The Rise of Eleusine indica as Brazil’s Most Troublesome Weed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biology of Eleusine indica
3. Impacts of Eleusine indica on Agriculture
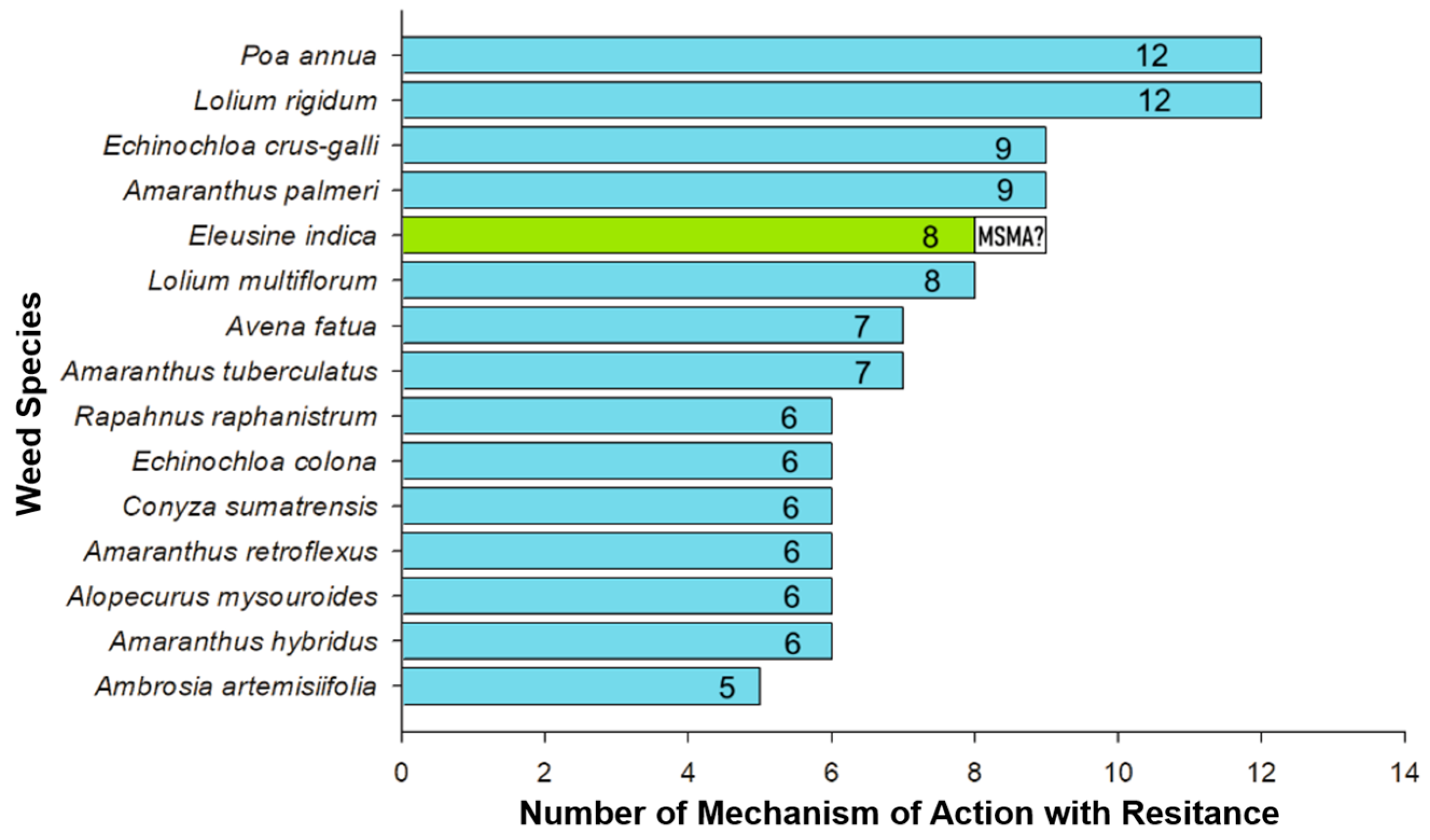
4. Herbicide Resistance in Eleusine indica
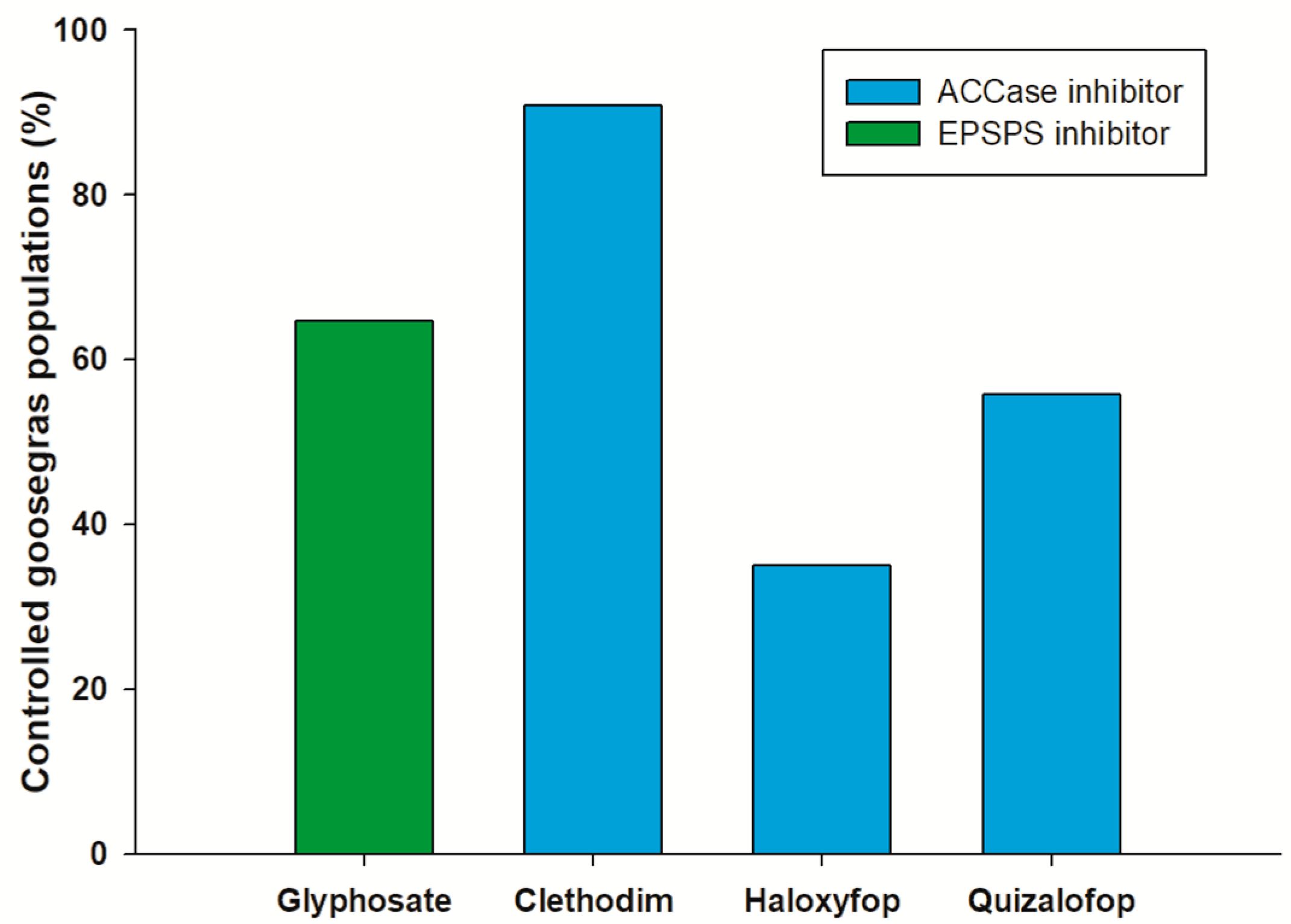
5. Resistance Mechanisms of Eleusine indica to Glyphosate
6. Resistance Mechanisms of Eleusine indica to Other Herbicides
7. Control Methods for Herbicide-Resistant Eleusine indica
7.1. Preventive Control
7.2. Cultural Control
7.3. Mechanical Control
7.4. Physical Control
7.5. Chemical Control
7.5.1. Post-Emergence Herbicides
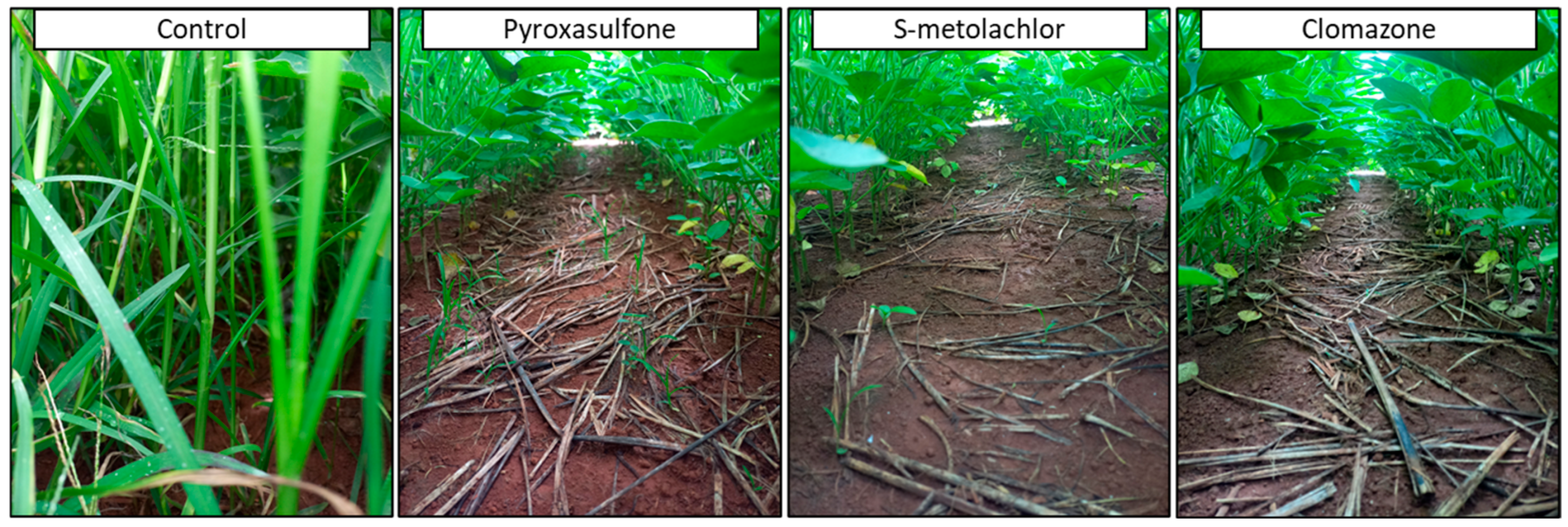
7.5.2. Pre-Emergence Herbicides
8. Challenges and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centro de Estudos Avançados em Economia Aplicada (CEPEA). PIB Do Agronegócio Brasileiro. 2024. Available online: https://cepea.esalq.usp.br/br/pib-do-agronegocio-brasileiro.aspx (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Alcántara-de la Cruz, R.; De Oliveira, G.M.; De Carvalho, L.B.; Silva, M.F.G.F. Herbicide resistance in Brazil: Status, impacts, and future challenges. In Pests, Weeds and Diseases in Agricultural Crop and Animal Husbandry Production; Kontogiannatos, D., Kourti, A., Mendes, K.M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 153–178. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Karaca, E.; Russell, D.; McElroy, S.; Maity, A. Biology and Status of Herbicide Resistant Goosegrass and its Control Options in Alabama. Available online: https://plainspress.scholasticahq.com/article/127714-biology-and-status-of-herbicide-resistant-goosegrass-and-its-control-options-in-alabama (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Oliveira, C.; Mathioni, S.; Thomasi, R.; Ozório, E.; Lemes, L.; Barcellos, L.; Correia, N.M. Goosegrass Multiple-Resistant to Glyphosate, Haloxyfop-Metyl and Clethodim in Brazil. Proceedings of the XXXIII Congresso Brasileiro da Ciência das Plantas Daninhas. 2024. Available online: https://sbcpd.org/uploads/trabalhos/xxxiii-congresso-brasileiro-da-ciencia-das-plantas-daninhas-2024-877.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Heap, I.; Duke, S.O. Overview of glyphosate-resistant weeds worldwide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I. The International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database. Available online: http://www.weedscience.org (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Lee, L.J.; Ngim, J. A first report of glyphosate-resistant goosegrass (Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn) in Malaysia. Pest Manag. Sci. Former. Pestic. Sci. 2000, 56, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.K.; Mendes, R.R.; Scoz, L.B.; Ovejero, R.F.L.; Constantin, J.; Gaines, T.A.; Westra, P.; Dayan, F.; Oliveira, R.S. Proline-106 EPSPs mutation imparting glyphosate resistance in goosegrass (Eleusine indica) emerges in South America. Weed Sci. 2019, 67, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, R.A.; Portes, E.D.S.; Lamego, F.P.; Trezzi, M.M. Resistência de Eleusine indica aos inibidores de ACCase. Planta Daninha 2006, 24, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, N.M.; Araújo, L.S.; Bueno, R.A. First report of multiple resistance of goosegrass to herbicides in Brazil. Adv. Weed Sci. 2022, 40, 020220007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.J.; Werle, R.; Freitas, M.A.D.; Cunha, P.C.D. Multiple resistance in goosegrass to clethodim, haloxyfop-methyl and glyphosate. Adv. Weed Sci. 2022, 40, 020220055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.; Karam, D.; Vargas, L.; Adegas, F.S.; Gazziero, D.L.P.; Ikeda, F.S.; Cavalieri, S.D.; Costa, A.G.F.; Perina, F.J. Monitoramento De Plantas Daninhas Resistentes a Glifosato no Brasil. 