Optimizing Parameters of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Application for Effective Management of Wheat Powdery Mildew
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Plant Material
2.1.2. Pathogen Isolate
2.1.3. Preparation of the Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals (SOR) Solution
2.2. Propagation and Collection of BgtYZ01
2.3. Preparation of Powdery Mildew Spore Suspension and Inoculation Procedure
2.4. Design of Treatments with Different Concentrations of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals for Powdery Mildew Control
2.5. Experimental Setup of Operation Time Treatments Using Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals
2.6. Spraying Height Optimization for Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Application in Wheat Powdery Mildew Control
2.7. Treatment Design Based on Pathogen Infection Timing in Powdery Mildew Control
2.8. Effect of Solution pH on Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals-Based Control of Wheat Powdery Mildew
2.9. Optimization of Strong Oxidative Free Radicals Application Parameters Against Wheat Powdery Mildew Using Box–Behnken Design
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
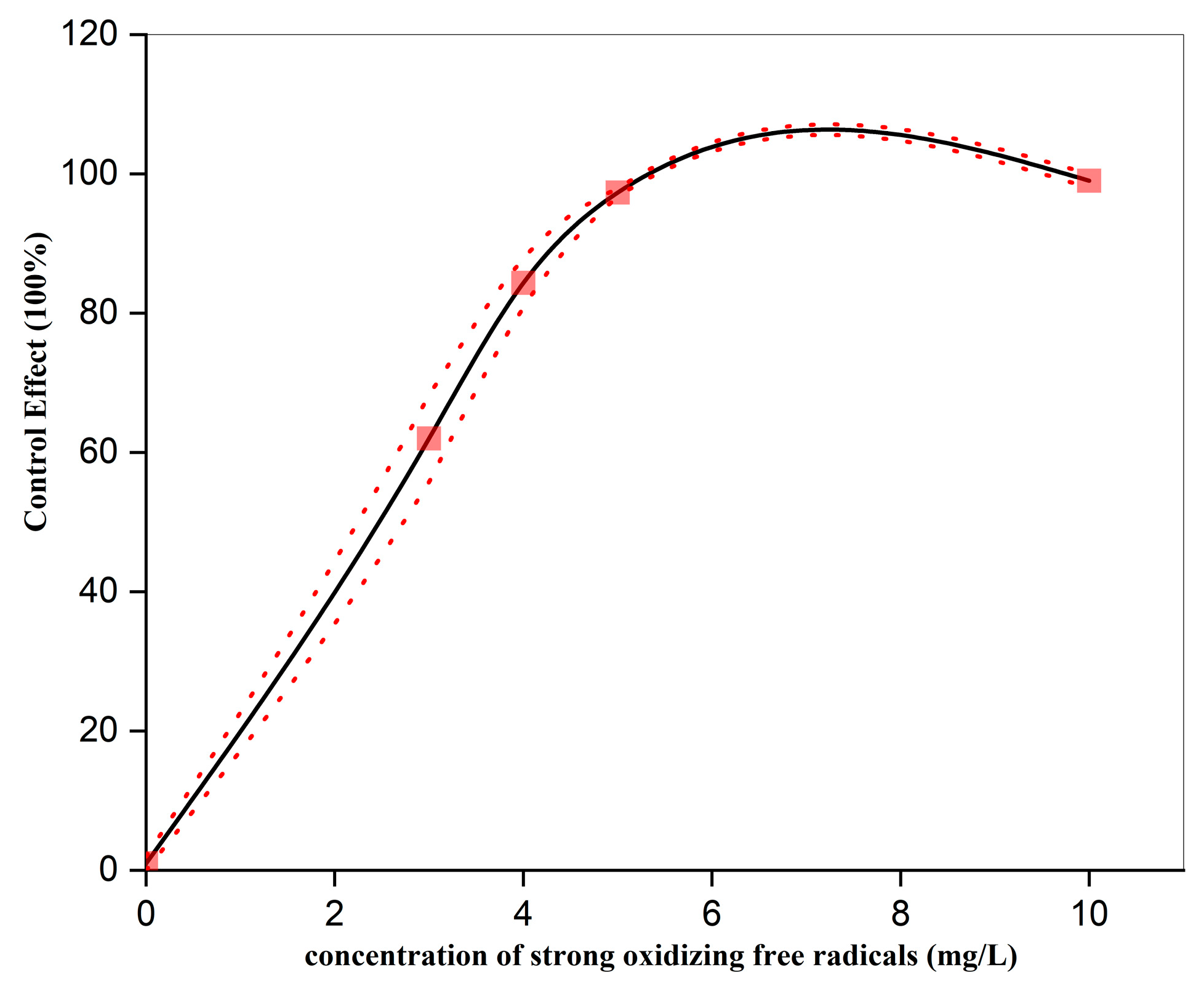
3.1. Effect of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Concentration on the Control of Wheat Powdery Mildew
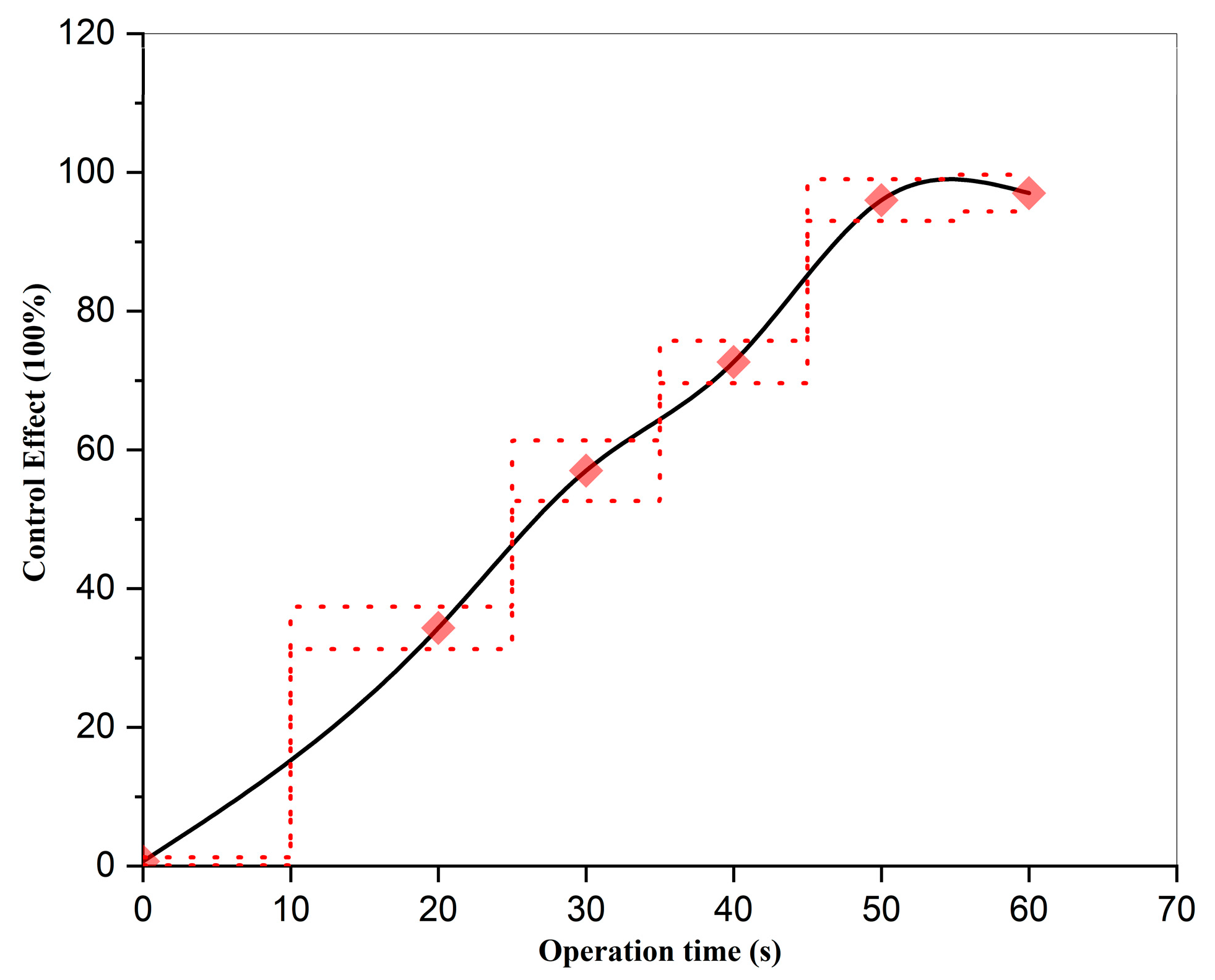
3.2. Effect of Operation Time on the Control Efficacy of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Against Wheat Powdery Mildew
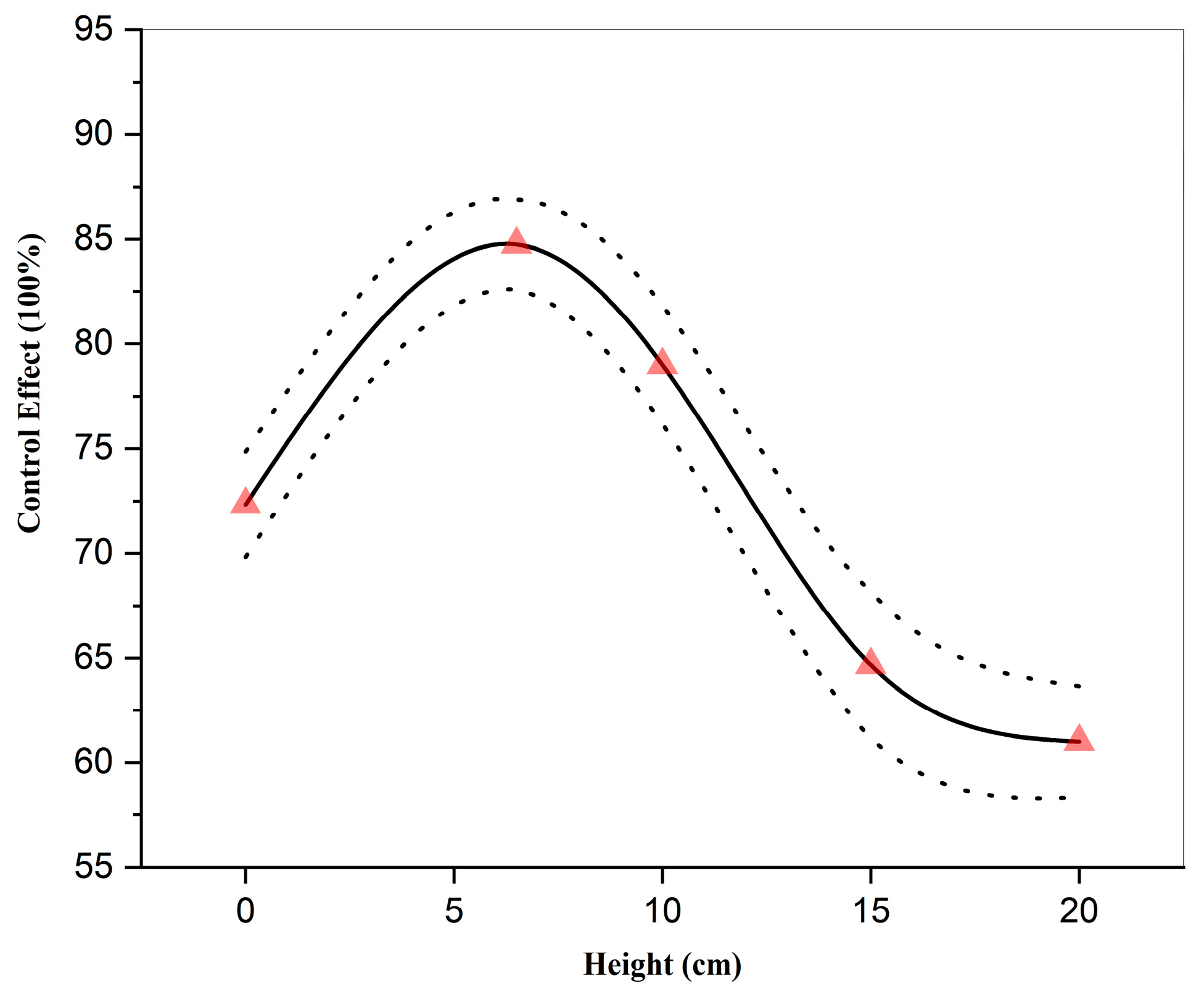
3.3. Effect of Spraying Height on the Control Efficacy of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Against Wheat Powdery Mildew
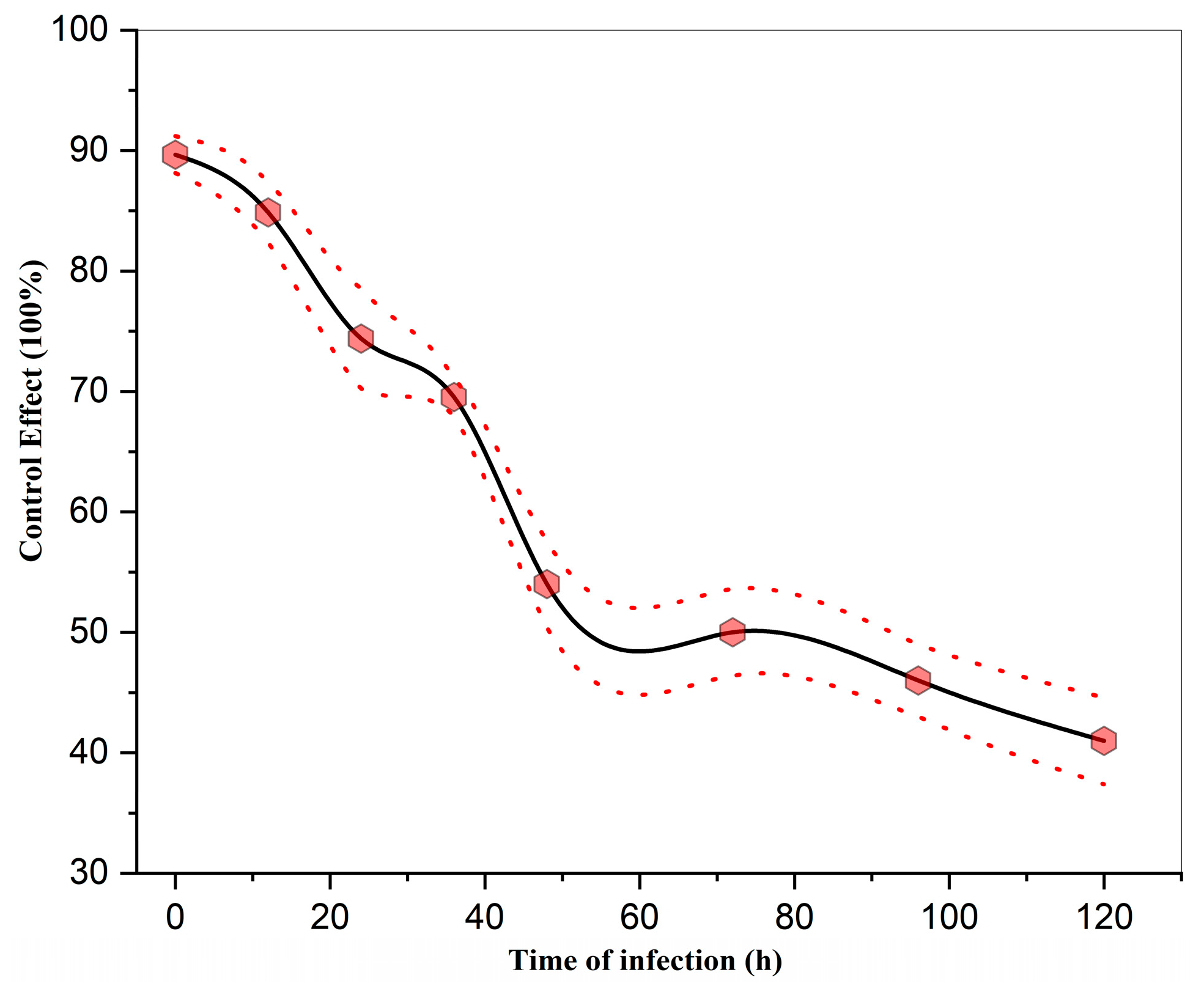
3.4. Effect of Infection Timing on the Control Efficacy of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Against Wheat Powdery Mildew
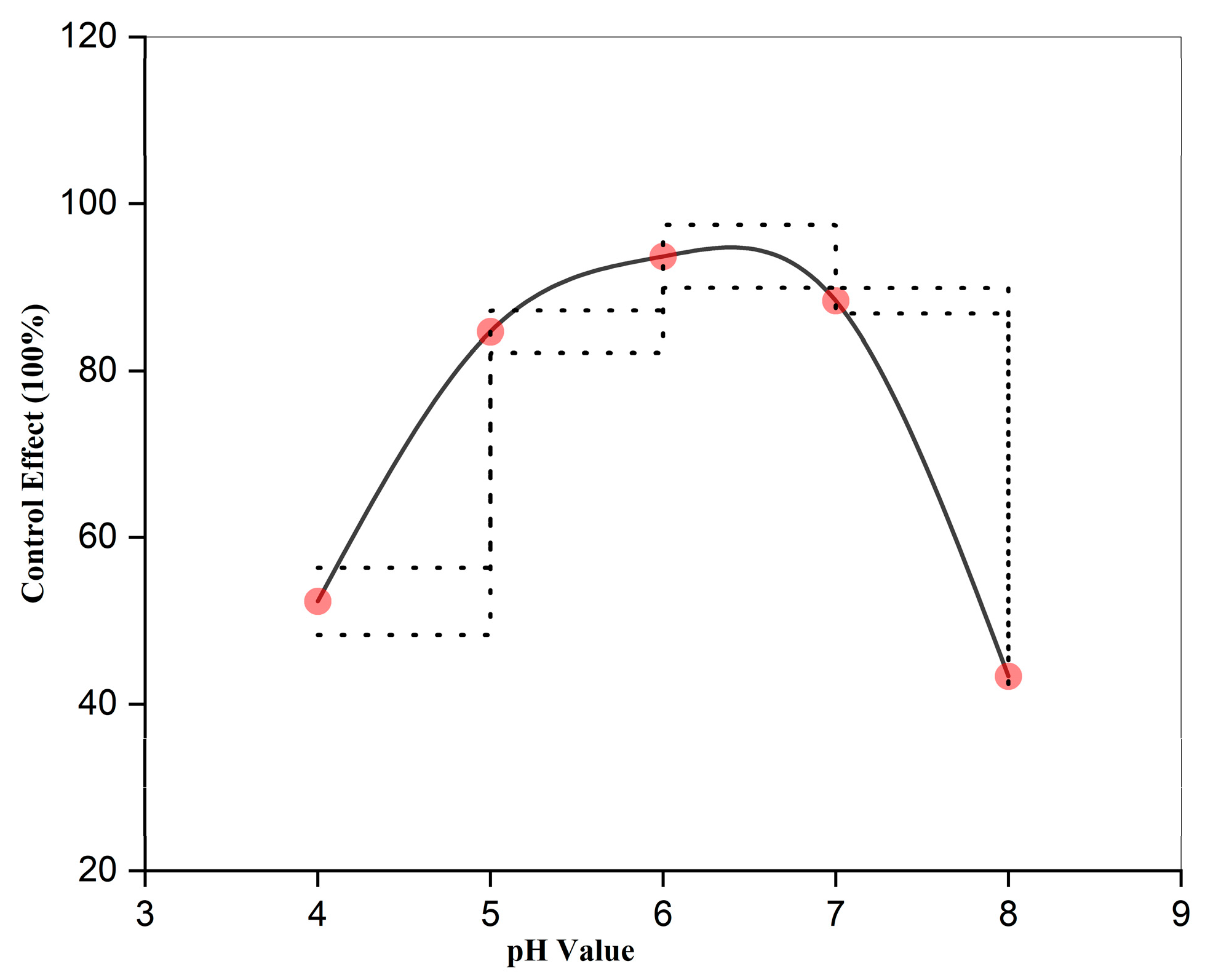
3.5. Effect of pH on the Control Efficacy of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Against Wheat Powdery Mildew
3.6. Box–Behnken Experimental Results
3.6.1. Experimental Results and Model Establishment
3.6.2. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and Significance Test
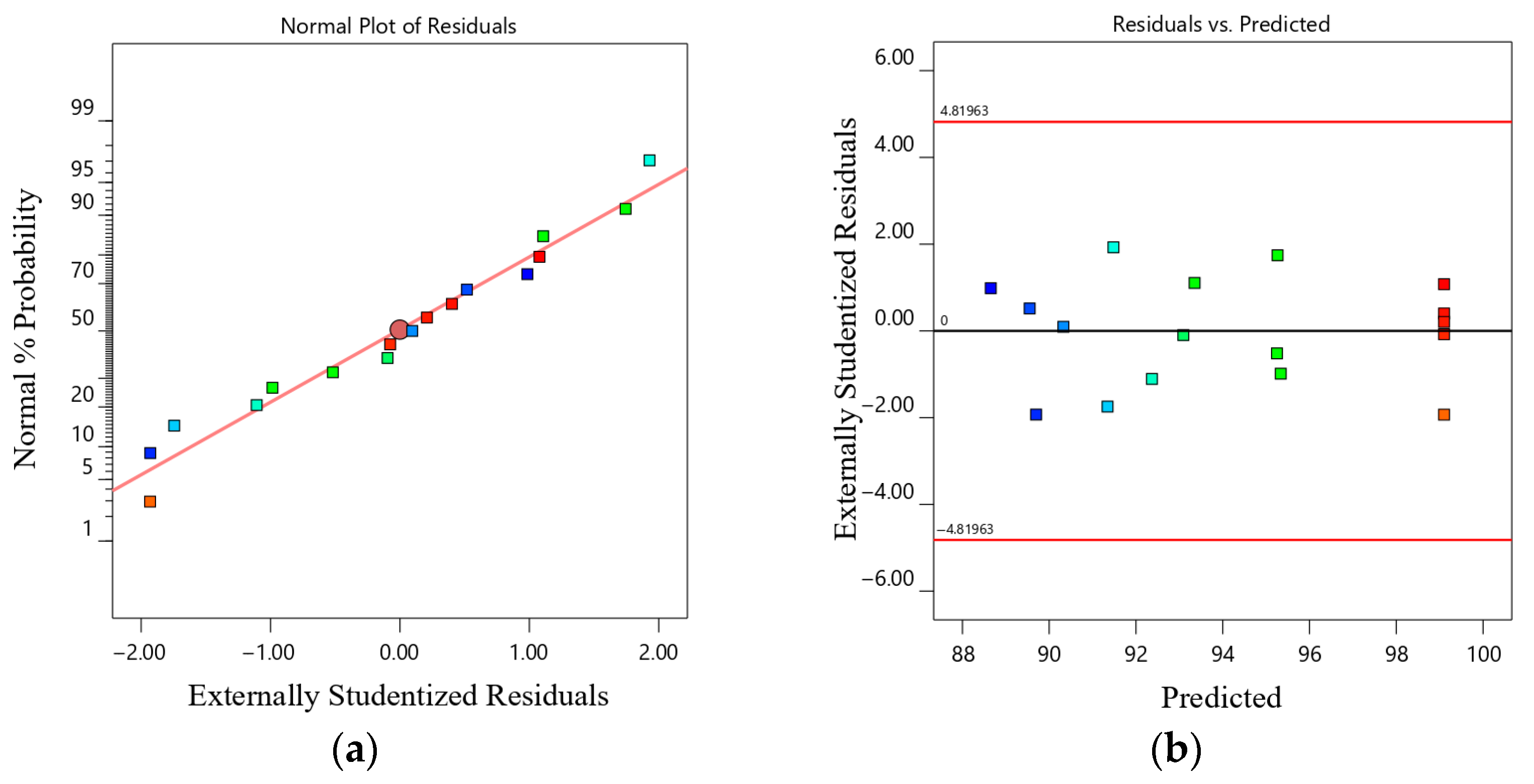
3.6.3. Model Diagnostics and Assumption Validation
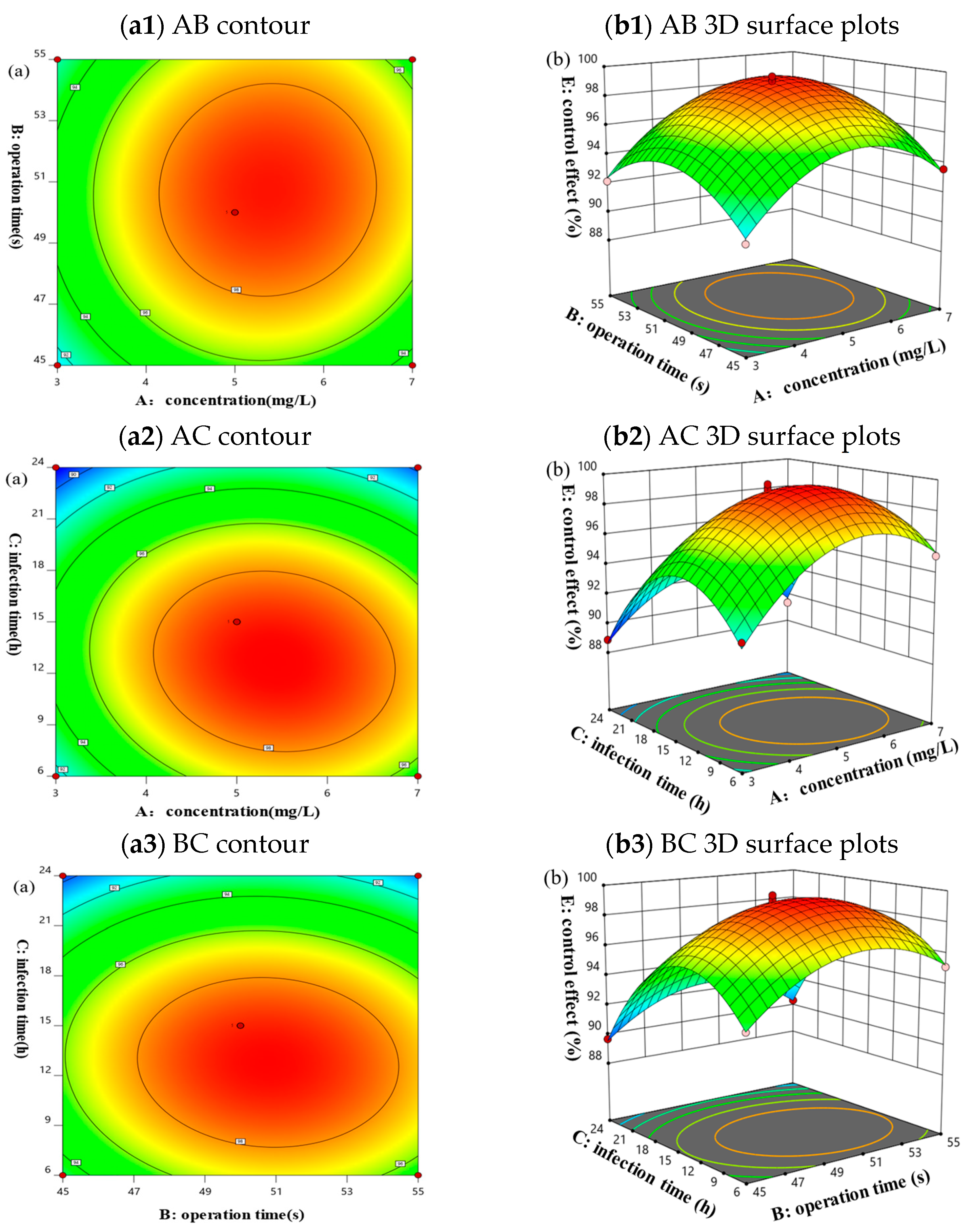
