Multi-Dimensional Analysis of Quality-Related Traits Affecting the Taste of Main Cultivated Japonica Rice Varieties in Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Equipment
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Determination of Taste Value
2.2.2. Determination of Appearance Characteristics
2.2.3. Determination of Different Forms of Water
2.2.4. Determination of Chemical Composition
2.2.5. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Taste Values of Different Rice Varieties
3.2. Appearance Characteristics of Different Varieties of Rice
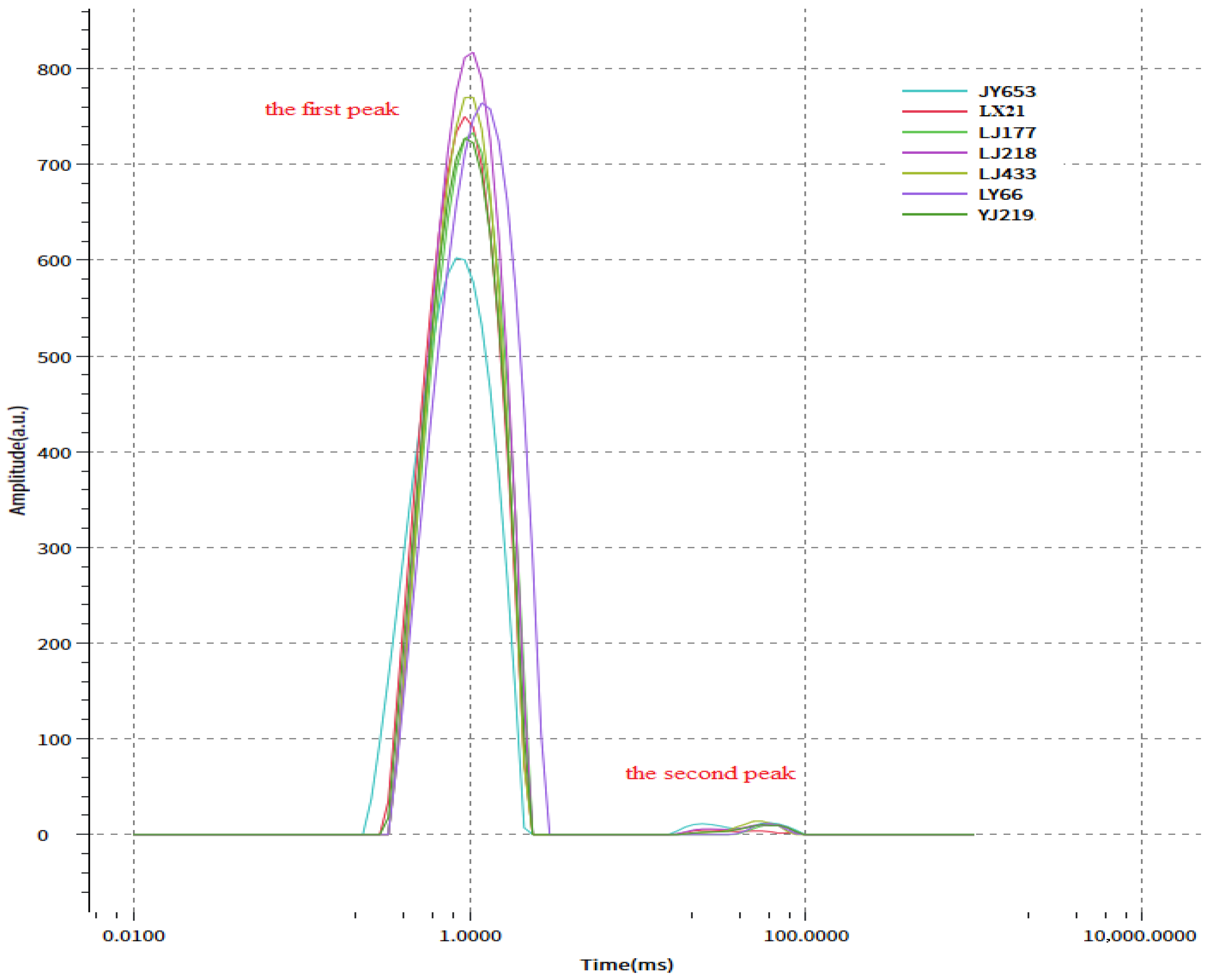
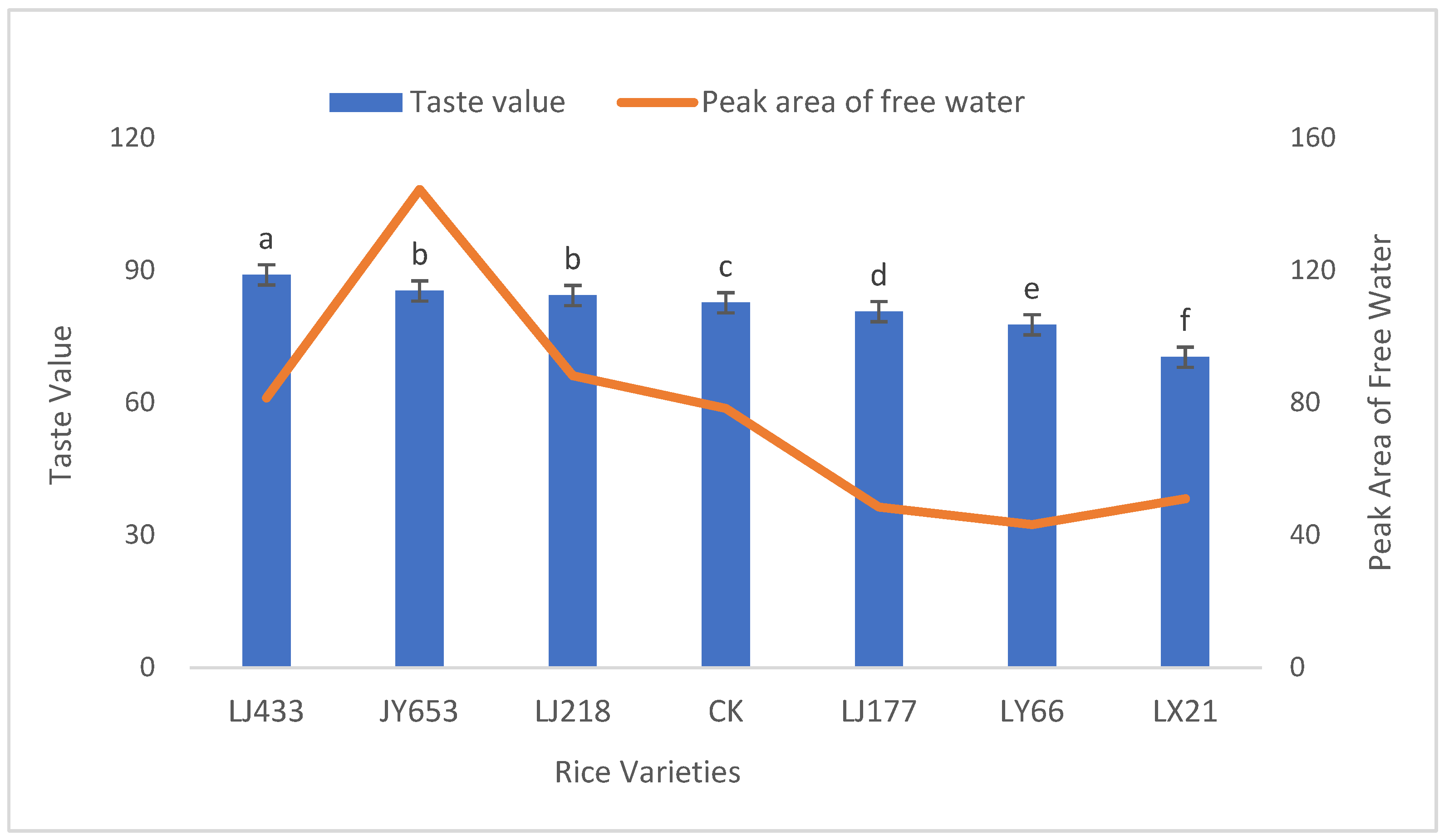
3.3. Contents of Free and Bound Water in Different Rice Varieties
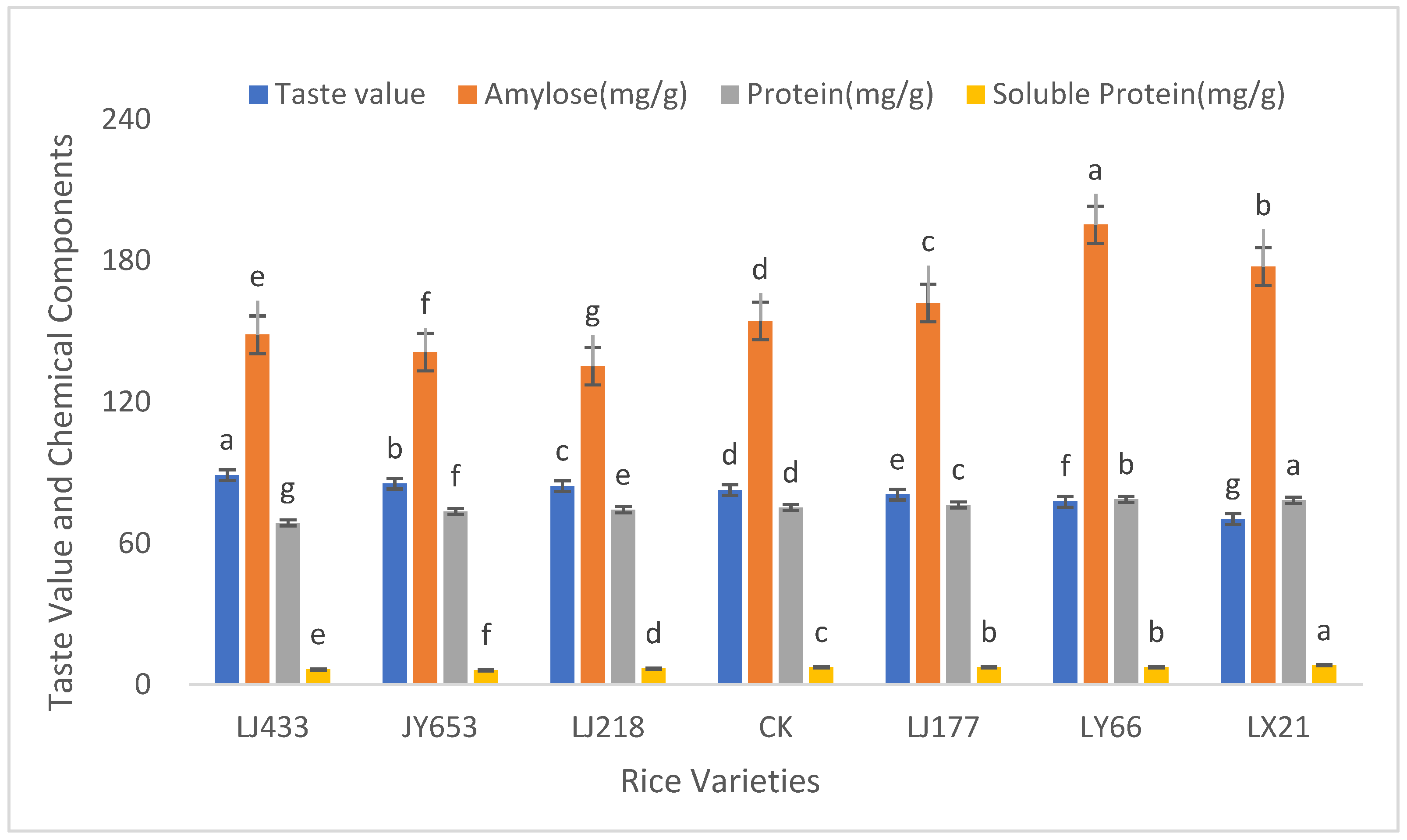
3.4. Intrinsic Chemical Components of Different Rice Varieties
3.5. Correlation Between Quality-Related Traits and Taste Values
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Appearance Characteristics on Taste Quality
4.2. Effects of Water Content in Different States on Taste Quality
4.3. Effects of Different Chemical Components on Taste Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsue, Y.; Moriwaki, C.; Abe, S.; Ito, S. Palatability characteristics of recent local-brand-rice cultivars. Plant Prod. Sci. 2024, 27, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amfo, B.; Abankwah, V.; Tanko, M. Consumer satisfaction with local rice attributes and willingness to pay for improvement by internal migrants and natives in urban Ghana. J. Agribus. Dev. Emerg. Econ. 2024, 14, 587–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; He, N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, W.; Ma, D.; Wang, H.; Tang, Z. Effects of Planting Methods and Varieties on Rice Quality in Northern China. Foods 2025, 14, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xue, P.; Wang, B.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Hong, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, Q.; et al. Modulation of rice grain shape and appearance by the GS10-encoded long coiled-coil protein. Crop J. 2025, 13, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Deng, F.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, X.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Cheng, H.; Wang, T.; et al. Appearance, components, pasting, and thermal characteristics of chalky grains of rice varieties with varying protein content. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Niu, S.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, G.; Peng, Y.; He, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Xie, X. Moderate Salinity Stress Affects Rice Quality by Influencing Expression of Amylose- and Protein-Content-Associated Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Shao, J.; Zeng, Z.; Li, Z.; Sun, S.; Peng, L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; He, Y. Knocking out isopropyl malate synthase simultaneously improves grain appearance and nutritional quality in rice. Plant J. 2024, 120, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, T. Effects of rice grain protein QTL, TGP12, on grain composition, yield components, and eating quality with different nitrogen applications. Field Crops Res. 2021, 263, 108051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Guan, C.; Wang, L.; Jia, L.; Xiangjin, F.; Lin, Q.; Huang, Z.; Liu, C. Rice Storage Proteins:Focus on Composition, Distribution, Genetic Improvement and Effects on Rice Quality. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, B.; Zhang, T.; Liu, P.; Yang, W.; Zheng, L.; Dai, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, X.; et al. The LCG1-OsBP5/OsEBP89-Wx module regulates the grain chalkiness and taste quality in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry Experiments; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Experimental Tutorial of Plant Physiology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nahid, F.; Atefeh, S.; Adel, B.; Amin, A. Combinatorial Approaches to Image Processing and MGIDI for the Efficient Selection of Superior Rice Grain Quality Lines. Agriculture 2025, 15, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyosumi, H.; Matthew, S.; Kenta, M.; Keitaro, S.; Ken, I.; Noriyuki, K.; Koka, S.; Kosuke, O.; Yuji, K.; Kazuhiko, S.; et al. QTN detection and candidate gene identification for improved eating and cooking quality in rice using GWAS and PLS regression analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2025, 138, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, L.; Wang, E.; Wang, K.; Cao, C.; Shi, S.; Jiang, Y. Nitrogen fertilization alters rice taste quality through layer-specific changes in protein and starch composition. J. Cereal Sci. 2025, 123, 104157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, K.; Guan, L.; Zhang, M.; Ye, G.; Li, S. Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on Taste and Flavor Quality of Japonica Rice. Foods 2025, 14, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Deng, B.; Zhang, L. Molecular and genetic bases of rice cooking and eating quality: An updated review. Cereal Chem. 2023, 100, 1220–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarna, S.G.; Ahmad, E.; Kadaru, S.; Aminul Islam, A.K.M. Grain Appearance Quality of Parental and Segregating Populations of Aus Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2024, 36, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, X.; Dai, Y.; Li, Y.; Ban, Y.; Tian, W.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Jia, L.; et al. Transcription factor OsNF-YC1 regulates grain size by coordinating the transcriptional activation of OsMADS1 in Oryza sativa L. Plant J. 2024, 119, 1465–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClung, A.; Chen, M.; Jodari, F.; Famoso, A.; Addison, C.; Linscombe, S.; Ottis, B.; Moldenhauer, K.; Walker, T.; Wilson, L.; et al. Use of objective imaging systems to assess subjective grain appearance traits important to the US rice industry. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, B.C.; Anil, K.N.C.; Harkamal, W.; Rajib, S. Transcriptome enhanced rice grain metabolic model identifies histidine level as a marker for grain chalkiness. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailo, H.; Khiangte, L.; Ralte, L.; Singh, Y.T. Grain quality and physicochemical evaluation coupled with untargeted metabolic identification provide new insight into the upland pigmented rice of Manipur, India. LWT 2025, 216, 117236. [Google Scholar]
- Khaled, M.H.A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Germine, M.A.S.; Medhat, A.E.E.D.; Abdelsalam, M.M.; Diaa, A.E.M.; Aly, A.A.E.B.; Sobhi, F.L.; Ahmed, M.A. Comprehensive quality profiling and multivariate analysis of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars: Integrating physical, cooking, nutritional, and micronutrient characteristics for enhanced varietal selection. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuna, S.; Deepak, G.; Abhinav, S.; Sagi, I.; Dharavath, N. Exploring Genetic Variability and Diversity in Advanced Breeding Lines of Rice for Yield-Attributing and Grain Quality Traits. J. Adv. Biol. Biotechnol. 