First Case of Conyza canadensis from Hungary with Multiple Resistance to Glyphosate and Flazasulfuron
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Dose–Response Assays with Glyphosate
2.3. Shikimic Acid Accumulation
2.4. Dose–Response Assays with Alternative Herbicides
2.5. ALS Enzyme Activity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
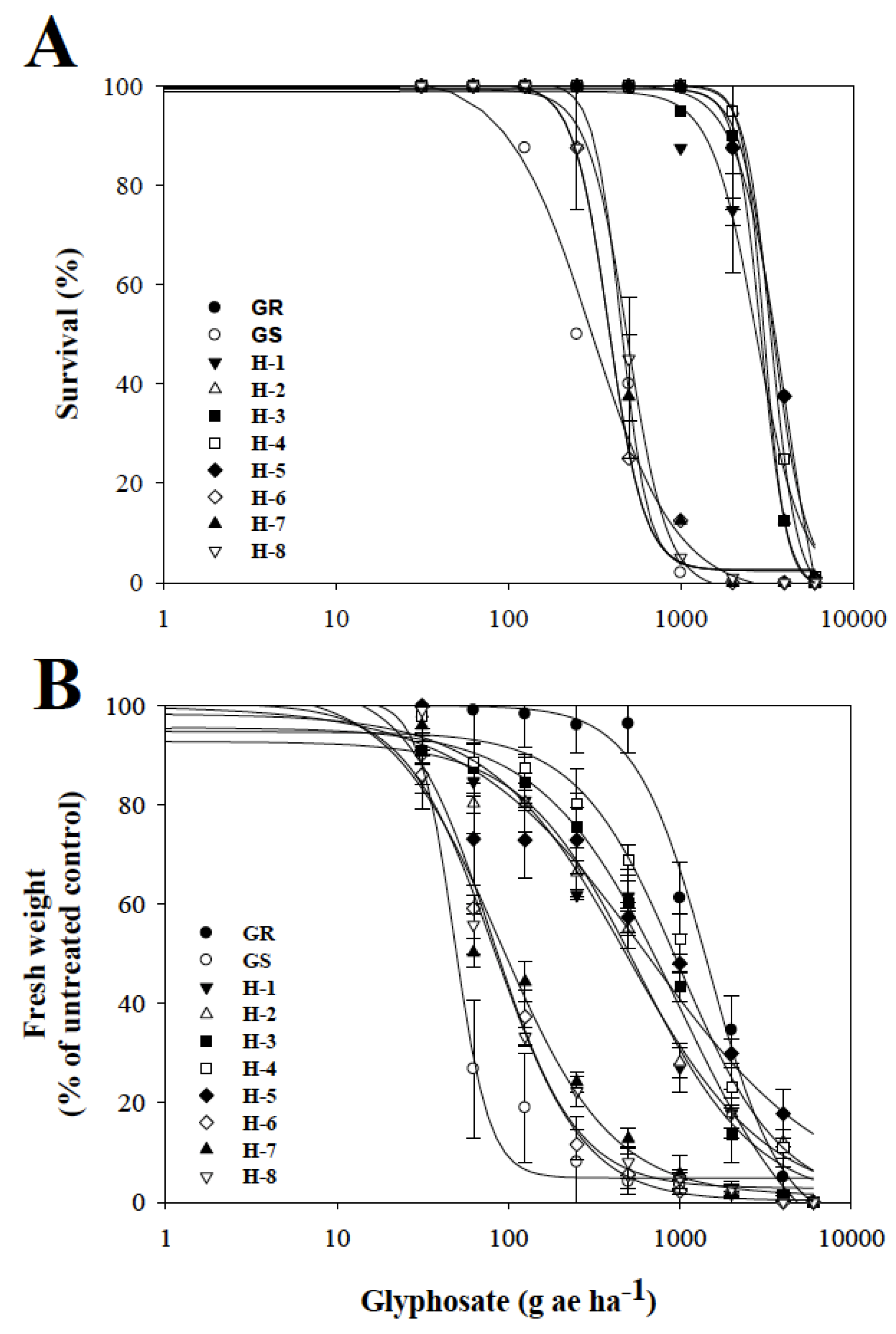
3.1. Dose–Response Assays with Glyphosate
3.2. Shikimic Acid Accumulation
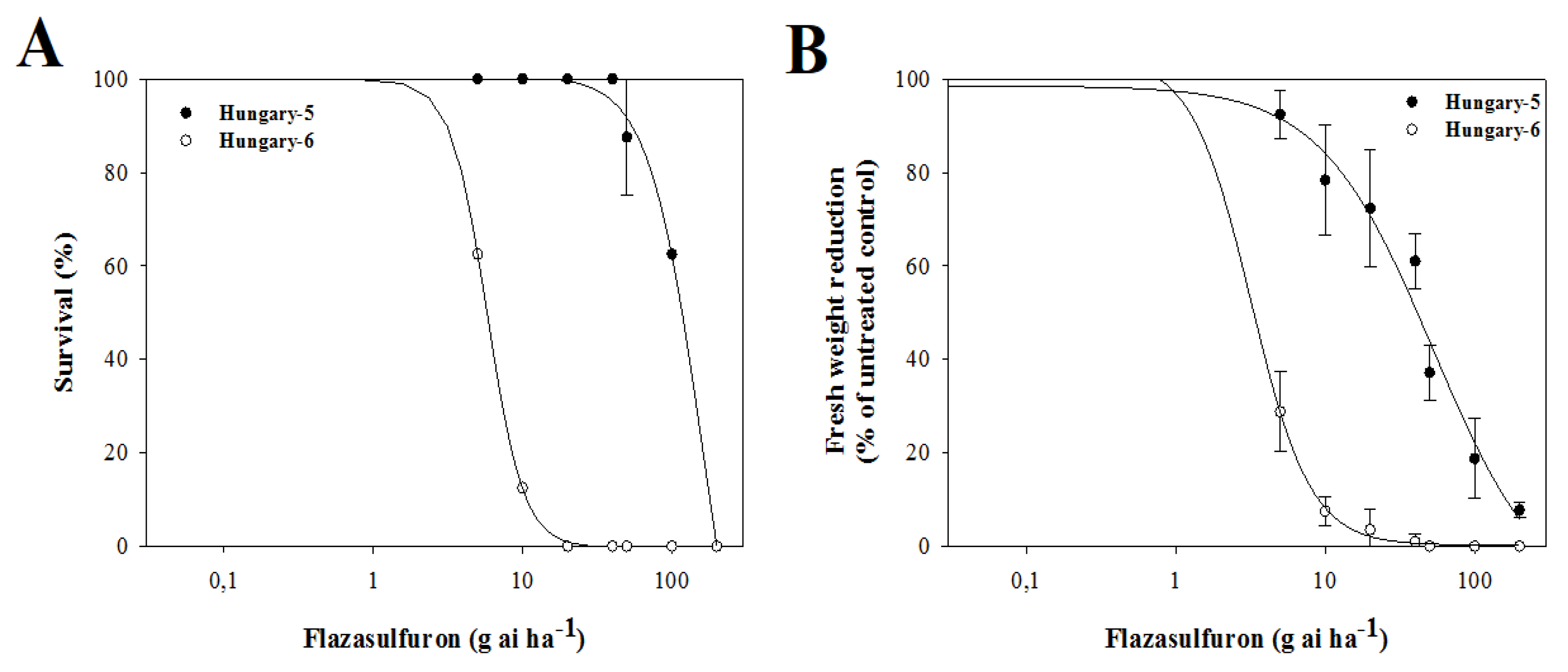
3.3. Dose–Response Assays with Alternative Herbicides
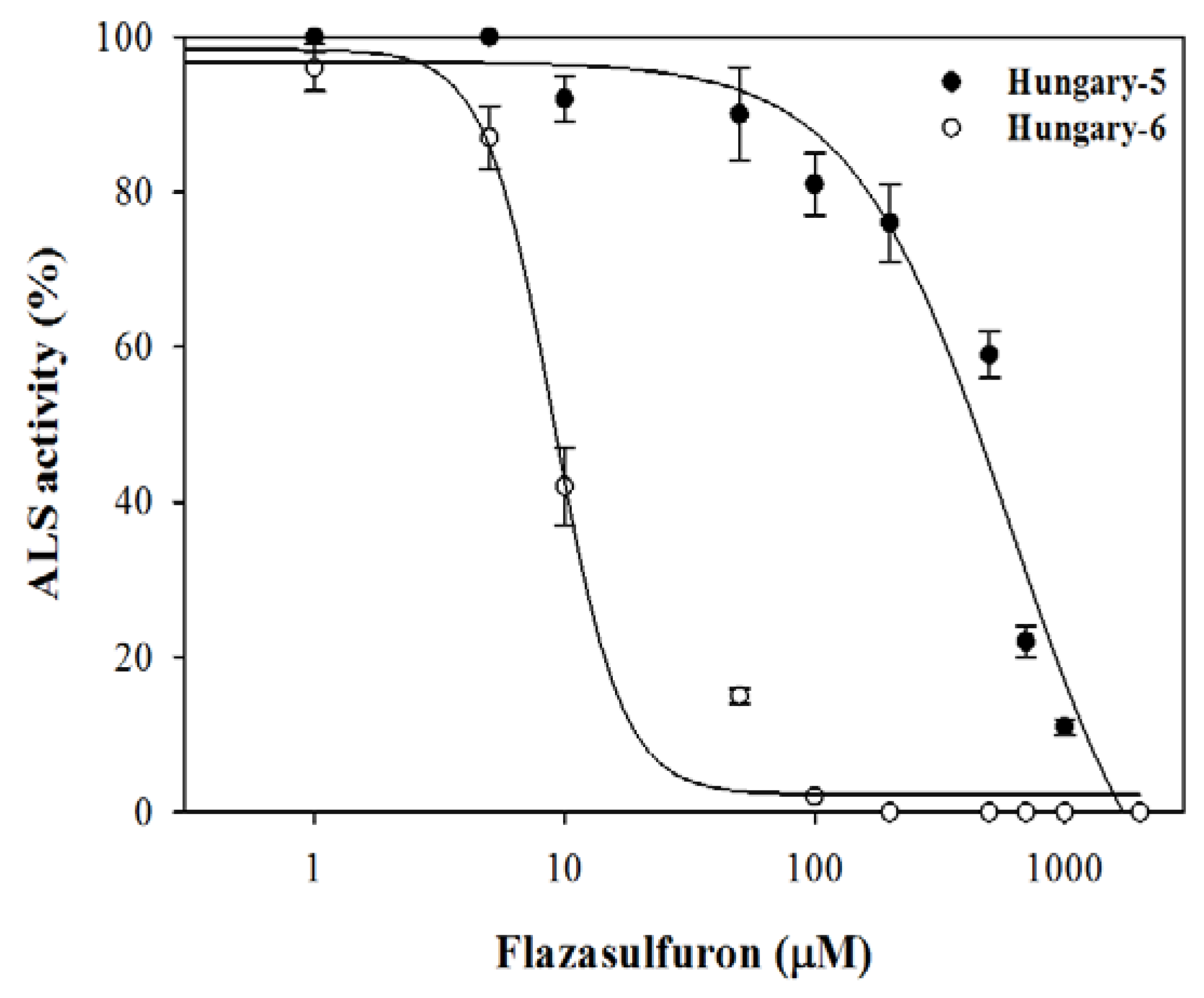
3.4. ALS Enzyme Activity
4. Discussion
4.1. Dose–Response Assays with Glyphosate
4.2. Shikimic Acid Accumulation
4.3. Dose–Response Assays with Alternative Herbicides
4.4. ALS Enzyme Activity
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- HRAC-Herbicide Resistance Action Committee (2018) Confirming resistance. Available online: http://hracglobal.com/herbicide-resistance/confirming-resistance (accessed on 7 January 2018).
