The Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Rhizophagus intraradices Reduces the Negative Effects of Arsenic on Soybean Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
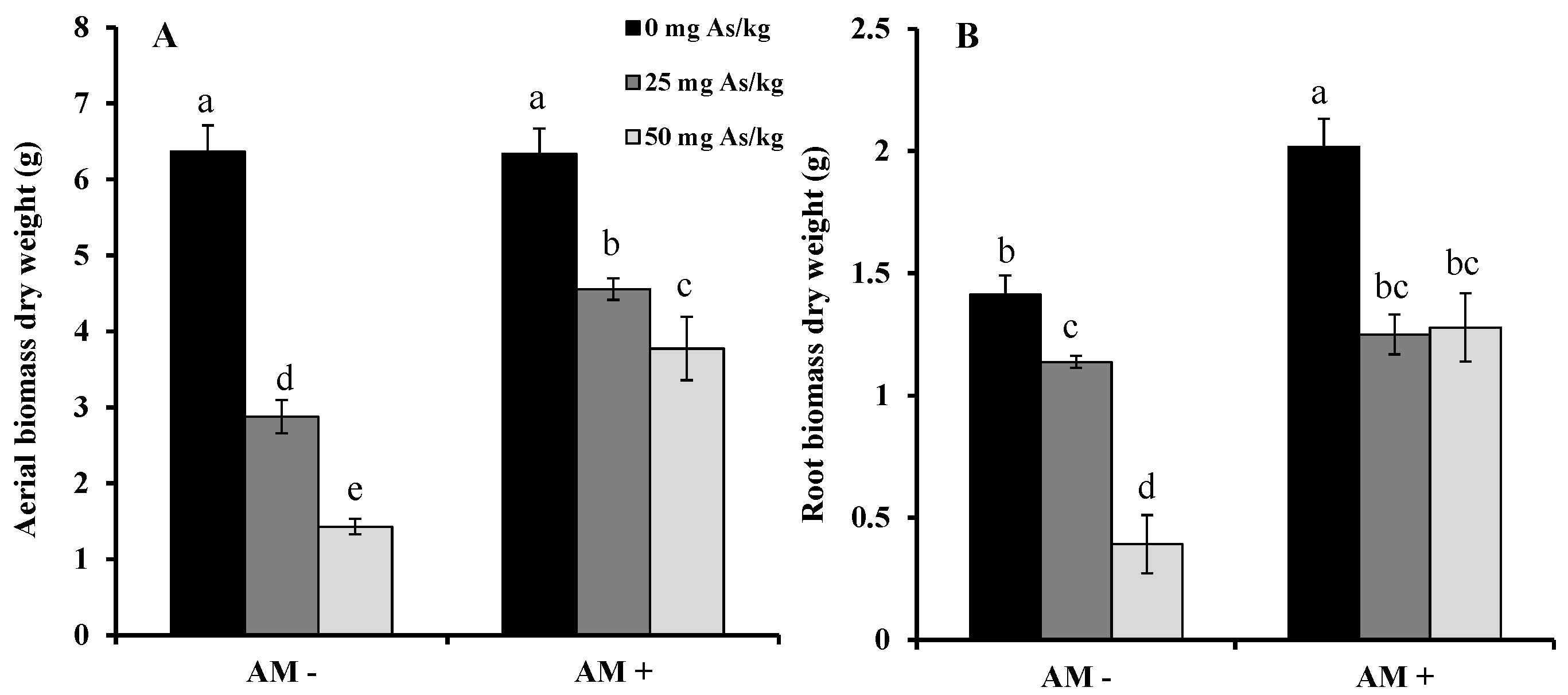
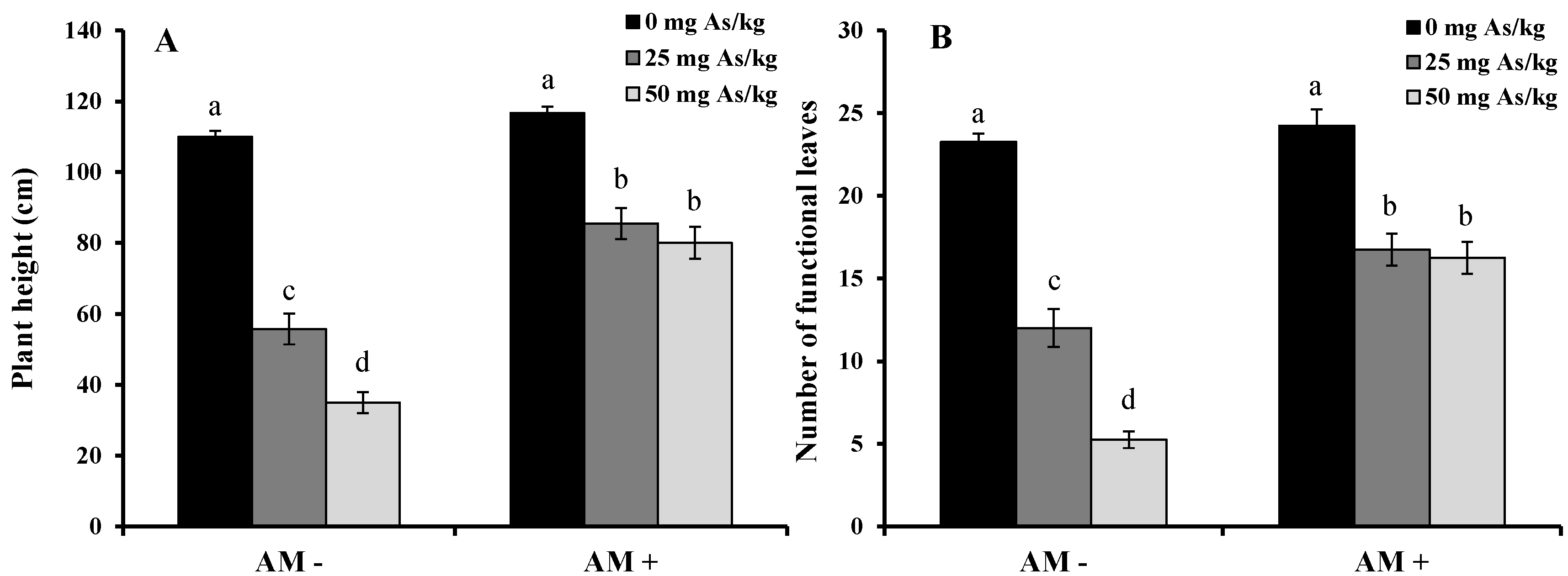
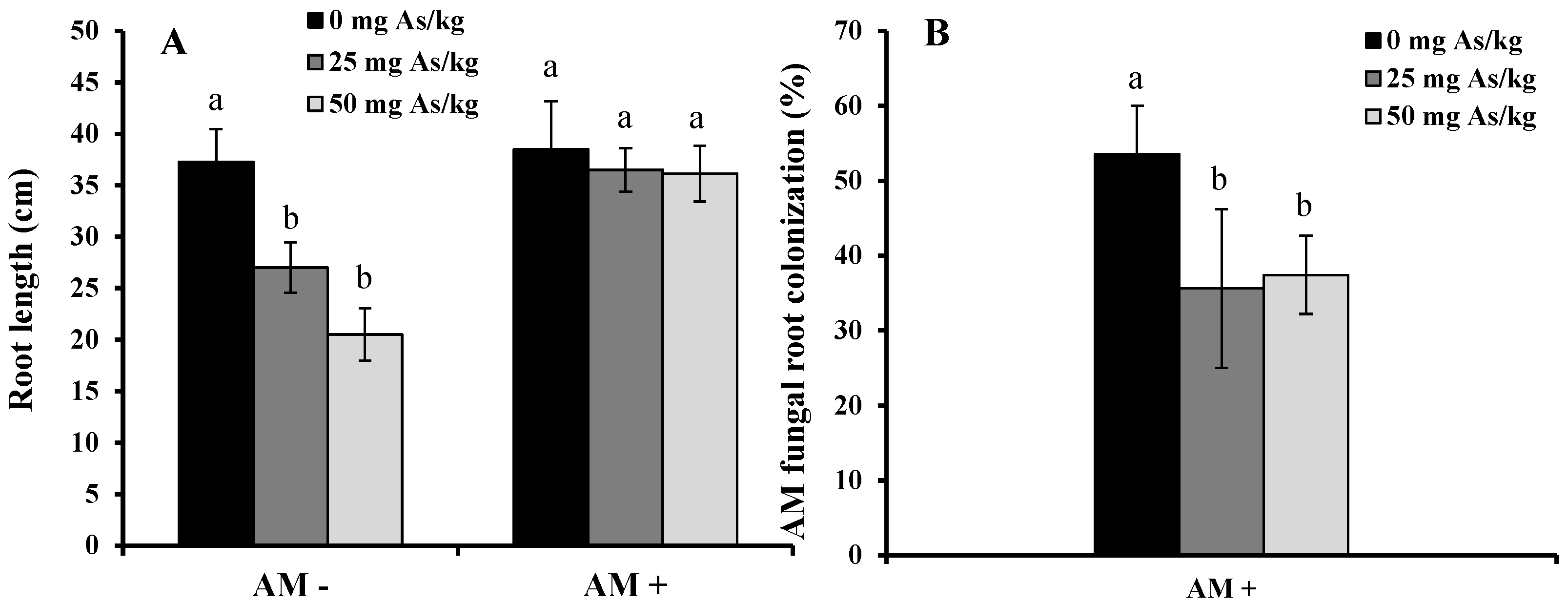
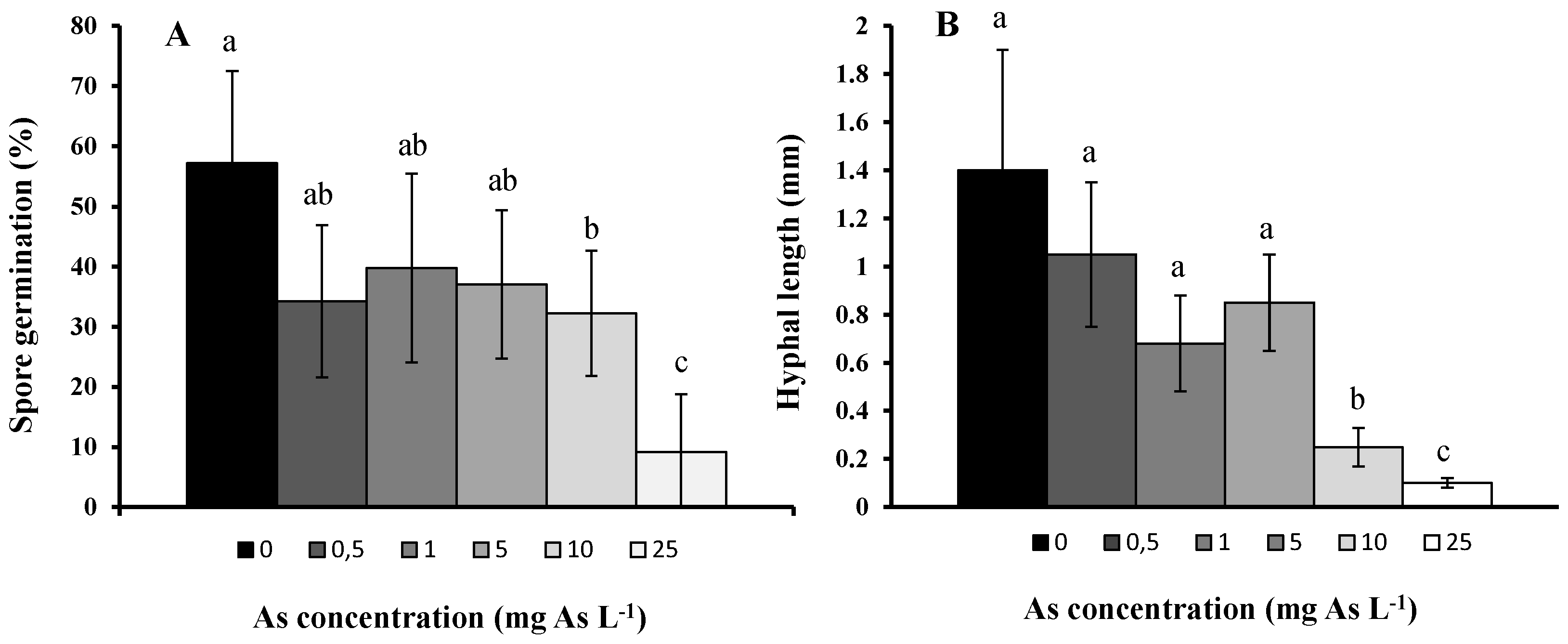
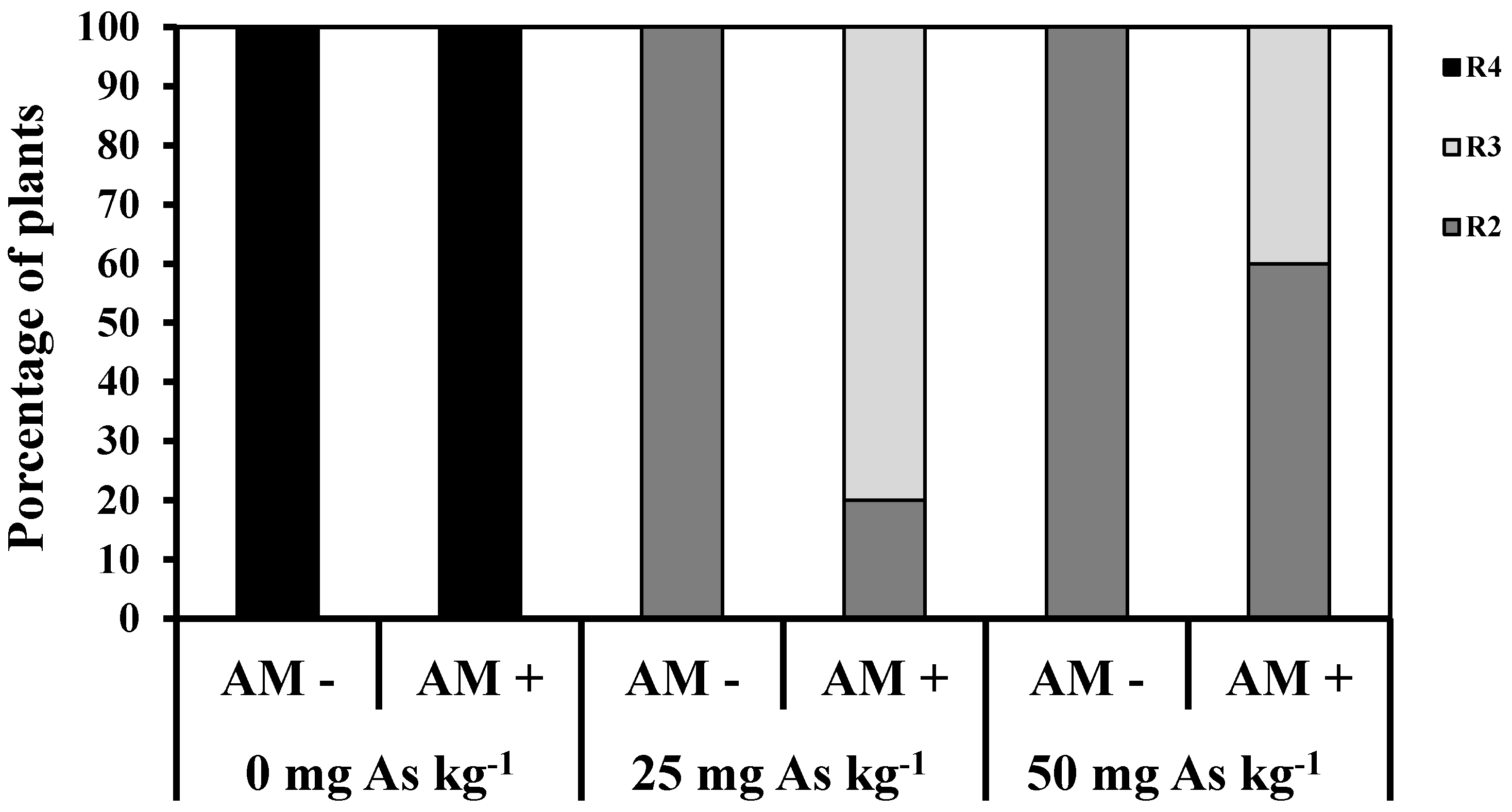
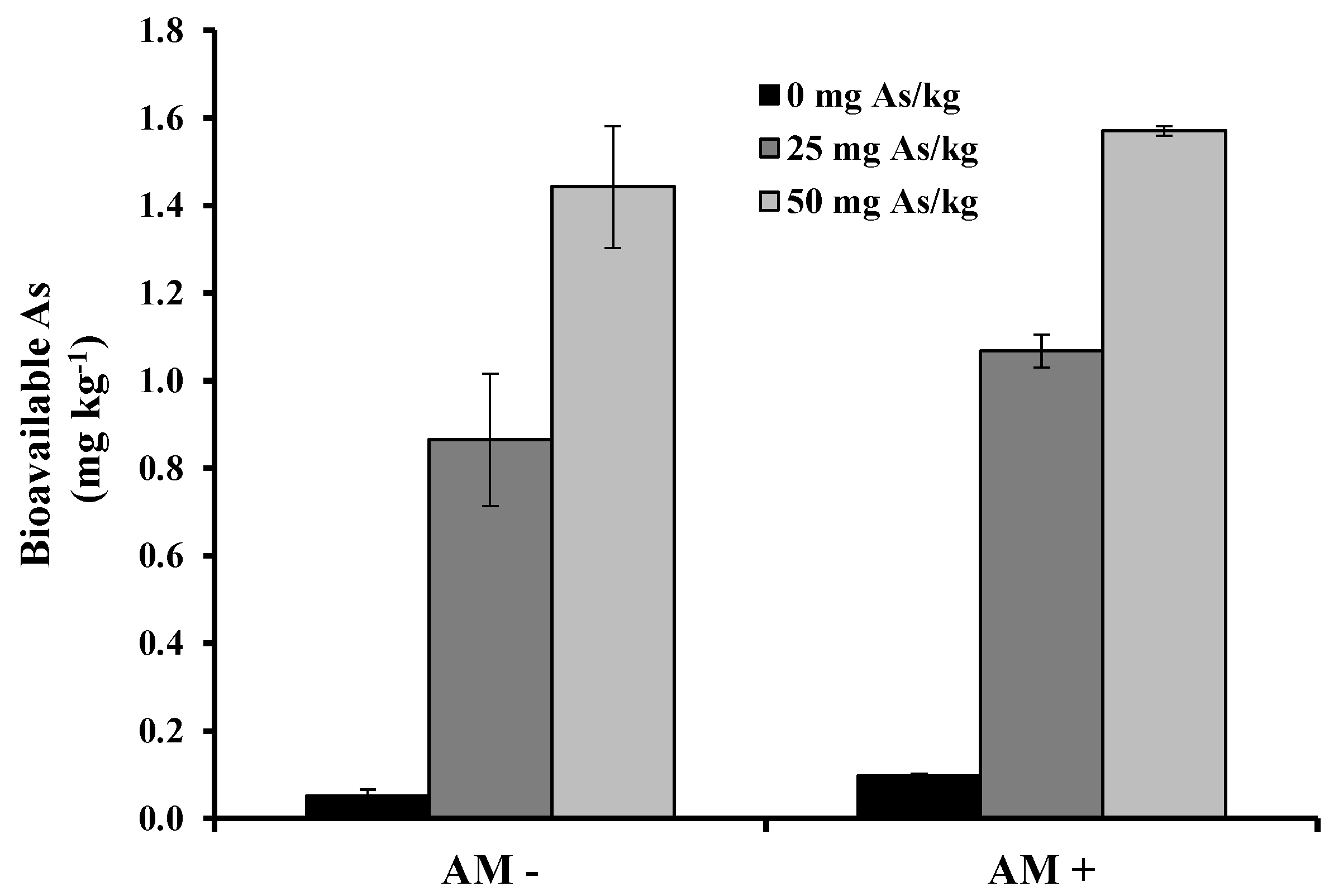
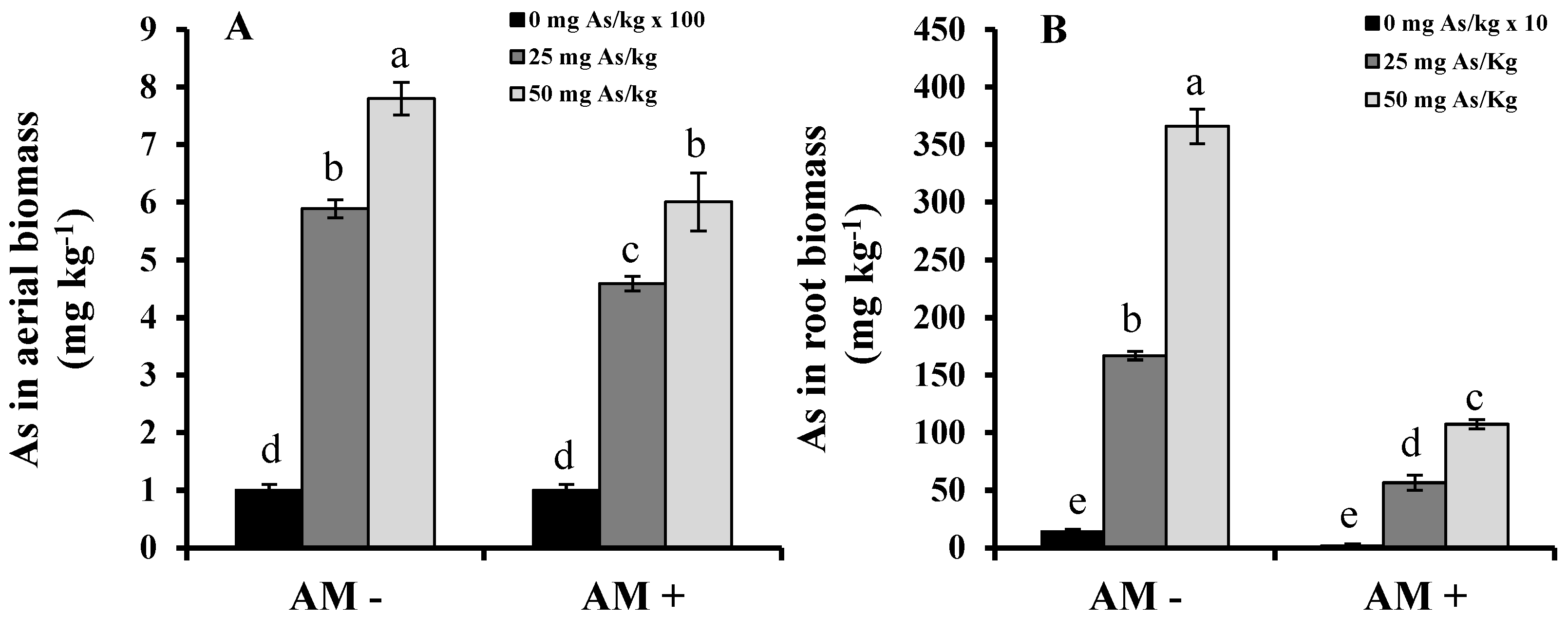
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Determinations
- TF = As concentration in leaves (mg kg−1) / As concentration in roots (mg kg−1)
- BCF = As concentration in plant biomass (mg kg-1) / As concentration in the soil (mg kg−1).
3.2. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandal, B.K.; Zuzuki, K.T. Arsenic around the world: A review. Talanta 2002, 58, 201–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behavior and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammer, H.; Ravenscroft, P. Arsenic in groundwater: A threat to sustainable agriculture in South and South-east Asia. Environ. Int. 2008, 35, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahal, B.M.; Fuerhacker, M.; Mentler, A.; Karki, K.B.; Shrestha, R.R.; Blum, W.E.H. Arsenic