2021. Available online: https://www.infoteca.cnptia.embrapa.br/infoteca/bitstream/doc/1136521/1/BOL-234-Monitoramento-plantas-resistentes-glifosato.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Takano, H.K.; Oliveira, R.S.; Constantin, J.; Braz, G.B.P.; Padovese, J.C. Growth, development and seed production of goosegrass. Planta Daninha 2016, 34, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.F.; Henckes, J.R.; Zobiole, L.H.S.; Oliveira, R.S.; Braz, G.B.P.; Constantin, J.; Machado, F.G.; Amarante, A.A.; Ferreira, C.J.B. Competitive response of maize against glyphosate-resistant Digitaria insularis and Eleusine indica. Crop Prot. 2024, 183, 106760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettebong, O.E.; Ubolom, P.M.E.; Obot, D. A systematic review on Eleusine Indica (L.) Gaertn.: From ethnomedical uses to pharmacological activities. J. Med. Plants Stud. 2020, 8, 262–274. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, B.S.; Johnson, D.E. Germination ecology of goosegrass (Eleusine indica): An important grass weed of rainfed rice. Weed Sci. 2008, 56, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, R.K.; Mccarty, L.B. Fluctuating temperature and light influence seed germination of goosegrass (Eleusine indica). Weed Sci. 1997, 45, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitelli, R.A. Competição e controle das plantas daninhas em áreas agrícolas. IPEF 1987, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sawaris, H. Capim-pé-de-Galinha e Capim-Amargoso: Manejo e Impacto na Cultura do Milho. Available online: https://xurl.ooo/5nkbj (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Duarte, E.; Peña, G.D.; Alves, M.A.; Da Silva, M.H.; Da Costa, E.A.; Sauer, A.V. Eficiência do produto reator (clomazona) para o controle de buva (Conyza spp.) e capim-pé-de-galinha (Eleusine indica) na cultura de soja. Rev. Científica Multidiscip. ISSN 2024, 5, 514763. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade Junior, E.R.; Cavenaghi, A.L.; Guimarães, S.C.; Scoz, L.B. Capim-pé-de-galinha (Eleusine indica) em Mato Grosso: Resistência a herbicidas inibidores da ACCase e indicação de sítios de ação alternativos. Circ. Técnica Inst. Mato Grossense Algodão 2018, 38, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Lucio, F.R.; Kalsing, A.; Adegas, F.S.; Rossi, C.V.S.; Correia, N.M.; Gazziero, D.L.P.; Silva, A.F. Dispersal and frequency of glyphosate-resistant and glyphosate-tolerant weeds in soybean-producing edaphoclimatic microregions in Brazil. Weed Technol. 2019, 33, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento (CONAB). Produtos 360. Brasília: Conab. Available online: https://portaldeinformacoes.conab.gov.br/produtos-360.html (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Correia, N.M.; Barcellos Júnior, L.H. Impactos de La Pata de Gallo en Los Cultivos de Soja y la Importancia del Manejo Integrado. Available online: https://revistacultivar-es.com/articulos/Impactos-del-pasto-de-gallina-en-los-cultivos-de-soja-y-la-importancia-del-manejo-integrado (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Mendes, R.R.; Takano, H.K. Resistência de capim-pé-de-galinha (Eleusine indica) a herbicidas. In Capim-pé-de-Galinha: Fundamentos e Recomendações Para Manejo; Albrecht, A.J.P., Biffe, D.F., Braz, G.B.P., Constantin, J., Albrecht, L.P., Oliveira, R.S., Eds.; FEPAF: Botucatu, Brazil, 2025; pp. 37–66. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, M.F.; Brighenti, A.M. Controle de Plantas Daninhas: Métodos físico, Mecânico, Cultural, Biológico e Alelopatia; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2018; p. 196. [Google Scholar]
