Effects of Continuous Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinization Characteristics and Dryland Jujube Tree
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
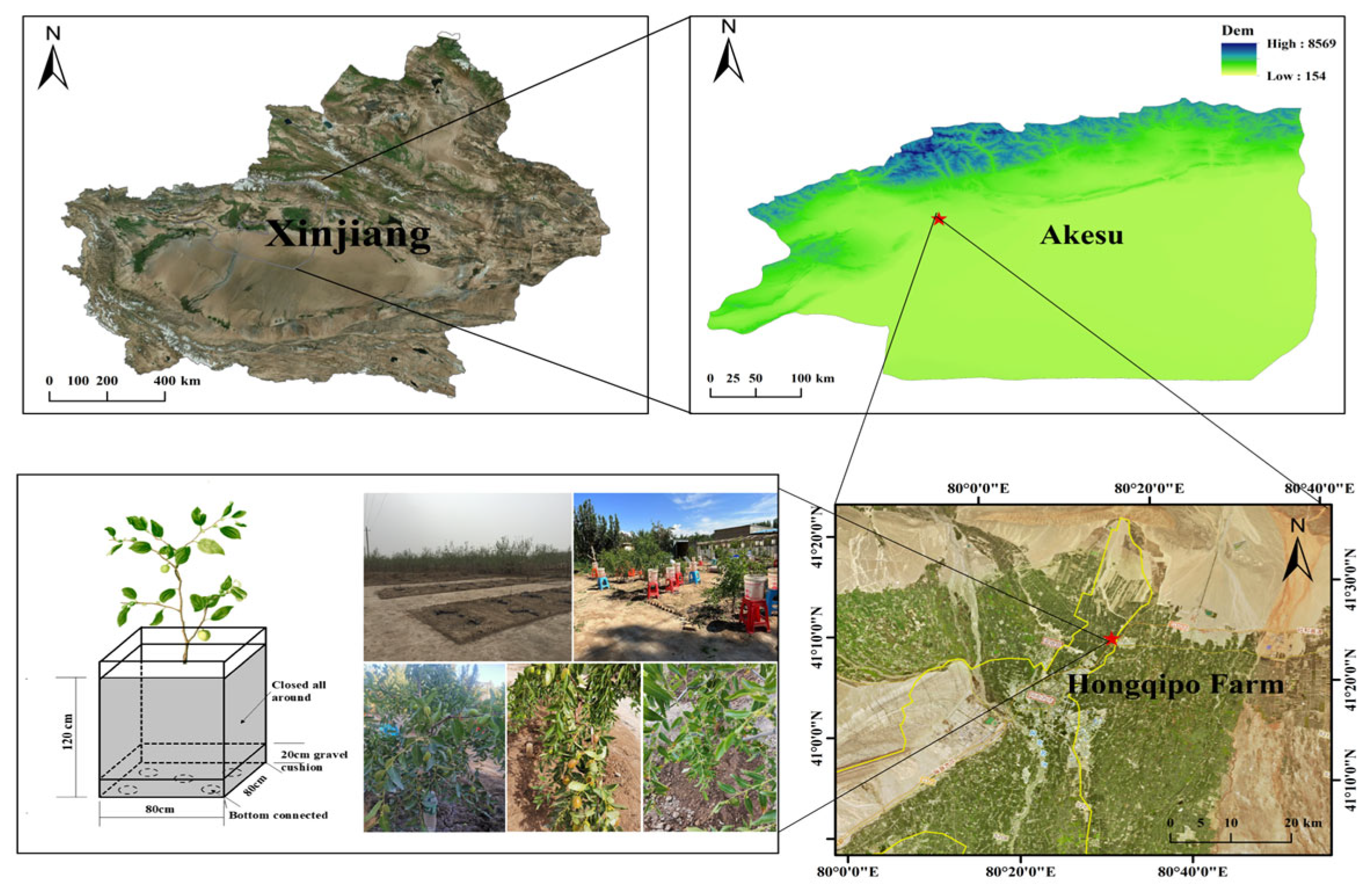
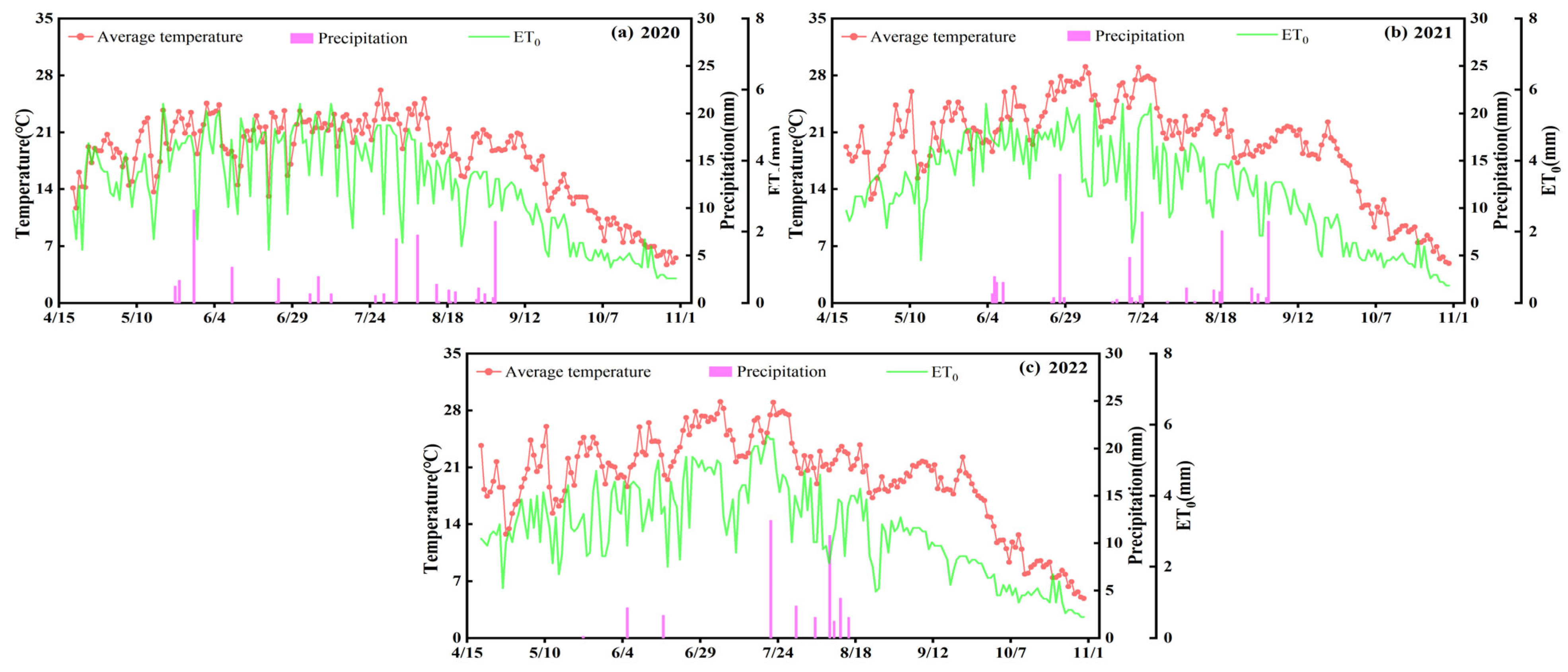
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement Parameters and Methods
2.3.1. Soil Salinity and Chemical Properties
2.3.2. Jujube Tree Growth Index
2.3.3. Jujube Yield and Quality
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
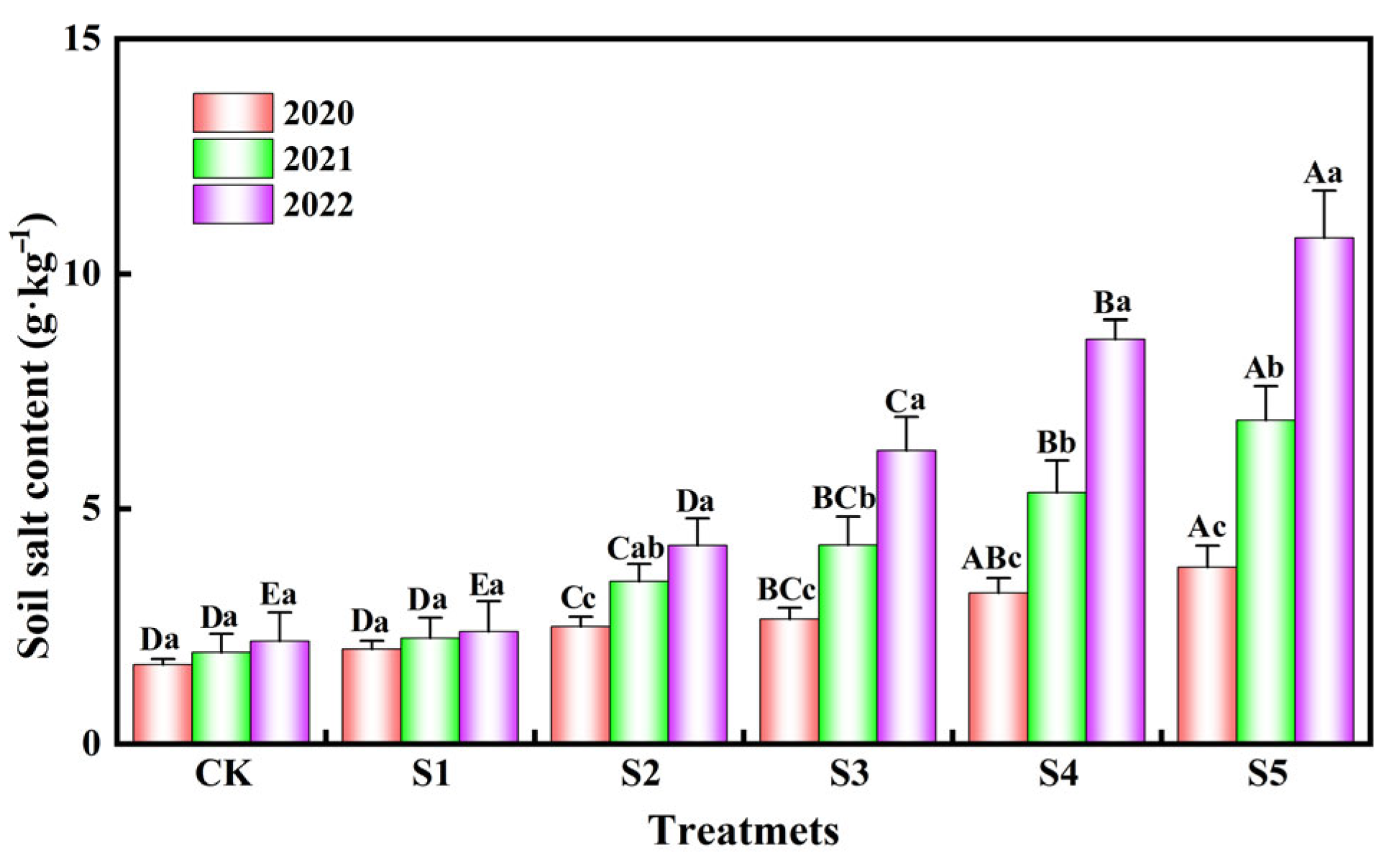
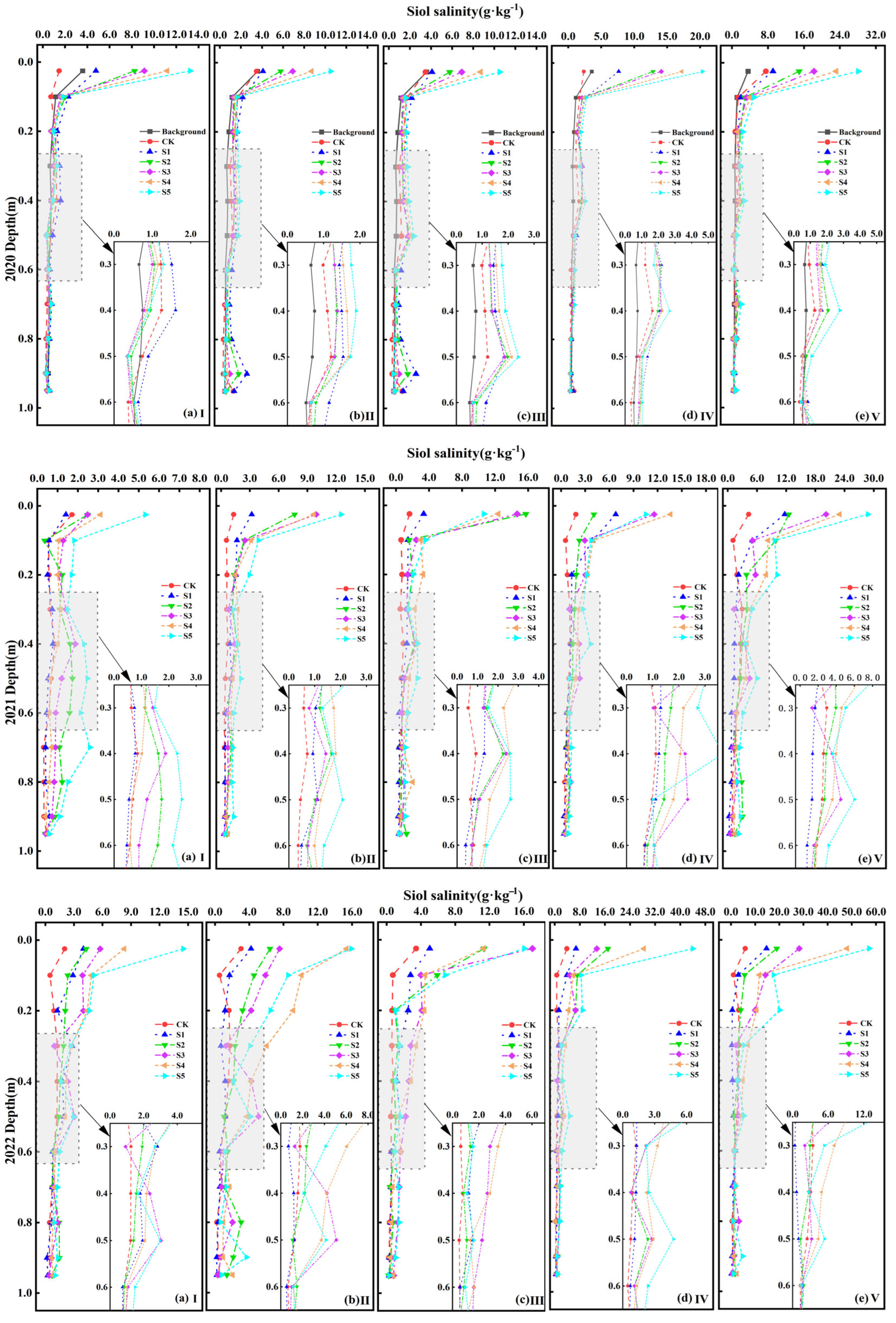
3.1. Dynamic Variations in Soil Salinity
3.2. Soil Chemical Properties
3.2.1. pH and SAR
3.2.2. Soil Hydrochemical Types
3.3. The Effects on Jujube Tree
3.4. Multi-Objective Evaluation Based on Entropy-Weighted TOPSIS
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects on Soil Salinity
4.2. Effects on Soil Hydrochemical Characteristics
4.3. Effects on the Growth of Jujube Trees
4.4. Multi-Objective Evaluation
4.5. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, T.; Sun, S.; Fu, G.; Hall, J.W.; Ni, Y.; He, L.; Yi, J.; Zhao, N.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; et al. Pollution Exacerbates China’s Water Scarcity and Its Regional Inequality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.M.; El-Shorbagy, W.; Kizhisseri, M.I.; Chowdhury, R.; McDonald, A. Evaluation of Policy Scenarios for Water Resources Planning and Management in an Arid Region. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 32, 100758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kumar, G. Scenario Planning for Water Resource Management in Semi Arid Zone. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2018, 105, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Ren, L. Conjunctive Use of Saline and Non-Saline Water in an Irrigation District of the Yellow River Basin. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 66, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, W.; Guo, H.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, W.; Ma, L.; Ye, J.; Hou, Z. Root Distribution and Growth of Cotton as Affected by Drip Irrigation with Saline Water. Field Crops Res. 2014, 169, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Zong, L.; Buonanno, M.; Xue, X.; Wang, T.; Tedeschi, A. Impact of Saline Water Irrigation on Yield and Quality of Melon (Cucumis melo cv. Huanghemi) in Northwest China. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 43, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, F. Crop Yield and Water Productivity under Salty Water Irrigation: A Global Meta-Analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zeng, F.; An, H. Formation, Distribution and Transport of Shallow Groundwater in Arid Areas, China. Arid. Zone Res. 2011, 28, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y. Distribution and quality evaluation of medium-salinity groundwater in the plain area of Tarim Basin, Xinjiang. CRWHP 2009, 9, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, T.; Bouksila, F.; Berndtsson, R.; Persson, M. Soil Water and Salinity Distribution under Different Treatments of Drip Irrigation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1144–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W.; Liu, J. Effects of Different Salinity Levels in Drip Irrigation with Brackish Water on Soil Water-Salt Transport and Yield of Protected Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Agronomy 2023, 13, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, C.; Ning, S.; Cao, C.; Li, K.; Dang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Impacts of Long-Term Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Properties and Crop Yields under Maize-Wheat Crop Rotation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 286, 108383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SBX. Xinjiang Statistical Yearbook in 2022; China Statistical Publishing House: Ürümqi, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rouzi, A.; Halik, Ü.; Thevs, N.; Welp, M.; Aishan, T. Water Efficient Alternative Crops for Sustainable Agriculture along the Tarim Basin: A Comparison of the Economic Potentials of Apocynum pictum, Chinese Red Date and Cotton in Xinjiang, China. Sustainability 2017, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Zhao, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Ma, Y. Magnetized Saline Water Drip Irrigation Alters Soil Water-Salt Infiltration and Redistribution Characteristics. Water 2024, 16, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, F.; Tian, L.; He, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ren, F. Soil Physicochemical Properties and Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Yield under Brackish Water Mulched Drip Irrigation. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiao, X.; Lu, S.; Zhu, C.; Zhai, Y.; Guo, W. Effects of Winter Irrigation on Soil Salinity and Jujube Growth in Arid Regions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leilei, G.; Zaimin, W. Interaction between Brackish Water Intermittent Infiltration and Cultivated Soil Environment: A Case Study from Arid Piedmont Plain of Northwest China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 894033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekakis, E.H.; Antonopoulos, V.Z. Modeling the Effects of Different Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Water Movement, Uptake and Multicomponent Solute Transport. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. Soil Chemistry Factors Confounding Crop Salinity Tolerance—A Review. Agronomy 2016, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zheng, C.; Li, K.; Dang, H.; Cao, C.; Rahma, A.E.; Zhang, J.; Feng, D. Responses of Soil Water-salt Variation and Cotton Growth to Drip Irrigation with Saline Water in the Low Plain near the Bohai Sea. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, F.S.; Harter, L.D.S.H.; Meneghello, G.E. Rice Seed Production under Conditions of Salinity Stres. Ciênc. Rural 2018, 48, e20170057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Feng, S.; Huo, Z.; Ji, Q. Effects of Deficit Irrigation with Saline Water on Soil Water-Salt Distribution and Water Use Efficiency of Maize for Seed Production in Arid Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Mostofa, M.G.; Keya, S.S.; Siddiqui, N.; Ansary, M.U.; Das, A.K.; Rahman, A.; Tran, L.S.-P. Adaptive Mechanisms of Halophytes and Their Potential in Improving Salinity Tolerance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Yang, Q.; Hou, M. The Effects of Saline Water Drip Irrigation on Tomato Yield, Quality, and Blossom-End Rot Incidence—A 3a Case Study in the South of China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wan, S.; Li, X.; Kang, Y.; Han, X. Effect of Water-Salt Regulation Drip Irrigation with Saline Water on Tomato Quality in an Arid Region. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, A.G.D.L.; Pessoa, A.M.D.S.; Sá, S.A.D.; Sousa, N.R.D.; Barros, E.S.; Morais, F.M.D.S.; Ferreira, F.N.; Silva, W.A.O.D.; Batista, R.O.; Silva, D.V.; et al. Potential of Ca-Complexed in Amino Acid in Attenuating Salt Stress in Sour Passion Fruit Seedlings. Plants 2024, 13, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarita; Bhupnesh; Goyal, V. Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Approaches for Mitigating Soil Salinity Challenges: A Review Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Approaches for Mitigating Soil Salinity Challenges: A Review. Agric. Rev. 2024, 46, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lou, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, S. Effects of Brackish Water Irrigation with Different Exogenous Salt Concentrations on the Growth and Rhizosphere Salinity of Lycium barbarum. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Howell, T.A.; Jensen, M.E. Evapotranspiration Information Reporting: I. Factors Governing Measurement Accuracy. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 899–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Analysis of Chemical Characteristics of High-Fluoride Groundwater in Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2013, 27, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Jia, R.L.; Zhou, J.L.; Yang, G.Y. Preliminary Analysis of High-Fluoride Groundwater in Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 610–613, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, P.; Ma, Y.; Hai, Y. Comparing Simulated Jujube Evapotranspiration from P–T, Dual Kc, and S–W Models against Measurements Using a Large Weighing Lysimeter under Drip Irrigation in an Arid Area. Agriculture 2023, 13, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, C.; Hoffman, M.; Eamus, D.; Kerp, N.; Higginson, S.; McMurtrie, R.; Adams, M. Estimation of Leaf Area Index in Eucalypt Forest Using Digital Photography. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 143, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, P.; Ma, Y.; Hai, Y. Influence of Jujube/Cotton Intercropping on Soil Temperature and Crop Evapotranspiration in an Arid Area. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Singh, K.A. Comprehensive Guide to Quality Analysis of Fruit Juices and Soft Drinks: Analytical Procedures, 1st ed.; Skyfox Publishing Group: New Delhi, India, 2020; ISBN 978-81-939536-1-7. [Google Scholar]
- You, L.; Ma, Y.; Hong, M. Study on a Simple Estimation Method of Single Fruit Weight of Southern Xinjiang Gray Jujube Based on Jujube Fruit Volume. J. Water Conserv. Constr. Eng. 2014, 12, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Jiang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Su, X. Research of Hydrochemical Properties of Hyporheic Zone along the WeiHe River in Shanxi Segment. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2017, 5, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stavi, I.; Thevs, N.; Priori, S. Soil Salinity and Sodicity in Drylands: A Review of Causes, Effects, Monitoring, and Restoration Measures. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 712831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Bai, Y.; Guo, S.; He, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhai, J.; Cao, H. Effect of Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Characteristics and Microbial Communities in Cotton Fields in Southern Xinjiang, China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Jin, Q. Effect of Different Thresholds of Drip Irrigation Using Saline Water on Soil Salt Transportation and Maize Yield. Water 2018, 10, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Guo, S. Reduced Co-Occurrence and Ion-Specific Preferences of Soil Microbial Hub Species after Ten Years of Irrigation with Brackish Water. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, F.; Wu, L.; Zhang, F.; Yin, F.; Abdelghany, A.E.; Fan, J.; Xiao, C.