The Effect of Visfatin on the Functioning of the Porcine Pituitary Gland: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Tissue Collection
2.2. Cell Isolation and In Vitro Cultures
2.3. Gonadotropins’ Secretion—ELISA (Expt. Nos. 1 and 5)
2.4. Cell Proliferation—Alamar Blue Assay (Expt. No. 2)
2.5. Cell Apoptosis—Flow Cytometry Technique (Expt. No. 3)
2.6. Activation of Signaling Pathways—ELISA and Western Blot Analysis (Expt. No. 4)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The In Vitro Effect of VIS on the Secretion of Gonadotropins (Expt. No. 1)
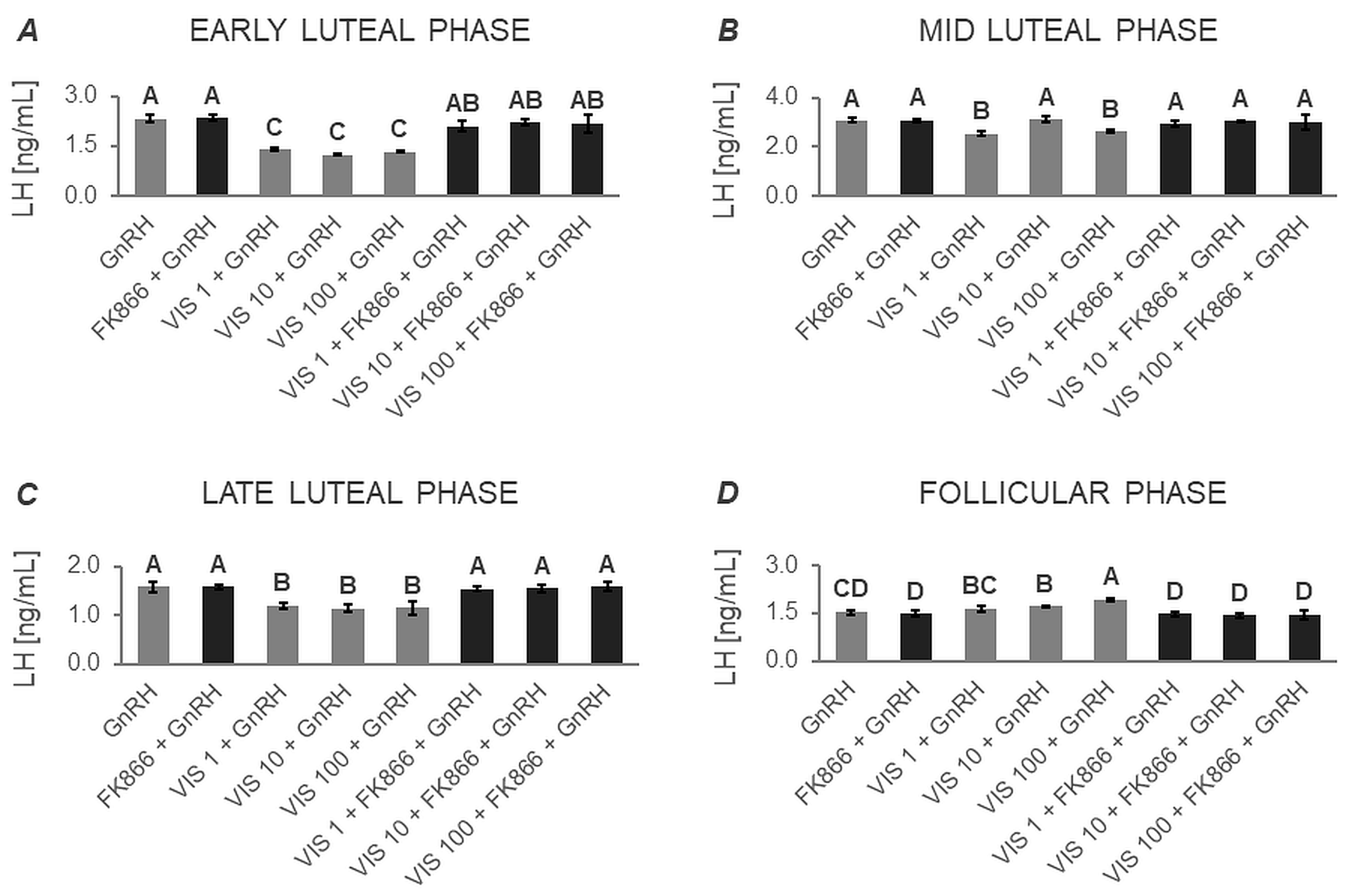
3.1.1. Secretion of LH by APc
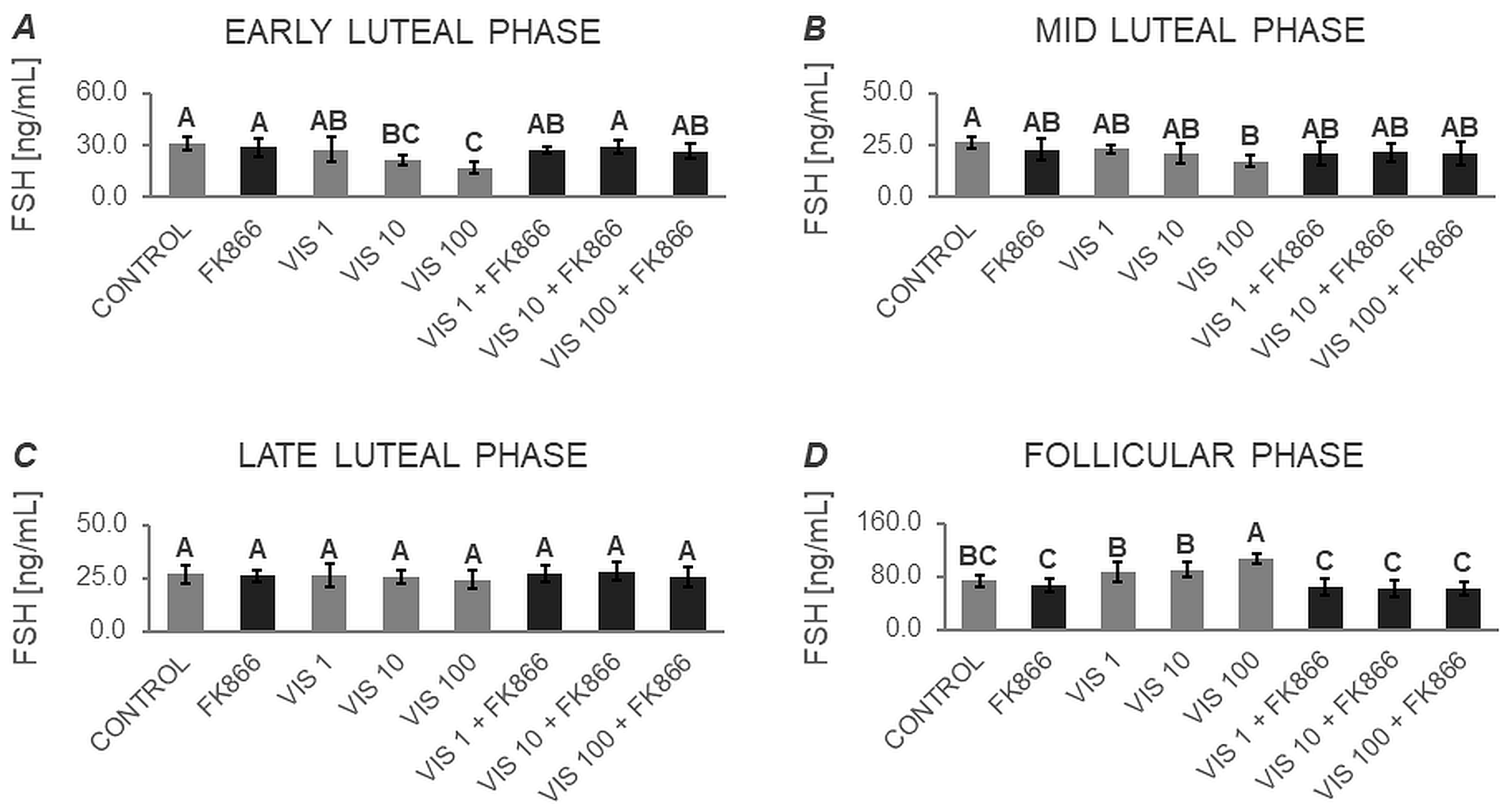
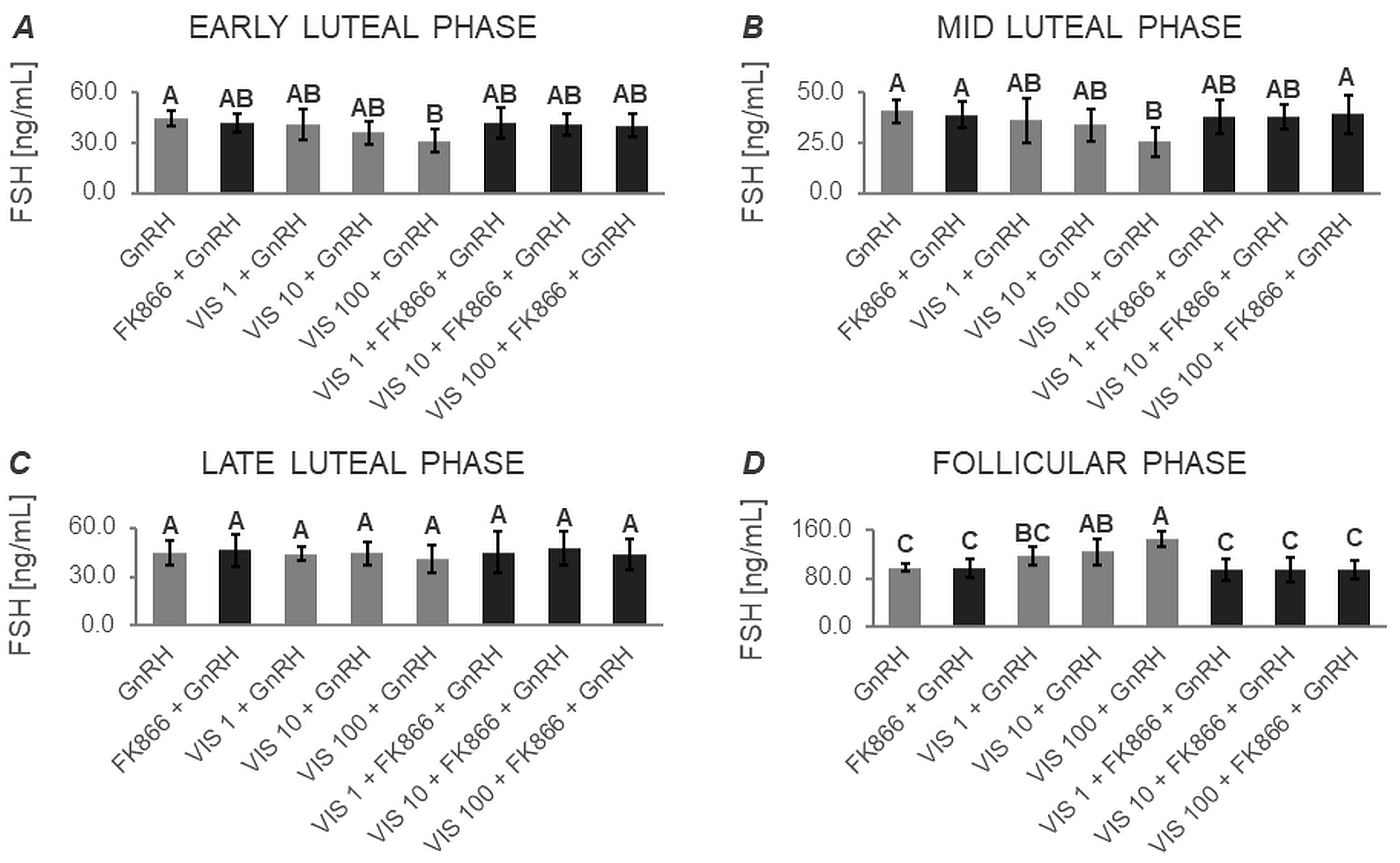
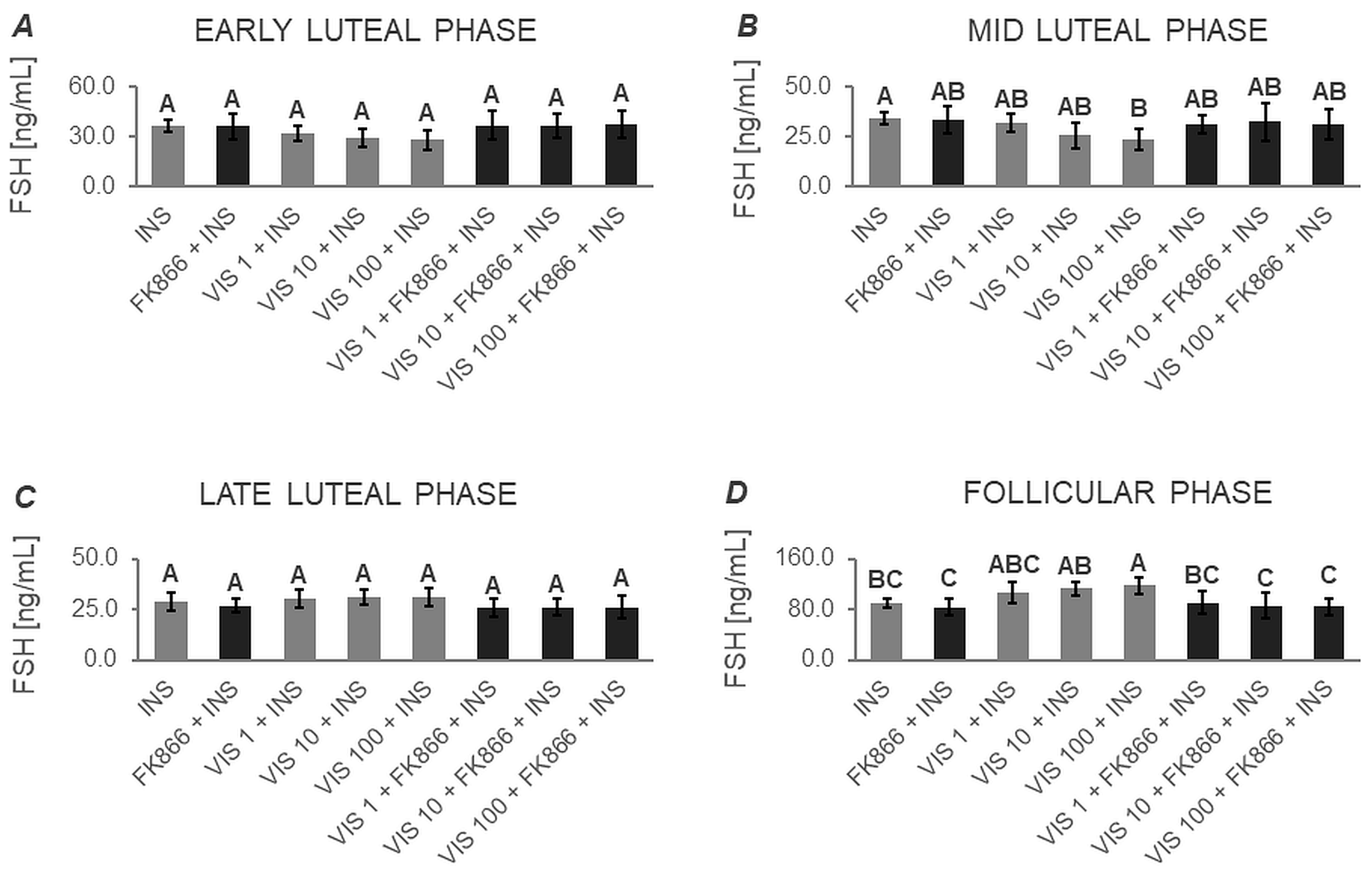
3.1.2. Secretion of FSH by APc
3.2. The In Vitro Effect of VIS on the Proliferation of APc (Expt. No. 2)
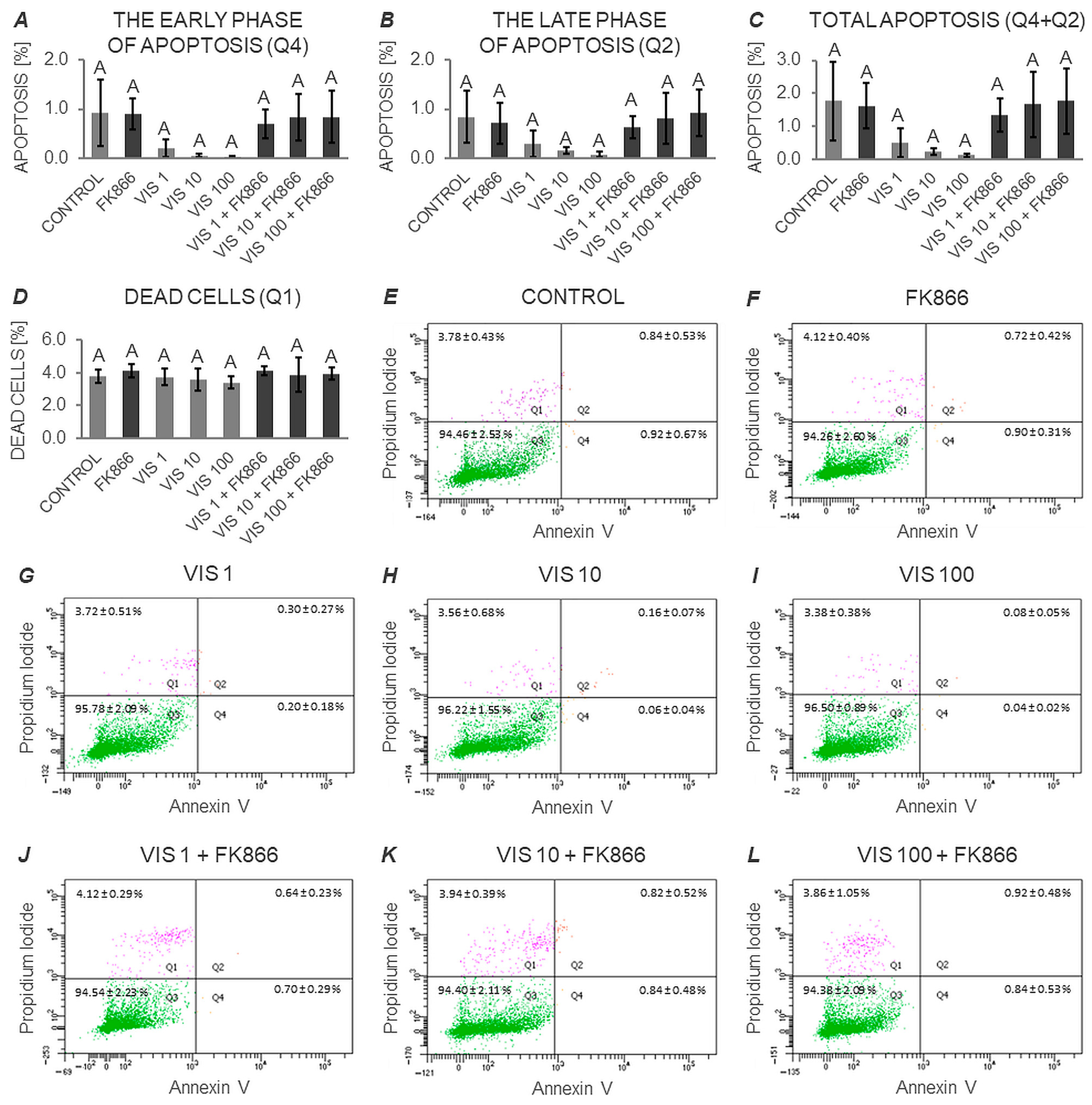
3.3. The In Vitro Effect of VIS on the Apoptosis Process in Anterior Pituitary Cells (Expt. No. 3)
3.4. The Mechanism of VIS’s Action in Anterior Pituitary Cells
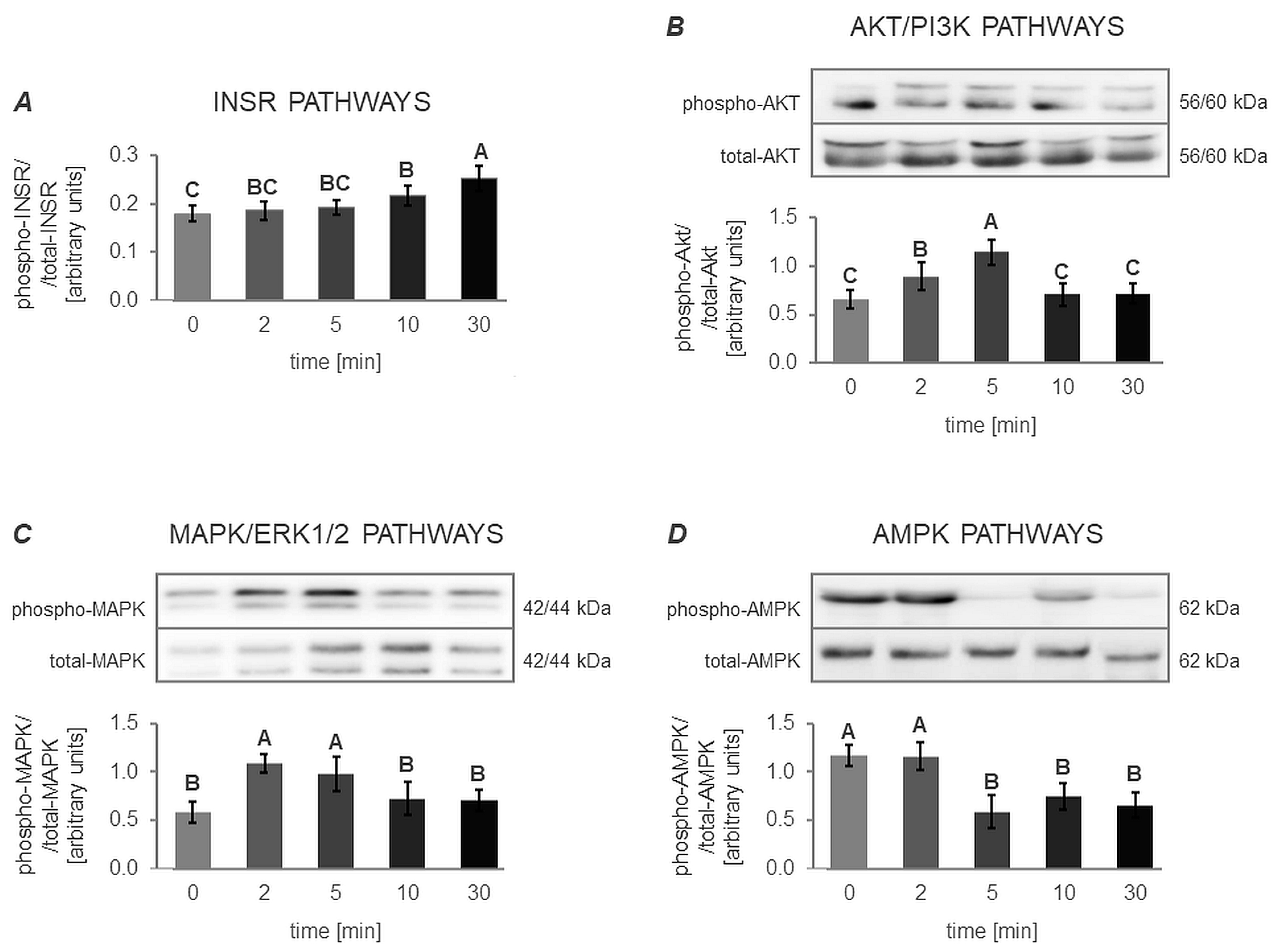
3.4.1. The In Vitro Effect of VIS on the Activation of INSR, AKT/PI3K, MAPK/ERK1/2 and AMPK Signaling Pathway (Expt. No. 4)
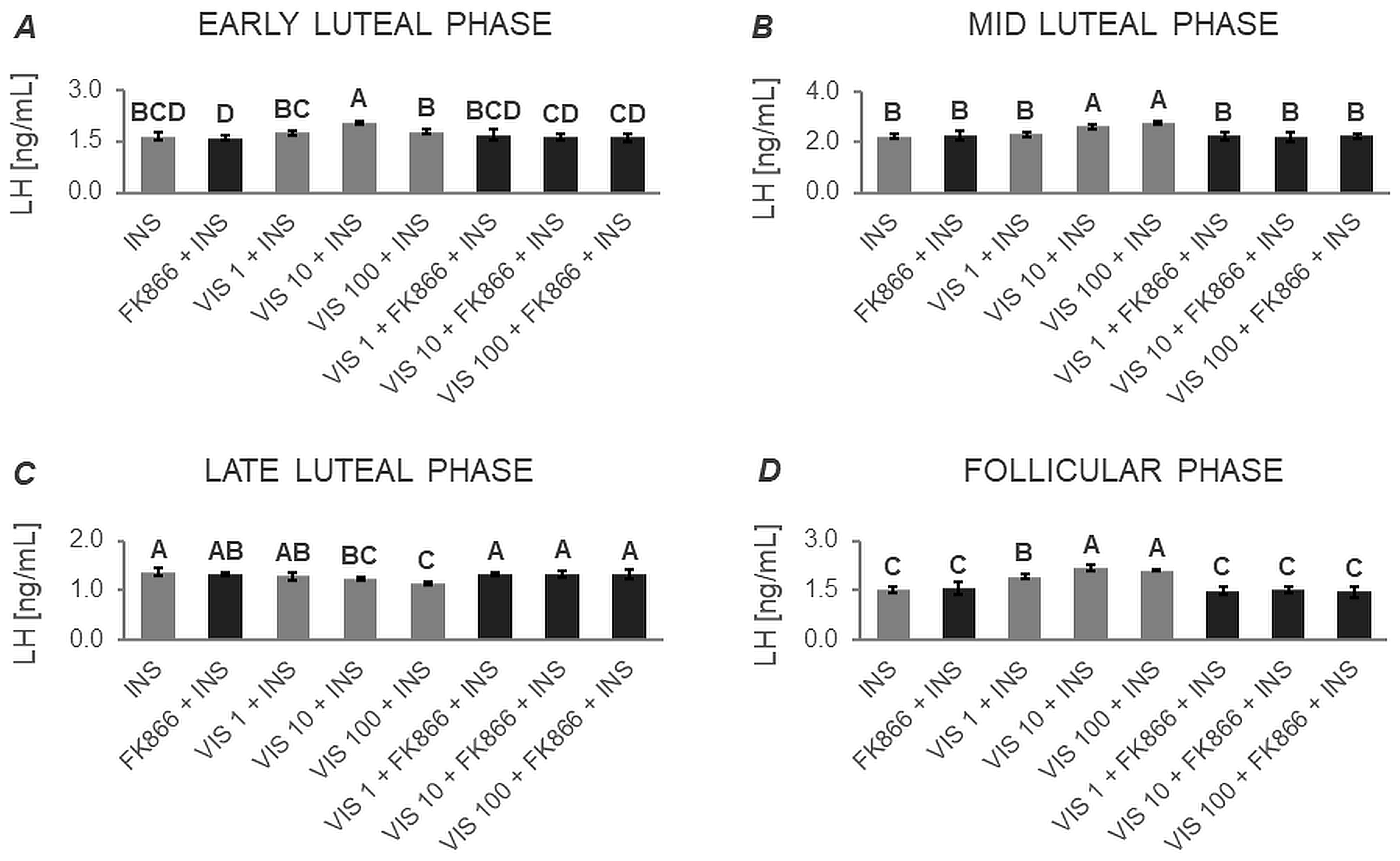
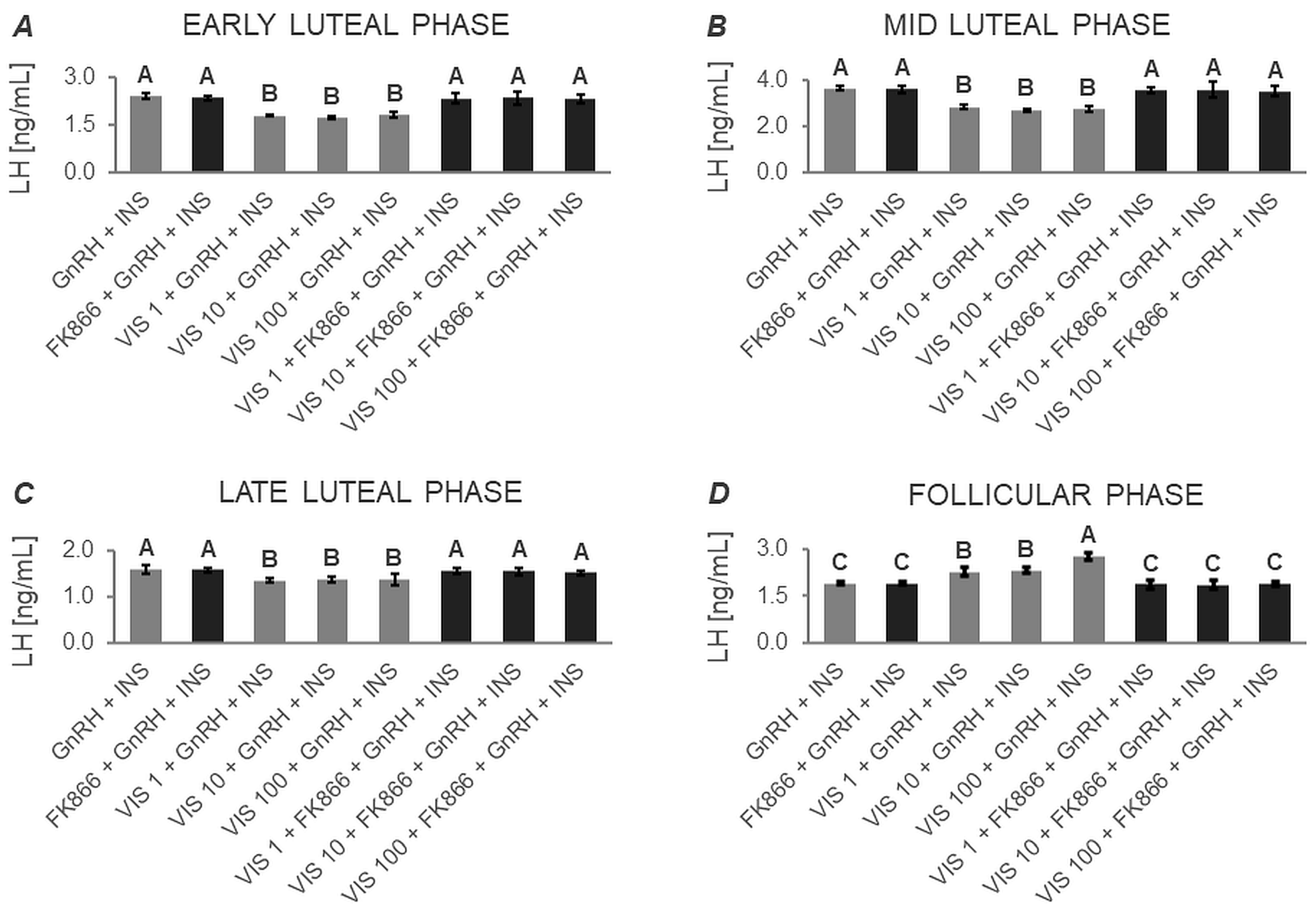
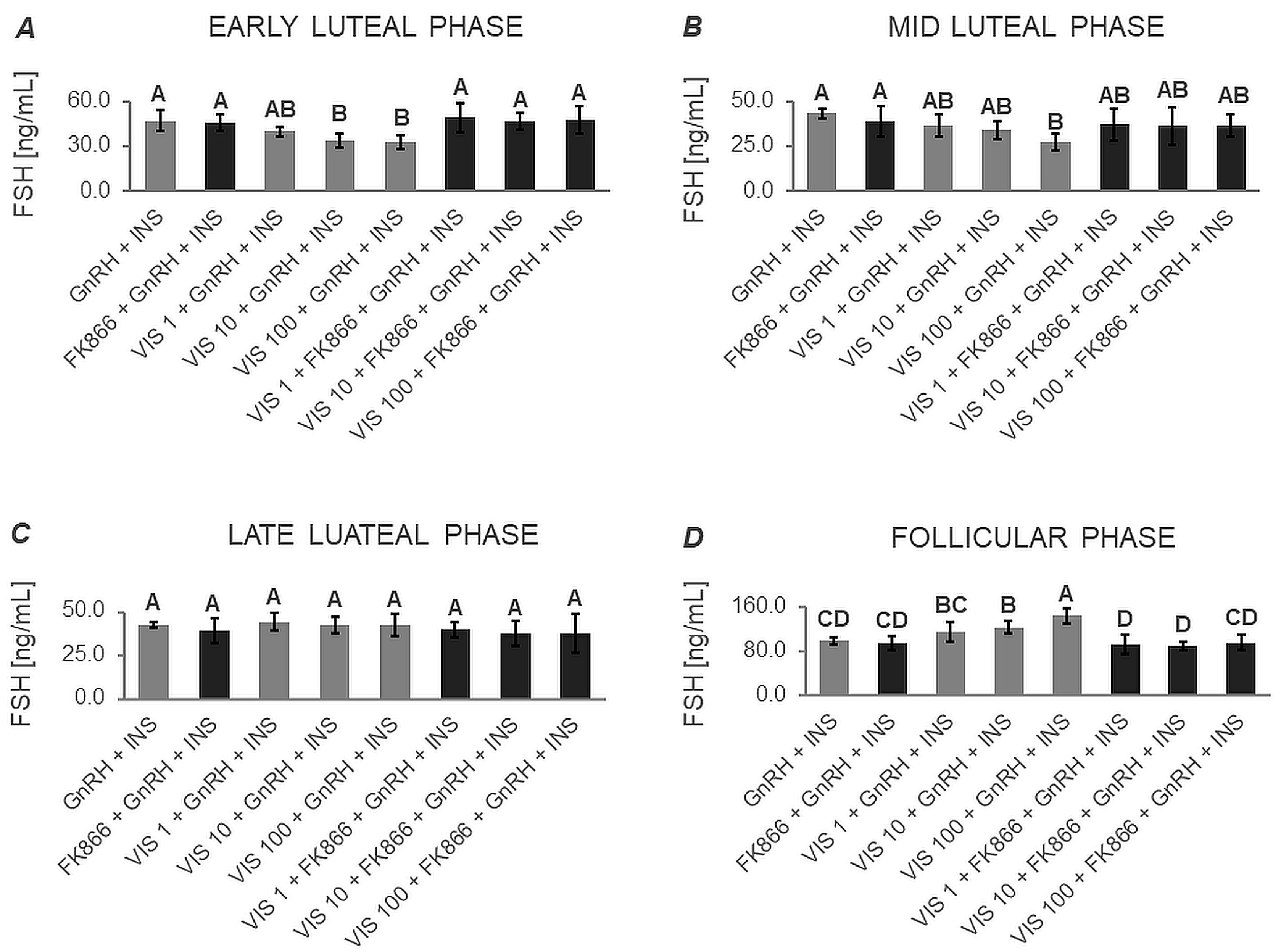
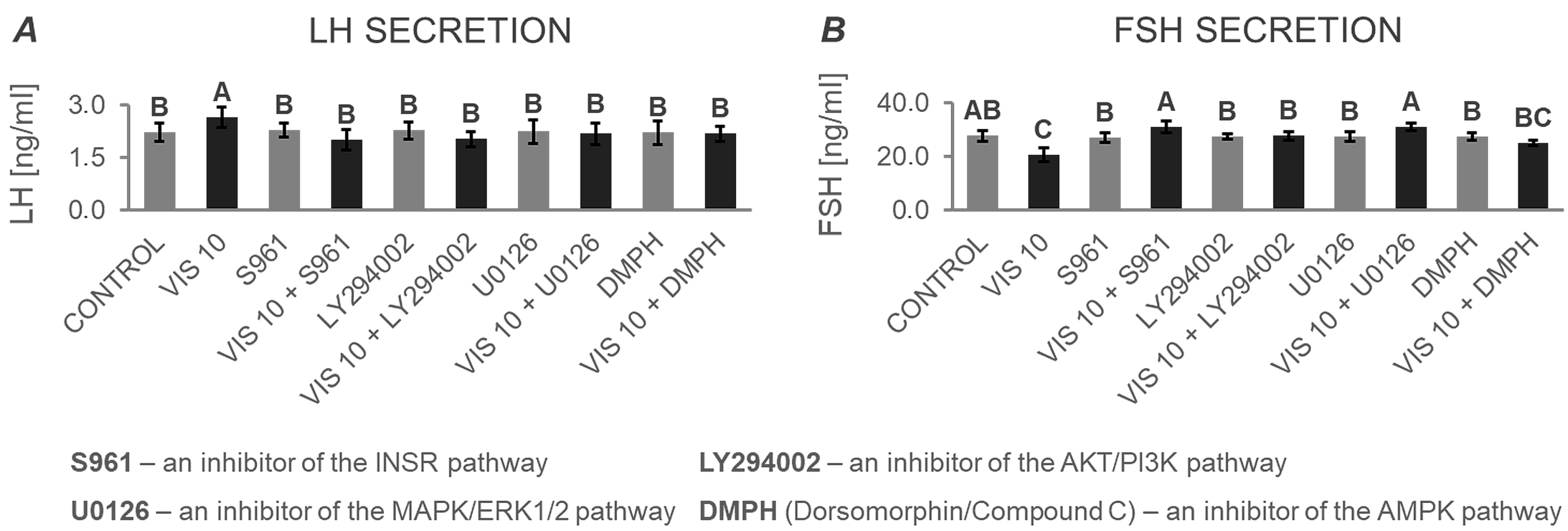
3.4.2. The In Vitro Effect of VIS on the Secretion of Gonadotropins by APc after Treatment with Inhibitors of the INSR, AKT/PI3K, MAPK/ERK1/2, and AMPK Signaling Pathways (Expt. No. 5)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amar, A.P.; Weiss, M.H. Pituitary Anatomy and Physiology. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 14, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.K.; Payne, S.C.; Jane, J.A. Anatomy, Physiology, and Laboratory Evaluation of the Pituitary Gland. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 49, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estienne, A.; Bongrani, A.; Reverchon, M.; Ramé, C.; Ducluzeau, P.-H.; Froment, P.; Dupont, J. Involvement of Novel Adipokines, Chemerin, Visfatin, Resistin and Apelin in Reproductive Functions in Normal and Pathological Conditions in Humans and Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Hung, A.C.; Lo, S.; Yuan, S.