The RNA-Binding Protein SBR (Dm NXF1) Is Required for the Constitution of Medulla Boundaries in Drosophila melanogaster Optic Lobes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Hybrids
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Immunohistochemical and Fluorescent Staining
2.4. Head Paraffin Sections
2.5. Microscopy
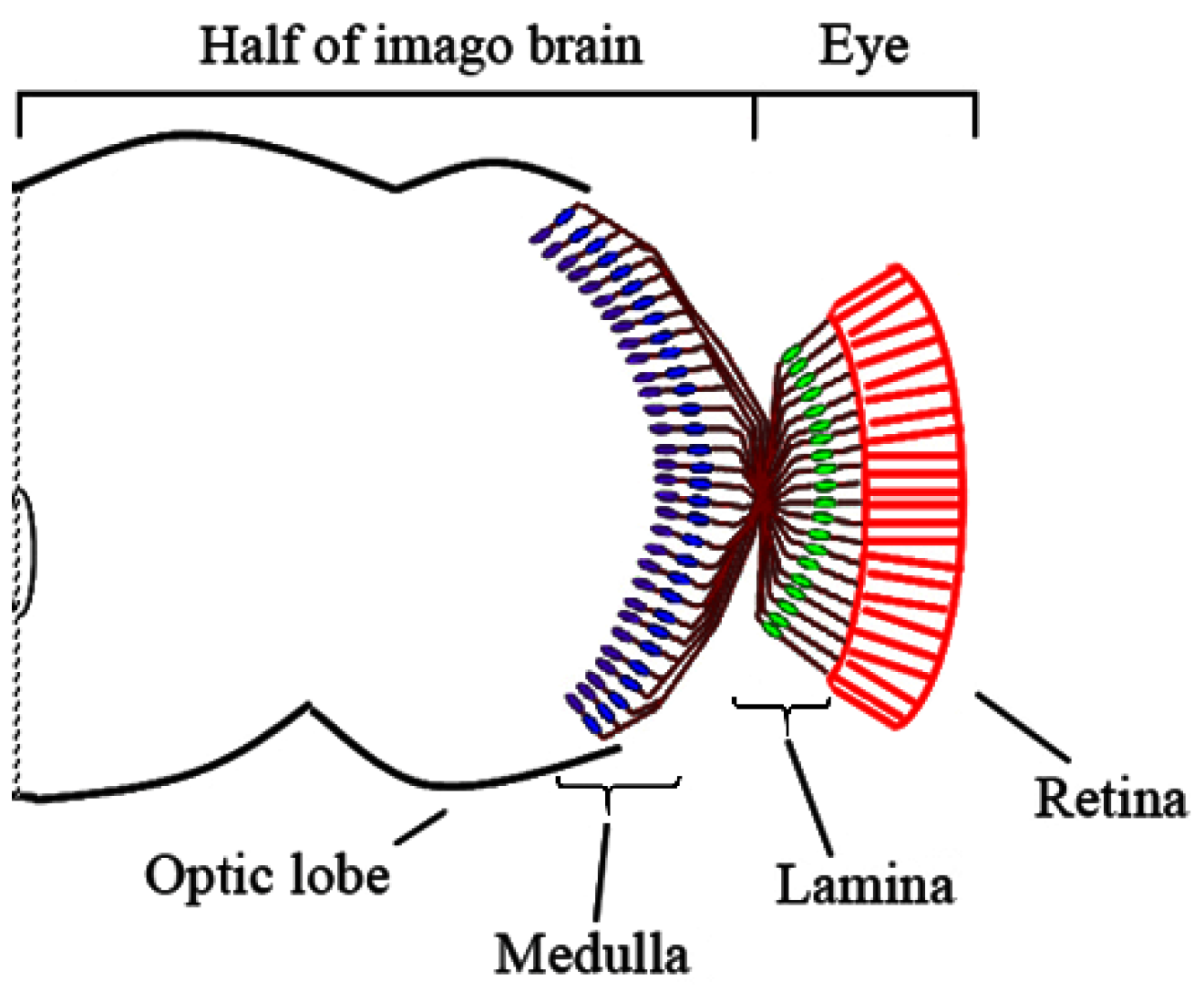
3. Results
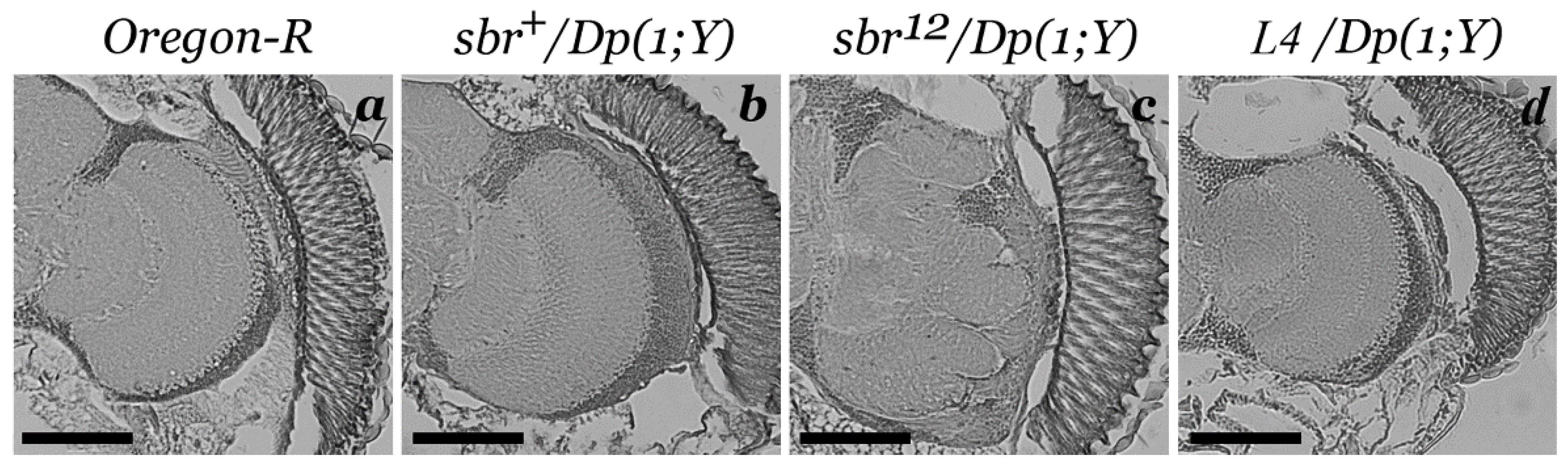
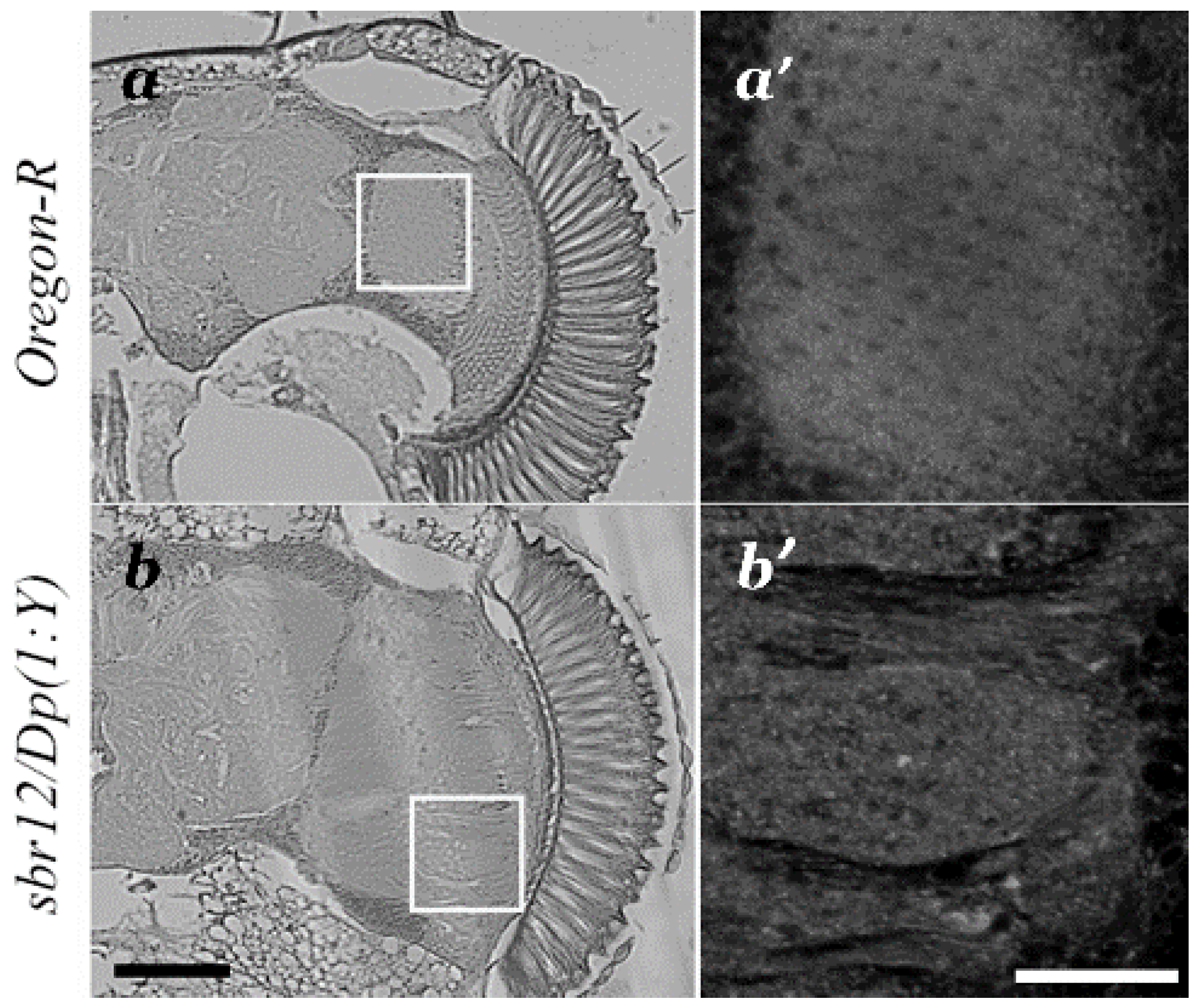
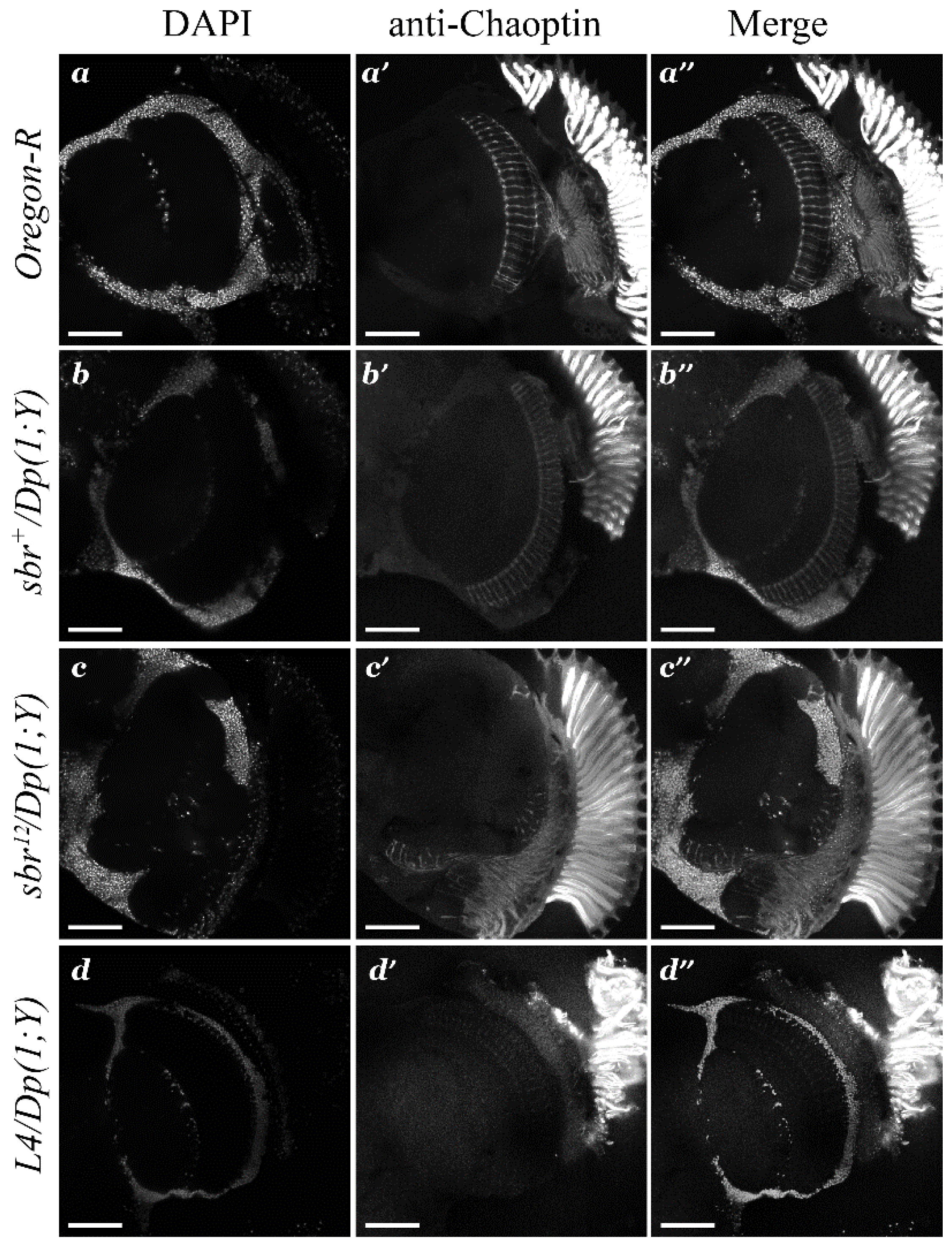
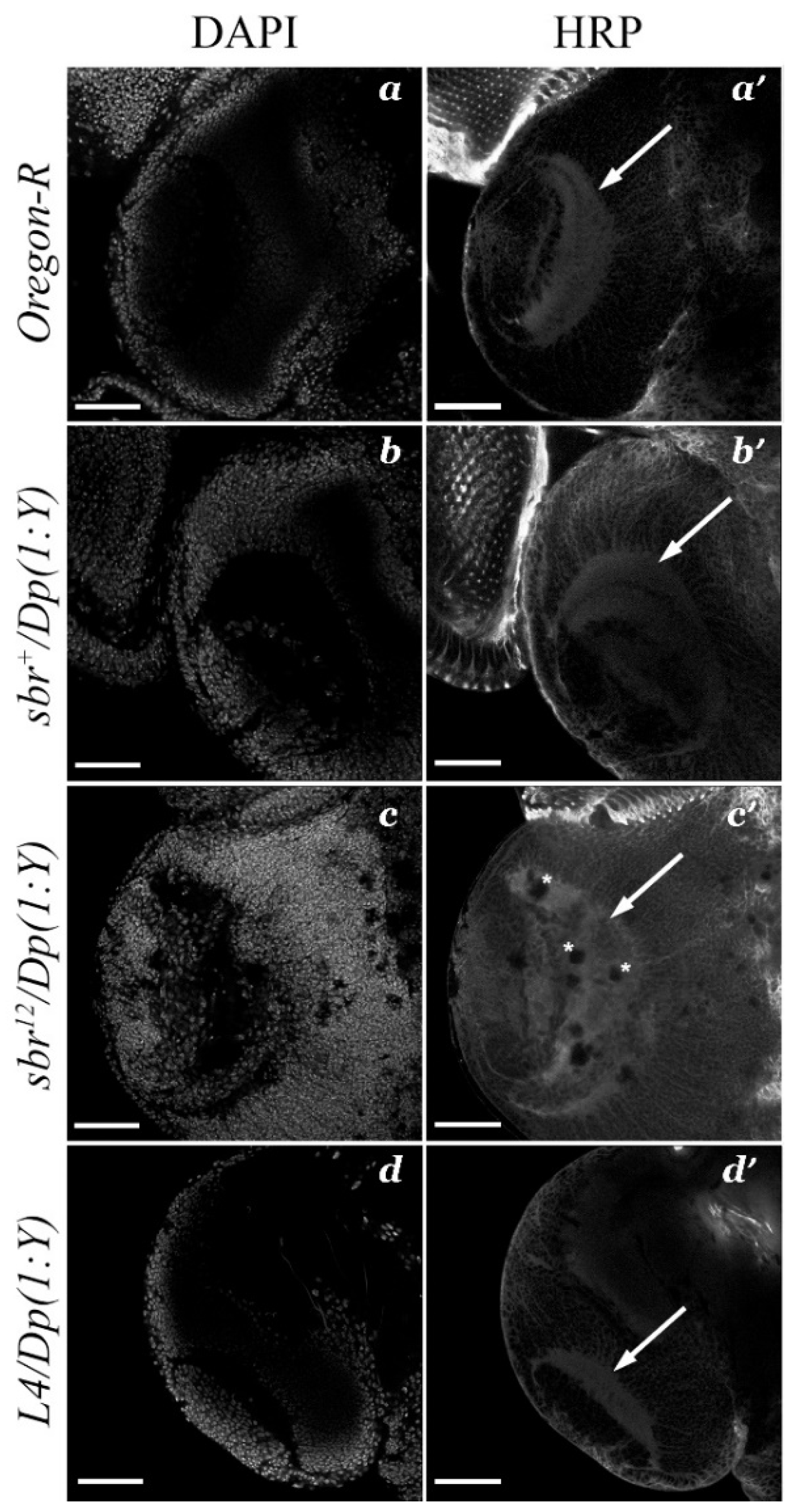
3.1. Medulla Malformations in sbr12/Dp(1;Y)y+v+ Males
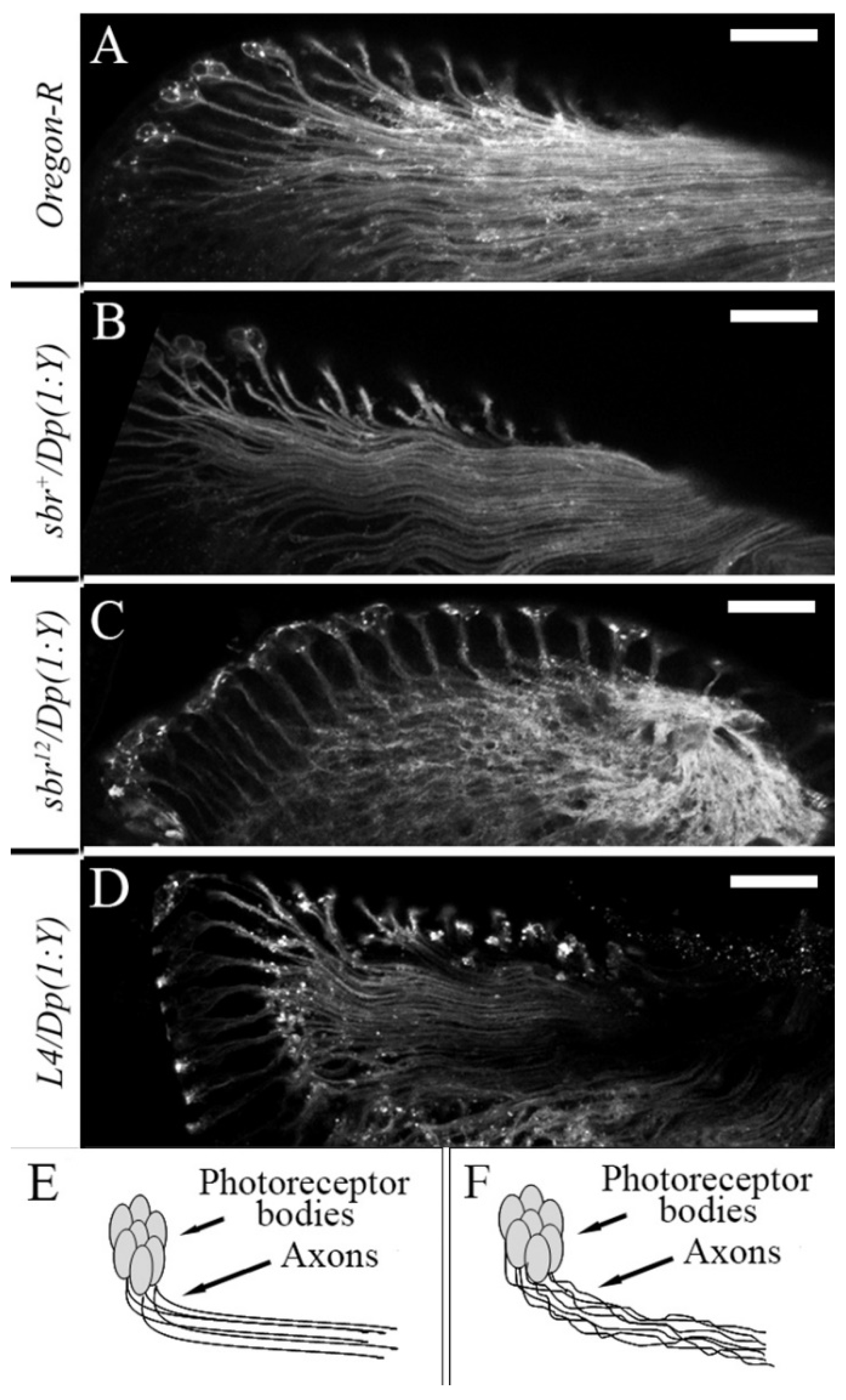
3.2. Defects in Fasciculation of Photoreceptor Axons in Eye-Antennal Imaginal Discs of sbr12/Dp(1;Y)y+v+ Male Larvae
3.3. Features of Neurodegeneration in the Medulla of sbr12/Dp(1;Y)y+v+ Third Instar Male Larvae
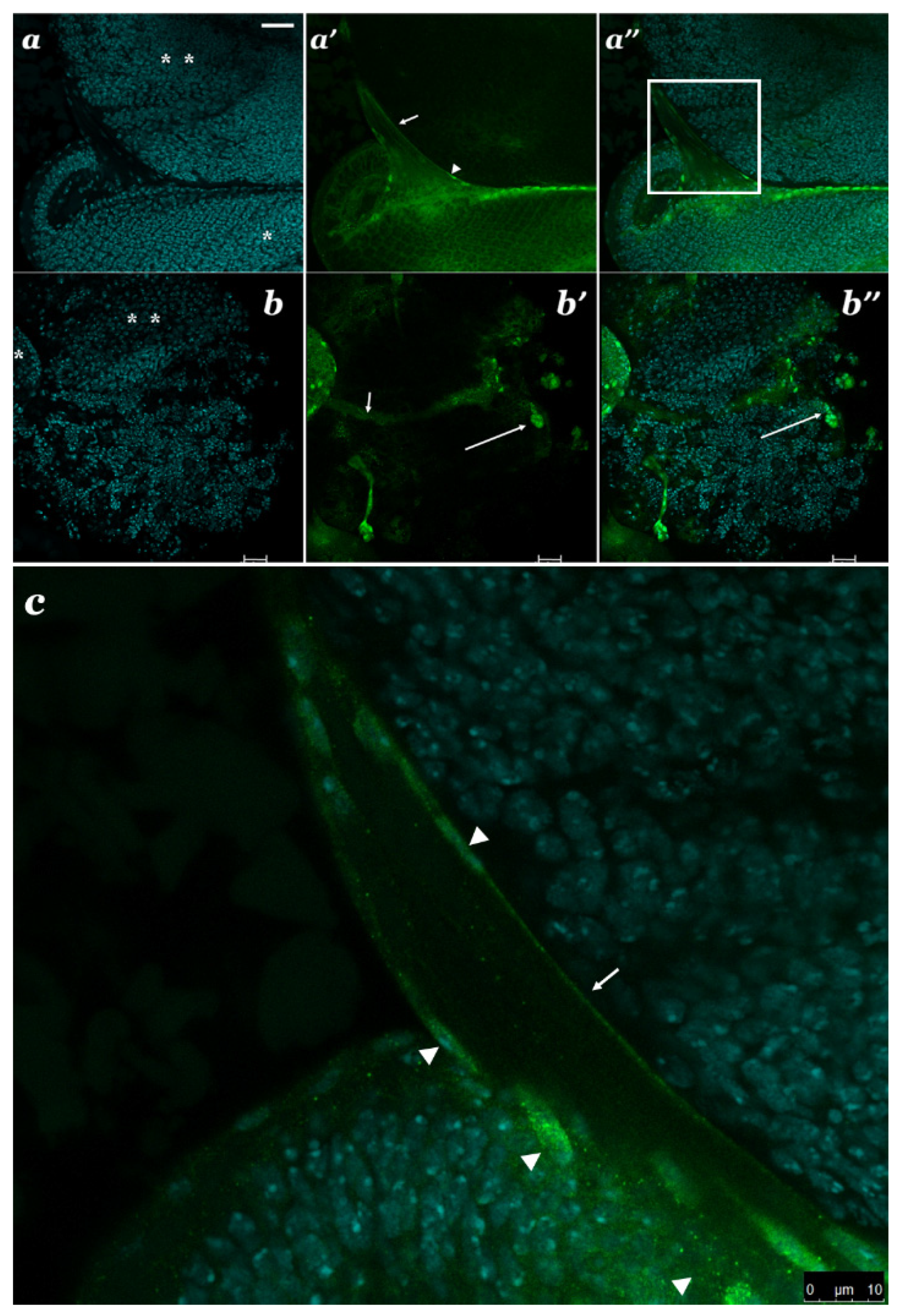
3.4. Localization of SBR Protein in Different Brain Cells
4. Discussion
4.1. The Assumed Cytoplasmic Functions of the SBR RNA-Binding Protein, an Orthologue of the Evolutionarily Conserved NXF1 Protein
4.2. The Non-Random Distribution of SBR in the Different Brain Cells
4.3. Allele-Specific Phenotypes of sbr Gene Mutations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Herold, A.; Klymenko, T.; Izaurralde, E. NXF1/p15 heterodimers are essential for mRNA nuclear export in Drosophila. RNA 2001, 7, 1768–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretyakova, I.V.; Lyozin, G.T.; Markova, E.G.; Evgen’ev, M.B.; Mamon, L.A. The sbr gene product in Drosophila melanogaster and its orthologs in yeast (Mex67p) and human (TAP). Russ. J. Genet. 2001, 37, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, G.S.; Zimyanin, V.; Kirby, R.; Korey, C.; Francis-Lang, H.; Van Vactor, D.; Davis, I. Small bristles, the Drosophila ortholog of NXF-1, is essential for mRNA export throughout development. RNA 2001, 7, 1781–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachi, A.; Braun, I.C.