- Sammons, R.D.; Gaines, T.A. Glyphosate resistance: State of knowledge. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heap, I.; Duke, S.O. Overview of glyphosate-resistant weeds worldwide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Torralva, F.; Rojano-Delgado, A.M.; de Castro, M.D.L.; Mülleder, N.; De Prado, R. Two non-target mechanisms are involved in glyphosate-resistant horseweed (Conyza canadensis L. Cronq.) biotypes. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Torralva, F.; Gil-Humanes, J.; Barro, F.; Domínguez-Valenzuela, J.A.; De Prado, R. First evidence for a target site mutation in the EPSPS2 gene in glyphosate-resistant Sumatran fleabane from citrus orchards. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, Z.; Rubin, B. Non-target-site glyphosate resistance in Conyza bonariensis is based on modified subcellular distribution of the herbicide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanGessel, M.J. Glyphosate-resistant horseweed from Delaware. Weed Sci. 2001, 49, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; d’Avignon, D.A.; Ackerman, J.J.; Sammons, R.D. Rapid vacuolar sequestration: The horseweed glyphosate resistance mechanism. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojano-Delgado, A.M.; Cruz-Hipolito, H.; De Prado, R.; Castro, M.D.L.; Franco, A.R. Limited uptake, translocation and enhanced metabolic degradation contribute to glyphosate tolerance in Mucuna pruriens var. utilis plants. Phytochemistry 2012, 73, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojano-Delgado, A.M.; Priego-Capote, F.; de Castro, M.D.L.; De Prado, R. Mechanism of imazamox resistance of the Clearfield® wheat cultivar for better weed control. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Délye, C. Unravelling the genetic bases of non-target-site-based resistance (NTSR) to herbicides: A major challenge for weed science in the forthcoming decade. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherekhloo, J.; Fernández-Moreno, P.T.; Alcántara-de la Cruz, R.; Sánchez-González, E.; Cruz-Hipolito, H.E.; Dominguez-Valenzuela, J.A.; De Prado, R. Pro-106-Ser mutation and EPSPS overexpression acting together simultaneously in glyphosate-resistant goosegrass (Eleusine indica). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, P.; Alcántara, R.; Osuna, M.D.; Vila-Aiub, M.M.; Prado, R. Forward selection for multiple resistance across the non-selective glyphosate, glufosinate and oxyfluorfen herbicides in Lolium weed species. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO-Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. ECA/40/17/INF/4 rev.1. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-mu357s.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2017).
