Deep Storage Irrigation Enhances Grain Yield of Winter Wheat by Improving Plant Growth and Grain-Filling Process in Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
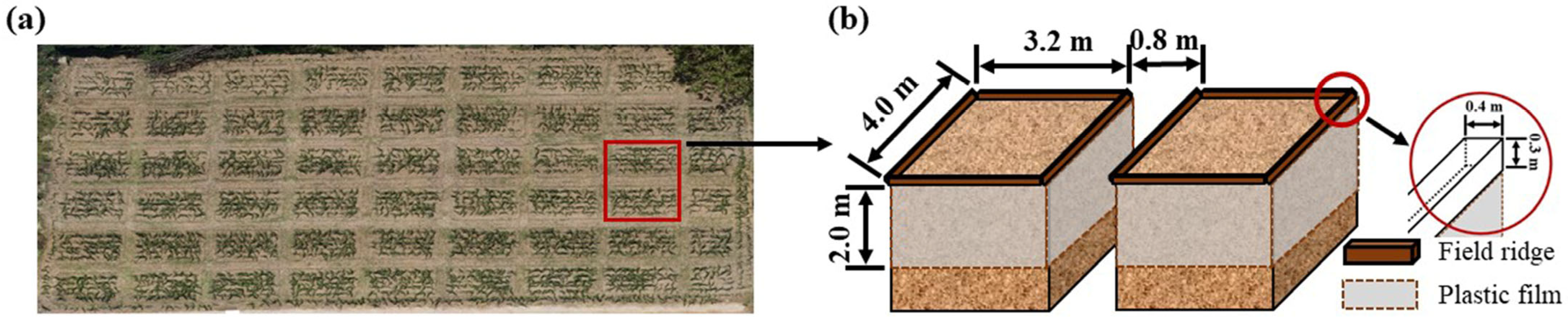
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Calculation of Deep Storage Irrigation Amount
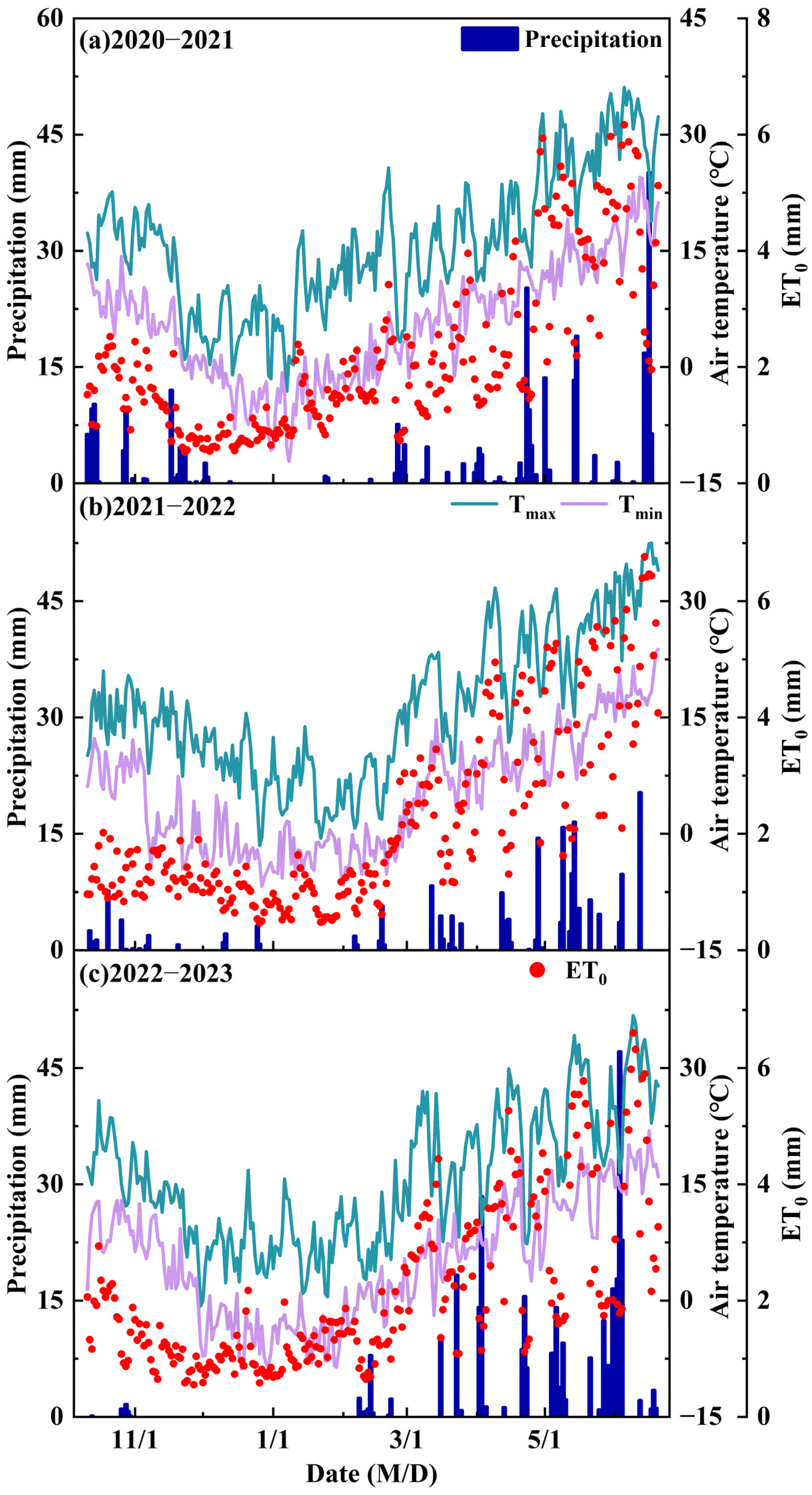
2.4. Division of Precipitation Type Years
Normal season: P − 0.33σ ≤ Pi ≤ P + 0.33σ;
Dry season: Pi < P − 0.33σ;
2.5. Measurement Methods
2.5.1. Methods of Soil Water Measurement
2.5.2. Plant Height and Leaf Area Index
2.5.3. Dry Matter Accumulation
2.5.4. Grain-Filling Process Measurement
2.5.5. Grain Yield and Yield Components
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
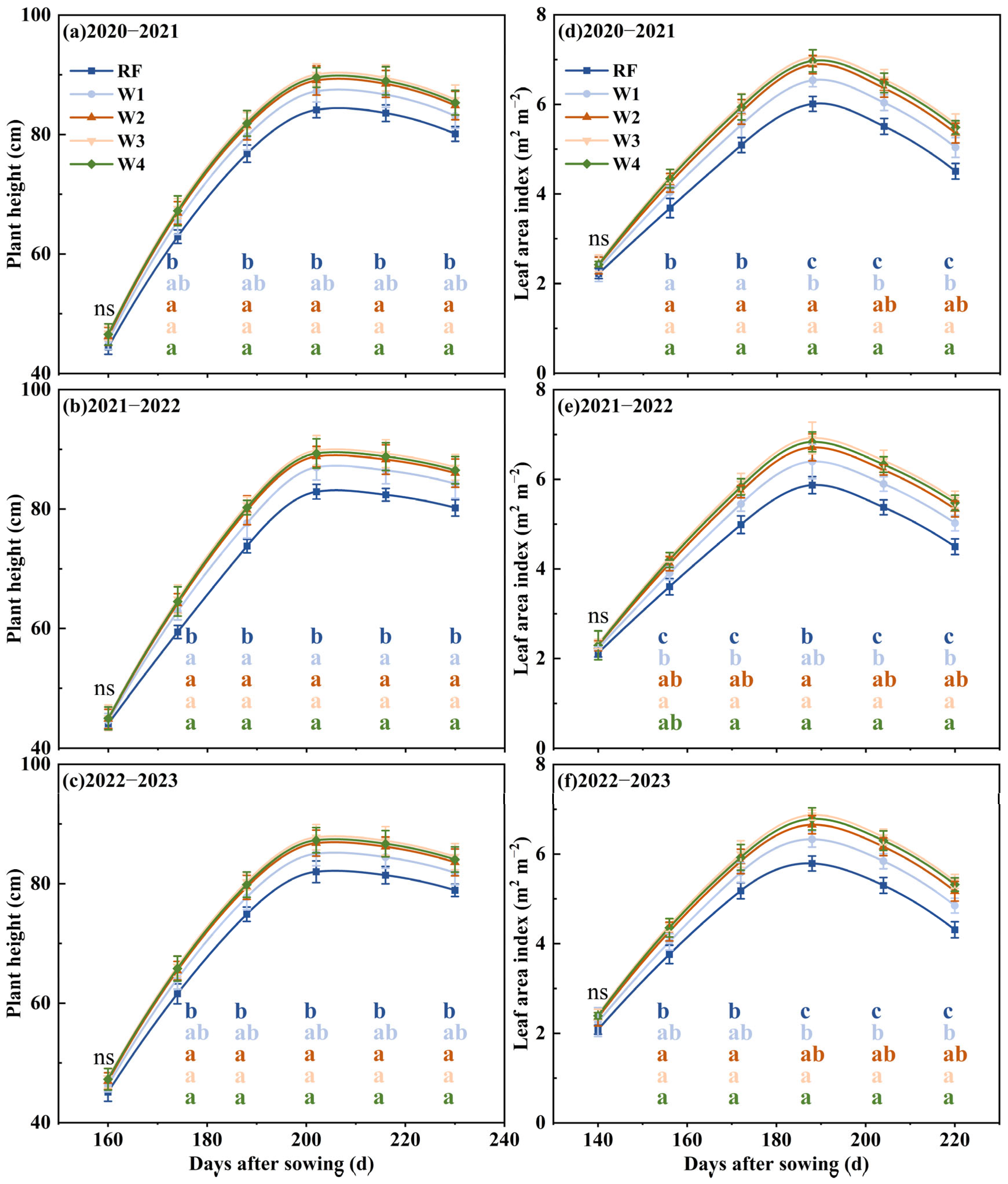
3.1. Plant Height and Leaf Area Index
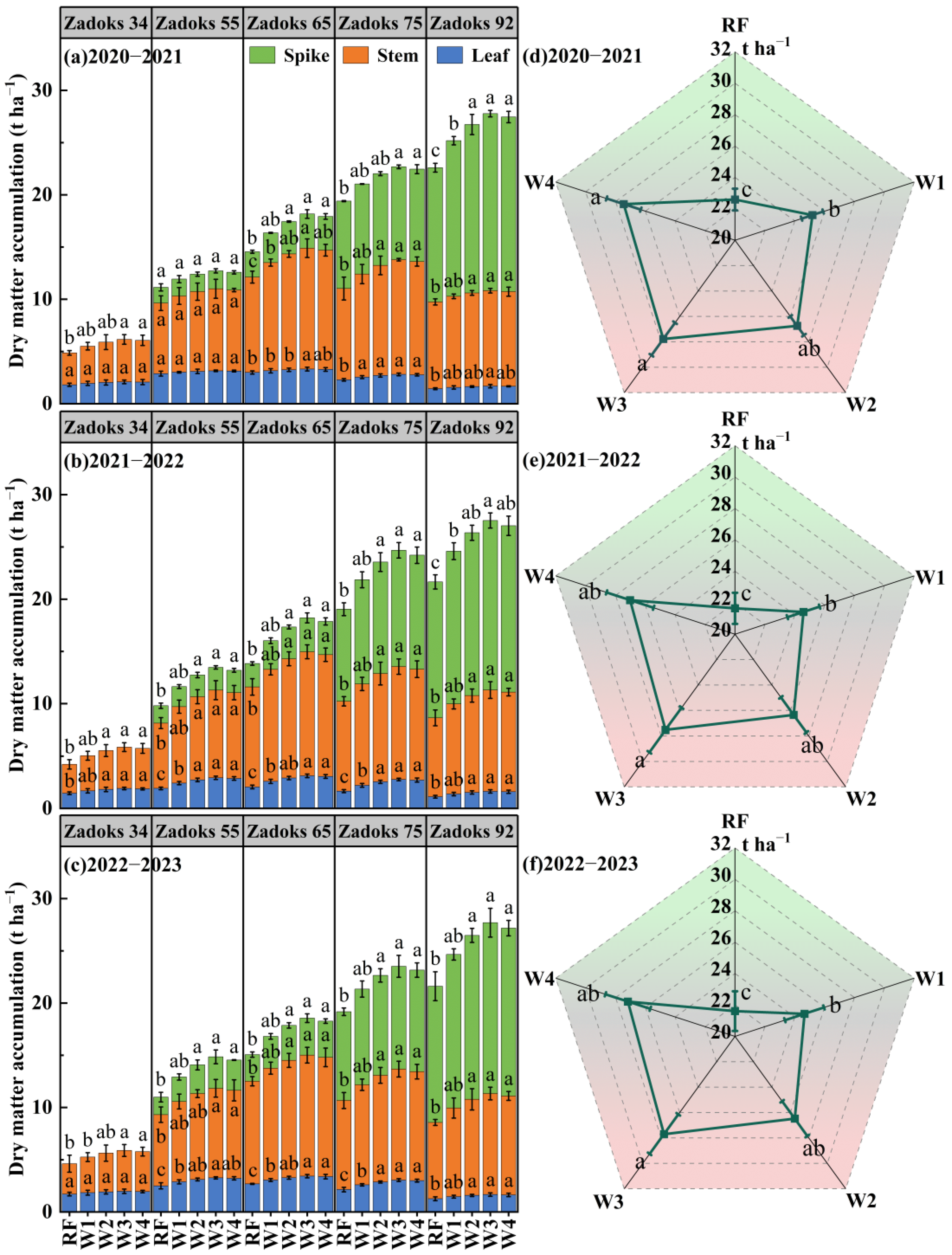
3.2. Dry Matter Accumulation
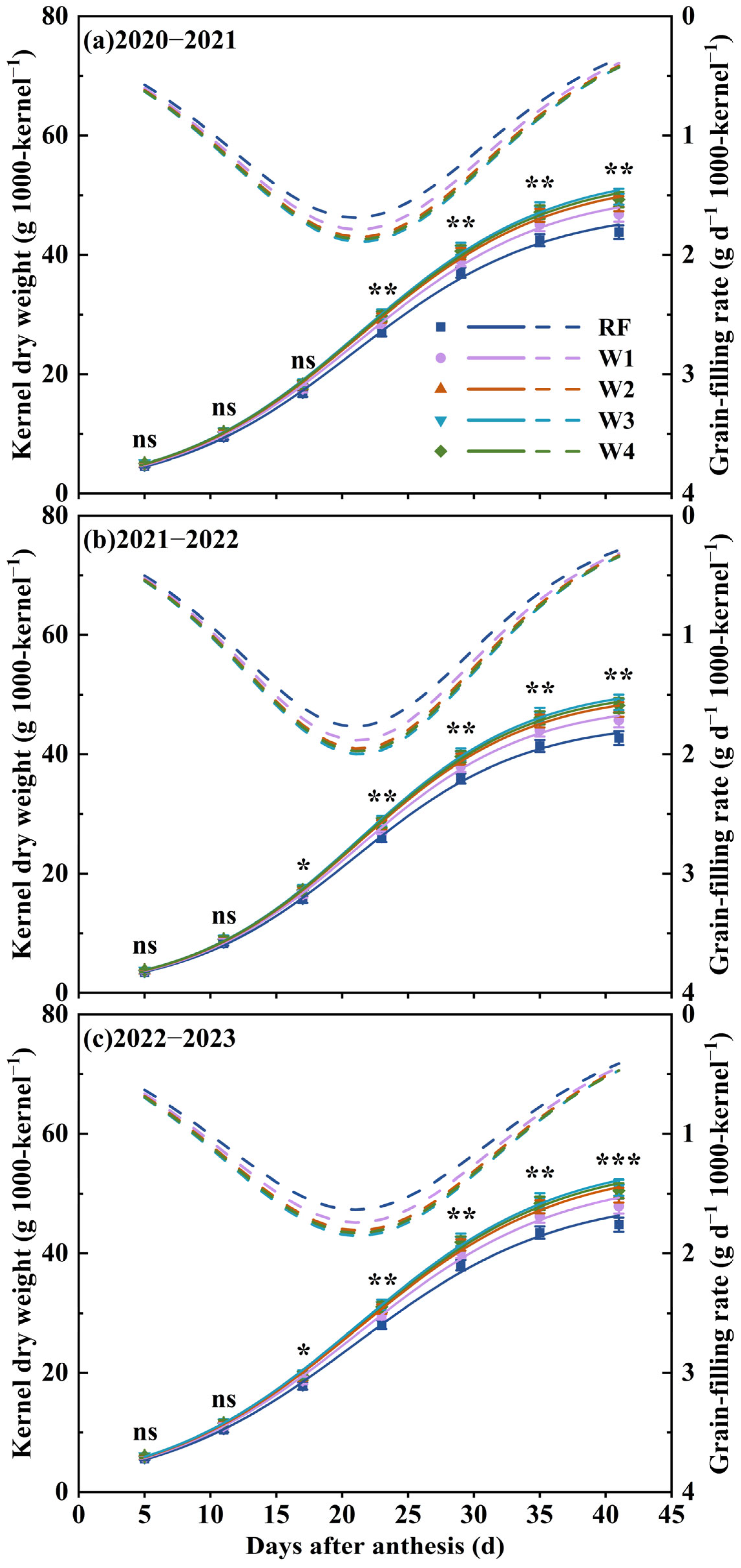
3.3. Grain-Filling Characteristics
3.3.1. Dynamic Changes of Grain Dry Matter Accumulation and Grain-Filling Rate
3.3.2. Grain-Filling Characteristic Parameters
3.3.3. Stage Characteristic Analysis of Grain-Filling Process
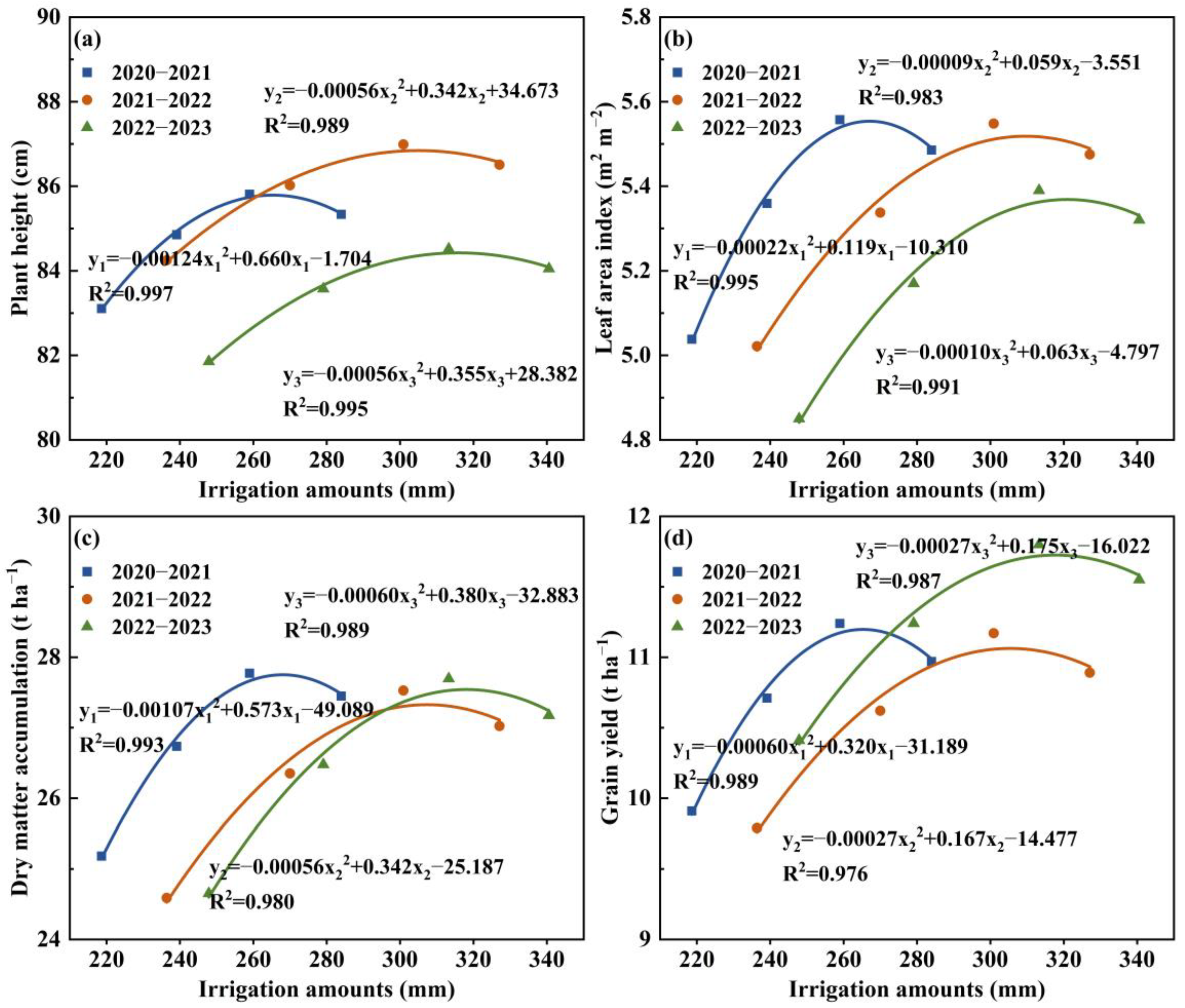
3.4. Grain Yield and Yield Components
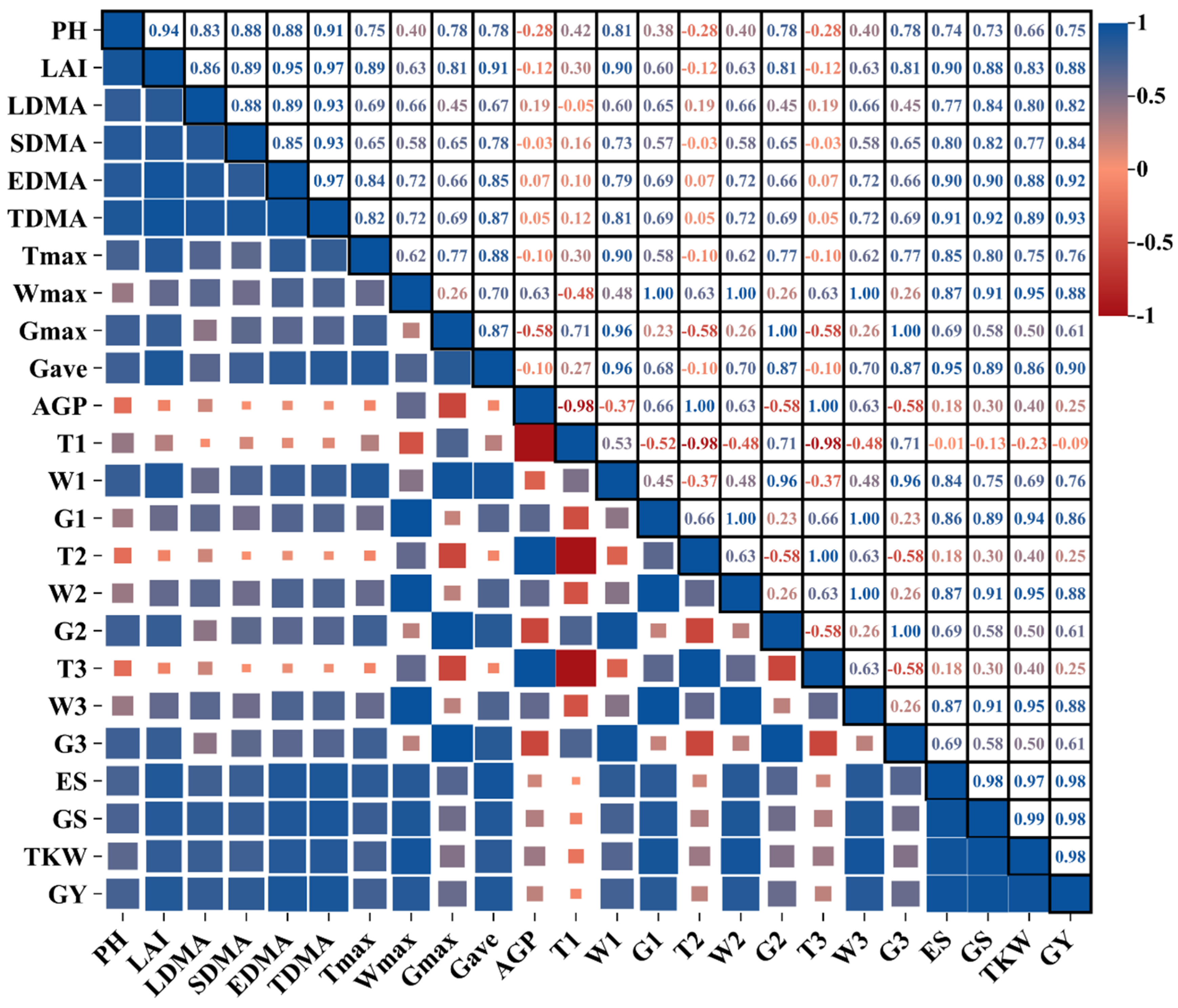
3.5. Correlation Analysis
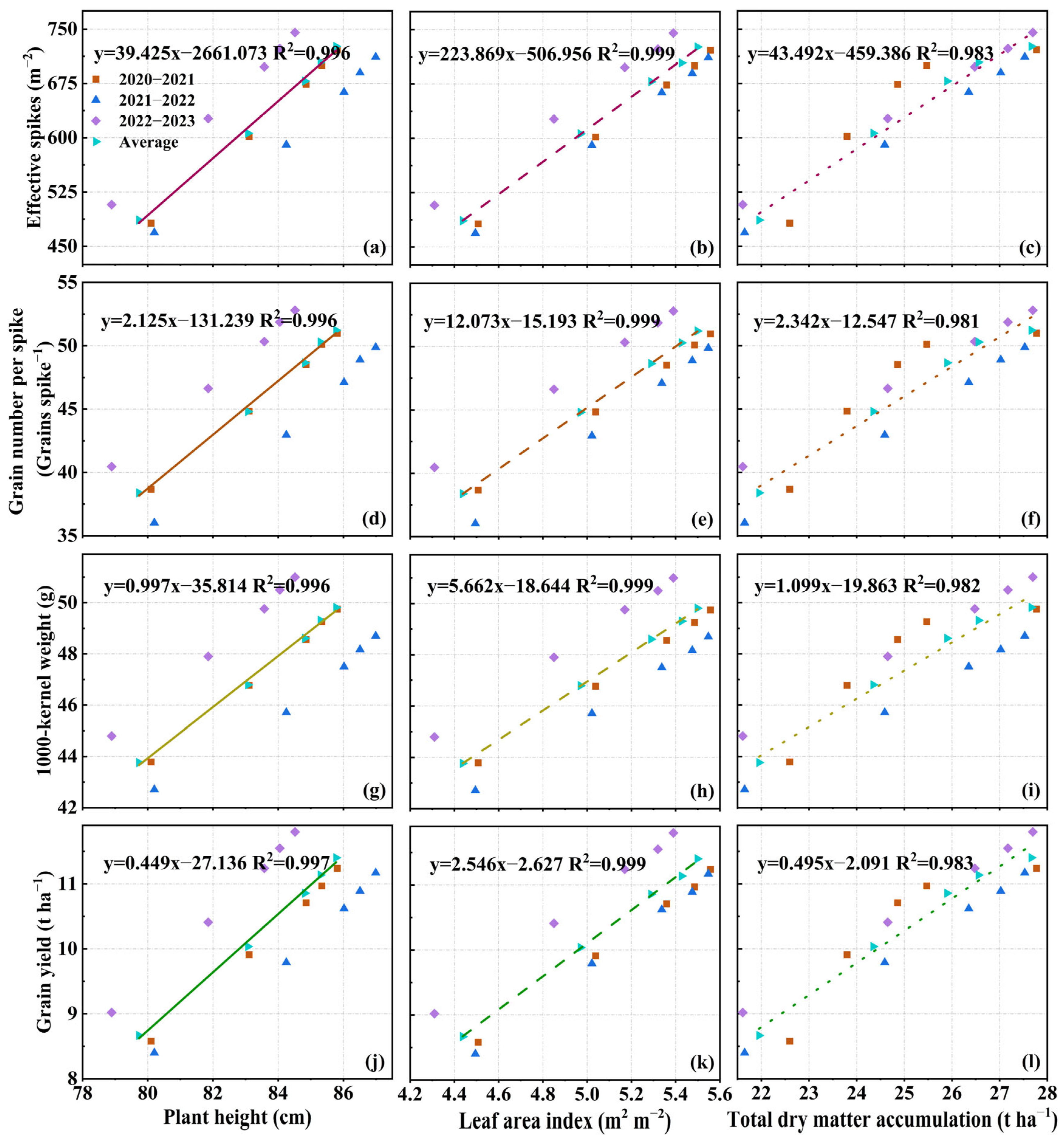
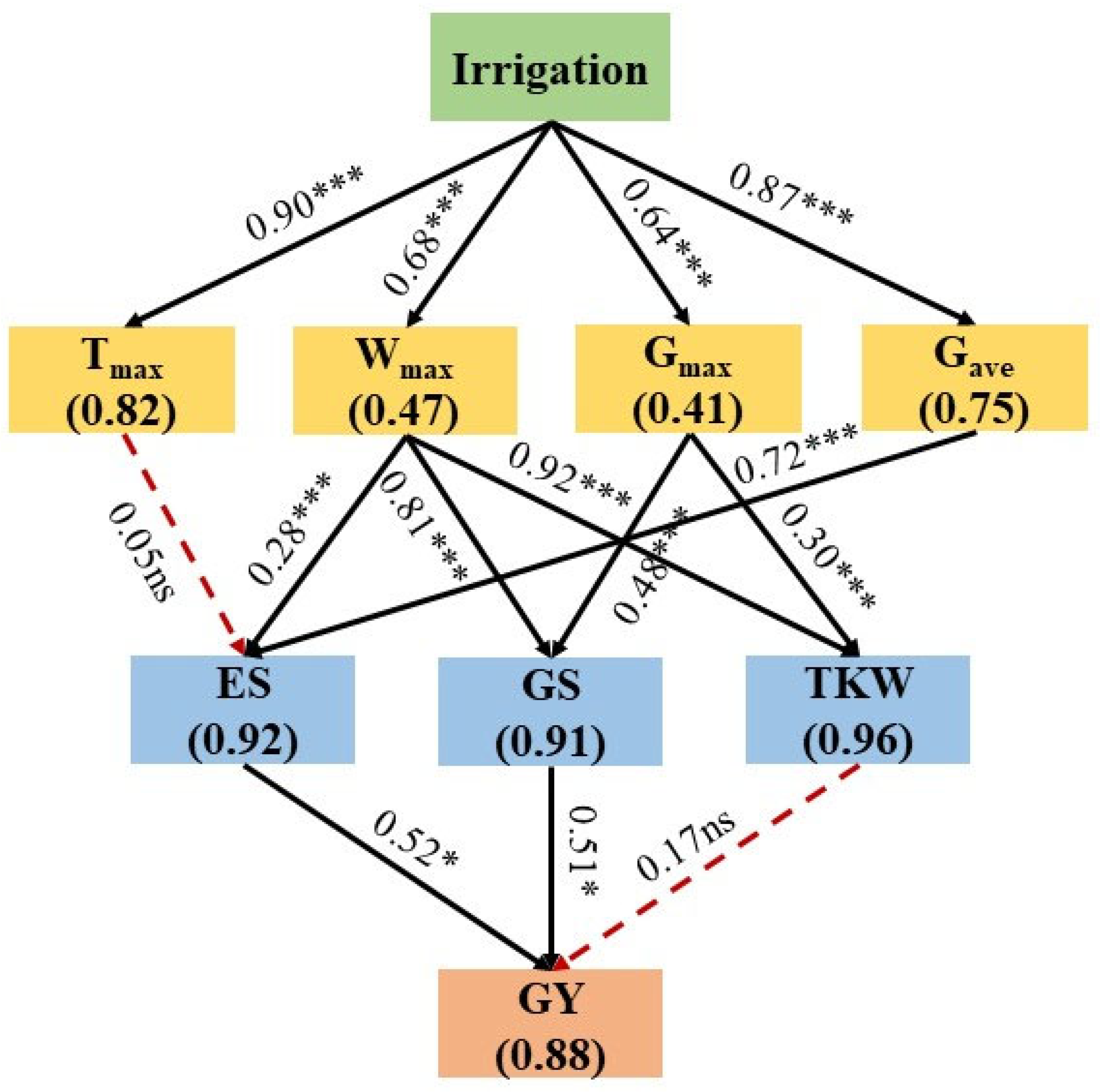
3.6. Structural Equation Modeling
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Deep Storage Irrigation on Wheat Growth
4.2. Effects of Deep Storage Irrigation on Grain-Filling Process of Wheat
4.3. Effects of Deep Storage Irrigation on Grain Yield and Yield Components of Wheat
4.4. Correlation Analysis and Structural Equation Modeling
4.5. Limitations and Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group Ⅱ to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, F.V.; Burke, M.; Diffenbaugh, N.S. Contribution of historical precipitation change to US flood damages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.B.; Guo, S.L.; Gentine, P.; Sullivan, S.C.; Gu, L.; He, S.K.; Chen, J.; Liu, P. Does the hook structure constrain future flood intensification under anthropogenic climate warming? Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.B.; Guo, S.L.; Gu, L.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Liu, D.D.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.J.; Xu, C.Y. Blending multi-satellite, atmospheric reanalysis and gauge precipitation products to facilitate hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.M.; Tian, S.T. A novel potential cause of extreme precipitation in the northwest China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Zhang, S.N.; Zhang, F.M.; Li, K.C.; Yang, K. On the increase of precipitation in the Northwestern China under the global warming. Adv. Earth Sci. 2021, 36, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Shar, A.G.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.L.; Shi, J.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tian, X.H. Effect of straw return mode on soil aggregation and aggregate carbon content in an annual maize-wheat double cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Hoogenboom, G.; Cai, H.J.; Wang, Z.K. Winter wheat production on the Guanzhong Plain of Northwest China under projected future climate with SimCLIM. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Fan, J.; Hao, M.D.; Hu, J.S.; Wang, H. Evaluating the effects of plastic film mulching patterns on cultivation of winter wheat in a dryland cropping system on the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.N.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.J.; Su, Z.H.; Liu, J.C.; He, J.Q. Multi-objective winter wheat irrigation strategies optimization based on coupling AquaCrop-OSPy and NSGA-Ⅲ: A case study in Yangling, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 157104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.B.; Wang, Y.F.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.A.; Gu, X.B.; Cai, H.J. Seasonal variation and controlling factors of carbon balance over dry semi-humid cropland in Guanzhong Plain. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 149, 126912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Li, P.Y. Appraisal of shallow groundwater quality with human health risk assessment in different seasons in rural areas of the Guanzhong Plain (China). Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.J.; Li, P.Y.; Mu, D.W. Spatial distribution, source apportionment and potential ecological risk assessment of trace metals in surface soils in the upstream region of the Guanzhong Plain, China. Environ. Res. 2023, 234, 116527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.Y.; Zain, M.; Mehmood, F.; Wang, G.S.; Gao, Y.; Duan, A.W. Effects of nitrogen application rate and irrigation regime on growth, yield, and water-nitrogen use efficiency of drip-irrigated winter wheat in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 231, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.S.; Hu, T.T.; Geng, C.M.; Cui, X.L.; Fan, J.L.; Zhang, F.C. Response of yield, yield components and water-nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat to different drip fertigation regimes in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Zhu, X.G.; Parry, M.A.J.; Kang, S.Z.; Du, T.S.; Tong, L.; Ding, R.S. Environmental burdens of groundwater extraction for irrigation over an inland river basin in Northwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Wang, Z.Z.; Zheng, T.L. Study on the present situation of groundwater resources and the networking of Monotoring Stations in Shaanxi Province. Ground Water 2018, 40, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Hou, L.Y.; Xiao, C.W.; Zhang, X.M.; Han, X.G. Dissolved methane in groundwater of domestic wells and its potential emissions in arid and semi-arid regions of Inner Mongolia, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Pacenka, S.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Sui, P. Managing food and bioenergy crops with declining groundwater levels in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2019, 234, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.C.; Wang, K.C.; Shang, M.F.; Qin, Y.S.; Bo, X.Z.; Chen, F.; Chu, Q.Q. Adopting different irrigation and nitrogen management based on precipitation year types balances winter wheat yields and greenhouse gas emissions. Field Crops Res. 2022, 280, 108484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Santini, A. Water retention and storage: Field. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 4: Physical Methods; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 721–738. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.K.; Lau, W.K.M.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, W.S. A GCM study of effects of radiative forcing of sulfate aerosol on large scale circulation and rainfall in East Asia during boreal spring. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L24701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, N.; Matsumoto, J.; Lwin, T. Trend in precipitation extremes over Southeast Asia. SOLA 2009, 5, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.A.; Hsu, H.H.; Liang, H.C.; Chiu, P.G.; Tu, C.Y. Future change in extreme precipitation in East Asian spring and Mei-yu seasons in two high-resolution AGCMs. Weather Clim Extreme. 2022, 35, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xie, P.X.; Zhuo, L.; Shang, K.H.; Ji, X.X.; Wu, P.T. Water footprints of irrigated crop production and meteorological driving factors at multiple temporal scales. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.M.; Si, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Kader Mounkaila Hamani, A.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wu, L.F.; Gao, Y.; Duan, A.W. Variations in water sources used by winter wheat across distinct rainfall years in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Niu, W.Q.; Ma, L.; Du, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.; Gan, H.C.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effects of drip irrigation upper limits on rhizosphere soil bacterial communities, soil organic carbon, and wheat yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 293, 108701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Ji, Q.Y.; Zhang, F.C.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.L.; Hou, X.H.; Yan, F.L.; Liu, X.Q.; Gong, K.Y. Effects of various soil water potential thresholds for drip irrigation on soil salinity, seed cotton yield and water productivity of cotton in northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 279, 108172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, M.R.; Fu, J.T.; Zhang, X.Z.; Li, Y.; Shao, Y.T.; Xing, Y.Y.; Wang, X.K. Coupling effects of irrigation amount and fertilization rate on yield, quality, water and fertilizer use efficiency of different potato varieties in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 287, 108446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L. Analysis of Water Use Efficiency and Influencing Factors of Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Under Different Irrigation Strategies; Henan Agricultural University: Zhengzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.X.; Zhang, W.Y.; Liu, X.W.; Wang, Q.S.; Liu, B.H.; Mei, X.R. Grain yield and water productivity of winter wheat controlled by irrigation regime and manure substitution in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 295, 108731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.D.; Niu, W.