Viability Analysis and High-Content Live-Cell Imaging for Drug Testing in Prostate Cancer Xenograft-Derived Organoids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PDXO Culture
2.2. PDXO Drug Testing
2.3. Assessment of PDXO Viability
2.4. Confocal High-Content Live-Cell Imaging of PDXOs
2.5. Image Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of PDXO Drug Testing Conditions
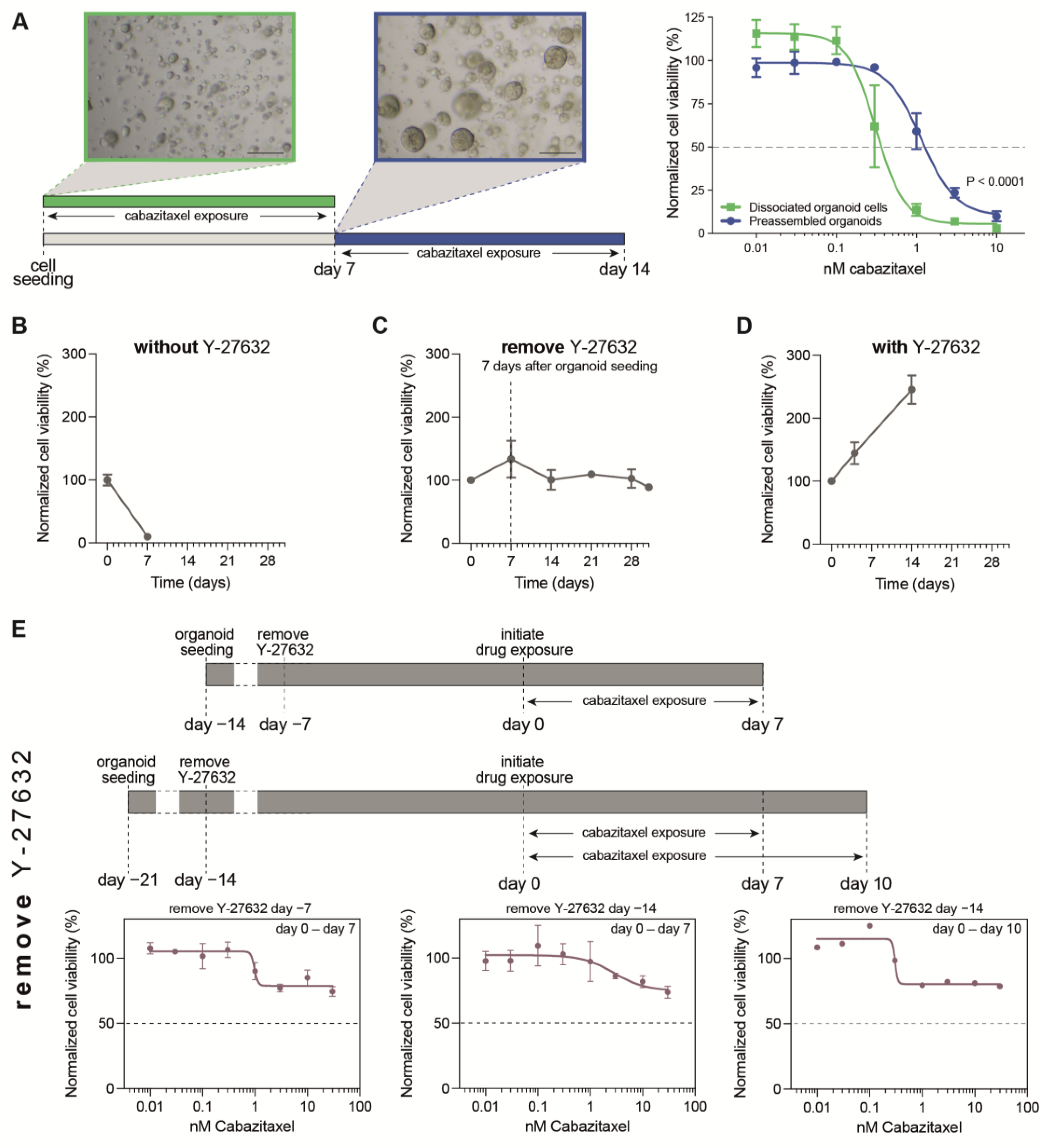

3.2. Optimization of Viability Assays for Drug Testing in PCa PDXOs
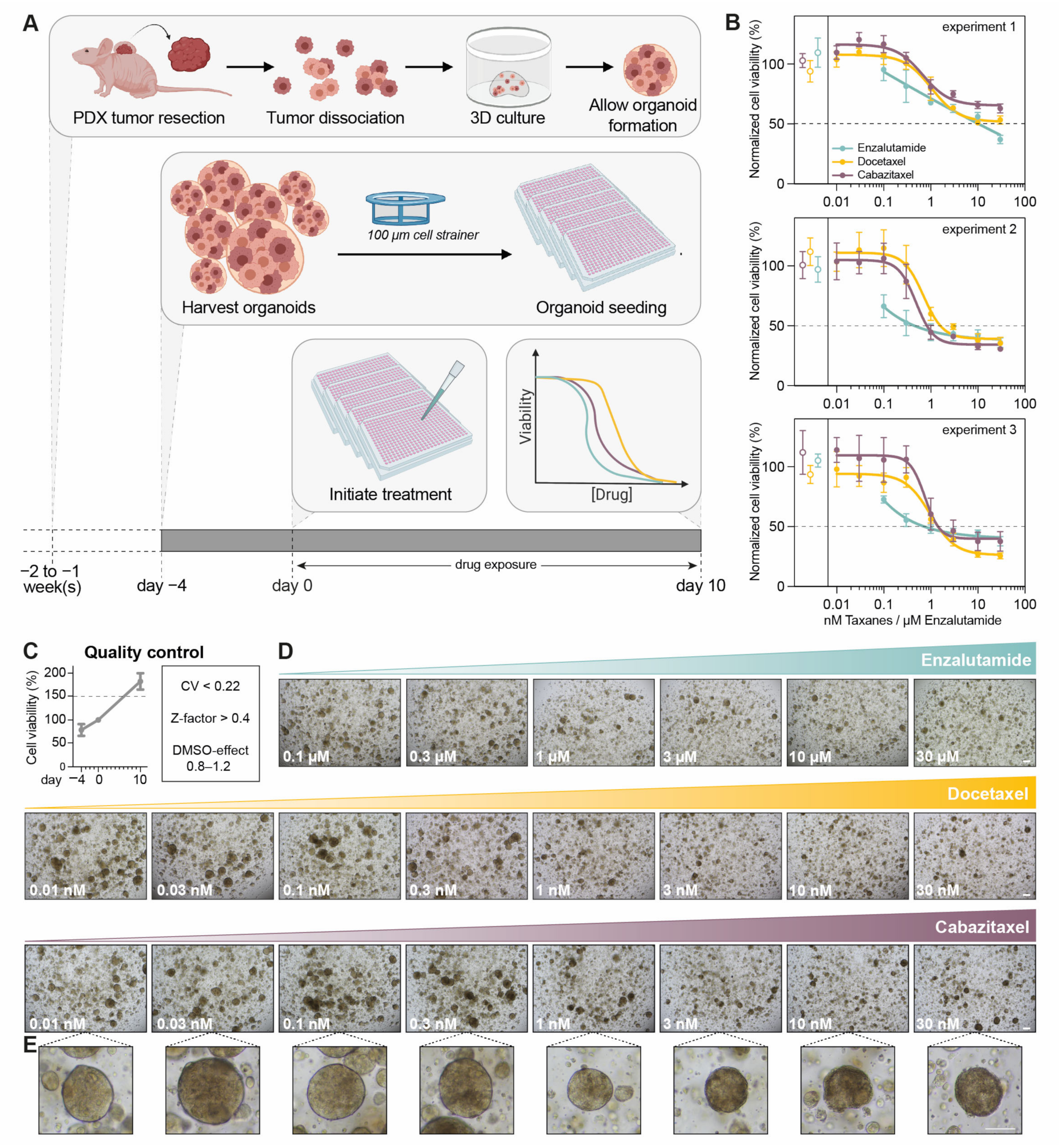
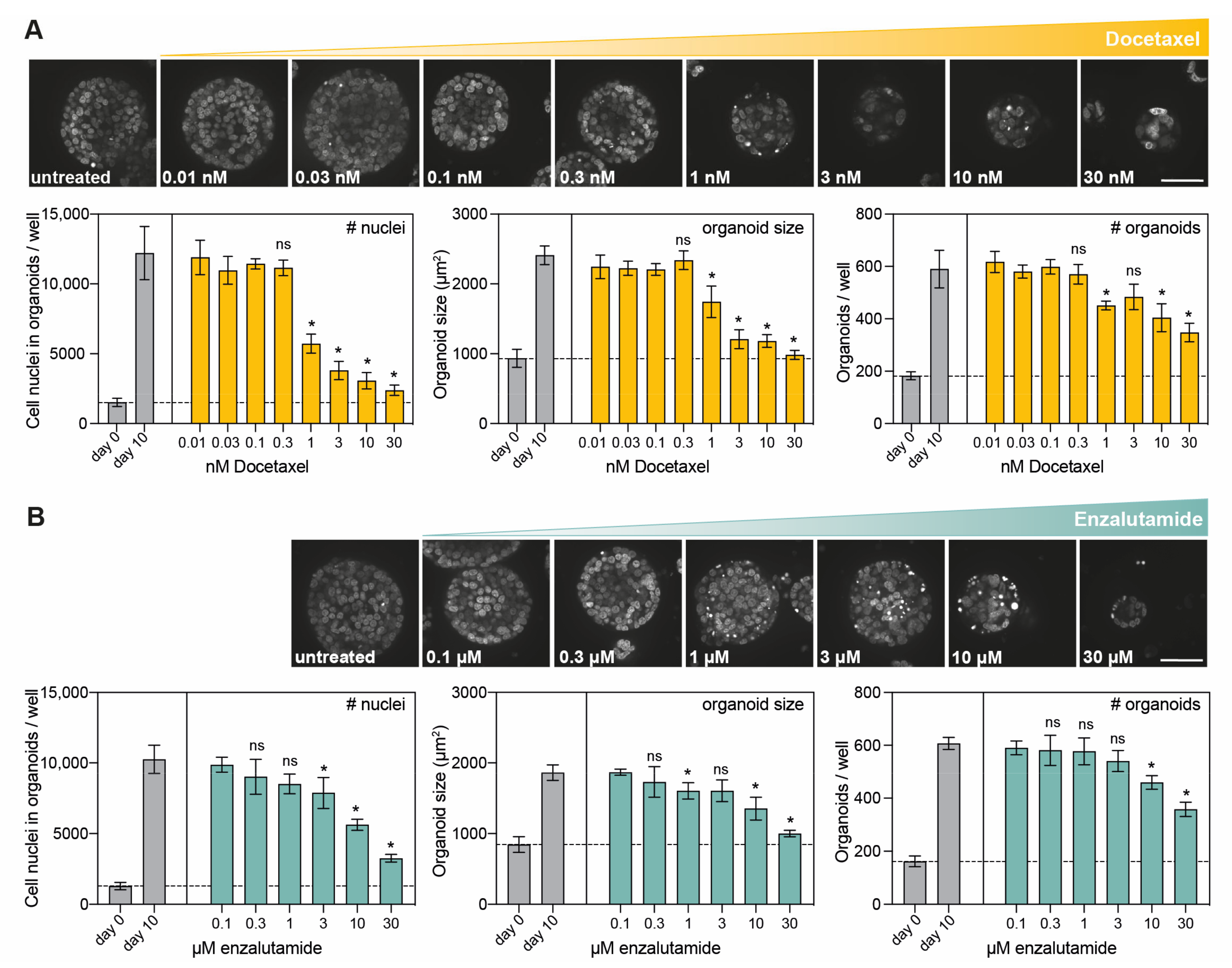
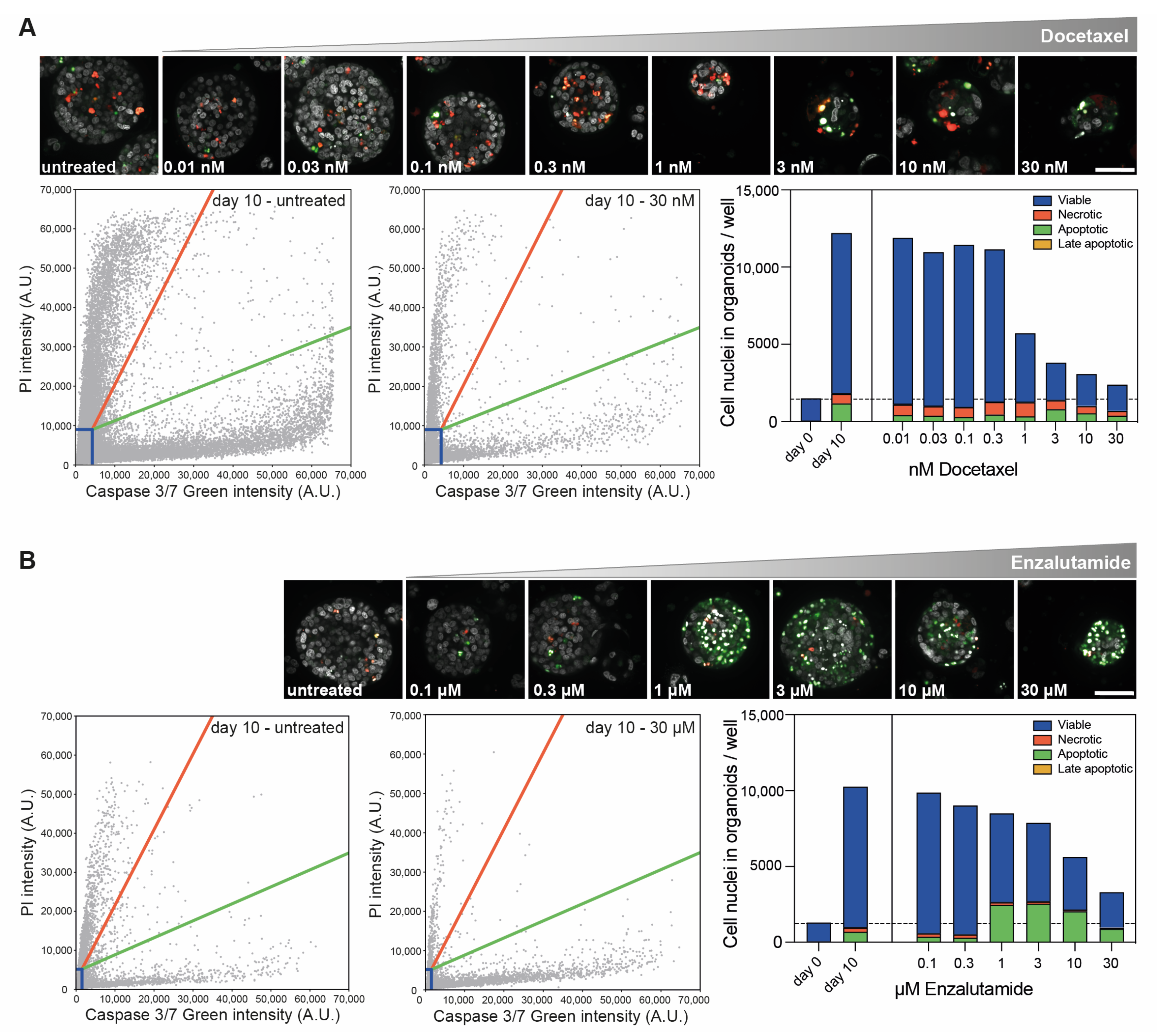
3.3. Confocal High-Content Live-Cell Imaging for Drug Testing in PCa PDXOs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Veninga, V.; Voest, E.E. Tumor organoids: Opportunities and challenges to guide precision medicine. Cancer Cell. 2021, 39, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Kumari, R.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Mao, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Tu, X.; An, X.; Chen, X.; et al. A living biobank of matched pairs of patient-derived xenografts and organoids for cancer pharmacology. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hemelryk, A.; Tomljanovic, I.; de Ridder, C.M.A.; Stuurman, D.C.; Teubel, W.J.; Erkens-Schulze, S.; Verhoef, E.I.; Remmers, S.; Mahes, A.J.; van Leenders, G.; et al. Patient-Derived Xenografts and Organoids Recapitulate Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer with Sustained Androgen Receptor Signaling. Cells 2022, 11, 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensink, G.E.; Elias, S.G.; Mullenders, J.; Koopman, M.; Boj, S.F.; Kranenburg, O.W.; Roodhart, J.M.L. Patient-derived organoids as a predictive biomarker for treatment response in cancer patients. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, B.M.; Kannan, M.; Langer, L.F.; Leibowitz, B.D.; Bentaieb, A.; Cancino, A.; Dolgalev, I.; Drummond, B.E.; Dry, J.R.; Ho, C.S.; et al. A pan-cancer organoid platform for precision medicine. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Peng, K.C.; Chen, Z.X.; Su, J.W.; Li, Y.F.; Li, W.F.; Gao, Q.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Chen, Y.Q.; et al. Using patient-derived organoids to predict locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer tumor response: A real-world study. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 100911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, J.E.; Muthuswamy, L.; Huang, L.; Akshinthala, D.; Perea, S.; Gonzalez, R.S.; Tsai, L.L.; Cohen, J.; Bockorny, B.; Bullock, A.J.; et al. Organoid Sensitivity Correlates with Therapeutic Response in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sui, X.; Song, F.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Lung cancer organoids analyzed on microwell arrays predict drug responses of patients within a week. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppala, T.T.; Zimmerman, J.W.; Suri, R.; Zlomke, H.; Ivey, G.D.; Szabolcs, A.; Shubert, C.R.; Cameron, J.L.; Burns, W.R.; Lafaro, K.J.; et al. Precision Medicine in Pancreatic Cancer: Patient-Derived Organoid Pharmacotyping Is a Predictive Biomarker of Clinical Treatment Response. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3296–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, V.; Wright, J.A.; Churchill, M.; Wang, T.; Rosati, R.; Lannagan, T.R.M.; Vrbanac, L.; Richardson, A.B.; Kobayashi, H.; Price, T.; et al. Medium-throughput Drug Screening of Patient-derived Organoids from Colorectal Peritoneal Metastases to Direct Personalized Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3662–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooft, S.N.; Weeber, F.; Schipper, L.; Dijkstra, K.K.; McLean, C.M.; Kaing, S.; van de Haar, J.; Prevoo, W.; van Werkhoven, E.; Snaebjornsson, P.; et al. Prospective experimental treatment of colorectal cancer patients based on organoid drug responses. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.; Barroso, M.; Chheda, M.G.; Clevers, H.; Elez, E.; Kaochar, S.; Kopetz, S.E.; Li, X.N.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Meyer, C.A.; et al. A path to translation: How 3D patient tumor avatars enable next generation precision oncology. Cancer Cell. 2022, 40, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Driehuis, E.; Kretzschmar, K.; Clevers, H. Establishment of patient-derived cancer organoids for drug-screening applications. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3380–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Olsen, K.A.; Bond, C.E.; Whitehall, V.L.J. The Efficacy of Using Patient-Derived Organoids to Predict Treatment Response in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Deng, J.; Ling, J.; Li, X.; Chiang, Y.J.; Koay, E.J.; Wang, H.; Burks, J.K.; Chiao, P.J.; Hurd, M.W.; et al. 3D imaging analysis on an organoid-based platform guides personalized treatment in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e151604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choung, S.; Sun, R.X.; Ung, N.; Hashemi, N.; Fong, E.J.; Lau, R.; Spiller, E.; Gasho, J.; Foo, J.; et al. Comparison of Cell and Organoid-Level Analysis of Patient-Derived 3D Organoids to Evaluate Tumor Cell Growth Dynamics and Drug Response. SLAS Discov. 2020, 25, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Compte, M.; Cardenas De La Hoz, E.; Peeters, S.; Smits, E.; Lardon, F.; Roeyen, G.; Vanlanduit, S.; Prenen, H.; Peeters, M.; Lin, A.; et al. Multiparametric Tumor Organoid Drug Screening Using Widefield Live-Cell Imaging for Bulk and Single-Organoid Analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 190, e64434. [Google Scholar]