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Panté, N.; Ribbeck, K.; von Kobbe, C.; Kutay, U.; Wilm, M.; Görlich, D.; Carmo-Fonseca, M.; et al. The C-terminal domain of TAP interacts with the nuclear pore complex and promotes export of specific CTE-bearing RNA substrates. RNA 2000, 6, 136–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atsapkina, A.A.; Golubkova, E.V.; Kasatkina, V.V.; Avanesyan, E.O.; Ivankova, N.A.; Mamon, L.A. Peculiarities of spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: Role of main transport receptor of mRNA (Dm NXF1). Cell Tissue Biol. 2010, 4, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkova, E.V.; Atsapkina, A.A.; Mamon, L.A. The role of sbr/ Dm nxf1 gene in syncytial development in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Tissue Biol. 2015, 9, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimova, A.O.; Pugacheva, O.M.; Golubkova, E.V.; Mamon, L.A. Cytoplasmic localization of SBR (Dm NXF1) protein and its zonal distribution in the ganglia of Drosophila melanogaster larvae. Invertebr. Neurosci. 2016, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamon, L.A.; Ginanova, V.R.; Kliver, S.F.; Yakimova, A.O.; Atsapkina, A.A.; Golubkova, E.V. RNA-binding proteins of the NXF (nuclear export factor) family and their connection with the cytoskeleton. Cytoskeleton 2017, 74, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C.E.; Schuman, E.M. The central dogma decentralized: New perspectives on RNA function and local translation in neurons. Neuron 2013, 80, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotard, C.; Salecker, I. Glial cell development and function in the Drosophila visual system. Neuron Glia Biol. 2007, 3, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindler, S.R.; Ortiz, I.; Fung, S.; Takashima, S.; Hartenstein, V. Drosophila cortex and neuropile glia influence secondary axon tract growth, pathfinding. And fasciculation in the developing larval brain. Dev. Biol. 2009, 334, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.N.; Meinertzhagen, I.A. The functional organization of glia in the adult brain of Drosophila and other insects. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 90, 471–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinertzhagen, I.A.; Hanson, T.E. The development of the optic lobe. In The Development of Drosophila Melanogaster; Bate, M., MartinezArias, A., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 1363–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Braitenberg, V. Patterns of projection in the visual system of the fly. I. Retina-lamina projections. Exp. Brain Res. 1967, 3, 271–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujilo-Cenóz, O.; Melamed, J. Compound eye of dipterans: Anatomical basis for integration—An electron microscope study. J. Ultrastruct Res. 1966, 16, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinertzhagen, I.A.; Sorra, K.E. Synaptic organization in the fly’s optic lamina: Few cells, many synapses and divergent microcircuits. Prog. Brain Res. 2001, 131, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, K.F.; Hiesinger, P.R. Optic lobe development. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 628, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gontang, A.C.; Hwal, J.J.; Mast, J.D.; Schwabe, T.; Clandinin, T.R. The cytoskeletal regulator Genghis khan is required for columnar target specificity in the Drosophila visual system. Development 2011, 138, 4899–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakimova, A.O.; Golubkova, E.V.; Sarantseva, S.V.; Mamon, L.A. Ellipsoid body and medulla defects and locomotion disturbances in sbr (small bristles) mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Russ. J. Genet. 2018, 54, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, M.I.; Hilfiker, A.; Lucchesi, J.C. Dosage compensation in Drosophila—A model for the coordinate regulation of transcription. Genetics 2016, 204, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Peña, A.; Acebes, A.; Rodríguez, J.-R.; Chevalier, V.; Casas-Tinto, S.; Triphan, T.; Strauss, R.; Ferrúset, A. Cell types and coincident synapses in the ellipsoid body of Drosophila. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 39, 1586–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Antibodies to horseradish peroxidase as specific neuronal markers in Drosophila and in grasshopper