Abstract
This study developed an efficient cultivation strategy for cabbage production in paddy fields. To address poor drainage, discarded coir substrates (CS) were reused and compared with conventional paddy soil (PS). Four irrigation levels (ETc140, ETc100, ETc60, and ETc0) were applied to both CS and PS to evaluate their interactive effects. An automated irrigation system was deployed, integrating a weather sensor and solenoid valves via a LoRa-based IoT network. Hourly ET0 was calculated based on Penman–Monteith in real time, and an irrigation event was triggered when cumulative ET0 reached 1 mm (CS) or 3 mm (PS). The automated irrigation system showed stable performance. Hourly ET0 estimates were 97% consistent with Korea Meteorological Administration data. The actual total irrigation depth (ID_actual) remained within 2% of the calculated depth (ID). Under moderate irrigation depths (ETc60 and ETc100), the reuse of CS significantly improved cabbage photosynthetic efficiency. Both CS-ETc60 and CS-ETc100 treatments maintained superior yield performance compared with other treatments. This integrated strategy not only offers a practical solution for improving water use efficiency but also enhances the multifunctional utilization of paddy fields, supporting the transition toward more sustainable agricultural practices.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of greenhouse horticulture, soilless cultivation systems have been widely adopted. However, these systems generate large amounts of waste materials such as rockwool, peat, coir substrates, and plant residues [1,2,3]. Coir substrates come from natural, biodegradable sources and are increasingly regarded as a sustainable substitute for peat, with usage steadily rising [4]. Currently, most of these waste substrates are disposed of through landfilling or incineration [5]. However, landfilling can lead to soil and groundwater contamination, whereas incineration results in increased greenhouse gas emissions. Previous studies have demonstrated the potential for reusing coir substrates after hydroponic cultivation [6,7,8]. However, most research has focused on recycling within hydroponic systems, with limited exploration of their application in open field cultivation. Based on this, we have previously conducted studies on the reuse of waste coir substrates for upland cultivation in paddy fields, involving crops such as soybean and cabbage [9,10]. When converting paddy fields to upland cropping, poor drainage and prolonged waterlogging often cause soil hypoxia. This inhibits root respiration and severely restricts crop growth, yield, and quality [11,12]. The superior drainage and aeration characteristics of coir substrate can effectively alleviate root hypoxia and improve crop productivity and quality. Although coir substrates improve aeration and drainage, their unique physical properties complicate water management. Therefore, integrating substrate cultivation with precise and efficient irrigation technologies is critical to sustaining crop productivity. Given the increasing scarcity of water resources worldwide, enhancing crop water use efficiency is critical to sustainable agricultural development. Precision irrigation technologies are pivotal in achieving this goal [13].
Precise irrigation management depends on the accurate quantification of crop water requirements. To address this, a variety of modeling approaches have been developed. Among the most widely adopted are the FAO56 crop coefficient method and crop simulation models, both applied extensively in open-field [14,15,16]. The FAO56 method (Kc–ET0) is particularly valued for its clarity, standardized parameters, and ease of use [17,18]. Recent studies have confirmed the robustness of FAO-provided Kc values across diverse crops and regions. Even under changing climate conditions, the ETc/ET0 ratio has generally remained stable, with no evident systematic bias across most crops and regions, supporting the method’s reliability and broad applicability [19,20]. Alternatively, crop simulation models such as DSSAT and AquaCrop simulate crop growth, physiological processes, and soil–water dynamics to assess the impacts of different management practices on yield and resource use efficiency [21,22]. These models provide detailed insights into plant physiology and soil water dynamics but require more complex structures and extensive input data. As such, they are well-suited for scenario analysis and the development of decision support systems. By contrast, the FAO56 method remains more practical for irrigation scheduling in practical field settings, particularly where data are limited or real-time decisions are required [23,24].
As crop water requirement estimation methods continue to advance, automated irrigation systems integrating sensor technologies, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence algorithms have become a major focus in the development of precision irrigation [25]. These systems typically incorporate soil moisture sensors, weather monitoring instruments, and crop models to collect real-time data on environmental conditions and crop physiological status. By setting irrigation thresholds or running decision algorithms, the system autonomously regulates irrigation timing and volume, enabling dynamic management of crop water supply [26,27,28,29]. However, despite their capability for real-time root-zone moisture monitoring, soil moisture sensors face significant practical challenges. Factors such as installation accuracy, calibration status, sensor depth, and soil salinity can affect measurement accuracy [30,31]. Advanced sensors such as Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) and Frequency Domain Reflectometry (FDR) measure soil dielectric constants and electrical impedance, respectively, but require complex installation and maintenance [32]. Furthermore, relying on just a few single-point sensors is insufficient to capture the spatial variability in soil moisture across large fields, which limits the reliability and representativeness of data. Ultrasonic sensors offer the advantage of large-area monitoring but are generally cost-prohibitive [33]. Accordingly, an automated irrigation system was designed and developed in this study based on the real-time estimation of crop reference evapotranspiration (ET0), using cumulative ET0 thresholds to regulate crop water supply dynamically. To test the potential of this approach for improving irrigation efficiency and conserving water resources, system performance, water use efficiency, and crop productivity were evaluated. Compared with irrigation strategies that rely on soil moisture sensors, the proposed system lowers equipment dependency and maintenance costs. It also enables timely and effective water management for large-scale crop production. By addressing the limitations of traditional soil moisture sensor-based strategies, the proposed system seeks to offer a more cost-effective and scalable solution for open field irrigation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Plant Material
The experiment was conducted at Chungnam National University in Daejeon, South Korea (36°22′ N, 127°21′ E, 45 m) from 16 April to 11 June 2024 (Figure 1a). The experimental site is characterized by a temperate monsoon climate, with an annual precipitation of approximately 1458.7 mm. Around 50% to 60% of the total precipitation occurs between late June and early September [34]. The experimental soil texture is classified as sandy loam according to the USDA Taxonomy (Table 1). The soil chemical characteristics and profile show that the organic matter content below 20 cm is lower than in the topsoil (Table 2). A black and gray–green soil layer is present between 20 and 40 cm, and the soil below this becomes whitish (Figure 1b). Based on these characteristics, it is speculated that the soil may belong to the Arenosol type [35].
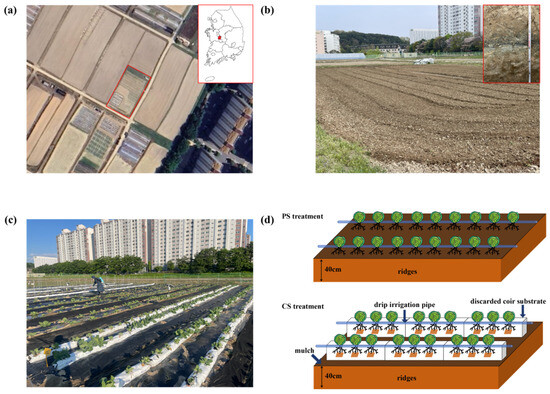
Figure 1.