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, B.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J. A synthetic analysis of the effect of water and nitrogen inputs on wheat yield and water- and nitrogen-use efficiencies in China. Field Crops Res. 2021, 265, 108105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.N.; Han, J.Y.; Gu, Y.N.; Li, T.; Xu, X.R.; Jiang, Y.H.; Li, Y.P.; Sun, J.F.; Pan, G.X.; Cheng, K. Impact of biochar amendment on soil hydrological properties and crop water use efficiency: A global meta-analysis and structural equation model. GCB Bioenergy 2022, 14, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.L.; Mak-Mensah, E.; Zhao, W.C.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, X.J.; Zhang, D.K.; Zhu, J.H.; Qi, W.J.; Liu, Q.L.; Li, X.L.; et al. Optimized ridge-furrow technology with biochar amendment for alfalfa yield enhancement and soil erosion reduction based on a structural equation model on sloping land. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 298, 108866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewdie, M.C.; Passel, S.V.; Cools, J.; Tenessa, D.B.; Ayele, Z.A.; Tsegaye, E.A.; Minale, A.S.; Nyssen, J. Direct and indirect effect of irrigation water availability on crop revenue in northwest Ethiopia: A structural equation model. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 220, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.G.; Gong, Z.; Yang, Y.H.; Tan, Z.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, D.W. Optimal irrigation water salinity enhances tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) yield in sand culture by regulating substrate salinity. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 317, 109632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.A.; Parthasarathy, N. Ecological drivers of soil carbon in Kashmir Himalayan forests: Application of machine learning combined with structural equation modelling. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.T.; Mu, Q.; Ding, Y.B.; Sun, S.K.; Zou, Y.F.; Yu, L.Y.; Zhang, P.Y.; Yang, N.; Guo, W.; Cai, H.J. Considering spatio-temporal dynamics of soil water with evapotranspiration partitioning helps to clarify water utilization characteristics of summer maize under deficit irrigation. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.L.; Liu, X.J.; Bao, X.Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Yin, B.Z.; Wang, W.T.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhen, W.C. Effects of spring limited irrigation on grain yield and root characteristics of winter wheat in groundwater-overexploitation areas in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 294, 108729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amine, B.E.; Mosseddaq, F.; Houssa, A.A.; Bouaziz, A.; Moughli, L.; Oukarroum, A. How far can the interactive effects of continuous deficit irrigation and foliar iron fertilization improve the physiological and agronomic status of soybeans grown in calcareous soils under arid climate conditions? Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 300, 108926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.C.; Gao, Z.Z.; Feng, Y.P.; Chu, Q.Q. Cleaner tillage and irrigation options for food-water-energy-carbon synergism in wheat-maize cropping systems. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.P. On Modern Flood Diversion and Silt Irrigation Technology in Guanzhong Area; Shaanxi Normal University: Xi’an, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Standard Operating Procedure for Soil pH Determination, Rome. 2021. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/cb3637en (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Standard Operating Procedure for Soil Electrical Conductivity, Soil/Water, 1:5. 2021. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/cb3354en (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- Reynolds, W.D. An analytic description of field capacity and its application in crop production. Geoderma 2018, 326, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural Chemical Elements Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 106–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kachurina, O.M.; Zhang, H.; Raun, W.R.; Krenzer, E.G. Simultaneous determination of soil aluminum, ammonium-and nitrate-nitrogen using 1M potassium chloride extraction. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2000, 31, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. In Circular No. 939; USDA, Ed.; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bemmelen, J.M. Über die Bestimmung des Wassers, des Humus, des Schwefels, der in den colloïdalen Silikaten gebundenen Kieselsäure, des Mangans u.s. w. im Ackerboden. Die Landwirthschaftlichen Versuchs-Stationen. 1890, 37, 279–290. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.S.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, G.H.; Qin, Y.Y.; Jiang, D.; Dong, S.T. Plant density and nitrogen supply affect the grain filling parameters of maize kernels located in different ear positions. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhao, S.Y.; Sha, Y.; Huang, Y.W.; Hao, Z.H.; Ke, L.H.; Chen, F.J.; Yuan, L.X.; Mi, G.H. Nitrogen responsiveness of leaf growth, radiation use efficiency and grain yield of maize (Zea mays L.) in Northeast China. Field Crops Res. 2023, 291, 108806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.R.; Li, C.; Li, P.; Zong, Y.Z.; Zhang, D.S.; Gao, Z.Q.; Hao, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Lam, S.K. Deep plowing increase soil water storage and wheat yield in a semiarid region of Loess Plateau in China: A simulation study. Field Crops Res. 2024, 308, 109299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.Y.; Yao, F.M.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.S.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, J.W.; Wang, X. Assessing the effects of precipitation and irrigation on winter wheat yield and water productivity in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Jia, B.; Wang, H.G.; Li, D.X.; Fang, Q.; He, J.N.; Li, R.Q. Yield response of supplementary irrigation at the anthesis stage of winter wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 284, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.G.; Jia, C.F.; Lyu, X.R.; Yang, T.Z.; Qin, H.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Hao, Q.L.; Liu, W.X.; Dai, X.H.; Zeng, J.B.; et al. In silico curation of QTL-rich clusters and candidate gene identification for plant height of bread wheat. Crop J. 2023, 11, 1480–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilniyaz, O.; Du, Q.Y.; Shen, H.F.; He, W.W.; Feng, L.W.; Azadi, H.; Kurban, A.; Chen, X. Leaf area index estimation of pergola-trained vineyards in arid regions using classical and deep learning methods based on UAV-based RGB images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 207, 107723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, M.Y.; Li, Q.; Ghafoor, A.; Zhu, J.Y.; Li, B.G.; Ma, Y.T. Using the plant height and canopy coverage to estimation maize aboveground biomass with UAV digital images. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 151, 126957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Han, M.M.; Pang, D.W.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Dong, H.H.; Chang, Y.L.; Jin, M.; Luo, Y.L.; Li, Y.; et al. Characteristics of lodging resistance of high-yield winter wheat as affected by nitrogen rate and irrigation managements. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 1290–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, T.H.; Cong, A.Q.; Lian, J. Integrated application of fertilization and reduced irrigation improved maize (Zea mays L.) yield, crop water productivity and nitrogen use efficiency in a semi-arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, M.; Mousavi, S.M.; Zarebanadkouki, M. Functions of rhizosheath on facilitating the uptake of water and nutrients under drought stress: A review. Plant Soil 2023, 491, 239–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, J.B.; Gruda, N.S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Duan, Z.Q.; Müller, C.; Li, X. The regulation of gross nitrogen transformation rates in greenhouse soil cultivated with cucumber plants under elevated atmospheric [CO2] and increased soil temperature. Geoderma 2023, 439, 116680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.S.; Wei, C.H.; Zhang, F.C.; Zhang, J.H.; Nong, M.L.; Kang, S.Z. Water-use efficiency and physiological responses of maize under partial root-zone irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, Z.W.; White, P.J. The effect of supplemental irrigation after jointing on leaf senescence and grain filling in wheat. Field Crops Res. 2013, 151, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Z.W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.L. Effects of micro-sprinkling with different irrigation levels on winter wheat grain yield and greenhouse gas emissions in the North China Plain. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 143, 126725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.L.; Hu, T.T.; Song, X. Effects of nitrogen application rates and irrigation regimes on grain yield and water efficiency of maize under alternate partial root-zone irrigation. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2792–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.L.; Zhang, F.C.; Fan, X.K.; Fan, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Zou, H.Y.; Wang, H.D.; Li, G.D. Determining irrigation amount and fertilization rate to simultaneously optimize grain yield, grain nitrogen accumulation and economic benefit of drip-fertigated spring maize in northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhusal, N.; Adhikari, A.; Lee, M.; Han, A.; Han, A.R.; Kim, H.S. Evaluation of growth responses of six gymnosperm species under long-term excessive irrigation and traits determining species resistance to waterlogging. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2022, 323, 109071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerer, S.; Puente, A.F.; Peichl, M.; Rakovec, O.; Samaniego, L.; Schneider, U.A. Limited potential of irrigation to prevent potato yield losses in Germany under climate change. Agric. Syst. 2023, 207, 103633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.T.; Xiang, Z.Q.; Ma, H.Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, P.H.; Zheng, S.L. Effect of N fertilizer dosage and base/topdressing ratio on potato growth characteristics and yield. Agronomy 2023, 13, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siluch, M.; Siedliska, A.; Bartmiński, P.; Kociuba, W.; Baranowski, P.; Krzyszczak, J. The impact of water availability on the discriminative status of nitrogen (N) in sugar beet and celery using hyperspectral imaging methods. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fang, X.Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, J.; Hou, X.Q.; Yang, Y.D.; Zang, H.D.; Zeng, Z.H. Optimal irrigation for wheat-maize rotation depending on precipitation in the North China Plain: Evidence from a four-year experiment. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 294, 108726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.W.; Zhao, B.; Li, X.L.; Liu, Q.L.; Feng, D.J.; Lan, T.Q.; Kong, F.L.; Li, Q.; Yuan, J.C. Nitrogen application affects maize grain filling by regulating grain water relations. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Hoogenboom, G.; Ma, Y.T.; Li, B.G.; Guo, Y. Maize kernel growth at different floret positions of the ear. Field Crops Res. 2013, 149, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Li, L.L.; Xie, J.H.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Anwar, S. Tillage and nitrogen supply affects maize yield by regulating photosynthetic capacity, hormonal changes and grain filling in the Loess Plateau. Soil Till Res. 2022, 218, 105317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Du, L.J.; Feng, D.J.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.X.; Kong, F.L.; Yuan, J.C. Grain-filling characteristics and yield differences of maize cultivars with contrasting nitrogen efficiencies. Crop J. 2020, 8, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.G.; Cui, H.Y.; Zhao, B.; Dong, S.T.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.W. Effect of light on yield and characteristics of grain-filling of summer maize from flowering to maturity. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2013, 46, 4427–4434. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.L.; Liu, J.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, J.Z.; Yin, F.H.; Guo, L.; Li, W.H.; He, J.; Ma, J.Y.; Liang, Y.H.; et al. Optimizing cotton yield through appropriate irrigation water salinity: Coordinating above- and below-ground growth and enhancing photosynthetic capacity. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 154, 127095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.C.; Wu, Y.; Fan, J.L.; Zhang, F.C.; Guo, J.J.; Zheng, J.; Wu, L.F. Optimization of drip irrigation and fertilization regimes to enhance winter wheat grain yield by improving post-anthesis dry matter accumulation and translocation in northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 271, 107782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.Z.; Wu, Y.P.