Abstract
Agronomic practices and future climate change lead to divergent responses in crop growth and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, which challenge a sustainable low-carbon agricultural economy. Therefore, this study developed a simulation-optimization hybrid model to identify long-term best management practices (BMPs) for economic and social benefits under the effects of future climate change. This model, i.e., RZWQM2 coupled with an orthogonal optimization algorithm (RZWQM2-OOA), integrates four core components, including an orthogonal sampling module, climate prediction module, RZWQM2 simulation module, and optimization analysis module. The model enabled a high-fidelity simulation of crop growth and carbon emissions across complex management practice-climate combinations, while efficiently identifying BMPs and circumventing dimensionality challenges through orthogonality and balanced dispersion mechanisms. To validate the applicability of the developed model, it was applied to a real-world, irrigated, continuous corn (Zea mays L.) production system in the USA. Results indicated that the maximum increases in direct and indirect economic benefits (F1 and F2) and potential social benefits (F3) were 35.7%, 42.6%, and 155.5%, respectively, compared to the actual practice. Fertilization amount was the key regulating factor for direct economic and potential social benefits, which exhibited the largest contribution rates (44.3% for direct economic benefit and 53.9% for potential social benefit). Irrigation exerted the most significant influence on indirect economic benefits (Contribution rate = 53.9%). This study provides a replicable and scalable methodology for policy-makers to balance the trade-offs between the economy and carbon emissions in agricultural sustainability.
1. Introduction
The agricultural sector is a major contributor to GHG emissions, accounting for approximately 22% of total anthropogenic GHG emissions [1]. Agricultural GHG emissions have shown an increasing tendency in the 21st century, from 7.9 × 109 ton CO2-eq in 2000 [2] to 12.5 × 109 ton CO2-eq in 2024 [3]. The growing GHG emissions have triggered negative impacts on a global scale, including global warming and the frequency of extreme climatic events, etc. [4]. Therefore, it is important to seek low-carbon agricultural economic strategies to effectively reduce GHG emissions in agricultural production.
Agricultural GHG emissions are closely intertwined with agronomic practices, such as fertilization [5], irrigation [6], and conservation tillage [7]. These practices can alter soil carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) dynamics by modifying microbial activity, redox conditions, and nutrient availability, thereby affecting GHG emissions [8]. Fertilization increases the contents of nitrate and ammonium N in soils, which provides extra substrates for nitrification-denitrification processes to produce nitrous oxide (N2O) [9]. Mboyerwa et al. [10] indicated that a 30% increase in N fertilizer application resulted in a 15% elevation in N2O emission. Irrigation affects GHG emissions by altering soil moisture and oxygen availability, which regulate the activity and function of methanogenic, anammox, nitrifying, and denitrifying bacteria [11]. Li et al. [12] found that N2O emissions in wheat fields increased from 0.51 kg-N ha−1/day to 0.62 kg-N ha−1/day by an increase of 50% irrigation amount. Lin et al. [13] documented that irrigation modes and scheduling also had significant impacts on GHG emissions. Stover retention and no-till are the main conservation tillage practices that mitigate GHG emissions through multiple pathways, including reducing soil disturbance, enhancing soil organic carbon (SOC) sequestration, and forming a protective biomass layer on the soil surface [14]. Cheng et al. [15] indicated that stover retention practice resulted in a 24% increase in CO2 emissions in an irrigated, continuous corn system in Ithaca, USA, compared to stover removal treatment (8700 kg-C/ha/yr).
Apart from agronomic practices, climate change plays an important role in influencing agricultural GHG emissions [16]. It has been reported that future climatic conditions show a tendency for daily temperatures and annual precipitation to rise, while shortwave radiation declines [17]. These changes alter the soil microbial living environment and function, thus indirectly affecting the production processes of GHG emissions [18]. Wu et al. [19] indicated that elevated soil temperatures enhance microbial abundance, biomass, and enzymatic functions. These changes subsequently modify oxygen consumption and soil carbon dynamics, while stimulating respiratory CO2 release. Li et al. [20] found similar phenomena in N2O emissions. Intense precipitation alters soil moisture (SWC), subsequently changing the aeration of soil and crop-available NH4+ and NO3−, thereby altering GHG emissions [21]. Zhang et al. [22] indicated that a 30% increase in precipitation stimulated plant root turnover and enhanced nitrogen cycling processes, which subsequently led to significant increases in soil emissions of N2O (45.6%) and CO2 (46.7%). Moreover, heightened atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration ([CO2]atm) typically enhances crop growth and accelerates soil organic matter (SOM) mineralization, supplying more substrate for denitrification processes [17]. Wang et al. [23] found that elevated [CO2]atm (+200 ppm above ambient) stimulated rice photosynthesis, boosting rhizodeposition of labile organic carbon that amplified GHG emissions by 26%. Thus, exploring the combined effects of agronomic practices and climate change on agricultural GHG emissions is meaningful.
Plentiful agricultural system models [e.g., APSIM [24], DAYCENT [25], DNDC [26], and RZWQM2 [27]] have been widely applied to simulate GHG emissions under different agronomic and climate scenarios. Previous studies have demonstrated that applications of these models entail respective limitations [28]. For instance, due to substrate consumption biases, APSIM overpredicted nitrification rates by 20–30%. Consequently, GHG emissions originating from mineralization and nitrification processes were overestimated [29]. Moreover, due to its insensitivity to soil temperature (Tsoil) variations, DAYCENT generates denitrification estimates with 15–25% inaccuracy, which leads to insufficient accuracy in soil N2O emission simulations [30]. Although DNDC has been extensively applied in agricultural systems to simulate GHG emissions, it exhibits limitations in simulating soil dynamic processes, particularly regarding its imprecise simulations of heterogeneous soil profiles, subsoil layers, and crop root density functions [31]. Compared to the other models, RZWQM2 demonstrates higher accuracy in simulating GHG emissions under climate change scenarios by integrating the OMNI and DASST sub-models [32]. Employing the RZWQM2 model, Wang et al. [33] demonstrated that N2O emissions from agricultural soils in Iowa, USA, would exceed current levels by 11.2%, which was attributed to elevated [CO2]atm reaching 548 ppm and a 2.2 °C rise in air temperature. Similarly, employing the RZWQM2 model for Quebec (Canada) sites, Jiang et al. [34] reported that soil CO2 and N2O emissions surpassed current baseline levels by 1.9% and 9.0%, respectively, under conditions of 8% higher precipitation and 2.6 °C elevated air temperatures. Despite RZWQM2 ‘s robust performance, identifying BMPs encountered significant challenges when facing high-dimensional combinations of agronomic practices, such as fertilization amounts and scheduling, irrigation amounts and scheduling, and tillage depth. Optimization of high-dimensional agronomic practices has resulted in substantial computational demands in modeling, which are typically computationally expensive and involve mixed discrete-continuous decision variables.