Experimental site and treatments: location of the experimental site (a); experimental site environment, with the soil profile shown in the upper right corner (b); photograph of the experimental setup (c); schematic diagram of PS and CS treatments (d).

Table 1.
Physical properties of paddy soil (PS) and discarded coir substrates (CS).

Table 2.
Chemical properties of paddy soil (PS) and coir substrates (CS).
The four-leaf stage seedlings of ‘KoKoMa F1’ cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) were transplanted in the field on April 16. Each ridge measured 20 m2 in area and 40 cm in height, with the surface covered by mulch film. A two-row planting pattern was used on each ridge, with an inter-row spacing of 60 cm and an intra-row spacing of 30 cm, resulting in approximately 133 plants per ridge. The trial adopted a split-plot design with three replicate ridges for each treatment. To eliminate the irrigation effects between plots, plastic boards were buried during ridge formation to isolate the plots.
2.2. Experimental Design and Cultivation Conditions
To evaluate the feasibility of reusing discarded coir substrate in paddy-converted fields, the main plot included two growth substrates: (1) Paddy soil (PS) treatment, consisting of paddy soil that was only plowed and fertilized after rice harvest, without drainage pipe installation; (2) Coir substrate (CS) treatment, consisting of discarded CS slab (100 × 20 × 10 cm; L × W × H, Daeyoung GS Co., Ltd., Daegu, Republic of Korea) that had been used for one year in hydroponic bell pepper cultivation. The substrates were then recycled and applied to the ridges for planting. The detailed cultivation method and treatment of the discarded coir substrate were described in our previous study [10]. The experimental field soil had been used for two years in upland crop planting experiments with discarded coir substrates, with only tillage and base fertilizer applied (Figure 1c,d). In order to apply the base fertilizer appropriately, paddy soil and discarded coir substrate samples were collected before the experiment and sent to the Daejeon Agricultural Technology Center for physical and chemical property analysis (Table 1 and Table 2). Based on the fertilizer formula provided by the Daejeon Agricultural Technology Center, a base fertilizer containing 129 kg∙ha−1 of nitrogen (N), 304 kg∙ha−1 of phosphorus (P2O5), and 114 kg∙ha−1 of potassium (K2O) was applied. Pest and disease management during the trial followed the cultivation standards provided by Asia Seed Co., Ltd., Seoul, Republic of Korea [36].
The subplot included four irrigation levels: over-irrigation (ETc140, 140% ETc), adequate irrigation (ETc100, 100% ETc), deficit irrigation (ETc60, 60% ETc), and no irrigation (ETc0, 0% ETc). The entire experiment utilized a drip irrigation system, with a drip emitter flow rate of 2 L·h−1 (SEOWON Co., Ltd., Goesan-gun, Republic of Korea). During the first week after transplanting cabbage, an average of 500 mL of water was applied per plant daily until root establishment. The irrigation depth was calculated based on the product of the hourly ET0 values and the crop coefficient (Kc) provided by FAO 56 [37], according to Equation (1).
ETc = ET0 × Kc
ET0 represents the reference evapotranspiration (mm∙h−1), and Kc is the crop coefficient. Since all treatments were covered with plastic mulch, the adjusted Kc values for different crop growth stages are presented in Table 3.
where ET0 is reference evapotranspiration (mm∙h−1); Rn is the net radiation at the grass surface (MJ∙m−2∙h−1); G is soil heat flux density (MJ∙m−2∙h−1); Thr represents hourly air temperature (°C); ∆ is saturation slope vapor pressure curve at Thr (kPa∙°C−1); γ is psychrometric constant (kPa∙°C−1); e°(Thr) is saturation vapor pressure at air temperature Thr (kPa); ea is average hourly actual vapor pressure (kPa); and u2 is average hourly wind speed (m∙s−1). The hourly net radiation, temperature, relative humidity, air pressure, and wind speed were calculated based on data collected by on-site sensors, as described in detail in Section 2.3 and Section 2.4.

Table 3.
The Kc values, cumulative ET0, and cumulative ETc for each growth stage of cabbage, with 100% ETc as the baseline.
The total irrigation depth (ID) was calculated for each treatment according to Equation (3).
where ETc is the crop evapotranspiration (mm), A is the area of one plot (20 m2), and 1000 is the conversion factor from mm to m3. The IDs of each treatment are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
The calculated total irrigation depth (ID) for each treatment during the experiment.
2.3. Automated Irrigation Algorithm
The irrigation algorithm used in this study proposed an automated control method based on cumulative ET0. First, the weather sensor collected field environmental data every 3 min and used the hourly average data to calculate the hourly ET0. Subsequently, the system accumulated the hourly ET0 values and determined whether they exceeded a preset threshold. If the accumulated ET0 reached the set threshold, the solenoid valve opening duration was calculated, and a command was sent through the LoRa gateway to trigger irrigation. During the irrigation process, the irrigation records were uploaded to the database to support data analysis and system optimization.
The irrigation threshold for cumulative ET0 was set based on the different characteristics of the coir substrate (CS) and paddy soil (PS). Due to the high porosity and excellent drainage properties of coir substrate, irrigation at appropriate intervals can enhance crop water use efficiency. Therefore, the irrigation threshold for the CS treatment was set when the cumulative ET0 reached 1 mm. In contrast, frequent irrigation in paddy soil with poor drainage can exacerbate surface waterlogging, which negatively impacts root health. To prevent this, and to achieve optimal soil moisture, the irrigation threshold for paddy field soil was set when the cumulative ET0 reaches 3 mm (Figure 2).
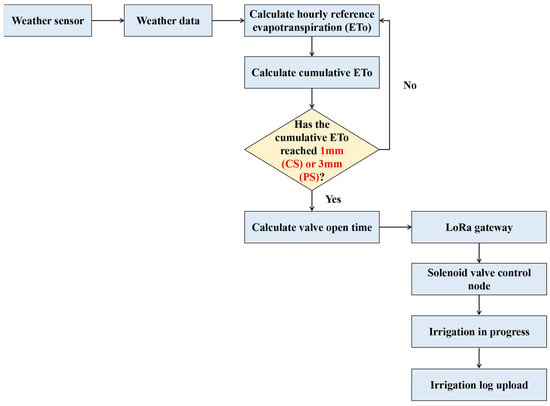
Figure 2.
Automated irrigation algorithm based on cumulative ET0.