2025, 28, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Hu, R.; Dong, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, D.; Yang, W. Genes controlling grain chalkiness in rice. Crop J. 2024, 12, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febina, M.; Deepa, J.; Maya, R. Physicochemical properties, eating and cooking quality and genetic variability: A comparative analysis in selected rice varieties of South India. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2023, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, I.; Bassama, J.; Diedhiou, P.M.; Mestres, C. Ways to improve the quality of local rice in Africa: Comparison between physicochemical and sensory properties of rice consumed in Senegal. Nutr. Food Sci. 2024, 54, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, C.; Tuhin, S.R.; Jun, I.S. Influence of γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Application on Aromatic Rice Under Shading and Drought Stress Conditions: Effects on Crop Yield, Grain Quality, and 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline Biosynthesis. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 44, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Fu, D.; Zhang, J. Identification of broken rice rate based on grading and morphological classification. LWT 2025, 215, 117175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swasti, M.; Narpinder, S. Physicochemical, functional, pasting, and amino acid compositions of milled rice, and extrusion behavior of milled rice from basmati and nonbasmati varieties. Cereal Chem. 2024, 101, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Qing, D.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; et al. Identifying Heat Adaptability QTLs and Candidate Genes for Grain Appearance Quality at the Flowering Stage in Rice. Rice 2025, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Gao, L.; Chen, W.; Huang, J.; Qing, D.; Pan, Y.; Ma, C.; Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Li, J.; et al. Genetic Effects of Grain Quality Enhancement in Indica Hybrid Rice: Insights for Molecular Design Breeding. Rice 2024, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitomi, W.; Takahiro, T.; Yasushi, I.; Motoki, N.; Mototaka, S.; Naoya, S.; Kosuke, A.; David, M.; Toshihiro, H. Effectiveness of heat tolerance rice cultivars in preserving grain appearance quality under high temperatures in Japan–A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2024, 310, 109303. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, I.; Nadeem, A.; Usman, Z.; Nauman, A.; Mumtaz, A.; Shakeel, A.A.; Muhammad, F. Influence of water management techniques on milling recovery, grain quality and mercury uptake in different rice production systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Han, Y.; Li, D. Effect of magnetic field treatment on the texture of cooked rice subjected to freeze-thaw cycles: Changes in water phase transition, starch retro gradation, and rice grain structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 311, 143670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mesery, H.S.; Omran, A.A.; Adelusi, O.A.; Kaveh, M.; Okechukwu, V.O.; Hu, Z.; Salem, A.; Badawy, S.A. Evaluating and predicting the impact of storage conditions and packaging materials on the physical properties of paddy rice using machine learning approaches and artificial neural networks. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2025, 112, 102659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effect of Low Temperature and Nitrogen Modified Atmosphere Treatments on the Storage of High Moisture Indica Rice: Quality, Microstructure, and Metabolome Characteristics. Foods 2025, 14, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talla, A.; Swain, D.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Tewari, V.K.; Sanju, P. Integrating Climatic Factors and Agronomic Management for Optimal Hybrid Rice Yield and Quality. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2025, 56, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecil, T.; Martha, H.; Kunda, K.; Benisiu, T. Consumption Preference and Willingness to Pay for Locally Produced Rice in Namibia: Implications for Upscaling Production. J. Agribus. Rural. Dev. 2025, 75, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotte, H.S.T.D.; Yasutaka, N.; Via, A.C.M.; Hiroshi, E.; Yoshiaki, I.; Mana, K.N. Rice Yield and Grain Quality under Fluctuating Soil Moisture Stress. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koustava, K.P.; Satpal, S.B.; Rojita, M.; Parmeshwar, K.S.; Amrita, K.P.; Roshan, S. Nutritional analysis of rice landraces from southern Odisha, India. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 12, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violina, B.; Suneetha, Y.; Srinivas, T.; Bhargavi, B.; Divya, K.; Neeraja, N.C.; Jyothi, B.; Raman, M.S.; Aravind, K.J. Mapping Genomic Regions for Grain Protein Content and Quality Traits in Milled Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants 2025, 14, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, E.O.; Iino, H.; Koyama, K.; Kawamura, S.; Koseki, S.; Lyu, S. Non-destructive quality classification of rice taste properties based on near-infrared spectroscopy and machine learning algorithms. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Gao, M.; Cheng, H.; Song, W.; Lu, L.; Lu, W. Differences in rice component distribution across layers and their relationship with taste. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadamasa, U.; Yojiro, T.; Shunsuke, A.; Matthew, S.; Kiyosumi, H.; Junichi, T. Gene Pyramiding Strategies for Sink Size and Source Capacity for High-Yield Japonica Rice Breeding. Rice 2025, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supriya, S.; Rakesh, S.; Avantika, M.; Vikas, K.S.; Uma, M.S.; Arvind, K.; Gyanendra, P.S. Multi-model genome-wide association studies for appearance quality in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1304388. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Li, C.; Hu, M.; He, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Duan, Q.; Peng, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Evaluating rice lipid content, yield, and quality in response to nitrogen application rate and planting density. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1469264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, H.; Tanaka, R.; Guan, S.; Okami, M.; Wada, H.; Hakata, M.; Ohdan, H. Identification of growth-related indicators affecting the appearance and protein content of rice grains. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veni, B.K.; Raja, D.S.; Tushara, M.; Suneetha, Y.; Mrudhula, K.A. Nutritional and cooking quality superiority of black rice genotype BPT 2841 with enhanced lysine content. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer on the quality traits of Indica rice with different amylose contents. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 8492–8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansah, B.O.; Chen, G.; Xiong, F.; Wu, Y. Endosperm starch in rice: What influences its structure, properties, and biosynthesis. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2023, 45, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinya, W.; Visaka, A.; Phunsiri, S.; Sutthiwal, S.; Matchima, N.; Saroat, R.; Kalidas, S. Nutritional quality, volatile organic compounds and element compositions of indigenous upland rice. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 142, 107517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Y.; Huang, F.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Peng, R.; Li, C.; Song, J.; Hao, Y.; Tian, Z. A Novel Allelic Variant of OsAGPL2 Influences Rice Eating and Cooking Quality. Cells 2025, 14, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Danso, F.; Zhang, J.; Tang, A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, K.; Meng, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; et al. Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduction at Different Rice Growth Stages and Increased Density Improve Rice Yield and Quality in Northeast China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamini, G.P.; Madhusudan, G.L. Detection of amylose content in rice samples with spectral augmentation and advanced machine learning. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 142, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wei, H.; Liu, G. Relationships between the appearance quality and starch structure of soft rice under different nitrogen levels. Food Energy Secur. 2024, 13, e574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, Z.; He, N.; Tang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zheng, W.; Wang, H.; Sui, G.; Gao, H.; Wang, L. Lodging Resistance of Japonica Hybrid Rice Plants Studied in Relation to Mechanical and Physicochemical Characteristics. Agronomy 2025, 15, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Xin, O.; Songpo, D.; Zaid, K.; Hong, S. Co-application of zinc and oligosaccharides enhances zinc bioavailability, yield and nutritional quality of rice. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 224, 109964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Chen, T.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, L.; Yao, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C. Correlation Analyses of Amylose Contents and Srarch RVA Profiles of New Rice Varieties (Lines) Carrying Wx-mq Gene. Acta Agric. Bor. Sin. 2013, 28, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, D.; Qu, C.; Li, Y.; Shen, H.; Li, G.; Meng, F.; Huang, X.; Bai, B. Analysis on Taste Quality and Physicochemical Properties of Black Rice with Similar Apparent Amylose Content. Starch-Stärke 2025, 77, e70004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Zheng, B.D.