- Hess, M.; Barralis, G.; Bleiholder, H.; Buhr, L.; Eggers, T.H.; Hack, H.; Stauss, R. Use of the extended BBCH scale-general for the descriptions of the growth stages of mono; and dicotyledonous weed species. Weed Res. 1997, 37, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, F.E.; Owens, D.K.; Corniani, N.; Silva, F.M.L.; Watson, S.B.; Howell, J.L.; Shaner, D.L. Biochemical markers and enzyme assays for herbicide mode of action and resistance studies. Weed Sci. 2015, 63, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, B.D.; Shrestha, A.; Shaner, D.L. Distribution of glyphosate-resistant horseweed (Conyza canadensis) and relationship to cropping systems in the central valley of California. Weed Sci. 2009, 57, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, Z.M.; Gherekhloo, J.; Rojano-Delgado, A.M.; Osuna, M.D.; Alcántara, R.; Fernández, P.; Sadeghipour, H.R.; De Prado, R. Multiple mechanisms increase levels of resistance in Rapistrum rugosum to ALS herbicides. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, C.; Baty, F.; Streibig, J.C.; Gerhard, D. Dose–response analysis using R. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornisielo, V.L.; Botelho, R.G.; Alves, P.A.T.; Bonfleur, E.J.; Monteiro, S.H. Pesticide tank mixes: An environmental point of view. In Herbicides-Current Research and Case Studies in Use; Price, A., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2013; pp. 473–487. [Google Scholar]
- Bracamonte, E.; Fernández-Moreno, P.T.; Barro, F.; De Prado, R. Glyphosate-resistant Parthenium hysterophorus in the Caribbean islands: Non target site resistance and target site resistance in relation to resistance levels. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Valenzuela, J.A.; Gherekhloo, J.; Fernández-Moreno, P.T.; Cruz-Hipolito, H.E.; Alcántara-de la Cruz, R.; Sánchez-González, E.; De Prado, R. First confirmation and characterization of target and non-target site resistance to glyphosate in Palmer amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) from Mexico. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Torralva, F.; Cruz-Hipolito, H.; Bastida, F.; Mülleder, N.; Smeda, R.J.; De Prado, R. Differential susceptibility to glyphosate among the Conyza weed species in Spain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4361–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcántara-de la Cruz, R.; Fernández-Moreno, P.T.; Ozuna, C.V.; Rojano-Delgado, A.M.; Cruz-Hipolito, H.E.; Domínguez-Valenzuela, J.A.; Barro, F.; De Prado, R. Target and non-target site mechanisms developed by glyphosate-resistant Hairy beggarticks (Bidens pilosa L.) populations from Mexico. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaner, D.L.; Nadler-Hassar, T.; Henry, W.B.; Koger, C.H. A rapid in vivo shikimate accumulation assay with excised leaf discs. Weed Sci. 2005, 53, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracamonte, E.; Silveira, H.M.; Alcántara-de la Cruz, R.; Domínguez-Valenzuela, J.A.; Cruz-Hipolito, H.E.; De Prado, R. From tolerance to resistance: Mechanisms governing the differential response to glyphosate in Chloris barbata. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, B.K.; Alebrahim, M.T.; Roldán-Gómez, R.A.; Silveira, H.M.; Carvalho, L.B.; Alcántara-de la Cruz, R.; De Prado, R. Effectiveness of alternative herbicides on three Conyza species from Europe with and without glyphosate resistance. Crop Prot. 2018, 112, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Hipolito, H.; Rosario, J.; Ioli, G.; Osuna, M.D.; Smeda, R.J.; González-Torralva, F.; De Prado, R. Resistance mechanism to tribenuron-methyl in white mustard (Sinapis alba) from southern Spain. Weed Sci. 2013, 61, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Kruger, G.R.; Singh, S.; Davis, V.M.; Tranel, P.J.; Weller, S.C.; Johnson, W.G. Cross-resistance of horseweed (Conyza canadensis) populations with three different ALS mutations. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byker, H.P.; Soltani, N.; Robinson, D.E.; Tardif, F.J.; Lawton, M.B.; Sikkema, P.H. Occurrence of glyphosate and cloransulam resistant Canada fleabane (Conyza canadensis L. Cronq.) in Ontario. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 93, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzrafi, M.; Lazar, T.W.; Sibony, M.; Rubin, B. Conyza species: Distribution and evolution of multiple target-site herbicide resistances. Planta 2015, 242, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Population | Location | Crops | Herbicide Application | Dose/Year | Coordinate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GR | Córdoba/ESP | Olive grove | Glyphosate | 1440 a/20 | 37.999, −4.448 |
| GS | Córdoba/ESP | Railway | Mechanical control | ------ | 37.916, −4.717 |
| H-1 | Badacsony/HUN | Vineyard | Glyphosate + 2,4-D | 1440 a/10 + 600 b/5 | 46.786, 17.382 |
| H-2 | Badacsony/HUN | Vineyard | Glyphosate + flazasulfuron | 1440 a/10 + 750 c/4 | 46.790, 17.428 |
| H-3 | Badacsony/HUN | Vineyard | Glyphosate | 1800 a/20 | 46.785, 17.449 |
| H-4 | Balaton/HUN | Vineyard | Glyphosate | 1800 a/20 | 46.787, 17.716 |
| H-5 | Balaton/HUN | Vineyard | Glyphosate + flazasulfuron | 1800 a/20 + 750 c/7 | 46.788, 17.770 |
| H-6 | Balaton/HUN | Vineyard | Organic crop | ---/20 | 46.811, 17.830 |
| H-7 | Balaton/HUN | No crop | No herbicide | ------ | 46.871, 17.944 |
| H-8 | Badacsony/HUN | Vineyard | Organic crop | ---/10 | 46.787, 17.487 |
| Herbicide | HRAC b | Formulation/Manufacturer | Dose–Response | Dose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glyphosate c | G | Roundup Energy® (SL 50.9% w/v)/Monsanto | 0/31.25/62.5/125/250/500/1000/2000/4000/6000 | 1080 |
| Flazasulfuron | B | Terafit® (WG 25% w/w)/Syngenta | 0/5/10/20/40/50/100/200 | 80 |
| 2,4-D | O | U46 D Complet® (SL, 60% w/v)/Nufarm | 0/45/90/180/360/720/1200 | 600 |
| Carfentrazone | E | Affinity 240 CE® (CE 22.3% w/v)/FMC | 0/3.75/7.5/15/30/60/100 | 100 |
| Flumioxazin | E | Pledge® (WP 50% w/w)/Kenogard | 0/25/50/100/300/600 | 400 |
| Fluroxypyr | O | Praxis® (EC 20% p/v)/Nufarm | 0/25/50/100/200/400 | 200 |
| Diflufenican | F1 | Mohican 50 SC® (SC 50% w/v)/Sapec | 0/125/250/500/1000/2000 | 375 |
| Fomesafen | E | Flex 25 SL® (25% w/v)/Syngenta | 0/50/100/200/300/600 | 400 |
