Polyamine Catabolism Revisited: Acetylpolyamine Oxidase Plays a Minor Role due to Low Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. RNAseq Data Analysis
2.3. Cell Culture Experiments
2.4. RT-qPCR
2.5. Polyamine Quantification
2.6. Cloning of the PAOX Gene and Plasmid Construction
2.7. Stable Cell Lines
2.8. Expression and Purification of PAOX from Escherichia coli Cells
2.9. PAOX Activity Assay
2.10. Drug Toxicity Assay
2.11. Virus Replication Assays
2.11.1. Influenza A and B Viruses
2.11.2. SARS-CoV-2
2.11.3. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
2.11.4. Other Viruses
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
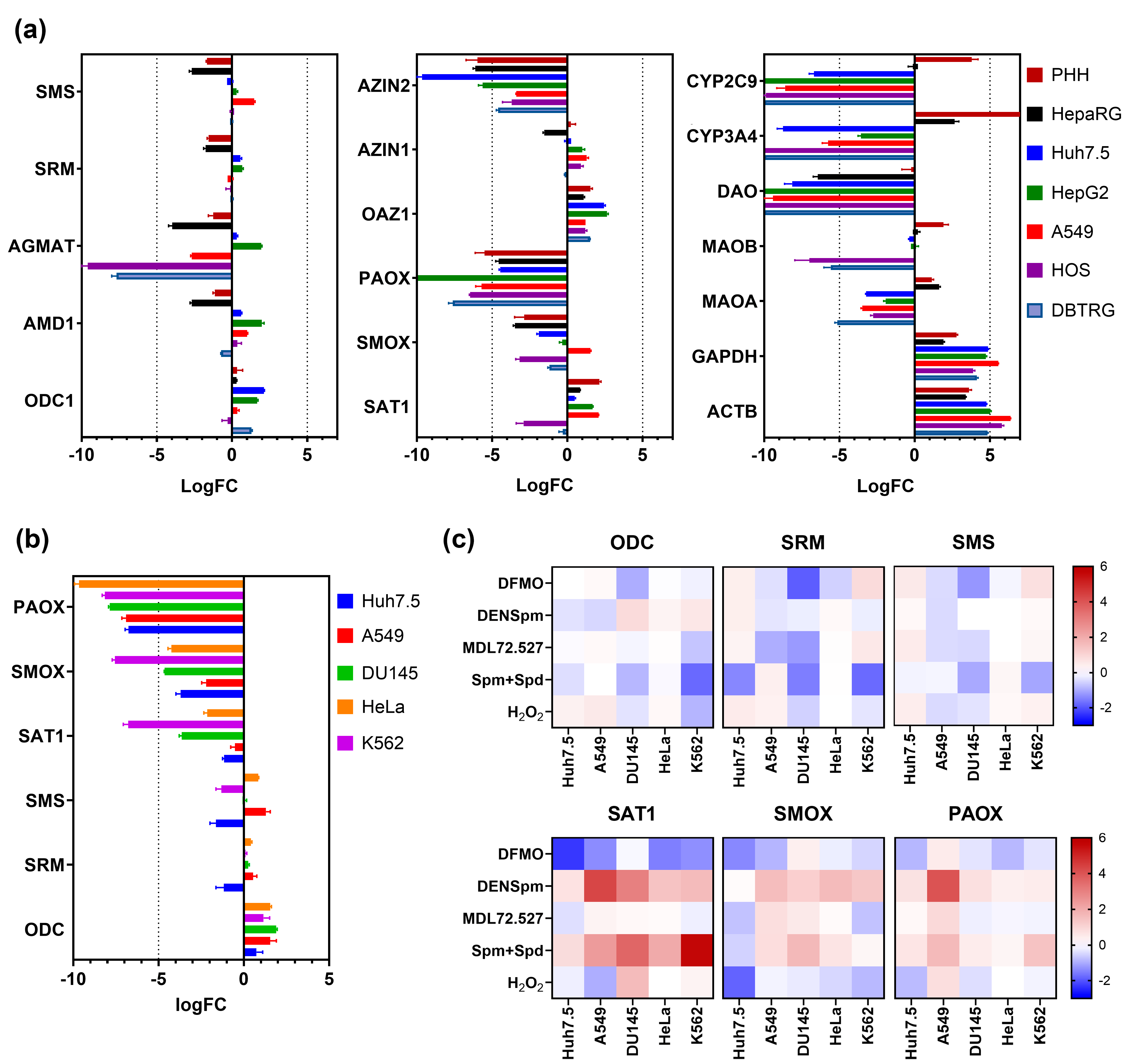
3.1. PAOX Expression Is Low in Various Human Cell Lines Based on RNA-Seq Data from NCBI SRA
3.2. Altered Polyamine Metabolism Has a Low Impact on Levels of PAOX mRNA
3.3. PAOX Activity Is Undetectable in Most Cell Lines, except a Few Glioblastoma Cell Lines
3.4. PAOX Activity Can Be Detectible in Glioblastoma and Neuroblastoma Cell Lines with High Polyamine Levels
3.5. Alternative PAOX Isoforms Have Impaired Catalytic Activity
3.6. PAOX Is Dispensable for the Replication of RNA Viruses
3.7. Expression of PAOX Does Not Modulate Sensitivity of Tumor Cells to Anticancer Drugs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pegg, A.E. Mammalian polyamine metabolism and function. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, O.A.; Bartosch, B.; Zakirova, N.F.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Ivanov, A.V. Polyamine Metabolism and Oxidative Protein Folding in the ER as ROS-Producing Systems Neglected in Virology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, T.; Abdellatif, M.; Schroeder, S.; Primessnig, U.; Stekovic, S.; Pendl, T.; Harger, A.; Schipke, J.; Zimmermann, A.; Schmidt, A.; et al. Cardioprotection and lifespan extension by the natural polyamine spermidine. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, H.A.; Ettinger, D.S.; Bowling, K.; Hoker, B.; Chen, T.L.; Zabelina, Y.; Casero, R.A., Jr. Phase I study of N1,N11-diethylnorspermine in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolff, A.C.; Armstrong, D.K.; Fetting, J.H.; Carducci, M.K.; Riley, C.D.; Bender, J.F.; Casero, R.A., Jr.; Davidson, N.E. A Phase II study of the polyamine analog N1,N11-diethylnorspermine (DENSpm) daily for five days every 21 days in patients with previously treated metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 5922–5928. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horn, Y.; Schechter, P.J.; Marton, L.J. Phase I-II clinical trial with alpha-difluoromethylornithine--an inhibitor of polyamine biosynthesis. Eur. J. Cancer Clin. Oncol. 1987, 23, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evageliou, N.F.; Haber, M.; Vu, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Murray, J.; Gamble, L.D.; Cheng, N.C.; Liu, K.; Reese, M.; Corrigan, K.A.; et al. Polyamine Antagonist Therapies Inhibit Neuroblastoma Initiation and Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4391–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados, M.D.; Wara, W.M.; Sneed, P.K.; McDermott, M.; Chang, S.M.; Rabbitt, J.; Page, M.; Malec, M.; Davis, R.L.; Gutin, P.H.; et al. Phase III trial of accelerated hyperfractionation with or without difluromethylornithine (DFMO) versus standard fractionated radiotherapy with or without DFMO for newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 49, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Leeuwenhoek, A.; Observationes, D. Anthonii Lewenhoeck, de natis e semine genitali animalculis. Letter dated November 1677. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1678, 12, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Dudley, H.W.; Rosenheim, O.; Starling, W.W. The Chemical Constitution of Spermine: Structure and Synthesis. Biochem. J. 1926, 20, 1082–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabor, H.; Rosenthal, S.M.; Tabor, C.W. The biosynthesis of spermidine and spermine from putrescine and methionine. J. Biol. Chem. 1958, 233, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujcic, S.; Liang, P.; Diegelman, P.; Kramer, D.L.; Porter, C.W. Genomic identification and biochemical characterization of the mammalian polyamine oxidase involved in polyamine back-conversion. Biochem. J. 2003, 370, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujcic, S.; Diegelman, P.; Bacchi, C.J.; Kramer, D.L.; Porter, C.W. Identification and characterization of a novel flavin-containing spermine oxidase of mammalian cell origin. Biochem. J. 2002, 367, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Devereux, W.; Woster, P.M.; Stewart, T.M.; Hacker, A.; Casero, R.A., Jr. Cloning and characterization of a human polyamine oxidase that is inducible by polyamine analogue exposure. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5370–5373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller-Fleming, L.; Olin-Sandoval, V.; Campbell, K.; Ralser, M. Remaining Mysteries of Molecular Biology: The Role of Polyamines in the Cell. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 3389–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, H.M.; Fraser, A.V.; Hughes, A. A perspective of polyamine metabolism. Biochem. J. 2003, 376, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casero, R.A.; Pegg, A.E. Polyamine catabolism and disease. Biochem. J. 2009, 421, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, K.; Igarashi, K. Molecular Characteristics of Toxicity of Acrolein Produced from Spermine. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, A.C.; Destefano Shields, C.E.; Wu, S.; Huso, D.L.; Wu, X.; Murray-Stewart, T.R.; Hacker-Prietz, A.; Rabizadeh, S.; Woster, P.M.; Sears, C.L.; et al. Polyamine catabolism contributes to enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis-induced colon tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15354–15359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.; Asim, M.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Barry, D.P.; Hoge, S.; de Sablet, T.; Delgado, A.G.; Wroblewski, L.E.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Yan, F.; et al. Spermine oxidase mediates the gastric cancer risk associated with Helicobacter pylori CagA. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1696–1708.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomitori, H.; Usui, T.; Saeki, N.; Ueda, S.; Kase, H.; Nishimura, K.; Kashiwagi, K.; Igarashi, K. Polyamine oxidase and acrolein as novel biochemical markers for diagnosis of cerebral stroke. Stroke 2005, 36, 2609–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsufuji, S.; Matsufuji, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Atkins, J.F.; Gesteland, R.F.; Hayashi, S. Autoregulatory frameshifting in decoding mammalian ornithine decarboxylase antizyme. Cell 1995, 80, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyvonen, M.T.; Smirnova, O.A.; Mitkevich, V.A.; Tunitskaya, V.L.; Khomutov, M.; Karpov, D.S.; Korolev, S.P.; Hakkinen, M.R.; Pietila, M.; Gottikh, M.B.; et