This study aimed to present an integrated simulation-optimization model (i.e., OOA-RZWQM2) to simulate crop growth and carbon emissions under complex combinations of agronomic practices and climatic conditions, thereby accurately evaluating the direct economic benefit (F1), indirect economic benefit (F2), and potential social benefit (F3). Optimal solutions within high-dimensional agronomic practice spaces can be identified using this model. By leveraging principles of orthogonality and balanced dispersion, the model mitigates the curse of dimensionality inherent to the vast combinatorial possibilities of these practices. Then, the applicability and effectiveness of the proposed methodology were verified in NE USA. Crop yield, total biomass, CO2, and N2O emissions were simulated by utilizing the methodology developed in this study. Three economic benefits were set as optimization objectives, and then universally applicable BMPs corresponding to each objective were identified. The study results provide a reference for identifying agronomic strategies for a low-carbon economy in the face of climate change.
2. Materials and Methods
The present study sought to develop a simulation-optimization model with a deterministic sampling strategy, climate prediction, and crop growth simulation processes, i.e., OOA-RZWQM2 hybrid model. As shown in Figure 1, the simulation sub-model comprises a climate prediction module and an RZWQM2 simulation module. The climate prediction module generates high-resolution daily future climate data, serving as critical climate scenarios to drive simulations within the RZWQM2 simulation module. The RZWQM2 simulation module simulates agricultural management scenarios defined by the decision variables, generating the outputs required for objective function quantification: crop yield, total biomass, CO2 and N2O emissions. The optimization sub-model integrates an orthogonal sampling module with an optimization analysis module. The orthogonal sampling module performs deterministic sampling of the decision variables, which are subsequently employed in the simulation sub-model. Subsequently, the optimization analysis module constructs objective functions to identify BMPs. The decision variables are defined as a series of agronomic practices, e.g., fertilization amount and date, irrigation amount and date, tillage depth and time, and proportion of returned straw. The objective functions are direct economic benefits, indirect economic benefits, or potential social benefits, identifying future BMPs, and achieving a low-carbon economy by integrating simulation and optimization sub-models.
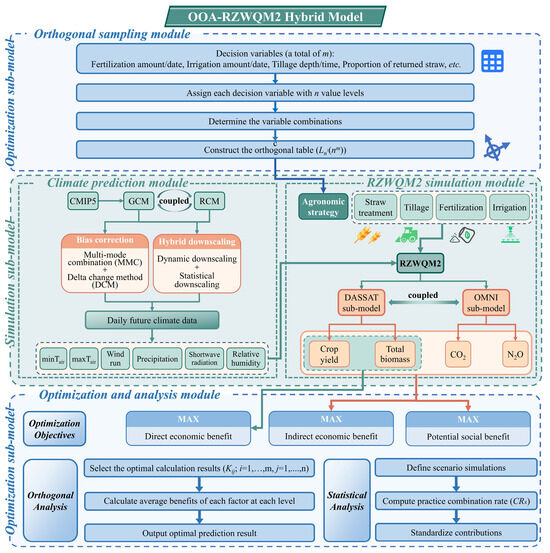
Figure 1.
Model framework for orthogonal optimization algorithm—RZWQM2 (OOA-RZWQM2) hybrid model.
2.1. Simulation Sub-Model
2.1.1. Climate Prediction Module
This module integrates multi-source climate data and downscaling techniques to generate high-resolution daily future climate scenarios. Future climate data are sourced from the NA-COR-DEX initiative, the successor to the North American Regional Climate Change Assessment Program (NARCCAP) [35]. In NA-CORDEX, general circulation model (GCMs) outputs are corrected by using a multi-model combination (MMC) bias correction to minimize systematic errors [36]. Regional climate models (RCMs) are then embedded into the GCMs to obtain regional weather variables at a spatial resolution of 50 km through dynamical downscaling. To make the RCM-GCM projections free from bias relative to the observation station, the delta change method (DCM) is employed to make a secondary correction for the RCM-GCM projections [37]. Detailed methods of DCM can be found in Text S1 in the Supplementary Information. RCM-GCM projections after the second correction can serve as different future meteorological scenarios. Furthermore, the atmospheric CO2 concentration in future scenarios can be set according to the value suggested by Wang et al. [38]. This module generates high-resolution daily future climate data, serving as a critical input for the RZWQM2 simulation module to conduct modeling under projected scenarios.
2.1.2. RZWQM2 Simulation Module
This module employs a comprehensive ecosystem mechanism model (i.e., RZWQM2) to simulate the crop growth and GHG emissions under varying agronomic combinations (provided by the orthogonal sampling module, Section 2.2.1) and future climate conditions (provided by the climate prediction module) [39]. The DASSAT sub-model of RZWQM2 simulates crop yield and total biomass by dynamically integrating biophysical processes, including photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and water balance. Concurrently, GHG emissions are simulated by the OMNI sub-model by quantifying carbon and nitrogen cycling under varying soil moisture and temperature regimes [40]. In RZWQM2, irrigation alters soil water content and redistribution, primarily regulating the transformation rate of soil organic matter (SOM) in the OMNI sub-model and crop nutrient uptake capacity in the DSSAT sub-model, thereby impacting CO2 and N2O emissions, crop yield, and biomass. Fertilization adds nutrients (primarily N) to the soil pool, driving plant growth and microbial transformations, which influence soil organic carbon turnover and are major sources of N2O emissions. Tillage modifies soil physical properties (e.g., soil bulk density and macroporosity), influencing water infiltration, root growth, and residue decomposition rates in the OMNI sub-model, thereby affecting crop yield, total biomass, and GHG emissions. Straw treatment (e.g., straw return) influences soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient supply via the OMNI sub-model, which is a major potential source of nitrogen and carbon for nutrient processes [39].
Detailed mechanisms of DASSAT and OMNI can be found in Ma et al. [41]. The mechanism of the OMNI sub-model is shown in Figure S1. The outputs of crop yield (Yt, kg/ha), total biomass (CBt, kg/ha), CO2 (kg-C/ha), and N2O (kg-N/ha) emissions (converted to carbon equivalent, ΔEG,t, t/ha) serve as critical inputs for the following optimization analysis module.
2.2. Optimization Sub-Model
2.2.1. Orthogonal Sampling Module
The Orthogonal Latin Squares method is employed to obtain deterministic samples from all solution spaces based on the mechanisms of orthogonality and balanced dispersion [42,43]. Specifically, a total of m agronomic practices can be set as decision variables of the orthogonal sampling, e.g., fertilization amount, irrigation amount, tillage depth and time, and proportion of returned straw. Each decision variable is assigned an n-value level. Then, an orthogonal table (i.e., Ln2(nm)) can be constructed based on orthogonality and balanced dispersion processes [42]. The purpose of this module is to generate n2 deterministic agronomic combinations from the nm possible combinations, which are subsequently employed in the simulation module.