- Mudge, L.C.; Gossett, B.J.; Murphy, T.R. Resistance of Goosegrass (Eleusine indica) to Dinitroaniline Herbicides. Weed Sci. 1984, 32, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, B.E.; Chaves, L.; González, J.; Garita, I. Field Evolved Imazapyr Resistance in Ixophorus unisetus and Eleusine indica in Costa Rica. In Brighton Crop Protection Conference–Weeds. Proceedings of International Conference; British Crop Protection Council: Brighton, UK, 1993; pp. 1189–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, G.E.; Kirwood, R.C. The Basis of Resistance Displayed to Fluazifop-Butyl by Biotypes of Eleusine indica. In Brighton Crop Protection Conference–Weeds. Proceedings of International Conference; British Crop Protection Council: Brighton, UK, 1993; pp. 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Buker, R.S.; Steed, S.T.; Stall, W.M. Confirmation and control of a Paraquat-Tolerant Goosegrass (Eleusine indica) Biotype. Weed Technol. 2002, 16, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, J.T.; Nishimoto, R.K.; DeFrank, J. Metribuzin-Resistant Goosegrass (Eleusine indica) in Bermudagrass Turf. Weed Technol. 2008, 22, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaludin, A.; Ngim, J.; Bakar, B.H.J.; Alias, Z. Preliminary Findings of Potentially Resistant Goosegrass (Eleusine indica) to Glufosinate-Ammonium in Malaysia. Weed Biol. Manag. 2010, 10, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, J.S.; Head, W.B.; Wehtje, G.R.; Spak, D. Identification of goosegrass (Eleusine indica) biotypes resistant to preemergence-applied oxadiazon. Weed Technol. 2017, 31, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, C.T.; Van Lun, L.O.W.; San, C.T.; Sahid, I.B. Initial report of glufosinate and paraquat multiple resistance that evolved in a biotype of goosegrass (Eleusine indica) in Malaysia. Weed Biol. Manag. 2010, 10, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shan, B.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Yu, H.; Cui, H.; Li, X. Unraveling the mechanisms of multiple resistance across glyphosate and glufosinate in Eleusine indica. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 206, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaludin, A.; Yu, Q.; Powles, S.B. Multiple resistance across glufosinate, glyphosate, paraquat and ACCase-inhibiting herbicides in an Eleusine indica population. Weed Res. 2015, 55, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, G.; Hoyos, V.; Vázquez-García, J.G.; Alcántara-de la Cruz, R.; De Prado, R. First Case of Multiple Resistance to EPSPS and PSI in Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn. Collected in Rice and Herbicide-Resistant Crops in Colombia. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Q.; Lu, B.; Jin, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L. Multiple herbicide resistance in Eleusine indica from sugarcane fields in China. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 182, 105040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azlan, M.I.; Kamarudin, K.N.; Chuah, T.S. Preliminary investigation of multiple resistance in goosegrass (Eleusine indica) to premix of diuron and MSMA, glyphosate, clethodim, quizalofop in Malaysia. Adv. Weed Sci. 2025, 43, 020250119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Xia, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, J.; Yuan, S. Cyhalofop-butyl and glyphosate multiple-herbicide resistance evolved in an Eleusine indica population collected in Chinese direct-seeding rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2623–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, S.; Huang, H.; Cui, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Characterization of glyphosate and quizalofop-p-ethyl multiple resistance. Eleusine indica. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 176, 104862. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanizadeh, H.; Buddenhagen, C.E.; Harrington, K.C.; James, T.K. The genetic inheritance of herbicide resistance in weeds. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2019, 38, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.K.; Oliveira, R.S.; Constantin, J.; Silva, V.F.V.; Mendes, R.R. Chemical control of glyphosate-resistant goosegrass. Planta Daninha 2018, 36, 018176124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, M.B.; Göergen, A.B.; Pedrollo, N.T.; Rubert, J.; Dornelles, S.H.B.; Lopes, S.J. Goosegrass: Morphophysiological Characterization Under Water Excess Conditions. Planta Daninha 2019, 37, 019180844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerson, S.R.; Rodriguez, D.J.; Tran, M.; Feng, Y.; Biest, N.A.; Dill, G.M. Glyphosate-resistant goosegrass. Identification of a mutation in the target enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Vila-Aiub, M.M.; Jalaludin, A.; Yu, Q.; Powles, S.B. A double EPSPS gene mutation endowing glyphosate resistance shows a remarkably high resistance cost. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 3031–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Jalaludin, A.; Han, H.; Chen, M.; Sammons, R.D.; Powles, S.B. Evolution of a double amino acid substitution in the 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase in Eleusine indica conferring high-level glyphosate resistance. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wei, S.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Mutations and amplification of EPSPS gene confer resistance to glyphosate in goosegrass (Eleusine indica). Planta 2015, 242, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherekhloo, J.; Fernández-Moreno, P.T.; Alcántara-de la Cruz, R.; Sánchez-González, E.; Cruz-Hipolito, H.E.; Domínguez-Valenzuela, J.A.; De Prado, R. Pro-106-Ser mutation and EPSPs overexpression acting together simultaneously in glyphosate resistant goosegrass (Eleusine indica). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, C.J.; Yu, Q.; Guo, W.L.; Zhang, T.J.; Tian, X.S. Evolution of multiple target-site resistance mechanisms in individual plants of glyphosate-resistant Eleusine indica from China. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 4810–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Wei, S.; Cui, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, C. Glyphosate resistance in Eleusine indica: EPSPS overexpression and P106A mutation evolved in the same individuals. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 164, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; D’avignon, D.A.; Ackerman, J.J.; Sammons, R.D. In vivo 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance studies of glyphosate uptake, vacuolar sequestration, and tonoplast pump activity in glyphosate-resistant horseweed. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Duan, Z.; Li, Y.; Peng, C.; Yuan, S. Multiple resistance mechanisms involved in glyphosate resistance in Eleusine indica. Plants 2022, 11, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amhrein, N.; Martinoia, E. An ABC transporter of the ABCC subfamily localized at the plasma membrane confers glyphosate resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 2104746118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yu, Q.; Han, H.; Mao, L.; Nyporko, A.; Fan, L.; Powles, S. Aldo-keto reductase metabolizes glyphosate and confers glyphosate resistance in Echinochloa colona. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 1519–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Tian, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Yu, Q.; Bai, L.; Pan, L. Glyphosate resistance in Eleusine indica: Involvement of CYP71AK44 in addition to EPSPS gene overexpression. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 23758–23765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, L.S.; Correia, N.M.; Tornisielo, V.L.; Labate, M.T.V.; Tsai, S.M.; Carbonari, C.A.; Victoria Filho, R. Capim-pé-de-galinha (Eleusine indica) resistente a múltiplos modos de ação de herbicidas no Brasil. Weed Sci. 2023, 71, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzioli, L.F.; Witter, A.P.W.; Accetti, J.M.S.; Garcia, V.A.N.; Coletta, M.B.D.; Biffe, D.F. Suspeita de Eleusine indica resistente ao herbicida glufosinato de amônio. Proceedings of the XXXIII Congresso Brasileiro da Ciência das Plantas Daninhas. 2024. Available online: https://sbcpd.org/uploads/trabalhos/xxxiii-congresso-brasileiro-da-ciencia-das-plantas-daninhas-2024-877.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Luiz, R.S.; Oliveira Júnior, R.S.; Constantin, J.; Biffe, D.F.; Witter, A.P.W. Estudos preliminares sobre capim-pé-de-galinha (Eleusine indica) possivelmente resistente ao glufosinate. Proceedings of the XXXIII Congresso Brasileiro da Ciência das Plantas Daninhas. 2024. Available online: https://sbcpd.org/uploads/trabalhos/xxxiii-congresso-brasileiro-da-ciencia-das-plantas-daninhas-2024-877.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Takano, H.K.; Ovejero, R.F.L.; Belchior, G.G.; Maymone, G.P.L.; Dayan, F.E. ACCase-inhibiting herbicides: Mechanism of action, resistance evolution and stewardship. Sci. Agric. 2021, 78, 20190102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, P.E.; Yu, J.; Raymer, P.L.; Chen, Z. First report of ACCase-resistant goosegrass (Eleusine indica) in the United States. Weed Sci. 2016, 64, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, T.A.; Duke, S.O.; Morran, S.; Rigon, C.A.; Tranel, P.J.; Küpper, A.; Dayan, F.E. Mechanisms of evolved herbicide resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 10307–10330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna, M.D.; Goulart, I.C.G.D.R.; Vidal, R.A.; Kalsing, A.; Ruiz Santaella, J.P.; De Prado, R. Resistance to ACCase inhibitors in Eleusine indica from Brazil involves a target site mutation. Planta Daninha 2012, 30, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Cha, T.; Najihah, M.G.; Sahid, I.B.; Chuah, T.S. Molecular basis for resistance to ACCase-inhibiting fluazifop in Eleusine indica from Malaysia. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 111, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Li, Y.; Yao, S.; Duan, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, S. ACCase gene mutations and P450-mediated metabolism contribute to cyhalofop-butyl resistance in Eleusine indica biotypes from direct-seeding paddy fields. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 194, 105530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Délye, C.; Michel, S.; Bérard, A.; Chauvel, B.; Brunel, D.; Guillemin, J.P.; Dessaint, F.; Le Corre, V. Geographical variation in resistance to acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase-inhibiting herbicides across the range of the arable weed Alopecurus myosuroides (black-grass). New Phytol. 