2.4. Irrigation System Design
Figure 3 illustrates the overall architecture of the irrigation system. The system consists of an IoT gateway, edge devices, irrigation components (including solenoid valves, flow meters, and a pump), and a weather sensor. These units are interconnected via LoRa wireless communication technology, enabling data acquisition, transmission, and coordinated system control. The IoT gateway serves as the data hub of the system. It is responsible for receiving environmental parameters monitored by the weather sensor (WS500-UMB; Lufft, Fellbach, Germany) and the operational status of the irrigation solenoid valves (HPW2110A; HYOSHIN MECHATRONICS Co., Ltd., Bucheon-si, Republic of Korea) installed on-site. These data are then transmitted to the edge devices for processing. The edge devices are responsible for real-time processing of irrigation decisions based on the integrated automatic irrigation algorithm. All system units are powered by solar panels (KF20M-12; Kf solar Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China), and energy is stored in batteries (ATLASBX BXKB4.5–12; Hankook & Company Co., Ltd., Seongnam-si, Republic of Korea), ensuring stable operation of the system in the absence of an external power supply. This irrigation system can improve water use efficiency and reduce water waste by adopting precise irrigation with frequent, small irrigation amounts.
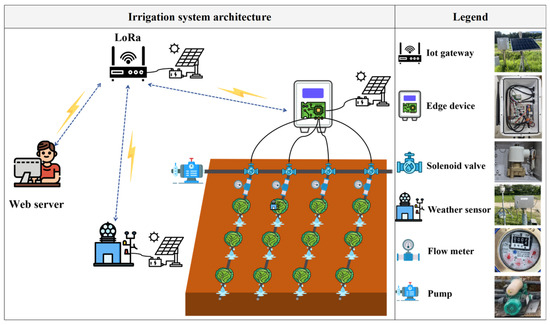
Figure 3.
Diagram of the irrigation system design and components.
2.5. Irrigation System Evaluation
As the automated irrigation algorithm developed in this study uses on-site meteorological data, the accuracy of weather sensor readings is critical for reliable ET0 estimation and irrigation scheduling. To verify the sensor’s reliability, hourly meteorological data were compared with corresponding records from the Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA, Daejeon Regional Office of Meteorology, 36°37.199′ N, 127°37.21′ E, 67.79 m) over the five days preceding the experiment (11–15 April 2024). Detailed meteorological data recorded during the entire experiment are presented in Table S1.
In addition, the accuracy of the automated irrigation system was assessed by comparing the ID (Table 4) with the actual total irrigation depth (IDactual) recorded by the flow meters. The flow meters (KTC 1-11-10; Korea Aichi Co., Ltd., Gimpo-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea) recorded the irrigation depth for each treatment based on the monitored ETc values at the end of the experiment. No flow meter was installed for the ETc0 treatment, as irrigation was only applied during the root establishment period. Mechanical flow meters were used for monitoring, and their technical specifications and accuracy details are provided in Table 5. The actual flow rate for each treatment was 0.266 m3·h−1 (calculated based on a drip emitter flow rate of 2 L·h−1 and 133 plants per plot), which falls within the Q2–Q3 range, with a measurement accuracy of ±2.0%. The relative error was calculated according to Equation (4).

Table 5.
The flow rate and accuracy specifications of the flow meters.
2.6. Soil Moisture Monitoring
Monitoring of soil moisture dynamics provides an effective means to evaluate irrigation system performance and assess the impact of varying irrigation amounts on the root-zone moisture for cabbage cultivation. Therefore, TDR soil moisture sensors (MTE 7; Transducer System Electronics Co., Ltd., Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea) were installed in each treatment plot to monitor the volumetric water content (VWC) in the root-zone throughout the experiment. In the CS treatment, sensors were vertically inserted into the substrate following the standard installation protocol and positioned directly beneath the drip emitter at a depth of approximately 10 cm, based on the size of the coir substrate. To ensure consistency across treatments, sensors in the PS treatment were installed at the same depth. All sensors continuously recorded soil moisture and temperature at 1 min intervals throughout the experimental period.
2.7. Evaluated Variables
2.7.1. Photosynthesis
The head formation stage is the period of maximum water requirement for cabbage [38]. Therefore, the photosynthetic characteristics of cabbage were measured at the head formation stage (on day 30 of the irrigation treatment) using a LI-6400 portable photosynthesis system (Licor. Inc., Lincoln, NE, USA). Five uniformly growing plants from each treatment were randomly selected, and measurements were taken on the 3rd to 5th fully expanded outer leaves (n = 5). Measurements were conducted under a CO2 concentration (Ca) of 450 μmol·mol−1 and a photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD) of 1100 μmol·m2·s−1. The measured parameters included the net photosynthetic rate (Pn; µmol·CO2·m−2·s−1), intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci; μmol·CO2·mol−1), stomatal conductance (gs; mol·H2O·m−2·s−1), and transpiration rate (Tr; mmol·H2O·m−2·s−1). In addition, the stomatal limitation index (Ls), instantaneous water use efficiency (WUEi, Equation (6)), and instantaneous carboxylation efficiency (iCE, Equation (7)) were calculated based on Pn, Tr, and Ci according to the method described by Liao [39].
2.7.2. Yield and Water Use Efficiency
At harvest, five representative cabbage plants were randomly selected from each treatment (n = 5). The heads were separated and measured for diameter (HD, cm), fresh weight (FW, g), and dry weight (DW, g). Samples were first dried at 105 °C for 24 h and then at 85 °C until reaching a constant weight for DW determination. Both FW and DW were recorded using an electronic scale (MW-2N, CAS Co., Ltd., Yangju, Republic of Korea). Yield was calculated based on head FW and planting density, and expressed as t∙ha−1. The yield water use efficiency (WUE) was calculated according to Equation (8):
where Y is the cabbage yield (kg·ha−1) and IDactual (m3) is the actual total irrigation depth measured using flow meters.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Due to the large volume of real-time soil moisture and meteorological data, Python (version 3.8.8) was used to calculate hourly averages. A two-way ANOVA was employed to examine the cabbage growth and production variables. Tukey’s test was used to analyze significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) between treatment means. All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics (Version 29.0.0, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA), and graphs were plotted using OriginPro 2021 (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Irrigation System Performance
To evaluate the accuracy of on-site meteorological sensors, hourly data from the test site and the Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA) were compared over five days (Figure 4). Key parameters used for reference evapotranspiration (ET0) calculation showed strong correlations: atmospheric pressure (R2 = 0.99), relative humidity (R2 = 0.96), solar radiation (R2 = 0.99), and temperature (R2 = 0.97). Minor systematic deviations were observed, with slightly higher pressure and humidity, and slightly lower radiation and temperature at the test site. Wind speed showed a low correlation (R2 = 0.21), likely because of local terrain and microclimatic effects. ET0 values calculated from sensor data were also consistent with KMA data (R2 = 0.97), indicating good overall reliability. These results suggest that, except for wind speed, the sensor data are sufficiently accurate for use in automated irrigation systems.
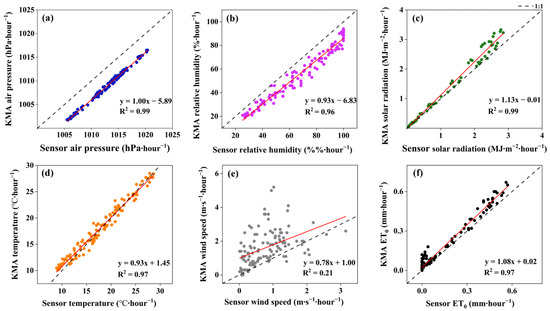
Figure 4.