contamination of soils and agricultural plants through irrigation water in Nepal. Environ. Poll. 2008, 155, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedin, M.J.; Cottep-Howells, J.; Meharg, A.A. Arsenic uptake and accumulation in rice (Oryza Sativa L.) irrigated with contaminated water. Plant Soil 2002, 240, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Hasegawa, H.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.N.; Miah, M.A.M.; Tasmen, A. Effect of arsenic on photosynthesis, growth and yield of five widely cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigna, M.; Cozzolino, V.; Violante, A.; Meharg, A. Influence of Phosphate on the Arsenic Uptake by Wheat (Triticum durum L.) Irrigated with Arsenic Solutions at Three Different Concentrations. Water Air Soil Poll. 2008, 197, 371–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talano, M.A.; Cejas, R.B.; González, P.S.; Agostini, E. Arsenic effect on the model crop symbiosis Bradyrhizobium-soybean. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 63, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich-Eberius, C.I.; Sanz, A.; Novacky, J. Evaluation of arsenate- and vanadate-associated changes of electrical membrane potential and phosphate transport in Lemna gibba G1. J. Exp. Bot. 1989, 40, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.E.; Christophersen, H.M.; Pope, S.; Smith, F.A. Arsenic uptake and toxicity in plants: Integrating mycorrhizal influences. Plant Soil 2010, 327, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meharg, A.A. Integrated tolerance mechanisms—Constitutive and adaptive plant-responses to elevated metal concentrations in the environment. Plant Cell Environ. 1994, 17, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P.; Meharg, A.A. Arsenic as a food chain contaminant: Mechanisms of plant uptake and metabolism and mitigation strategies. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustingorri, C.; Lavado, R.S. Soybean as affected by high concentrations of arsenic and fluoride in irrigation water in controlled conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 144, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustingorri, C.; Lavado, R.S. Effects of high arsenic and fluoride soil concentrations on soybean plants. Phyton 