Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Q-Type C2H2 Zinc Finger Proteins in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and Their Expression Patterns Across Tissues and Under Abiotic Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Retrieval and Q-Type C2H2-ZFPs Identification in B. napus
2.2. Conserved Motifs and Gene Structural Analysis
2.3. Chromosomal Localization and Gene Duplication
2.4. Phylogenetic Relationship Analysis
2.5. Expression Profile Analysis of BnaQ-Type C2H2-ZFP Genes in Different Tissues and Under Abiotic Stress Conditions
2.6. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and qPCR Analysis of Freezing-Stress-Responsive Genes in Different Cold-Tolerant Winter B. napus
2.7. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of Q-Type C2H2-ZFP in B. napus
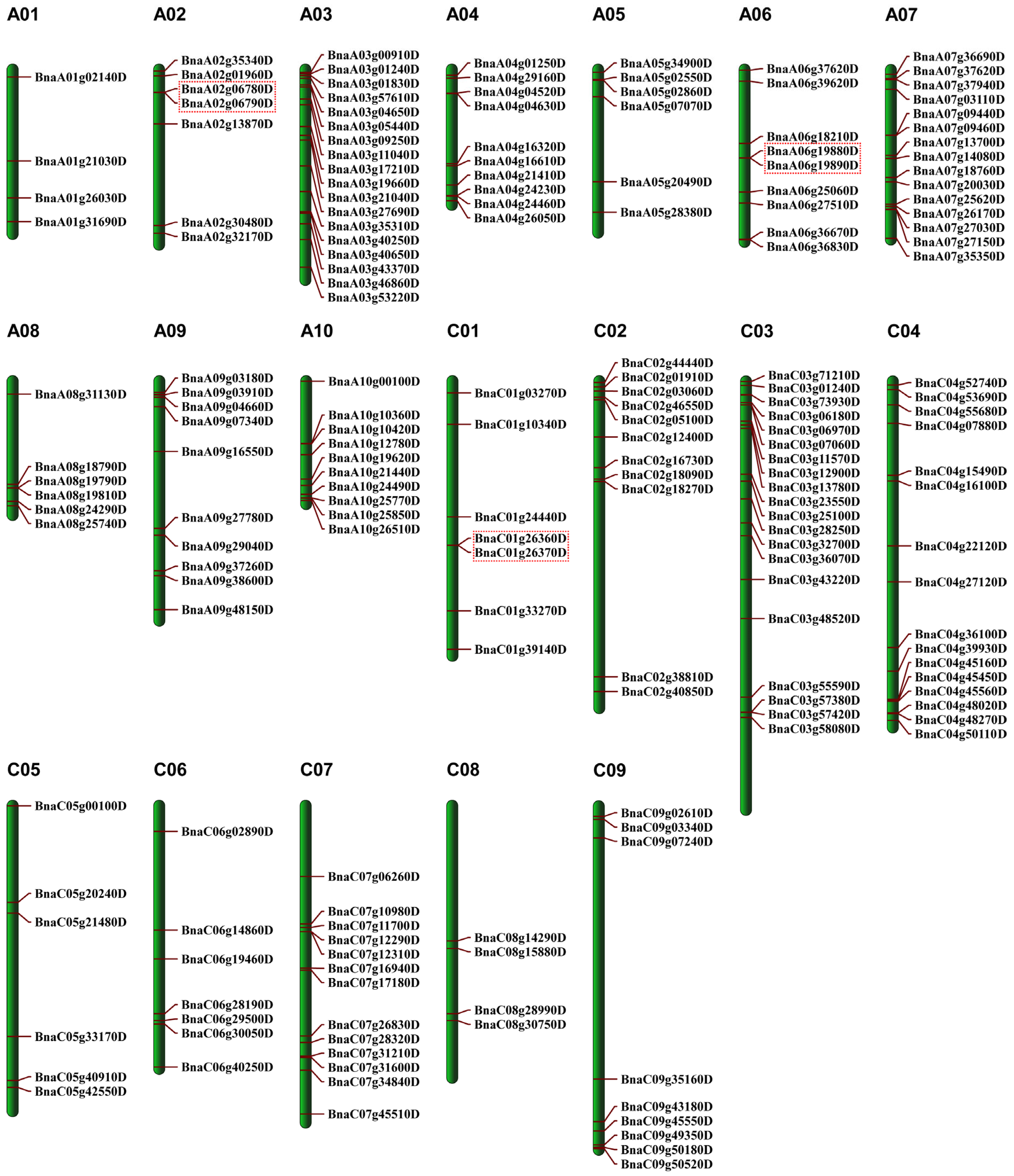
3.2. Chromosomal Localization and Gene Structure Analysis of BnaQ-Type C2H2-ZFP Genes in B. napus
3.3. Conservative Motif Analysis of BnaQ-Type C2H2-ZFPs
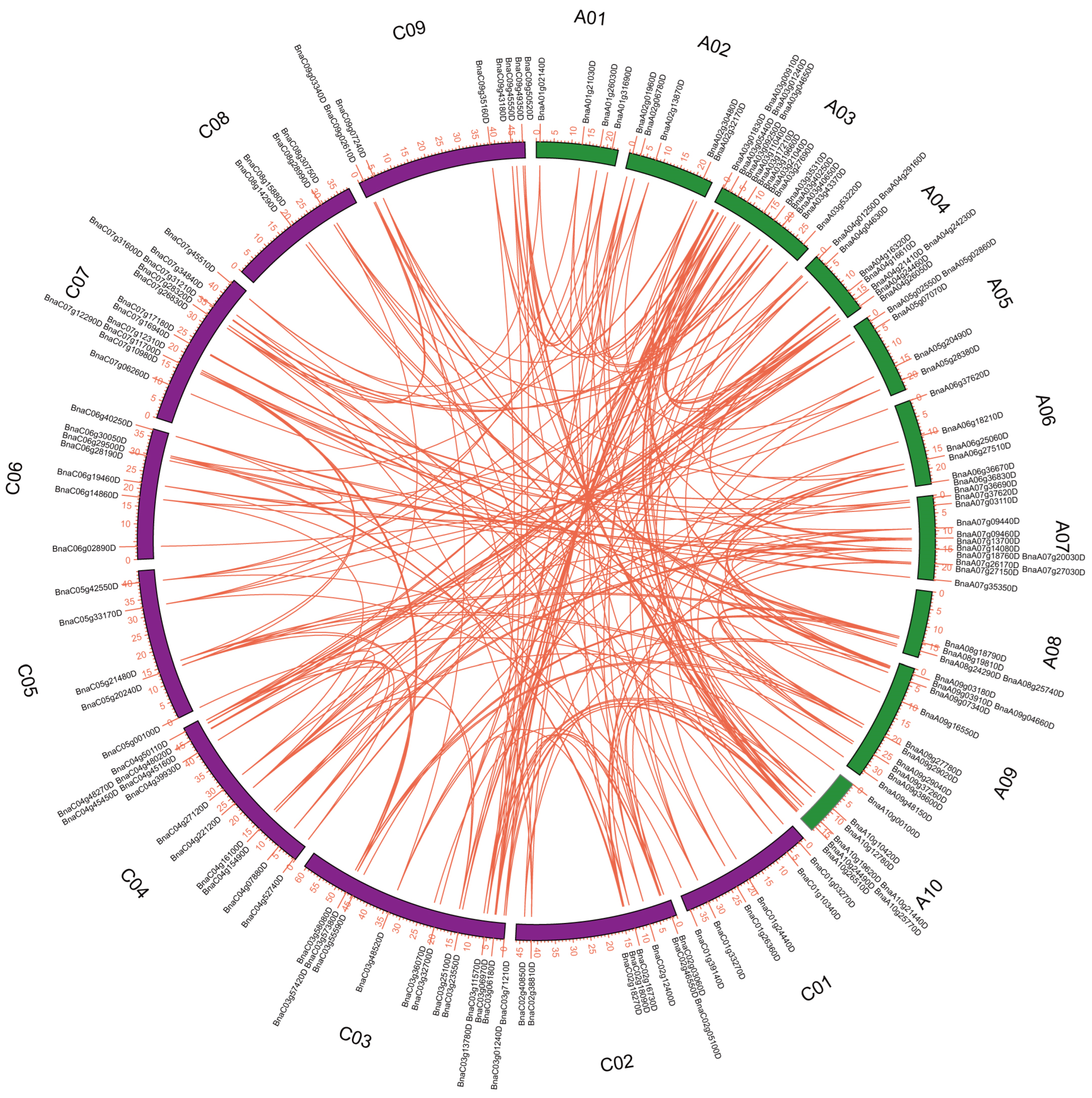
3.4. Gene Duplication and Genomic Collinearity Analysis of BnaQ-Type C2H2-ZFPs
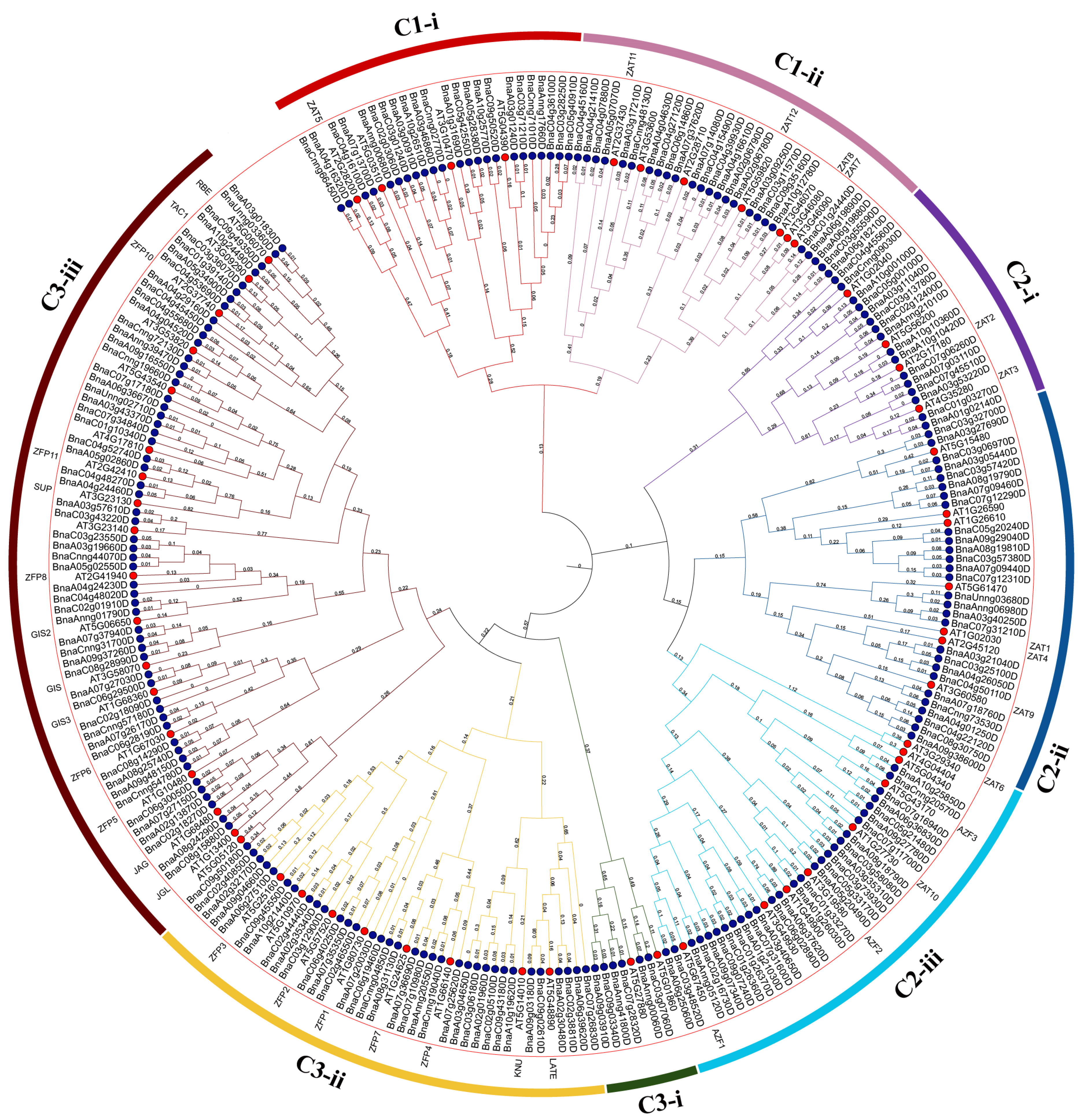
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of BnaQ-Type C2H2-ZFPs
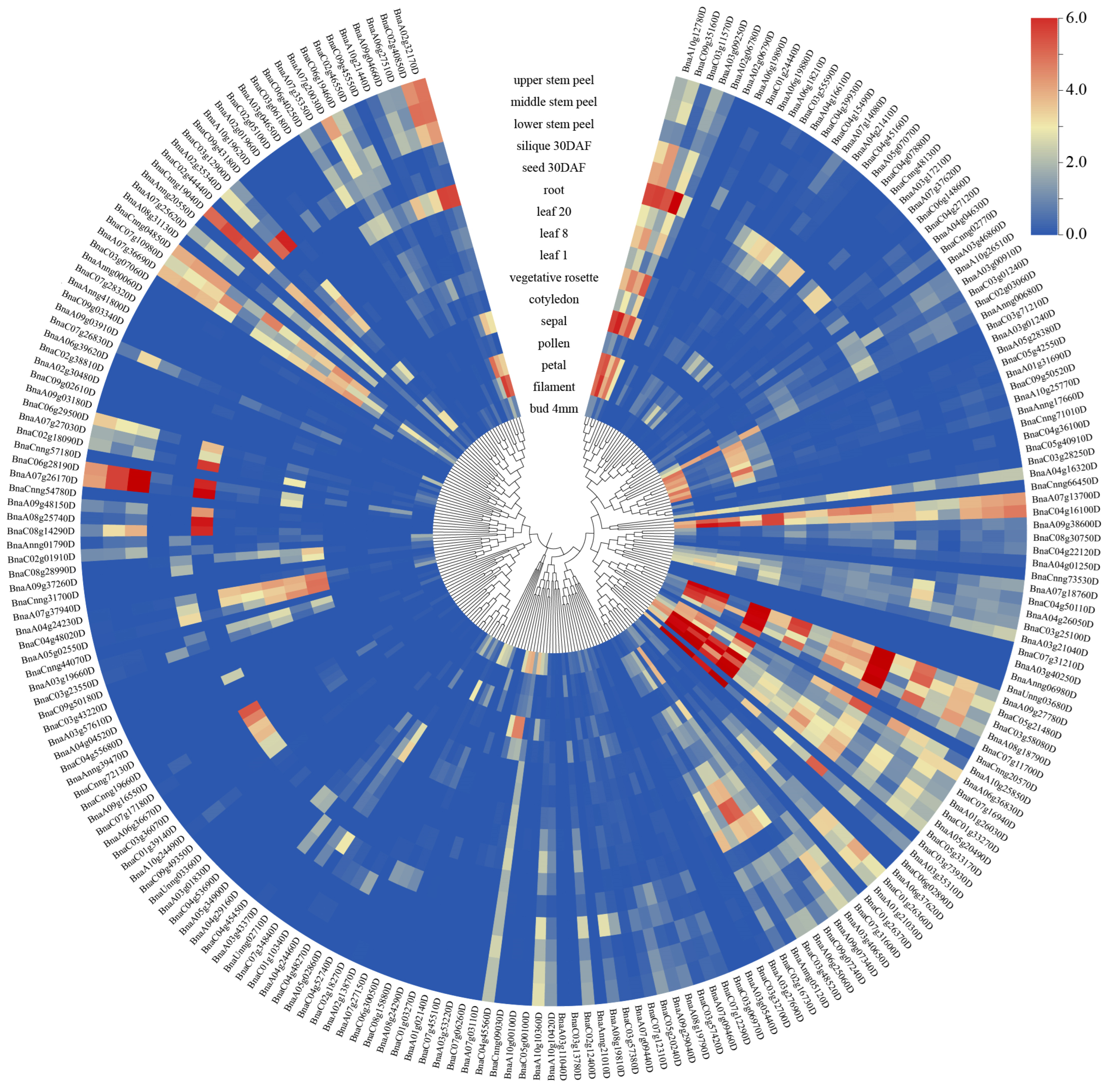
3.6. Expression Analysis of BnaQ-Type C2H2-ZFPs in Different Tissues of B. napus
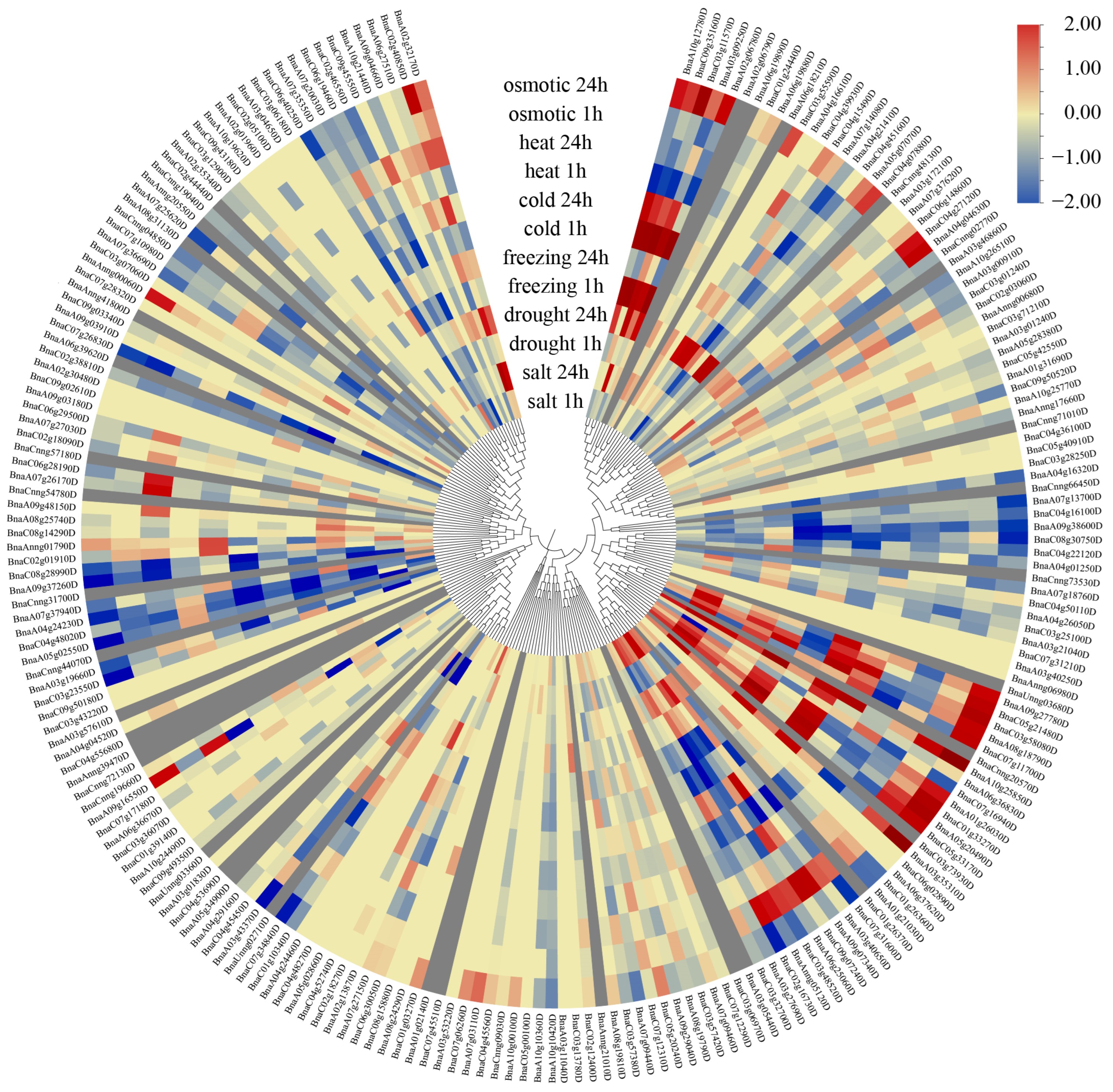
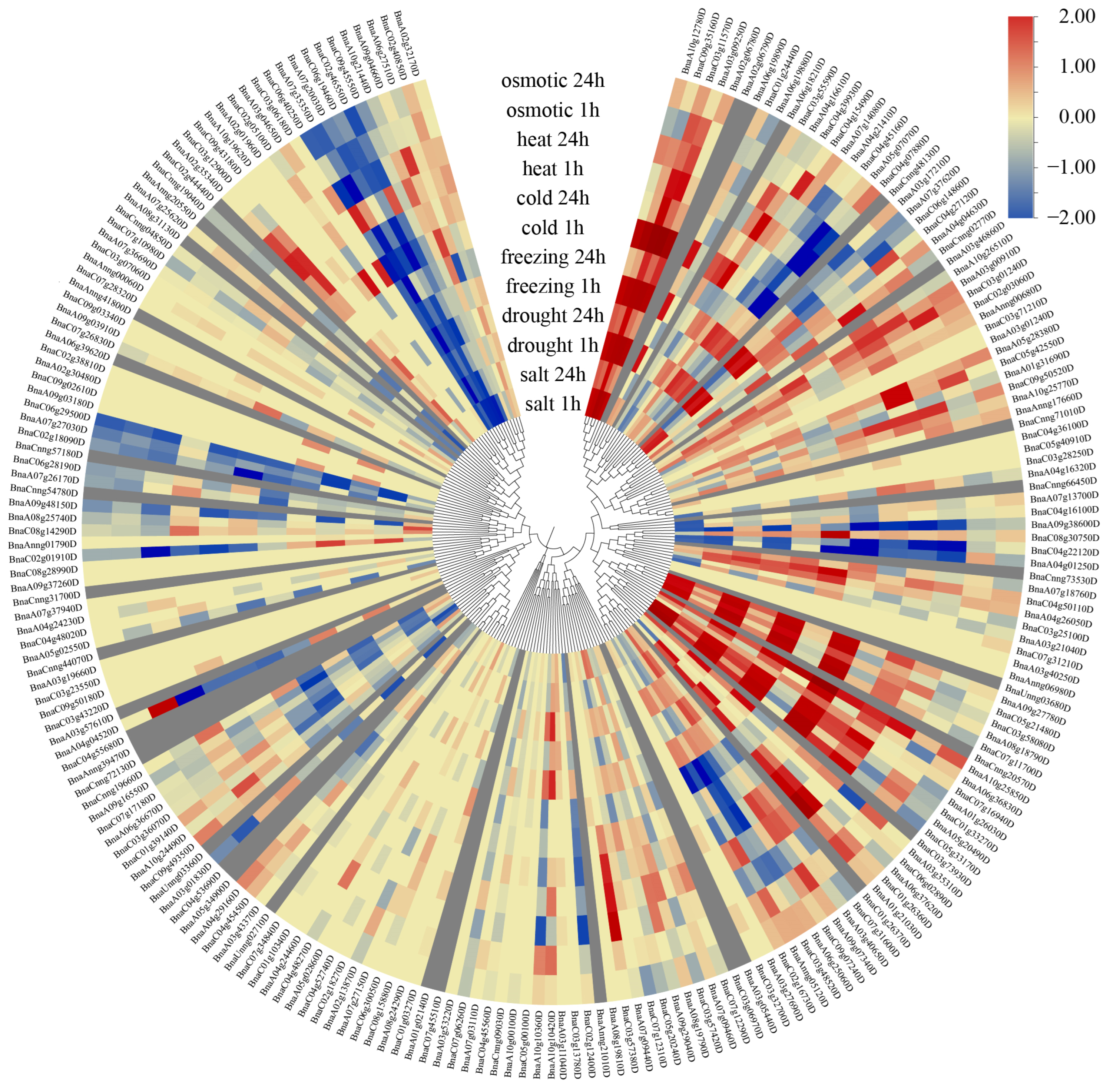
3.7. Expression Analysis of BnaQ-Type C2H2-ZFPs Under Different Abiotic Stress
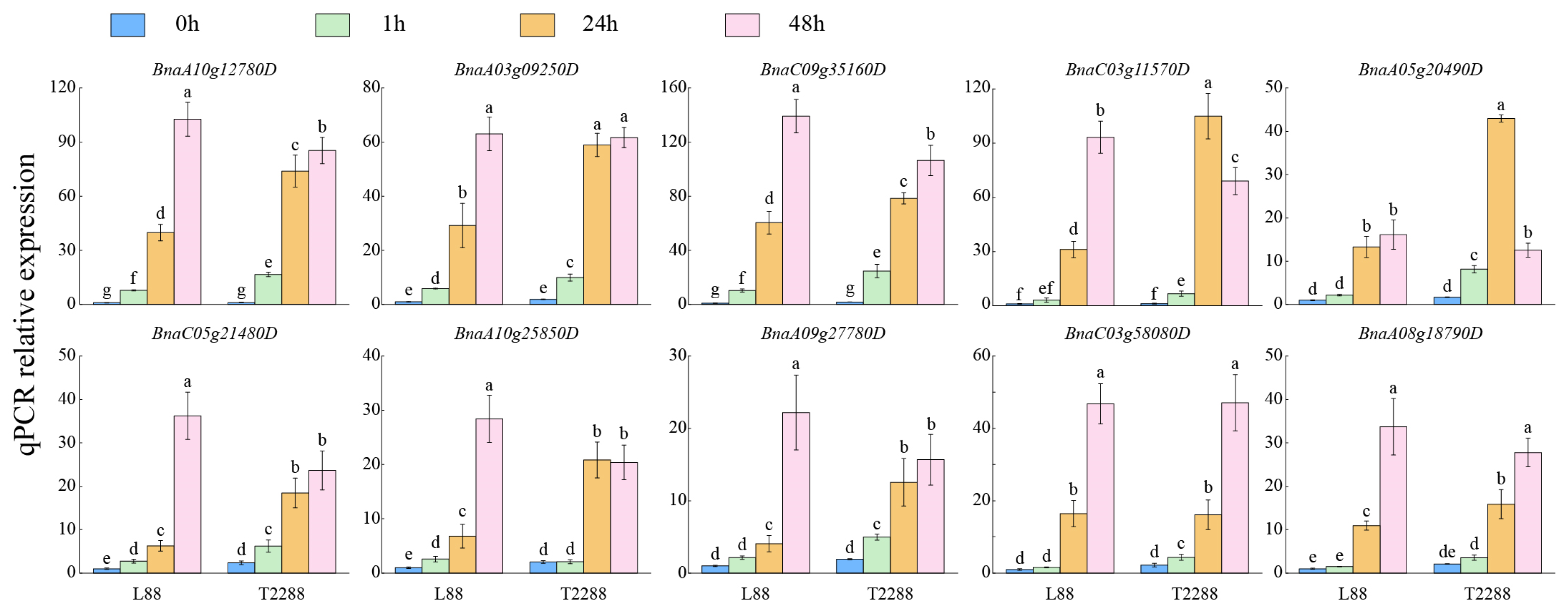
3.8. Expression Levels of BnaQ-Type C2H2-ZFPs in Different Winter-Type B. napus Varieties Under Freezing Stress
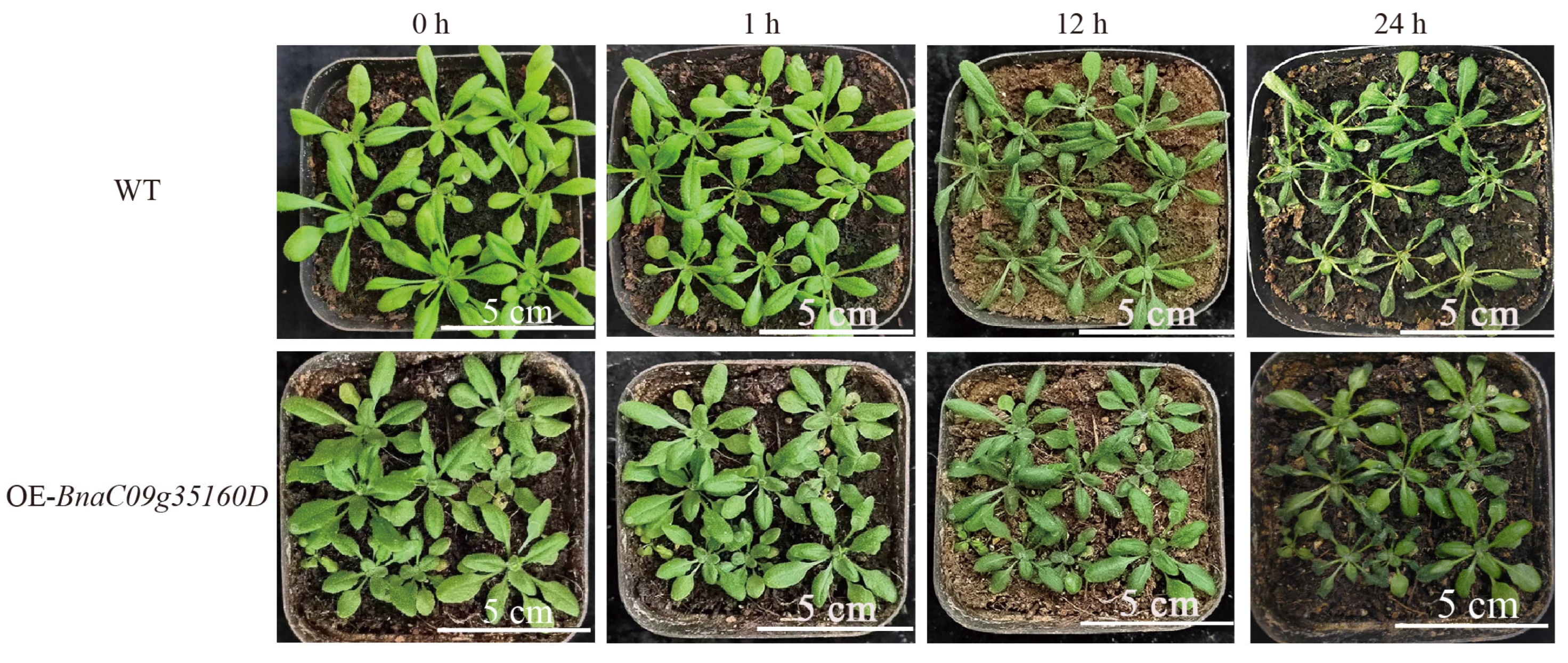