2.2.2. Optimization and Analysis Module
This module aims to derive optimal future BMP combinations and achieve a low-carbon economy. In this module, the maximum direct economic benefit (max F1), indirect economic benefit (max F2), and potential social benefit (max F3) are considered as the objective functions, which represent the net income from crop sales, additional revenue from carbon trading, and social value of GHG reduction, respectively [44]. Within the RZWQM2 simulation module, systematic variation of the decision variables generates the objective function inputs: crop yield (YCt, kg/ha), amount of returned straw (YSt, kg/ha), and amount of GHG reduced by changing the decision variables (ΔEGt, t/ha). The year 2025 is taken as the base year, and each objective takes into account the time value of funds. These three objective functions can consider any possible costs and benefits and apply discounting to project future benefits and costs in present value terms [45]. The objective functions are calculated as follows:
Direct economic benefits:
Indirect economic benefits:
Potential social benefits:
where F1 ($/ha), F2 ($/ha), and F3 ($/ha) represent the total direct economic benefit (F1), indirect economic benefit (F2), and potential social benefit (F3), respectively, obtained through agricultural production. YCt (kg/ha) is the crop yield in the tth year. PC ($/kg) and PS ($/kg) are the sales prices of the crop and returned straw, respectively. YSt (kg/ha) is the amount of returned straw in the tth year. η is the straw harvesting efficiency; CA ($/ha) and CP ($/ha) are the management and production costs, respectively. DR is the discount rate. q is the total number of years predicted. RG ($/t) is the carbon credit rate. ΔEGt (t/ha) is the amount of GHG reduced by changing agronomic practices in the tth year. RS ($/t) is the social price of GHG emissions.
Optimal future agronomic practice combinations can be obtained by systematically optimizing F1, F2, and F3 using the orthogonal analysis method [46]. This method employs range analysis principles in three sequential steps: First, select the optimal calculation results of all sampling combinations. Then, building on this, the average benefits of each factor at each level were calculated and analyzed using the range analysis method, enabling a quantitative comparison of their relative influences. Finally, through comprehensive factor-level optimization, we obtained optimal future agronomic practice combinations that were better than the initial sorting. This step is crucial for orthogonal sampling to approach the global optimal solution. The calculation formulas for the range method are shown in Equations (4) and (5):
where kij is the average response for the jth level of the ith experimental parameter (j = 1 − n, i = 1 − m). Kij is the total response for the jth level of the ith experimental parameter. Ri is the extreme difference value of the ith experimental parameter (a higher R value induces a stronger prioritization of the experimental parameter).
CO2 and N2O are the dominant greenhouse gases [47]. N2O emissions (i.e., EN2O) have 273 times the global warming potential (GWP, CO2-t/ha) of CO2 emissions (i.e., ECO2) (100-year horizon) [4]:
The relative contribution rate (CRx, %) of distinct decision variable x was calculated to evaluate its effect on economic and social benefits in the experimental fields. The formula is as follows [48]:
where x refers to IA, FA, TD, TT, and PRS, which stand for irrigation, fertilization, tillage depth, tillage time, and proportion of returned straw, respectively. CRx is standardized (i.e., CRIA +CRFA + CRTD + CRTT + CRPRS = 100%). f(HRCT), f(BMP), and f(x) refer to the economic and social benefits simulated under the actual practice, BMP for max F1, BMP for max F2, and BMP for max F3, and the actual practice altered by a distinct decision variable x, respectively.
3. Application
The applicability and effectiveness of the proposed optimization-simulation model were verified using a real-world, irrigated, continuous corn (Zea mays L.) production system in the USA. The applied area and model parameters are provided below.
3.1. Study Area
The site was located at the University of Nebraska (lat. 41.16 N, long. 96.41 W, 349 m asl), Ithaca, NE, USA. Continuous corn (Zea mays L.) has been cultivated in the study area since 2001. Detailed descriptions of the site characteristics, including soil properties (e.g., series, texture, pH, N, and SOC), historical and current cropping systems, agronomic management practices (seeding, fertilization, and irrigation), and long-term climate data (mean annual precipitation and temperature) are provided in the Supplementary Information (Text S2 and Table S1). A 2 × 2 factorial combination of three stover removal rates (no removal (NR) vs. high removal (HR)) and two tillage treatments (conventional tillage (CT) vs. no-till (NT)) with a randomized complete block design was tested over four crop years (i.e., NRCT, HRCT, NRNT, and HRNT) (Table S2) with details available in [21].
3.2. Data Collection and Processing
Orthogonal table design: In this case study, five agronomic practices were considered as experimental parameters, including fertilization, irrigation (with seven independent seasonal applications annually), proportion of returned straw (PRS), tillage depth, and tillage time (with separate optimization for month and date components), resulting in a total of 12 optimizable experimental parameters (i.e., m = 12). Each parameter was assigned 51 value levels (i.e., n = 51). Following the orthogonal table construction principles established by Diane [35], an L2601(5112) orthogonal table was adopted to systematically organize the experimental design. Considering interannual climatic change, twenty consecutive orthogonal tables were designed repeatedly during the 20-year simulation period (2065–2084).
RZWQM2 parameter settings: In this study area, the calibration and verification of RZWQM2 were completed. The long-term conservation practice impacts on biogeochemical cycling (C/N) and soil-water-crop interactions can be simulated using this model. Model parameters were calibrated using site-collected NRCT data, and validation was conducted across the NRNT, HRCT, and HRNT treatment datasets. Edaphic variables (soil moisture and temperature), crop productivity metrics (yield and biomass), and greenhouse gas fluxes (CO2 and N2O) were collected throughout a four-year cropping cycle (2011–2015) [15]. The detailed calibration process and parameters can be found in the SI provided by Cheng et al. [15].
Historical and future climate data: The mean climatic values projected for 2065–2084, which were obtained from the climate prediction module, were used as an example for executing RZWQM2 in this case study. The observational climate records (2001–2020) employed for future projection bias adjustment were retrieved from a nearby weather station (Station ID: MEMPHIS5N) (Figure S2). Detailed future climate scenarios of the RCM-GCM combinations are presented in Table S3 in the Supplementary Information. Historical [CO2]atm, centered in 2010 at 390.1 ppm, utilized Earth System Research Laboratory reanalysis data (https://gml.noaa.gov, accessed on 20 September 2024). The future climate scenario employed representative concentration pathway 8.5 (RCP 8.5), with [CO2]atm set at 714.1 ppm for the 2075-centered 2065–2084 period [49].