2010, 186, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira Freitas, M.L.; Witter, A.P.W.; Nalin, D.; Sanches, A.K.S.; Oliveira Junior, R.S.; Biffe, D.F.; Constantin, J.; Granzioli, L. Primeiro caso de resistência cruzada de capim-pé-de-galinha (Eleusine indica) a inibidores da ACCase no Estado do Paraná. Rev. De Ciências Agroveterinárias 2024, 23, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Liu, M.; Chen, W.; Bai, D.; Liao, Y.; Bai, L.; Pan, L. Eleusine indica cytochrome P450 and glutathione S-transferase are linked to high-level resistance to glufosinate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 14243–14250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, T.; Feng, T.; Wang, L.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L.; Wu, B.; Du, J.; Li, J.; Ma, H. Metabolic resistance mechanism to glufosinate in Eleusine indica. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 204, 106083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Garcia, J.G.; Alcántara-De La Cruz, R.; Rojano-Delgado, A.M.; Palma-Bautista, C.; De Portugal Vasconcelos, J.M.; De Prado, R. Multiple herbicide resistance evolution: The case of Eleusine indica in Brazil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckie, H.J.; Harker, K.N. Our top 10 herbicide-resistant weed management practices. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petelewicz, P.; Macdonald, G.E.; Schiavon, M.; Sánchez-Quintanilla, M.C. Identificación, Biología, y Manejo de Pata de Gallina Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn. en Céspedes de Florida: SS-AGR-488-Span/AG487, 4/2025. Available online: https://doi.org/10.32473/edis-ag487-2025 (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Menegat, A.; Nilsson, A.T. Interaction of preventive, cultural, and direct methods for integrated weed management in winter wheat. Agronomy 2019, 9, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Lei nº 10.711, de 5 de Agosto de 2003. Dispõe Sobre a Política Nacional de Sementes e Mudas e Outras Providências. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/2003/l10.711.htm (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Brasil. Lei nº 14.785, de 2 de Agosto de 2023. Dispõe Sobre Agrotóxicos e Afins Outras Providências. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2023-2026/2023/lei/l14785.htm (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Marochi, A.; Ferreira, A.; Takano, H.K.; Oliveira Júnior, R.S.; Ovejero, R.F.L. Managing glyphosate-resistant weeds with cover crop associated with herbicide rotation and mixture. Ciência E Agrotecnologia 2018, 42, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, C.T.; Basso, F.J.M.; Galon, L.; Agazzi, L.R.; Nonemacher, F.; Concenço, G. Competitive ability of transgenic soybean cultivars coexisting with weeds. Rev. Bras. De Ciências Agrárias 2017, 12, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnhold, S.; Lindner, S.; Lee, B.; Martin, E.; Kettering, J.; Nguyen, T.T.; Koellner, T.; Ok, Y.S.; Huwe, B. Conventional and organic farming: Soil erosion and conservation potential for row crop cultivation. Geoderma 2014, 219, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.C.C.; Ferreira, G.W.D.; Souza, J.L.S.; Vieira, M.E.O.; Pedrotti, A. Soil physical properties and soil organic carbon content in northeast Brazil: Long-term. Sci. Agric. 2020, 77, 20180166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauti, M.S.; Barroso, A.A.M.; Giancotti, P.P.F.; Squassoni, V.L.; Revolti, L.T.M.; Alves, P.L.C.A. Emergence of weed species in relation to seed position and sugarcane straw quantity. Sci. Agrar. 