-S.F. Adipocytokines Visfatin and Resistin in Breast Cancer: Clinical Relevance, Biological Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Potential. Cancer Lett. 2021, 498, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rongvaux, A.; Shea, R.J.; Mulks, M.H.; Gigot, D.; Urbain, J.; Leo, O.; Andris, F. Pre-B-Cell Colony-Enhancing Factor, Whose Expression Is up-Regulated in Activated Lymphocytes, Is a Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase, a Cytosolic Enzyme Involved in NAD Biosynthesis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 3225–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakroub, A.; Nasser, A.S.; Younis, N.; Bhagani, H.; Al-Dhaheri, Y.; Pintus, G.; Eid, A.A.; El-Yazbi, A.F.; Eid, A.H. Visfatin: A Possible Role in Cardiovasculo-Metabolic Disorders. Cells 2020, 9, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovren, F.; Pan, Y.; Shukla, P.C.; Quan, A.; Teoh, H.; Szmitko, P.E.; Peterson, M.D.; Gupta, M.; Al-Omran, M.; Verma, S. Visfatin Activates ENOS via Akt and MAP Kinases and Improves Endothelial Cell Function and Angiogenesis in Vitro and in Vivo: Translational Implications for Atherosclerosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E1440–E1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.O.; Kim, N.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, H.I.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Visfatin, a Novel Adipokine, Stimulates Glucose Uptake through the Ca2+-Dependent AMPK–P38 MAPK Pathway in C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 54, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeghate, E. Visfatin: Structure, Function and Relation to Diabetes Mellitus and Other Dysfunctions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bergh, R.; Morin, S.; Sass, H.J.; Grzesiek, S.; Vekemans, M.; Florence, E.; Tran, H.T.T.; Imiru, R.G.; Heyndrickx, L.; Vanham, G.; et al. Monocytes Contribute to Differential Immune Pressure on R5 versus X4 HIV through the Adipocytokine Visfatin/NAMPT. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romacho, T.; Valencia, I.; Ramos-González, M.; Vallejo, S.; López-Esteban, M.; Lorenzo, O.; Cannata, P.; Romero, A.; San Hipólito-Luengo, A.; Gómez-Cerezo, J.F.; et al. Visfatin/ENampt Induces Endothelial Dysfunction in Vivo: A Role for Toll-Like Receptor 4 and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupré, S.M.; Burt, D.W.; Talbot, R.; Downing, A.; Mouzaki, D.; Waddington, D.; Malpaux, B.; Davis, J.R.E.; Lincoln, G.A.; Loudon, A.S.I. Identification of Melatonin-Regulated Genes in the Ovine Pituitary Pars Tuberalis, a Target Site for Seasonal Hormone Control. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 5527–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, V.; Elis, S.; Desmarchais, A.; Hivelin, C.; Lardic, L.; Lomet, D.; Uzbekova, S.; Monget, P.; Dupont, J. Visfatin and Resistin in Gonadotroph Cells: Expression, Regulation of LH Secretion and Signalling Pathways. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2017, 29, 2479–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Szymanska, K.; Zaobidna, E.; Rytelewska, E.; Mlyczynska, E.; Kurowska, P.; Dobrzyn, K.; Kiezun, M.; Kaminska, B.; Smolinska, N.; Rak, A.; et al. Visfatin in the Porcine Pituitary Gland: Expression and Regulation of Secretion during the Oestrous Cycle and Early Pregnancy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akins, R.; Morrissette, J. Gross Ovarian Changes during Estrous Cycle of Swine. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1968, 29, 1953–1957. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, T.; Kiezun, M.; Zaobidna, E.; Dobrzyn, K.; Wasilewska, B.; Mlyczynska, E.; Rytelewska, E.; Kisielewska, K.; Gudelska, M.; Bors, K.; et al. Plasma Level and Expression of Visfatin in the Porcine Hypothalamus during the Estrous Cycle and Early Pregnancy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverchon, M.; Cornuau, M.; Cloix, L.; Rame, C.; Guerif, F.; Royere, D.; Dupont, J. Visfatin Is Expressed in Human Granulosa Cells: Regulation by Metformin through AMPK/SIRT1 Pathways and Its Role in Steroidogenesis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 19, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogacka, I.; Siawrys, G.; Okrasa, S.; Kaminski, T.; Przala, J. The Influence of GnRH, Oxytocin and Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide on the Secretion of β-Endorphin and Production of CAMP and CGMP by Porcine Pituitary Cells in Vitro. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2002, 69, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavin, J.R., III; Roth, J.; Neville, D.M.; De Meyts, P.; Buell, D.N. Insulin-Dependent Regulation of Insulin Receptor Concentrations: A Direct Demonstration in Cell Culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.D.; Ustione, A.; Piston, D.W. Somatostatin and Insulin Mediate Glucose-Inhibited Glucagon Secretion in the Pancreatic α-Cell by Lowering CAMP. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E130–E143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zheng, N.