Soybean Response to Saflufenacil Doses, Alone or Combined with Glyphosate, Simulating Tank Contamination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
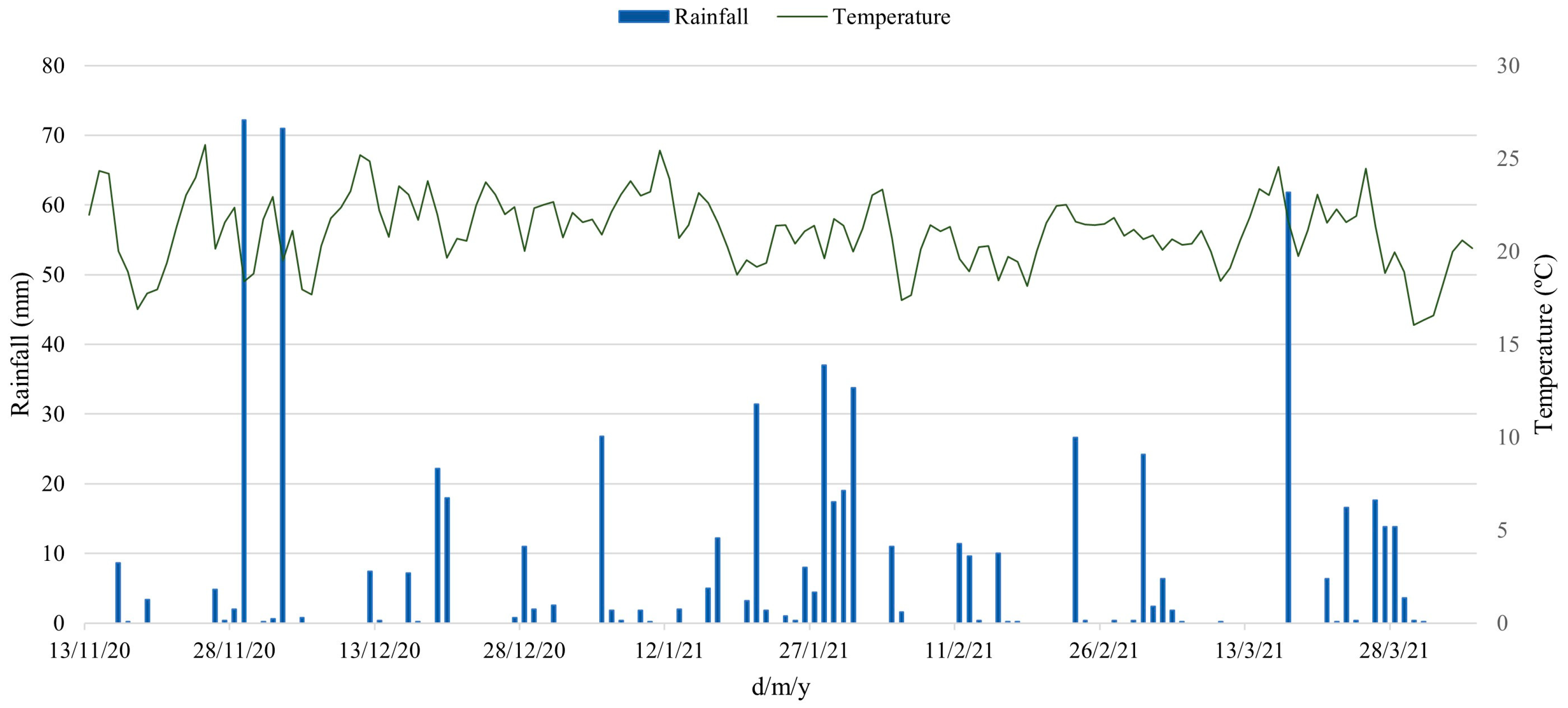
2.1. Description of the Experimental Area
2.2. Treatments and Experimental Design
2.3. Variables Evaluated
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phytotoxicity in Soybean Due to Application of Saflufenacil Alone or Combined with Glyphosate
3.2. Effects of Saflufenacil and Glyphosate, Applied Alone or in Tank Mix, on Soybean Physiology
3.3. Impact of Saflufenacil and Glyphosate, Applied Alone or Combined with Glyphosate, on Soybean Yield Components
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USDA—United States Department of Agriculture. Available online: https://www.usda.gov (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- CONAB—Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento. Monitoring the Brazilian Grain Harvest. Available online: https://www.conab.gov.br/info-agro/safras/graos (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Adegas, F.S.; Correia, N.M.; Silva, A.F.; Concenço, G.; Gazziero, D.L.P.; Dalazen, G. Glyphosate-resistant (GR) soybean and corn in Brazil: Past, present, and future. Adv. Weed Sci. 2022, 40, e0202200102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holkem, A.S.; Silva, A.L.; Bianchi, M.A.; Corassa, G.; Ulguim, A.R. Weed management in Roundup Ready® corn and soybean in Southern Brazil: Survey of consultants’ perception. Adv. Weed Sci. 2022, 40, e020220111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heap, I. The International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database [Internet]. Available online: http://www.weedscience.org (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Liu, X.; Merchant, A.; Xiang, S.; Zong, T.; Zhou, X.; Bai, L. Managing herbicide resistance in China. Weed Sci. 2021, 69, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreja, F.H.; Inman, M.D.; Jordan, D.L.; Vann, M.; Jennings, K.M.; Leon, R.G. Effect of cotton herbicide programs on weed population trajectories and frequency of glyphosate-resistant Amaranthus palmeri. Weed Sci. 2022, 70, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamego, F.P.; Nachtigall, J.R.; Machado, Y.M.S.; Langer, C.O.; Polino, R.C.; Bastiani, M.O. Amaranthus hybridus resistance to glyphosate: Detection, mechanisms involved and alternatives for integrated management. Adv. Weed Sci. 2024, 42, e020240046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavichioli, B.G.; Barbieri, G.F.; Pigatto, C.S.; Leães, G.P.; Kruse, N.D.; Ulguim, A.R. Control and translocation of saflufenacil in fleabane (Conyza spp.) according to plant integrity. Rev. Fac. Nac. Agro Medellín. 2021, 74, 9523–9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreira, M.L.; Côrrea, F.R.; Silva, N.F.; Cavalcante, W.S.S.; Ribeiro, D.F.; Rodrigues, E. Herbicides with potential for desiccation of pre-sowing areas of soybean crops. Braz. J. Sci. 2023, 2, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalazen, G.; Kruse, N.D.; Machado, S.L.O.; Balbinot, A. Synergism in the combination of glyphosate and saflufenacil for the control of horseweed. Pesqui. Agropecu. Trop. 2015, 45, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, N.M. Management and development of fleabane plants in central Brazil. Planta Daninha 2020, 38, e020238215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.K.; Oliveira, R.S., Jr.; Constantin, J.; Osipe, J.B.; Alonso, D.G.; Pagnoncelli, F. Biotypes of Conyza sumatrensis resistant to glyphosate and ALS-inhibiting herbicides. Planta Daninha 2013, 31, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, D.; Song, R. Design and synthesis of novel PPO-inhibiting pyrimidinedione derivatives safed towards cotton. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 193, 105449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnica, V.C.; Jhala, A.J.; Harveson, R.M.; Giesler, L.J. Impact assessment of residual soil-applied pre-emergence herbicides on the incidence of soybean seedling diseases under field conditions. Crop Prot. 2022, 158, e105987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, H.H.; Soares, G.D.D.; Dias-Pereira, J.; Silva, L.C.; Machado, V.M. Impact of safufenacil and glyphosate based herbicides on the morphoanatomical and development of Enterolobium contortisiliquum (Vell.) Morong (Fabaceae): New insights into a non-target tropical tree species. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 31, 61254–61269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, C.L.; Robert, E.; Nurse, R.E.; Cowbrough, M.; Peter, H.; Sikkema, P.H. How long can a herbicide remain in the spray tank without losing efficacy? Crop Prot. 2009, 28, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Nurse, R.E.; Sikkema, P.H. Response of glyphosate-resistant soybean to dicamba spray tank contamination during vegetative and reproductive growth stages. Can. J. Plant. Sci. 2016, 96, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.S.; Vieira, B.C.; Ynfante, R.S.; Santana, T.M.; Moraes, J.G.; Golus, J.A.; Kruger, G.R. Tank contamination and simulated drift effects of dicamba-containing formulations on soybean cultivars. Agrosystems Geosci. Environ. 2020, 3, e20065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuvaca, I.; Knezevic, S.; Scott, J.; Osipitan, O.A. Growth and yield losses of Roundup Ready soybean as influenced by micro-rates of 2,4-D. Sustain. Agric. Res. 2021, 10, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAPA/AGROFIT. Plant Health Agrotsystems–Open Consultation. [Internet]. Available online: http://agrofit.agricultura.gov.br/agrofit_cons/principal_agrofit_cons (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Budd, C.M.; Soltani, N.; Robinson, D.E.; Hooker, D.C.; Miller, R.T.; Sikkema, P.H. Glyphosate-resistant horseweed (Conyza canadensis) dose response to saflufenacil, saflufenacil plus glyphosate, and metribuzin plus saflufenacil plus glyphosate in soybean. Weed Sci. 2016, 64, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, L.; Konzen, A.; Bagnara, M.A.M.; Brunetto, L.; Aspiazú, I.; Silva, A.M.L.; Brandler, D.; Piazetta, H.V.P.; Radüns, A.L.; Perin, G.F. Interference and threshold level of Sida rhombifolia in transgenic soybean cultivars. Rev. De La Fac. De Cienc. Agrar. UNCuyo 2022, 54, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Shropshire, C.; Sikkema, P.H. Sensitivity of leguminous crops to saflufenacil. Weed Technol. 2017, 24, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streck, E.V.; Kampf, N.; Dalmolin, R.S.D.; Klamt, E.; Nascimento, P.C.; Giasson, E.; Pinto, L.F.S. Soils of Rio Grande do Sul, 3rd ed.; Emater/RS-Ascar, BR: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2018; 252p. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INMET—National Institute of Meteorology. Climatological Data. Available online: https://portal.inmet.gov.br (accessed on 29 April 2025). (In Portuguese)