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Eickhout, B.; Bouwman, A.F.; van Zeijts, H. The role of nitrogen in world food production and environmental sustainability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 116, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinaudi, N.B.; Lavado, R.S. Contaminación con arsénico, paralela a la salinización y alcalinización por el agua de riego. Turrialba 1978, 28, 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Panaullah, G.M.; Alam, T.; Hossain, M.; Loeppert, R.; Lauren, J.; Meisner, C.A.; Ahmed, Z.; Duxbury, J.M. Arsenic toxicity to rice in Bangladesh. Plant Soil 2009, 317, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Yu, W.C. Evaluation of legume growth in arsenic-polluted acidic soils with various pH values. J. Water Sustain. 2012, 2, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Heikens, A.; Panaullah, G.M.; Meharg, A.A. Arsenic behaviour from groundwater and soil to crops: Impacts on agriculture and food safety. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 189, 43–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.E.; Read, D.J. Mycorrhizal Symbiosis, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.D.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Christie, P. Metal concentrations and mycorrhizal status of plants colonizing copper mine tailings, potential for revegetation. Sci. China Ser. C: Life Sci. 2005, 48, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Ye, Z.H.; Wu, S.C.; Wong, M.H. Metal accumulation and arbuscular mycorrhizal status in metallicolus and nonmetallicolus populations of Pteris vitatta L. and Sedum alfredii Hance. Planta 2007, 226, 1363–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Chavez, M.C.; Harris, P.J.; Dodd, J.; Meharg, A.A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhanced arsenate resistance on Holcus lanatus. New Phytol. 2002, 155, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meharg, A.A.; Hartley-Whitaker, J. Arsenic uptake and metabolism in arsenic resistant and non resistantplant species. New Phytol. 2002, 154, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Larrocea, M.P.; Siebe, C.; Estrada, A.; Webster, R. Mycorrhizal inoculum potential of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in soils irrigated with wastewater for various lengths of time, as affected by heavy metals and available P. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 37, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowska, E.; Godzik, B.; Turnau, K. Effect of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal isolates on growth and arsenic accumulation in Plantago lanceolata L. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 168, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapustka, L.A.; Lipton, J.; Galbraith, H.; Cacela, D.; Lejeune, K. Metalic and arsenic impacts to soils, vegetation communities and wildlife habitat in southwest Montana uplands contained by smelter emmisions: II. Laboratory phytotoxicity studies. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1995, 14, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley-Whitaker, J.; Ainsworth, G.; Meharg, A.A. Copper and arsenate induced oxidative stress in Holcus lanatus L. clones with differential sensitivity. Plant Cell Environ. 2001, 24, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Chen, B.D.; Christie, P.; Li, X.L. Yield and arsenate uptake of arbuscular mycorrhizal tomato colonized by Glomus mosseae BEG167 in As spiked soil under glasshouse conditions. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, H.; Wu, N. Uptake of arsenic by maize inoculated with three different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Comun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildon, A.; Tinker, P.B. Interactions of vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection and heavy metals in plants: The effects of heavy metals on the development of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas. New Phytol. 1983, 95, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Barrachina, A.A.; Burló-Carbonell, F.M.; Mataix Beneyto, J.J. Arsénico en el Sistema Suelo-Planta: Significado Ambiental; Universidad de Alicante: Alicante, España, 1995; pp. 1–139. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, A.T.M.; Sen, R.; Haque, M.A.; Panaullah, G.M.; Meisner, C.A.; Loeppert, R.H.; Duxbury, J.M. Arsenic status of water, soil, rice grain and straw of individual shallow tube well command area of Brahmanbaria. CIMMYT/USGS. In Proceedings of Symposium on the Behaviour of Arsenic in Aquifers, Soils and Plants: Implications for Management, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 16–18 January 2005; pp. 20–25.