al. Role of Polyamine-Induced Dimerization of Antizyme in Its Cellular Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiler, N. Polyamine oxidase, properties and functions. Prog. Brain Res. 1995, 106, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, H.M.; Duthie, J.; Evans, D.M.; Lamond, S.; Nicoll, K.M.; Heys, S.D. Alterations in polyamine catabolic enzymes in human breast cancer tissue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 3657–3661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bunjobpol, W.; Dulloo, I.; Igarashi, K.; Concin, N.; Matsuo, K.; Sabapathy, K. Suppression of acetylpolyamine oxidase by selected AP-1 members regulates DNp73 abundance: Mechanistic insights for overcoming DNp73-mediated resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorova, N.E.; Chernoryzh, Y.Y.; Vinogradskaya, G.R.; Emelianova, S.S.; Zavalyshina, L.E.; Yurlov, K.I.; Zakirova, N.F.; Verbenko, V.N.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Kushch, A.A.; et al. Inhibitor of polyamine catabolism MDL72.527 restores the sensitivity to doxorubicin of monocytic leukemia Thp-1 cells infected with human cytomegalovirus. Biochimie 2019, 158, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pledgie, A.; Huang, Y.; Hacker, A.; Zhang, Z.; Woster, P.M.; Davidson, N.E.; Casero, R.A., Jr. Spermine oxidase SMO(PAOh1), Not N1-acetylpolyamine oxidase PAO, is the primary source of cytotoxic H2O2 in polyamine analogue-treated human breast cancer cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 39843–39851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, C.M.; Nevsten, P.; Johansson, F.; Carlemalm, E.; Oredsson, S.M. Subcellular distribution of spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase. Cell Biol. Int. 2008, 32, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Young, B.A.; Coleman, C.S.; Pegg, A.E.; Sheppard, D. Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase specifically binds to the integrin alpha9 subunit cytoplasmic domain and enhances cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, T.; Yerushalmi, H.F.; Tsaprailis, G.; Stringer, D.E.; Pastorian, K.E.; Hawel, L., III; Byus, C.V.; Gerner, E.W. Identification and characterization of a diamine exporter in colon epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26428–26435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Yankovskaya, V.; McIntire, W.S. Cloning, sequencing, and heterologous expression of the murine peroxisomal flavoprotein, N1-acetylated polyamine oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20514–20525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipatova, A.V.; Soboleva, A.V.; Gorshkov, V.A.; Bubis, J.A.; Solovyeva, E.M.; Krasnov, G.S.; Kochetkov, D.V.; Vorobyev, P.O.; Ilina, I.Y.; Moshkovskii, S.A.; et al. Multi-Omics Analysis of Glioblastoma Cells’ Sensitivity to Oncolytic Viruses. Cancers 2021, 13, 5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, O.N.; Snezhkina, A.V.; Krasnov, G.S.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Khomich, O.A.; Khomutov, A.R.; Keinanen, T.A.; Alhonen, L.; Bartosch, B.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; et al. Activation of Polyamine Catabolism by N1,N11-Diethylnorspermine in Hepatic HepaRG Cells Induces Dedifferentiation and Mesenchymal-Like Phenotype. Cells 2018, 7, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, T.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Lei, J.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. Analysis of Expression Profiles of Long Noncoding RNAs and mRNAs in A549 Cells Infected with H3N2 Swine Influenza Virus by RNA Sequencing. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitina, A.S.; Lipatova, A.V.; Goncharov, A.O.; Kliuchnikova, A.A.; Pyatnitskiy, M.A.; Kuznetsova, K.G.; Hamad, A.; Vorobyev, P.O.; Alekseeva, O.N.; Mahmoud, M.; et al. Multiomic Profiling Identified EGF Receptor Signaling as a Potential Inhibitor of Type I Interferon Response in Models of Oncolytic Therapy by Vesicular Stomatitis Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golikov, M.V.; Karpenko, I.L.; Lipatova, A.V.; Ivanova, O.N.; Fedyakina, I.T.; Larichev, V.F.; Zakirova, N.F.; Leonova, O.G.; Popenko, V.I.; Bartosch, B.; et al. Cultivation of Cells in a Physiological Plasmax Medium Increases Mitochondrial Respiratory Capacity and Reduces Replication Levels of RNA Viruses. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, V.B. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Korovina, A.N.; Tunitskaya, V.L.; Kostyuk, D.A.; Rechinsky, V.O.; Kukhanova, M.K.; Kochetkov, S.N. Development of the system ensuring a high-level expression of hepatitis C virus nonstructural NS5B and NS5A proteins. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 48, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolosa, L.; Donato, M.T.; Gomez-Lechon, M.J. General Cytotoxicity Assessment by Means of the MTT Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1250, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Manual on Animal Influenza Diagnosis and Surveillance; World Health organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Date, T.; Murayama, A.; Morikawa, K.; Akazawa, D.; Wakita, T. Cell culture and infection system for hepatitis C virus. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2334–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinelli, E.; Arancia, G.; Vedova, L.D.; Belli, F.; Marra, M.; Salvi, M.; Toninello, A. The biological functions of polyamine oxidation products by amine oxidases: Perspectives of clinical applications. Amino Acids 2004, 27, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishilevich, S.; Zimmerman, S.; Kohn, A.; Iny Stein, T.; Olender, T.; Kolker, E.; Safran, M.; Lancet, D. Genic insights from integrated human proteomics in GeneCards. Database 2016, 2016, baw030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Pulido, Y.E.; Mounce, B.C. Good cop, bad cop: Polyamines play both sides in host immunity and viral replication. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 146, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mounce, B.C.; Cesaro, T.; Moratorio, G.; Hooikaas, P.J.; Yakovleva, A.; Werneke, S.W.; Smith, E.C.; Poirier, E.Z.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Prot, M.; et al. Inhibition of Polyamine Biosynthesis Is a Broad-Spectrum Strategy against RNA Viruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9683–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firpo, M.R.; LoMascolo, N.J.; Petit, M.J.; Shah, P.S.; Mounce, B.C. Polyamines and eIF5A hypusination facilitate SREBP2 synthesis and cholesterol production leading to enhanced enterovirus attachment and infection. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, M.E.; Filone, C.M.; Rozelle, D.; Mire, C.E.; Agans, K.N.; Hensley, L.; Connor, J.H. Polyamines and Hypusination Are Required for Ebolavirus Gene Expression and Replication. mBio 2016, 7, e00882-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Smirnova, O.A.; Yanvarev, D.V.; Karpenko, I.L.; Fedyakina, I.T. Application of N,N′-bis-(2,3-Butadienyl)-1,4-Diaminobutane Dihydrochloride (MDL72.527) for Suppressing Replication of SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Patent RU #2761565C1, 10 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zakirova, N.F.; Khomich, O.A.; Smirnova, O.A.; Molle, J.; Duponchel, S.; Yanvarev, D.V.