver disease, offering a valuable tool for early detection and risk stratification. The use of circulating EV miRNAs as non-invasive liver disease signatures is advantageous for both clinicians and patients. Indeed, the EV miRNA panel permits detection of liver disease in AATD patients early to start therapeutic interventions before cirrhosis and HCC development. Moreover, the EV miRNA signature could replace the need for liver biopsies that are invasive and risky for patients. Notably, the identified EV miRNA signature may also be useful to monitor responses to anti-fibrotic therapeutic treatments. The use of circulating EV miRNA signatures opens a new perspective in precision medicine to predict severity and progression of disease and to monitor responses to therapeutic interventions.
6. Technical Challenges and Considerations
The absence of standardized protocols for EV isolation can result in variability and inconsistency across studies. Selecting a method that offers high purity and yield, while remaining cost-effective and feasible in resource-limited research or clinical settings, remains a key challenge. Accurate quantification of EV-associated miRNAs requires highly sensitive and reproducible techniques, such as digital PCR or next-generation sequencing. However, consensus on robust normalization strategies is still lacking, complicating data interpretation. The expression levels of EV miRNAs can also be significantly influenced by individual factors including comorbid conditions, medication use, and age, introducing further variability in biomarker studies. In systemic circulation, distinguishing EVs derived from specific liver cell types remains technically challenging, limiting the ability to assign functional relevance or diagnostic specificity to EV miRNA signatures. In disease contexts such as MASH/MAFLD, PSC, and biliary atresia, this variability adds complexity to EV-based biomarker discovery, as EV composition and surface signatures may differ depending on both disease state and microenvironmental factors.
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
EV-associated miRNAs demonstrate significant potential as non-invasive biomarkers for the detection, staging, and monitoring of liver fibrosis. Their expression levels correlate with fibrogenic pathways, and they are readily detected in accessible body fluids, such as blood, for instance in the case of steatotic liver diseases, while research is still lagging behind in cases of cholangiopathies-associated fibrogenesis. EV corona-associated biomolecules could potentially develop into disease-associated biomarkers and require further investigation. Regarding the clinical application of EV-based biomarkers, the greatest breakthrough in the clinical setting will come from the possibility to enrich EVs from drop-sized blood samples. Blood volume sufficiency EV analysis remains challenging. Recently, Guerrero-Alba et al. employed the PEG-based NTI-EXO method to successfully isolate EVs from just two drops of blood [115]. Several challenges remain, including the standardization and harmonization of isolation, detection, and normalization methods across laboratories to enable reproducible EV miRNA measurements. Large multicenter validation trials in patient cohorts are also needed to confirm the performance of EV miRNA biomarkers and to develop tailored EV miRNA signatures for distinct fibrotic etiologies, such as MASH or cholestatic liver diseases. Gradually, EV miRNA-based biomarker panels are making their way into clinical practice through coordinated research efforts worldwide. However, the world of EVs is under constant evolution as tools for analyzing these nanoparticles are increasing in resolution and throughput, and we are gathering multidisciplinary knowledge about their potential. One of the latest studies shows another tremendous discovery in the EV field. Blebbisomes, unusually large, functional extracellular vesicles that are actively released by human and mouse cells, are capable of moving independently and can both internalize other EVs and release exosomes and microvesicles [116]. How this may impact the biomarker profile across liver diseases remains to be explored.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.F.; writing—original draft preparation, S.F. and S.B.; writing—review and editing, V.M. and D.D.C.; supervision, S.F. and S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank Emanuela Tolosano for granting us permission to use Biorender in order to generate the graphical abstract (created in BioRender. Tolosano, E. (2024) https://BioRender.com/k14f417, accessed on 30 June 2025). In this study, some sentences were improved using ChatGPT, a language model created by OpenAI for text generation and linguistic analysis. ChatGPT is a state-of-the-art natural language processing model built on the GPT-3.5 architecture (OpenAI, 2022, https://chatgpt.com/; last accessed on 30 June 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Petrillo, S.; Manco, M.; Altruda, F.; Fagoonee, S.; Tolosano, E. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells at the Crossroad of Iron Overload and Liver Fibrosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 35, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berumen, J.; Baglieri, J.; Kisseleva, T.; Mekeel, K. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. WIREs Mech. Dis. 2021, 13, e1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, R.; Ferro, A.; Cicerchia, F.; Mattivi, S.; Fagoonee, S.; Durazzo, M. Autoimmune Hepatitis and Fibrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, M.; Ferro, A.; Navarro-Tableros, V.M.; Gaido, A.; Fornengo, P.; Altruda, F.; Romagnoli, R.; Moestrup, S.K.; Calvo, P.L.; Fagoonee, S. Current Treatment Regimens and Promising Molecular Therapies for Chronic Hepatobiliary Diseases. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaizola, P.; Lee-Law, P.Y.; Arbelaiz, A.; Lapitz, A.; Perugorria, M.J.; Bujanda, L.; Banales, J.M. MicroRNAs and extracellular vesicles in cholangiopathies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, D.; Baglieri, J.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its role in liver cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghe, A.; Klinge, M.; Jonassaint, N. PRO: This Patient Should Have a Liver Biopsy. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 14, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagoonee, S.; Arigoni, M.; Manco, M.; Olivero, M.; Bizzaro, F.; Magagnotti, C.; Andolfo, A.; Miniscalco, B.; Forni, M.; Todeschi, S.; et al. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Contain Liver-Derived RNA Species as Indicators of Severe Cholestasis-Induced Early Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2022, 36, 480–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, M. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Liver Fibrosis: Friends or Foes? Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, A.; Saccu, G.; Mattivi, S.; Gaido, A.; Herrera Sanchez, M.B.; Haque, S.; Silengo, L.; Altruda, F.; Durazzo, M.; Fagoonee, S. Extracellular Vesicles as Delivery Vehicles for Non-Coding RNAs: Potential Biomarkers for Chronic Liver Diseases. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, G.A.D. MicroRNAs: Circulating biomarkers for the early detection of imperceptible cancers via biosensor and machine-learning advances. Oncogene 2024, 43, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzan, E.; Tinè, M.; Casara, A.; Biondini, D.; Semenzato, U.; Cocconcelli, E.; Balestro, E.; Damin, M.; Radu, C.M.; Turato, G.; et al. Critical Review of the Evolution of Extracellular Vesicles’ Knowledge: From 1946 to Today. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, D.; Simoncini, S.; Lacroix, R.; Sabatier, F.; Dignat-George, F. Extracellular Vesicles in Angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1658–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagoonee, S. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Therapy of Human Diseases; Edizioni Minerva Medica: Turin, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharkasy, O.M.; Nordin, J.Z.; Hagey, D.W.; de Jong, O.G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Andaloussi, S.E.; Vader, P. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: Why and how? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagoonee, S. Stem Cell Delivery Routes: From Preclinical Models to Clinical Applications; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kalluri, R.; McAndrews, K.M. The role of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Cell 2023, 186, 1610–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, S.; Swenson, S.; Wang, J. Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Tang, H.; Li, S.; Bai, L.; Chen, Y. Extracellular vesicles as potential biomarkers and treatment options for liver failure: A systematic review up to March 2022. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1116518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Jothimani, G.; Banerjee, A.; Dey, A.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Pathak, S. A brief review on recent advances in diagnostic and therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2024, 173, 106616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilsiz, N. A comprehensive review on recent advances in exosome isolation and characterization: Toward clinical applications. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 50, 102121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, K.P.; Rossi, I.; Abdullahi, M.; Ramirez, M.I.; Stratton, D.; Inal, J.M. Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles and future directions in diagnosis and therapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 15, e1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Kaslan, M.; Lee, S.H.; Yao, J.; Gao, Z. Progress in Exosome Isolation Techniques. Theranostics 2017, 7, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momen-Heravi, F.; Balaj, L.; Alian, S.; Trachtenberg, A.J.; Hochberg, F.H.; Skog, J.; Kuo, W.P. Impact of biofluid viscosity on size and sedimentation efficiency of the isolated microvesicles. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, R.J.; Becker, M.; Wen, S.W.; Wong, C.S.; Wiegmans, A.P.; Leimgruber, A.; Möller, A. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.D.; Samuels, M.; Jones, W.; Stewart, N.; Eravci, M.; Mazarakis, N.K.; Gilbert, D.; Critchley, G.; Giamas, G. Confirming size-exclusion chromatography as a clinically relevant extracellular vesicles separation method from 1mL plasma through a comprehensive comparison of methods. BMC Methods 2024, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deregibus, M.C.; Figliolini, F.; D’Antico, S.; Manzini, P.M.; Pasquino, C.; De Lena, M.; Tetta, C.; Brizzi, M.F.; Camussi, G. Charge-based precipitation of extracellular vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.L.; Khosroheidari, M.; Kanchi Ravi, R.; DiStefano, J.K. Comparison of protein, microRNA, and mRNA yields using different methods of urinary exosome isolation for the discovery of kidney disease biomarkers. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, M.A.; Hurwitz, S.N.; Meckes, D.G. ExtraPEG: A Polyethylene Glycol-Based Method for Enrichment of Extracellular Vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, K.; Wei, X.; Zhi, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cui, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, J.; Zhang, H. Comparison of Different Isolation Methods for Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Patients with Hyperlipidemia. Life 2022, 12, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.P.; Ruiz, A.B.; Bezemer, S.; Detmers, F.; Hermans, P.; Peixoto, C. Targeted isolation of extracellular vesicles from cell culture supernatant using immuno-affinity chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 358, 130312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarovni, N.; Corrado, A.; Guazzi, P.; Zocco, D.; Lari, E.; Radano, G.; Muhhina, J.; Fondelli, C.; Gavrilova, J.; Chiesi, A. Integrated isolation and quantitative analysis of exosome shuttled proteins and nucleic acids using immunocapture approaches. Methods 2015, 87, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liga, A.; Vliegenthart, A.D.; Oosthuyzen, W.; Dear, J.W.; Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M. Exosome isolation: A microfluidic road-map. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2388–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, A.; Malekian, F.; Baghban, N.; Kodam, S.P.; Ullah, M. Methodologies to Isolate and Purify Clinical Grade Extracellular Vesicles for Medical Applications. Cells 2022, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, P.S.; Rani, K.; Singh, R.; Rai, S.; Rastogi, S.; Batra, M.; Mishra, A.; Zehra, S.; Gorai, P.K.; Sasidhar, M.V.; et al. A simplified and efficient method for isolating small extracellular vesicles for comparative and comprehensive translational research. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eirin, A.; Riester, S.M.; Zhu, X.Y.; Tang, H.; Evans, J.M.; O’Brien, D.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Lerman, L.O. MicroRNA and mRNA cargo of extracellular vesicles from porcine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Gene 2014, 551, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, T.; Tschannen, M.; Sun, Z.; Jacob, H.; Du, M.; Liang, M.; Dittmar, R.L.; Liu, Y.; Kohli, M.; et al. Characterization of human plasma-derived exosomal RNAs by deep sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellingham, S.A.; Coleman, B.M.; Hill, A.F. Small RNA deep sequencing reveals a distinct miRNA signature released in exosomes from prion-infected neuronal cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 10937–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skog, J.; Würdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collino, F.; Deregibus, M.C.; Bruno, S.; Sterpone, L.; Aghemo, G.; Viltono, L.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from adult human bone marrow and tissue specific mesenchymal stem cells shuttle selected pattern of miRNAs. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huang, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guescini, M.; Genedani, S.; Stocchi, V.; Agnati, L.F. Astrocytes and Glioblastoma cells release exosomes carrying mtDNA. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaj, L.; Lessard, R.; Dai, L.; Cho, Y.J.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J. Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Becker, A.; Matei, I.; Huang, Y.; Costa-Silva, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Brazier, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: A novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, C.; Melo, S.A.; Protopopov, A.; Tang, J.; Seth, S.; Koch, M.; Zhang, J.; Weitz, J.; Chin, L.; Futreal, A.; et al. Identification of double-stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3869–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, H.F.; Schiel, A.E.; Fijnheer, R.; Geuze, H.J.; Sixma, J.J. Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: Microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and alpha-granules. Blood 1999, 94, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauro, B.J.; Greening, D.W.; Mathias, R.A.; Ji, H.; Mathivanan, S.; Scott, A.M.; Simpson, R.J. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods 2012, 56, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, E.; Sandrin, V.; Chung, H.Y.; Morham, S.G.; Gygi, S.P.; Rodesch, C.K.; Sundquist, W.I. Human ESCRT and ALIX proteins interact with proteins of the midbody and function in cytokinesis. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4215–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Ignatchenko, V.; Ignatchenko, A.; Mejia-Guerrero, S.; Kislinger, T. In-depth proteomic analyses of ovarian cancer cell line exosomes reveals differential enrichment of functional categories compared to the NCI 60 proteome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 445, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Peng, P.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Cao, D.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Gui, T.; Li, X.; et al. Characterization and proteomic analysis of ovarian cancer-derived exosomes. J. Proteom. 2013, 80, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nedawi, K.; Meehan, B.; Micallef, J.; Lhotak, V.; May, L.; Guha, A.; Rak, J. Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laulagnier, K.; Motta, C.; Hamdi, S.; Roy, S.; Fauvelle, F.; Pageaux, J.F.; Kobayashi, T.; Salles, J.P.; Perret, B.; Bonnerot, C.; et al. Mast cell- and dendritic cell-derived exosomes display a specific lipid composition and an unusual membrane organization. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorente, A.; Skotland, T.; Sylvänne, T.; Kauhanen, D.; Róg, T.; Orłowski, A.; Vattulainen, I.; Ekroos, K.; Sandvig, K. Molecular lipidomics of exosomes released by PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Baghaban Eslaminejad, M.; Hosseini, S. Biomolecular corona potential in extracellular vesicle engineering for therapeutic applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 188, 118202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radeghieri, A.; Bergese, P. The biomolecular corona of extracellular nanoparticles holds new promises for advancing clinical molecular diagnostics. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 23, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, R.D.; Kanel, G.C.; Gaarde, W.A.; Deleve, L.D. Role of differentiation of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in progression and regression of hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 918–927.e916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, K.; Guo, Q.; Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H. Emerging Roles of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Biology 2020, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, A.; Yan, R.; Pan, S.Q.; Wu, R.; Kim, J.; Chen, Y.; Ansong, C.; Smith, R.D.; Tempaku, M.; Ohno-Machado, L.; et al. Comprehensive characterization of hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles identifies direct miRNA-based regulation of hepatic stellate cells and DAMP-based hepatic macrophage IL-1β and IL-17 upregulation in alcoholic hepatitis mice. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Xie, L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Jin, C.; Chen, H.; Song, G.Q.; Ding, J.; Wu, J. Secretome of senescent hepatic stellate cells favors malignant transformation from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-fibrotic progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 2023, 13, 4430–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, P.; Pellicoro, A.; Vernon, M.A.; Boulter, L.; Aucott, R.L.; Ali, A.; Hartland, S.N.; Snowdon, V.K.; Cappon, A.; Gordon-Walker, T.T.; et al. Differential Ly-6C expression identifies the recruited macrophage phenotype, which orchestrates the regression of murine liver fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3186–E3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Krishnan, A.; Verma, V.K.; Bronk, S.F.; Werneburg, N.W.; Charlton, M.R.; Shah, V.H.; Malhi, H.; Gores, G.J. Lipid-Induced Signaling Causes Release of Inflammatory Extracellular Vesicles From Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuta, M.; Szabo, G. Extracellular vesicles in inflammation: Focus on the microRNA cargo of EVs in modulation of liver diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 111, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Xia, M.; Salas, S.S.; Ospina, J.A.; Buist-Homan, M.; Harmsen, M.C.; Moshage, H. Extracellular vesicles derived from liver sinusoidal endothelial cells inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells and Kupffer cells in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K.; Wu, J.; Gao, P.; Zhang, C. Exosomes in liver fibrosis: The role of modulating hepatic stellate cells and immune cells, and prospects for clinical applications. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1133297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Brenner, D.A.; Kisseleva, T. Combatting Fibrosis: Exosome-Based Therapies in the Regression of Liver Fibrosis. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Fang, H.; Claridge, B.; Simpson, R.J.; Greening, D.W. Proteomic dissection of large extracellular vesicle surfaceome unravels interactive surface platform. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Lu, Y.; Wan, M.; Cheng, J.; Liu, J. MitoEVs: A new player in multiple disease pathology and treatment. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Xu, M.J.; Koritzinsky, E.H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, W.; Cao, H.; Yuen, P.S.; Ross, R.A.; Star, R.A.; Liangpunsakul, S.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA-enriched microparticles promote acute-on-chronic alcoholic neutrophilia and hepatotoxicity. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e92634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Shim, Y.R.; Seo, W.; Kim, M.H.; Choi, W.M.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, Y.E.; Yang, K.; Ryu, T.; Jeong, J.M.; et al. Mitochondrial Double-Stranded RNA in Exosome Promotes Interleukin-17 Production Through Toll-Like Receptor 3 in Alcohol-associated Liver Injury. Hepatology 2020, 72, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; He, F.; Liu, Q.; Dai, D.; Wu, D.; Shi, Y.; Yao, Q. Elevated GGT to HDL ratio as a marker for the risk of NAFLD and liver fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cançado, G.G.L.; Fucuta, P.D.S.; Gomes, N.M.F.; Couto, C.A.; Cançado, E.L.R.; Terrabuio, D.R.B.; Villela-Nogueira, C.A.; Braga, M.H.; Nardelli, M.J.; Faria, L.C.; et al. Alkaline phosphatase and liver fibrosis at diagnosis are associated with deep response to ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cholangitis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2024, 48, 102453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mei, L.; Zhong, R.; Han, P.; Wen, J.; Han, X.; Zhai, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, J. Serum liver fibrosis markers predict hepatic decompensation in compensated cirrhosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, W.; Zhao, D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Xia, H. Diagnostic Value of Serum Procollagen III N-Terminal Peptide for Liver Fibrosis in Infantile Cholestasis. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelia, C.; Collyer, E.; Mansoor, S.; Lopez, R.; Lappe, S.; Nobili, V.; Alkhouri, N. Plasma Cytokeratin-18 Level As a Novel Biomarker for Liver Fibrosis in Children with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonkaew, B.; Satthawiwat, N.; Pinjaroen, N.; Chuaypen, N.; Tangkijvanich, P. Circulating Extracellular Vesicle-Derived microRNAs as Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Non-Viral-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.A. Human bile as a rich source of biomarkers for hepatopancreatobiliary cancers. Biomark. Med. 2010, 4, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urman, J.M.; Herranz, J.M.; Uriarte, I.; Rullán, M.; Oyón, D.; González, B.; Fernandez-Urién, I.; Carrascosa, J.; Bolado, F.; Zabalza, L.; et al. Pilot Multi-Omic Analysis of Human Bile from Benign and Malignant Biliary Strictures: A Machine-Learning Approach. Cancers 2020, 12, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, H.; Yu, W.; Lai, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Huang, S.; Li, Y. Extracellular vesicles long RNA profiling identifies abundant mRNA, circRNA and lncRNA in human bile as potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis. Carcinogenesis 2023, 44, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, C.; Haga, H.; Makino, N.; Inuzuka, T.; Kurimoto, A.; Ueda, T.; Matsuda, A.; Kakizaki, Y.; Ishizawa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Utility of Claudin-3 in extracellular vesicles from human bile as biomarkers of cholangiocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Shao, S.; Sun, H.; Zhu, H.; Fang, H. Bile-derived exosome noncoding RNAs as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for cholangiocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 985089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Yukawa, H.; Hayashi, K.; Naitoh, I.; Miyabe, K.; Hori, Y.; Natsume, M.; Jinno, N.; Kato, A.; Kachi, K.; et al. Clinical impact of bile-derived exosomal microRNAs as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for biliary tract cancers. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Masica, D.; Ishida, M.; Tomuleasa, C.; Umegaki, S.; Kalloo, A.N.; Georgiades, C.; Singh, V.K.; Khashab, M.; Amateau, S.; et al. Human bile contains microRNA-laden extracellular vesicles that can be used for cholangiocarcinoma diagnosis. Hepatology 2014, 60, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, H.; Ao, Z.; Xu, H.; Luo, J.; Kaurich, C.; Yang, R.; Zhu, P.W.; Chen, S.D.; Wang, X.D.; et al. Lipidomic identification of urinary extracellular vesicles for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis diagnosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapitz, A.; Arbelaiz, A.; O’Rourke, C.J.; Lavin, J.L.; Casta, A.; Ibarra, C.; Jimeno, J.P.; Santos-Laso, A.; Izquierdo-Sanchez, L.; Krawczyk, M.; et al. Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma Present Specific RNA Profiles in Serum and Urine Extracellular Vesicles Mirroring the Tumor Expression: Novel Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers for Disease Diagnosis. Cells 2020, 9, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Z.; Sun, Q.; Tang, W. Research advances and challenges in tissue-derived extracellular vesicles. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1036746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejovič, A.; Wakao, S.; Kitada, M.; Kushida, Y.; Dezawa, M. Comparison of separation methods for tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in the liver, heart, and skeletal muscle. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornek, M.; Lynch, M.; Mehta, S.H.; Lai, M.; Exley, M.; Afdhal, N.H.; Schuppan, D. Circulating microparticles as disease-specific biomarkers of severity of inflammation in patients with hepatitis C or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povero, D.; Yamashita, H.; Ren, W.; Subramanian, M.G.; Myers, R.P.; Eguchi, A.; Simonetto, D.A.; Goodman, Z.D.; Harrison, S.A.; Sanyal, A.J.; et al. Characterization and Proteome of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers for NASH. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, Y.; Amrollahi, P.; Parthasarathy, G.; Mauer, A.S.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Vanderboom, P.; Nair, K.S.; Nakao, K.; Allen, A.M.; Hu, T.Y.; et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles are a biomarker for NAFLD resolution and response to weight loss surgery. Nanomedicine 2021, 36, 102430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povero, D.; Eguchi, A.; Li, H.; Johnson, C.D.; Papouchado, B.G.; Wree, A.; Messer, K.; Feldstein, A.E. Circulating extracellular vesicles with specific proteome and liver microRNAs are potential biomarkers for liver injury in experimental fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoldi, M.; Vujic Spasic, M.; Altamura, S.; Elmén, J.; Lindow, M.; Kiss, J.; Stolte, J.; Sparla, R.; D’Alessandro, L.A.; Klingmüller, U.; et al. The liver-specific microRNA miR-122 controls systemic iron homeostasis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Petrasek, J.; Mundkur, S.; Catalano, D.; Levin, I.; Ward, J.; Alao, H.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. Circulating microRNAs in exosomes indicate hepatocyte injury and inflammation in alcoholic, drug-induced, and inflammatory liver diseases. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, E.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, H.S.; Yoo, Y.J.; Je, J.; Suh, S.J.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Exosomes derived from palmitic acid-treated hepatocytes induce fibrotic activation of hepatic stellate cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Pan, Q.; Cao, H.X.; Xin, F.Z.; Zhao, Z.H.; Yang, R.X.