- Vilgelm, A.E.; Bergdorf, K.; Wolf, M.; Bharti, V.; Shattuck-Brandt, R.; Blevins, A.; Jones, C.; Phifer, C.; Lee, M.; Lowe, C.; et al. Fine-Needle Aspiration-Based Patient-Derived Cancer Organoids. iScience 2020, 23, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.B.; Erkens-Schulze, S.; de Ridder, C.M.; Hermans, K.G.; Waltering, K.; Visakorpi, T.; Trapman, J.; Romijn, J.C.; van Weerden, W.M.; Jenster, G. Androgen receptor modifications in prostate cancer cells upon long-termandrogen ablation and antiandrogen treatment. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mout, L.; van Dessel, L.F.; Kraan, J.; de Jong, A.C.; Neves, R.P.L.; Erkens-Schulze, S.; Beaufort, C.M.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; van Riet, J.; Woo, T.L.C.; et al. Generating human prostate cancer organoids from leukapheresis enriched circulating tumour cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 150, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hemelryk, A.; Mout, L.; Erkens-Schulze, S.; French, P.J.; van Weerden, W.M.; van Royen, M.E. Modeling Prostate Cancer Treatment Responses in the Organoid Era: 3D Environment Impacts Drug Testing. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Ueno, M.; Kamiya, D.; Nishiyama, A.; Matsumura, M.; Wataya, T.; Takahashi, J.B.; Nishikawa, S.; Nishikawa, S.; Muguruma, K.; et al. A ROCK inhibitor permits survival of dissociated human embryonic stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francies, H.E.; Barthorpe, A.; McLaren-Douglas, A.; Barendt, W.J.; Garnett, M.J. Drug Sensitivity Assays of Human Cancer Organoid Cultures. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1576, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Valdez, J.M.; Zhang, B.; Wei, L.; Chang, J.; Xin, L. ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 suppresses dissociation-induced apoptosis of murine prostate stem/progenitor cells and increases their cloning efficiency. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putker, M.; Millen, R.; Overmeer, R.; Driehuis, E.; Zandvliet, M.; Clevers, H.; Boj, S.F.; Li, Q.X. Medium-Throughput Drug- and Radiotherapy Screening Assay using Patient-Derived Organoids. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 170, e62495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witte, C.J.; Espejo Valle-Inclan, J.; Hami, N.; Lohmussaar, K.; Kopper, O.; Vreuls, C.P.H.; Jonges, G.N.; van Diest, P.; Nguyen, L.; Clevers, H.; et al. Patient-Derived Ovarian Cancer Organoids Mimic Clinical Response and Exhibit Heterogeneous Inter- and Intrapatient Drug Responses. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Nickel, S.; Lieshout, R.; Lissek, S.M.; Leskova, M.; van der Laan, L.J.W.; Verstegen, M.M.A.; Christ, B.; Pampaloni, F. Label-Free Imaging Analysis of Patient-Derived Cholangiocarcinoma Organoids after Sorafenib Treatment. Cells 2022, 11, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.M.; Schuster, B.; Kashaf, S.S.; Liu, P.; Ben-Yishay, R.; Ishay-Ronen, D.; Izumchenko, E.; Shen, L.; Weber, C.R.; Bielski, M.; et al. OrganoID: A versatile deep learning platform for tracking and analysis of single-organoid dynamics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, N.; Ramm, S.; Luu, J.; Winter, J.M.; Selth, L.A.; Dwyer, A.R.; Frydenberg, M.; Grummet, J.; Sandhu, S.; Hickey, T.E.; et al. High-Throughput Imaging Assay for Drug Screening of 3D Prostate Cancer Organoids. SLAS Discov. 