Relevant economic parameters: In the optimization and analysis module, the prices involved in the economic and social benefits accounting model are based on the latest published data (e.g., government databases, agricultural extension documents, and recent papers), and the results of the study are intended to assess BMPs in the future economy. Table S4 shows the price parameters for different input costs, income, and potential values. The calculation formula is provided in Section 2. Specifically, the calculation of CA is as follows , where C9 ($/ha) is the fixed cost of the agricultural machinery equipment; C10 ($/ha) is the maintenance and repair costs of the equipment. The calculation of CP is as follows , where Ci is the variable cost; detailed prices are summarized in Table S4.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Effects of Long-Term Agronomic Practices on Economic and Social Benefits
All optimized BMPs (i.e., BMP for max F1, BMP for max F2, and BMP for max F3) tended to increase direct economic benefit (F1) compared with the actual practice (Figure 2(a-1)). Excluding the indirect economic benefit (F2) and potential social benefit (F3) associated with carbon emission reduction, the economic and social benefits (i.e., F1, F2, and F3) under the actual practice were all 871,516 $/ha over the period 2065–2084 (Figure 2a). F1 ranged from 871,516–1,182,559 $/ha, and the maximum F1 was achieved under the BMP for max F1, increasing by 311,043 $/ha. The maximum relative change in F1 (max RCF1) was +35.7% compared with the actual practice (Figure 2(a-1,b-1)). This increase is possibly because both the annual mean yield (AMYield) and total biomass (AMTotal bio) reached their maximum under the BMP for max F1; these increases were the primary drivers enhancing F1. AMYield and AMTotal bio under the BMP for max F1 increased by 1895 kg/ha and 2387 kg/ha, respectively (Figure 2(c-1,c-2,d-1,d-2)). This result was due to synergistic effects of crop yield-derived revenue and value-adding biomass resource utilization [50,51].
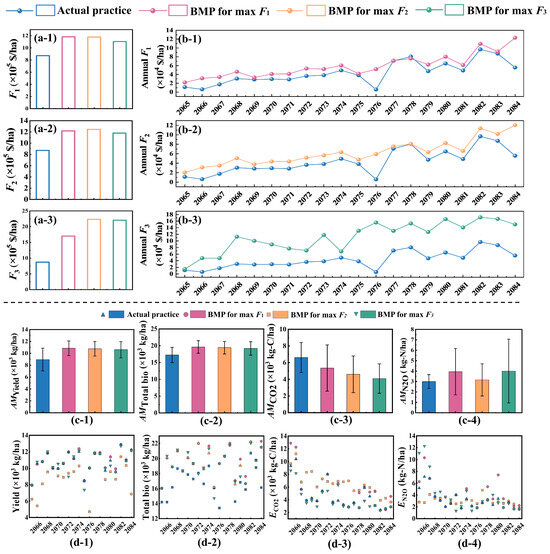
Figure 2.
(a) Direct economic benefit, indirect economic benefit, and potential social benefit (F1, F2, and F3) under the actual practice, BMP for max F1, BMP for max F2, and BMP for max F3, respectively. (b) Maximum direct economic benefit, indirect economic benefit, and potential social benefit (max F1, max F2, and max F3) compared to the economic benefit under actual practice. (c) Annual mean values of yield (AMYield), total biomass (AMTotal bio), CO2 emissions (AMCO2), and N2O emissions (AMN2O) under the actual practice, BMP for max F1, BMP for max F2, and BMP for max F3 from 2065 to 2084. (d) Interannual yield, total biomass, CO2 emissions (ECO2), and N2O emissions (ECO2) from 2065 to 2084.
Compared to actual practice, greater increases in indirect economic benefits (F2) were observed across all three BMPs (Figure 2(a-2)). The F2 ranged from 871,516 to 1,244,702 $/ha; the maximum F2 was achieved under the BMP for max F2, increasing by 373,186 $/ha. The maximum relative change in F2 (max RCF2) was +42.8% relative to the actual practice (Figure 2(a-2,b-2)). This outcome was primarily attributed to sustained increases in AMYield and AMTotal bio relative to the actual practice (+1807 kg/ha and +2173 kg/ha, respectively) (Figure 2(c-1,c-2,d-1,d-2)), coupled with enhanced reductions in CO2 and N2O emissions (ECO2 and EN2O) (Figure 2(c-3,c-4,d-3,d-4)), compared to the BMP for max F1, which drove greater decreases in GWP [4], evidenced by an 11.6% reduction in relative GWP change (RCGWP) versus BMP for max F1 (Figure S2). Revenue from the sale of carbon credits can offset and even exceed the potential loss of traditional agricultural income or increased costs arising from altered production practices [52,53].
For each BMP, potential socio-economic benefit (F3) consistently exhibited the most substantial increase among the economic objectives (Figure 2(a-1–a-3)). This result occurred because F3 incorporates not only direct and indirect economic benefits but also ancillary social benefits derived from carbon emission reduction [44]. F3 ranged from 871,516–2,229,117 $/ha; maximum F3 was achieved under the BMP for max F3, increasing by 1,357,601 $/ha. The maximum relative change in F3 (max RCF3) was +155.7% compared to the actual practice (Figure 2(a-3,b-3)). This increase is primarily because the annual mean CO2 (AMCO2) under the BMP for max F3 exhibited the most pronounced reduction among the three BMPs, −38.6% relative to the actual practice (Figure 2(c-4,d-4)). Although the annual mean N2O (AMN2O) peaked under the BMP for max F3 (Figure 2(c-3,d-3)), this increase contributed minimally to the total GWP (converted to CO2-eq), accounting for only 6.3% [4]; consequently, the AMGWP was ultimately minimized under the BMP for max F3. Quantifying the potential social benefits arising from carbon reduction and ensuring pricing consistency for these benefits are critical aspects in the calculation of F3. Similar results were also found by Song et al. [54].
4.2. Long-Term Best Management Practices (BMPs) for Economic and Social Benefits
4.2.1. BMP for Direct Economic Benefit
Based on modeling results with altered agronomic practices, the AMYield and AMTotal bio significantly increased under BMP for max F1 and were the highest among the three BMPs and the actual practice (Figure 2(c-1,c-2,d-1,d-2)). Compared with the actual practice and BMPs for max F2 and max F3, the relative changes in AMYield (RCYield) values were +26.6%, +0.8%, and +2.8%, respectively, and the relative changes in AMTotal bio values (RCTotal bio) were +15.0%, +1.2%, and +2.6%, respectively (Figure S2). Optimal fertilization was the primary factor driving the simultaneous maximization of both crop yield and total biomass under BMP for max F1. Both insufficient fertilization and excessive fertilization lead to nutrient limitation, which induces physiological stress, reduces crop yield, and inhibits total biomass [9]. Concurrently, the synergistic effect of reduced tillage depth and appropriately increased PRS had an impact on yield and total biomass, with the annual mean tillage depth (AMTD) decreasing by 11.55 cm and the annual mean PRS (AMPRS) increasing by 0.16, respectively, compared with the actual practice (Figure 3(a-3,a-4,b-3,b-4)). In RZWQM2, reduced tillage depth triggers adjustments in soil physical properties, specifically increasing bulk density (BD) and reducing saturated hydraulic conductivity and macroporosity in the affected layers. These changes increase root biomass but compromise soil aeration, thereby elevating compaction risk, which potentially increases denitrification-derived N2O emissions and restricts root growth, ultimately reducing crop yield [39,55]. However, the increased PRS reduced evaporation and enhanced water conservation. Given that water demand during the critical growth stage of maize accounts for approximately 50% of the total growing season requirement, improved water retention capacity directly determines kernel plumpness [7]. Therefore, under the BMP for max F1, the increase in crop yield resulting from a higher PRS more than compensates for the yield reduction caused by shallow tillage, leading to an overall increase in crop yield.