Pearson correlation analysis of hourly weather data from the Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA) and on-site sensors, from 11 to 15 April 2024. Red lines represent the regression lines. Air pressure (a); relative humidity (b); solar radiation (c); temperature (d); wind speed (e); reference evapotranspiration (ET0) (f).
To evaluate the performance of the automated irrigation system, the calculated irrigation depth (ID) was compared with the actual total irrigation depth (IDactual) recorded by mechanical flow meters for each treatment (Figure 5). The IDactual in both the coir substrate (CS) and paddy soil (PS) treatments were close to the target volumes derived from ETc-based calculations. In the PS treatments, the relative errors ranged from 0.88 to 1.26%, while in the CS treatments, the relative errors ranged from 0.49 to 1.82%. All relative errors were within the stated accuracy of the flow meters (±2.0%), indicating a high level of reliability in the automated irrigation system. These results also indicated that the irrigation system performed consistently and accurately across different growing media and irrigation levels, with only minor variations attributable to allowable measurement errors or slight operational differences.
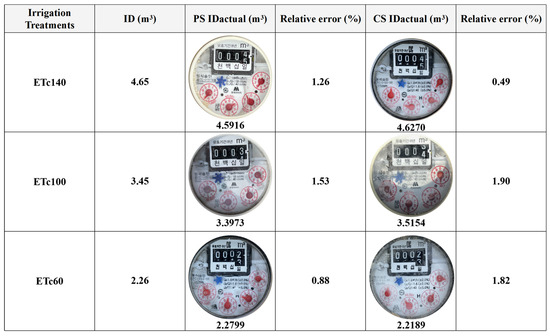
Figure 5.
Actual irrigation depth (IDactual) in coir substrates (CS) and paddy soil (PS) compared with ETc-based calculated irrigation depth (ID), with representative photos of the flow meters for each irrigation treatment. The treatments consisted of four irrigation depths based on: ETc140 (140% of ETc), ETc100 (100%), ETc60 (60%), and ETc0 (no flow meter installed).
3.2. Soil Moisture Dynamics
Figure 6 illustrates the hourly solar radiation, cumulative ET0, soil moisture data, and irrigation events under different irrigation treatments for CS and PS collected from 22 May to 24 May 2024. Solar radiation followed a typical diurnal cycle, reaching zero at night and peaking around noon, indicating that the on-site weather sensor was functioning correctly. The daily cumulative ET0 values for 22, 23, and 24 May were 5.01, 5.04, and 4.01 mm, respectively. According to the irrigation algorithm, irrigation events were triggered for the PS treatment when the cumulative ET0 reached 3 mm. Consequently, one irrigation event occurred on 22 May. On 23 May, the cumulative ET0 from the previous day and continued accumulation caused the 3 mm threshold to be reached twice, leading to two irrigation events. On 24 May, the cumulative ET0 exceeded the threshold again, prompting one irrigation event. In the CS treatment, an irrigation event was triggered when the cumulative ET0 reached 1 mm. Based on daily cumulative ET0 values, five irrigation events occurred on both 22 and 23 May, and four events occurred on 24 May.
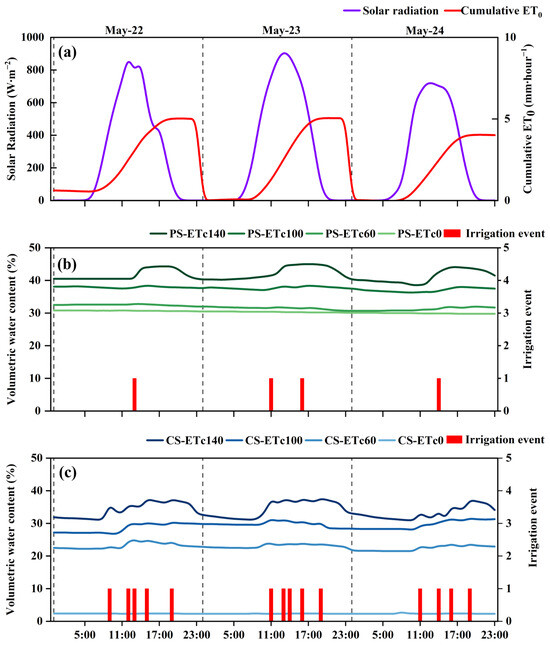
Figure 6.
Soil moisture dynamics under different irrigation levels in coir substrates (CS) and paddy soil (PS) from 22 to 24 May 2024. Hourly solar radiation and cumulative reference evapotranspiration (ET0) (a); volumetric water content in paddy soil (PS) under four irrigation levels in response to irrigation events (b); volumetric water content in coir substrates (CS) under four irrigation levels in response to irrigation events (c). The treatments consisted of four irrigation depths based on: ETc140 (140% of ETc), ETc100 (100%), ETc60 (60%), and ETc0 (no irrigation control). Irrigation events are indicated by a value of 1 on the right Y-axis for visualization purposes only.
Differential soil moisture responses to irrigation events were observed among treatments. In the PS treatment, soil moisture dynamics varied with irrigation treatments. In PS-ETc140, volumetric water content (VWC) ranged from 38.5 to 45.0%. Due to the relatively high irrigation volume per event and the poor drainage of paddy soil, a delayed increase in VWC was observed after irrigation, with notable overall fluctuations. In PS-ETc100, VWC ranged from 36.3 to 38.4%, with a slightly smaller fluctuation range compared with PS-ETc140. In PS-ETc60, VWC ranged from 30.7 to 32.8%, with a further reduction in fluctuation range, indicating that reduced irrigation amount led to more stable moisture conditions. In PS-ETc0, VWC remained within a lower range of 29.8 to 30.8% and showed a slow decline over time. The CS exhibited distinct responses to different irrigation treatments. In CS-ETc140, VWC ranged from 30.9 to 37.6%. High irrigation volumes caused a rapid increase in VWC after irrigation, followed by a gradual decrease, resulting in noticeable fluctuations. In CS-ETc100, VWC ranged from 26.7 to 31.5%, showing slightly less fluctuation compared with CS-ETc140. In CS-ETc60, the VWC range further narrowed to 21.5–25.0%, showing a trend toward more stable moisture conditions with reduced irrigation. In CS-ETc0, VWC remained consistently low, ranging from 2.3 to 2.8%, with minimal fluctuation throughout the period.