3.9. Phenotypic Analysis of BnaC09g35160D Overexpression in Transgenic Arabidopsis Under Freezing Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tong, C.; Edwards, D.; Parkin, I.A.; Zhao, M.; Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, S.; et al. The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wei, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Jian, H.; et al. Whole-genome resequencing reveals Brassica napus origin and genetic loci involved in its improvement. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, J.; Ma, L.; Yue, J.; Jin, J.; Niu, Z.; Fang, Y.; et al. Transcriptome Profile Analysis of Winter Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) in Response to Freezing Stress, Reveal Potentially Connected Events to Freezing Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laity, J.H.; Lee, B.M.; Wright, P.E. Zinc finger proteins: New insights into structural and functional diversity. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001, 11, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englbrecht, C.C.; Schoof, H.; Böhm, S. Conservation, diversification and expansion of C2H2 zinc finger proteins in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. BMC Genom. 2004, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuji, H. Zinc-finger proteins: The classical zinc finger emerges in contemporary plant science. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 39, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, J.M.; Shi, Y. The galvanization of biology: A growing appreciation for the roles of zinc. Science 1996, 271, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavletich, N.P.; Pabo, C.O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: Crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science 1991, 252, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jiang, F.; Wen, J.; Wu, Z. Overexpression of Solanum habrochaites microRNA319d (sha-miR319d) confers chilling and heat stress tolerance in tomato (S. lycopersicum). BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Chan, Z. The cysteine2/histidine2-type transcription factor ZINC FINGER OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA 6-activated C-REPEAT-BINDING FACTOR pathway is essential for melatonin-mediated freezing stress resistance in Arabidopsis. J. Pineal. Res. 2014, 57, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Ye, T.; Chen, F.; Deng, J.