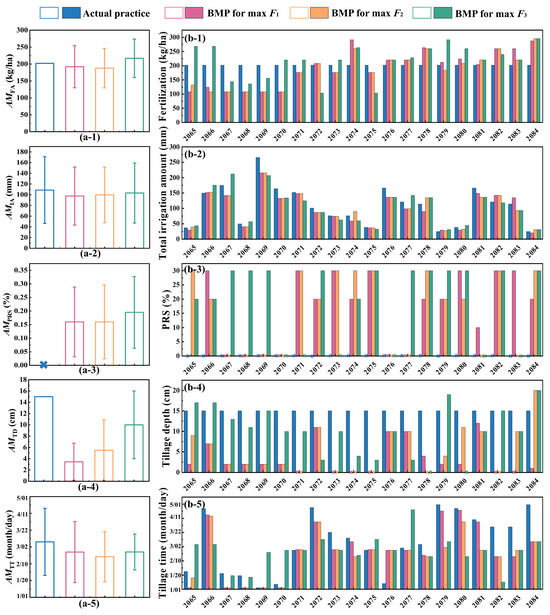
Figure 3.
(a) Annual mean values of fertilization (AMFA), irrigation (AMIA), proportion of returned straw (AMPRS), tillage depth (AMTD), and tillage time (AMTT) under the actual practice, BMP for max F1, BMP for max F2, and BMP for max F3 from 2065 to 2084, respectively. (b) Interannual fertilization, irrigation, proportion of returned straw (PRS), tillage depth, and tillage time from 2065 to 2084.
Under optimized BMP for max F1, the AMCO2 exhibited a declining trend, but not so the AM N2O (Figure 2(c-3,c-4,d-3,d-4)). This may be due to the advanced annual mean tillage time (AMTT) and reduced irrigation (AMIA) compared to the actual practice (Figure 3(a-2,a-4,b-2,b-5)). Earlier tillage time led to lower soil temperatures, slowing residue decomposition, and limiting readily available carbon for microorganisms, thereby decreasing basal soil respiration by 30–50% [56]. Concurrently, reduced irrigation concentrated soil nitrogen, enhancing the efficiency of denitrifiers in utilizing carbon to reduce nitrogen, and consequently increasing N2O emissions [57].
4.2.2. BMP for Indirect Economic Benefit
Compared with the actual practice, both AMYield and AMTotal bio still increased under the BMP for max F2, with RCYield and RCTotal bio values of +26.6% and +2.8%, respectively, but the magnitude of this increase was lower than that under the BMP for max F1 (Figure 2(c-1,c-2,d-1,d-2)). These alterations likely still originated from the synergy of reduced tillage depth and increased PRS [7]. Compared to the BMP for max F1, the relative changes in fertilization (RCFA) increased under the BMP for max F2. The increase in irrigation may be the reason why the magnitudes of the increases in AMYield and AMTotal bio were slightly lower than those under the BMP for max F1 (Figure 3(a-4,b-4)). Increased irrigation causes soil anoxia and root damage, which reduces crop yield and inhibits total biomass accumulation [58]. Moreover, compared to the BMP for max F1, the GWP exhibited a further reduction (RCGWP: −11.6% relative to the BMP for max F1) (Figure S2). Both ECO2 and EN2O showed pronounced contributions (RCCO2: −10.8%, RCN2O: −14.8% relative to the BMP for max F1) in reducing the GWP (Figure S2). These reductions in ECO2 and EN2O may be due to decreased nitrogen fertilization (Figure 3(a-1,b-1)), which enhances microbial carbon use efficiency (CUE) in the short term by reducing respiratory losses, thereby promoting carbon sequestration under conditions of adequate soil nitrogen availability (SOC:N ratio < 20). However, in nitrogen-limited soils (SOC:N ratio > 20), prolonged N reduction may constrain microbial biomass synthesis and stable carbon formation, potentially increasing CO2 emissions via accelerated organic matter decomposition [59]. The SOC:N ratio was 12.1 (shown in Text S2) in this study; therefore, the reduction of nitrogen fertilization did not induce nitrogen limitation but instead likely enhanced CUE, promoting carbon sequestration and ultimately reducing CO2 emissions. Decreased nitrogen fertilization directly reduces the substrates for nitrogen transformation (NH4+/NO3−) and inhibits nitrification-denitrification processes, thereby decreasing N2O emissions [57].
4.2.3. BMP for Potential Social Benefit
As shown in Figure 2(c-1,c-2), under the BMP for maxF3, both AMCO2 and AMN2O reached their minimum and maximum values, respectively, compared to the actual practice and BMPs for F1 and F2. The relative changes in AMCO2 (RCCO2) values were −38.6% relative to the actual practice, −29.5% relative to the BMP for maxF1, and −12.5% relative to the BMP for maxF2. The relative changes in AMN2O (RCN2O) values were +33.7% relative to the actual practice, +25.0% relative to the BMP for max F1, and +14.0% relative to the BMP for max F2 (Figure S2). The decreased ECO2 is potentially attributable to the further increased PRS compared to BMPs for max F1 and max F2 (Figure 3(a-3),b-3). Lignin in straw is converted to humic acids via microbial activity. These humic acids exhibit high resistance to decomposition, promoting carbon sequestration and thereby decreasing CO2 emissions [60]. For EN2O, the increase might be attributable to the increased fertilization amount (Figure 3(a-1,b-1)), which more easily elevates soil nitrate and ammonium-N content [28]. However, as the increase in EN2O contributed minimally to the GWP (i.e., only 6.1%), the ECO2 showed a substantial predominance (−38.6%) in explaining GWP, the BMP for max F3 showed the most pronounced decrease in GWP (RCGWP: −35.7% relative to the actual practice, −26.9% relative to the BMP for max F1, and −9.8% relative to the BMP for max F2) (Figure S2). For AMYield and AMTotal bio, while both still showed increases relative to the actual practice (RCYield: +24.1%, RCTotal bio: +12.4% relative to the actual practice), they exhibited slight declines compared to the BMPs for max F1 and max F2. The RCYield and RCTotal bio values were −2.8% and −2.6% relative to the BMP for max F1, −1.9% and −1.4% relative to the BMP for max F2, respectively (Figure 2(c-1,c-2,d-1,d-2)). These reductions were attributed to the synergistic effect of concurrently increased irrigation, fertilization, and PRS (Figure 3(a-1–a-3,b-1–b-3). High irrigation may cause soil anoxia, impairing root uptake, while elevated fertilization can induce ion toxicity, damaging root cells [5,6]. High PRS may lead to organic acid toxicity and reduced substance accumulation [7].