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Leaching Amount and Timing Modified the Ionic Composition of Saline-Alkaline Soil and Increased Seed Cotton Yield under Mulched Drip Irrigation. Field Crops Res. 2023, 299, 108988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, M.S.; Hira, G.S.; Singh, N.T. Effect of Sodium and Bicarbonate Irrigation Waters on Sodium Accumulation and on Maize and Wheat Yields in Northern India. Irrig. Sci. 1983, 4, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, M.; Sun, Q.; Hou, G.; Zhao, Y. Formation and Evolution of Soil Salinization Based on Multivariate Statistical Methods in Ningxia Plain, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1186779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Liu, W.; Qu, J.; Cao, W. Accumulation of Na+ in Cotton Field under Mulched Drip Irrigation of Brackish Water in Arid Areas. Separations 2023, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, L.; Amanipoor, H.; Battaleb-Looie, S. Effect of Salinity of Irrigation Water on Soil Properties (Abadan Plain, SW Iran). Geocarto Int. 2021, 36, 1884–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.X.; Qi, S.T. The Effect of Soil Salinity on the Growth and Development of Jinsi Jujube. J. Fruit Sci. 1985, 2, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wen, Y.; Song, L.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z. Multi-Objective Optimization of Saline Water Irrigation in Arid Oasis Regions: Integrating Water-Saving, Salinity Control, Yield Enhancement, and CO2 Emission Reduction for Sustainable Cotton Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yan, M.; Pu, X.; Lu, D.; Yuan, H.; Wu, C. Transcriptome Analyses Reveal the Mechanism of Changes in the Sugar Constituents of Jujube Fruits under Saline–Alkali Stress. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuban State Agrarian University named after I.T.; Trubilin; Prikhodko, I.A.; Romanova, A.S.; Sergeev, A.E. The Problem of Soil Salinization. Sci. Life 2022, 17, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora, J.; Oteyza, M.A.P.D.; Fuentetaja, P.; Hormaza, J.I. Low Temperature Storage and in Vitro Germination of Cherimoya (Annona cherimola Mill.) Pollen. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 108, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauc, S.; De Vooght, E.; Claeys, M.; Höfte, M.; Angenon, G. Influence of Over-Expression of Cytosolic Aspartate Aminotransferase on Amino Acid Metabolism and Defence Responses against Botrytis cinerea Infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.S.; Verma, R.P.; Verma, S.K.; Yadav, A.L.; Verma, A.K. Responses of Ber (Zizyphus mauritiana Lamk.) Varieties to Different Level of Salinity. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Chakraborty, S. Development of a Meta-Model for the Determination of Technological Value of Cotton Fiber Using Design of Experiments and the TOPSIS Method. J. Nat. Fibers 2018, 15, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, P.; Hu, C.; Gao, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Cui, B. Response of Soil Microenvironment and Crop Growth to Cyclic Irrigation Using Reclaimed Water and Brackish Water. Plants 2023, 12, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; He, P.; Chen, J.; Hamad, A.A.A.; Dai, X.; Jin, Q.; Ding, S. Tomato Performance and Changes in Soil Chemistry in Response to Salinity and Na/Ca Ratio of Irrigation Water. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 285, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, P.; Petry, M.T.; Oliveira, C.M.; Montoya, F.; López-Urrea, R.; Pereira, L.S. Single and Basal Crop Coefficients for Estimation of Water Requirements of Subtropical and Tropical Orchards and Plantations with Consideration of Fraction of Ground Cover, Height, and Training System. Irrig. Sci. 2024, 42, 1059–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
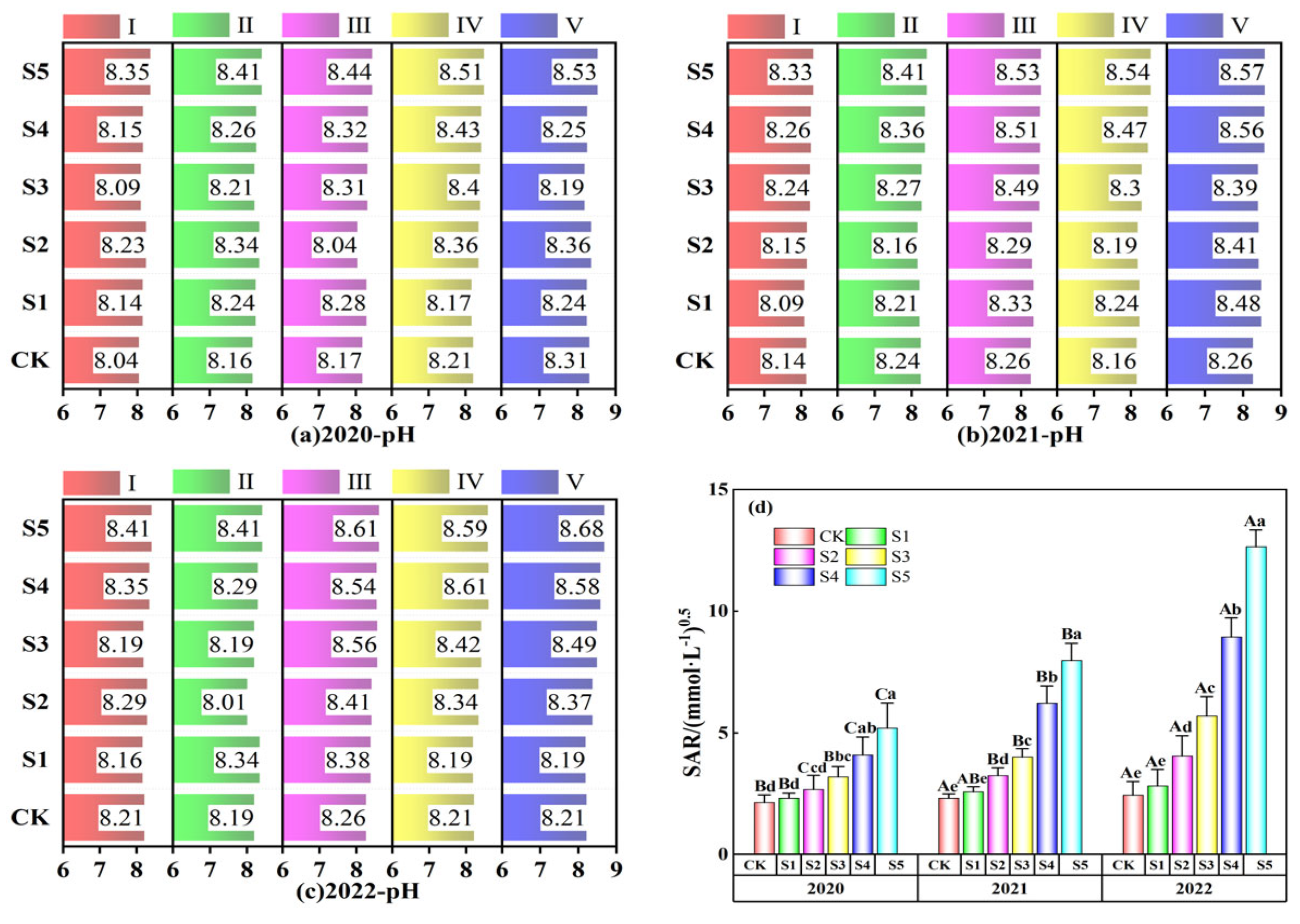
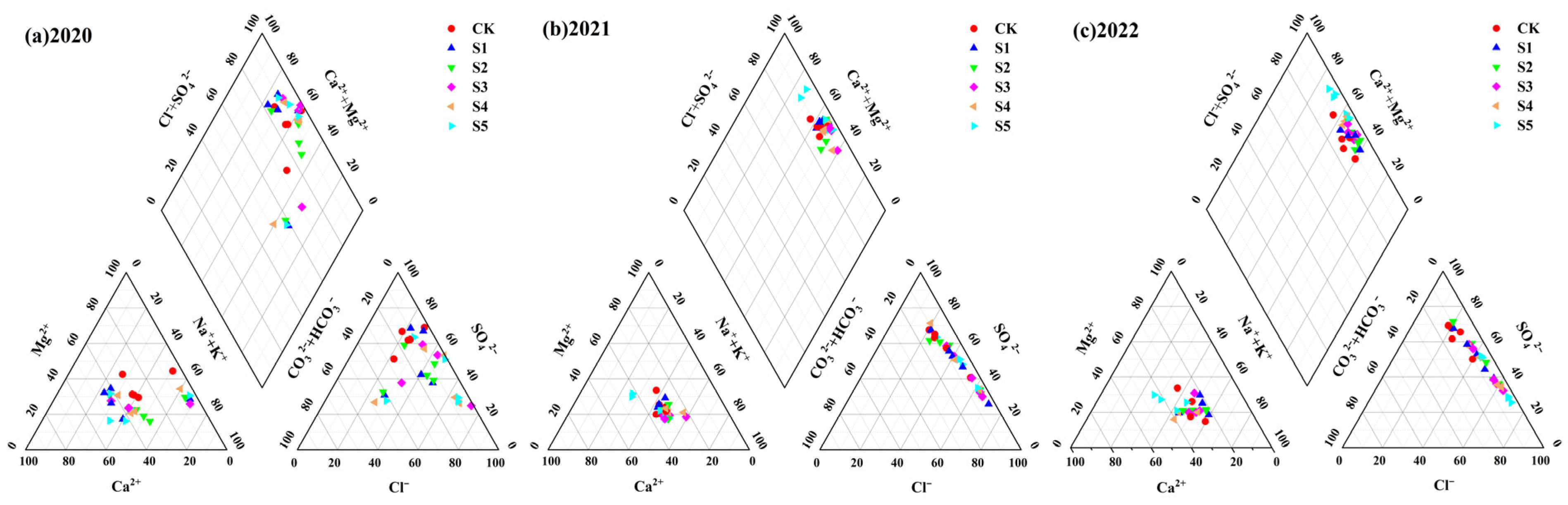
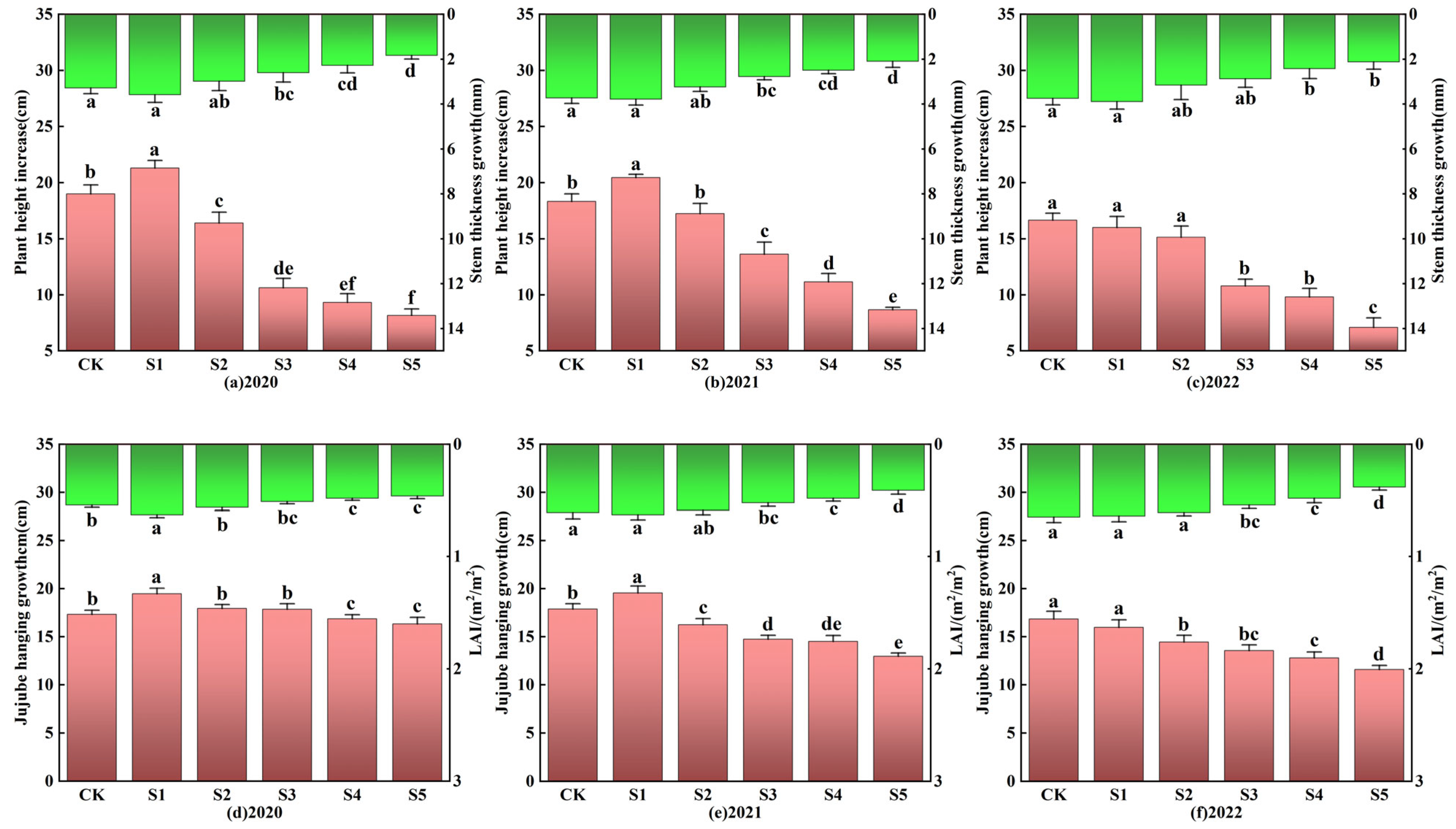
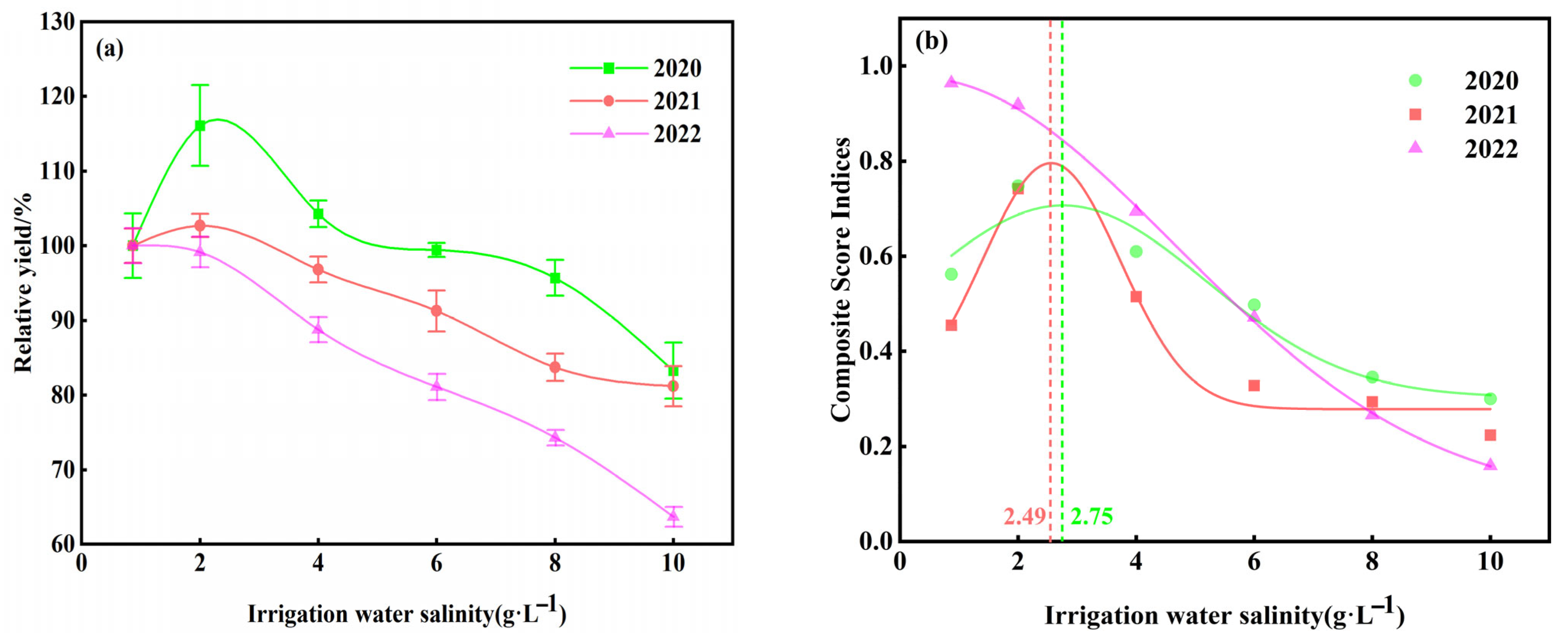
| Depth | Bulk Density | Textural Characteristics (%) | pH | Salt Content | SAR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (g·cm−3) | Clay | Silt | Sand | (g·kg−1) | (mmol·L−1)0.5 | |
| Surface layer | 1.51 | 6.7 | 66 | 27.3 | 8.18 | 3.58 | 2.85 |
| 0–0.5 | 1.54 | 7.64 | 45.1 | 47.26 | 7.8 | 0.82 | 2.062 |
| 0.5–1 | 1.54 | 4.94 | 26.26 | 68.8 | 8.31 | 0.52 | 2.086 |
| Depth | CO32− | HCO3− | Cl− | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | SO42− | K+ | Na+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (mg·kg−1) | (mg·kg−1) | (mg·kg−1) | (mg·kg−1) | (mg·kg−1) | (mg·kg−1) | (mg·kg−1) | (mg·kg−1) |
| Surface layer | 0 | 269.36 | 954.5 | 254.07 | 194.19 | 1232.98 | 111.77 | 563.64 |
| 0–0.5 | 0 | 130.18 | 215.38 | 82.71 | 46.56 | 579.76 | 36.78 | 190.30 |
| 0.5–1 | 0 | 73.63 | 51.73 | 32.36 | 11.37 | 275.74 | 27.02 | 102.80 |
| Treatments | Ionic Content (mmol·L−1) | pH | Salt Content | SAR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCO3− | Cl− | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | SO42− | K+ | Na+ | (g·kg−1) | (mmol·L−1)0.5 | ||
| CK | 1.41 | 1.08 | 2.29 | 3.48 | 3.46 | 0.62 | 0.76 | 8.14 | 0.87 | 1.87 |
| S1 | 1.77 | 4.68 | 4.14 | 6.06 | 13.68 | 2.69 | 2.86 | 8.18 | 2.03 | 5.26 |
| S2 | 2.55 | 5.73 | 6.27 | 9.29 | 24.76 | 6.73 | 7.35 | 8.27 | 4.09 | 10.94 |