embryos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2700–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopytova, D.; Popova, V.; Kurshakova, M.; Shidlovskii, Y.; Nabirochkina, E.; Brechalov, A.; Georgiev, G.; Georgieva, S. ORC interacts with THSC/TREX-2 and its subunits promote Nxf1 association with mRNP and mRNA export in Drosophila. Nucl. Acid Res. 2016, 44, 4920–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiszely, D. Practical Microtechniques and Histochemistry; Hungarian Academy of Sciences Publishing House: Budapest, Hungary, 1962; p. 382. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach, K.F.; Dittrich, A.P.M. The optic lobe of Drosophila melanogaster. I. A Golgi analysis of wild type structure. Cell Tissue Res. 1989, 258, 441–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apitz, H.; Salecker, I. A Challenge of Numbers and Diversity: Neurogenesis in the Drosophila Optic Lobe. J. Neurogenet. 2014, 28, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Miura, M. Programmed cell death in neurodevelopment. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeck, B.; Fischer, S.; Gunning, D.; Zipursky, S.L.; Salecker, I. Glial Cells Mediate Target Layer Selection of Retinal Axons in the Developing Visual System of Drosophila. Neuron 2001, 29, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, A.; Teixeira, L.; Izaurralde, E. Genome-wide analysis of nuclear mRNA export pathways in Drosophila. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2472–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginanova, V.; Golubkova, E.; Kliver, S.; Bychkova, E.; Markoska, K.; Ivankova, N.; Tretyakova, I.; Evgen’ev, M. Testis-specific products of the Drosophila melanogaster sbr gene, encoding nuclear export factor 1, are necessary for male fertility. Gene 2016, 577, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fribourg, S.; Braun, I.C.; Izaurralde, E.; Conti, E. Structural basis for the recognition of a nucleoporin FG repeat by the NTF2-like domain of the TAP/p15 mRNA nuclear export factor. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, I.C.; Herold, A.; Rode, M.; Izaurralde, E. Nuclear export of mRNA by TAP/NXF1 requires two nucleoporin-binding sites but not p15. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 5405–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibara, S.; Katahira, J.; Valkov, E.; Stewart, M. The principal mRNA nuclear export factor NXF1:NXT1 forms a symmetric binding platform that facilitates export of retroviral CTE-RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katahira, J.; Dimitrova, L.; Imai, Y.; Hurt, E. NTF2-like domain of Tap plays a critical role in cargo mRNA recognition and export. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 1894–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivankova, N.; Tretyakova, I.; Lyozin, G.; Avanesyan, E.; Zolotukhin, A.; Zatsepina, O.G.; Evgen’ev, M.B.; Mamon, L.A. Alternative transcripts expressed by small bristles, the Drosophila melanogaster nxf1 gene. Gene 2010, 458, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarata, G.M.; Bearce, E.; Lowery, L.A. Cytoskeletal social networking in the growth cone: +TIPs mediate microtubule-actin cross-linking to drive axon outgrowth and guidance. Cytoskeleton 2016, 73, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Herman, P.K. It is all about the process(ing): P-body granules and the regulation of signal transduction. Curr. Genet. 2020, 66, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, D.W.; Lee, H.; Seol, W.; DeMaria, M.; Rosenzweig, M.; Jung, J.U. Tap: A novel protein that interacts with tip of herpesvirus saimiri and induces lymphocyte aggregation. Immunity 1997, 6, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, A.; Suyama, M.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Braun, I.C.; Kutay, U.; Carmo-Fonseca, M.; Bork, P.; Izaurralde, E. TAP (NXF1) belongs to a multigene family of putative RNA export factors with a conserved modular architecture. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 8996–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurusu, M.; Katsuki, T.; Zinn, K.; Suzuki, E. Developmental changes in expression, subcellular distribution, and function of Drosophila N-cadherin, guided by a cell-intrinsic program during neuronal differentiation. Dev. Biol. 2012, 366, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaire, M.; Hindges, R. The role of cell adhesion molecules in visual circuit formation: From neurite outgrowth to maps and synaptic specificity. Dev. Neurobiol 2015, 75, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buss, R.R.; Sun, W.; Oppenheim, R.W. Adaptive roles of programmed cell death during nervous system development. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 29, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogulja-Ortmann, A.; Luer, K.; Seibert, J.; Rickert, C.; Technau, G.M. Programmed cell death in the embryonic central nervous system of Drosophila melanogaster. Development 2007, 134, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Reichert, H. Programmed cell death in type II neuroblast lineages is required for central complex development in the Drosophila brain. Neural Dev. 2012, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, M.; Enriquez, J.; Mann, R.S. Dual role for Hox genes and Hox co-factors in conferring leg motoneuron survival and identity in Drosophila. Development 2013, 140, 2027–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sephton, C.F.; Yu, G. The function of RNA-binding proteins at the synapse: Implications for neurodegeneration. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3621–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Conti, L.; Baralle, M.; Buratti, E. Neurodegeneration and RNA-binding proteins. WIREs RNA 2017, 8, e1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, E.G.; Manley, J.L. RNA-binding proteins in neurodegeneration: Mechanisms in aggregate. Gene Dev. 2017, 31, 1509–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, D.; Hatano, M.; Suzuki, N. RNA binding proteins and the pathological cascade in ALS/FTD neurodegeneration. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cafferty, P. Carpet cells regulate glial cell motility in the developing Drosophila eye. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2686–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafferty, P.; Xie, X.; Browne, K.; Auld, V.J. Live imaging of glial cell migration in the eye imaginal disc. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 29, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, J.P.; Santiago-Medina, M.; Gomez, T.M. Regulation of axonal outgrowth and pathfinding by integrin-ECM interactions. Dev. Neurobiol. 