2021, 26, 1107–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, R.J.; Ernst, M.; Poh, A.R. Longitudinal quantification of mouse gastric tumor organoid viability and growth using luminescence and microscopy. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 102110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booij, T.H.; Price, L.S.; Danen, E.H.J. 3D Cell-Based Assays for Drug Screens: Challenges in Imaging, Image Analysis, and High-Content Analysis. SLAS Discov. 2019, 24, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Powell, R.T.; Yuan, X.; Bae, G.; Roarty, K.P.; Stossi, F.; Strempfl, M.; Toneff, M.J.; Johnson, H.L.; Mani, S.A.; et al. Morphological screening of mesenchymal mammary tumor organoids to identify drugs that reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deben, C.; De La Hoz, E.C.; Compte, M.L.; Van Schil, P.; Hendriks, J.M.H.; Lauwers, P.; Yogeswaran, S.K.; Lardon, F.; Pauwels, P.; Van Laere, S.; et al. OrBITS: Label-free and time-lapse monitoring of patient derived organoids for advanced drug screening. Cell. Oncol. 2022, 46, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laissue, P.P.; Alghamdi, R.A.; Tomancak, P.; Reynaud, E.G.; Shroff, H. Assessing phototoxicity in live fluorescence imaging. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garagna, S.; Merico, V.; Sebastiano, V.; Monti, M.; Orlandini, G.; Gatti, R.; Scandroglio, R.; Redi, C.A.; Zuccotti, M. Three-dimensional localization and dynamics of centromeres in mouse oocytes during folliculogenesis. J. Mol. Histol. 2004, 35, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenatri, M.; Bailly, D.; Maison, C.; Almouzni, G. Mouse centric and pericentric satellite repeats form distinct functional heterochromatin. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijmans, J.; van Lidth de Jeude, J.F.; Koo, B.K.; Rosekrans, S.L.; Wielenga, M.C.; van de Wetering, M.; Ferrante, M.; Lee, A.S.; Onderwater, J.J.; Paton, J.C.; et al. ER stress causes rapid loss of intestinal epithelial stemness through activation of the unfolded protein response. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.A.; Kakitani, M.; Zhao, J.; Oshima, T.; Tang, T.; Binnerts, M.; Liu, Y.; Boyle, B.; Park, E.; Emtage, P.; et al. Mitogenic influence of human R-spondin1 on the intestinal epithelium. Science 2005, 309, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Hemelryk, A.; Erkens-Schulze, S.; Lim, L.; de Ridder, C.M.A.; Stuurman, D.C.; Jenster, G.W.; van Royen, M.E.; van Weerden, W.M. Viability Analysis and High-Content Live-Cell Imaging for Drug Testing in Prostate Cancer Xenograft-Derived Organoids. Cells 2023, 12, 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12101377
Van Hemelryk A, Erkens-Schulze S, Lim L, de Ridder CMA, Stuurman DC, Jenster GW, van Royen ME, van Weerden WM. Viability Analysis and High-Content Live-Cell Imaging for Drug Testing in Prostate Cancer Xenograft-Derived Organoids. Cells. 2023; 12(10):1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12101377
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Hemelryk, Annelies, Sigrun Erkens-Schulze, Lifani Lim, Corrina M. A. de Ridder, Debra C. Stuurman, Guido W. Jenster, Martin E. van Royen, and Wytske M. van Weerden. 2023. "Viability Analysis and High-Content Live-Cell Imaging for Drug Testing in Prostate Cancer Xenograft-Derived Organoids" Cells 12, no. 10: 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12101377
APA StyleVan Hemelryk, A., Erkens-Schulze, S., Lim, L., de Ridder, C. M. A., Stuurman, D. C., Jenster, G. W., van Royen, M. E., & van Weerden, W. M. (2023). Viability Analysis and High-Content Live-Cell Imaging for Drug Testing in Prostate Cancer Xenograft-Derived Organoids. Cells, 12(10), 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12101377