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, H.; Fan, J.G. Lipotoxic Hepatocyte-Derived Exosomal MicroRNA 192-5p Activates Macrophages Through Rictor/Akt/Forkhead Box Transcription Factor O1 Signaling in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2020, 72, 454–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Qian, Y.; Shen, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Gao, R.; Shen, M.; Chen, S.; Fu, Q.; Yang, T. Circulating microRNA-135a-3p in serum extracellular vesicles as a potential biological marker of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, A.M.; Kandeil, M.A.; Sabry, D.; Abdel-Ghany, A.A.; Mahmoud, M.O. Exosomal miR-122, miR-128, miR-200, miR-298, and miR-342 as novel diagnostic biomarkers in NAFL/NASH: Impact of LPS/TLR-4/FoxO3 pathway. Arch. Pharm. 2024, 357, e2300631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gim, J.A.; Bang, S.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, Y.; Yim, S.Y.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, Y.S.; et al. Evaluation of the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through analysis of serum exosomal miRNA expression. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, L.A.; Useckaite, Z.; Johnson, J.; Sorich, M.J.; Hopkins, A.M.; Rowland, A. Selective Isolation of Liver-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Redefines Performance of miRNA Biomarkers for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Huang, H.; Jia, M.; Xu, M.; Chen, M.; Wu, J.; Gu, S.; Liang, H.; Zhou, H.; Gong, Y. A panel of miRNAs in the serum extracellular vesicles serve as novel diagnostic biomarkers for MASLD. Biomed. J. 2025, 100838, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, Z.; Qin, S.; Ruan, X.; Jiang, H. Serum-derived miR-574-5p-containing exosomes contribute to liver fibrosis by activating hepatic stellate cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, X.L.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.; Ye, L.; Li, Y. MiR-542-3p controls hepatic stellate cell activation and fibrosis via targeting BMP-7. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 4573–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wang, S.; Sun, P.; Qie, J. Integrated MicroRNA Expression Profile Reveals Dysregulated miR-20a-5p and miR-200a-3p in Liver Fibrosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9583932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povero, D.; Tameda, M.; Eguchi, A.; Ren, W.; Kim, J.; Myers, R.; Goodman, Z.D.; Harrison, S.A.; Sanyal, A.J.; Bosch, J.; et al. Protein and miRNA profile of circulating extracellular vesicles in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, T.; Yang, G.X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, W.; Tanaka, H.; Wang, J.; Leung, P.S.; Okazaki, K.; He, X.S.; Lu, Q.; et al. The modulation of co-stimulatory molecules by circulating exosomes in primary biliary cirrhosis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahm, A.M.; Hand, N.J.; Boateng, L.A.; Friedman, J.R. Circulating microRNA is a biomarker of biliary atresia. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Shen, Z.; Zheng, C.; Chen, G.; Zheng, S. Serum microRNA microarray analysis identifies miR-4429 and miR-4689 are potential diagnostic biomarkers for biliary atresia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, A.; Marquart, L.; Calvopina, D.A.; Genz, B.; Ramm, G.A.; Skoien, R. Serum MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Hepatitis C: Preliminary Evidence of a MicroRNA Panel for the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshins, R.; Huo, Z.; Greenberg, Z.; Clark, V.; Duarte, S.; Zhou, H.; West, J.; He, M.; Brantly, M.; Khodayari, N. Plasma Extracellular Vesicle-derived MicroRNA Associated with Human Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency-mediated Liver Disease. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2025, 13, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Alba, A.; Bansal, S.; Sankpal, A.N.; Mitra, G.; Rahman, M.; Ravichandran, R.; Poulson, C.; Fleming, T.P.; Smith, M.A.; Bremner, R.M.; et al. Enhanced enrichment of extracellular vesicles for laboratory and clinical research from drop-sized blood samples. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1365783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Sanchez, Z.C.; Kelley, N.M.; Hayes, J.B.; Ambroise, J.; Koory, E.N.; Krystofiak, E.; Taneja, N.; Zhang, Q.; Dungan, M.M.; et al. Blebbisomes are large, organelle-rich extracellular vesicles with cell-like properties. Nat. Cell Biol. 2025, 27, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).