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, X.X.; Shao, Y.H.; Feng, W.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Guo, T.C. Grain number responses to pre-anthesis dry matter and nitrogen in improving wheat yield in the Huang-Huai Plain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.B.; Cai, H.J.; Fang, H.; Chen, P.P.; Li, Y.P.; Li, Y.N. Soil hydro-thermal characteristics, maize yield and water use efficiency as affected by different biodegradable film mulching patterns in a rain-fed semi-arid area of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.G.; Tai, A.P.K.; Mao, J.; Tam, O.H.F.; Li, R.K.K.; Wu, J.; Li, S.E. Effects of different irrigation methods on regional climate in North China Plain: A modeling study. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2023, 342, 109728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Z.; Wang, Y.X.; Feng, Y.P.; Laraib, I.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.C.; Chu, Q.Q. Optimized irrigation management mitigates reactive nitrogen loss and shapes nitrogen fate in wheat production. Field Crops Res. 2024, 308, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Shi, W.; Kamran, M.; Chang, S.H.; Jia, Q.M.; Hou, F.J. Effects of intercropping and regulated deficit irrigation on the yield, water and land resource utilization, and economic benefits of forage maize in arid region of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 298, 108876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Anh, T. Irrigation and Drainage Systems. Department of Agronomy-Vietnam Academy of Agriculture. 2009. Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/lophocphank57vnua/ (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Huang, C.; Gao, Y.; Qin, A.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Ning, D.; Ma, S.; Duan, A.; Liu, Z. Effects of waterlogging at different stages and durations on maize growth and grain yields. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Qin, W.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Shao, L.W.; Sun, H.Y. Responses of yield and WUE of winter wheat to water stress during the past three decades-a case study in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.W.; Chai, Q.; Yang, C.G.; Chen, Y.Z.; Li, R.; Li, Y.W.; Chang, L.; Lan, X.M.; Cheng, H.B.; Chai, S.X. Plastic film mulching increases yield, water productivity, and net income of rain-fed winter wheat compared with no mulching in semiarid Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 262, 107420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, X.L.; Li, M.; Xiong, T.; Li, C.S.; Tang, Y.L. Innovative no-till seeding technology improves yield and nitrogen use efficiency while reducing environmental pressure in wheat after rice harvesting. Soil Till Res. 2024, 235, 105908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Kong, T.T.; Xie, J.R.; Yang, T.G.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z. Appropriate water and fertilizer supply can increase yield by promoting growth while ensuring the soil ecological environment in melon production. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Wang, C.J.; Qin, J.J.; Qiu, X.F.; Wen, Y.X.; Wang, J.D.; Mei, X.R. Biogas slurry topdressing enhances the comprehensive benefits of maize: New perspectives on grain filling process, yield, and endogenous microbiome. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 22, 102111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, N.; Ebrahimi, A.; Asadi, E. Comparative analysis of random forest, exploratory regression, and structural equation modeling for screening key environmental variables in evaluating rangeland above-ground biomass. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.Y.; Li, C.L.; Tian, L.B.; Shen, Z.Y.; Feng, G.Z.; Hou, W.F.; Liu, F.L.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y. Mixture of controlled-release and normal urea to improve maize root development, post-silking plant growth, and grain filling. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 151, 126994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, N.Y.; Li, W.; Qin, W.L.; Li, J.P.; Gao, Y.M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.C.; Yu, K.; et al. Spike growth affects spike fertility through the number of florets with green anthers before floret abortion in wheat. Field Crops Res. 2021, 260, 108007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Mo, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X. Optimal dispatching rules of hydropower reservoir in flood season considering flood resources utilization: A case study of Three Gorges Reservoir in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 388, 135975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiang, C.; Chin, R.; Xiang, Z.; Long, Y.; Deng, B.; Wu, Z. Water storage capacity estimation for a large complex lake system incorporating the water levels during flooding season. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 51, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reading, L.; Bajracharya, K.; Wang, J. Simulating deep drainage and nitrate leaching on a regional scale: Implications for groundwater management in an intensively irrigated area. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, W. Modeling soil water balance and irrigation strategies in a flood-irrigated wheat-maize rotation system. A case in dry climate, China. Agric. Water Manage 2019, 221, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Property | Soil Depth (cm) | Measurement Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 | 20–40 | 40–60 | 60–80 | 80–100 | ||
| pH | 8.1 | 8.2 | 8.2 | 8.3 | 8.1 | Acid–Alkali indicator method [43] |
| Electrical conductivity (μs cm−1) | 171.1 | 139.1 | 118.6 | 124.0 | 122.2 | Time domain reflectometer (TDR) technology [44] |
| Field capacity soil moisture (cm3 cm−3) | 0.326 | 0.336 | 0.344 | 0.339 | 0.337 | Ring knife method [45] |
| Total nitrogen (g kg−1) | 1.555 | 0.951 | 0.631 | 0.507 | 0.535 | Kjeldahl digestion [46] |
| Available nitrogen (mg kg−1) | 159.5 | 85.3 | 51.4 | 39.7 | 35.2 | Colorimetric method by 2 mol L−1 cold Kcl extractable [47] |
| Available phosphorus (mg kg−1) | 44.707 | 22.563 | 10.680 | 7.449 | 7.703 | Olsen method by 0.5 mol L−1 NaHCO3 extractable [48] |
| Available potassium (mg kg−1) | 259 | 140 | 138 | 124 | 127 | Colorimetric method by 2 mol L−1 cold HNO3 extractable [46] |
| Organic matter (g kg−1) | 19.281 | 8.752 | 5.250 | 4.234 | 4.964 | Potassium dichromate oxidation method [49] |
| Experiment Years | Irrigation Depth and Abbreviation | Total Irrigation Amounts for Winter Wheat (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020–2021 | Rain-fed (RF) | - |
| 120 cm (W1, CK) | 218.64 mm | |
| 140 cm (W2) | 239.11 mm | |
| 160 cm (W3) | 258.97 mm | |
| 180 cm (W4) | 283.95 mm | |
| 2021–2022 | Rain-fed (RF) | - |
| 120 cm (W1, CK) | 236.41 mm | |
| 140 cm (W2) | 269.98 mm | |
| 160 cm (W3) | 300.91 mm | |
| 180 cm (W4) | 327.08 mm | |
| 2022–2023 | Rain-fed (RF) | - |
| 120 cm (W1, CK) | 247.87 mm | |
| 140 cm (W2) | 279.09 mm | |
| 160 cm (W3) | 313.27 mm | |
| 180 cm (W4) | 340.54 mm |
| No. | Wheat Phenology | Measured Data |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zadoks 34 | Crop data: plant height, leaf area index, dry matter accumulation; soil data: moisture content |
| 2 | Zadoks 55 | Crop data: plant height, leaf area index, dry matter accumulation |
| 3 | Zadoks 65 | Crop data: plant height, leaf area index, dry matter accumulation |
| 4 | Zadoks 75 | Crop data: plant height, leaf area index, dry matter accumulation, grain-filling parameters |
| 5 | Zadoks 92 | Crop data: plant height, leaf area index, dry matter accumulation, grain yield and yield components |
| Year | Treatment | R2 | A | B | C | Tmax | Wmax | Gmax | Gave | AGP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (d) | (g 1000-kernels) | (g 1000-grains−1 d−1) | (g 1000-grains−1 d−1) | (d) | ||||||
| 2020–2021 | RF | 0.9991 | 47.72 | 19.57 | 0.1416 | 21.00 | 23.86 | 1.6892 | 0.8837 | 42.37 |
| W1 | 0.9993 | 50.94 | 19.68 | 0.1405 | 21.21 | 25.47 | 1.7888 | 0.9352 | 42.71 | |
| W2 | 0.9993 | 52.87 | 19.76 | 0.1399 | 21.33 | 26.44 | 1.8494 | 0.9663 | 42.88 | |
| W3 | 0.9994 | 54.12 | 19.85 | 0.1398 | 21.38 | 27.06 | 1.8908 | 0.9874 | 42.93 | |
| W4 | 0.9994 | 53.61 | 19.72 | 0.1395 | 21.38 | 26.80 | 1.8695 | 0.9771 | 43.01 | |
| 2021–2022 | RF | 0.9994 | 45.51 | 26.01 | 0.1554 | 20.97 | 22.76 | 1.7677 | 0.8913 | 38.62 |
| W1 | 0.9996 | 48.58 | 26.60 | 0.1551 | 21.15 | 24.29 | 1.8839 | 0.9472 | 38.68 | |
| W2 | 0.9996 | 50.44 | 26.90 | 0.1549 | 21.26 | 25.22 | 1.9530 | 0.9805 | 38.74 | |
| W3 | 0.9997 | 51.67 | 27.14 | 0.1549 | 21.32 | 25.83 | 2.0001 | 1.0031 | 38.75 | |
| W4 | 0.9997 | 51.12 | 26.94 | 0.1546 | 21.30 | 25.56 | 1.9759 | 0.9919 | 38.81 | |
| 2022–2023 | RF | 0.9985 | 49.71 | 15.80 | 0.1314 | 21.00 | 24.85 | 1.6331 | 0.8792 | 45.66 |