3.3. Photosynthetic Performance
The photosynthetic characteristics of cabbage were significantly influenced by growth substrates and irrigation depth (Figure 7). Overall, cabbages grown in CS exhibited higher net photosynthetic rate (Pn), transpiration rate (Tr), and stomatal conductance (gs) compared with those grown in PS. This indicated that CS was more conducive to photosynthesis. Additionally, CS treatment showed higher instantaneous carboxylation efficiency (iCE), suggesting that CS enhances CO2 utilization efficiency. The stomatal limitation index (Ls) in CS was generally lower than in PS, indicating that the poor aeration of paddy soil limited stomatal regulation, thereby affecting photosynthetic efficiency. In CS treatment, Pn, Tr, and iCE first increased and then decreased as irrigation depth decreased. The best performance was observed in the CS-ETc100 and CS-ETc60 treatments, which were significantly higher than both the non-irrigation (CS-ETc0) and over-irrigated (CS-ETc140) treatments. In contrast, photosynthetic parameters in the PS treatment were generally lower. However, PS-ETc60 showed significantly higher Pn and iCE compared with the other irrigation treatments. No significant differences in gs and Ls were observed as a function of irrigation depth in PS, which may be attributed to the limited aeration capacity of paddy soil. Although cabbage grown in CS exhibited enhanced photosynthetic performance, instantaneous water use efficiency (WUEi) did not significantly differ between the two growth substrates and irrigation depths.
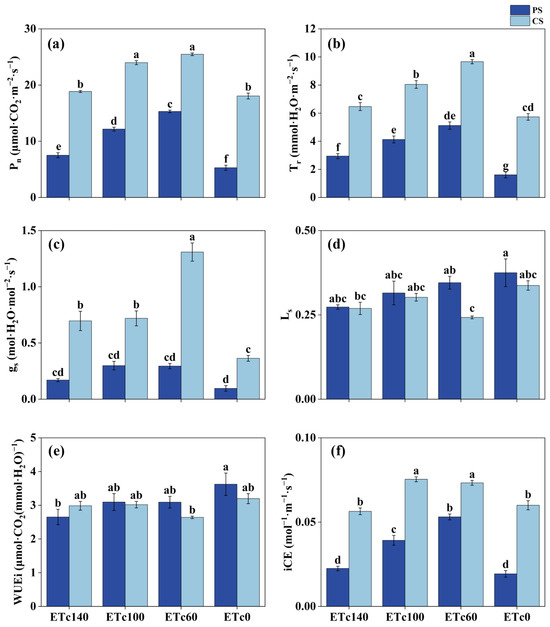
Figure 7.
The photosynthesis characteristics of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) under different irrigation levels in coir substrates (CS) and paddy soil (PS) during the head formation stage. Net photosynthetic rate (Pn) (a); transpiration rate (Tr) (b); stomatal conductance (gs) (c); stomatal limitation index (Ls) (d); instantaneous water use efficiency (WUEi) (e); instantaneous carboxylation efficiency (iCE) (f). The treatments consisted of four irrigation depths based on: ETc140 (140% of ETc), ETc100 (100%), ETc60 (60%), and ETc0 (no irrigation control). All data are expressed as mean ± standard error (n = 5). Different letters indicated significant differences (p < 0.05) according to Tukey’s multiple range test.
3.4. Yield and Growth Traits
The yield and growth traits of cabbage were significantly affected by both growth substrate and irrigation depth (Table 6). Overall, cabbage grown in CS exhibited significantly higher head diameter, fresh weight, dry weight, total yield, and water use efficiency (WUE) compared with PS. When comparing irrigation depth independently, no significant differences were observed among them. Within the PS treatments, the effect of irrigation depth on yield and growth traits was minimal, with PS-ETc100 showing a slight advantage over the other treatments. In contrast, within the CS treatments, both CS-ETc100 and CS-ETc60 increased head diameter, fresh and dry weight, compared with CS-ETc140 and CS-ETc0. Correspondingly, total yield followed a similar trend, with CS-ETc100 achieving the highest yield and CS-ETc60 slightly less, although no significant difference was observed between them. WUE was also significantly influenced by both growth substrates and irrigation depth. The highest WUE was observed in CS-ETc60, followed by CS-ETc100, suggesting that moderate deficit irrigation under CS conditions was beneficial for optimizing water use. In contrast, WUE in PS remained relatively low and showed no significant differences among irrigation depths. Additionally, the interaction between growth substrates and irrigation depths significantly affected all yield and growth traits, indicating that cabbage responses to irrigation strategies differed by root-zone conditions. These results suggest that irrigation optimization strategies should be adapted to the specific characteristics of the growth substrates. Morphological observations in Figure 8 showed that cabbage heads grown in CS-ETc100 and CS-ETc60 were not only larger but also firmer. Therefore, future crop management should optimize irrigation by considering both the dynamic water requirements of plants and the properties of the growth substrate, aiming to maximize yield and water use efficiency.

Table 6.
Yield and growth traits of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) under different irrigation depths (IDs) and grown on growth substrates (GS) (coir substrates-CS and paddy soil-PS).
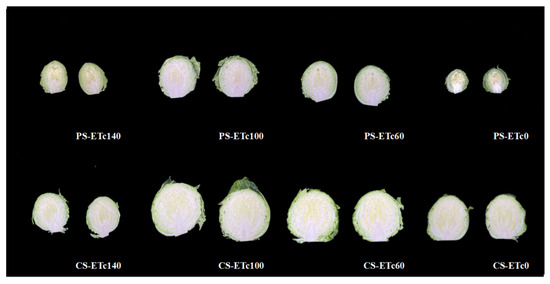
Figure 8.
Images of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) at the harvesting stage under different irrigation levels in coir substrates (CS) and paddy soil (PS). The treatments consisted of four irrigation depths based on: ETc140 (140% of ETc), ETc100 (100%), ETc60 (60%), and ETc0 (no irrigation control).
4. Discussion
4.1. Functionality and Effectiveness of the Automated Irrigation System
In this study, we developed a precise irrigation system based on real-time weather sensing and the cumulative reference evapotranspiration (ET0) concept. Among the parameters used for calculating ET0, the on-site wind speed data showed some discrepancies compared with KMA data (Figure 4). In our previous research, we also applied the XGBoost model to predict weather parameters for ET0 calculation, but the wind speed prediction showed a relatively low R2 value (0.730) [40]. Previous studies have demonstrated that wind speed exhibits strong spatial variability, with significant differences possible even over short distances [41,42]. This variability is influenced by multiple factors such as surrounding buildings, topography, and microclimate, resulting in discrepancies in wind speed data among different measurement sites [43]. Moreover, the contribution of wind speed to ET0 calculation exhibits significant seasonal variation. During summer, ET0 shows the lowest sensitivity to wind speed, while solar radiation and temperature exert greater influence [44,45]. Conversely, ET0 responds more strongly to wind speed in winter [46]. Therefore, the installation of on-site weather sensors remains essential for precise irrigation management based on the Penman–Monteith equation.