- CQFS-RS/SC—Comissão de Química e Fertilidade do Solo. Liming and Fertilization Manual for the States of Rio Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina, 11th ed.; Sociedade Brasileira de Ciência do Solo—Núcleo Regional Sul, BR: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2016; 376p. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Velini, E.D.; Osipe, R.; Gazziero, D.L.P. Procedures for the Establishment, Evaluation, and Analysis of Experiments with Herbicides; SBCPD/BR: Londrina, Brazil, 1995; 42p. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, G.F.; Pigatto, C.S.; Leães, G.P.; Kruse, N.D.; Agostinetto, D.; da Rosa Ulguim, A. Physicochemical properties of soil and rates of saflufenacil in emergence and growth of soybean. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2021, 61, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y. Efficient and practical synthesis of saflufenacil. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 2023, 55, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.F.; Hong, H.L.; Han, J.N.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, Z.X.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, L.J. Development and identification of glyphosate-tolerant transgenic soybean via direct selection with glyphosate. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valença, D.C.; Lelis, D.C.C.; Pinho, C.F.; Bezerra, A.N.M.; Ferreira, M.A.; Junqueira, N.E.G.; Macrae, A.; Medici, L.O.; Reinert, F.; Silva, B.O. Changes in leaf blade morphology and anatomy caused by clomazone and saflufenacil in Setaria viridis, a model C4 plant. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 135, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomão, H.M.; Trezzi, M.M.; Viecelli, M.; Pagnocelli Junior, F.D.B.; Patel, F.; Damo, L.; Frizzon, G. Weed management with pre-emergent herbicides in soybean crops. Commun. Plant Sci. 2021, 1, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.M.; Owen, M.D.K. Herbicide-resistant crops: Utilities and limitations for herbicide-resistant weed management. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5819–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Evans, R.; Singh, B. Herbicidal inhibitors of amino acid biosynthesis and herbicide-tolerant crops. J. Amino Acids 2006, 30, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCown, S.; Barber, T.; Norsworthy, J.K. Response of non–dicamba-resistant soybean to dicamba as influenced by growth stage and herbicide rate. Weed Technol. 2018, 32, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.J.P.; Magalhães, T.B.; Ovejero, R.F.L.; Palhano, M.G. Phytotoxicity of low doses of dicamba when sprayed in pre-emergence on non-tolerant soybean. Rev. De Ciências Agroveterinárias 2022, 21, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Nelson, K.A.; Singh, G.; Udawatta, R.P. Cover crop impacts water quality in a tile-terraced no-till field with corn-soybean rotation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 360, e108794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.T.; Soltani, N.; Robinson, D.E.; Kraus, T.E.; Sikkema, P.H. Soybean (Glycine max) cultivar tolerance to saflufenacil. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 92, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.E.; Geist, M.L.; Pereira, J.P.M.; Schedenffeldt, B.F.; Nunes, F.A.; da Silva, P.V.; Dupas, E.; Mauad, M.; Monquero, P.A.; Medeiros, E.S. Selectivity of post-emergence herbicides and foliar fertilizer in soybean crop. Rev. Ciênc Agrovet. 2022, 21, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungria, M.; Mendes, I.C.; Nakatani, A.S.; Reis Junior, F.B.; Morais, J.Z.; de Oliveira, M.C.N.; Fernandes, M.F. Effects of the glyphosate-resistance gene and herbicides on soybean: Field trials monitoring biological nitrogen fixation and yield. Field Crops Res. 2014, 158, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, V.H.V.; Maia, L.S.G.; Arneson, N.J.; Oliveira, M.C.; Read, H.W.; Ané, J.M.; Santos, J.B.; Werle, R. Influence of pre-emergence herbicides on soybean development, root nodulation and symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Crop Prot. 2021, 144, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, Z.A.; Jhala, A.J. Weed control and crop safety in sulfonylurea/glyphosate-resistant soybean. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2020, 100, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilliott, M.; Soltani, N.; Hooker, D.C.; Robinson, D.E.; Sikkema, P.H. The addition of saflufenacil to glyphosate plus dicamba improves glyphosate-resistant Canada fleabane (Erigeron canadensis L.). J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, F.M.; Cestonaro, L.V.; Piton, Y.V.; Guimarães, N.; Garcia, S.C.; Silva, D.D.; Arbo, M.D. Toxicity of pesticides widely applied on soybean cultivation: Synergistic effects of fipronil, glyphosate and imidacloprid in HepG2 cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2022, 84, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapado, L.P.; Kölpin, F.U.G.; Zeyer, S.; Anders, U.; Piccard, L.; Porri, A.; Asher, S. Complementary activity of trifludimoxazin and saflufenacil when used in combination for postemergence and residual weed control. Weed Sci. 2024, 73, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Ou, W.; Ahmed, W.; Bundschuh, J.; Rizwan, M.; Mahmood, M.; Sultan, H.; Alatalo, J.M.; Elnahal, A.S.M.; Liu, W.; et al. ZnO nanoparticles mediated by Azadirachta indica as nano fertilizer: Improvement in physiological and biochemical indices of Zea mays grown in Cr-contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 339, 122755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, S.; Ahmed, W.; Rizwan, M.; Bundschuh, J.; Elnahal, A.S.M.; Li, W. Green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles for removal of carbamazepine in water and soil systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 334, 125988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| pH (H2O) | OM (%) | BS (%) | Clay (%) | CECt (cmolc dm−3) | CECpH=7.0 (cmolc dm−3) | H + Al (cmolc dm−3) |
| 5.6 | 3.2 | 51.0 | 62.0 | 10.2 | 14.6 | 4.5 |
| P (mg dm−3) | K (mg dm−3) | Al+3 (cmolc dm−3) | Ca+2 (cmolc dm−3) | Mg+2 (cmolc dm−3) | Sand (%) | Silt (%) |
| 9.7 | 134.4 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 3.1 | 15.0 | 23.0 |
| Treatment | Dose (g ha−1) | Product Name Commercial | Dose (L or kg ha−1) | Adjuvant (0.5% v/v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weed-free control | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| Glyphosate | 1440 | Roundup Original® Mais | 3.000 | --- |
| Saflufenacil | 1.09 | Heat® | 0.0016 | Assist |
| Saflufenacil | 2.17 | Heat® | 0.0031 | Assist |
| Saflufenacil | 4.38 | Heat® | 0.00625 | Assist |
| Saflufenacil | 8.75 | Heat® | 0.0125 | Assist |
| Saflufenacil | 17.50 | Heat® | 0.0250 | Assist |
| Saflufenacil | 35.00 | Heat® | 0.0500 | Assist |
| Saflufenacil | 52.50 | Heat® | 0.0750 | Assist |
| Saflufenacil | 70.00 | Roundup Original® Mais + Heat® + Heat® | 0.1000 | Assist |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 1.09 | Roundup Original® Mais + Heat® + Heat® | 3.00 + 0.0160 | Assist |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 2.17 | Roundup Original® Mais + Heat® + Heat® | 3.00 + 0.0031 | Assist |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 4.38 | Roundup Original® Mais + Heat® + Heat® | 3.00 + 0.0625 | Assist |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 8.75 | Roundup Original® Mais + Heat® + Heat® | 3.00 + 0.0125 | Assist |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 17.50 | Roundup Original® Mais + Heat® + Heat® | 3.00 + 0.0250 | Assist |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 35.00 | Roundup Original® Mais + Heat® + Heat® | 3.00 + 0.0500 | Assist |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 52.50 | Roundup Original® Mais + Heat® + Heat® | 3.00 + 0.0750 | Assist |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 70.00 | Roundup Original® Mais + Heat® + Heat® | 3.00 + 0.1000 | Assist |