| MCPA | O | U 46 SP Fluid® (SL 40% p/v)/Nufarm | 0/250/500/750/1000/2000 | 1000 |
| Pyraflufen-ethyl | E | Gozai® CE, 2.65% w/v)/Belchim | 0/1/2/3/6/8 | 6.62 |
| Glufosinate | H | Finale® (SL, 20% w/v)/BayerCropScience | 0/31.25/62.5/125/250/500/1000/2000/4000 | 750 |
| Diquat | D | Reglone® (SL, 17% w/w)/Syngenta | 0/5/25/50/100/200/400/600/800 | 400 |
| Population | d | b | LD50 | RF * | P | d | b | GR50 | RF * | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GR | 100.3 | 4.53 | 3453.6 ± 91.4 | 11.3 | 0.0001 | 100.0 | 2.03 | 1474.0 ± 106.4 | 30.5 | 0.0001 |
| GS | 102.1 | 1.81 | 305.7 ± 33.1 | 101.3 | 4.23 | 48.3 ± 4.3 | ||||
| H-1 | 98.9 | 3.33 | 2761.8 ± 62.5 | 9.0 | 0.0001 | 98.7 | 1.26 | 574.5 ± 38.6 | 11.9 | 0.0001 |
| H-2 | 100.2 | 6.96 | 3055.8 ± 87.2 | 10. | 0.0001 | 98.3 | 1.08 | 500.1 ± 29.8 | 10.3 | 0.0001 |
| H-3 | 99.3 | 5.88 | 2937.7 ± 83.8 | 9.6 | 0.0001 | 99.6 | 1.10 | 990.9 ± 102.4 | 20.5 | 0.0001 |
| H-4 | 99.6 | 5.72 | 3358.6 ± 102.9 | 11.0 | 0.0001 | 99.7 | 1.46 | 995.5 ± 74.4 | 20.6 | 0.0001 |
| H-5 | 100.0 | 3.18 | 4029.4 ± 115.4 | 13.2 | 0.0001 | 99.9 | 0.82 | 638.4 ± 21.5 | 13.2 | 0.0001 |
| H-6 | 100.4 | 4.20 | 383.0 ± 21.9 | 1.5 | 0.2671 | 100.5 | 1.67 | 83.3 ± 5.4 | 1.7 | 0.1227 |
| H-7 | 100.9 | 5.09 | 436.4 ± 38.9 | 1.4 | 0.1089 | 102.4 | 1.33 | 89.4 ± 9.6 | 1.8 | 0.1098 |
| H-8 | 99.3 | 3.78 | 493.2 ± 17.5 | 1.6 | 0.3516 | 100.5 | 1.76 | 79.7 ± 12.0 | 1.6 | 0.2539 |
| Populations | Glyphosate Concentration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 50 | 100 | 500 | 1000 | |
| GR | 4.3 ± 0.7 G | 23.5 ± 3.9 DE | 54.9 ± 6.4 C | 63.1 ± 7.3 B | 65.8 ± 6.1 B |
| GS | 10.2 ± 1.8 EF | 78.7 ± 7.6 B | 160.4 ± 15.3 B | 273.7 ± 23.1 A | 289.5 ± 24.3 A |
| H-1 | 6.2 ± 1.3 G | 20.1 ± 4.6 E | 60.1 ± 8.1 C | 66.7 ± 5.5 B | 71.5 ± 7.5 B |
| H-2 | 13.9 ± 2.1 CDE | 22.0 ± 2.6 DE | 56.6 ± 6.9 C | 62.5 ± 7.0 B | 69.4 ± 5.4 B |
| H-3 | 10.5 ± 3.3 DEF | 25.5 ± 3.0 CD | 61.8 ± 5.4 C | 70.4 ± 6.1 B | 76.0 ± 8.3 B |
| H-4 | 7.7 ± 2.5 FG | 29.1 ± 4.4 C | 52.3 ± 7.1 C | 64.5 ± 5.8 B | 71.5 ± 7.1 B |
| H-5 | 14.3 ± 3.8 BCD | 25.1 ± 3.7 CDE | 61.3 ± 6.5 C | 68.3 ± 7.3 B | 75.0 ± 6.4 B |
| H-6 | 18.2 ± 3.1 AB | 83.9 ± 6.1 A | 176.5 ± 20.1 AB | 250.9 ± 24.3 A | 276.8 ± 29.2 A |
| H-7 | 16.9 ± 2.4 ABC | 75.6 ± 7.4 B | 171.9 ± 17.6 AB | 268.8 ± 27.3 A | 283.2 ± 25.1 A |
| H-8 | 20.1 ± 5.4 A | 80.4 ± 6.0 AB | 182.7 ± 18.3 AB | 276.3 ± 30.6 A | 288.9 ± 27.4 A |
| Herbicide/Population | d | b | LD50 | RF * | P | d | b | GR50 | RF * | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flazasulfuron | H-5 | 100.6 | 2.41 | 161.2 ± 24.4 | 27.9 | 0.0001 | 98.5 | 1.15 | 52.6 ± 5.7 | 16.5 | 0.0001 |
| H-6 | 100.0 | 3.55 | 5.8 ± 0.4 | 102.5 | 2.18 | 3.2 ± 0.3 | |||||
| 2,4-D | H-5 | 102.7 | 2.11 | 184.4 ± 21.0 | 1.1 | 0.3902 | 99.3 | 0.82 | 124.8 ± 25.4 | 1.6 | 0.0968 |
| H-6 | 101.6 | 1.72 | 164.8 ± 22.7 | 102.3 | 0.87 | 79.5 ± 18.6 | |||||
| Carfentrazone | H-5 | 100.9 | 2.64 | 30.9 ± 0.8 | 1.3 | 0.2571 | 99.0 | 1.13 | 19.1 ± 1.7 | 1.3 | 0.2861 |
