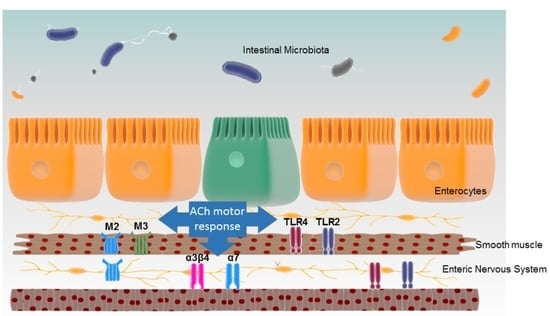
TLR2 and TLR4 Modulate Mouse Ileal Motility by the Interaction with Muscarinic and Nicotinic Receptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Muscle Contractility Studies
2.3. Gene Expression by Real-Time PCR
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Data Analysis and Statistics
2.6. Drugs and Solutions
3. Results
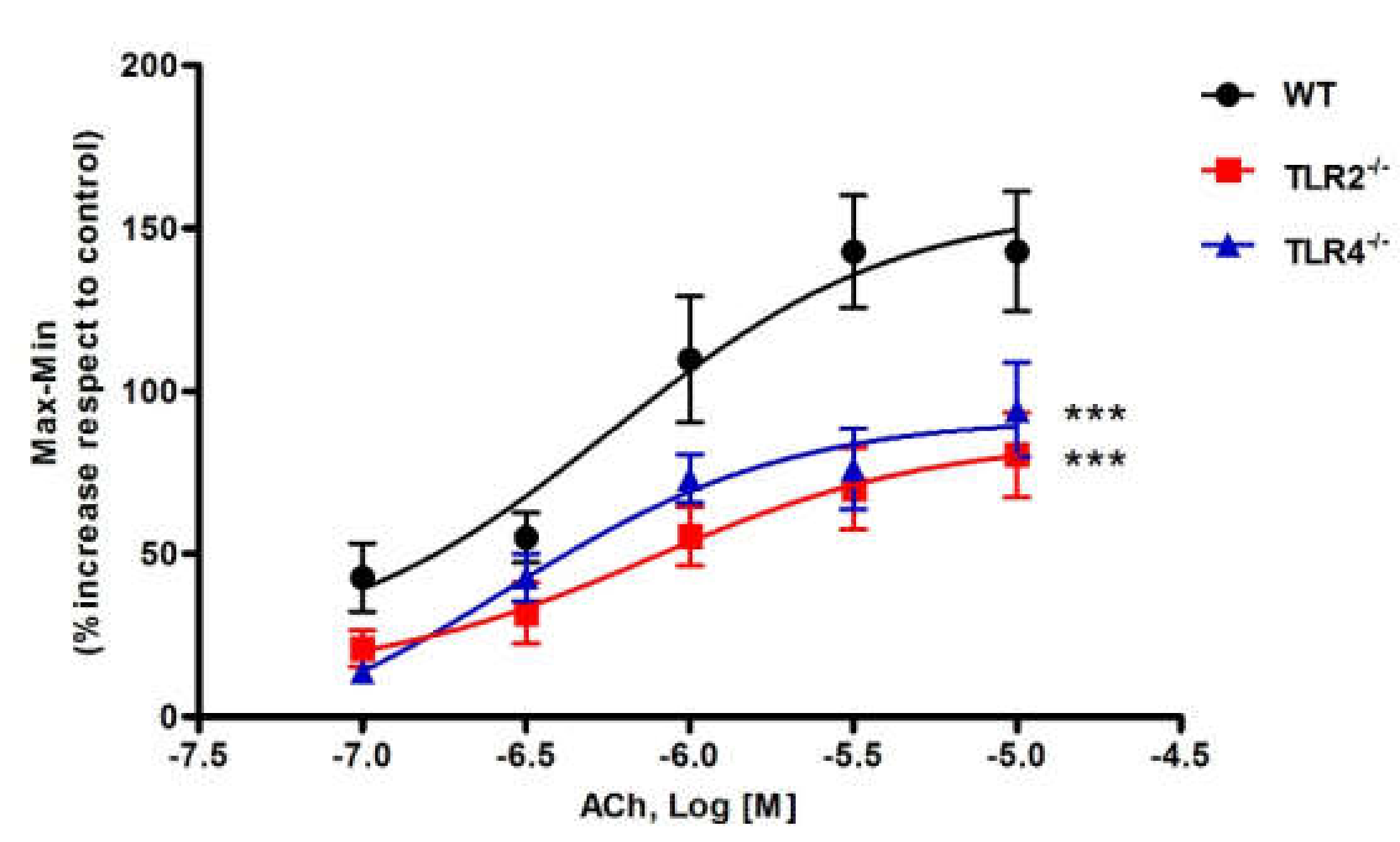
3.1. Effect of ACh on Ileal Motility of WT, TLR2−/− and TLR4−/− Mice
3.2. Effects of Muscarinic and Nicotinic ACh Receptors Antagonists on ACh-Evoked Response in Ileum from WT, TLR2−/− and TLR4−/− Mice
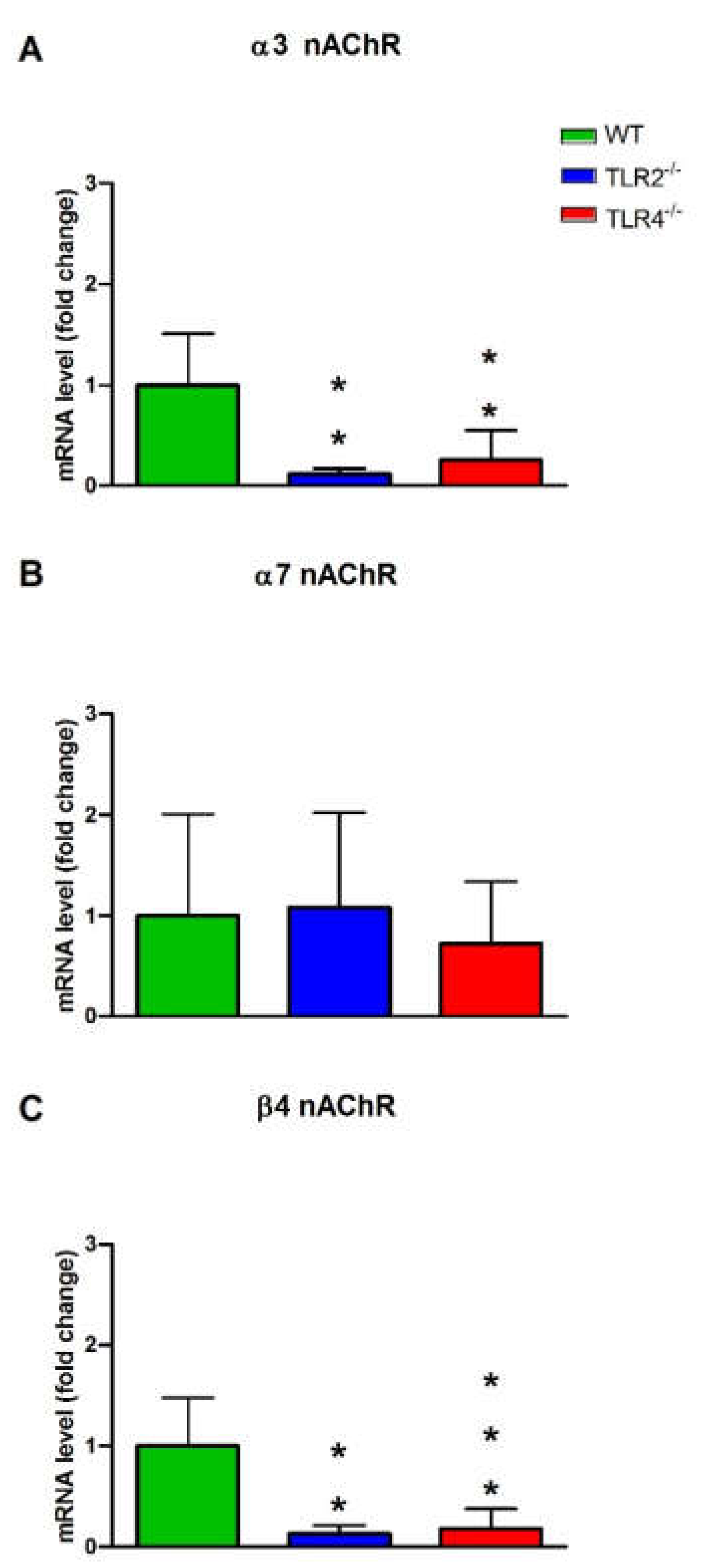
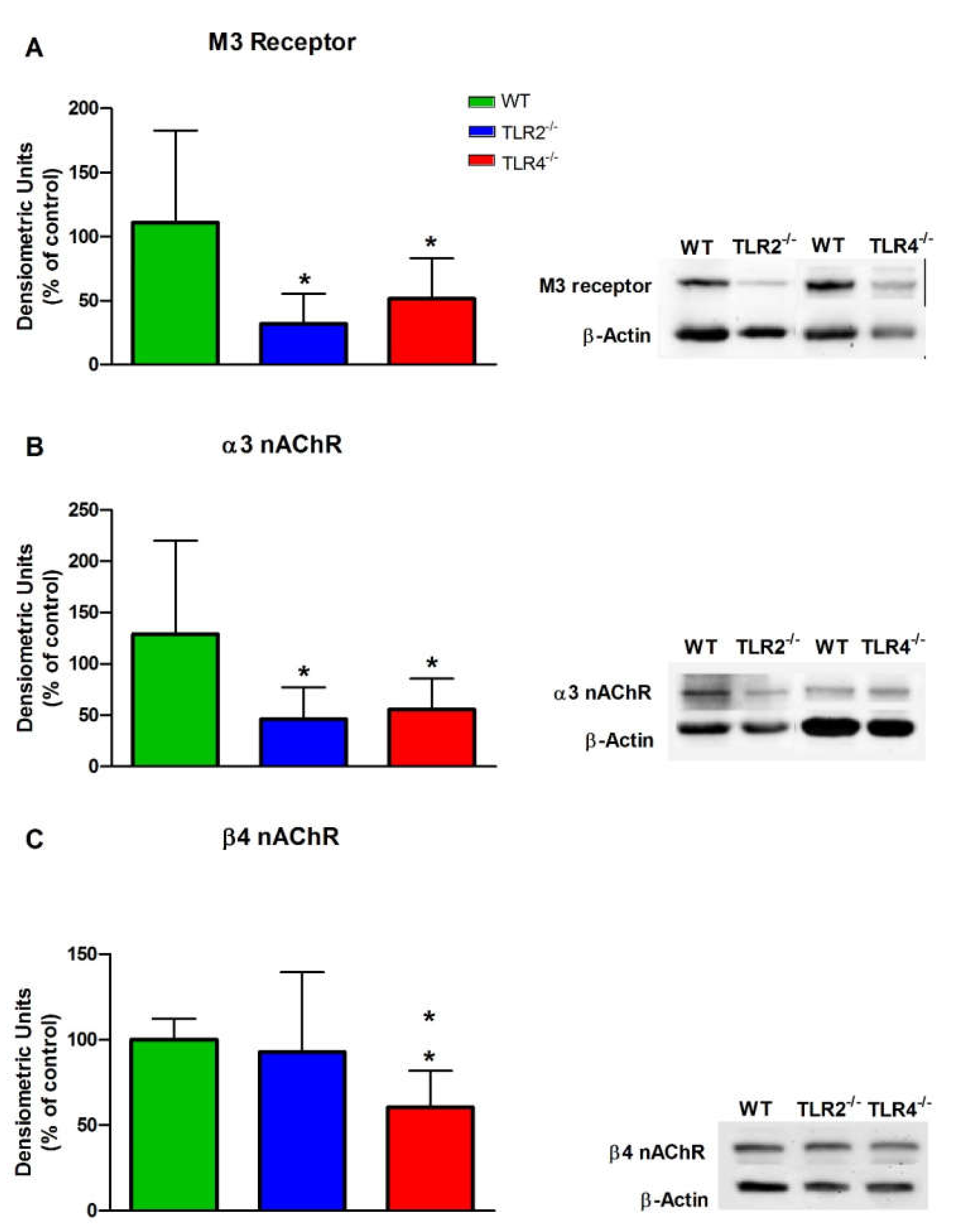
3.3. mRNA and Protein Expression Levels of Muscarinic and Nicotinic ACh Receptors in WT, TLR2−/− and TLR4−/− Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Enck, P.; Aziz, Q.; Barbara, G.; Farmer, A.D.; Fukudo, S.; Mayer, E.A.; Niesler, B.; Quigley, E.M.; Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Schemann, M.; et al. Irritable bowel syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, M.P.; Cicala, M.; Putignani, L.; Severi, C. Gastrointestinal neuromuscular apparatus: An underestimated target of gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9871–9879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, E.M. Microflora modulation of motility. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 17, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.V.; Wong, M.H.; Thelin, A.; Hansson, L.; Falk, P.G.; Gordon, J.I. Molecular analysis of commensal host-microbial relationships in the intestine. Science 2001, 291, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didari, T.; Mozaffari, S.; Nikfar, S.; Abdollahi, M. Effectiveness of probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome: Updated systematic review with meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3072–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimidi, E.; Christodoulides, S.; Scott, S.M.; Whelan, K. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics and the Gastrointestinal Microbiota on Gut Motility and Constipation. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, F.; Von Koschitzky, H.; Roblick, U.; Bruch, H.P.; Schulze, L.; Sonnenborn, U.; Bottner, M.; Wedel, T. Cell-free supernatants of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 modulate human colonic motility: Evidence from an in vitro organ bath study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2009, 21, 559-e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, M.P.; Altomare, A.; Stasi, E.; Marignani, M.; Severi, C.; Alloni, R.; Dicuonzo, G.; Morelli, L.; Coppola, R.; Cicala, M. Effect of acute mucosal exposure to Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on human colonic smooth muscle cells. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, S185–S190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2015, 109, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea-Donohue, T.; Notari, L.; Sun, R.; Zhao, A. Mechanisms of smooth muscle responses to inflammation. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, P.; Giron, M.C.; Qesari, M.; Porzionato, A.; Caputi, V.; Zoppellaro, C.; Banzato, S.; Grillo, A.R.; Spagnol, L.; De Caro, R.; et al. Toll-like receptor 2 regulates intestinal inflammation by controlling integrity of the enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barajon, I.; Serrao, G.; Arnaboldi, F.; Opizzi, E.; Ripamonti, G.; Balsari, A.; Rumio, C. Toll-like receptors 3, 4, and 7 are expressed in the enteric nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 2009, 57, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippova, L.V.; Malyshev, F.S.; Bykova, A.A.; Nozdrachev, A.D. Expression of toll-like receptors 4 in nerve plexuses of the rat duodenum, jejunum, and colon. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2012, 445, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputi, V.; Marsilio, I.; Cerantola, S.; Roozfarakh, M.; Lante, I.; Galuppini, F.; Rugge, M.; Napoli, E.; Giulivi, C.; Orso, G.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 4 Modulates Small Intestine Neuromuscular Function through Nitrergic and Purinergic Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcen, R.; Latorre, E.; Pardo, J.; Alcalde, A.I.; Murillo, M.D.; Grasa, L. Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 modulate the contractile response induced by serotonin in mouse ileum: Analysis of the serotonin receptors involved. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcen, R.; Latorre, E.; Pardo, J.; Alcalde, A.I.; Murillo, M.D.; Grasa, L. Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 exert opposite effects on the contractile response induced by serotonin in mouse colon: Role of serotonin receptors. Exp. Physiol. 