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Monnier, L.; Grigorov, B.; Ivanova, O.N.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Dysregulates Polyamine and Proline Metabolism and Perturbs the Urea Cycle. Cells 2024, 13, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, V.; Korner, F.; Koch, J.; Herian, U.; Theilmann, L.; Bartenschlager, R. Replication of subgenomic hepatitis C virus RNAs in a hepatoma cell line. Science 1999, 285, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blight, K.J.; McKeating, J.A.; Rice, C.M. Highly permissive cell lines for subgenomic and genomic hepatitis C virus RNA replication. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 13001–13014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, O.N.; Krasnov, G.S.; Snezhkina, A.V.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; Fedorov, V.S.; Zakirova, N.F.; Golikov, M.V.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Bartosch, B.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Redox Systems and Polyamine Metabolic Pathway in Hepatoma and Non-Tumor Hepatocyte-like Cells. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Nie, Z.; Huang, D.; Gao, Y.; Cao, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, S. Development of a polyamine gene expression score for predicting prognosis and treatment response in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1048204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Noda, K.; Murata, M.; Liu, Y.; Kanda, A.; Ishida, S. Regulation of Spermine Oxidase through Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha Signaling in Retinal Glial Cells under Hypoxic Conditions. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affronti, H.C.; Rowsam, A.M.; Pellerite, A.J.; Rosario, S.R.; Long, M.D.; Jacobi, J.J.; Bianchi-Smiraglia, A.; Boerlin, C.S.; Gillard, B.M.; Karasik, E.; et al. Pharmacological polyamine catabolism upregulation with methionine salvage pathway inhibition as an effective prostate cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obakan, P.; Arisan, E.D.; Calcabrini, A.; Agostinelli, E.; Bolkent, S.; Palavan-Unsal, N. Activation of polyamine catabolic enzymes involved in diverse responses against epibrassinolide-induced apoptosis in LNCaP and DU145 prostate cancer cell lines. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, H.; Ma, C.; Li, H.; Yu, F.; Wei, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Ren, Y. Rebalance of the Polyamine Metabolism Suppresses Oxidative Stress and Delays Senescence in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8033353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, T.J.; Thomas, T.; John, S.; Hsu, H.C.; Yang, P.; Keinanen, T.A.; Hyvonen, M.T. Tamoxifen metabolite endoxifen interferes with the polyamine pathway in breast cancer. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, D.J.R.; Bae, D.H.; Siafakas, A.R.; Suryo Rahmanto, Y.; Al-Akra, L.; Jansson, P.J.; Casero, R.A., Jr.; Richardson, D.R. Coupling of the polyamine and iron metabolism pathways in the regulation of proliferation: Mechanistic links to alterations in key polyamine biosynthetic and catabolic enzymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 2793–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.T. Polyamine Oxidase Expression Is Downregulated by 17beta-Estradiol via Estrogen Receptor 2 in Human MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervelli, M.; Bellavia, G.; Fratini, E.; Amendola, R.; Polticelli, F.; Barba, M.; Federico, R.; Signore, F.; Gucciardo, G.; Grillo, R.; et al. Spermine oxidase (SMO) activity in breast tumor tissues and biochemical analysis of the anticancer spermine analogues BENSpm and CPENSpm. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossmann, D.; Muller, C.; Park, S.; Ryback, B.; Colombi, M.; Ritter, N.; Weissenberger, D.; Dazert, E.; Coto-Llerena, M.; Nuciforo, S.; et al. Arginine reprograms metabolism in liver cancer via RBM39. Cell 2023, 186, 5068–5083.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salati, S.; Zini, R.; Nuzzo, S.; Guglielmelli, P.; Pennucci, V.; Prudente, Z.; Ruberti, S.; Rontauroli, S.; Norfo, R.; Bianchi, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of copy number and gene expression data suggests novel pathogenetic mechanisms in primary myelofibrosis. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, Y.; Itoi, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Sofuni, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Tanaka, R.; Tonozuka, R.; Honjo, M.; Mukai, S.; Fujita, M.; et al. Elevated Polyamines in Saliva of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Li, Q.; Ma, R.; Lin, X.; Xu, H.; Bi, K. Determination of polyamine metabolome in plasma and urine by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method: Application to identify potential markers for human hepatic cancer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 791, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Fukuzawa, M.; Itoi, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Aizawa, Y.; Sunamura, M.; Kawai, T.; Nemoto, D.; Shinohara, H.; Muramatsu, T.; et al. Targeted Metabolomic Profiling of Plasma Samples in Gastric Cancer by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Digestion 2023, 104, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjogren, T.; Wassvik, C.M.; Snijder, A.; Aagaard, A.; Kumanomidou, T.; Barlind, L.; Kaminski, T.P.; Kashima, A.; Yokota, T.; Fjellstrom, O. The Structure of Murine N1-Acetylspermine Oxidase Reveals Molecular Details of Vertebrate Polyamine Catabolism. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, J.; Guo, B.; Li, P.; Liu, X.; Song, J.; Xie, S.; Wu, R.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Enzymatic-related network of catalysis, polyamine, and tumors for acetylpolyamine oxidase: From calculation to experiment. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 2867–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logotheti, S.; Richter, C.; Murr, N.; Spitschak, A.; Marquardt, S.; Putzer, B.M. Mechanisms of Functional Pleiotropy of p73 in Cancer and Beyond. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 737735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Gene ID | Orientation | Sequence | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ODC | Forward Reverse | 5′-TTGCGGATTGCCACTGATGATTCC-3′ 5′-ATCAGAGATTGCCTGCACGAAGGT-3′ | 186 |
| SRM | Forward Reverse | 5′-CCCGCCGAAAGTCTCTTCAA-3′ 5′-GGAAGTTCGTGCTCGGGTTC-3′ | 241 |
| SMS | Forward Reverse | 5′-CACAGCACGCTCGACTTCA-3′ 5′-TGCCGTTCTTGTTTGTGTAGGTT-3′ | 154 |
| SSAT | Forward Reverse | 5′-ATCTAAGCCAGGTTGCAATGA-3′ 5′-GCACTCCTCACTCCTCTGTTG-3′ | 189 |
| SMOX | Forward Reverse | 5′-GATCCCGGCGGACCATGTGATTGTG-3′ 5′-CCTGCATGGGCGCTGTCTTTG-3′ | 576 |