Irrigated agriculture uses about 70% of the world’s available freshwater each year, yet irrigates only around 25% of cultivated land [47]. Consequently, the concept of ‘more yield per water drop’ (MYWD) has emerged as a priority for ensuring water security and sustainable food production. However, the adoption of advanced water-saving technologies remains limited in low-income countries [48]. In some regions, irrigation scheduling is still based on manual measurements and empirical judgment, which can result in improperly timed irrigation that fails to match the crop’s critical water demand periods, thereby leading to water wastage and yield loss [49]. Currently, increasing research efforts are directed toward developing low-cost, efficient precision irrigation technologies [13]. Most automated irrigation systems rely on real-time soil moisture monitoring for feedback control. However, their operational stability is often limited by the spatial distribution and accuracy of the sensors, particularly in drip irrigation systems, where non-uniform wetting can lead to inaccurate soil moisture readings [31,50]. Remote sensing technologies have shown potential in large-scale irrigation monitoring, particularly in irrigation detection and quantitative estimation. Nevertheless, their application remains limited by low spatial resolutions, long revisit intervals, and significant data uncertainties, making it difficult to achieve precise irrigation management at the field scale [51]. In contrast, the system developed in this study enables continuous and dynamic estimation of crop water requirements and allows precise control of irrigation timing and volume at the plot scale by adjusting the Kc value in real time according to the target crop and its growth stage.
4.2. Effects of Automated Irrigation System on Soil Moisture Dynamics
Considering the significant differences in physical properties between PS and CS, different cumulative ET0 thresholds were adopted in this study to adjust irrigation frequency accordingly. CS exhibited better aeration and a more pronounced and rapid increase in soil moisture after irrigation, whereas PS showed a more muted and stable soil moisture response (Figure 6). These differences in moisture dynamics reflect the fundamental disparity in drainage performance between the two substrates. Previous studies have demonstrated that the plow sole layer in PS has the lowest permeability, with a hydraulic conductivity significantly lower than that of the surface and subsoil layers, thereby restricting vertical water infiltration [52,53]. As a result, high-frequency and low-volume irrigation in PS maintains a persistently saturated surface layer, inhibiting oxygen diffusion and creating hypoxic or even anaerobic conditions in the root-zone [54,55]. Such conditions are particularly detrimental to shallow-rooted vegetables such as cabbage, often resulting in leaf chlorosis and root rot [56]. Additionally, the high clay content in PS leads to rapid surface evaporation and crusting under high temperatures, further limiting plant growth [57,58]. In contrast, CS has a higher water-holding capacity and moderate capillarity, enabling it to maintain a stable root-zone water potential without causing waterlogging [59]. High-frequency and low-volume irrigation helps to reduce soil moisture fluctuations and enhance water use efficiency [60,61]. Previous research has applied irrigation scheduling based on cumulative crop evapotranspiration (ETc), combined with soil sensor-controlled irrigation [60], which shows methodological similarity to this study. The key distinction of this study is the use of cumulative ET0 as the irrigation trigger, enabling dynamic adjustment of Kc values and irrigation thresholds based on crop growth stages. Our irrigation system provides enhanced flexibility and broader applicability, supporting the management of diverse crops and practical implementation.
4.3. Cabbage Photosynthesis
The interaction between growth substrates and irrigation depth influences cabbage photosynthetic performance, likely because of differences in root-zone aeration (Figure 7). Enhanced root-zone aeration has been reported to improve the effective quantum yield of photosystem II (ΦPSII), facilitating photosynthetic electron transport and increasing CO2 assimilation through the Calvin–Benson cycle [62]. In this context, CS likely provides a more favorable root environment than PS, supporting higher photosynthetic efficiency. These findings are consistent with a previous report showing that root-zone oxygen supply can enhance photosynthetic performance in tomato [63]. Although CS treatments showed significantly higher gs, the Ls did not differ significantly between the two substrates under ETc140, ETc100, and ETc0 irrigation treatments. This suggests that factors beyond stomatal regulation, such as alleviation of non-stomatal limitations, contributed to improved carbon assimilation. Research indicates that better root-zone aeration supports photosynthesis by improving stomatal behavior and alleviating non-stomatal limitations such as Rubisco activity, thereby enhancing CO2 assimilation [64,65,66]. Notably, although both Pn and Tr were significantly higher in CS than in PS under the same irrigation depth, the instantaneous water use efficiency (WUEi) showed no significant variation. This response may reflect a leaf thermal regulation strategy [67]. Under high light and moderate water conditions, plants may enhance transpiration to cool leaf surfaces, thereby preserving the activity of heat-sensitive enzymes such as Rubisco [68]. Different irrigation depths also significantly influenced the photosynthetic performance of cabbage. The Pn and Tr reduction in ETc140 is likely due to large soil moisture fluctuations disrupting root-zone oxygen diffusion and soil redox potential (Eh), which impair root respiration and nutrient availability [69,70]. Such conditions can limit key biochemical processes involved in carbon fixation, reducing photosynthetic capacity [66,71]. These results highlight the importance of precise irrigation management to minimize moisture fluctuations and sustain crop productivity across substrates.
4.4. Interaction Effects on Cabbage Yield
The efficiency of photosynthetic carbon assimilation plays a crucial role in determining biomass accumulation and crop yield [72]. In this study, the trends in photosynthetic performance were closely reflected in yield performance. Both GS and IL had highly significant effects on cabbage yield (p < 0.001), and their interaction was also significant (p < 0.05). Improved aeration and water availability in CS treatments likely enhanced CO2 assimilation efficiency, facilitating head formation and contributing to increased fresh yield, as supported by previous studies [73]. Conversely, poor drainage in PS induced root-zone hypoxia, which has been shown to delay vegetative development and reduce head growth [74,75]. These physiological constraints may explain the significantly lower yields observed under PS treatments. Despite higher irrigation in CS-ETc140, yield decreased, likely because of excessive moisture causing root hypoxia, which limits photosynthesis and reduces biomass and head growth [11,75]. In both substrates, a yield reduction was observed under the ETc0 treatment. This was mainly caused by stomatal closure and reduced photosynthesis resulting from drought stress [76]. Previous studies have shown that moderate irrigation promotes the allocation of assimilates and improves head firmness [77]. These results underscore the importance of balancing substrate properties and irrigation levels to optimize cabbage growth and maximize yield.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that reusing discarded coir substrates in paddy fields, in combination with an automated ET0-based irrigation system, can substantially improve water use efficiency, optimize root-zone moisture conditions, and enhance cabbage yield. The proposed high-frequency, low-volume irrigation approach maintained stable performance across different irrigation levels and substrates, providing a practical alternative to conventional drainage systems. The results showed that the CS-ETc100 treatment achieved the highest yield, whereas the CS-ETc60 treatment provided the maximum WUE with no significant yield reduction. By integrating organic substrate reutilization with precision irrigation, this strategy offers a sustainable and adaptable solution for paddy field conversion and holds strong potential for wider adoption in multi-crop production systems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15081981/s1. Table S1: Hourly weather data recorded during the entire experiment period (16 April 2024 to 11 June 2024), including air pressure, relative humidity, solar radiation, temperature, wind speed, and ET0 measured by an on-site automated weather station.