2016, 101, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasa, L.; Abecia, L.; Pena-Cearra, A.; Robles, S.; Layunta, E.; Latorre, E.; Mesonero, J.E.; Forcen, R. TLR2 and TLR4 interact with sulfide system in the modulation of mouse colonic motility. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, Y.; Komori, S.; Matsuyama, H.; Kitazawa, T.; Unno, T. Functions of Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes in Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle: A Review of Studies with Receptor-Knockout Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 20926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Nakajima, M.; Teraoka, H.; Unno, T.; Komori, S.; Yamada, M.; Kitazawa, T. Muscarinic receptor subtypes involved in regulation of colonic motility in mice: Functional studies using muscarinic receptor-deficient mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, A.M.; Peck, C.J.; Liu, L.; Burcher, E.; Hutson, J.M.; Southwell, B.R. Localization of muscarinic receptors M1R, M2R and M3R in the human colon. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papke, R.L. Merging old and new perspectives on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 89, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foong, J.P.; Hirst, C.S.; Hao, M.M.; McKeown, S.J.; Boesmans, W.; Young, H.M.; Bornstein, J.C.; Vanden Berghe, P. Changes in Nicotinic Neurotransmission during Enteric Nervous System Development. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 7106–7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ren, J.; Brown, E.; Schneider, D.; Caraballo-Lopez, Y.; Galligan, J.J. Pharmacological properties of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed by guinea pig small intestinal myenteric neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, J.; Wallich, R.; Martin, P.; Urban, C.; Rongvaux, A.; Flavell, R.A.; Mullbacher, A.; Borner, C.; Simon, M.M. Granzyme B-induced cell death exerted by ex vivo CTL: Discriminating requirements for cell death and some of its signs. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.K.; Gray, R.R.; Reaves, C.B.; Butler, D.L.; Chiang, P.K. Induced release of acetylcholine from guinea pig ileum longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus by anatoxin-a. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992, 263, 997–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, K.; Takano, Y.; Kamiya, H. Pharmacological profiles of muscarinic receptors in the longitudinal smooth muscle of guinea pig ileum. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 62, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gericke, A.; Sniatecki, J.J.; Mayer, V.G.; Goloborodko, E.; Patzak, A.; Wess, J.; Pfeiffer, N. Role of M1, M3, and M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in cholinergic dilation of small arteries studied with gene-targeted mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H1602–H1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedmi, M.; Beaudet, A.L.; Orr-Urtreger, A. Mice lacking neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor β4-subunit and mice lacking both α5- and β4-subunits are highly resistant to nicotine-induced seizures. Physiol. Genom. 2004, 17, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somm, E.; Guerardel, A.; Maouche, K.; Toulotte, A.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F.; Maskos, U.; Huppi, P.S.; Schwitzgebel, V.M. Concomitant α7 and β2 nicotinic AChR subunit deficiency leads to impaired energy homeostasis and increased physical activity in mice. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014, 112, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, B.M.; Merriam, L.A.; Tompkins, J.D.; Vizzard, M.A.; Parsons, R.L. Decrease in neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit and PSD-93 transcript levels in the male mouse MPG after cavernous nerve injury or explant culture. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 305, F1504–F1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchholz, B.M.; Chanthaphavong, R.S.; Bauer, A.J. Nonhemopoietic cell TLR4 signaling is critical in causing early lipopolysaccharide-induced ileus. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6744–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killoran, K.E.; Miller, A.D.; Uray, K.S.; Weisbrodt, N.W.; Pautler, R.G.; Goyert, S.M.; van Rooijen, N.; Conner, M.E. Role of innate immunity and altered intestinal motility in LPS- and MnCl2-induced intestinal intussusception in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G445–G453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tattoli, I.; Petitta, C.; Scirocco, A.; Ammoscato, F.; Cicenia, A.; Severi, C. Microbiota, innate immune system, and gastrointestinal muscle: Ongoing studies. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, S6–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barona, I.; Fagundes, D.S.; Gonzalo, S.; Grasa, L.; Arruebo, M.P.; Plaza, M.A.; Murillo, M.D. Role of TLR4 and MAPK in the local effect of LPS on intestinal contractility. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, S.; Valero, M.S.; Martinez de Salinas, F.; Vergara, C.; Arruebo, M.P.; Plaza, M.A.; Murillo, M.D.; Grasa, L. Roles of Toll-Like Receptor 4, IkappaB Kinase, and the Proteasome in the Intestinal Alterations Caused by Sepsis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, G.W.; Ehlert, F.J. Contractile roles of the M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors in the guinea pig colon. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 284, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Papke, R.L.; Dwoskin, L.P.; Crooks, P.A.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; McIntosh, J.M.; Stokes, C. Extending the analysis of nicotinic receptor antagonists with the study of α6 nicotinic receptor subunit chimeras. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thomsen, M.S.; Zwart, R.; Ursu, D.; Jensen, M.M.; Pinborg, L.H.; Gilmour, G.; Wu, J.; Sher, E.; Mikkelsen, J.D. α7 and β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subunits Form Heteromeric Receptor Complexes that Are Expressed in the Human Cortex and Display Distinct Pharmacological Properties. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galligan, J.J. Nerve terminal nicotinic cholinergic receptors on excitatory motoneurons in the myenteric plexus of guinea pig intestine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 291, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Obaid, A.L.; Nelson, M.E.; Lindstrom, J.; Salzberg, B.M. Optical studies of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in the guinea-pig enteric nervous system. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 2981–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hayashi, E.; Yamada, S.; Mori, M. Comparative studies on anti-nicotinic action of hexamethonium, mecamylamine and adenosine in the guinea pig isolated ileum. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1977, 27, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwelyn, V.; Lefebvre, R.A. 5-HT4 receptors facilitate cholinergic neurotransmission throughout the murine gastrointestinal tract. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e13064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonzo-Mendez, M.A.; Alcantara-Hernandez, R.; Garcia-Sainz, J.A. Novel Structural Approaches to Study GPCR Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 18, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Fernandez, W.; Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Alea, M.P.; Garcia-Mesa, Y.; Garriga, P. Altered trafficking and unfolded protein response induction as a result of M3 muscarinic receptor impaired N-glycosylation. Glycobiology 2011, 21, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, E.X.; Pereira, E.F.; Alkondon, M.; Rogers, S.W. Mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: From structure to function. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 73–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasa, L.; Abecia, L.; Forcen, R.; Castro, M.; de Jalon, J.A.; Latorre, E.; Alcalde, A.I.; Murillo, M.D. Antibiotic-Induced Depletion of Murine Microbiota Induces Mild Inflammation and Changes in Toll-like Receptor Patterns and Intestinal Motility. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, C.; Duncan, G.S.; Brustle, A.; Brenner, D.; Tusche, M.W.; Olofsson, P.S.; Rosas-Ballina, M.; Tracey, K.J.; Mak, T.W. Lymphocyte-derived ACh regulates local innate but not adaptive immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, J.; Musette, P.; Douin-Echinard, V.; Laude, K.; Henry, J.P.; Arnal, J.F.; Thuillez, C.; Richard, V. Toll-like receptors 2-deficient mice are protected against postischemic coronary endothelial dysfunction. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishibe, M.; Griffin, T.M.; Radek, K.A. Keratinocyte nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation modulates early TLR2-mediated wound healing responses. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Kimura, S.; Takada, N.; Takemura, M.; Iwamoto, M.; Hisaoka-Nakashima, K.; Nakata, Y.; Morioka, N. Stimulation of toll-like receptor 4 downregulates the expression of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors via histone deacetylase in rodent microglia. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 138, 104751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Reference | GenBank Accession Number | Forward and Reverse Primers |
|---|---|---|---|
| mAChRs M2 | [28] | NM_203491.3 | CGGACCACAAAAATGGCAGGCAT CCATCACCACCAGGCATGTTGTTGT |
| mAChRs M3 | [28] | NM_033269.4 | CCTCTTGAAGTGCTGCGTTCTGACC TGCCAGGAAGCCAGTCAAGAATGC |
