Comprehensive Omics Analysis of a Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Chemoresistant Oncogenic Signatures in Colorectal Cancer Cell with Antitumor Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
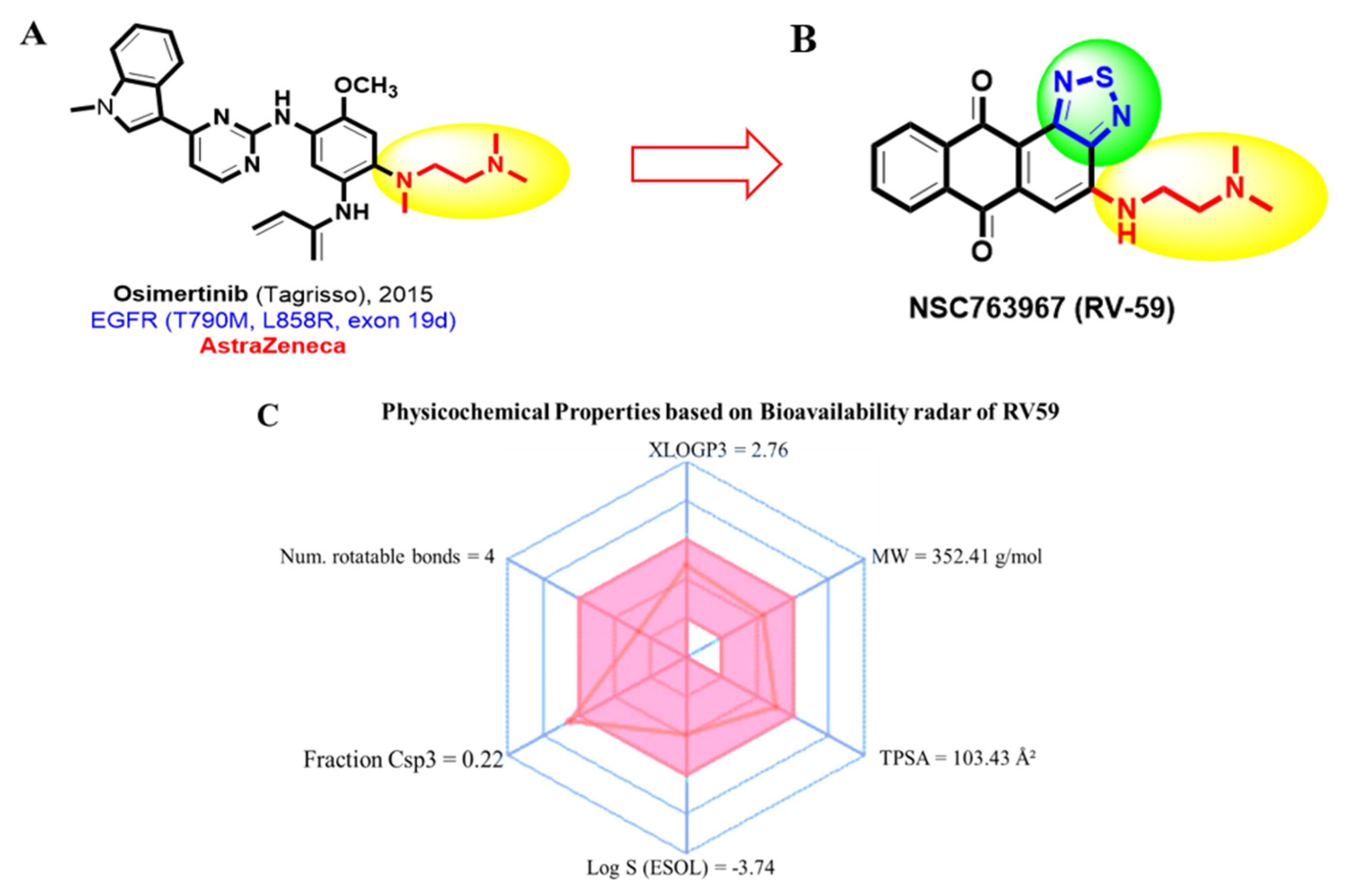
2.1. Identifying Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Classes of RV59
2.2. Gene Expression Microarray Data Extraction
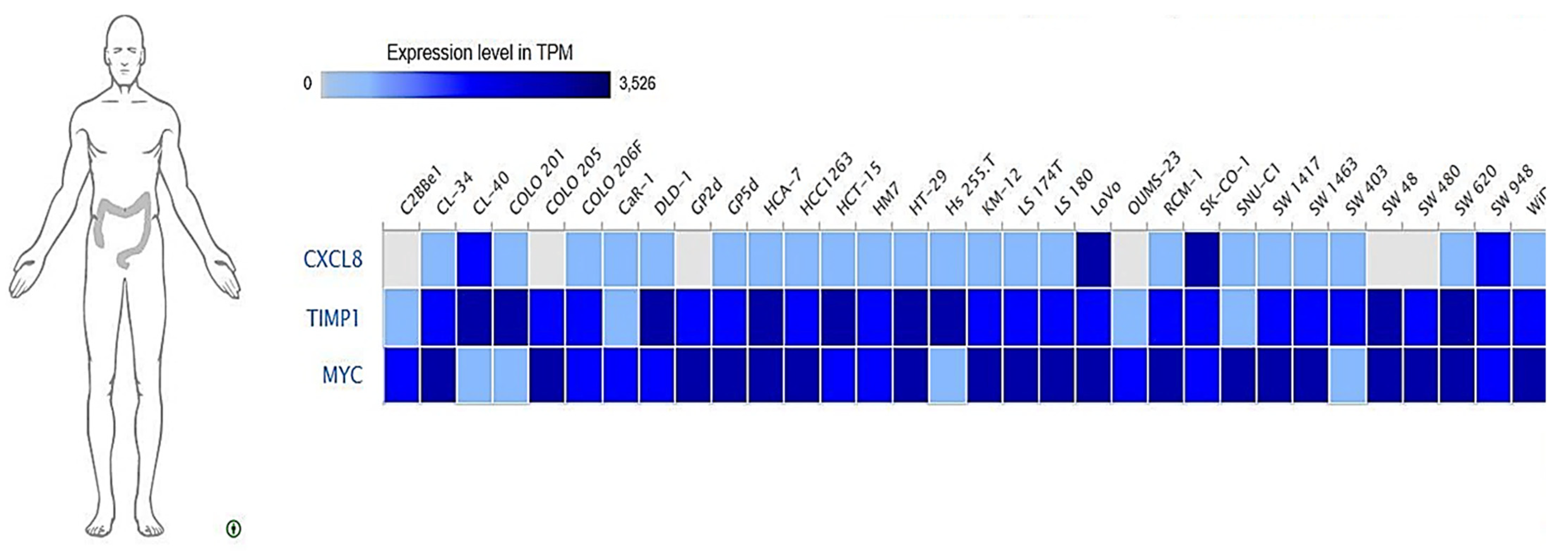
2.3. Validation of MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Expression Levels in CRC
2.4. Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Network, Gene Ontology (GO), and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway Analyses
2.5. Interpretation of Gene Co-Expression in MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Genes Network
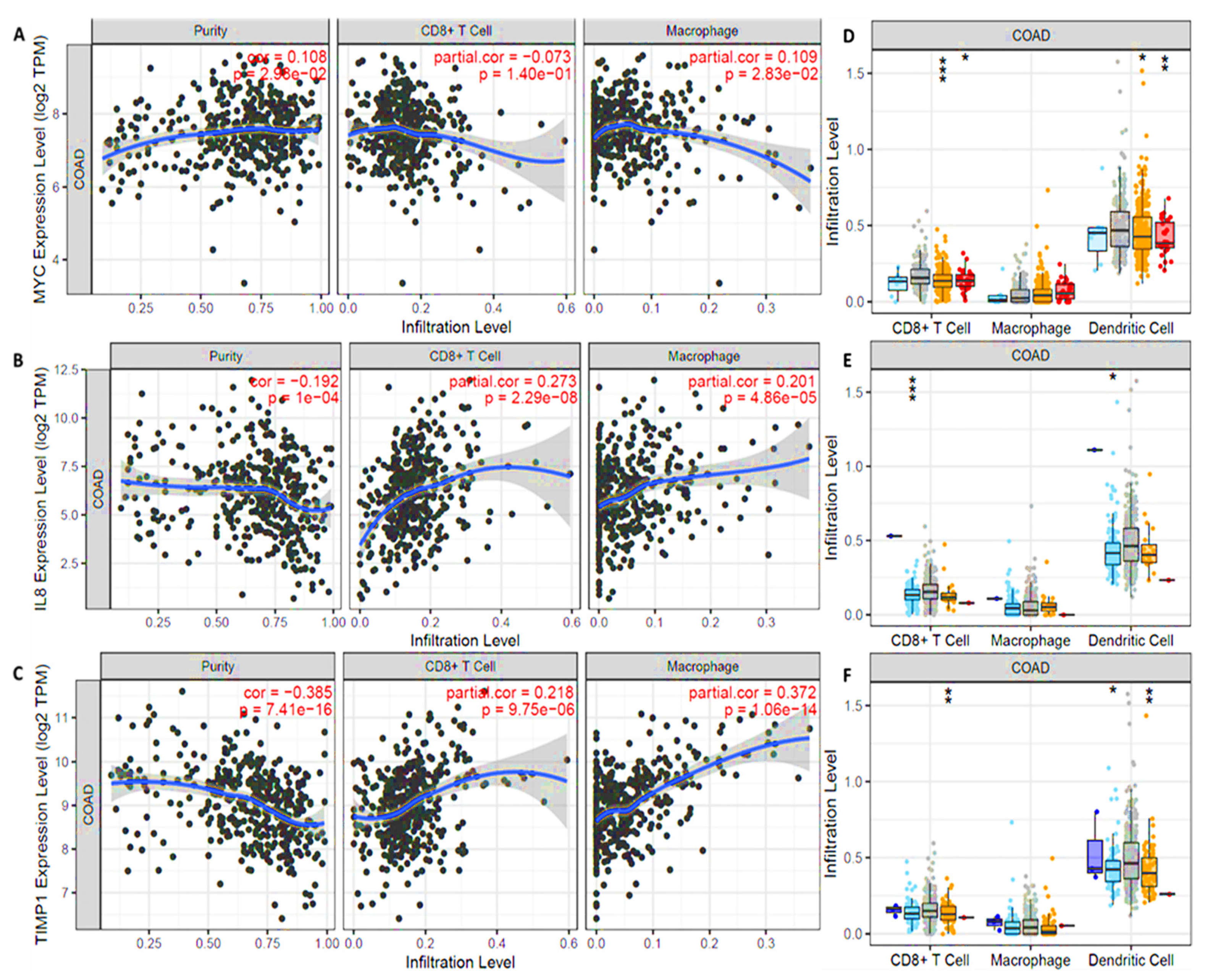
2.6. Correlation Analysis of MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Expressions and Tumor Infiltration Levels
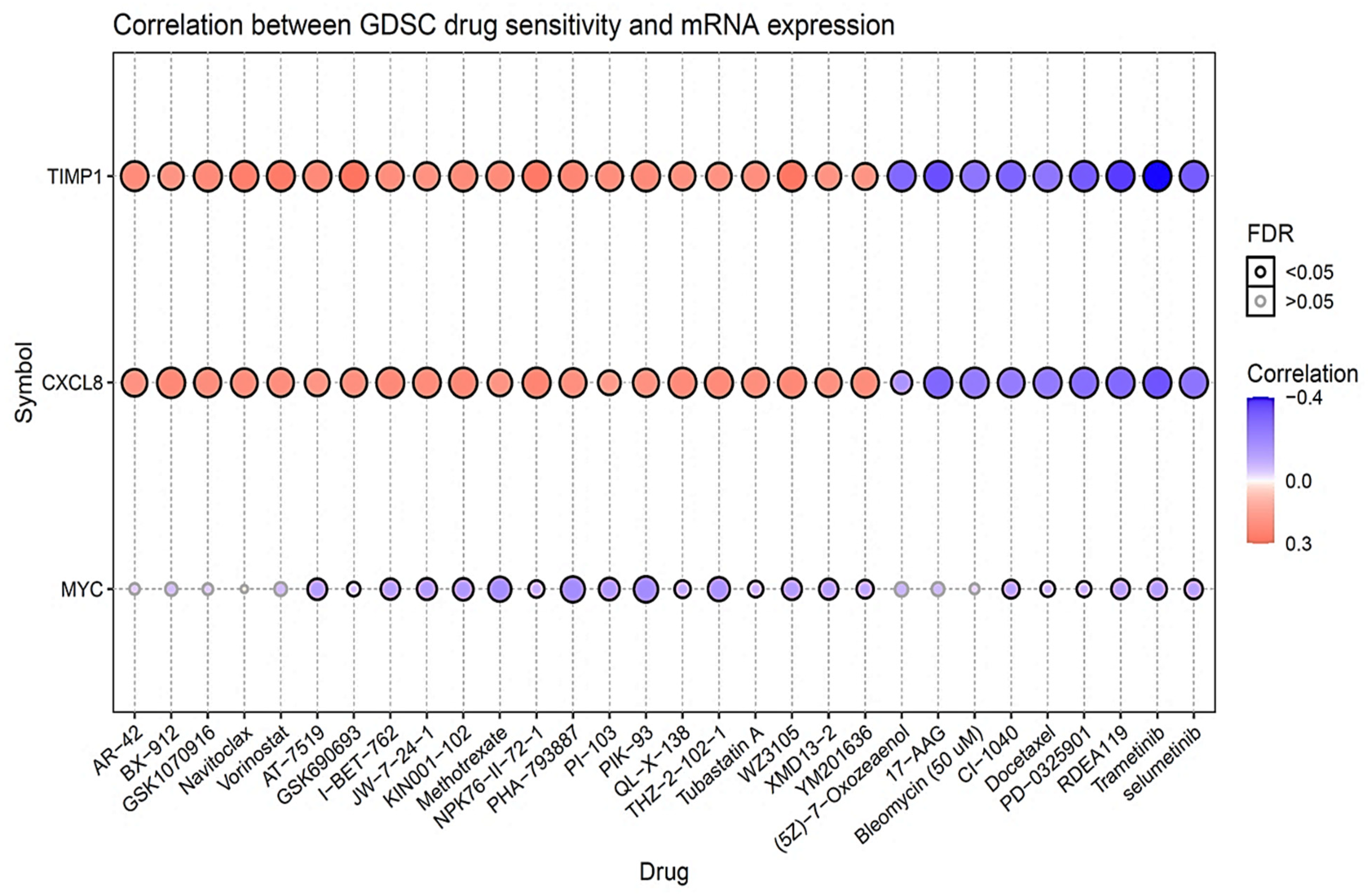
2.7. Drug Sensitivity Analysis of MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Oncogenes
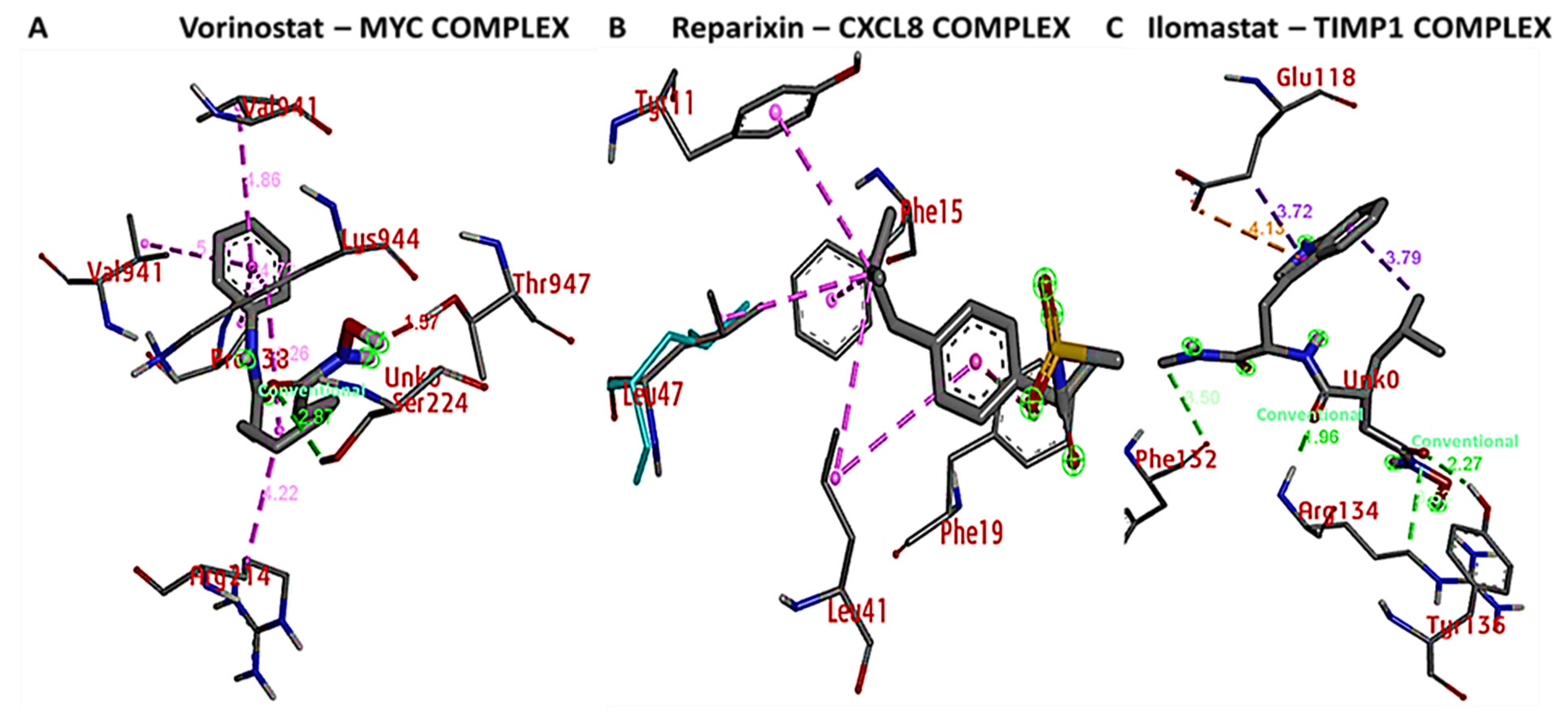
2.8. Molecular Docking of Protein-Ligand Interactions
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Oncogenes Are Potential Drug Targets for RV59
3.2. RV59 Passed the Required Drug-Likeness Criteria
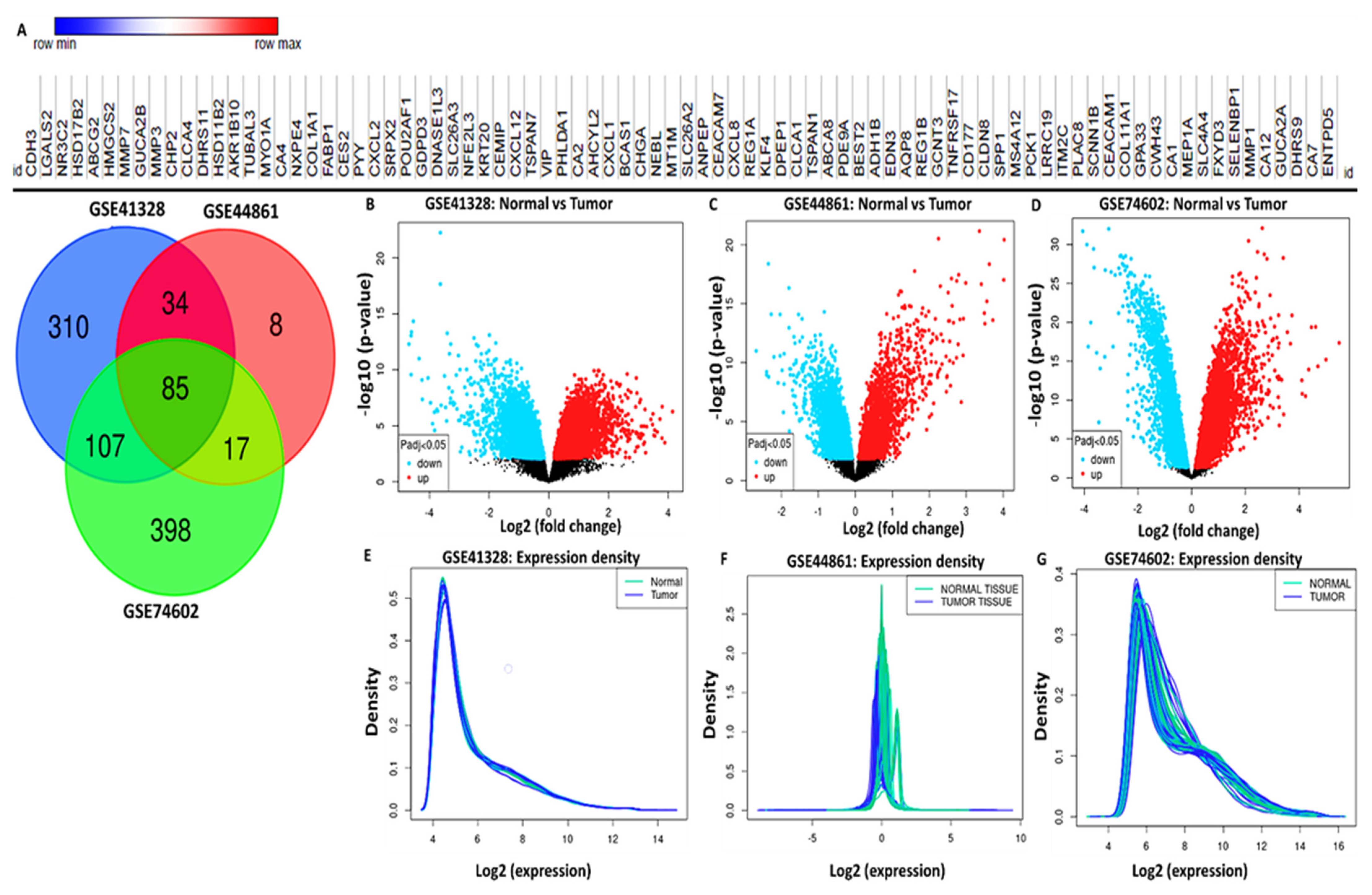
3.3. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in CRC
3.4. Validation of MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Expression Levels in CRC
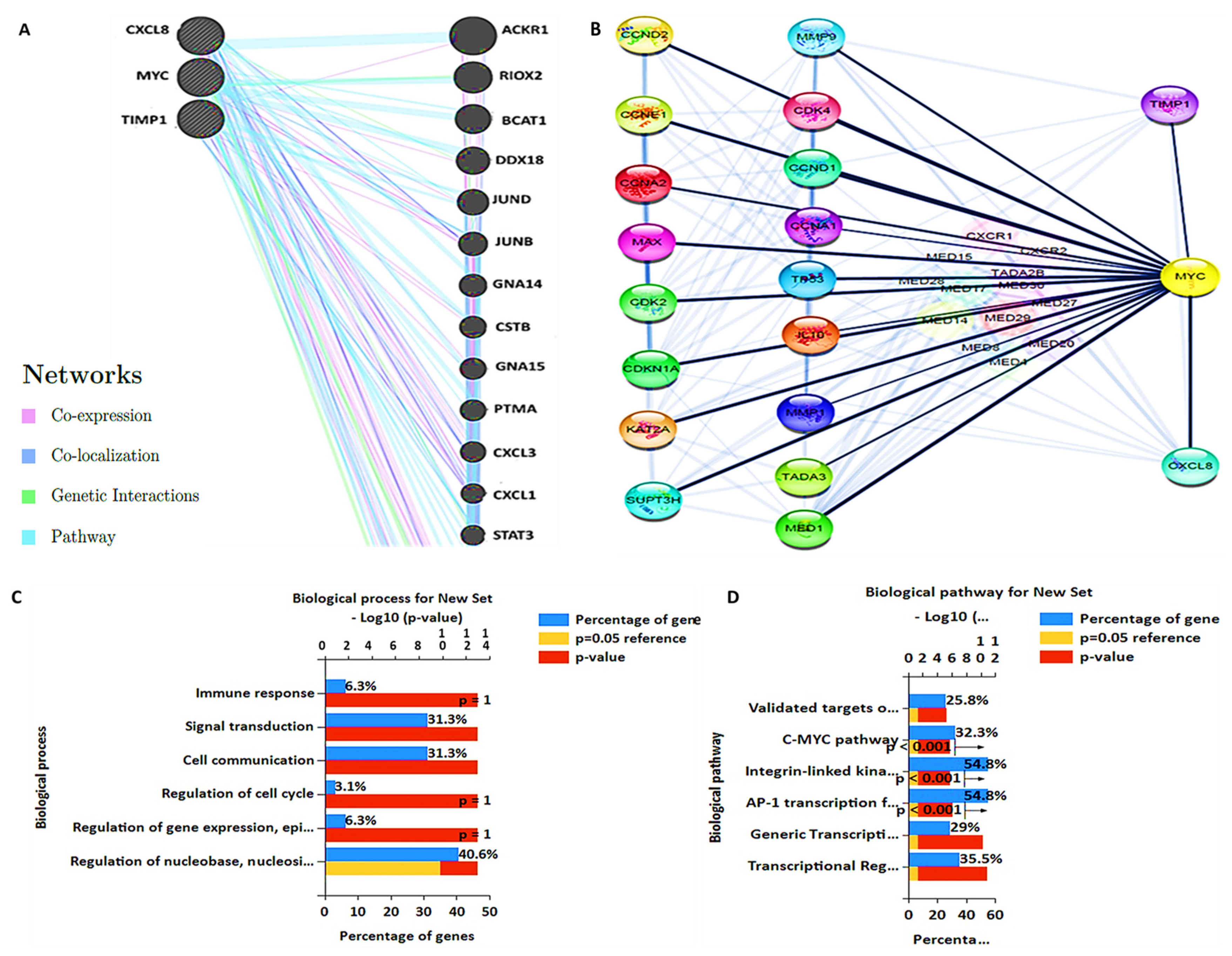
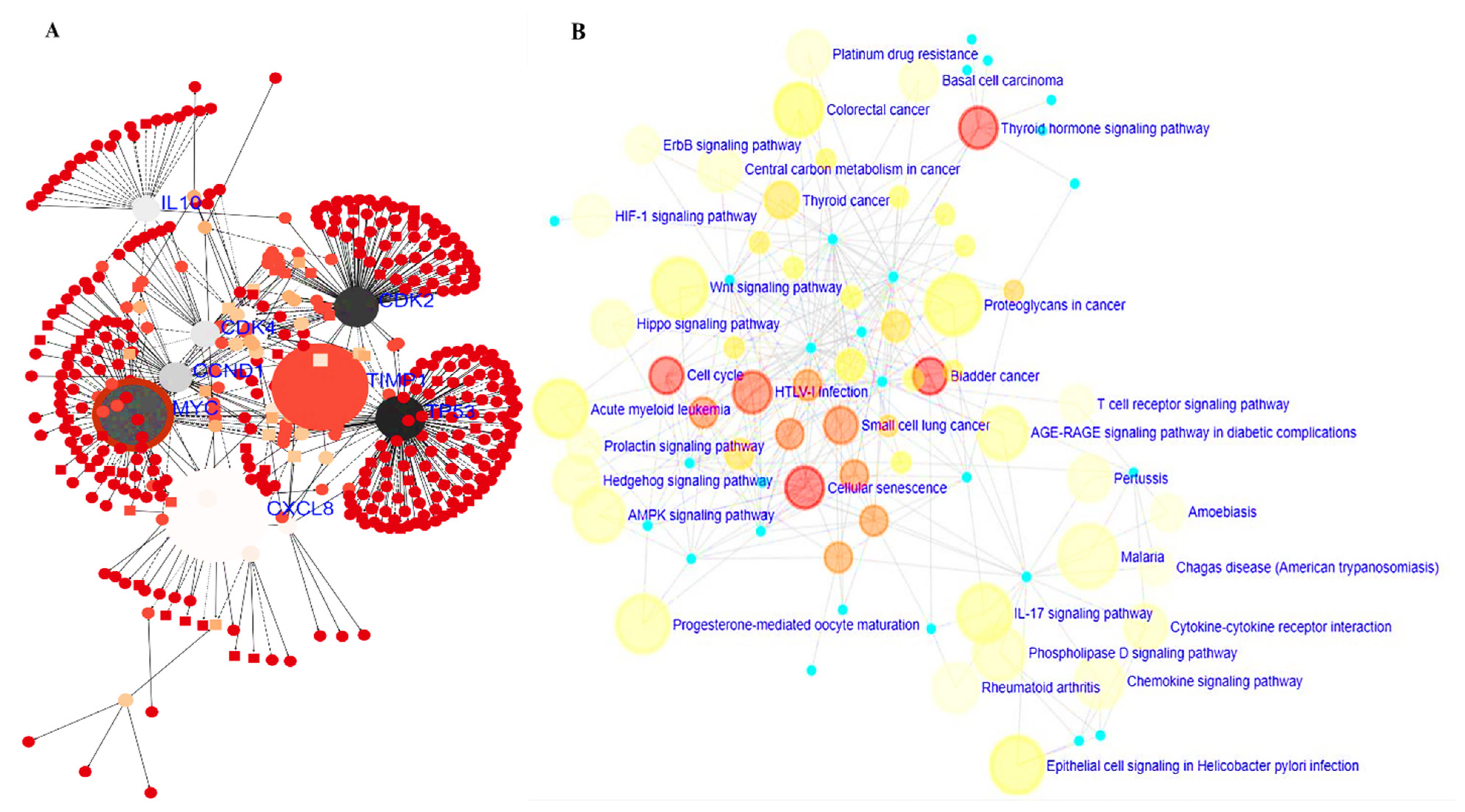
3.5. PPI Network and GO and KEGG Pathway Analysis
3.6. MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Gene Co-Expression and Functional Enrichment Analysis
3.7. MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Expressions Were Correlated with Immune Cell Infiltration in Both Cancer and Normal Tissues
3.8. Drug Sensitivity Analysis of MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Oncogenes
3.9. Docking Results Displayed Strong Binding Energies between RV59 and the MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Oncogenes
3.10. Expressions of MYC/CXCL8/TIMP1 Oncogenes across Colon Cancer Cell Lines
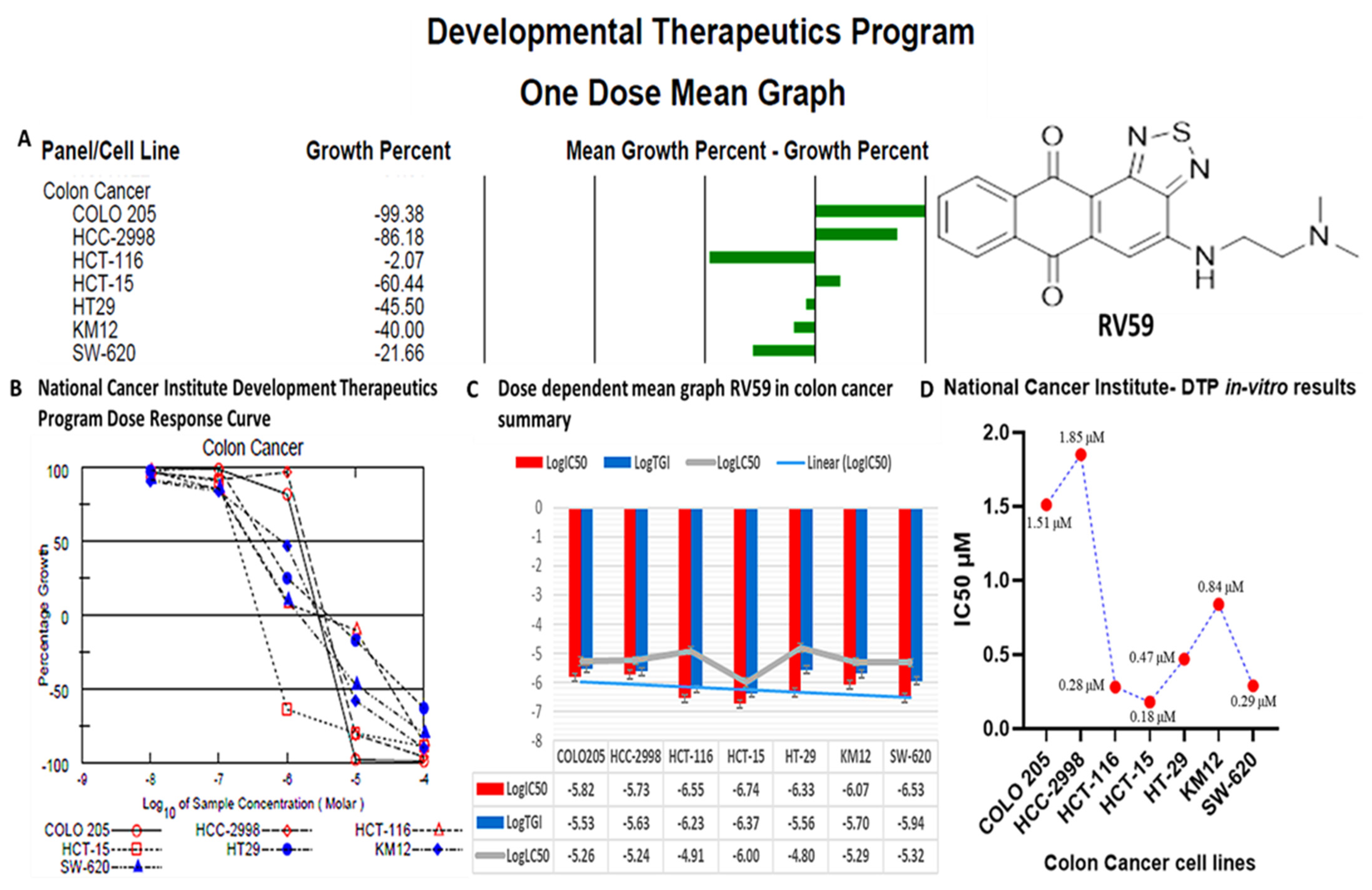
3.11. RV59 Displayed Anti-Proliferative and Cytotoxic Effects in NCI60 Human Colon Cancer Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Böckelman, C.; Beilmann-Lehtonen, I.; Kaprio, T.; Koskensalo, S.; Tervahartiala, T.; Mustonen, H.; Stenman, U.H.; Sorsa, T.; Haglund, C. Serum MMP-8 and TIMP-1 predict prognosis in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łukaszewicz-Zając, M.; Mroczko, B. Circulating Biomarkers of Colorectal Cancer (CRC)-Their Utility in Diagnosis and Prognosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibutani, M.; Maeda, K.; Nagahara, H.; Fukuoka, T.; Iseki, Y.; Matsutani, S.; Kashiwagi, S.; Tanaka, H.; Hirakawa, K.; Ohira, M. Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes Predict the Chemotherapeutic Outcomes in Patients with Stage IV Colorectal Cancer. In Vivo 2018, 32, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, K.; Stadler, Z.K.; Cercek, A.; Mendelsohn, R.B.; Shia, J.; Segal, N.H.; Diaz, L.A., Jr. Immunotherapy in colorectal cancer: Rationale, challenges and potential. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, M.; Vymetalkova, V.; Neves, R.P.L.; Duran-Sanchon, S.; Vedeld, H.M.; Tham, E.; van Dalum, G.; Flügen, G.; Garcia-Barberan, V.; Fijneman, R.J.; et al. Circulating biomarkers for early detection and clinical management of colorectal cancer. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 69, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.L.; Wang, P.; Lu, M.Z.; Zhang, S.D.; Zheng, L. c-Myc maintains the self-renewal and chemoresistance properties of colon cancer stem cells. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4487–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.C.; Hessman, C.; Levin, T.G.; Monroe, M.M.; Wong, M.H. The role of colorectal cancer stem cells in metastatic disease and therapeutic response. Cancers 2011, 3, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Y.; Cao, D. The origin of cancer stem cells. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- de Sousa e Melo, F.; Kurtova, A.V.; Harnoss, J.M.; Kljavin, N.; Hoeck, J.D.; Hung, J.; Anderson, J.E.; Storm, E.E.; Modrusan, Z.; Koeppen, H.; et al. A distinct role for Lgr5(+) stem cells in primary and metastatic colon cancer. Nature 2017, 543, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, W.L.; Yang, M.H.; Tsai, M.L.; Lan, H.Y.; Su, S.H.; Chang, S.C.; Teng, H.W.; Yang, S.H.; Lan, Y.T.; Chiou, S.H.; et al. SNAIL regulates interleukin-8 expression, stem cell-like activity, and tumorigenicity of human colorectal carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 279–291.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommer, G.T.; Fearon, E.R. Role of c-Myc in Apc mutant intestinal phenotype: Case closed or time for a new beginning? Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.V. MYC on the path to cancer. Cell 2012, 149, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, P.J. beta-catenin signaling and cancer. Bioessays 1999, 21, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, E.M.F.; Colak, S.; Buikhuisen, J.; Koster, J.; Cameron, K.; de Jong, J.H.; Tuynman, J.B.; Prasetyanti, P.R.; Fessler, E.; van den Bergh, S.P.; et al. Methylation of cancer-stem-cell-associated Wnt target genes predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 9, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, S.C.; Tong, L.; Li, Y.; Do, R.; Walz, S.; Fitzgerald, K.N.; Gouw, A.M.; Baylot, V.; Gütgemann, I.; Eilers, M.; et al. MYC regulates the antitumor immune response through CD47 and PD-L1. Science 2016, 352, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugimiya, N.; Nishimoto, A.; Hosoyama, T.; Ueno, K.; Enoki, T.; Li, T.S.; Hamano, K. The c-MYC-ABCB5 axis plays a pivotal role in 5-fluorouracil resistance in human colon cancer cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 1569–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strippoli, A.; Cocomazzi, A.; Basso, M.; Cenci, T.; Ricci, R.; Pierconti, F.; Cassano, A.; Fiorentino, V.; Barone, C.; Bria, E.; et al. c-MYC Expression Is a Possible Keystone in the Colorectal Cancer Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors. Cancers 2020, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbadawy, M.; Usui, T.; Yamawaki, H.; Sasaki, K. Emerging Roles of C-Myc in Cancer Stem Cell-Related Signaling and Resistance to Cancer Chemotherapy: A Potential Therapeutic Target Against Colorectal Cancer. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermeking, H.; Eick, D. Mediation of c-Myc-induced apoptosis by p53. Science 1994, 265, 2091–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garte, S.J. The c-myc oncogene in tumor progression. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 1993, 4, 435–449. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.H.; Jung, D.B.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Kang, S.E.; Srivastava, S.K.; Yun, M.; Kim, S.H. Zinc finger protein 746 promotes colorectal cancer progression via c-Myc stability mediated by glycogen synthase kinase 3β and F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3715–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.J.; Byron, K.; Gibson, P.R. Interleukin-8 stimulates the migration of human colonic epithelial cells in vitro. Clin. Sci. 1999, 97, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitadai, Y.; Haruma, K.; Sumii, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Ue, T.; Yokozaki, H.; Yasui, W.; Ohmoto, Y.; Kajiyama, G.; Fidler, I.J.; et al. Expression of interleukin-8 correlates with vascularity in human gastric carcinomas. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Setrerrahmane, S.; Xu, H. Tumor-related interleukins: Old validated targets for new anti-cancer drug development. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, B.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, X.; Xu, C.; et al. Gastric cancer mesenchymal stem cells derived IL-8 induces PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer cells via STAT3/mTOR-c-Myc signal axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, H.; Debnath, B.; Neamati, N. Role of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 Axis in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1543–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, A.; Tian, Y.; Wu, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Wu, K. The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 pathways in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 31, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabkeviciene, D.; Jonusiene, V.; Zitkute, V.; Zalyte, E.; Grigaitis, P.; Kirveliene, V.; Sasnauskiene, A. The role of interleukin-8 (CXCL8) and CXCR2 in acquired chemoresistance of human colorectal carcinoma cells HCT116. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; He, Y.; Li, P.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y.; Ruan, H. IL-8 regulates the doxorubicin resistance of colorectal cancer cells via modulation of multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1). Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2018, 81, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Masaki, T.; Nozaki, E.; Sugiyama, M.; Nagashima, F.; Furuse, J.; Onishi, H.; Watanabe, T.; Ohkura, Y. Microarray Analysis of Gene Expression at the Tumor Front of Colon Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 6577–6581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.S.; Li, Y.F.; Tan, J.; Sun, B.; Xiao, Y.C.; Fang, X.B.; Zhang, X.F.; Li, Q.; Dong, J.H.; Li, M.; et al. CCL20 and CXCL8 synergize to promote progression and poor survival outcome in patients with colorectal cancer by collaborative induction of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 2014, 348, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Jing, C.; Shi, Y.; Miao, R.; Peng, L.; Kong, S.; Ma, Y.; Li, L. microRNA-20a enhances the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells by modulating matrix metalloproteinases. Exp. Med. 2015, 10, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egea, V.; Zahler, S.; Rieth, N.; Neth, P.; Popp, T.; Kehe, K.; Jochum, M.; Ries, C. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) regulates mesenchymal stem cells through let-7f microRNA and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E309–E316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, N.M.; Byström, P.; Christensen, I.J.; Berglund, A.; Nielsen, H.J.; Brünner, N.; Glimelius, B. TIMP-1 is significantly associated with objective response and survival in metastatic colorectal cancer patients receiving combination of irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, and folinic acid. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4117–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirco, R.; Liu, X.W.; Jung, K.K.; Kim, H.R. Novel functions of TIMPs in cell signaling. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, Y.S. Plasma or serum TIMP-1 is a predictor of survival outcomes in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2011, 20, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Yin, H.; Zhao, C.; Cao, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Osimertinib-Based HDAC and EGFR Dual Inhibitors. Molecules 2019, 24, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Chen, G.; Gao, M.; Wu, J. Design, synthesis and evaluation of the osimertinib analogue (C-005) as potent EGFR inhibitor against NSCLC. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 6135–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Chen, T.C.; Lee, C.C.; Chen, C.L.; Ahmed Ali, A.A.; Tikhomirov, A.; Guh, J.H.; Yu, D.S.; Huang, H.S. Ring fusion strategy for synthesis and lead optimization of sulfur-substituted anthra[1,2-c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-6,11-dione derivatives as promising scaffold of antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogodin, P.V.; Lagunin, A.A.; Filimonov, D.A.; Poroikov, V.V. PASS Targets: Ligand-based multi-target computational system based on a public data and naïve Bayes approach. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2015, 26, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, R.H. The NCI60 human tumour cell line anticancer drug screen. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; He, X.; Ji, H.; Shi, L.; Davis, R.W.; Zhong, S. Reproducibility Probability Score--incorporating measurement variability across laboratories for gene selection. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1476–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, B.M.; Zanetti, K.A.; Robles, A.I.; Schetter, A.J.; Goodman, J.; Hayes, R.B.; Huang, W.Y.; Gunter, M.J.; Yeager, M.; Burdette, L.; et al. Germline variation in NCF4, an innate immunity gene, is associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pek, M.; Yatim, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Gong, M.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, J.; Wu, X.; Yu, Q. Oncogenic KRAS-associated gene signature defines co-targeting of CDK4/6 and MEK as a viable therapeutic strategy in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4975–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Qiu, H.; Xu, J.; Mo, J.; Liu, Y.; Gui, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhang, S.; Yao, H.; Huang, X.; et al. Expression and prognostic potential of GPX1 in human cancers based on data mining. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafov, J.; Najafov, A. GECO: Gene expression correlation analysis after genetic algorithm-driven deconvolution. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mering, C.; Huynen, M.; Jaeggi, D.; Schmidt, S.; Bork, P.; Snel, B. STRING: A database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Soufan, O.; Ewald, J.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Basu, N.; Xia, J. NetworkAnalyst 3.0: A visual analytics platform for comprehensive gene expression profiling and meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W234–W241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimand, J.; Isserlin, R.; Voisin, V.; Kucera, M.; Tannus-Lopes, C.; Rostamianfar, A.; Wadi, L.; Meyer, M.; Wong, J.; Xu, C.; et al. Pathway enrichment analysis and visualization of omics data using g:Profiler, GSEA, Cytoscape and EnrichmentMap. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 482–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Fan, J.; Wang, B.; Traugh, N.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER: A Web Server for Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e108–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Hu, F.F.; Xia, M.X.; Han, L.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, A.Y. GSCALite: A web server for gene set cancer analysis. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3771–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Lim-Wilby, M. Molecular docking. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 443, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temml, V.; Kaserer, T.; Kutil, Z.; Landa, P.; Vanek, T.; Schuster, D. Pharmacophore modeling for COX-1 and -2 inhibitors with LigandScout in comparison to Discovery Studio. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashukova, A.; Forteza, R.; Wald, F.A.; Salas, P.J. PDK1 in apical signaling endosomes participates in the rescue of the polarity complex atypical PKC by intermediate filaments in intestinal epithelia. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Anuar, N.N.; Nor Hisam, N.S.; Liew, S.L.; Ugusman, A. Clinical Review: Navitoclax as a Pro-Apoptotic and Anti-Fibrotic Agent. Front. Pharm. 2020, 11, 564108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Martínez, M.; Orozco-Samperio, E.; Montaño, S.; Ariza-Ortega, J.A.; Flores-García, Y.; López-Contreras, L. Vorinostat as potential antiparasitic drug. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 24, 7412–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzner, L.; Scuto, A.; Dino, P.M.; Kowolik, C.M.; Wu, J.; Ventura, P.; Jove, R.; Forman, S.J.; Yen, Y.; Kirschbaum, M.H. Combining histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat with aurora kinase inhibitors enhances lymphoma cell killing with repression of c-Myc, hTERT, and microRNA levels. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3912–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Kang, M.H.; Hong, K.; Kim, J.H. Tubastatin A inhibits HDAC and Sirtuin activity rather than being a HDAC6-specific inhibitor in mouse oocytes. Aging 2019, 11, 1759–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodorou, I.; Fonseca, N.A.; Keays, M.; Tang, Y.A.; Barrera, E.; Bazant, W.; Burke, M.; Füllgrabe, A.; Fuentes, A.M.; George, N.; et al. Expression Atlas: Gene and protein expression across multiple studies and organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D246–D251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Jeught, K.; Xu, H.C.; Li, Y.J.; Lu, X.B.; Ji, G. Drug resistance and new therapies in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol 2018, 24, 3834–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaeger, R.; Kotani, D.; Mondaca, S.; Parikh, A.R.; Bando, H.; Van Seventer, E.E.; Taniguchi, H.; Zhao, H.; Thant, C.N.; de Stanchina, E.; et al. Response to Anti-EGFR Therapy in Patients with BRAF non-V600-Mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7089–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: A 2020 update. Pharm. Res. 2020, 152, 104609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yang, Z.; Yang, X.; Rao, Y. Synthesis and evaluation of osimertinib derivatives as potent EGFR inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 4553–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.J.; Lin, P.L.; Lin, H.C.; Cheng, Y.W.; Huang, H.S.; Lee, H. RV-59 suppresses cytoplasmic Nrf2-mediated 5-fluorouracil resistance and tumor growth in colorectal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2789–2796. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.A.A.; Lee, Y.-R.; Wu, A.T.H.; Yadav, V.K.; Yu, D.-S.; Huang, H.-S. Structure-based strategies for synthesis, lead optimization and biological evaluation of N-substituted anthra[1,2-c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-6,11-dione derivatives as potential multi-target anticancer agents. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, I.H.; Akce, M.; Alese, O.; Shaib, W.; Lesinski, G.B.; El-Rayes, B.; Wu, C. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of MSI-H/MMR-D colorectal cancer and a perspective on resistance mechanisms. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Jain, A.D.; Truica, M.I.; Izquierdo-Ferrer, J.; Anker, J.F.; Lysy, B.; Sagar, V.; Luan, Y.; Chalmers, Z.R.; Unno, K.; et al. Small-Molecule MYC Inhibitors Suppress Tumor Growth and Enhance Immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 483–497.e415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, L.; Ding, G.; Huang, H.; Cao, G.; Sun, X.; Lou, N.; Wei, Q.; Shen, T.; Xu, X.; et al. Interferon gamma inhibits CXCL8-CXCR2 axis mediated tumor-associated macrophages tumor trafficking and enhances anti-PD1 efficacy in pancreatic cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, E.; Sato, Y.; Minagawa, A.; Okuyama, R. Pathogenesis of psoriasis and development of treatment. J. Derm. 2018, 45, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seubert, B.; Grünwald, B.; Kobuch, J.; Cui, H.; Schelter, F.; Schaten, S.; Siveke, J.T.; Lim, N.H.; Nagase, H.; Simonavicius, N.; et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP)-1 creates a premetastatic niche in the liver through SDF-1/CXCR4-dependent neutrophil recruitment in mice. Hepatology 2015, 61, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| NCI-Synthetic Compounds | NCI-Standard Agents | ArrayCGH-Gray | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | r | CCLC | Target Descriptor | r | CCLC | Target Descriptor | r | CCLC | Target Descriptor |
| 1 | 0.6 | 50 | 3-Nitro-5-Formylisoxazole | 0.51 | 58 | Trimetrexate | 0.27 | 57 | MET |
| 2 | 0.58 | 58 | CI.49700 | 0.49 | 59 | Methotrexate | 0.27 | 57 | CDK4 |
| 3 | 0.56 | 57 | Tryptanthrin | 0.46 | 58 | Dichloroali lawsone | 0.2 | 55 | YES1 |
| 4 | 0.55 | 58 | Tolonium Chloride | 0.46 | 58 | 5HP | 0.18 | 53 | DRD3 |
| 5 | 0.54 | 57 | Metoprine (USAN) | 0.46 | 59 | Cyclocytidine | 0.13 | 55 | TP53 |
| 6 | 0.54 | 45 | Bafilomycin Deriv | 0.42 | 59 | Thioguanine | 0.13 | 55 | WNT1 |
| 7 | 0.53 | 53 | Brilliant cresyl blue | 0.41 | 58 | Hycanthone | 0.11 | 55 | MYC |
| 8 | 0.52 | 46 | Bafilomycin Antibiotic | 0.4 | 45 | Tetraplatin | 0.11 | 57 | AKT1 |
| 9 | 0.52 | 41 | Lapachol | 0.4 | 58 | Cytosine arabinoside | 0.1 | 56 | ABR |
| 10 | 0.51 | 58 | Piroctone olamine | 0.38 | 58 | Pyrazofurin | 0.1 | 56 | CCND1 |
| Pa | Pi | Activity |
|---|---|---|
| 0.477 | 0.029 | MYC inhibitor |
| 0.375 | 0.166 | Catenin beta inhibitor |
| 0.302 | 0.139 | MAP kinase stimulant |
| 0.238 | 0.086 | Antineoplastic (colon cancer) |
| 0.113 | 0.058 | Protein kinase (CK1) inhibitor |
| 0.268 | 0.227 | MAP kinase 8 inhibitor |
| 0.210 | 0.174 | Transcription factor NF kappa A inhibitor |
| 0.143 | 0.110 | Protein kinase (CK1) delta inhibitor |
| 0.136 | 0.109 | Acetylcholine M2 receptor antagonist |
| 0.146 | 0.134 | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 8 (CXCL8) antagonist |
| Pharmacokinetics | GI Absorption (High) | BBB (Low) |
|---|---|---|
| Drug-likeness (Yes to all) | Lipinski, Ghose, Veber, Egan, Muegge | |
| Bioavailability score | 55% | |
| Medical Chemistry | Synthetic accessibility: | 2.95 |