| S3 | 3.62 | 7.73 | 8.02 | 12.11 | 30.03 | 7.77 | 9.82 | 8.13 | 6.18 | 12.86 |
| S4 | 4.74 | 9.75 | 10.18 | 14.98 | 36.45 | 12.85 | 14.44 | 8.32 | 8.21 | 16.90 |
| S5 | 5.52 | 12.41 | 12.22 | 17.77 | 43.76 | 17.95 | 19.20 | 8.38 | 10.28 | 20.57 |
| Years | Project | Budding 4/19~5/16 | Flowering 5/17~7/16 | Young Fruit Stage 7/17~8/7 | Fruit Developing 8/8~9/6 | Maturity 9/7~10/27 | ∑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | KC | 0.42 | 0.78 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.81 | - |
| 2020 | ETo (mm) | 94.30 | 265.90 | 90.10 | 101.60 | 89.30 | 641.20 |
| Irrigation amount (mm) | 35.62 | 172.81 | 78.44 | 89.51 | 26.09 | 402.47 | |
| Irrigation unit | 2 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 16 | |
| 2021 | ETo (mm) | 82.60 | 268.60 | 87.30 | 102.80 | 88.40 | 629.70 |
| Irrigation amount (mm) | 28.94 | 225.94 | 52.19 | 120.41 | 43.21 | 470.69 | |
| Irrigation unit | 2 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 17 | |
| 2022 | ETo (mm) | 79.20 | 234.30 | 96.60 | 90.40 | 90.1 | 590.60 |
| Irrigation amount (mm) | 25.43 | 175.41 | 93.30 | 75.50 | 39.67 | 409.31 | |
| Irrigation unit | 2 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 16 |
| Years | Treatments | Fruit Volume (cm3) | Calculated Yield (kg·ha−1) | WP (kg·m−3) | Total Sugar (%) | Total Acid (%) | Vitamin C (mg·100 g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | CK | 6.78 bc | 673.5 bc | 1.15 bc | 55.1 a | 0.57 ab | 175.67 cd |
| S1 | 8.20 a | 781.67 a | 1.34 a | 57.17 a | 0.57 ab | 204.20 a | |
| S2 | 7.18 bc | 702.17 b | 1.20 b | 54.03 ab | 0.61 a | 187.03 b | |
| S3 | 6.73 bc | 669.67 bc | 1.15 bc | 50.77 bc | 0.56 ab | 167.67 cd | |
| S4 | 6.55 c | 644.5 c | 1.11 c | 50.3 c | 0.56 ab | 158.03 d | |
| S5 | 6.52 c | 560.67 d | 0.96 d | 47.33 c | 0.52 b | 155.23 d | |
| 2021 | CK | 7.20 c | 843.67 ab | 1.37 ab | 55.05 ab | 0.61 a | 174.76 c |
| S1 | 8.27 ab | 866.50 a | 1.41 a | 56.12 ab | 0.57 a | 198.82 a | |
| S2 | 8.65 a | 816.83 b | 1.33 b | 53.44 bc | 0.55 a | 186.48 b | |
| S3 | 7.89 b | 770.00 c | 1.25 c | 57.66 a | 0.54 a | 170.17 cd | |
| S4 | 7.12 c | 706.02 d | 1.15 d | 53.85 bc | 0.56 a | 163.46 de | |
| S5 | 6.74 c | 684.67 d | 1.11 d | 50.75 c | 0.55 a | 159.59 e | |
| 2022 | CK | 8.23 a | 856.21 a | 1.34 a | 55.44 a | 0.58 ab | 182.42 a |
| S1 | 8.08 a | 832.83 a | 1.29 a | 55.70 a | 0.62 a | 184.42 a | |
| S2 | 7.67 b | 796.33 b | 1.23 b | 53.30 b | 0.56 ab | 171.11 b | |
| S3 | 6.87 bc | 710.00 c | 1.17 c | 50.78 c | 0.52 b | 165.45 bc | |
| S4 | 6.51 c | 633.83 d | 1.01 d | 49.10 cd | 0.55 ab | 159.53 c | |
| S5 | 5.83 d | 514.33 e | 0.91 e | 47.50 c | 0.53 b | 145.70 d |