- Reichman, S.M. The potential use of the legume-rhizobium symbiosis for the remediation of arsenic contaminated sites. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2587–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.R.S.; Killham, K.; Alexander, I. Influences of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae on growth and nutrition of lentil irrigated with arsenic contaminated water. Plant Soil 2006, 283, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.D.; Xiao, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Smith, F.A.; Xie, Z.M.; Smith, S.E. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae gives contradictory effects on phosphorus and arsenic acquisition by Medicago sativa Linn. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 379, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ultra, V.U.; Tanaka, S.; Sakurai, K.; Iwasaki, K. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza and phosphorus application on arsenic toxicity in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) and on the transformation of arsenic in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 2007, 290, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Smith, F.A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B. Arbuscular mycorrhiza enhanced arsenic resistance of both white clover (Trifolium repens Linn.) and ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) plants in an arsenic-contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 155, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barea, J.M.; Jeffries, P. Arbuscular mycorrhizas in sustainable soil plants systems. In Mycorrhiza Structure, Function, Molecular Biology and Biotechnology; Hock, B., Varma, A., Eds.; Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 521–559. [Google Scholar]
- Leyval, C.; Singh, B.R.; Janer, E.J. Occurrence and infectivity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in some Norwegian soils influenced by heavy metals and soil properties. Water Air Soil Poll. 1995, 83, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Val, C.; Barea, J.M.; Azcon-Aguilar, C. Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus populations in heavy-metal-contaminated soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pawlowska, T.E.; Chaney, R.L.; Chin, M.; Charvat, I. Effects of metal phytoextraction practices on the indigenous community of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at a metal contaminated landfill. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 6, 2526–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H.; Soltanpour, P.N.; Tabatabai, M.A.; Johnson, C.T.; Sumner, M.E. Chemical Methods; Book Series; ASA-SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fracchia, S.; Menendez, A.; Godeas, A.; Ocampo, J.A. A method to obtain monosporic cultures of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1283–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anawar, H.M.; Garcia-Sanchez, A.; Santa Regina, I. Evaluation of various chemical extraction methods to estimate plant-available arsenic in mine soils. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Physical/Chemical Methods SW-846; National Technical Information Service (NTIS): Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Mc Gonigle, T.P.; Miller, M.H.; Evans, D.G.; Fairchild, G.S.; Swan, J.A. A new method which gives an objective measure of colonization of roots by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 1990, 115, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.M.; Hayman, D.S. Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc. 1970, 55, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audet, P.; Charest, C. Heavy metal phytoremediation from a meta-analysis perspective. Environ. Poll. 2007, 147, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, S.K.; Nayak, A.K.; Sharma, Y.K. Fluoride toxicity effects in onion (Allium cepa L.) grown in contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishnu, R.; Twanabasu, B.R.; Stevens, K.J.; Venables, B.J. The effects of triclosan on spore germination and hyphal growth of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 454, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spagnoletti, F.; Lavado, R.S. The Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Rhizophagus intraradices Reduces the Negative Effects of Arsenic on Soybean Plants. Agronomy 2015, 5, 188-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy5020188
Spagnoletti F, Lavado RS. The Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Rhizophagus intraradices Reduces the Negative Effects of Arsenic on Soybean Plants. Agronomy. 2015; 5(2):188-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy5020188
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpagnoletti, Federico, and Raúl S. Lavado. 2015. "The Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Rhizophagus intraradices Reduces the Negative Effects of Arsenic on Soybean Plants" Agronomy 5, no. 2: 188-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy5020188
APA StyleSpagnoletti, F., & Lavado, R. S. (2015). The Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Rhizophagus intraradices Reduces the Negative Effects of Arsenic on Soybean Plants. Agronomy, 5(2), 188-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy5020188




