Verification of Agricultural Practices for Winter Pea–Cereals Intercropping
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Field
2.2. Morphological Analysis of Aboveground Part of Plants
2.3. Morphological and Anatomical Analysis of Nodules and Roots
2.4. Competition Indices
2.5. Nitrogen Uptake
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
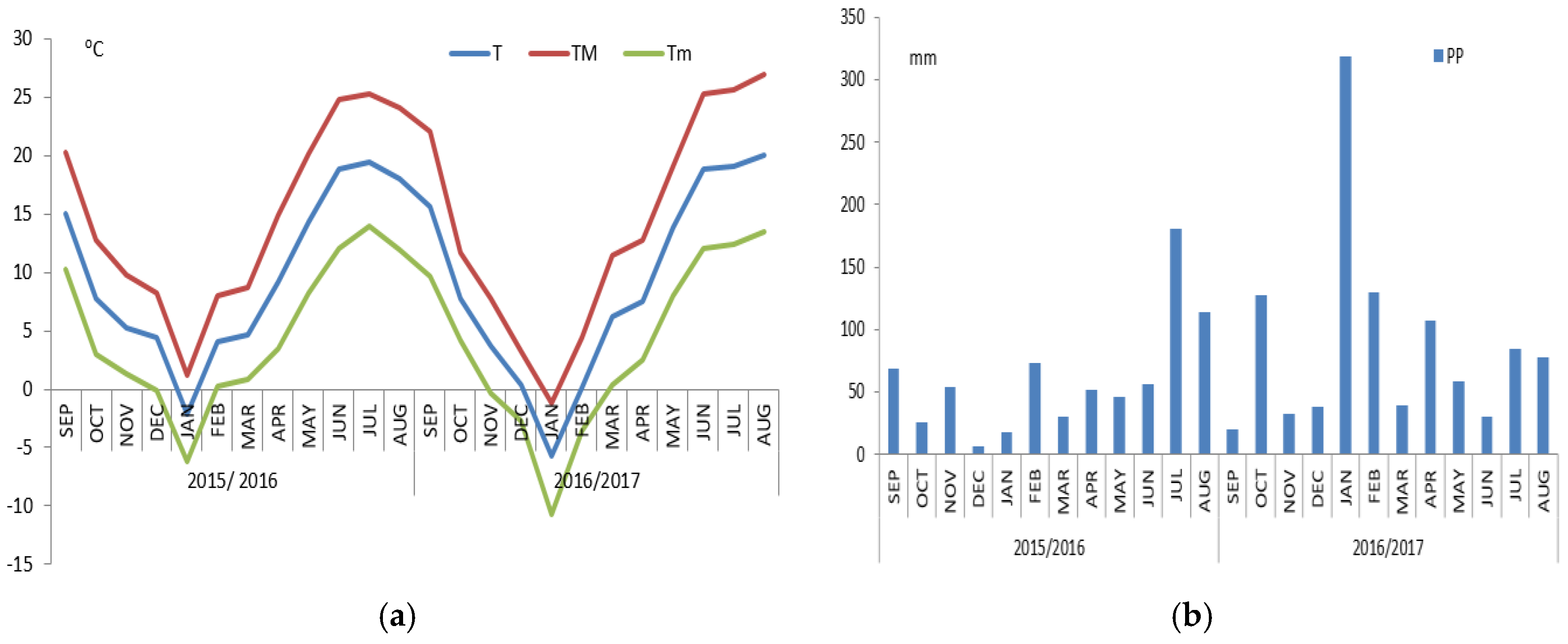
3.1. Weather Conditions
3.2. Yield, Yield Parameters and Competition Index (CR)
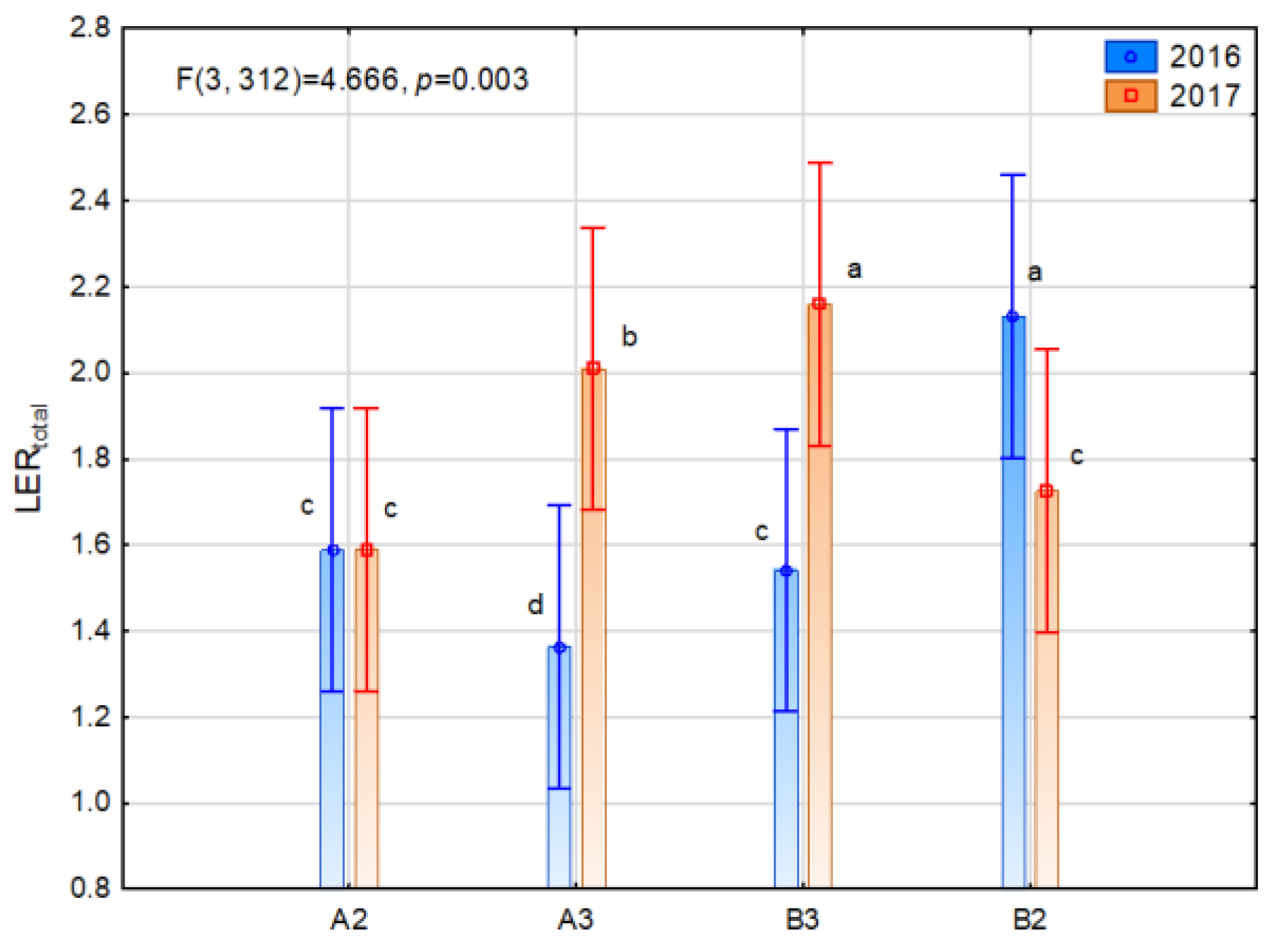
3.3. Land Equivalent Ration (LER)
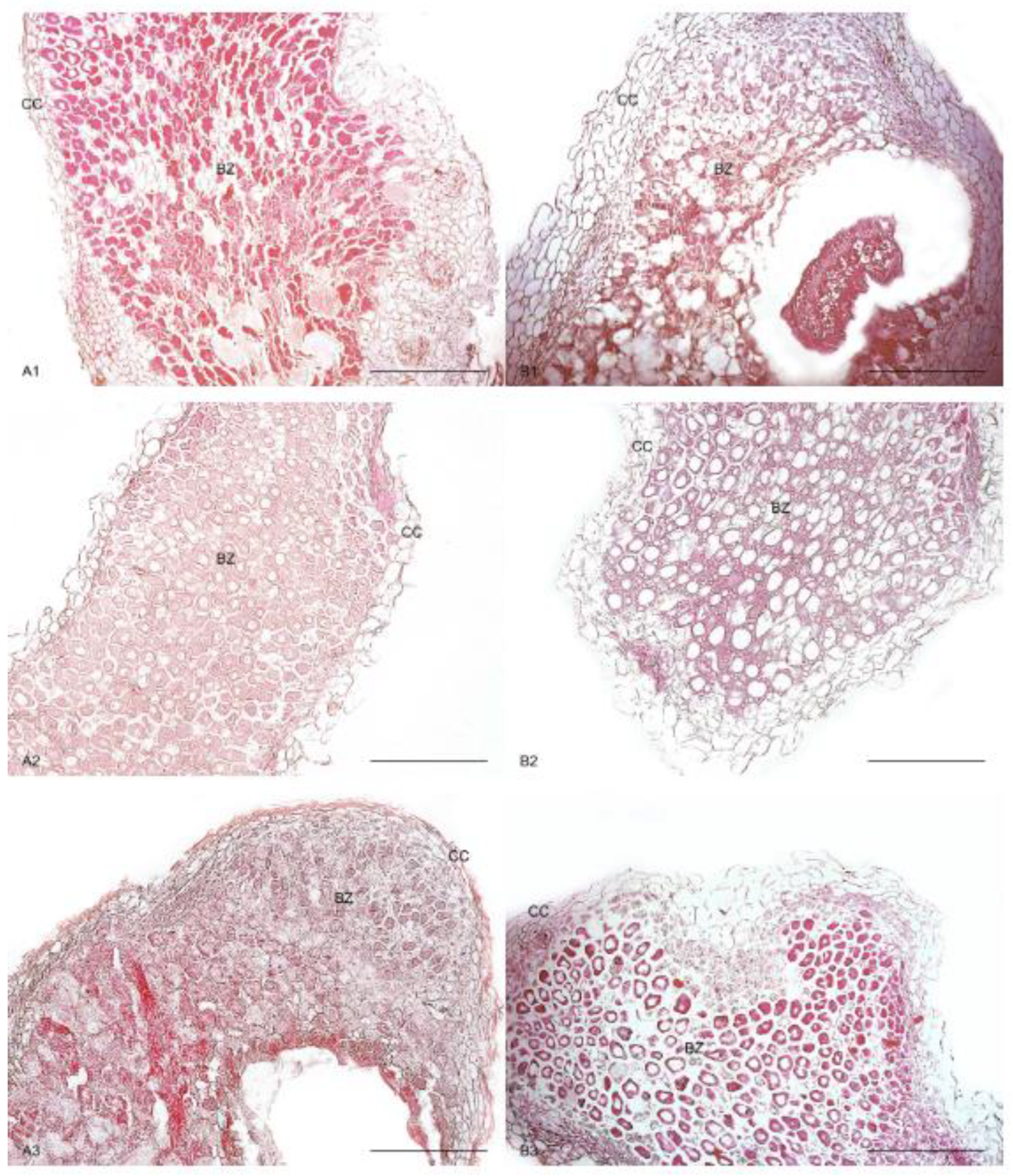
3.4. Anatomical Characteristics of Root Nodules
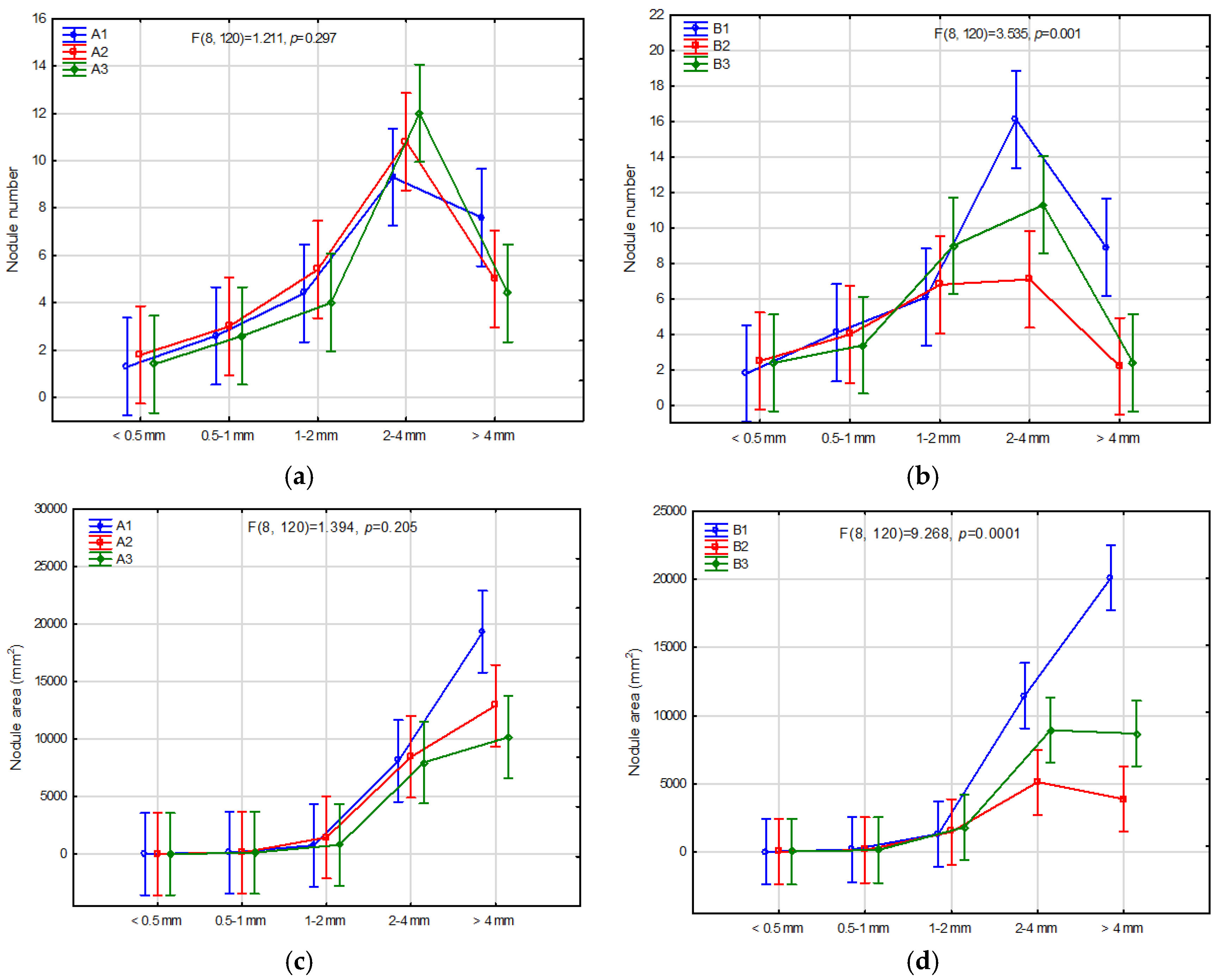
3.5. Parameters of Root Nodules Depending on Study Factor
3.6. Classification of the Number and Size of Root Nodules and the Root Weight and Diameter
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Kaul, H.-P.; Moitzi, G.; Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Losak, T.; Wagentristl, H. A low nitrogen fertilizer rate in oat-pea intercrops does not impair N2 fixation. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2021, 71, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarazo, C.I.; Tuulos, A.; Jokela, V.; Mäkelä, P.S.A. Sustainable Mixed Cropping Systems for the Boreal-Nemoral Region. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Bacior, M.; Zając, T. Biodiversity as a creator of productivity and interspecific competitiveness of winter cereal species in mixed cropping. Ecol. Model. 2017, 343, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeijer, A.J.; Melander, B.; Salonen, J.; Lundkvist, A.; Zarina, L. Crop diversification affects weed communities and densities in organic spring cereal fields in northen Europe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 308, 107251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Kaul, H.-P. Sowing ratio and N fertilization affect yield and yield components of oat and pea in intercrops. Field Crops Res. 2014, 155, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchi, M.; Monti, M.; Calvi, A.; Presti, E.L.; Pellicanó, A.; Preiti, G. Forage Potential of Cereal/Legume Intercrops: Agronomic Performances, Yield, Quality Forage and LER in Two Harvesting Times in Mediterranean Environment. Agronomy 2021, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, T.; Oleksy, A.; Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Stokłosa, A.; Kulig, B. Morphological-developmental reaction and productivity of plants and canopy of semileafless pea (Pisum sativum L.) after seeds vaccination with Rhizobium and foliar micronutrient fertilization. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2012, 85, 188–197. [Google Scholar]
- Sońta, M.; Rekiel, A. Legumes—Use for nutritional and feeding purposes. J. Elem. 2020, 25, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, M.J.; Kasyanova, E.; Ruske, R.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Jenden, E.S.; Dahlmann, C.; Fragstein, P.; Dibet, A.; Corre-Hellou, G.; Crozat, Y.; et al. Intercropping with pulses to concentrate nitrogen and sulphur In wheat. J. Agric. Sci. 2007, 145, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malézieux, E.; Crozat, Y.; Dupraz, C.; Laurans, M.; Makowski, D.; Ozier-Lafontaine, H.; Rapidel, B.; de Tourdonnet, S.; Valantin-Morison, M. Mixing plant species in cropping systems: Concepts, tools and models. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 29, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Zając, T.; Oleksy, A.; Kulig, B. Biological and production responses of intercropped plants of pea, spring wheat, and linseed. Acta Agrobot. 2018, 71, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Kaul, H.-P. Nitrogen uptake, use and utilization efficiency by oat-pea intercrops. Field Crops Res. 2015, 179, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.E.; Brennan, E.B.; Cavigelli, M.A.; Smith, R.F. Winter cover crops increase readily decompostable soil carbon during eight years of intensive, organic vegetable production in California. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Miller, P.; Muehlbauer, F.; Neil, K.; Wichman, D.; McPhee, K. Winter pea and lentil response to seedling date and micro- and macro-environments. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Bernhuber, A.; Kammlander, S.; Wagentristl, H.; Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Kaul, H.-P. Agronomic potential of winter grain legumes for Central Europe: Development, soil coverage and yields. Field Crops Res. 2019, 241, 107576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljevic, S.; Djalovic, I.; Miladinovic, J.; Xu, N.; Sui, X.; Wang, Q.; Prasad, P.V.V. Winter Pea Mixtures with Triticale and Oat for Biogas and Methane Production in Semiarid Conditions of the South Pannonian Basin. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, A. Advantages of grain legume-cereal intercropping in sustainable agriculture. Turk. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 9, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothardt, S.; Kage, H. Model-based biomass incorporation to mitigate nitrogen losses from arable fields in Central Europe. Front. Agron. 2023, 5, 1155187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Stomph, T.J.; Makowski, D.; Zhang, L.; der Werf, W. A meta-analysis of relative crop yields in cereal/legume mixtures suggest options for management. Field Crops Res. 2016, 198, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuśmierek-Tomaszewska, R.; Żarski, J. Assessment of Meteorological and Agricultural Drought Occurrence in Central Poland in 1961–2020 as an element of the Climatic Risk to Crop Production. Agriculture 2021, 11, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakl, J.; Brant, V.; Maskova, K.; Neckar, K.; Pivec, J. The forage utilization of winter pea-cereal mixture in agriculture low-input system. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2011, 59, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Kliszcz, A.; Ślizowska, A.; Kot, D. Application of biostimulants influences shoot and root characteristics of seedlings of winter pea (Pisum sativum L.). Acta Agrobot. 2019, 72, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Głąb, T.; Zając, T. The key role of variety and method of sowing selection in pea root’s parameters development under sustainable practice. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronle, A.; Heß, J.; Böhm, H. Effect of intercropping normal-leafed or semi-leafless winter peas and triticale after shallow and deep ploughing on agronomic performance, grain quality and succeeding winter wheat yield. Field Crops Res. 2015, 180, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujkowska, M.; Górska-Czekaj, M.; Bederska, M.; Borucki, W. Vacuolar organization in the nodule parenchyma is important for the functioning of pea root nodules. Symbiosis 2011, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sujkowska, M.; Borucki, W.; Golinowski, W. Localization of expansin-like protein in apoplast of pea (Pisum sativum L.) root nodules during interaction with Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae 248. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2007, 78, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bovin, S.; Lahmidi, N.A.; Sherlock, D.; Bonhomme, M.; Dijon, D.; Heulin-Gotty, K.; Le-Querré, A.; Perevent, M.; Tauzin, M.; Carlsson, G.; et al. Host-specific competitiveness to form nodules in Rhizobium leguminosarum synbiovar viciae. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 555–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riah, N.; de Lajudie, P.; Béna, G.; Heullin, K.; Djekoun, A. Variability in symbiotic efficiency with respect to the growth of pea and lentil inoculated with various rhizobial genotypes originating from sub-humid and semi-arid regions of eastern Algeria. Symbiosis 2021, 85, 371–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosolapowa, A.O.; Belousov, M.V.; Sulatsky, M.I.; Tsyganova, A.V.; Sulatskaya, A.I.; Bobylev, A.G.; Shtark, O.Y.; Tcyganov, V.E.; Volkov, K.V.; Zhukov, V.A.; et al. RopB protein of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae adopts amyloid state during symbiotic interactions with pea (Pisum sativum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1014699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Félix, J.D.; Carro, L.; Creda-Castillo, E.; Squartini, A.; Rivas, R.; Velázquez, E. Analysis of the Interaction between Pisum sativum L. and Rhisobium laguerrae Strains Nodulating This Legume in Northwest Spain. Plants 2020, 9, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morzhina, E.V.; Tsyganov, V.E.; Borisov, A.Y.; Lebsky, V.K.; Tikhonovich, I.A. Four developmental stages identified by genetic dissection of pea (Pisum sativum L.) root nodule morphogenesis. Plant Sci. 2000, 155, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borucki, W.; Sujkowska, M. The effect of sodium chloride salinity upon growth, nodulation, and root nodule structure of pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2008, 30, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, E.J.; Nogueira, M.A.; Ferraz, S.M. Biological N2 fixation and mineral N in common bean-maize intercropping or sole cropping in Southeastern Brazil. Exp. Agric. 