Cannabinoid Signaling in Kidney Disease
Abstract
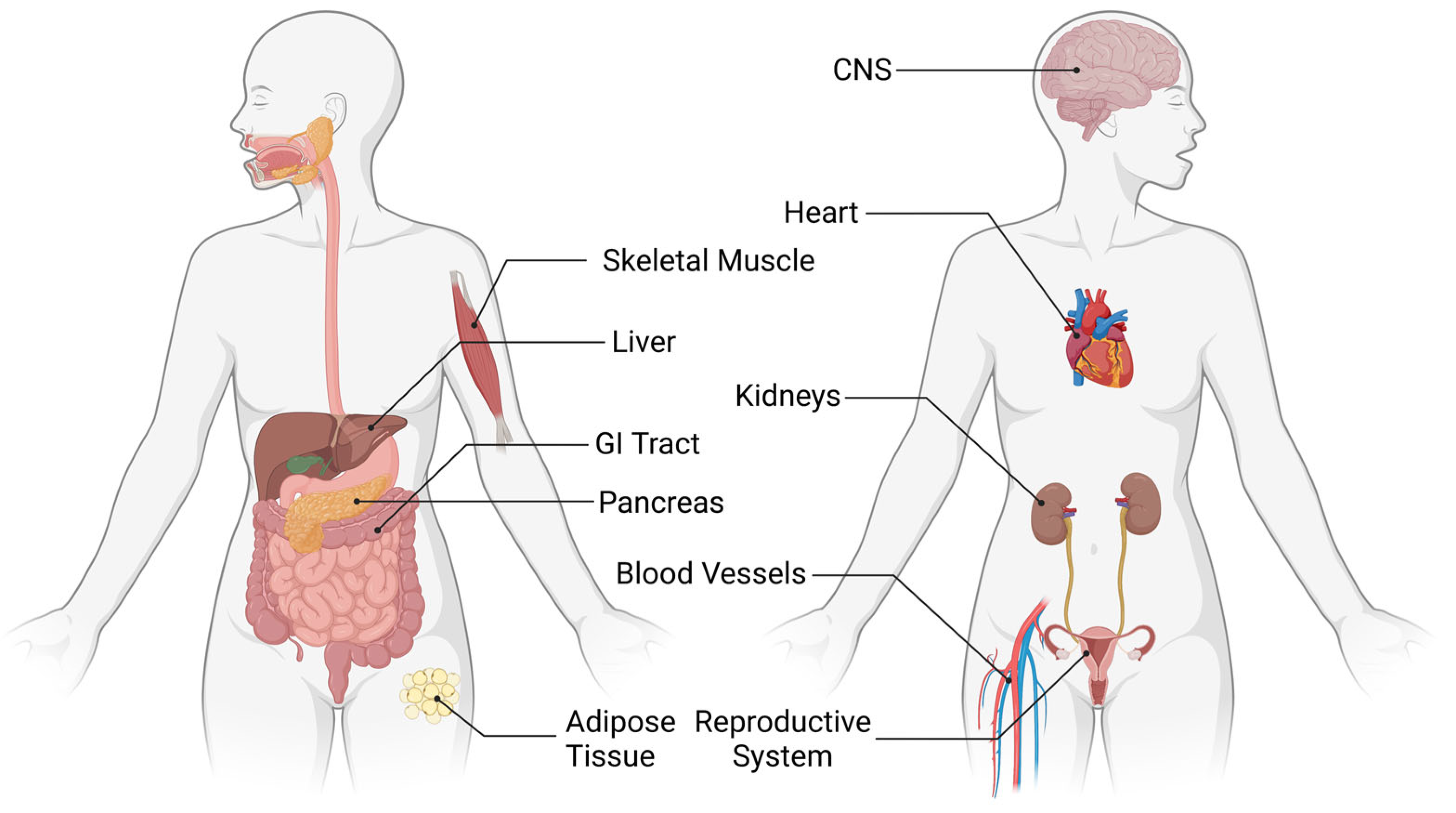
1. Introduction: Overview of Cannabinoid Signaling
1.1. The Cannabinoid Receptors: An Emphasis on CB1
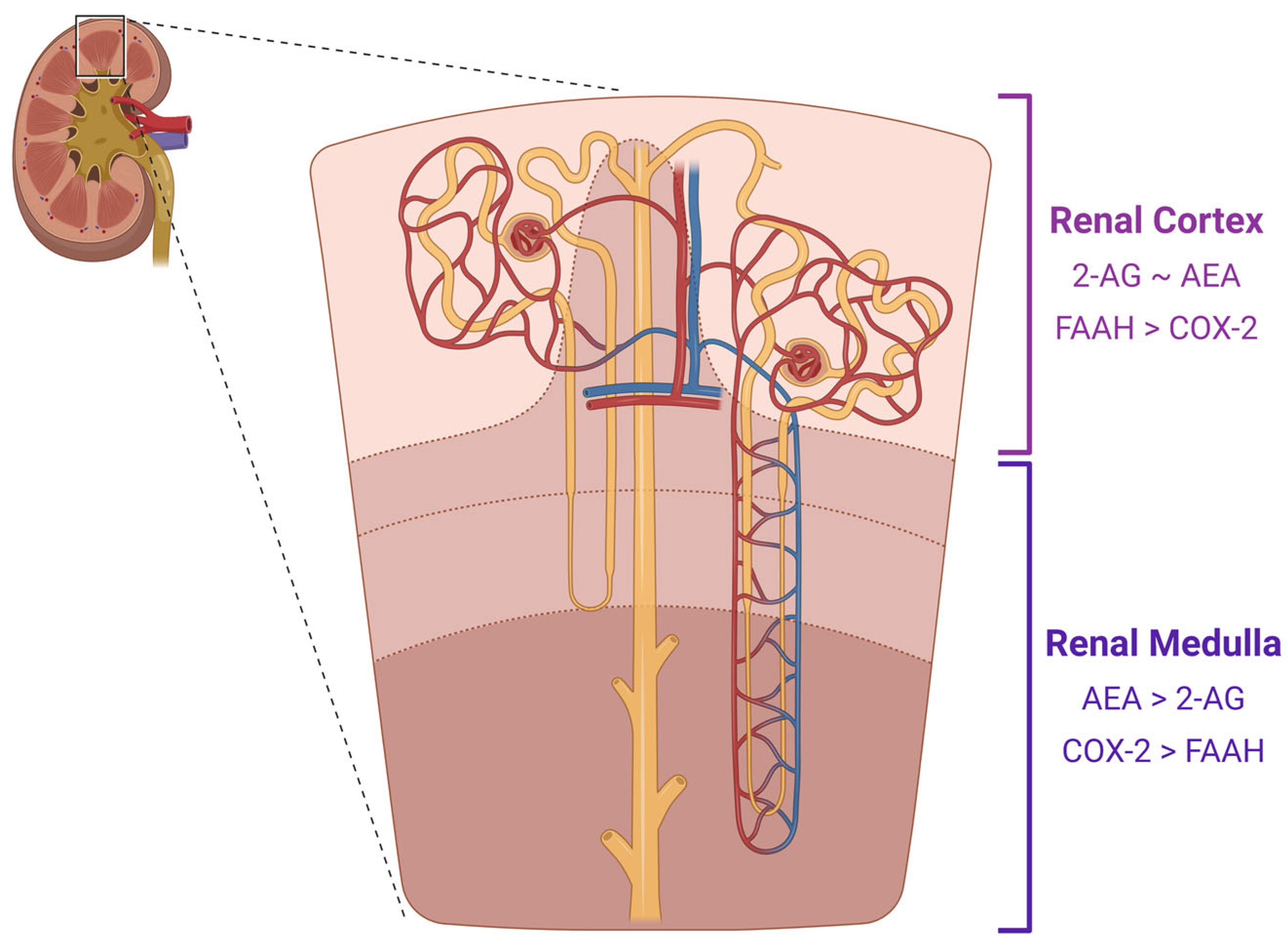
1.2. The Endocannabinoids of CB1
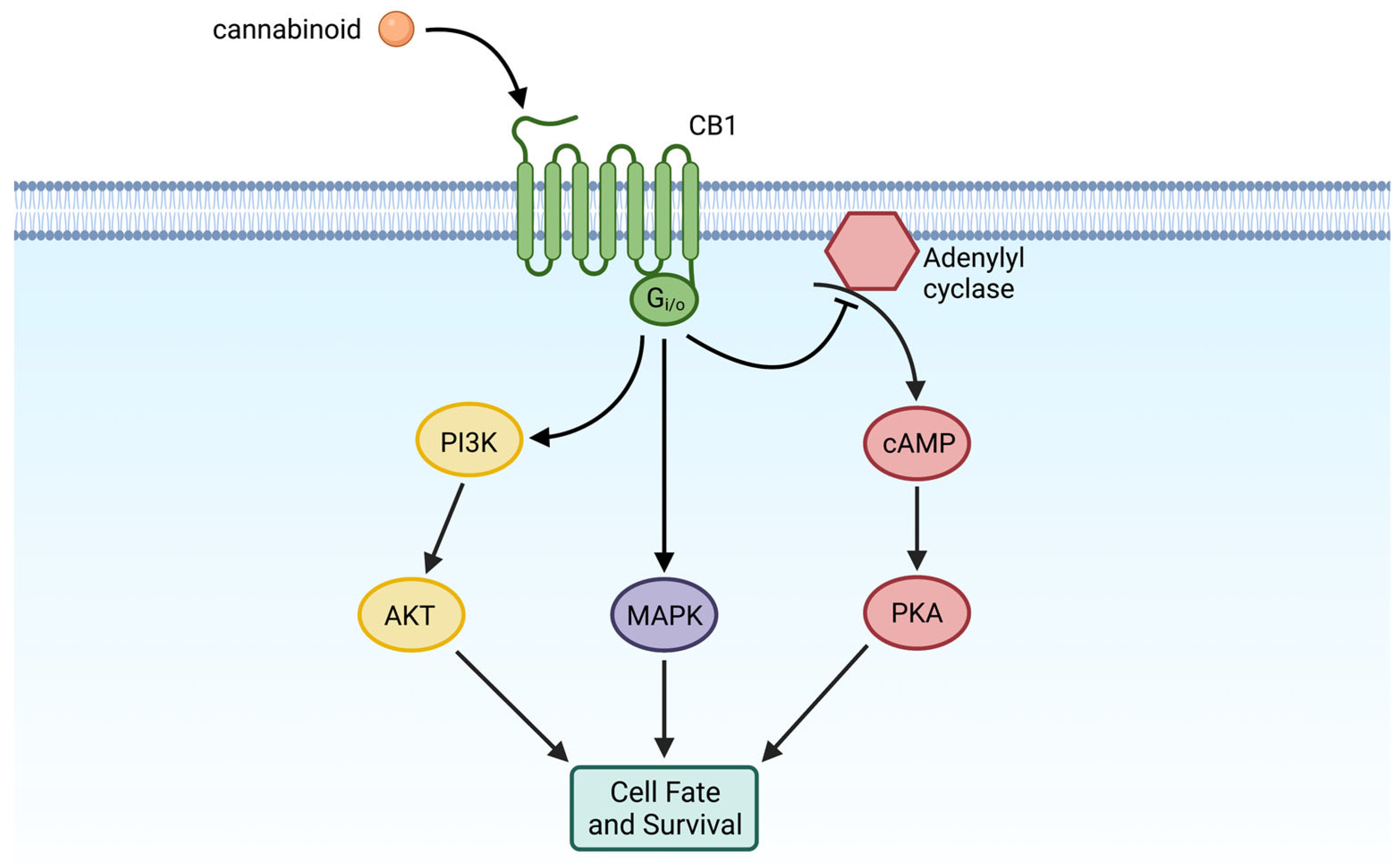
1.3. Cellular Processes of the ECS
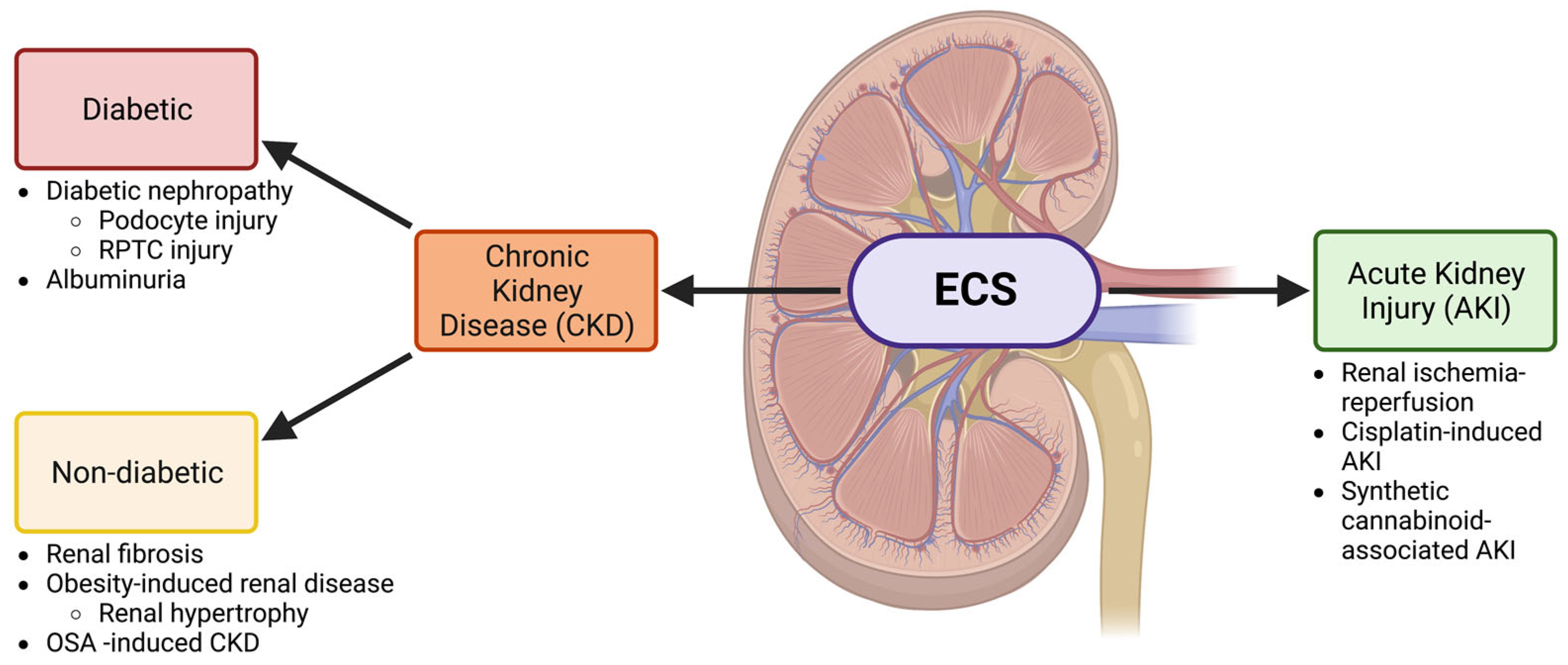
2. The ECS and Chronic Kidney Disease
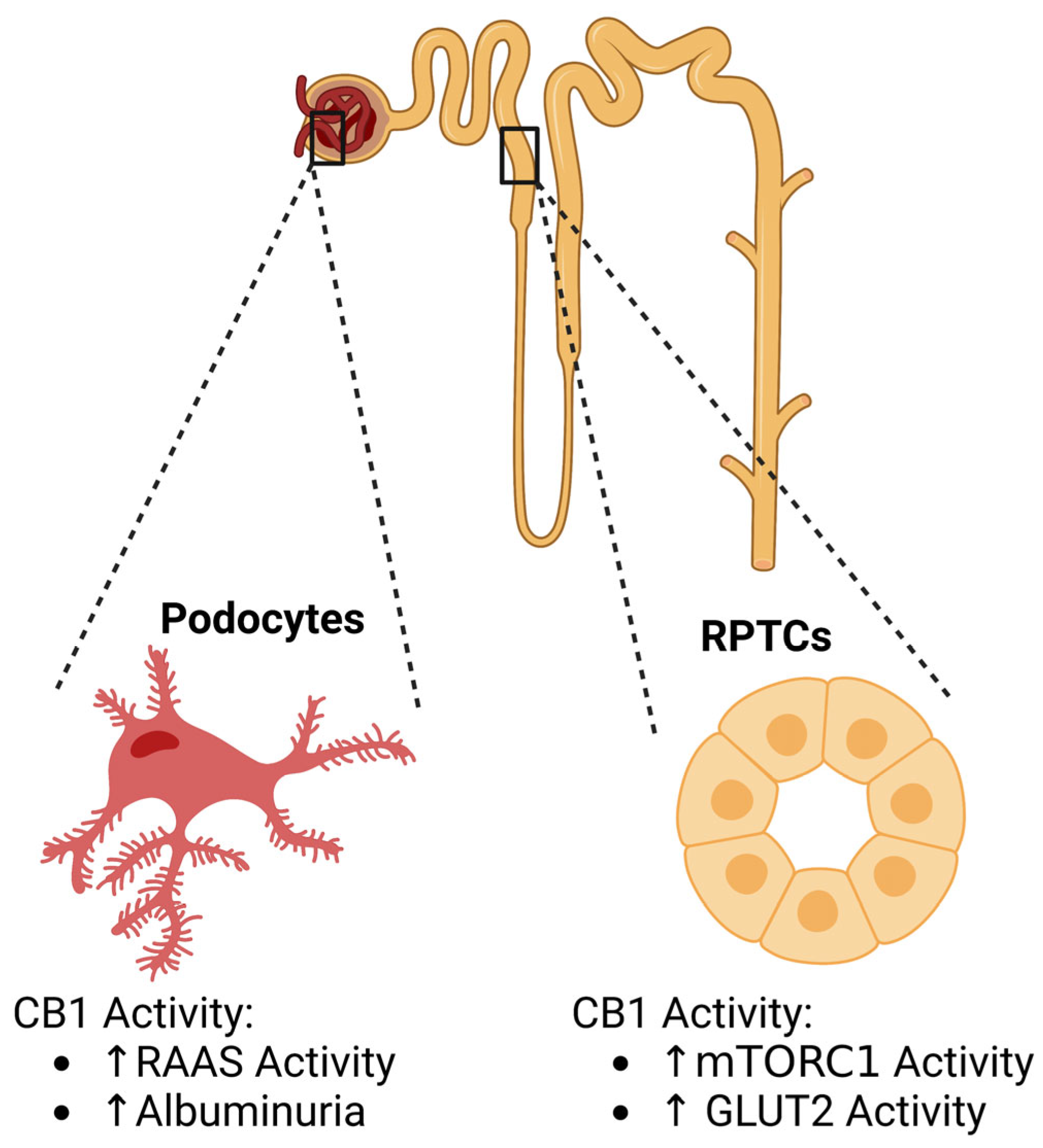
2.1. Diabetic Kidney Disease
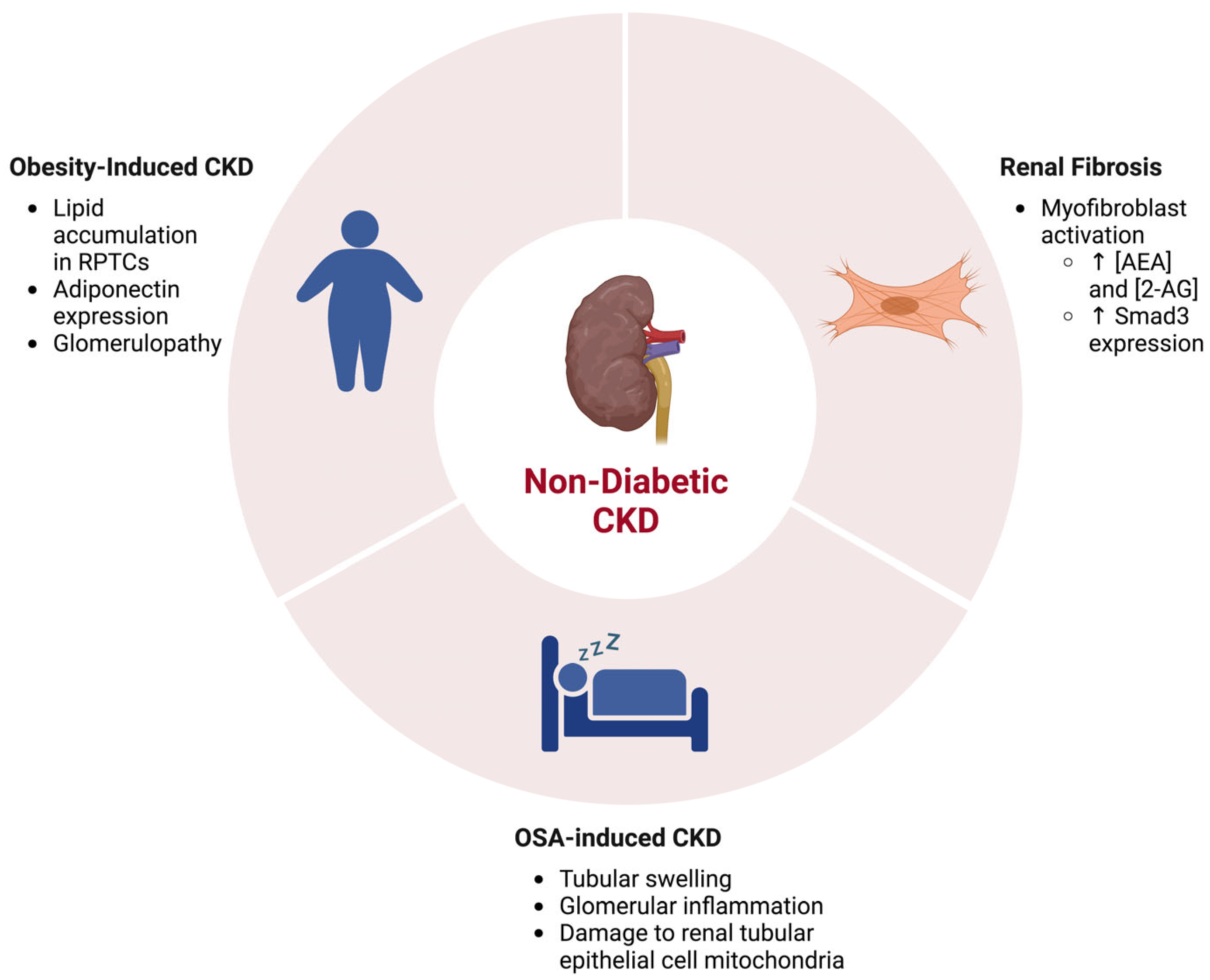
2.2. The ECS in Renal Fibrosis and Other Non-Diabetic CKDs
3. The ECS and Acute Kidney Injury
4. Therapeutic Potential
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fezza, F.; Bari, M.; Florio, R.; Talamonti, E.; Feole, M.; Maccarrone, M. Endocannabinoids, related compounds and their metabolic routes. Molecules 2014, 19, 17078–17106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, A.C.; Barth, F.; Bonner, T.I.; Cabral, G.; Casellas, P.; Devane, W.A.; Felder, C.C.; Herkenham, M.; Mackie, K.; Martin, B.R.; et al. International union of pharmacology. XXVII. classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 161–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, S.; Yang, P.; Tian, Y.; Feng, Z.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y. Targeted inhibition of the type 2 cannabinoid receptor is a novel approach to reduce renal fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 756–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, B.E.; Weaver, N.E.; Wingert, R.A. The “3Ds” of growing kidney organoids: Advances in nephron development, disease modeling, and drug screening. Cells 2023, 12, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, J.T.; Argueta, D.A.; DiPatrizio, N.V.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Vaziri, N.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Moradi, H. Endocannabinoid system and the kidneys: From renal physiology to injury and disease. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2019, 4, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCampbell, K.K.; Wingert, R.A. Renal stem cells: Fact or science fiction? Biochem. J. 2012, 444, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wingert, R.A. Regenerative medicine for the kidney: Stem cell prospects & challenges. Clin. Transl. Med. 2013, 2, 11. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, R.A.; Wingert, R.A. Zebrafish renal pathology: Emerging models of acute kidney injury. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2015, 3, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: An update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergraft, W.F., 3rd; Herlitz, L.C.; Thornley-Brown, D.; Rosner, M.; Niles, J.L. Nephrotoxic effects of common and emerging drugs of abuse. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyravian, N.; Deo, S.; Daunert, S.; Jimenez, J.J. Cannabidiol as a novel therapeutic for immune modulation. Immunotargets Ther. 2020, 9, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazi, F.; Grandi, V.; Banerjee, A.; Trant, J.F. Cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors: The story so far. iScience 2020, 23, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, D.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhong, L.; Cai, X.; Dai, A.; Jang, W.; Shakhnovich, E.I.; et al. Common activation mechanism of class A GPCRs. eLife 2019, 8, e50279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Vemuri, K.; Pu, M.; Qu, L.; Han, G.W.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shui, W.; Li, S.; Korde, A.; et al. Crystal structure of the human cannabinoid receptor CB1. Cell 2016, 167, 750–762.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, D.A.; Yudowski, G.A. Cannabinoid receptors in the central nervous system: Their signaling and roles in disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, P.E.; Younts, T.J.; Chávez, A.E.; Hashimotodani, Y. Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function. Neuron 2012, 76, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allam, S.; Paris, E.; Lazcano, I.; Bitterman, P.; Basu, S.; O’Donnell, J.; Barua, A. Detection of cannabinoid receptor expression by endometriotic lesions in women with endometriosis as an alternative to opioid-based pain medication. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 4323259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.; François, H. Cannabinoid receptor 1 inhibition in chronic kidney disease: A new therapeutic toolbox. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 720734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenoehrl, C.; Taschler, U.; Storr, M.; Schicho, R. The gastrointestinal tract—A central organ of cannabinoid signaling in health and disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 1765–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haspula, D.; Clark, M.A. Cannabinoid receptors: An update on cell signaling, pathophysiological roles and therapeutic opportunities in neurological, cardiovascular, and inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Alexa, K.; Cortes, M.; Schatzman-Bone, S.; Kim, A.J.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Cinar, R.; Kunos, G.; North, T.E.; Goessling, W. Cannabinoid receptor signaling regulates liver development and metabolism. Development 2016, 143, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barutta, F.; Bellini, S.; Gruden, G. Mechanisms of podocyte injury and implications for diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Sci. 2022, 136, 493–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, D.G.; Goligorsky, M.S.; Schmid, P.C.; Krebsbach, R.J.; Schmid, H.H.; Das, S.K.; Dey, S.K.; Arreaza, G.; Thorup, C.; Stefano, G.; et al. Production and physiological actions of anandamide in the vasculature of the rat kidney. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drori, A.; Permyakova, A.; Hadar, R.; Udi, S.; Nemirovski, A.; Tam, J. Cannabinoid-1 receptor regulates mitochondrial dynamics and function in renal proximal tubular cells. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koura, Y.; Ichihara, A.; Tada, Y.; Kaneshiro, Y.; Okada, H.; Temm, C.J.; Hayashi, M.; Saruta, T. Anandamide decreases glomerular filtration rate through predominant vasodilation of efferent arterioles in rat kidneys. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrinaga, G.; Varona, A.; Pérez, I.; Sanz, B.; Ugalde, A.; Cándenas, M.L.; Pinto, F.M.; Gil, J.; López, J.I. Expression of cannabinoid receptors in human kidney. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Hsu, Y.; Lee, P.; Lei, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, F. Cannabinoid receptor 1 disturbance of PPARγ2 augments hyperglycemia induction of mesangial inflammation and fibrosis in renal glomeruli. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.B.; Atchison, D.K.; Juncos, L.I.; García, N.H. Anandamide inhibits transport-related oxygen consumption in the loop of henle by activating CB1 receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2013, 304, F376–F381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecru, L.; Desterke, C.; Grassin-Delyle, S.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Vandermeersch, S.; Devocelle, A.; Vernochet, A.; Ivanovski, N.; Ledent, C.; Ferlicot, S.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor 1 is a major mediator of renal fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esain, V.; Kwan, W.; Carroll, K.J.; Cortes, M.; Liu, S.Y.; Frechette, G.M.; Sheward, L.M.V.; Nissim, S.; Goessling, W.; North, T.E. Cannabinoid receptor-2 regulates embryonic hematopoietic stem cell development via prostaglandin E2 and P-selectin activity. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 2596–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, J.K.; Li, G.; Xia, M.; Boini, K. Anandamide and its metabolites: What are their roles in the kidney? Front. Biosci. (Schol. Ed.) 2016, 8, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devane, W.A.; Hanus, L.; Breuer, A.; Pertwee, R.G.; Stevenson, L.A.; Griffin, G.; Gibson, D.; Mandelbaum, A.; Etinger, A.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 1992, 258, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechoulam, R.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Hanus, L.; Ligumsky, M.; Kaminski, N.E.; Schatz, A.R.; Gopher, A.; Almog, S.; Martin, B.R.; Compton, D.R.; et al. Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherma, M.; Masia, P.; Satta, V.; Fratta, W.; Fadda, P.; Tanda, G. Brain activity of anandamide: A rewarding bliss? Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Oka, S.; Waku, K. Biosynthesis and degradation of anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol and their possible physiological significance. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2002, 66, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, J.K.; Li, C.; Xia, M.; Poklis, J.L.; Lichtman, A.H.; Abdullah, R.A.; Dewey, W.L.; Li, P. Production and actions of the anandamide metabolite prostamide E2 in the renal medulla. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 342, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Waku, K. Cannabinoid receptors and their endogenous ligands. J. Biochem. 2002, 132, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.Z.; LaCava, M.; Jin, X.; Cravatt, B.F. An anatomical and temporal portrait of physiological substrates for fatty acid amide hydrolase. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, L.S.; Taveira Da Silva, R.; Lima, D.; Sampaio, C.L.C.; Iannotti, F.A.; Mazzarella, E.; Di Marzo, V.; Vieyra, A.; Reis, R.A.M.; Einicker-Lamas, M. The endocannabinoid system in renal cells: Regulation of Na(+) transport by CB1 receptors through distinct cell signalling pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4615–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Ives, D.; Ramesha, C.S. Synthesis of prostaglandin E2 ethanolamide from anandamide by cyclooxygenase-2. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21181–21186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, K.; Uyama, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Ueda, N. Endocannabinoids and related N-acylethanolamines: Biological activities and metabolism. Inflamm. Regen. 2018, 38, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemtiri-Chlieh, F.; Levine, E.S. 2-AG and anandamide enhance hippocampal long-term potentiation via suppression of inhibition. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1023541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, H.; Oveisi, F.; Khanifar, E.; Moreno-Sanz, G.; Vaziri, N.D.; Piomelli, D. Increased renal 2-arachidonoylglycerol level is associated with improved renal function in a mouse model of acute kidney injury. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán, M. Cannabinoids: Potential anticancer agents. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, N.E.; Koh, W.S.; Yang, K.H.; Lee, M.; Kessler, F.K. Suppression of the humoral immune response by cannabinoids is partially mediated through inhibition of adenylate cyclase by a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein coupled mechanism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 48, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, A.R.; Kessler, F.K.; Kaminski, N.E. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase by delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in mouse spleen cells: A potential mechanism for cannabinoid-mediated immunosuppression. Life Sci. 1992, 51, PL25–PL30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Kumar, U. Cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system: Signaling and function in the central nervous system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cardona, A.P.; Pérez-Cerezales, S.; Fernández-González, R.; Laguna-Barraza, R.; Pericuesta, E.; Agirregoitia, N.; Gutiérrez-Adán, A.; Agirregoitia, E. CB1 cannabinoid receptor drives oocyte maturation and embryo development via PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3372–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Luo, H.; Tang, X.; Wang, H. Cannabinoids inhibit ethanol-induced activation of liver toxicity in rats through JNK/ERK/MAPK signaling pathways. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Pan, H.; Rajesh, M.; Bátkai, S.; Patel, V.; Harvey-White, J.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Haskó, G.; Gao, B.; Mackie, K.; et al. CB1 cannabinoid receptors promote oxidative/nitrosative stress, inflammation and cell death in a murine nephropathy model. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, B.E.; Ercanbrack, W.S.; Wingert, R.A. Modeling Podocyte Ontogeny and Podocytopathies with the Zebrafish. J. Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussolati, B.; Deregibus, M.C.; Fonsato, V.; Doublier, S.; Spatola, T.; Procida, S.; Di Carlo, F.; Camussi, G. Statins prevent oxidized LDL-induced injury of glomerular podocytes by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-signaling pathway. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgewater, D.J.; Ho, J.; Sauro, V.; Matsell, D.G. Insulin-like growth factors inhibit podocyte apoptosis through the PI3 kinase pathway. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourdan, T.; Szanda, G.; Rosenberg, A.Z.; Tam, J.; Earley, B.J.; Godlewski, G.; Cinar, R.