| H-6 | 100.4 | 1.76 | 23.6 ± 1.6 | 100.6 | 1.14 | 15.1 ± 2.4 | |||||
| Flumioxazin | H-5 | 100.3 | 2.92 | 200.6 ± 25.9 | 1.4 | 0.0984 | 101.4 | 0.97 | 75.7 ± 7.9 | 1.6 | 0.3875 |
| H-6 | 103.3 | 2.01 | 141.5 ± 20.6 | 99.9 | 0.79 | 47.4 ± 10.8 | |||||
| Fluroxypyr | H-5 | 101.3 | 3.75 | 114.8 ± 4.6 | 1.1 | 0.0996 | 100.0 | 3.31 | 28.7 ± 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.4392 |
| H-6 | 100.5 | 2.69 | 101.2 ± 2.3 | 100.3 | 2.90 | 24.5 ± 4.0 | |||||
| Diflufenican | H-5 | 101.0 | 3.01 | 258.0 ± 32.2 | 1.1 | 0.1583 | 101.3 | 2.99 | 208.7 ± 13.8 | 1.1 | 0.2447 |
| H-6 | 101.3 | 5.86 | 231.4 ± 9.3 | 100.5 | 2.78 | 183.3 ± 10.8 | |||||
| Fomesafen | H-5 | 102.1 | 3.53 | 206.8 ± 15.5 | 1.0 | 0.1034 | 98.5 | 1.66 | 189.2 ± 17.7 | 1.4 | 0.2816 |
| H-6 | 99.1 | 3.58 | 198.6 ± 10.9 | 97.1 | 1.65 | 131.2 ± 21.8 | |||||
| MCPA | H-5 | 100.4 | 6.03 | 545.2 ± 12.3 | 1.0 | 0.2190 | 99.9 | 0.97 | 172.3 ± 21.1 | 1.3 | 0.1648 |
| H-6 | 96.8 | 4.13 | 506.01 ± 27.7 | 100.0 | 0.93 | 130.3 ± 18.4 | |||||
| Pyraflufen-ethyl | H-5 | 96.3 | 6.03 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 1.1 | 0.1693 | 99.9 | 1.02 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.1 | 0.1739 |
| H-6 | 97.4 | 3.88 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 100.0 | 1.39 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | |||||
| Glufosinate | H-5 | 100.6 | 2.47 | 77.7 ± 6.0 | 1.2 | 0.3591 | 101.5 | 2.05 | 46.1 ± 4.4 | 1.2 | 0.1520 |
| H-6 | 100.1 | 3.66 | 62.8 ± 3.5 | 102.8 | 3.23 | 38.1 ± 5.5 | |||||
| Diquat | H-5 | 100.3 | 1.77 | 14.1 ± 1.9 | 1.3 | 0.2745 | 102.0 | 0.98 | 7.3 ± 0.6 | 1.3 | 0.3435 |
| H-6 | 99.9 | 2.42 | 11.1 ± 1.4 | 101.1 | 1.11 | 5.7 ± 0.3 | |||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palma-Bautista, C.; Tahmasebi, B.K.; Fernández-Moreno, P.T.; Rojano-Delgado, A.M.; Alcántara de la Cruz, R.; De Prado, R. First Case of Conyza canadensis from Hungary with Multiple Resistance to Glyphosate and Flazasulfuron. Agronomy 2018, 8, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8080157
Palma-Bautista C, Tahmasebi BK, Fernández-Moreno PT, Rojano-Delgado AM, Alcántara de la Cruz R, De Prado R. First Case of Conyza canadensis from Hungary with Multiple Resistance to Glyphosate and Flazasulfuron. Agronomy. 2018; 8(8):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8080157
Chicago/Turabian StylePalma-Bautista, Candelario, Behroz Khalil Tahmasebi, Pablo Tomás Fernández-Moreno, Antonia M. Rojano-Delgado, Ricardo Alcántara de la Cruz, and Rafael De Prado. 2018. "First Case of Conyza canadensis from Hungary with Multiple Resistance to Glyphosate and Flazasulfuron" Agronomy 8, no. 8: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8080157
APA StylePalma-Bautista, C., Tahmasebi, B. K., Fernández-Moreno, P. T., Rojano-Delgado, A. M., Alcántara de la Cruz, R., & De Prado, R. (2018). First Case of Conyza canadensis from Hungary with Multiple Resistance to Glyphosate and Flazasulfuron. Agronomy, 8(8), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8080157