2007, 43, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pary, F.A.; Chattoo, M.A.; Magray, M.; Gaineie, S.A.; Dar, Z.M.; Masood, A. Effect of different levels of sulphur and boron on nodulation of garden pea (Pisum sativum L.). Legume Res. 2016, 39, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; Schad, P., van Huyssteen, C., Michéli, E., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; ISBN 978-92-5-108370-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pridham, J.C.; Entz, M.H.; Martin, R.C.; Hucl, R.J. Weed, disease and grain yield effects of cultivar mixtures in organically managed spring wheat. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2007, 87, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasaya, A.; Ahmad, R.; Hassan, F.U.; Ansar, M.; Manaf, A.; Sher, A. Enhancing crop productivity through wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)—Fenugreek intercropping system. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2013, 23, 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, T.P.; Reiter, M.S.; Welbaum, G.; Arancibia, R.A. Nitrogen uptake and use efficiency in sweet basil production under low tunnels. Hortic. Sci. 2020, 55, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smytkiewicz, K.; Podlésny, J.; Wielbo, J.; Podlésna, A. The Effect of a Preparation Containing Rhizobial Nod Factors on Pea Morphological Traits and Physiology. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori, F.; Stern, W.R. Cereal–legume intercropping systems. Adv. Agron. 1987, 41, 41–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, H.H. Rhizobium-legume symbiosis and nitrogen fixation under severe conditions and in an arid climate. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. J. 1999, 63, 968–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyganova, A.V.; Brewin, N.J.; Tsyganov, V.E. Structure and Development of the Legume-Rhizobial Symbiotic Interface in Infection Threads. Cells 2021, 10, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Istanbuli, T.; Abu Assar, A.; Tawkaz, S.; Kumar, T.; Alsamman, A.M.; Hamwieh, A. The interaction between drought stress and nodule formation under multiple environments in chickpea. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Timmers, A.C.; Soupene, E.; Auriac, M.C.; de Billy, F.; Vasse, J.; Boistrad, P.; Truchet, G. Saprophytic intracellular rhizobia in alfalfa nodules. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2000, 13, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Qin, X.M.; Xiao, J.X.; Tang, L.; Wei, C.Z.; Wei, J.J.; Zheng, Y. Intercropping influences component and content change of flavonoids in root exudates and nodulation of Faba bean. J. Plant Interact. 2017, 12, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.B.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.S. The interspecific nitrogen facilitation and the subsequent nitrogen transfer between the intercropped wheat and fababean. Zhong Guo Nongye Kexue 2005, 38, 965–973. [Google Scholar]
- Eaglesham, A.R.; Hassouna, S.; Seegers, R. Fertilizer–N effects on N2 fixation by cowpea and soybean. Agron. J. 1983, 75, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corre-Hellou, G.; Fustec, J.; Crozat, Y. Interspecific competition for soil N and its interaction with N2 fixation leaf expansion and crop growth in pea-barley intercrops. Plant Soil 2006, 282, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.B.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, C.J.; Sun, J.H.; He, X.H.; Zhang, F.S.; Li, L. An improved nitrogen difference method for estimating biological nitrogen fixation in legume-based intercropping systems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 46, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Yu, C.B.; Cheng, X.; Li, C.J.; Sun, J.H.; Zhang, F.S.; Lambers, H.; Li, L. Intercropping alleviates the inhibitory effect of N fertilization on nodulation and symbiotic N2 fixation of faba bean. Plant Soil 2009, 323, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Item | Seed Yield (t ha−1) | Length of Fruiting Stem (cm) | Number of Pods per Plant | Mass of Pods per Plant (g) | Number of Seeds per Plant | Mass of Seeds per Plant (g) | CR Legume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015/2016 | 3.08 b* | 86.8 b | 11.7 b | 7.49 b | 61.5 b | 6.30 b | 1.63 |
| 2016/2017 | 3.43 a | 91.8 a | 19.4 a | 9.68 a | 72.9 a | 8.10 a | 1.80 |
| p < 0.05 | <0.001 | <0.01 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | n.s. |
| Pandora (A1) | 3.32 | 85.2 c,b | 11.4 b | 5.99 b | 51.9 b | 4.66 b | - |
| E.F.B. 33 (B1) | 4.36 | 89.2 c | 13.4 b,c | 7.34 b,d | 56.3 b | 6.29 b,c | - |
| Pandora + SC (A2) | 2.76 | 79.0 b | 15.3 c | 12.2 a | 80.3 a | 10.1 a | 1.72 |