| RV59 | Standard Inhibitotrs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RV59-MYC Complex (ΔG = −7.6 Kcal/mol) | Vorinostat-MYC Complex (ΔG = −6.3 Kcal/mol) | ||
| Type of interactions and number of bonds | distance of interacting Amino acids | Type of interactions and number of bonds | distance of interacting Amino acid |
| Conventional Hydrogen bond (1) | LYS944 (2.49 Å) | Conventional Hydrogen bond (1) | SER (2.87Å) |
| Pi sigma | LEU217 | Van der Waals forces | LEU94, SER221, LUE225, LYS213, ASP220, VAL940 |
| Pi-pi stacked | HIS217 | Alkyl | ARG214, LYS944 |
| Pi-Alkyl | ARG214,LYS213 | ||
| RV59-CXCL8 Complex (ΔG = −7.7 Kcal/mol) | Reparixinx-CXCL8 Complex (ΔG = −6.3 Kcal/mol) | ||
| Type of interactions and number of bonds | distance of interacting Amino acids | Type of interactions and number of bonds | distance of interacting Amino acids |
| Conventional Hydrogen bond (1) | CYS47 (2.03 Å) | Van der Waals forces | ASP43, ARG45 |
| Carbon hydrogen bond | GLU46 | Pi-pi stacked | PHE19 |
| Pi-cation | LYS9 | Alkyl | LEU41, TYR11 |
| Pi-Alkyl | LEU47 | Pi-Alkyl | LEU47, PHE15 |
| RV59-TIMP1 Complex (ΔG = −6.9 Kcal/mol) | Ilomastat-TIMP1 Complex (ΔG = −7.4 Kcal/mol) | ||
| Type of interactions and number of bonds | distance of interacting Amino acids | Type of interactions and number of bonds | distance of interacting Amino acids |
| Conventional Hydrogen bond (4) | PHE132 (3.29 Å), TRY99 (3.41 Å), GLU118 (3.4 Å), ARG134 (2.51 Å) | Conventional Hydrogen bond (2) | ARG134, TYR136 |
| Carbon hydrogen bond | SER133 | Van der Waals | THR131, TYR99, GLU118, ASP114, GLU125, LYS122 |
| Pi-cation | SER115 | Carbon hydrogen bond | PHE132 |
| Pi-Alkyl | PHE132 | Pi-Anion | GLU118 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, T.-H.; Mokgautsi, N.; Huang, Y.-J.; Wu, A.T.H.; Huang, H.-S. Comprehensive Omics Analysis of a Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Chemoresistant Oncogenic Signatures in Colorectal Cancer Cell with Antitumor Effects. Cells 2021, 10, 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081970
Huang T-H, Mokgautsi N, Huang Y-J, Wu ATH, Huang H-S. Comprehensive Omics Analysis of a Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Chemoresistant Oncogenic Signatures in Colorectal Cancer Cell with Antitumor Effects. Cells. 2021; 10(8):1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081970
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Tse-Hung, Ntlotlang Mokgautsi, Yan-Jiun Huang, Alexander T. H. Wu, and Hsu-Shan Huang. 2021. "Comprehensive Omics Analysis of a Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Chemoresistant Oncogenic Signatures in Colorectal Cancer Cell with Antitumor Effects" Cells 10, no. 8: 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081970
APA StyleHuang, T.-H., Mokgautsi, N., Huang, Y.-J., Wu, A. T. H., & Huang, H.-S. (2021). Comprehensive Omics Analysis of a Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Chemoresistant Oncogenic Signatures in Colorectal Cancer Cell with Antitumor Effects. Cells, 10(8), 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081970