4.3. Contribution Analysis of Agronomic Practices
To evaluate the effect of a distinct decision variable on the three economic benefits (F1, F2, and F3), the relative contribution rate of agronomic practice (CRx, x = IA, FA, TD, TT, and PRS) was assessed (Figure 4). The results showed that fertilization and irrigation had a large effect on F1, F2, and F3, and the sum of CRFA and CRIA exceeded 80.2% under all BMPs. The phenomenon might be explained by the following results. On the one hand, the three economic and social benefits were affected by crop yield and biomass. Within DSSAT, key maize traits (e.g., crop yield and biomass) were emulated using crop parameters, and these outputs demonstrated strong relevance to edaphic moisture and nutrient levels [39]. Meanwhile, three economic and social benefits were also influenced by GHG emissions. Using first-order chemical kinetics, the OMNI sub-model simulates GHG emissions during organic matter interconversions across its five constituent pools. These processes are primarily governed by edaphic moisture status and nutrient availability [39].
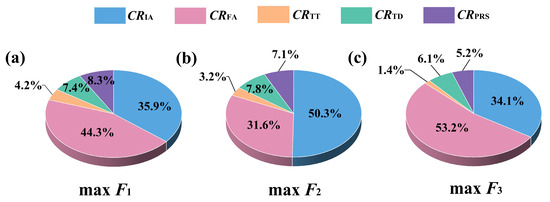
Figure 4.
(a) The relative contribution rates of irrigation (CRIA), fertilization (CRFA), tillage depth (CRTD), tillage time (CRTT), and proportion of returned straw (CRPRS) on maximum direct economic benefit (max F1). (b) The relative contribution rates of CRIA, CRFA, CRTD, CRTT, and CRPRS on maximum indirect economic benefit (max F2). (c) The relative contribution rates of CRIA, CRFA, CRTD, CRTT, and CRPRS on maximum potential social benefit (max F3).
Results of the contribution rate assessment demonstrated that the CRFA and CRIA for max F1 were 44.3% and 35.9%, respectively (Figure 4a). Fertilization had the greatest effect on max F1. This is because yield and total biomass directly determine the magnitude of F1, which is predominantly regulated by fertilization. The nitrogen stress index in the DSSAT sub-model associated with yield and biomass was regulated by changes in fertilization [39,61]. Notably, PRS also exerted a significant influence on max F1 (CRPRS = 8.3%), likely because crop rhizosphere microbial activity and plant growth exhibited differential responses to varying PRS [7]. For max F2, irrigation was the most influential variable (CRIA = 50.1%), followed by fertilization (CRFA = 32.1%). This is likely because the irrigation amount simultaneously influences crop growth and GHG emissions. Variations in irrigation modified the water stress index computed by the DSSAT sub-model, thereby governing crop yield and biomass [62]. Concurrently, the C/N cycling processes in the OMNI sub-model were associated with water content [39,63]. Additionally, the value of CRFA for max F3 was the largest, with a value of 53.9%, followed by CRIA (34.4%). This might be because fertilization plays an important role in GHG emissions [5]. Variations in fertilization modified the respiration of microorganisms and the nitrification and denitrification processes in the OMNI sub-model [39,61].
5. Conclusions
The main contribution of this study is the development of a simulation-optimization hybrid model (i.e., RZWQM2-OOA) for identifying agronomic BMPs to achieve a sustainable low-carbon economy under the effects of future climate change. The model enables high-fidelity simulation of crop growth and GHG emissions under complex combinations of agronomic practices and climatic conditions, thereby accurately evaluating direct economic benefit, indirect economic benefit, and potential social benefit. The model can avoid the curse of dimensionality due to the orthogonality and balanced dispersion mechanisms, and can efficiently filter out the optimal BMPs from a vast array of agronomic practice combinations.
The validity and applicability of the proposed model were validated using a real-world irrigated continuous corn (Zea mays L.) production system in the USA. It was found that the future economic and social benefits could be significantly increased by regulating fertilization, irrigation, and conservation tillage. Fertilization amount was the key regulating factor for direct economic benefit and potential social benefit, which exhibited the largest contribution rates (44.3% and 50.1% for direct economic benefit and potential social benefit, respectively). Irrigation had the most important influence on indirect economic benefits (contribution rate = 53.9%). Conservation practices, such as residue and tillage practices, demonstrated a marginal contribution to economic and social benefits (contribution rate < 8.3%). This model enables decision-makers to develop sustainable strategies that reconcile economic and carbon emissions in agricultural production. Although the OOA-RZWQM2 model demonstrated effectiveness in optimizing BMPs for a monoculture corn system, future research should validate the model across various agricultural contexts (e.g., diverse crops, climates, and regions) to enhance its robustness and broader applicability for sustainable agricultural planning under climate change.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15081980/s1, Text S1: The method of downscaling; Text S2: Site description, soil characteristics, climate data, and agronomic management details of the study area; Table S1: Agronomic practices from 2001 to 2020; Table S2: Stover management, tillage practices, and N fertilizer application in each experimental treatment; Table S3: Annual mean values of climatic variables derived from ensembles within modified future climate projections; Table S4: Cost parameters in the process of farmland management; Figure S1: Carbon (C), nitrogen (N) cycles and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the organic Matter and Nitrogen module (OMNI). IF: Influencing factors, including fertilization, irrigation, tillage, and straw treatment.; Figure S2: Monthly average historical climate observation data from 2001 to 2020; Figure S3: Annual (2065–2084) parameter growth rate under the BMPs for max F1, max F2, and max F3 compared with the actual practice compared with the actual practice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.C. and S.S.; methodology, Q.Y.; formal analysis, W.M.; investigation, W.J.; resources, S.F.; writing—original draft preparation, H.C. and S.S.; writing—review and editing, H.C.; visualization, S.S. and F.W.; supervision, Z.X. and W.M.; project administration, Z.X. and W.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52479076 and 42177365), Jiangsu Provincial Water Conservancy Technology Project (Grant No. 2025030), and the Yangzhou city-school cooperation project (Grant No. YZ2023216). This study was also sponsored by the Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province, the Qing Lan Project of Yangzhou University, China, and the High-end Talent Support Program of Yangzhou University.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article. Further inquiries should be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Qilin Yu was employed by the company Ningbo Dianxi Environmental Protection Technology Co. Author Fusheng Wang was employed by the company Huai’an Water Conservancy Survey and Design Institute Co., Ltd. All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Mulya, K.S.; Tan, J.P.; Yeat, S.P.; Yeat, C.N.C.; Farooque, A.A.; Zhou, S.; Woon, K.S. Toward Carbon Mitigation Resiliency in the Agriculture Sector: An Integrated LCA-GHG Protocol-IPCC Guidelines Framework for Biofertilizer Application in Paddy Field. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 389, 126005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I. Urgent Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions Is Needed to Avoid Irreversible Tipping Points: Time Is Running Out. All Earth. 