2011, 12, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Salvador, F.L. Germination and Emergence of Weed Species in Relation to Light and Sugarcane Straw (Saccharum spp.). Master’s Thesis, University of São Paulo, Piracicaba, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.C.B.; Lamas, F.M. Espécies vegetais para cobertura do solo: Influência sobre plantas daninhas e a produtividade do algodoeiro em sistema plantio direto. Rev. Ceres 2010, 57, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezutte, A.J.; Calegare, F.; Alves, P.L.; Pitelli, R.A. Eficiência do herbicida oxyfluorfen, quando veiculado ao papel, no controle de algumas espécies daninhas. Planta Daninha 1995, 13, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qasem, J.R. Herbicides applications: Problems and Considerations. In Herbicides and Environment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sistema de Agrotóxicos Fitossanitários. Ministério da Agricultura do Governo Federal. Available online: https://agrofit.agricultura.gov.br/agrofit_cons (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Júnior, L.H.B. (Fundação MT, Rondonópolis, MT, Brazil); Barroso, A.A.M. (UFPR, Curitiba–Paraná Goosegrass monitoring in Mato Grosso State). Unpublished work, 2025.
- Takano, H.K.; Beffa, R.; Preston, C.; Westra, P.; Dayan, F.E. Glufosinate enhances the activity of protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitors. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.K.; Dayan, F.E. Glufosinate-ammonium: A review of the current state of knowledge. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3911–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, F.E.; Barker, A.; Tranel, P.J. Origins and structure of chloroplastic and mitochondrial plant protoporphyrinogen oxidases: Implications for the evolution of herbicide resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, J.L.; Barroso, A.A.M.; Solis-Rosas-Diaz, L.F.; Alvarado-Huamán, L.; Silva, E.; Alves, P.L.D.C.A. Herbicidas pós-emergentes para o controle do capim-pé-de-galinha (Eleusine indica L.) nos estádios de pré-perfilhamento e em perfilhamento. Rev. UDCA Actual. Divulg. Científica 2024, 27, 2361. [Google Scholar]
- Fluttert, J.C.; Soltani, N.; Galla, M.; Hooker, D.C.; Robinson, D.E.; Sikkema, P.H. Additive and synergistic interactions of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) and photosystem II (PSII) inhibitors for the control of glyphosate-resistant horseweed (Conyza canadensis) in corn. Weed Sci. 2022, 70, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerveld, D.B.; Soltani, N.; Hooker, D.C.; Robinson, D.E.; Sikkema, P.H. Efficacy of tiafenacil applied preplant alone or mixed with metribuzin for glyphosate-resistant horseweed control in soybean. Weed Technol. 2021, 35, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, J.R.; Askew, W.L.B.; Askew, S.D. Differences in selectivity between bermudagrass and goosegrass (Eleusine indica) to low-rate topramezone and metribuzin combinations. Weed Sci. 2022, 70, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spricigo, H.; Schenddelfdt, B.F.; Da Silva, R.O.; Hirata, A.C.S.; Monquero, P.A. Manejo de biótipos resistentes de Eleusine indica e de Spermacocea latifolia tolerante ao glifosato com herbicidas pré-emergentes associados à aplicação sequencial de dessecantes. Rev. De Ciências Agroveterinárias 2024, 2, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morota, F.K.; Matte, W.D.; Silva, R.; Biffe, D.F.; Franchini, L.H.M.; Constantin, J. Sistemas de manejo de plantas daninhas utilizando o novo herbicida pyroxasulfone visando ao controle químico de gramíneas em soja. Rev. Bras. De Herbic. 2018, 17, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubiani, L.F. Performance de Herbicidas Pré-Emergentes no Controle de Capim-Pé-de-Galinha na Cultura da Soja. Undergraduate Thesis, Universidade Federal do Paraná, Curitiba, Brazil, 2024. [Google Scholar]