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Ju, C.; et al. Overactive cannabinoid 1 receptor in podocytes drives type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5420–E5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes management in chronic kidney disease: A consensus report by the american diabetes association (ADA) and kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 3075–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohbeck, E.; Eckel, J.; Romacho, T. Cannabinoid receptors in metabolic regulation and diabetes. Physiology 2021, 36, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutta, F.; Corbelli, A.; Mastrocola, R.; Gambino, R.; Di Marzo, V.; Pinach, S.; Rastaldi, M.P.; Perin, P.C.; Gruden, G. Cannabinoid receptor 1 blockade ameliorates albuminuria in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.H.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.E.; Song, H.K.; Kang, Y.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.W.; Cha, J.J.; Hyun, Y.Y.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Blockade of cannabinoid receptor 1 improves insulin resistance, lipid metabolism, and diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutta, F.; Bellini, S.; Mastrocola, R.; Gambino, R.; Piscitelli, F.; di Marzo, V.; Corbetta, B.; Vemuri, V.K.; Makriyannis, A.; Annaratone, L.; et al. Reversal of albuminuria by combined AM6545 and perindopril therapy in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 4371–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, T.; Park, J.K.; Varga, Z.V.; Pálóczi, J.; Coffey, N.J.; Rosenberg, A.Z.; Godlewski, G.; Cinar, R.; Mackie, K.; Pacher, P.; et al. Cannabinoid-1 receptor deletion in podocytes mitigates both glomerular and tubular dysfunction in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, P.; Maxwell, A.P.; Brazil, D.P. The potential of albuminuria as a biomarker of diabetic complications. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2021, 35, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogot-Levin, A.; Hinden, L.; Riahi, Y.; Israeli, T.; Tirosh, B.; Cerasi, E.; Mizrachi, E.B.; Tam, J.; Mosenzon, O.; Leibowitz, G. Proximal tubule mTORC1 is a central player in the pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy and its correction by SGLT2 inhibitors. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinden, L.; Ahmad, M.; Hamad, S.; Nemirovski, A.; Szanda, G.; Glasmacher, S.; Kogot-Levin, A.; Abramovitch, R.; Thorens, B.; Gertsch, J.; et al. Opposite physiological and pathological mTORC1-mediated roles of the CB1 receptor in regulating renal tubular function. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkin, K.A.; McAinch, A.J.; Grinfeld, E.; Hryciw, D.H. Role for cannabinoid receptors in human proximal tubular hypertrophy. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 26, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udi, S.; Hinden, L.; Earley, B.; Drori, A.; Reuveni, N.; Hadar, R.; Cinar, R.; Nemirovski, A.; Tam, J. Proximal tubular cannabinoid-1 receptor regulates obesity-induced CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3518–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, H.; Huber, T.B.; Isermann, B.; Schiffer, M. CKD in diabetes: Diabetic kidney disease versus nondiabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakoura, N.; Hadchouel, J.; Chatziantoniou, C. Novel targets for therapy of renal fibrosis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2019, 67, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosova, D.; Levchenko, V.; Kravtsova, O.; Palygin, O.; Staruschenko, A. Acute and long-term effects of cannabinoids on hypertension and kidney injury. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6080–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Muragaki, Y.; Saika, S.; Roberts, A.B.; Ooshima, A. Targeted disruption of TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling protects against renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Lan, H. Smad3 signatures in renal inflammation and fibrosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 2795–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Tang, P.M.; Li, J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-β/smad signaling in renal fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Tang, H.; Jiang, H.; Sun, L.; Zhao, W.; Qian, F. ACPA alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β-Smad2/3 signaling-mediated lung fibroblast activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 835979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinaga, T.; Uwabe, K.; Naito, S.; Higashino, K.; Nakano, T.; Numata, Y.; Kihara, A. AM251 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, K.; Mehrpouya-Bahrami, P.