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chan, Z. The Cysteine2/Histidine2-Type Transcription Factor ZINC FINGER OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA6 Modulates Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses by Activating Salicylic Acid-Related Genes and C-REPEAT-BINDING FACTOR Genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaiah, B.N.; Nagarajan, V.K.; Raghothama, K.G. Phosphate homeostasis and root development in Arabidopsis are synchronized by the zinc finger transcription factor ZAT6. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mito, T.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Matsui, K. Generation of chimeric repressors that confer salt tolerance in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Nguyen, X.C.; Kim, K.E.; Han, H.J.; Yoo, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, M.C.; Yun, D.J.; Chung, W.S. Phosphorylation of the zinc finger transcriptional regulator ZAT6 by MPK6 regulates Arabidopsis seed germination under salt and osmotic stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, J.T.; Zarka, D.G.; Van Buskirk, H.A.; Fowler, S.G.; Thomashow, M.F. Roles of the CBF2 and ZAT12 transcription factors in configuring the low temperature transcriptome of Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2005, 41, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.C.; Ho, S.K.; Hussain, S.; Shah, H.; Jonguk, A.; Yeji, Y.; Ju, H.; Soon, J.; Oh, C.; Dae-Jin, Y.; et al. A positive transcription factor in osmotic stress tolerance, ZAT10, is regulated by MAP kinases in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Biol. 2016, 59, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci-Yilmaz, S.; Morsy, M.R.; Song, L.; Coutu, A.; Krizek, B.A.; Lewis, M.W.; Warren, D.; Cushman, J.; Connolly, E.L.; Mittler, R. The EAR-motif of the Cys2/His2-type zinc finger protein Zat7 plays a key role in the defense response of Arabidopsis to salinity stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9260–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; An, J.; Han, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, C.O.; Yun, D.J.; Chung, W.S. ZAT11, a zinc finger transcription factor, is a negative regulator of nickel ion tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Quan, W.; Yang, L.; Wang, Q.; Chan, Z. The Arabidopsis Cys2/His2 zinc finger transcription factor ZAT18 is a positive regulator of plant tolerance to drought stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2991–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, H. BnLATE, a Cys2/His2-Type Zinc-Finger Protein, Enhances Silique Shattering Resistance by Negatively Regulating Lignin Accumulation in the Silique Walls of Brassica napus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, D.; Yin, F.; Yu, P.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lu, C.; Yao, X.; Dai, C.; et al. Interaction between phenylpropane metabolism and oil accumulation in the developing seed of Brassica napus revealed by high temporal-resolution transcriptomes. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, Q.U.; Chu, W.; Hao, M.; Shi, Y.; Sun, M.; Sang, S.F.; Mei, D.; Cheng, H.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Multiplex Genome Editing of JAGGED Gene in Brassica napus L. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 725. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Mu, T.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hua, W.; Yuan, W.; Li, H. Targeted mutagenesis and functional marker development of two Bna.TAC1s conferring novel rapeseed germplasm with compact architecture. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2025, 138, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, C. Genome-Wide Analysis of C2H2 Zinc-Finger Family Transcription Factors and Their Responses to Abiotic Stresses in Poplar (Populus trichocarpa). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, C.H.; Hwang, J.K. Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins 2006, 64, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry Jeremy, D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.-H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: A Toolkit Incorporating Gamma-Series Methods and Sliding Window Strategies. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2010, 8, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador, V.; Monte, E.; García-Martínez, J.L.; Prat, S. Gibberellins signal nuclear import of PHOR1, a photoperiod-responsive protein with homology to Drosophila armadillo. Cell 2001, 106, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wei, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Jia, Y.; Luo, C.; Lin, Y.; Liang, C.; Hu, Y.; et al. BnIR: A multi-omics database with various tools for Brassica napus research and breeding. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xia, R.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various HTS-data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owji, H.; Hajiebrahimi, A.; Seradj, H.; Hemmati, S. Identification and functional prediction of stress responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors in Brassica napus by genome-wide analysis. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2017, 71, 32–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; King, G.J.; Liu, K. Genome-wide analysis of the auxin/indoleacetic acid (Aux/IAA) gene family in allotetraploid rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Niu, F.; Liu, W.Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Cheng, H.; Han, F.; Jiang, Y.Q. Identification, cloning and characterization of R2R3-MYB gene family in canola (Brassica napus L.) identify a novel member modulating ROS accumulation and hypersensitive-like cell death. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Mao, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wu, D.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; Qian, W. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of WRKY Transcription Factors under Multiple Stresses in Brassica napus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Bian, Z.; Mao, J.; Chen, B. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the Genes Encoding Q-Type C2H2 Zinc Finger Proteins in Grapevine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Coulter, J.A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Meng, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the Q-type C2H2 gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourcilleau, D.; Lenne, C.; Armenise, C.; Moulia, B.; Julien, J.L.; Bronner, G.; Leblanc-Fournier, N. Phylogenetic study of plant Q-type C2H2 zinc finger proteins and expression analysis of poplar genes in response to osmotic, cold and mechanical stresses. DNA Res. 2011, 18, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, A.; Wu, Q.; Zou, X.; Chen, F.; Cai, R.; Xie, H.; Zhang, M.; Guo, X. Comprehensive genomic survey, structural classification and expression analysis of C2H2-type zinc finger factor in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.D.; Novak, N.G. Comparative analysis of the genetic variability within the Q-type C2H2 zinc-finger transcription factors in the economically important cabbage, canola and Chinese cabbage genomes. Hereditas 2018, 155, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, T.; Liu, W.; Hu, Z.; Xiang, X.; Liu, T.; Xiong, X.; Cao, J. Molecular characterization and expression analysis reveal the roles of Cys2/His2 zinc-finger transcription factors during flower development of Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2020, 102, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, J. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the WUSCHEL-related homeobox (WOX) gene family in allotetraploid Brassica napus reveals changes in WOX genes during polyploidization. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazan, K. Negative regulation of defence and stress genes by EAR-motif-containing repressors. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Hu, R.; Gu, T.; Han, J.; Qiu, D.; Su, P.; Feng, J.; Chang, J.; Yang, G.; He, G. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of trihelix gene family under abiotic stresses in wheat. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Dong, X.; Long, G.; Zhang, Z.; Han, C.; Wang, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of Q-Type C2H2 ZFP Genes in Response to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Sugar Beet. Biology 2023, 12, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; Pan, J.; Wen, H.; Du, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, K.; Lv, D.; He, H.; Cai, R.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Analysis and Expression Profiling of the C2H2 Zinc Finger Protein Family Under Abiotic Stresses in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Genes 2020, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthamilarasan, M.; Bonthala, V.S.; Mishra, A.K.; Khandelwal, R.; Khan, Y.; Roy, R.; Prasad, M. C2H2 type of zinc finger transcription factors in foxtail millet define response to abiotic stresses. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2014, 14, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, C.M.; Doherty, C.J.; Gilmour, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Thomashow, M.F. Regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF regulon by a complex low-temperature regulatory network. Plant J. 2015, 82, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Yang, S. Insights into the regulation of C-repeat binding factors in plant cold signaling. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xu, J.; Tao, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Pu, Y.; Yang, G.; Fang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of C2H2 ZFPs and Functional Analysis of BRZAT12 under Low-Temperature Stress in Winter Rapeseed (Brassica rapa). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pu, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, L.; Yang, G.; Wang, W.; Fan, T.; Wu, J.; Sun, W. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Q-Type C2H2 Zinc Finger Proteins in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and Their Expression Patterns Across Tissues and Under Abiotic Stress. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092085
Pu Y, Liu L, Ma L, Yang G, Wang W, Fan T, Wu J, Sun W. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Q-Type C2H2 Zinc Finger Proteins in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and Their Expression Patterns Across Tissues and Under Abiotic Stress. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092085
Chicago/Turabian StylePu, Yuanyuan, Lijun Liu, Li Ma, Gang Yang, Wangtian Wang, Tingting Fan, Junyan Wu, and Wancang Sun. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Q-Type C2H2 Zinc Finger Proteins in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and Their Expression Patterns Across Tissues and Under Abiotic Stress" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092085
APA StylePu, Y., Liu, L., Ma, L., Yang, G., Wang, W., Fan, T., Wu, J., & Sun, W. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Q-Type C2H2 Zinc Finger Proteins in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and Their Expression Patterns Across Tissues and Under Abiotic Stress. Agronomy, 15(9), 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092085