2023, 35, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAOSTAT Emissions Database; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Panique-Casso, D.; Pacheco-Bueno, N.F.; Forio, M.A.E.; Goethals, P.; Ho, L. How Do Varying Nitrogen Fertilization Rates Affect Crop Yields and Riverine N2O Emissions? A Hybrid Modeling Study. Water Res. 2025, 276, 123242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Dheri, G.S.; Brar, A.S.; Kalia, A. Methane and Nitrous Oxide Emissions in Rice Fields Influenced with Duration of Cultivars and Irrigation Regimes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 365, 108923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B. Comparative Analysis of Soil and Water Dynamics in Conventional and Sod-Based Crop Rotation in Florida. Front. Agron. 2025, 7, 1552425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, A.; Ashraf, F.; Shakoor, S.; Mustafa, A.; Rehman, A.; Altaf, M.M. Biogeochemical Transformation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Terrestrial to Atmospheric Environment and Potential Feedback to Climate Forcing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 38513–38536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamyab, H.; SaberiKamarposhti, M.; Hashim, H.; Yusuf, M. Carbon Dynamics in Agricultural Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Removals: A Comprehensive Review. Carbon Lett. 2024, 34, 265–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mboyerwa, P.A.; Kibret, K.; Mtakwa, P.; Aschalew, A. Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Irrigated Paddy Rice as Influenced by Crop Management Practices and Nitrogen Fertilization Rates in Eastern Tanzania. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 868479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; She, D.; Pan, Y.; Abulaiti, A.; Huang, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, F.; Xia, Y.; Shan, J. Ditch Level-Dependent N Removal Capacity of Denitrification and Anammox in the Drainage System of the Ningxia Yellow River Irrigation District. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, W.; Oenema, O.; Chen, T.; Hu, C.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, L. Irrigation Reduces the Negative Effect of Global Warming on Winter Wheat Yield and Greenhouse Gas Intensity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, G. Investigating the Effects of Various Irrigation Methods on Bacterial Communities in Paddy Soil. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 306, 10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; Miao, L.; Chen, X.; Qiu, J.; Shu, J.; Cheng, J. Optimal Allocation of Agricultural Water and Land Resources Integrated with Virtual Water Trade: A Perspective on Spatial Virtual Water Coordination. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Shu, K.; Qi, Z.; Ma, L.; Jin, V.L.; Li, Y.; Schmer, M.R.; Wienhold, B.J.; Feng, S. Effects of Residue Removal and Tillage on Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Continuous Corn Systems as Simulated with RZWQM2. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Feng, H.; Peng, C.; Chen, H.; Xu, X.; Ma, X.; Li, L.; Kneeshaw, D.; Ruan, H.; Yang, H.; et al. Global Climate Change Increases Terrestrial Soil CH4 Emissions. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2023, 37, e2021GB007255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Ullah, S.; Dar, A.A.; Sardar, M.F.; Mehmood, T. Nexus on climate change: Agriculture and possible solution to cope future climate change stresses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14211–14232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, J.K.; Hofmockel, K.S. Soil Microbiomes and Climate Change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ling, J.; Xu, Y.-P.; Zhao, D.-Q.; Liu, Z.-X.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, S.-L. Effects of Soil Warming and Straw Return on Soil Organic Matter and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Winter Wheat Seasons in the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 356, 13181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, C.; Winiwarter, W.; Tian, H.; Canadell, J.G.; Ito, A.; Jain, A.K.; Kou-Giesbrecht, S.; Pan, S.; Pan, N.; et al. Enhanced Nitrous Oxide Emission Factors Due to Climate Change Increase the Mitigation Challenge in the Agricultural Sector. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Shu, K.; Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Cai, W.; Qi, Z.; Feng, S. Effects of Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation on Yield, Water and Nitrogen Use, and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Rice Paddy Fields. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 349, 13148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, J.; Chen, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Bai, T.; He, T.; et al. Moderate Precipitation Reduction Enhances Nitrogen Cycling and Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions in a Semi-arid Grassland. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 3114–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, Z.; Chen, S. Methane Emissions in Japonica Rice Paddy Fields under Different Elevated CO2 Concentrations. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2022, 122, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Mollabashi, E.; Huth, N.I.; Holzwoth, D.P.; Ordóñez, R.A.; Hatfield, J.L.; Huber, I.; Castellano, M.J.; Archontoulis, S.V. Enhancing APSIM to Simulate Excessive Moisture Effects on Root Growth. Field Crop Res. 2019, 236, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, P.; Machado, S.; Ghimire, R.; Del Grosso, S.J.; Reyes-Fox, M. Simulating Soil Organic Carbon in a Wheat–Fallow System Using the Daycent Model. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 2554–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Gao, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, J.; Deng, J.; Li, C.; Frolking, S. The Development of China-DNDC and Review of Its Applications for Sustaining Chinese Agriculture. Ecol. Model. 2017, 348, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahadha, S.S.; Zeki, S.L.; Dawood, I.A.; Salih, R.M.; Salim, A.H. Modeling the Impact of Field Irrigation Management on Soil Water-Nitrate Dynamics: Experimental Measurements and Model Simulations. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2023, 56, S354–S365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, W.; Komal, K.; Miao, S. Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Agricultural Systems: A Comparative Analysis of Process Models. Ecol. Model. 2024, 490, 110646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Macdonald, B.C.T.; Xing, H.; Denmead, O.T.; Wang, E.; McLachlan, G.; Tuomi, S.; Turner, D.; Chen, D. Measurements and APSIM Modelling of Soil C and N Dynamics. Soil Res. 2020, 58, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Amon, B.; Schulz, K.; Mehdi, B. Factors That Influence Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Agricultural Soils as Well as Their Representation in Simulation Models: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thentu, T.L.; Forster, D.; Li, Y.; Virkajärvi, P.; Harrison, M.T.; Mitra, B.; Deng, J.; Korhonen, P.; Shurpali, N. DNDC Modelling of Greenhouse Gas Exchange from a Boreal Legume Grassland under Organic and Mineral Nitrogen Management. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 390, 126344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ma, L.; Qi, Z.; Fang, Q.; Harmel, R.D.; Schmer, M.R.; Jin, V.L. Measured and Simulated Effects of Residue Removal and Amelioration Practices in No-till Irrigated Corn (Zea mays L.). Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 146, 126807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, Z.; Xue, L.; Bukovsky, M. RZWQM2 Simulated Management Practices to Mitigate Climate Change Impacts on Nitrogen Losses and Corn Production. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 84, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Qi, Z.; Xue, L.; Bukovsky, M.; Madramootoo, C.A.; Smith, W. Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Greenhouse Gas Emissions, N Losses in Drainage and Crop Production in a Subsurface Drained Field. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mearns, L.O.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; McGinnis, S. Uses of Results of Regional Climate Model Experiments for Impacts and Adaptation Studies: The Example of NARCCAP. Curr. Clim. Change Rep. 2015, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Ikeda, K.; Liu, C. A New Approach to Construct Representative Future Forcing Data for Dynamic Downscaling. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anapalli, S.S.; Pinnamaneni, S.R.; Fisher, D.K.; Reddy, K.N. Vulnerabilities of Irrigated and Rainfed Corn to Climate Change in a Humid Climate in the Lower Mississippi Delta. Clim. Change 2021, 164, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, Z.; Xue, L.; Bukovsky, M.; Helmers, M.J. Modeling the Impacts of Climate Change on Nitrogen Losses and Crop Yield in a Subsurface Drained Field. Clim. Change 2015, 129, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, L.; Rojas, K.W.; Hanson, J.D. Root Zone Water Quality Model: Modelling Management Effects on Water Quality and Crop Production, 7th ed.; Water Resour. Pubns: Highlands Ranch, CO, USA, 2000; pp. 119–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Douglas-Mankin, K.R.; Han, M.; Trout, T.J. Modeling Maize Production under Growth Stage-Based Deficit Irrigation Management with RZWQM2. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 248, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ahuja, L.R.; Nolan, B.T.; Malone, R.W.; Trout, T.J.; Qi, Z. Root Zone Water Quality Model (Rzwqm2): Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1425–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, D.M.; Mike, G.; Emine, Ş.Y. Constructing and Embedding Mutually Orthogonal Latin Squares: Reviewing Both New and Existing Results. Comment. Math. Univ. Carol. 2021, 61, 437–445. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 10th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Qi, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Sima, N. An Economic Analysis Software for Evaluating Best Management Practices to Mitigate Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Cropland. Agric. Syst. 2021, 186, 102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, A.; Zhang, J.; Nong, X.; Jiang, X.; Wu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Cheng, J. Divergent Responses of Optimal Land and Water Allocation to Different Hydrological Regimes in the Agricultural Water-Food-Carbon Nexus System. J. Hydrol. 2025, 653, 132730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cheng, H.; Shao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Cheng, J. Optimizing Agricultural Water-Land Resource Allocation in Water-Economic-Environment Cycles Considering Uncertainties of Spatiotemporal Water Footprints. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 501, 145348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, R.; Hörtnagl, L.; Buchmann, N. Greenhouse Gas Fluxes (CO2, N2O and CH4) of Pea and Maize during Two Cropping Seasons: Drivers, Budgets, and Emission Factors for Nitrous Oxide. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, I.M. Global Sensitivity Indices for Nonlinear Mathematical Models and Their Monte Carlo Estimates. Math. Comput. Simul. 2001, 55, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.L.; Zeleke, K.T.; Wang, B.; Macadam, I.; Scott, F.; Martin, R.J. Crop Residue Incorporation Can Mitigate Negative Climate Change Impacts on Crop Yield and Improve Water Use Efficiency in a Semiarid Environment. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 85, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Shao, Y.; He, L.; Li, X.; Hou, G.; Li, S.; Feng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y. Optimizing Nitrogen Management to Achieve High Yield, High Nitrogen Efficiency and Low Nitrogen Emission in Winter Wheat. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Hou, R.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Zhou, G.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, J.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, F.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Conservation Agriculture Improves Soil Health and Sustains Crop Yields after Long-Term Warming. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, S.; Yin, X.; Schneider, L.; Sykes, V.; Jagadamma, S.; Lee, J. Carbon Footprint and Net Carbon Gain of Major Long-Term Cropping Systems under No-Tillage. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.; Lessa Derci Augustynczik, A.; Havlík, P.; Boere, E.; Ermolieva, T.; Fricko, O.; Di Fulvio, F.; Gusti, M.; Krisztin, T.; Lauri, P.; et al. Enhanced Agricultural Carbon Sinks Provide Benefits for Farmers and the Climate. Nat. Food 2024, 5, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Su, M.; Kong, L.; Kong, M.; Ma, Y. Assessing the Economic Value of Carbon Sinks in Farmland Using a Multi-Scenario System Dynamics Model. Agriculture 2025, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.M.; Nelsen, T.S.; Scow, K.M.; Lundy, M.E. No-till Annual Wheat Increases Plant Productivity, Soil Microbial Biomass, and Soil Carbon Stabilization Relative to Intermediate Wheatgrass in a Mediterranean Climate. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 10587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeema, T.; Lee, A.H.; Richter, A.; Ng, K.T.W.; Chang, W. Sub-Zero Soil CO2 Respiration in Biostimulated Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Cold-Climate Soil Can Be Linked to the Soil-Freezing Characteristic Curve. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 1783–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Arneth, A.; Smith, B.; Anthoni, P.; Xu-Ri; Eliasson, P.; Wårlind, D.; Wittenbrink, M.; Olin, S. Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Global Land Ecosystems and Their Drivers within the LPJ-GUESS Model (v4.1). Geosci. Model Dev. 2025, 18, 3131–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, Y.; Li, S.; Geng, Y.; Sun, J. Air-Water-Fertilizer-Coupling Drip Irrigation Facilitates Lettuce Growth by Shaping Rhizosphere Microbiome Associated with Soil Nutrient Cycling. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 3699–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaraz, M.; Simmonds, M.; Boudinot, F.G.; Di Vittorio, A.V.; Bingham, N.; Khalsa, S.D.S.; Ostoja, S.; Jones, A.; Holzer, I.; Manaigo, E.; et al. Undervaluing Soil Carbon Sequestration Potential Enables Climate Inaction. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Dong, Y.; Halder, M.; Adingo, S.; Yin, L.; Zhou, H.; Ma, Y.; Peng, X. Vertical Dynamics of Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration under Contrasting Groundwater Table Levels after 35-Year Straw Return. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 252, 106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdemir, B.; Sağlam, C.; Bellitürk, K.; Makaracı, A.Z.; Şener, M.; Ürüşan, A.Y.; Atik, M. Effect of Spatial Variability of Plant Nutrients on Fertilizer Requirement and Yield in Table Olive Growing. Appl. Fruit Sci. 2025, 67, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Negm, L.; Jeong, H.; Cooke, R.; Bhattarai, R. Comparison of Simulated Nitrogen Management Strategies Using DRAINMOD-DSSAT and RZWQM2. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 266, 107597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, C.; Shi, M.; Fan, L.; Wei, C. Dominant Role of Irrigation Regime over Biochar in Controlling GHG Emissions from Paddy Fields. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).