| W1 | 0.9988 | 52.93 | 16.13 | 0.1316 | 21.12 | 26.46 | 1.7419 | 0.9352 | 45.58 | |
| W2 | 0.9990 | 54.86 | 16.34 | 0.1318 | 21.19 | 27.43 | 1.8081 | 0.9691 | 45.51 | |
| W3 | 0.9991 | 56.08 | 16.45 | 0.1321 | 21.20 | 28.04 | 1.8524 | 0.9919 | 45.41 | |
| W4 | 0.9990 | 55.61 | 16.33 | 0.1316 | 21.22 | 27.81 | 1.8297 | 0.9807 | 45.59 |
| Gradual Increase Period (GIP) | Rapid Increase Period (RIP) | Slight Increase Period (SIP) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Treatment | T1 | W1 | G1 | T2 | W2 | G2 | T3 | W3 | G3 |
| (d) | (g) | (g 1000-grains−1 d−1) | (d) | (g) | (g 1000-grains−1 d−1) | (d) | (g) | (g 1000-grains−1 d−1) | ||
| 2020–2021 | RF | 11.70 | 7.76 | 0.6635 | 18.60 | 27.55 | 1.4810 | 23.15 | 9.61 | 0.4149 |
| W1 | 11.84 | 8.30 | 0.7013 | 18.75 | 29.41 | 1.5684 | 23.34 | 10.25 | 0.4394 | |
| W2 | 11.91 | 8.63 | 0.7241 | 18.83 | 30.53 | 1.6216 | 23.43 | 10.64 | 0.4543 | |
| W3 | 11.96 | 8.84 | 0.7393 | 18.85 | 31.25 | 1.6579 | 23.46 | 10.90 | 0.4645 | |
| W4 | 11.93 | 8.74 | 0.7324 | 18.88 | 30.95 | 1.6391 | 23.50 | 10.79 | 0.4592 | |
| 2021–2022 | RF | 12.50 | 7.93 | 0.6348 | 16.96 | 26.28 | 1.5499 | 21.10 | 9.16 | 0.4342 |
| W1 | 12.66 | 8.51 | 0.6718 | 16.98 | 28.05 | 1.6518 | 21.13 | 9.78 | 0.4628 | |
| W2 | 12.75 | 8.85 | 0.6940 | 17.01 | 29.12 | 1.7123 | 21.17 | 10.15 | 0.4797 | |
| W3 | 12.81 | 9.08 | 0.7088 | 17.01 | 29.83 | 1.7537 | 21.17 | 10.40 | 0.4913 | |
| W4 | 12.78 | 8.97 | 0.7019 | 17.04 | 29.51 | 1.7324 | 21.20 | 10.29 | 0.4854 | |
| 2022–2023 | RF | 10.98 | 7.55 | 0.6871 | 20.04 | 28.70 | 1.4319 | 24.94 | 10.01 | 0.4012 |
| W1 | 11.12 | 8.09 | 0.7281 | 20.01 | 30.56 | 1.5273 | 24.90 | 10.66 | 0.4279 | |
| W2 | 11.20 | 8.43 | 0.7526 | 19.98 | 31.68 | 1.5853 | 24.87 | 11.04 | 0.4442 | |
| W3 | 11.23 | 8.64 | 0.7693 | 19.94 | 32.38 | 1.6241 | 24.81 | 11.29 | 0.4550 | |
| W4 | 11.21 | 8.54 | 0.7618 | 20.01 | 32.11 | 1.6043 | 24.91 | 11.20 | 0.4495 | |
| Treatments | Effective Spikes (m−2) | Grain Number Per Spike (Grains Spike−1) | 1000-Kernel Weight (g) | Grain Yield (t ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020–2021 | ||||
| RF | 482.00 ± 13.73 e | 38.67 ± 0.72 d | 43.79 ± 0.25 d | 8.58 ± 0.08 d |
| W1 | 601.84 ± 5.44 d | 44.84 ± 1.28 c | 46.77 ± 0.54 c | 9.91 ± 0.05 c |
| W2 | 673.74 ± 7.83 c | 48.53 ± 0.47 b | 48.56 ± 0.42 b | 10.71 ± 0.33 b |
| W3 | 721.67 ± 12.00 a | 51.00 ± 2.16 a | 49.75 ± 0.30 a | 11.24 ± 0.29 a |
| W4 | 699.70 ± 7.32 b | 50.12 ± 0.72 ab | 49.26 ± 0.31 a | 10.97 ± 0.29 ab |
| 2021–2022 | ||||
| RF | 469.00 ± 8.33 e | 36.03 ± 1.33 d | 42.71 ± 0.61 d | 8.40 ± 0.49 d |
| W1 | 590.29 ± 7.83 d | 42.96 ± 1.34 c | 45.71 ± 0.48 c | 9.79 ± 0.32 c |
| W2 | 663.06 ± 11.83 c | 47.11 ± 1.69 b | 47.50 ± 0.50 b | 10.62 ± 0.18 b |
| W3 | 711.57 ± 10.71 a | 49.88 ± 1.57 a | 48.70 ± 0.21 a | 11.17 ± 0.33 a |
| W4 | 689.78 ± 7.38 b | 48.89 ± 0.75 ab | 48.17 ± 0.57 ab | 10.89 ± 0.28 ab |
| 2022–2023 | ||||
| RF | 507.67 ± 14.18 e | 40.46 ± 1.22 c | 44.80 ± 0.75 d | 9.02 ± 0.71 d |
| W1 | 626.56 ± 9.23 d | 46.63 ± 1.92 b | 47.90 ± 0.72 c | 10.41 ± 0.41 c |
| W2 | 697.89 ± 10.48 c | 50.33 ± 1.46 a | 49.76 ± 0.51 b | 11.24 ± 0.32 b |
| W3 | 745.44 ± 11.11 a | 52.80 ± 0.97 a | 51.00 ± 0.45 a | 11.80 ± 0.40 a |
| W4 | 723.22 ± 11.40 b | 51.87 ± 0.94 a | 50.50 ± 0.60 ab | 11.55 ± 0.28 ab |
| ANOVA analysis | ||||
| Years | ns | ns | * | ns |
| Treatments | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| Years × Treatments | ns | ns | ns | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, X.; Chen, D.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Hu, X. Deep Storage Irrigation Enhances Grain Yield of Winter Wheat by Improving Plant Growth and Grain-Filling Process in Northwest China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081852
Fan X, Chen D, Che H, Wang Y, Du Y, Hu X. Deep Storage Irrigation Enhances Grain Yield of Winter Wheat by Improving Plant Growth and Grain-Filling Process in Northwest China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081852
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Xiaodong, Dianyu Chen, Haitao Che, Yakun Wang, Yadan Du, and Xiaotao Hu. 2025. "Deep Storage Irrigation Enhances Grain Yield of Winter Wheat by Improving Plant Growth and Grain-Filling Process in Northwest China" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081852
APA StyleFan, X., Chen, D., Che, H., Wang, Y., Du, Y., & Hu, X. (2025). Deep Storage Irrigation Enhances Grain Yield of Winter Wheat by Improving Plant Growth and Grain-Filling Process in Northwest China. Agronomy, 15(8), 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081852