| PAOX | Forward Reverse | 5′-GTCACCGTGCCCTTAGGTT-3′ 5′-TCCCAAAGCCTATCTTCCTG-3′ | 103 |
| HCV | Forward Reverse | 5′-GTCTAGCCATGGCGTTAGTA-3′ 5′-CTCCCGGGGCACTCGCAAGC-3′ | 246 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Forward Reverse | 5′-CACATTGGCACCCGCAATC-3′ 5′-GAGGAACGAGAAGAGGCTTG-3′ | 128 |
| GUS | Forward Reverse | 5′-CGTGGTTGGAGAGCTCATTTGGAA-3′ 5′-ATTCCCCAGCACTCTCGTCGGT-3′ | 73 |
| Primer # | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| 1 | GACCTCCCGGCTACTCAGAA |
| 2 | GAGAAGGTGGCCCTGGTTAC |
| 3 | ATTTCTAGAATGGAGTCGACCGGCAGC |
| 4 | ATTGAATTCCTAGAGCCTGGGCCTGGG |
| 5 | TGTCACTCTCCGGAGCACT |
| 6 | GCTCCAGATCCTGTTTGCG |
| 7 | CCTAAGGGCACGGTGACG |
| 8 | TCTGTCCACGTTCTCTGTGG |
| 9 | ATTGAATTCGACCGGCAGCGTCGG |
| 10 | ATTCTCGAGGAGCCTGGGCCTGGGCT |
| Cell Line | Description | PAOX Activity | Spd Synthesis in the Presence of AcSpm (pmol/min*mg Protein) | Spd (pmol/mg Protein) | Spm (pmol/mg Protein) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huh7.5 | Hepatoma | No | <1 | 7.16 ± 1.14 | 1.53 ± 0.21 |
| A549 | Lung carcinoma | No | <1 | 8.34 ± 1.3 | 4.96 ± 0.79 |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | No | <1 | 3.75 ± 0.52 | 3.51 ± 0.56 |
| HeLa | Cervix carcinoma | No | <1 | 11.4 ± 1.6 | 24.2 ± 3.4 |
| GBM4114 | Glioblastoma | Yes | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 7.1 ± 1.1 | 23.7 ± 3.8 |
| GBM6067 | Glioblastoma | Yes | 13.6 ± 2.2 | 7.1 ± 1.1 | 7.0 ± 1.0 |
| GBM6138 | Glioblastoma | Yes | 112.4 ± 16.8 | 6.1 ± 0.5 | 45.4 ± 3.6 |
| SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Yes | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 21.5 ± 3.4 | 178.4 ± 26.7 |
| mRNA | Protein | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Splice Variant | ID | Isoform | Amino Acid Residues | ID |
| 1 | NM_152911 | 1 | 511 | NP_690875 |
| 4 | NM_207127 | 2 | 325 | NP_997010 |
| 5 | NM_207128 | 4 | 486 | NP_997011 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivanova, O.N.; Gavlina, A.V.; Karpenko, I.L.; Zenov, M.A.; Antseva, S.S.; Zakirova, N.F.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Krasnov, G.S.; Fedyakina, I.T.; Vorobyev, P.O.; et al. Polyamine Catabolism Revisited: Acetylpolyamine Oxidase Plays a Minor Role due to Low Expression. Cells 2024, 13, 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131134
Ivanova ON, Gavlina AV, Karpenko IL, Zenov MA, Antseva SS, Zakirova NF, Valuev-Elliston VT, Krasnov GS, Fedyakina IT, Vorobyev PO, et al. Polyamine Catabolism Revisited: Acetylpolyamine Oxidase Plays a Minor Role due to Low Expression. Cells. 2024; 13(13):1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131134
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvanova, Olga N., Anna V. Gavlina, Inna L. Karpenko, Martin A. Zenov, Svetlana S. Antseva, Natalia F. Zakirova, Vladimir T. Valuev-Elliston, George S. Krasnov, Irina T. Fedyakina, Pavel O. Vorobyev, and et al. 2024. "Polyamine Catabolism Revisited: Acetylpolyamine Oxidase Plays a Minor Role due to Low Expression" Cells 13, no. 13: 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131134
APA StyleIvanova, O. N., Gavlina, A. V., Karpenko, I. L., Zenov, M. A., Antseva, S. S., Zakirova, N. F., Valuev-Elliston, V. T., Krasnov, G. S., Fedyakina, I. T., Vorobyev, P. O., Bartosch, B., Kochetkov, S. N., Lipatova, A. V., Yanvarev, D. V., & Ivanov, A. V. (2024). Polyamine Catabolism Revisited: Acetylpolyamine Oxidase Plays a Minor Role due to Low Expression. Cells, 13(13), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131134