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Cannabinoid receptor 1 blockade attenuates obesity and adipose tissue type 1 inflammation through miR-30e-5p regulation of delta-like-4 in macrophages and consequently downregulation of Th1 cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janiak, P.; Poirier, B.; Bidouard, J.; Cadrouvele, C.; Pierre, F.; Gouraud, L.; Barbosa, I.; Dedio, J.; Maffrand, J.P.; Le Fur, G.; et al. Blockade of cannabinoid CB1 receptors improves renal function, metabolic profile, and increased survival of obese Zucker rats. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Wan, H.; Chen, Y.; Xia, F.; Yu, S.; Wang, N.; Ye, L.; et al. Cardiovascular and renal burdens among patients with MAFLD and NAFLD in China. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 968766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udi, S.; Hinden, L.; Ahmad, M.; Drori, A.; Iyer, M.R.; Cinar, R.; Herman-Edelstein, M.; Tam, J. Dual inhibition of cannabinoid CB1 receptor and inducible NOS attenuates obesity-induced chronic kidney disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuyassin, B.; Badran, M.; Ayas, N.T.; Laher, I. Intermittent hypoxia causes histological kidney damage and increases growth factor expression in a mouse model of obstructive sleep apnea. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Gao, X.; Jia, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.J.; Liu, T.; Wang, M.T.; Yang, C.; et al. CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant protects against chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced bone metabolism disorder and destruction in rats. Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Hung, S.; Wang, H.; Lin, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Chang, M.Y.; Ho, L.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Liou, H.H.; et al. Sleep apnea and the risk of chronic kidney disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Sleep 2015, 38, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, T.; Dou, Z.; Wang, M.; Hu, Z.; Wang, B. CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant protects against chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced renal injury in rats. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, M.; Nematbakhsh, M. Renal ischemia/reperfusion injury; from pathophysiology to treatment. J. Renal Inj. Prev. 2015, 4, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Dong, W.; Remer, E.; Li, J.; Demirjian, S.; Zabell, J.; Campbell, S.C. Acute kidney injury after partial nephrectomy: Role of parenchymal mass reduction and ischemia and impact on subsequent functional recovery. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Haskó, G. Endocannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors in ischaemia-reperfusion injury and preconditioning. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, L.S.; Iannotti, F.A.; Veneziani, L.; Borelli-Tôrres, R.T.; De Maio, F.; Piscitelli, F.; Reis, R.A.M.; Di Marzo, V.; Einicker-Lamas, M. Experimental ischemia/reperfusion model impairs endocannabinoid signaling and Na+/K+ ATPase expression and activity in kidney proximal tubule cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 154, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Gong, D.; Hai, K.; Ke, B.; Zuo, Y. The critical role of cannabinoid receptor 2 in URB602-induced protective effects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat. Shock 2020, 54, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, Q.; Lin, X.; Ling, X.; Miao, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, N.; Hou, F.F.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor type 2 promotes kidney fibrosis through orchestrating β-catenin signaling. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 364–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothner, A.; Gov, T.; Hinden, L.; Nemirovski, A.; Tam, J.; Rosenzweig, B. Systemic changes in endocannabinoids and endocannabinoid-like molecules in response to partial nephrectomy-induced ischemia in humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, K.R.; Gadanec, L.K.; Qaradakhi, T.; Ali, B.A.; Zulli, A.; Apostolopoulos, V. Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury: Pathological mechanisms, pharmacological interventions, and genetic mitigations. Cancers 2021, 13, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lippard, S.J. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, F.; Klastersky, J. Nephrotoxicity induced by cancer chemotherapy with special emphasis on cisplatin toxicity. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1986, 8, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Ramesh, G.; Norbury, C.C.; Reeves, W.B. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-α produced by renal parenchymal cells. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. Cannabinoid pharmacology: The first 66 years. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S163–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneto, M.S.; Gorelick, D.A.; Desrosiers, N.A.; Hartman, R.L.; Pirard, S.; Huestis, M.A. Synthetic cannabinoids: Epidemiology, pharmacodynamics, and clinical implications. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 144, 12–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seely, K.A.; Lapoint, J.; Moran, J.H.; Fattore, L. Spice drugs are more than harmless herbal blends: A review of the pharmacology and toxicology of synthetic cannabinoids. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 39, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.E. Exposure to bath salts and synthetic tetrahydrocannabinol from 2009 to 2012 in the United States. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo, Y.; Takai, M.; Fujita, Y.; Sakamoto, T. A multicenter retrospective survey of poisoning after consumption of products containing novel psychoactive substances from 2013 to 2014 in Japan. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 2016, 42, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luciano, R.L.; Perazella, M.A. Nephrotoxic effects of designer drugs: Synthetic is not better! Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, R.J.; Caldicott, D.; Mountain, D.; Hill, S.L.; Lenton, S. A systematic review of adverse events arising from the use of synthetic cannabinoids and their associated treatment. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, A.; Akdam, H.; Avcıoğlu, B.Y.; Ersan, S. Synthetic cannabinoids in the kidneys. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2017, 63, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, R.; Zeng, X.; Upadhyay, K. Synthetic cannabinoid-associated acute interstitial nephritis: An emerging cause of pediatric acute kidney injury? Clin. Nephrol. Case Stud. 2023, 11, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazory, A.; Aiyer, R. Synthetic marijuana and acute kidney injury: An unforeseen association. Clin. Kidney J. 2013, 6, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Errico, S.; Zanon, M.; Radaelli, D.; Concato, M.; Padovano, M.; Scopetti, M.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in young synthetic cannabinoids abusers. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhanushali, G.K.; Jain, G.; Fatima, H.; Leisch, L.J.; Thornley-Brown, D. AKI associated with synthetic cannabinoids: A case series. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acute Kidney Injury Associated with Synthetic Cannabinoid Use—Multiple States. 2012. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6206a1.htm?s_cid=mm6206a1_w (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Riederer, A.M.; Campleman, S.L.; Carlson, R.G.; Boyer, E.W.; Manini, A.F.; Wax, P.M.; Brent, J.A.; Toxicology Investigators Consortium (ToxIC). Acute poisonings from synthetic cannabinoids—50 U.S. toxicology investigators consortium registry sites, 2010–2015. MMWR. Morb. Mort. Wkly Rep. 2016, 65, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.J.; Genelhu, V.; Di Marzo, V.; Francischetti, E.A. The endocannabinoid system--back to the scene of cardiometabolic risk factors control? Horm. Metab. Res. 2014, 46, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, C.; Di Marzo, V. The endocannabinoid system in energy homeostasis and the etiopathology of metabolic disorders. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.A.; Grieb, M.; Lutz, B. Central side-effects of therapies based on CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonists and antagonists: Focus on anxiety and depression. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 23, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, E.J.; Bousser, M.G.; Fox, K.A.; Creager, M.A.; Despres, J.P.; Easton, J.D.; Hamm, C.W.; Montalescot, G.; Steg, P.G.; Pearson, T.A.; et al. Rimonabant for prevention of cardiovascular events (CRESCENDO): A randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulp, A.; Zhang, Y.; Bortoff, K.; Seltzman, H.; Snyder, R.; Wiethe, R.; Amato, G.; Maitra, R. Pyrazole antagonists of the CB1 receptor with reduced brain penetration. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulp, A.; Bortoff, K.; Seltzman, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mathews, J.; Snyder, R.; Fennell, T.; Maitra, R. Design and synthesis of cannabinoid receptor 1 antagonists for peripheral selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 2820–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, R.; Iyer, M.R.; Kunos, G. The therapeutic potential of second and third generation CB1R antagonists. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 208, 107477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorvat, R.J.; Berbaum, J.; Seriacki, K.; McElroy, J.F. JD-5006 and JD-5037: Peripherally restricted (PR) cannabinoid-1 receptor blockers related to SLV-319 (Ibipinabant) as metabolic disorder therapeutics devoid of CNS liabilities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 6173–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Shui, F.; Liu, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, W.; Zheng, Z.; Fu, W.; Wang, L. Novel peripherally restricted cannabinoid 1 receptor selective antagonist TXX-522 with prominent weight-loss efficacy in diet induced obese mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluny, N.L.; Vemuri, V.K.; Chambers, A.P.; Limebeer, C.L.; Bedard, H.; Wood, J.T.; Lutz, B.; Zimmer, A.; Parker, L.A.; Makriyannis, A.; et al. A novel peripherally restricted cannabinoid receptor antagonist, AM6545, reduces food intake and body weight, but does not cause malaise, in rodents. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, B.G.; Neamatallah, T.; Hanafy, A.; El-Bassossy, H.M.; Binmahfouz, L.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Hasan, A.; El-Aziz, G.A.; Vemuri, K.; Makriyannis, A. Interference with TGFβ1-mediated inflammation and fibrosis underlies reno-protective effects of the CB1 receptor neutral antagonists AM6545 and AM4113 in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. Molecules 2021, 26, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barutta, F.; Bruno, G.; Mastrocola, R.; Bellini, S.; Gruden, G. The role of cannabinoid signaling in acute and chronic kidney diseases. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Liu, H.; Ke, B.; Jiang, J.; Wu, B. The peripheral CB1 receptor antagonist JD5037 attenuates liver fibrosis via a CB1receptor/β-arrestin1/Akt pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 2830–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, T.; Godlewski, G.; Cinar, R.; Bertola, A.; Szanda, G.; Liu, J.; Tam, J.; Han, T.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Skarulis, M.C.; et al. Activation of the Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages by endocannabinoids mediates beta cell loss in type 2 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, R.; Iyer, M.R.; Liu, Z.; Cao, Z.; Jourdan, T.; Erdelyi, K.; Godlewski, G.; Szanda, G.; Liu, J.; Park, J.K.; et al. Hybrid inhibitor of peripheral cannabinoid-1 receptors and inducible nitric oxide synthase mitigates liver fibrosis. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e87336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remiszewski, P.; Pędzińska-Betiuk, A.; Mińczuk, K.; Schlicker, E.; Klimek, J.; Dzięcioł, J.; Malinowska, B. Effects of the peripheral CB1 receptor antagonist JD5037 in mono– and polytherapy with the AMPK activator metformin in a monocrotaline-induced rat model of pulmonary hypertension. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 965613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinar, R.; Iyer, M.R.; Kunos, G. Dual inhibition of CB1 receptors and iNOS, as a potential novel approach to the pharmacological management of acute and long COVID-19. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechoulam, R.; Parker, L.A.; Gallily, R. Cannabidiol: An overview of some pharmacological aspects. J. Clinical Pharmacol. 2002, 42, 11S–19S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Bátkai, S.; Kunos, G. The endocannabinoid system as an emerging target of pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 389–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, M.; Cohen, I.; Bar-Sela, G. “The Two Sides of the Same Coin”-medical cannabis, cannabinoids and immunity: Pros and cons explained. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almogi-Hazan, O.; Or, R. Cannabis, the endocannabinoid system and immunity-the journey from the bedside to the bench and back. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.I.; Nguyen, L.C.; Oumeslakht, L.; Bensussan, A.; Ben Mkaddem, S. Cannabinoids as immune system modulators: Cannabidiol potential therapeutic approaches and limitations. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2023, 8, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J.M.; Carlini, E.A.; Pereira, A.E.; Ramos, O.L.; Pimentel, C.; Gagliardi, R.; Sanvito, W.L.; Lander, N.; Mechoulam, R. Chronic administration of cannabidiol to healthy volunteers and epileptic patients. Pharmacology 1980, 21, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Peters, M.; Murillo-Rodriguez, E.; Hanus, L.O. Cannabidiol–recent advances. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 1678–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Bagher, A.M.; Kelly, M.E.M.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. Cannabidiol is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4790–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Rajesh, M.; Patel, V.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Gao, B.; Haskó, G.; Pacher, P. Cannabidiol attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by decreasing oxidative/nitrosative stress, inflammation, and cell death. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 328, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinden, L.; Kogot-Levin, A.; Tam, J.; Leibowitz, G. Pathogenesis of diabesity-induced kidney disease: Role of kidney nutrient sensing. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 901–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Rajesh, M.; Pan, H.; Patel, V.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Bátkai, S.; Gao, B.; Haskó, G.; Pacher, P. Cannabinoid-2 receptor limits inflammation, oxidative/nitrosative stress, and cell death in nephropathy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barutta, F.; Piscitelli, F.; Pinach, S.; Bruno, G.; Gambino, R.; Rastaldi, M.P.; Salvidio, G.; Di Marzo, V.; Cavallo Perin, P.; Gruden, G. Protective role of cannabinoid receptor type 2 in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, B.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Kechrid, M.; Patel, V.; Tanchian, G.; Wink, D.A.; Gertsch, J.; Pacher, P. β-Caryophyllene ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in a cannabinoid 2 receptor-dependent manner. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutta, F.; Grimaldi, S.; Franco, I.; Bellini, S.; Gambino, R.; Pinach, S.; Corbelli, A.; Bruno, G.; Rastaldi, M.P.; Aveta, T.; et al. Deficiency of cannabinoid receptor of type 2 worsens renal functional and structural abnormalities in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Baggelaar, M.; Erdelyi, K.; Cao, Z.; Cinar, R.; Fezza, F.; Ignatowska-Janlowska, B.; Wilkerson, J.; van Gils, N.; Hansen, T.; et al. The novel, orally available and peripherally restricted selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist LEI-101 prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressly, J.D.; Mustafa, S.M.; Adibi, A.H.; Alghamdi, S.; Pandey, P.; Roy, K.K.; Doerksen, R.J.; Moore, B.M., Jr.; Park, F. Selective cannabinoid 2 receptor stimulation reduces tubular epithelial cell damage after renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 364, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressly, J.D.; Soni, H.; Jiang, S.; Wei, J.; Liu, R.; Moore, B.M.; Adebiyi, A.; Park, F. Activation of the cannabinoid receptor 2 increases renal perfusion. Physiol. Genom. 2019, 51, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojnar, E.; Erdelyi, K.; Matyas, C.; Zhao, S.; Paloczi, J.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Varga, Z.V.; Hasko, G.; Pacher, P. Cannabinoid-2 receptor activation ameliorates hepatorenal syndrome. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, M.L.; Regner, K.R.; Moore, B.M., 2nd; Park, F. Cannabinoid type 2 receptor activation reduces the progression of kidney fibrosis using a mouse model of unilateral ureteral obstruction. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2022, 7, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arceri, L.; Nguyen, T.K.; Gibson, S.; Baker, S.; Wingert, R.A. Cannabinoid Signaling in Kidney Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12101419
Arceri L, Nguyen TK, Gibson S, Baker S, Wingert RA. Cannabinoid Signaling in Kidney Disease. Cells. 2023; 12(10):1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12101419
Chicago/Turabian StyleArceri, Liana, Thanh Khoa Nguyen, Shannon Gibson, Sophia Baker, and Rebecca A. Wingert. 2023. "Cannabinoid Signaling in Kidney Disease" Cells 12, no. 10: 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12101419
APA StyleArceri, L., Nguyen, T. K., Gibson, S., Baker, S., & Wingert, R. A. (2023). Cannabinoid Signaling in Kidney Disease. Cells, 12(10), 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12101419