2011, 71, 901–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, V.M.; Chen, Z.; Rossi, A.M.; Zipfel, J.; Desplan, C. Glia relay differentiation cues to coordinate neuronal development in Drosophila. Science 2017, 357, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L. Actin cytoskeleton regulation in neuronal morphogenesis and structural plasticity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 18, 601–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, E.W.; Merriam, E.B.; Hu, X. The dynamic cytoskeleton: Backbone of dendritic spine plasticity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.V.V.G.; Irvine, K.D. Regulation of Drosophila glial cell proliferation by Merlin-Hippo signaling. Development 2011, 138, 5201–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silies, M.; Yuva, Y.; Engelen, D.; Aho, A.; Stork, T.; Klämbt, C. Glial cell migration in the eye disc. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 13130–13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Gilbert, M.; Petley-Ragan, L.; Auld, V.J. Loss of focal adhesions in glia disrupts both glial and photoreceptor axon migration in the Drosophila visual system. Development 2014, 141, 3072–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Tsao, C.-K.; Sun, H. Temporal and spatial order of photoreceptor and glia protections into optic lobe in Drosophila. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayler, T.D.; Robichaux, M.B.; Garrity, P.A. Compartmentalization of visual centers in the Drosophila brain requires Slit and Robo proteins. Development 2004, 131, 5935–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Liu, C.; Kato, S.; Nishimura, K.; Takechi, H.; Yasugi, T.; Takayama, R.; Hakeda-Suzuki, S.; Suzuki, T.; Sato, M. Netrin signaling defines the regional border. Science 2018, 8, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://flybase.org/reports/FBgn0003321 (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Knoblich, J.A. Mechanisms of asymmetric cell division during animal development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roegiers, F.; Jan, Y.N. Asymmetric cell division. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 195205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, B.; Chell, J.M.; Brand, A.H. Insights into neural stem cell biology from flies. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumüller, R.A.; Knoblich, J.A. Dividing cellular asymmetry: Asymmetric cell division and its implications for stem cells and cancer. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 2675–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viphakone, N.; Hautbergue, G.M.; Walsh, M.; Chang, C.T.; Holland, A.; Folco, E.G.; Reed, R.; Wilson, S.A. TREX exposes the RNA-binding domain of Nxf1 to enable mRNA export. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkov, E.; Dean, J.C.; Jani, D.; Kuhlmann, S.I.; Stewart, M. Structural basis for the assembly and disassembly of mRNA nuclear export complexes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 181, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamon, L.; Yakimova, A.; Kopytova, D.; Golubkova, E. The RNA-Binding Protein SBR (Dm NXF1) Is Required for the Constitution of Medulla Boundaries in Drosophila melanogaster Optic Lobes. Cells 2021, 10, 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051144
Mamon L, Yakimova A, Kopytova D, Golubkova E. The RNA-Binding Protein SBR (Dm NXF1) Is Required for the Constitution of Medulla Boundaries in Drosophila melanogaster Optic Lobes. Cells. 2021; 10(5):1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051144
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamon, Ludmila, Anna Yakimova, Daria Kopytova, and Elena Golubkova. 2021. "The RNA-Binding Protein SBR (Dm NXF1) Is Required for the Constitution of Medulla Boundaries in Drosophila melanogaster Optic Lobes" Cells 10, no. 5: 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051144
APA StyleMamon, L., Yakimova, A., Kopytova, D., & Golubkova, E. (2021). The RNA-Binding Protein SBR (Dm NXF1) Is Required for the Constitution of Medulla Boundaries in Drosophila melanogaster Optic Lobes. Cells, 10(5), 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051144