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Xia, G.; Zhang, M. MAPK3/1 Participates in the Activation of Primordial Follicles through MTORC1-KITL Signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisielewska, K.; Rytelewska, E.; Gudelska, M.; Kiezun, M.; Dobrzyn, K.; Bogus-Nowakowska, K.; Kaminska, B.; Smolinska, N.; Kaminski, T. Expression of Chemerin Receptors CMKLR1, GPR1 and CCRL2 in the Porcine Pituitary during the Oestrous Cycle and Early Pregnancy and the Effect of Chemerin on MAPK/Erk1/2, Akt and AMPK Signalling Pathways. Theriogenology 2020, 157, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapper, J.; Taylor, A. Components of the Porcine Anterior Pituitary Insulin-like Growth Factor System throughout the Estrous Cycle. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2011, 40, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayes, F.C.; Britt, J.H.; Esbenshade, K.L. Role of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Pulse Frequency in Differential Regulation of Gonadotropins in the Gilt. Biol. Reprod. 1997, 56, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, R.M.; Kineman, R.D. Impact of Obesity on the Growth Hormone Axis: Evidence for a Direct Inhibitory Effect of Hyperinsulinemia on Pituitary Function. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 2754–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navratil, A.M.; Song, H.; Hernandez, J.B.; Cherrington, B.D.; Santos, S.J.; Low, J.M.; Do, M.-H.T.; Lawson, M.A. Insulin Augments Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Induction of Translation in LβT2 Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 311, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buggs, C.; Weinberg, F.; Kim, E.; Wolfe, A.; Radovick, S.; Wondisford, F. Insulin Augments GnRH-Stimulated LHβ Gene Expression by Egr-1. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 249, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, J.W.; Lange, W. Insulin Receptors in the Pituitary Gland: Morphological Evidence for Influence on Opioid Peptide-Synthesizing Cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1997, 288, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.M.; Polack, S.; Treeck, O.; Diedrich, K.; Ortmann, O. Regulation of GnRH I Receptor Gene Expression by the GnRH Agonist Triptorelin, Estradiol, and Progesterone in the Gonadotroph-Derived Cell Line AT3-1. Endocrine 2006, 30, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nett, T.M.; Turzillo, A.M.; Baratta, M.; Rispoli, L.A. Pituitary Effects of Steroid Hormones on Secretion of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2002, 23, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, M.; Park, D.; Park, Y.; Kam, K.; Park, S.D.; Ryu, K. Progesterone Together with Estrogen Attenuates Homologous Upregulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor MRNA in Primary Cultured Rat Pituitary Cells. Endocrine 2000, 13, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer-Dantoin, A.C.; Weiss, J.; Jameson, J.L. Roles of Estrogen, Progesterone, and Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) in the Control of Pituitary GnRH Receptor Gene Expression at the Time of the Preovulatory Gonadotropin Surges. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nett, T.M.; Crowder, M.E.; Wise, M.E. Role of Estradiol in Inducing an Ovulatory-Like Surge of Luteinizing Hormone in Sheep 1. Biol. Reprod. 1984, 30, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones-Jenab, V.; Jenab, S.; Ogawa, S.; Funabashi, T.; Weesner, G.D.; Pfaff, D.W. Estrogen Regulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor Messenger RNA in Female Rat Pituitary Tissue. Mol. Brain Res. 1996, 38, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.C.; Sealfon, S.C.; Miller, W.L. Gonadal Hormones and Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Alter Messenger Ribonucleic Acid Levels for GnRH Receptors in Sheep. Endocrinology 1994, 134, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, V.A.; Pompolo, S.; Clarke, I.J. The Percentage of Pituitary Gonadotropes with Immunoreactive Oestradiol Receptors Increases in the Follicular Phase of the Ovine Oestrous Cycle. J. Neuroendocr. 2001, 13, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rempel, L.A.; Clapper, J.A. Administration of Estradiol-17β Increases Anterior Pituitary IGF-I and Relative Amounts of Serum and Anterior Pituitary IGF-Binding Proteins in Barrows. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Weiss, J.; Polack, S.; Diedrich, K.; Ortmann, O. Interactions of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I, Insulin and Estradiol with GnRH-Stimulated Luteinizing Hormone Release from Female Rat Gonadotrophs. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 144, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Kim, E.O.; Jeong, B.R.; Min, Y.J.; Park, J.W.; Kim, E.S.; Namgoong, I.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Lee, B.J. Visfatin Stimulates Proliferation of MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cells 2010, 30, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, S.; Shimizu, M.; Imai, K.; Takai, K.; Shiraki, M.; Hara, T.; Tsurumi, H.; Ishizaki, S.; Moriwaki, H. Possible Role of Visfatin in Hepatoma Progression and the Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids on Visfatin-Induced Proliferation in Human Hepatoma Cells. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 2092–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Long, Y.X.; Li, Y.J.; Guo, X.D.; Wei, M.N.; Liu, W.J. Role of Visfatin in Promoting Proliferation and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Downregulating SDF-1/CXCR4-Mediated MiR-140-3p Expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 5367–5377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bułdak, R.J.; Bułdak, Ł.; Polaniak, R.; Kukla, M.; Birkner, E.; Kubina, R.; Kabała-Dzik, A.; Duława-Bułdak, A.; Żwirska-Korczala, K. Visfatin Affects Redox Adaptative Responses and Proliferation in Me45 Human Malignant Melanoma Cells: An in Vitro Study. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Teng, F.; Tian, W.; Yang, W.; Yan, Y.; Xue, F. Visfatin Stimulates Endometrial Cancer Cell Proliferation via Activation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK1/2 Signalling Pathways. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 143, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, S.; Kridel, S. Visfatin/Nampt: A Potential Regulator of Prostate Tumor Cell Proliferation, Metabolism, and Survival. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 68, 4362. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Dong, W.; Qian, L.; Wu, J.; Peng, Y. Visfatin Inhibits Apoptosis of Pancreatic β-Cell Line, MIN6, via the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase/Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Pathway. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 47, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, K.; Wang, S.; Ansari, A.R.; Niu, X.; Yang, W.; Lu, M.; Yang, Z.; Rehman, Z.U.; Zou, W.; et al. Visfatin Is a Multifaceted Molecule That Exerts Regulation Effects on Inflammation and Apoptosis in RAW264.7 Cells and Mice Immune Organs. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1018973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, R.L.; Mei, M.; Su, Y.C.; Li, L.; Wang, J.Y.; Wu, L.L. Visfatin Protects Rat Pancreatic β-Cells against IFN-γ-Induced Apoptosis through AMPK and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Erfani, S.; Aboutaleb, N.; Oryan, S.; Shamsaei, N.; Khaksari, M.; Kalalian-Moghaddam, H.; Nikbakht, F. Visfatin Inhibits Apoptosis and Necrosis of Hippocampus CA3 Cells Following Transient Global Ischemia/Reperfusion in Rats. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2015, 21, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Long, Y.; Cheng, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; et al. Visfatin Inhibits Colon Cancer Cell Apoptosis and Decreases Chemosensitivity to 5-FU by Promoting the SDF-1/CXCR4/Akt Axis. Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 60, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Lee, J.T.; Navolanic, P.M.; Steelman, L.S.; Shelton, J.G.; Blalock, W.L.; Franklin, R.A.; McCubrey, J.A. Involvement of PI3K/Akt Pathway in Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis, and Neoplastic Transformation: A Target for Cancer Chemotherapy. Leukemia 2003, 17, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, W.-Z.; Liu, T.; Feng, X.; Yang, N.; Zhou, H.-F. Signaling Pathway of MAPK/ERK in Cell Proliferation, Differentiation, Migration, Senescence and Apoptosis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2015, 35, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholinejad, Z.; Kheiripour, N.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Ilbeigi, D.; Behroozfar, K.; Hesari, Z.; Golestani, A.; Shabani, M.; Einollahi, N. Extracellular NAMPT/Visfatin Induces Proliferation through ERK1/2 and AKT and Inhibits Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells. Peptides 2017, 92, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miethe, C.; Torres, L.; Zamora, M.; Price, R.S. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt and ERK Signaling Decreases Visfatin-Induced Invasion in Liver Cancer Cells. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2021, 42, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saddi-Rosa, P.; Oliveira, C.S.; Giuffrida, F.M.; Reis, A.F. Visfatin, Glucose Metabolism and Vascular Disease: A Review of Evidence. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2010, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin Receptor Signaling in Normal and Insulin-Resistant States. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihaylova, M.M.; Shaw, R.J. The AMPK Signalling Pathway Coordinates Cell Growth, Autophagy and Metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garten, A.; Petzold, S.; Körner, A.; Imai, S.; Kiess, W. Nampt: Linking NAD Biology, Metabolism and Cancer. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Qiu, X.; Li, M.; Liu, R.; He, T.; Tang, Q. AMPK Phosphorylates NAMPT to Regulate NAD + Homeostasis under Ionizing Radiation. Open Biol. 2022, 12, 220213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Expt. No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase of the Estrous Cycle * |
|
| |||
| Treatments |
|
|
|
|
|
| Incub. Time | 24 h | 24 h | 24 h | 0 min 2 min 5 min 10 min 30 min | 24 h |
| Objective of the Expt. | the in vitro effect of VIS on the secretion of LH and FSH by APc in pigs | the in vitro effect of VIS on the proliferation of APc in pigs | the in vitro effect of VIS on the apoptosis of APc in pigs | the in vitro effect of VIS on the activation of INSR, AKT/PI3K, MAPK/ERK1/2, and AMPK signaling pathways in APc in pigs | the in vitro effect of VIS on the secretion of LH and FSH by APc in pigs |