3.6.4. Interaction Analysis Based on Response Surface Methodology
3.6.5. Model Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, B.; Zhao, L.; Chen, H.; Sun, D.; Deng, B.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F. Inactivation of lipase and lipoxygenase of wheat germ with temperature-controlled short wave infrared radiation and its effect on storage stability and quality of wheat germ oil. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Xu, B. Study of the interfacial activity of wheat germ lipase. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2019, 11, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunio, M.H.; Gao, J.; Talpur, M.A.; Lakhiar, I.A.; Chandio, F.A.; Shaikh, S.A.; Solangi, K.A. Effects of different irrigation frequencies and incorporation of rice straw on yield and water productivity of wheat crop. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Sun, B.; Cai, J.; Xu, Y.; Lu, F.; Ma, H. Inspection and classification of wheat quality using image processing. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2023, 15, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.-C.; Liu, C.-H.; Wang, B.-T.; Xue, Y.-R. Genomic and metabolic traits endow Bacillus velezensis CC09 with a potential biocontrol agent in control of wheat powdery mildew disease. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 196, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Guo, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; et al. Genetic and physical mapping of powdery mildew resistance gene MlHLT in Chinese wheat landrace Hulutou. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovics, T.; Komáromi, J.; Fábián, A.; Jäger, K.; Vida, G.; Kiss, L. New insights into the life cycle of the wheat powdery mildew: Direct observation of ascosporic infection in Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Dong, L.; Han, X.; Jin, H.; Yin, C.; Han, Y.; Li, B.; Qin, H.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Q.; et al. The TuMYB46L-TuACO3 module regulates ethylene biosynthesis in einkorn wheat defense to powdery mildew. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 2526–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo-Garcia, J.; Spencer, D.; Thieron, H.; Reinstädler, A.; Hammond-Kosack, K.; Phillips, A.L.; Panstruga, R. mlo-based powdery mildew resistance in hexaploid bread wheat generated by a non-transgenic TILLING approach. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sönmezoğlu, Ö.A.; Yildirim, A.; Türk, Ü.; Yanar, Y. Bazı yerel makarnalık buğday çeşitlerinde küllemeye (Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici) karşı da-yanıklılığın belirlenmesi. Avrupa Bilim Ve Teknol. Derg. 2019, 17, 944–950. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, M.; Tang, C.; Wang, R.; Cao, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Li, M.; Wu, L. A novel nanocomposite that effectively prevents powdery mildew infection in wheat. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 279, 153858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lück, S.; Strickert, M.; Lorbeer, M.; Melchert, F.; Backhaus, A.; Kilias, D.; Seiffert, U.; Douchkov, D. “Macrobot”: An automated segmentation-based system for powdery mildew disease quantification. Plant Phenomics 2020, 2020, 5839856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Guo, X.; Tian, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Q.; Chen, H.; Yang, H. Control of wheat powdery mildew using fluopyram seed treatment. Pest Manag. Sci. 2025, 81, 3328–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, D.; Cai, X.; Yang, C.; Xie, L.; Qin, G.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Gong, G.; Chang, X.; Chen, H. Studies on the control effect of Bacillus subtilis on wheat powdery mildew. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 4375–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.-J.; Yin, Y.-N.; Yang, Y.-A.; Liang, Y.-Q.; Shan, Y.-T.; Zhang, C.-F.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Liang, Z.-P. Antagonistic Activity and Mechanism of Bacillus subtilis XZ16-1 Suppression of Wheat Powdery Mildew and Growth Promotion of Wheat. Phytopathology 2022, 112, 2476–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzen, N.; Heick, T.M.; Jørgensen, L.N. Control of powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis spp.) in cereals by Serenade® ASO (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (former subtilis) strain QST 713). Biol. Control. 2019, 139, 104067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twamley, T.; Gaffney, M.; Feechan, A. A microbial fermentation mixture primes for resistance against powdery mildew in wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, R.; Jiang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Ji, J.; Qiu, D.; Li, H.; Bie, T. Pm21, Encoding a Typical CC-NBS-LRR Protein, Confers Broad-Spectrum Resistance to Wheat Powdery Mildew Disease. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Li, M.; Wu, H.; Zhang, D.; Dong, L.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Lu, P.; Guo, G.; et al. Fine mapping of powdery mildew resistance gene MlWE74 derived from wild emmer wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. dicoccoides) in an NBS-LRR gene cluster. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Merry, A.; Barry, K. Mechanisms of powdery mildew resistance of wheat—A review of molecular breeding. Plant Pathol. 2020, 69, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Chun, W.; Ke, H.; Shan, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, C. Killing of Escherichia coli by Exogenous Hydroxyl Radicals. In Proceedings of the 2010 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.; Song, W. Research on the Feasibility of Spraying Micro/Nano Bubble Ozonated Water for Airborne Disease Prevention. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2015, 37, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Duan, Y.; Fan, W.; Guo, T.; Huo, M.; Yang, W.; Zhu, S.; An, W. Intensifying ozonation treatment of municipal secondary effluent using a combination of microbubbles and ultraviolet irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 21915–21924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatgilialoglu, C.; Ferreri, C.; Krokidis, M.G.; Masi, A.; Terzidis, M.A. On the relevance of hydroxyl radical to purine DNA damage. Free Radic. Res. 2021, 55, 384–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebicki, J.M. Oxidative stress, free radicals and protein peroxides. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 595, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ji, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Sun, C. Fate of deoxynivalenol and degradation products degraded by aqueous ozone in contaminated wheat. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Shao, H.; Chen, Z. Effect of deoxynivalenol detoxification by ozone treatment in wheat grains. Food Control 2016, 66, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, F.; Faccini, M.; Fitarelli, F.; Ortiz, M.A.L.; Salmeron, S.; Oliveira, R.C.G.; Valarelli, F.P.; Oliveira, R.C.; Freitas, K.M.S. In Vitro Comparison of Antibacterial Effect of Ozonated Water and Ozonated Gas. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2020, 43, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaidez, C.; Lopez, J.; Vidales, J.; Campo, N.C.-D. Efficacy of chlorinated and ozonated water in reducing Salmonella typhimurium attached to tomato surfaces. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2007, 17, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Ma, F.; Li, P.-W.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X.-X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.-R.; Xu, B.-C. Effect of ozone on aflatoxins detoxification and nutritional quality of peanuts. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contigiani, E.V.; Kronberg, M.F.; Sánchez, G.J.; Gómez, P.L.; García-Loredo, A.B.; Munarriz, E.; Alzamora, S.M. Ozone washing decreases strawberry susceptibility to Botrytis cinerea while maintaining antioxidant, optical and sensory quality. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittoe, D.K.; Feye, K.M.; Peyton, B.; Worlie, D.; Draper, M.J.; Ricke, S.C. The Addition of Viriditec(TM) Aqueous Ozone to Peracetic Acid as an Antimicrobial Spray Increases Air Quality While Maintaining Salmonella Typhimurium, Non-pathogenic Escherichia coli, and Campylobacter jejuni Reduction on Whole Carcasses. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3180. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, Z.; Kalbasi-Ashtari, A.; Riskowski, G.; Castillo, A. Reduction of Salmonella and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli on alfalfa seeds and sprouts using an ozone generating system. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 289, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.-P.; Zhou, H.-M. Impact of aqueous ozone mixing on microbiological, quality and physicochemical characteristics of semi-dried buckwheat noodles. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowron, K.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Grudlewska, K.; Białucha, A.; Wiktorczyk, N.; Bartkowska, A.; Kowalska, M.; Kruszewski, S.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Biocidal Effectiveness of Selected Disinfectants Solutions Based on Water and Ozonated Water against Listeria monocytogenes Strains. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savi, G.D.; Piacentini, K.C.; Bittencourt, K.O.; Scussel, V.M. Ozone treatment efficiency on Fusarium graminearum and deoxynivalenol degradation and its effects on whole wheat grains (Triticum aestivum L.) quality and germination. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2014, 59, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cheng, Z.; Liang, Y.; Hu, X.; Shen, T.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X. A Novel Strategy for Accelerating Pumpable Ice Slurry Production with Ozone Micro–Nano Bubbles and Extending the Shelf Life of Larimichthys polyactis. Foods 2023, 12, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustapha, A.T.; Zhou, C. Novel assisted/unassisted ultrasound treatment: Effect on respiration rate, ethylene production, enzymes activity, volatile composition, and odor of cherry tomato. LWT 2021, 149, 111779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.-W.; Li, D.-D.; Aheto, J.H.; Qi, Z.-Y.; Reziwanguli, A.; Cai, J.-R.; Tian, X.-Y. Effects of three emerging non-thermal pretreatments on Drying kinetics, Physicochemical Quality, and microstructure of garlic slices. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 4325–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, B.; Zhao, R.; Jiang, Z.; Bie, T. Genetic, physical and comparative mapping of the powdery mildew resistance gene Pm21 originating from Dasypyrum villosum. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Effect of different concentrations of ozone on in vitro plant pathogens development, tomato yield and quality, photosynthetic activity and enzymatic activities. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni, E.; Moroni, C.; Cigarini, M.; Brindani, D.; Cardoso, C.C.; Imperiale, D. Effect of Ozonized Water against Pathogenic Bacteria and Filamentous Fungi on Stainless Steel. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Ishizuka, S.; Tonokura, K.; Sato, K.; Inomata, S.; Enami, S. Effects of pH on Interfacial Ozonolysis of α-Terpineol. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 7148–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Jiang, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Experimental study on forced ventilation and dust-control in a heading face based on response surface method. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 175, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdi, H.; Esfahani, J.; Mohebbi, M. Optimization of convective drying by response surface methodology. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Hou, K.; He, H.; Zhu, S.; Shi, L.; Yi, C.; Chu, J. Killing of Bacillus subtilis by Exogenous Hydroxyl Radicals. In Proceedings of the 2011 5th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Wuhan, China, 10–12 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Li, M.; Bian, K. Recent progress in the degradation effects of mycotoxins in food with ozone and the related influencing factors. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 282–286. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, K.; Fujii, T. Effects of Spraying Ozonated Water on the Severity of Powdery Mildew Infection on Cucumber Leaves. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2002, 24, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wu, C.; Qiao, K. Increasing spray volume and ozone spray of tetraconazole improve control against strawberry powdery mildew. Crop Prot. 2024, 179, 106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hong, B.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Z. Application Effect of O3 on Control Disease & Pest for Greenhouse Vegetables. Agric. Eng. 2012, 2, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, K.; Fujii, T.; Park, J.-S. Comparison of Foliar Spray Efficacy of Electrolytically Ozonated Water and Acidic Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water for Controlling Powdery Mildew Infection on Cucumber Leaves. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2009, 31, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Li, D.; Xu, G.; Sun, Y.; Han, B.; Shi, L. Effects of ozone sterilization on field disease incidence, yield and quality of tomato and pepper in greenhouse. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 30, 2769–2774. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Che, H.; He, Q.; Wang, L.; Yao, B. Effect of ozone sterilization on controlling leaf mildew and gray mold tomato disease in a glasshouse and its influence on other growth parameters. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 4097–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Factor | Unit | −1 | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: concentration | mg/L | 3 | 5 | 7 |
| B: operation time | s | 45 | 50 | 55 |
| C: infection time | h | 6 | 15 | 24 |
| NO. | A/Concentration (mg/L) | B/Operation Time (s) | C/Infection Time (h) (mg/L) | Y/Control Effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 45 | 15 | 91.01 |
| 2 | 7 | 45 | 15 | 93.59 |
| 3 | 3 | 55 | 15 | 92.13 |