| Active Ingredient | Mode of Action | HRAC Group |
|---|---|---|
| Clethodim | Inhibition of ACCase | 1 |
| Cyhalofop | ||
| Fenoxaprop-ethyl | ||
| Fluazifop-butyl | ||
| Haloxyfop-methyl | ||
| Profoxydim | ||
| Propaquizafop | ||
| Quizalofop-ethyl | ||
| Sethoxydim | ||
| Tepraloxydim | ||
| Nicosulfuron | Inhibition of ALS | 2 |
| Imazapic + imazapyr | ||
| Prometryne | Inhibition of PS II | 5 |
| Propanil | ||
| Glyphosate | Inhibition of EPSPS | 9 |
| Glufosinate-ammonium | Inhibition of GS | 10 |
| Tiafenacil | Inhibition of PPO | 14 |
| Fluroxipyr + Clethodim | Auxin Mimics + Inhibition of ACCase | 4 + 1 |
| Diquat + Flumioxazin | Inhibition of PS I + Inhibition of PPO | 22 + 14 |
| Terbuthylazine + Tolpyralate | Inhibition of PS II + Inhibition of HPPD | 5 + 27 |
| Atrazine + Mesotrione | ||
| Terbuthylazine + Mesotrione |
| Active Ingredient | Mode of Action | HRAC Group |
|---|---|---|
| Pendimethalin | Inhibition of Microtubule Assembly | 3 |
| Trifluralin | ||
| Ametryn | Inhibition of PS II | 5 |
| Amicarbazone | ||
| Atrazine | ||
| Diuron | ||
| Metribuzin | ||
| Simazine | ||
| Tebuthiuron | ||
| Terbuthylazine | ||
| Bixlozone | Inhibition of DXS | 13 |
| Clomazone | ||
| Flumioxazin | Inhibition of PPO | 14 |
| Oxadiazon | ||
| Sulfentrazone | ||
| Oxifluorfen | ||
| Acetochlor | Inhibition of VLCFA | 15 |
| Alachlor | ||
| Pyroxasulfone | ||
| S-metolachlor | ||
| Isoxaflutole | Inhibition of HPPD | 27 |
| Indaziflam | Inhibition of Cellulose Synthesis | 29 |
| Fomesafem + S-metolachlor | Inhibition of PPD + Inhibition of VLCFA | 14 + 15 |
| Isoxaflutole + Thiencarbazone-methyl | Inhibition of HPPD + Inhibition of ALS | 27 + 2 |
| Diuron + Hexazinone | Inhibition of PS II | 5 |
| Alachlor + Atrazine | Inhibition of VLCFA + Inhibition of PS II | 15 + 5 |
| Diclosulam + Halauxifen | Inhibition of ALS + Auxin Mimics | 2 + 4 |
| Indaziflam + Metribuzin | Inhibition of Cellulose Synthesis + Inhibition of PS II | 19, 5 |
| Imazetapyr + Sulfentrazone | Inhibition of ALS + Inhibition of PPO | 2 + 14 |
| Flumioxazin + S-metolachlor | Inhibition of PPO + Inhibition of VLCFA | 14 + 15 |
| Tebuthiuron + Diuron | Inhibition of PS II | 5 |
| Metribuzin + S-metolachlor | Inhibition of PS II + Inhibition of VLCFA | 5, 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcántara-de la Cruz, R.; Silva, L.B.X.d.; Takano, H.K.; Barcellos Júnior, L.H.; Mendes, K.F. The Rise of Eleusine indica as Brazil’s Most Troublesome Weed. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081759
Alcántara-de la Cruz R, Silva LBXd, Takano HK, Barcellos Júnior LH, Mendes KF. The Rise of Eleusine indica as Brazil’s Most Troublesome Weed. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081759
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcántara-de la Cruz, Ricardo, Laryssa Barbosa Xavier da Silva, Hudson K. Takano, Lucas Heringer Barcellos Júnior, and Kassio Ferreira Mendes. 2025. "The Rise of Eleusine indica as Brazil’s Most Troublesome Weed" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081759
APA StyleAlcántara-de la Cruz, R., Silva, L. B. X. d., Takano, H. K., Barcellos Júnior, L. H., & Mendes, K. F. (2025). The Rise of Eleusine indica as Brazil’s Most Troublesome Weed. Agronomy, 15(8), 1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081759