| Expt. No. | 1 and 5 | 4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Protein | LH | FSH | phospho-INSR | total-INSR |
| Catalog Number and Supplier’s Name | Cat. No. EP0105; FineTest Biotech Inc., Nanjing, China | Cat. No. EP0060; FineTest Biotech Inc., Nanjing, China | Cat. No. EIA09483p; Enlibio Biotech Co., Wuhan, China | Cat. No. EIA05929p; Enlibio Biotech Co., Wuhan, China |
| Elisa Type | competitive ELISA | competitive ELISA | double-antibody sandwich ELISA | double-antibody sandwich ELISA |
| Detection Range | 0.781–50 ng/mL | 6.25–400 ng/mL | 0.156–10 ng/mL | 0.312–20 ng/mL |
| Sensitivity of the Assay | 0.469 ng/mL | <3.75 ng/mL | 0.05 ng/mL | 0.06 ng/mL |
| Mean Intra-Assay Coefficient of Variation | 2.69 ± 1.60% | 3.16 ± 1.76% | 1.57 ± 0.81% | 1.63 ± 0.83% |
| Mean Inter-Assay Coefficient of Variation | 6.58 ± 1.67% | 7.34 ± 1.84% | does not apply | does not apply |
| R2 | 0.9638 | 0.9525 | 0.9998 | 0.9994 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szymanska, K.; Rytelewska, E.; Zaobidna, E.; Kiezun, M.; Gudelska, M.; Kopij, G.; Dobrzyn, K.; Mlyczynska, E.; Kurowska, P.; Kaminska, B.; et al. The Effect of Visfatin on the Functioning of the Porcine Pituitary Gland: An In Vitro Study. Cells 2023, 12, 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242835
Szymanska K, Rytelewska E, Zaobidna E, Kiezun M, Gudelska M, Kopij G, Dobrzyn K, Mlyczynska E, Kurowska P, Kaminska B, et al. The Effect of Visfatin on the Functioning of the Porcine Pituitary Gland: An In Vitro Study. Cells. 2023; 12(24):2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242835
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzymanska, Karolina, Edyta Rytelewska, Ewa Zaobidna, Marta Kiezun, Marlena Gudelska, Grzegorz Kopij, Kamil Dobrzyn, Ewa Mlyczynska, Patrycja Kurowska, Barbara Kaminska, and et al. 2023. "The Effect of Visfatin on the Functioning of the Porcine Pituitary Gland: An In Vitro Study" Cells 12, no. 24: 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242835
APA StyleSzymanska, K., Rytelewska, E., Zaobidna, E., Kiezun, M., Gudelska, M., Kopij, G., Dobrzyn, K., Mlyczynska, E., Kurowska, P., Kaminska, B., Nynca, A., Smolinska, N., Rak, A., & Kaminski, T. (2023). The Effect of Visfatin on the Functioning of the Porcine Pituitary Gland: An In Vitro Study. Cells, 12(24), 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242835