| 4 | 7 | 55 | 15 | 95.60 |
| 5 | 3 | 50 | 6 | 91.84 |
| 6 | 7 | 50 | 6 | 95.12 |
| 7 | 3 | 50 | 24 | 88.87 |
| 8 | 7 | 50 | 24 | 89.34 |
| 9 | 5 | 45 | 6 | 93.07 |
| 10 | 5 | 55 | 6 | 95.13 |
| 11 | 5 | 45 | 24 | 89.67 |
| 12 | 5 | 55 | 24 | 90.35 |
| 13 | 5 | 50 | 15 | 98.46 |
| 14 | 5 | 50 | 15 | 99.27 |
| 15 | 5 | 50 | 15 | 99.19 |
| 16 | 5 | 50 | 15 | 99.07 |
| 17 | 5 | 50 | 15 | 99.52 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 232.15 | 9 | 25.79 | 134.27 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| A (concentration) | 12.01 | 1 | 12.01 | 62.49 | <0.0001 | ** |
| B (operation time) | 4.31 | 1 | 4.31 | 22.42 | 0.0021 | ** |
| C (infection time) | 35.83 | 1 | 35.83 | 186.50 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AB | 0.1980 | 1 | 0.1980 | 1.03 | 0.3438 | - |
| AC | 1.97 | 1 | 1.97 | 10.28 | 0.0149 | * |
| BC | 0.4761 | 1 | 0.4761 | 2.48 | 0.1594 | - |
| A2 | 48.42 | 1 | 48.42 | 252.03 | <0.0001 | ** |
| B2 | 29.09 | 1 | 29.09 | 151.43 | <0.0001 | ** |
| C2 | 82.20 | 1 | 82.20 | 427.90 | <0.0001 | |
| Residual | 1.34 | 7 | 0.1921 | - | - | |
| Lack of fit | 0.7209 | 3 | 0.2403 | 1.54 | 0.3344 | Not significant |
| Pure error | 0.6239 | 4 | 0.1560 | - | - | - |
| Cor total | 233.49 | 16 | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Du, X.; Wu, C. Optimizing Parameters of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Application for Effective Management of Wheat Powdery Mildew. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081785
Zhang H, Zhang B, He H, Zhang L, Hu X, Du X, Wu C. Optimizing Parameters of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Application for Effective Management of Wheat Powdery Mildew. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081785
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huanhuan, Bo Zhang, Huagang He, Lulu Zhang, Xinkang Hu, Xintong Du, and Chundu Wu. 2025. "Optimizing Parameters of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Application for Effective Management of Wheat Powdery Mildew" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081785
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhang, B., He, H., Zhang, L., Hu, X., Du, X., & Wu, C. (2025). Optimizing Parameters of Strong Oxidizing Free Radicals Application for Effective Management of Wheat Powdery Mildew. Agronomy, 15(8), 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081785