Author Contributions
Experimental design and manuscript writing, data analysis, and protocol development by X.W.; experimental setup preparation by Y.L. and T.K.; project management, supervision, and manuscript review by J.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out with the support of “Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. RS-2025-06582971)”, Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. RS-2022-00155857, Artificial Intelligence Convergence Innovation Human Resources Development (Chungnam National University)).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kwon, D.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, E.E. Circular economy approach to valorizing horticultural waste via thermochemical process. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2025, 197, 107088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruda, N.S. Increasing sustainability of growing media constituents and stand-alone substrates in soilless culture systems. Agronomy 2019, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesendouz, S.O.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Rasouli, F. Using agricultural waste as an alternative growing medium for cultivating Cucumis sativus L. greenhouse transplants. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Yadav, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumari, K. Waste utilization in horticulture: An overview. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2024, 46, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, T.C.; Machado, R.M.; Alves-Pereira, I.; Ferreira, R.; Gruda, N.S. Coir-based growing media with municipal compost and biochar and their impacts on growth and some quality parameters in lettuce seedlings. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S.; Urayama, H.; Karunaratne, K.M.P.D.; Yamashita, T. Effects of coir application on soil properties and cucumber production as a reuse model of organic medium used in soilless culture. J. Trop. Agric. 2009, 53, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-B.; Park, E.-J.; Park, Y.-H.; Yeo, K.-H.; Rhee, H.-C.; Kang, J.-S. Effect of recycled coir organic substrates on vegetable crop growth. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2016, 25, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woznicki, T.; Kusnierek, K.; Vandecasteele, B.; Sønsteby, A. Reuse of coir, peat, and wood fiber in strawberry production. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1307240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Park, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Park, J. Enhancement of the growth and quality of soybeans using wasted coir substrates on multi-purpose utilization land. J. Bio-Environ. Control 2023, 32, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lee, Y.; Kang, T.; Park, J. Optimizing cabbage cultivation in paddy-converted fields using discarded coir substrates and controlled irrigation. Agronomy 2024, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Liu, S.; Song, Y.; Qin, T.; Xiao, S.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Zhou, X. Effects of waterlogging stress on root growth and soil nutrient loss of winter wheat at seedling stage. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhao, D.; Lin, X. Effects of waterlogging on nitrogen accumulation and alleviation of waterlogging damage by application of nitrogen fertilizer and mixtalol in winter rape (Brassica napus L.). J. Plant Growth Regul. 1997, 16, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.N.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Hussain, F.; Wu, R.-S. Precision irrigation: Challenges and opportunities. In Precision Agriculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingre, S.; Gorantiwar, S. Determination of the water requirement and crop coefficient values of sugarcane by field water balance method in semiarid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 232, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, J. Determination of crop water use and coefficient in drip-irrigated cotton fields in arid regions. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 236, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallo, G.; Paço, T.; Paredes, P.; Puig-Sirera, À.; Massai, R.; Provenzano, G.; Pereira, L. Updated single and dual crop coefficients for tree and vine fruit crops. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezera, K.; Dirirsa, G.; Hordofa, T. Determination of crop water requirement and crop coefficient of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) at Melkassa, Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. In Results of Natural Resources Management Research; Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020; pp. 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- Gabr, M.E.-S. Management of irrigation requirements using FAO-CROPWAT 8.0 model: A case study of Egypt. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 3127–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Paredes, P.; Hunsaker, D.; López-Urrea, R.; Shad, Z.M. Standard single and basal crop coefficients for field crops. Updates and advances to the FAO56 crop water requirements method. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Paredes, P.; López-Urrea, R.; Hunsaker, D.; Mota, M.; Shad, Z.M. Standard single and basal crop coefficients for vegetable crops, an update of FAO56 crop water requirements approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, A.; Prasad, P.; Ciampitti, I.; Jha, P. Using crop simulation model to evaluate influence of water management practices and multiple cropping systems on crop yields: A case study for Ethiopian highlands. Field Crop. Res. 2021, 260, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, K.; Mhatre, P.H.; Venkatasalam, E.; Sudha, R. Crop simulation models as decision-supporting tools for sustainable potato production: A review. Potato Res. 2021, 64, 387–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzimande, T.N.M. Application and Evaluation of AquaCrop, DSSAT and Simple Model in Modelling Yield and Water Use of Selected Underutilised Cereal Crops. Master’s Thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Pietermaritzburg, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Ahmad, S.; Fahad, S. Potential applications of DSSAT, AquaCrop, APSIM models for crop water productivity and irrigation scheduling. In Fertigation Technologies for Micro Irrigated Crops; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 137–170. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Awais, M.; Ru, W.; Shi, W.; Ajmal, M.; Uddin, S.; Liu, C. Review of sensor network-based irrigation systems using IoT and remote sensing. Adv. Meteorol. 2020, 2020, 8396164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Wu, H.; Zhangzhong, L. Development of smart irrigation systems based on real-time soil moisture data in a greenhouse: Proof of concept. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, A.; Cai, X.; Qiao, X.; Garcia, L.; Wang, J.; Amori, A.; Yang, H. Real-Time irrigation scheduling based on weather forecasts, field observations, and human-machine interactions. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2023WR035810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glória, A.; Cardoso, J.; Sebastião, P. Sustainable irrigation system for farming supported by machine learning and real-time sensor data. Sensors 2021, 21, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.K.; Misra, S.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Das, S.K. AgriSens: IoT-based dynamic irrigation scheduling system for water management of irrigated crops. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 5023–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, J.; Conejero, W.; Mira-Garcia, A.B.; Conesa, M.R.; Ruiz-Sánchez, M.C. Towards irrigation automation based on dielectric soil sensors. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, Z.; Gheysari, M.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Amiri, S.; Tabatabaei, M.S. An attempt to find a suitable place for soil moisture sensor in a drip irrigation system. Inf. Process. Agric. 2022, 9, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Gao, W.; Shamshiri, R.R.; Tao, S.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, G. Review of research progress on soil moisture sensor technology. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Zhou, Q.; Fu, L.; Zhan, L.; Wu, W. From lab to field: Advancements and applications of on-the-go soil sensors for real-time monitoring. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2024, 57, 1730–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Ham, Y.; Kim, J.; Cha, D.; Chang, E.; Lee, G.; Kug, J.; Lee, W. Record-breaking summer rainfall in South Korea in 2020: Synoptic characteristics and the role of large-scale circulations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2021, 149, 3085–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2015.
- ‘KoKoMa F1’ Cabbage Cultivation Method. Available online: https://www.asiaseedmall.com/board/view.php?bdId=notice&sno=19 (accessed on 2 March 2020).