| Treatment | Dose (g ha−1) | Phytotoxicity (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 DAT 1 | 14 DAT | 21 DAT | 28 DAT | 35 DAT | ||
| Weed-free control | --- | 0.00 e 2 | 0.00 e | 0.00 d | 0.00 d | 0.00 d |
| Glyphosate | 1440 | 0.00 e | 0.00 e | 0.00 d | 0.00 d | 0.00 d |
| Saflufenacil | 1.09 | 16.25 d | 12.50 d | 7.50 d | 5.00 d | 3.75 d |
| Saflufenacil | 2.17 | 23.25 d | 17.00 d | 10.00 d | 6.25 d | 2.50 d |
| Saflufenacil | 4.38 | 36.25 c | 28.75 d | 22.50 c | 20.00 c | 17.50 c |
| Saflufenacil | 8.75 | 55.00 b | 50.00 c | 46.25 b | 45.00 b | 38.75 b |
| Saflufenacil | 17.50 | 76.25 a | 65.00 b | 58.75 b | 56.25 b | 48.75 b |
| Saflufenacil | 35.00 | 80.00 a | 73.75 a | 67.50 a | 67.50 a | 65.00 a |
| Saflufenacil | 52.50 | 81.50 a | 76.25 a | 75.00 a | 81.25 a | 79.50 a |
| Saflufenacil | 70.00 | 94.00 a | 90.00 a | 87.75 a | 90.00 a | 85.00 a |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 1.09 | 45.00 c | 40.00 c | 32.50 c | 28.75 c | 21.25 c |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 2.17 | 47.50 c | 43.75 c | 40.00 b | 37.00 c | 32.50 c |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 4.38 | 68.75 b | 61.25 b | 51.25 b | 47.50 b | 40.00 b |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 8.75 | 68.75 b | 61.25 b | 55.00 b | 48.75 b | 43.75 b |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 17.50 | 70.00 b | 63.75 b | 58.75 b | 57.50 b | 51.25 b |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 35.00 | 76.25 a | 61.25 b | 56.25 b | 55.00 b | 50.00 b |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 52.50 | 82.50 a | 77.00 a | 67.50 a | 73.75 a | 71.25 a |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 70.00 | 83.25 a | 79.50 a | 75.00 a | 73.75 a | 73.25 a |
| Mean average | --- | 55.74 | 50.06 | 45.08 | 44.07 | 40.22 |
| C.V. 3 (%) | --- | 21.13 | 21.11 | 24.57 | 27.80 | 30.13 |
| Treatment | Dose (g ha−1) | Physiological Variables | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ci | gS | A | E | WUE | CE | ||
| Weed-free control | --- | 261.75 a 1 | 0.40 b | 21.79 b | 3.52 a | 6.36 b | 0.08 b |
| Glyphosate | 1440 | 250.75 b | 0.38 b | 22.44 b | 2.99 a | 7.05 a | 0.09 b |
| Saflufenacil | 1.09 | 277.25 a | 0.40 b | 18.18 c | 3.18 a | 5.91 b | 0.07 c |
| Saflufenacil | 2.17 | 273.25 a | 0.44 a | 19.84 c | 3.20 a | 6.28 b | 0.07 c |
| Saflufenacil | 4.38 | 249.00 b | 0.40 b | 23.67 a | 3.17 a | 7.58 a | 0.09 b |
| Saflufenacil | 8.75 | 245.25 b | 0.45 a | 23.80 a | 3.08 a | 7.80 a | 0.09 b |
| Saflufenacil | 17.50 | 248.75 b | 0.43 a | 22.36 b | 2.99 a | 7.58 a | 0.09 b |
| Saflufenacil | 35.00 | 243.00 b | 0.43 a | 22.04 b | 2.93 a | 7.67 a | 0.09 b |
| Saflufenacil | 52.50 | 271.75 a | 0.37 b | 15.45 d | 2.93 a | 5.39 b | 0.06 c |
| Saflufenacil | 70.00 | 268.50 a | 0.40 b | 18.38 c | 2.65 a | 6.95 a | 0.07 c |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 1.09 | 265.25 a | 0.42 b | 18.63 c | 3.15 a | 6.07 b | 0.07 c |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 2.17 | 222.67 b | 0.41 b | 24.48 a | 3.03 a | 8.29 a | 0.11 a |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 4.38 | 262.50 a | 0.46 a | 22.68 b | 3.10 a | 7.41 a | 0.09 b |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 8.75 | 262.25 a | 0.45 a | 21.22 b | 2.95 a | 7.26 a | 0.08 b |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 17.50 | 257.25 b | 0.44 a | 23.17 a | 3.15 a | 7.47 a | 0.09 b |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 35.00 | 262.00 a | 0.43 a | 20.61 b | 3.02 a | 6.90 a | 0.07 c |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 52.50 | 249.25 b | 0.42 a | 23.41 a | 2.90 a | 8.11 a | 0.09 b |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 70.00 | 252.50 b | 0.42 a | 22.73 b | 3.02 a | 7.67 a | 0.09 b |