| Indicators | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Average Weight | Weight | Average Weight | Weight | Average Weight | ||
| Soil saline–alkali properties | Soil salinity | 0.0611 | 0.0717 | 0.0647 | 0.0769 | 0.0766 | 0.0734 |
| pH | 0.0995 | 0.1039 | 0.0785 | ||||
| SAR | 0.0544 | 0.0622 | 0.0652 | ||||
| Agronomic traits of jujube trees | Plant height increase | 0.0659 | 0.0755 | 0.0749 | 0.0744 | 0.0792 | 0.0795 |
| Stem thickness growth | 0.0740 | 0.0754 | 0.0889 | ||||
| Jujube hanging growing | 0.0769 | 0.0823 | 0.0835 | ||||
| LAI | 0.0850 | 0.0651 | 0.0663 | ||||
| Yield and quality | Jujube fruit volume | 0.1545 | 0.0805 | 0.0876 | 0.0786 | 0.0708 | 0.0770 |
| Theoretical yield | 0.0552 | 0.0848 | 0.0749 | ||||
| WP | 0.0548 | 0.0838 | 0.0755 | ||||
| Total sugar | 0.0639 | 0.0615 | 0.0875 | ||||
| Total acid | 0.0539 | 0.0509 | 0.0839 | ||||
| Vitamin C | 0.1009 | 0.1030 | 0.0691 | ||||
| Years | Treatments | Distance to the Ideal Solution | Distance to the Antideal Solution | Composite Score Indices | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | CK | 0.394 | 0.505 | 0.562 | 3 |
| S1 | 0.219 | 0.649 | 0.748 | 1 | |
| S2 | 0.320 | 0.500 | 0.610 | 2 | |
| S3 | 0.396 | 0.393 | 0.498 | 4 | |
| S4 | 0.534 | 0.282 | 0.346 | 5 | |
| S5 | 0.669 | 0.286 | 0.300 | 6 | |
| 2021 | CK | 0.194 | 0.156 | 0.445 | 3 |
| S1 | 0.094 | 0.270 | 0.742 | 1 | |
| S2 | 0.151 | 0.161 | 0.515 | 2 | |
| S3 | 0.209 | 0.102 | 0.328 | 4 | |
| S4 | 0.272 | 0.113 | 0.294 | 5 | |
| S5 | 0.245 | 0.071 | 0.224 | 6 | |
| 2022 | CK | 0.010 | 0.273 | 0.964 | 1 |
| S1 | 0.024 | 0.264 | 0.918 | 2 | |
| S2 | 0.087 | 0.198 | 0.694 | 3 | |
| S3 | 0.149 | 0.133 | 0.471 | 4 | |
| S4 | 0.207 | 0.075 | 0.266 | 5 | |
| S5 | 0.279 | 0.064 | 0.159 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; Xin, M.; Ai, P.; Ma, Y. Effects of Continuous Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinization Characteristics and Dryland Jujube Tree. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081898
Zhao Q, Xin M, Ai P, Ma Y. Effects of Continuous Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinization Characteristics and Dryland Jujube Tree. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081898
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qiao, Mingliang Xin, Pengrui Ai, and Yingjie Ma. 2025. "Effects of Continuous Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinization Characteristics and Dryland Jujube Tree" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081898
APA StyleZhao, Q., Xin, M., Ai, P., & Ma, Y. (2025). Effects of Continuous Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinization Characteristics and Dryland Jujube Tree. Agronomy, 15(8), 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081898