| Pandora + TC (A3) | 2.77 | 86.8 c,b | 13.9 c | 8.53 c,d | 69.9 c | 7.68 c | 1.71 |
| E.F.B. 33 + SC (B2) | 3.20 | 101.7 a | 25.2 a | 9.44 c | 76.4 a,c | 7.69 c | 1.71 |
| E.F.B. 33 + TC (B3) | 3.12 | 94.1 a,c | 14.1 c | 8.02 c,d | 68.2 b | 6.75 c | 1.74 |
| p < 0.05 | n.s. | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | n.s. |
| Item | Nodule Area (cm2) | Nodules Number per Plant | Nodules Dry Mass per Plant | N Uptake with 1 t of Seed (kg per ha) | RDM of Roots (mg cm3) | MRD (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015/2016 | 384.6 b* | 21.0 b | 0.07 b | 41.7 b | 0.32 b | 0.33 b |
| 2016/2017 | 507.9 a | 27.7 a | 0.26 a | 45.2 a | 1.68 a | 0.47 a |
| p < 0.05 | <0.001 | <0.001 | n.s. | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Pandora (A1) | 567.7 a,b | 23.1 | 0.19 | 41.3 a | 0.73 b | 0.40 |
| E.F.B. 33 (B1) | 661.9 a | 25.3 | 0.29 | 41.1 a | 0.69 b | 0.32 |
| Pandora + SC (A2) | 459.8 a,b,c | 24.2 | 0.13 | 43.4 a,b | 0.72 b | 0.42 |
| Pandora + TC (A3) | 382.1 bc | 22.3 | 0.11 | 46.8 b | 1.11 a,b | 0.33 |
| E.F.B. 33 + SC (B2) | 213.2 c | 24.0 | 0.13 | 48.8 a,b | 1.30 a,b | 0.44 |
| E.F.B. 33 + TC (B3) | 392.6 a,b,c | 26.7 | 0.16 | 44.8 b | 1.44 a | 0.50 |
| p < 0.05 | <0.001 | n.s. | n.s. | <0.001 | <0.001 | n.s. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Hanus-Fajerska, E.; Kamińska, I.; Głąb, T.; Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Chudzik, W. Verification of Agricultural Practices for Winter Pea–Cereals Intercropping. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092017
Klimek-Kopyra A, Hanus-Fajerska E, Kamińska I, Głąb T, Neugschwandtner RW, Chudzik W. Verification of Agricultural Practices for Winter Pea–Cereals Intercropping. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092017
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlimek-Kopyra, Agnieszka, Ewa Hanus-Fajerska, Iwona Kamińska, Tomasz Głąb, Reinhard W. Neugschwandtner, and Wiktor Chudzik. 2025. "Verification of Agricultural Practices for Winter Pea–Cereals Intercropping" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092017
APA StyleKlimek-Kopyra, A., Hanus-Fajerska, E., Kamińska, I., Głąb, T., Neugschwandtner, R. W., & Chudzik, W. (2025). Verification of Agricultural Practices for Winter Pea–Cereals Intercropping. Agronomy, 15(9), 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092017