| Mean average | --- | 256.88 | 0.42 | 21.38 | 3.05 | 7.10 | 0.09 |
| C.V. 2 (%) | --- | 5.96 | 8.34 | 5.89 | 8.70 | 8.87 | 10.49 |
| Treatment | Dose (g ha−1) | Yield Components | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPP | NGP | TGW | GY | ||
| Weed-free control | --- | 63.25 a 1 | 127.00 a | 163.93 b | 3549.22 b |
| Glyphosate | 1440 | 65.55 a | 147.35 a | 168.86 a | 3977.32 a |
| Saflufenacil | 1.09 | 49.20 b | 124.10 a | 167.90 a | 3522.21 b |
| Saflufenacil | 2.17 | 54.40 b | 122.35 a | 155.36 b | 3666.61 b |
| Saflufenacil | 4.38 | 49.55 b | 106.55 a | 158.34 b | 3271.05 c |
| Saflufenacil | 8.75 | 46.53 b | 95.87 b | 164.79 b | 2581.03 d |
| Saflufenacil | 17.50 | 60.05 a | 109.00 a | 178.10 a | 2313.32 e |
| Saflufenacil | 35.00 | 56.07 a | 96.70 b | 172.50 a | 947.13 g |
| Saflufenacil | 52.50 | 53.17 b | 86.80 b | 170.17 a | 376.05 h |
| Saflufenacil | 70.00 | 25.73 d | 55.47 c | 167.75 a | 275.19 h |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 1.09 | 49.05 b | 91.45 b | 159.87 b | 3634.61 b |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 2.17 | 50.40 b | 97.30 b | 167.90 a | 3076.72 c |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 4.38 | 39.10 c | 75.75 c | 175.16 a | 2840.30 d |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 8.75 | 36.93 c | 88.73 b | 173.32 a | 2507.97 d |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 17.50 | 53.33 b | 88.30 b | 165.87 b | 2153.19 e |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 35.00 | 54.40 b | 104.25 a | 171.47 a | 1805.88 f |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 52.50 | 58.28 a | 118.00 a | 179.33 a | 1209.59 g |
| Glyphosate + Saflufenacil | 1440 + 70.00 | 56.93 a | 121.65 a | 175.06 a | 601.11 h |
| Mean average | --- | 51.21 | 103.15 | 168.65 | 2349.99 |
| C.V. 2 (%) | --- | 10.73 | 16.12 | 3.99 | 9.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galon, L.; Tedesco, L.; Tonin, R.J.; Anjos, A.D.R.d.; Giacomolli, E.B.; Dassoler, O.A.; Ortiz, F.B.; Perin, G.F. Soybean Response to Saflufenacil Doses, Alone or Combined with Glyphosate, Simulating Tank Contamination. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081758
Galon L, Tedesco L, Tonin RJ, Anjos ADRd, Giacomolli EB, Dassoler OA, Ortiz FB, Perin GF. Soybean Response to Saflufenacil Doses, Alone or Combined with Glyphosate, Simulating Tank Contamination. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081758
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalon, Leandro, Lucas Tedesco, Rodrigo José Tonin, Aline Diovana Ribeiro dos Anjos, Eduarda Batistelli Giacomolli, Otávio Augusto Dassoler, Felipe Bittencourt Ortiz, and Gismael Francisco Perin. 2025. "Soybean Response to Saflufenacil Doses, Alone or Combined with Glyphosate, Simulating Tank Contamination" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081758
APA StyleGalon, L., Tedesco, L., Tonin, R. J., Anjos, A. D. R. d., Giacomolli, E. B., Dassoler, O. A., Ortiz, F. B., & Perin, G. F. (2025). Soybean Response to Saflufenacil Doses, Alone or Combined with Glyphosate, Simulating Tank Contamination. Agronomy, 15(8), 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081758