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 56, p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Beshir, S. Review on estimation of crop water requirement, irrigation frequency and water use efficiency of cabbage production. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2017, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zeng, H.; Fan, J.; Lai, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Cheng, M.; Guo, J.; Li, Z. Effects of plant density, nitrogen rate and supplemental irrigation on photosynthesis, root growth, seed yield and water-nitrogen use efficiency of soybean under ridge-furrow plastic mulching. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 268, 107688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Ha, S.-u.; Wang, X.; Hahm, S.; Lee, K.; Park, J. An automatic irrigation system based on hourly cumulative evapotranspiration for reducing agricultural water usage. Agriculture 2025, 15, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazda, J.; Mann, J. Mitigating impact of spatial variance of turbulence in wind energy applications. Wind. Energy Sci. 2020, 5, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, G.; Yang, M.; Wang, D.; Yan, G.; Qi, Y. Spatial dispersion of wind speeds and its influence on the forecasting error of wind power in a wind farm. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean. Energy 2016, 4, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Jin, H. Field study on the microclimate of public spaces in traditional residential areas in a severe cold region of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle Júnior, L.C.G.d.; Vourlitis, G.L.; Curado, L.F.A.; Palácios, R.d.S.; Nogueira, J.d.S.; Lobo, F.d.A.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Rodrigues, T.R. Evaluation of FAO-56 procedures for estimating reference evapotranspiration using missing climatic data for a Brazilian tropical savanna. Water 2021, 13, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, R.; Li, M.; Shen, S.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Cao, W.; Tao, S.; Gao, P. Changes in reference evapotranspiration and its contributing factors in Jiangsu, a major economic and agricultural province of eastern China. Water 2017, 9, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Revuelto, J.; Morán-Tejeda, E.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Espejo, F. Sensitivity of reference evapotranspiration to changes in meteorological parameters in Spain (1961–2011). Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 8458–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhiar, I.A.; Yan, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; He, B.; Hao, B.; Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Bao, R.; Syed, T.N. A review of precision irrigation water-saving technology under changing climate for enhancing water use efficiency, crop yield, and environmental footprints. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghari, S.J.; Han, W.; Hu, K.; Laghari, Y.; Wei, Y.; Cui, L. What should we do for water security? A technical review on more yield per water drop. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyhu, B.; Dagalo, S.; Muluneh, M. Soil moisture-based irrigation interval and irrigation performance evaluation: In the case of lower kulfo catchment, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulis, K.X.; Elmaloglou, S.; Dercas, N. Investigating the effects of soil moisture sensors positioning and accuracy on soil moisture based drip irrigation scheduling systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 148, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa, L.; Schlaffer, S.; Brocca, L.; Vreugdenhil, M.; Nendel, C.; Dorigo, W. How accurately can we retrieve irrigation timing and water amounts from (satellite) soil moisture? Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 113, 102979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-K.; Liu, C.W. Analysis of water movement in paddy rice fields (I) experimental studies. J. Hydrol. 2002, 260, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbist, K.; Cornelis, W.; Schiettecatte, W.; Oltenfreiter, G.; Van Meirvenne, M.; Gabriëls, D. The influence of a compacted plow sole on saturation excess runoff. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 96, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, Z.; Niu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M. Effect of post-infiltration soil aeration at different growth stages on growth and fruit quality of drip-irrigated potted tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-z.; Wang, H.-x.; Yu, D.-s.; Yin, N.-x.; Zhang, J. The effect of aeration and irrigation on the improvement of soil environment and yield in dryland maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1464624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buga, N.; Petek, M. Use of biostimulants to alleviate anoxic stress in waterlogged cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata)—A review. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negyesi, G.; Szabó, S.; Buró, B.; Mohammed, S.; Loki, J.; Rajkai, K.; Holb, I.J. Influence of soil moisture and crust formation on soil evaporation rate: A wind tunnel experiment in Hungary. Agronomy 2021, 11, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramarachchi, K.; Betti, G.; Azam, G. Effect of clay amendment and strategic deep tillage on soil water dynamics and plant growth under controlled environments. Plants 2025, 14, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Choi, G.L. Characteristics of domestic net type melon in hydroponic spring cultivars using coir substrates. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2020, 38, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Guo, W.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, W.; Li, J. Effects of irrigation scheduling on the yield and irrigation water productivity of cucumber in coconut coir culture. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.-J.; Choi, E.-Y.; Lee, Y.-B. Irrigation control for improving irrigation efficiency in coir substrate hydroponic system. J. Bio-Environ. Control 2015, 24, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, R.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Geng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Z. Root-zone aeration improves fruit yield and quality of tomato by enhancement of leaf photosynthetic performance. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 291, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cheng, H.; Qiao, C.; Feng, J.; Yan, P.; Yang, R.; Song, J.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Root-zone oxygen supply mitigates waterlogging stress in tomato by enhancing root growth, photosynthetic performance, and antioxidant capacity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 222, 109744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, E.d.S.; Mota, J.C.A.; Lacerda, C.F.d.; Silva, F.G.d.; Romero, R.E. Gas exchange in maize as a function of aeration porosity in a cohesive soil. Rev. Ciência Agron. 2021, 52, e20196823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosta, H.R. The responses of pepper plants to nitrogen form and dissolved oxygen concentration of nutrient solution in hydroponics. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.; Gao, L.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Jiang, D.; Dai, T.; Tian, Z. Low nitrogen priming enhances Rubisco activation and allocation of nitrogen to the photosynthetic apparatus as an adaptation to nitrogen-deficit stress in wheat seedling. J. Plant Physiol. 2024, 303, 154337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kitudom, N.; Fauset, S.; Slot, M.; Fan, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Lin, H. Leaf thermal regulation strategies of canopy species across four vegetation types along a temperature and precipitation gradient. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 343, 109766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scafaro, A.P.; Posch, B.C.; Evans, J.R.; Farquhar, G.D.; Atkin, O.K. Rubisco deactivation and chloroplast electron transport rates co-limit photosynthesis above optimal leaf temperature in terrestrial plants. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Furman, A. Soil redox dynamics under dynamic hydrologic regimes-A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Long, H.; Zhang, R.; Yu, K. Effects of stable and fluctuating soil water on the agronomic and biological performance of root vegetables. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1325078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, N. Effects of redox potential on the environmental behavior of nitrogen in riparian zones of West Dongting Lake Wetlands, China. Wetlands 2020, 40, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Zheng, G.; Hamdani, S.; Essemine, J.; Song, Q.; Wang, H.; Chu, C.; Sirault, X.; Zhu, X.-G. Leaf photosynthetic parameters related to biomass accumulation in a global rice diversity survey. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, M.; Abo-Elyousr, K.A.; AL-Solaimani, S.G. Organic production of cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) for agricultural sustainability and healthy nutrition: An overview. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2025, 17, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.; Patrick, W., Jr. Soil aeration and plant productivity. In Handbook of Agricultural Productivity; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 51–70. [Google Scholar]
- Manghwar, H.; Hussain, A.; Alam, I.; Khoso, M.A.; Ali, Q.; Liu, F. Waterlogging stress in plants: Unraveling the mechanisms and impacts on growth, development, and productivity. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 224, 105824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driesen, E.; De Proft, M.; Saeys, W. Drought stress triggers alterations of adaxial and abaxial stomatal development in basil leaves increasing water-use efficiency. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H.; Kaman, H.; Sönmez, İ.; Uçan, U.; Akgün, İ.H. Yield and yield parameters response of cabbage to partial root drying and conventional deficit irrigation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).