| nAChRs α3 | [29] | NM_145129.3 | GTGGAGTTCATGCGAGTCCCTG TAAAGATGGCCGGAGGGATCC |
| nAChRs α7 | [30] | NM_007390.3 | CAGCAGCTATATCCCCAATGG GGCTCTTTGCAGCATTCATAGA |
| nAChRs β4 | [31] | NM_148944.4 | TGTACAACAATGCCGATGGG CCTGTGGGTTCACTGTCCTT |
| HPRT | [16] | NM_013556.2 | CTGGTGAAAAGGACCTCTCGAA CTGAAGTACTCATTATAGTCAAGGGCAT |
| GAPDH | [16] | NM_008084 | AACGACCCCTTCATTGAC TCCACGACATACTCAGCAC |
| WT | TLR2−/− | TLR4−/− | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LogEC50 | EC50 (µM) | LogEC50 | EC50 (µM) | LogEC50 | EC50 (µM) | |
| (95% Confidence Intervals) | n | (95% Confidence Intervals) | n | (95% Confidence Intervals) | n | |
| ACh | −6.234 | 0.58 | −6.123 | 0.75 | −6.560 | 0.27 |
| (−6.944 to −5.524) | n = 16 | (−6.946 to −5.300) | n = 29 | (−7.336 to −5.784) | n = 25 | |
| AF-DX 116 + ACh | −5.787 | 1.63 | −6.224 | 0.59 | −7.140 | 0.07 |
| (−7.786 to −3.788) | n = 13 | (−6.963 to −5.484) | n = 11 | (−10.268 to −4.011) | n = 11 | |
| 4-DAMP + ACh | −6.106 | 0.78 | −6.727 | 0.18 | - | - |
| (−7.238 to −4.974) | n = 9 | (−10.217 to −3.237) | n = 8 | n = 12 | ||
| Mecamylamine + ACh | −6.063 | 0.86 | −5.949 | 1.12 | −7.178 | 0.07 |
| (−7.330 to −4.797) | n = 8 | (−6.801 to −5.097) | n = 8 | (−9.097 to −5.259) | n = 11 | |
| α-Bungarotoxin + ACh | −5.874 | 1.33 | −5.890 | 1.28 | −6.245 | 0.56 |
| (−6.385 to −5.362) | n = 10 | (−6.612 to −5.169) | n = 11 | (−7.162 to −5.329) | n = 9 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Layunta, E.; Forcén, R.; Grasa, L. TLR2 and TLR4 Modulate Mouse Ileal Motility by the Interaction with Muscarinic and Nicotinic Receptors. Cells 2022, 11, 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111791
Layunta E, Forcén R, Grasa L. TLR2 and TLR4 Modulate Mouse Ileal Motility by the Interaction with Muscarinic and Nicotinic Receptors. Cells. 2022; 11(11):1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111791
Chicago/Turabian StyleLayunta, Elena, Raquel Forcén, and Laura Grasa. 2022. "TLR2 and TLR4 Modulate Mouse Ileal Motility by the Interaction with Muscarinic and Nicotinic Receptors" Cells 11, no. 11: 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111791
APA StyleLayunta, E., Forcén, R., & Grasa, L. (2022). TLR2 and TLR4 Modulate Mouse Ileal Motility by the Interaction with Muscarinic and Nicotinic Receptors. Cells, 11(11), 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111791