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.L. A comprehensive review of the factors influencing the formation of retrograded starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; San, Y.; Xing, Y.; Joe, M.R. Rice proteins: A review of their extraction, modification techniques and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 131705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
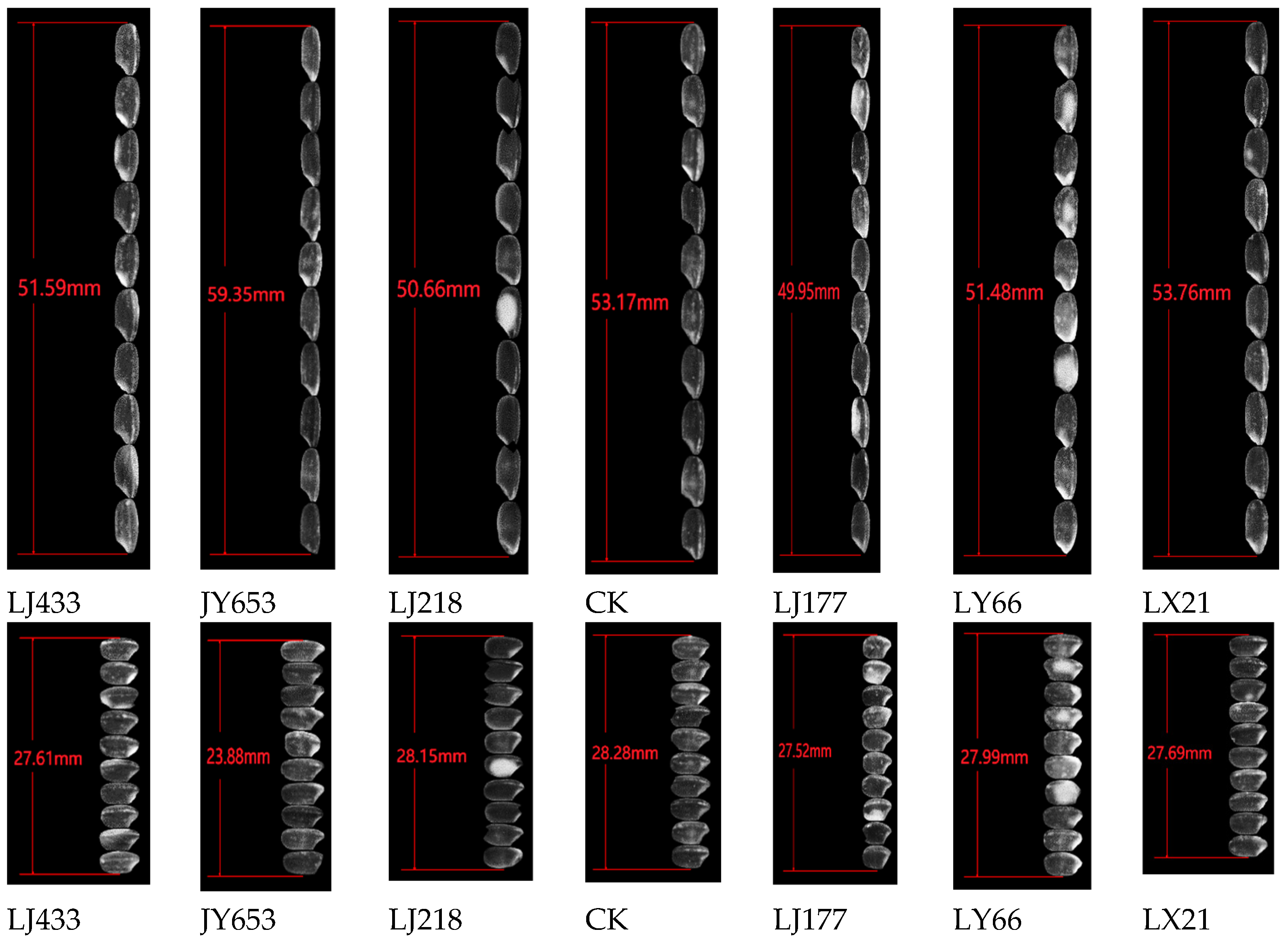
| Variety | Mean Area/mm2 | Mean Perimeter/mm | Mean Length/mm | Mean Width/mm | Mean Diameter/mm | Mean Roundness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LJ433 | 10.38 ± 0.32c | 12.77 ± 0.18 d | 4.84 ± 0.11 c | 2.62 ± 0.07 a | 3.63 ± 0.12 b | 0.56 ± 0.03 b |
| JY653 | 10.34 ± 0.41 c | 13.52 ± 0.25 a | 5.45 ± 0.14 a | 2.25 ± 0.09 c | 3.62 ± 0.15 b | 0.43 ± 0.04 c |
| LJ218 | 9.95 ± 0.28 d | 12.44 ± 0.15 f | 4.69 ± 0.09 d | 2.65 ± 0.06 a | 3.55 ± 0.10 c | 0.59 ± 0.02 a |
| CK | 10.42 ± 0.35 b | 12.89 ± 0.20 c | 4.93 ± 0.12 b | 2.63 ± 0.08 a | 3.64 ± 0.13 b | 0.56 ± 0.03 b |
| LJ177 | 9.72 ± 0.25 e | 12.33 ± 0.17 g | 4.67 ± 0.10 d | 2.58 ± 0.05 b | 3.51 ± 0.11 c | 0.57 ± 0.03 b |
| LY66 | 10.39 ± 0.30 c | 12.69 ± 0.19 e | 4.80 ± 0.11 c | 2.62 ± 0.07 a | 3.63 ± 0.12 b | 0.57 ± 0.02 b |
| LX21 | 10.69 ± 0.38 a | 12.99 ± 0.22 b | 4.92 ± 0.13 b | 2.65 ± 0.08 a | 3.68 ± 0.14 a | 0.56 ± 0.03 b |
| Variety | Grain Shape (LS/T 6116) | Mean Area/mm2 | Mean Perimeter/mm | Mean Length/mm | Mean Width/mm | Mean Roundness | Head Rice Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LJ433 | medium–short | 10.59 ± 0.35 b | 12.93 ± 0.25 d | 4.92 ± 0.08 c | 2.62 ± 0.05 a | 0.55 ± 0.03 a | 96.04 ± 1.20 b |
| JY653 | medium–long | 10.49 ± 0.40 c | 13.66 ± 0.30 a | 5.54 ± 0.10 a | 2.24 ± 0.07 c | 0.42 ± 0.02 b | 96.09 ± 1.53 b |
| LJ218 | medium–short | 10.22 ± 0.30 d | 12.66 ± 0.20 e | 4.81 ± 0.07 d | 2.65 ± 0.06 a | 0.56 ± 0.02 a | 93.63 ± 1.81 d |
| CK | medium–short | 10.63 ± 0.38 b | 13.05 ± 0.28 c | 5.03 ± 0.09 b | 2.63 ± 0.04 a | 0.54 ± 0.03 a | 95.79 ± 1.36 c |
| LJ177 | medium–short | 9.90 ± 0.25 e | 12.48 ± 0.18 f | 4.75 ± 0.06 e | 2.58 ± 0.05 b | 0.56 ± 0.02 a | 95.54 ± 1.42 c |
| LY66 | medium–short | 10.66 ± 0.32 b | 12.90 ± 0.28 d | 4.91 ± 0.07 c | 2.61 ± 0.04 a | 0.55 ± 0.03 a | 94.71 ± 1.61 d |
| LX21 | medium–short | 10.91 ± 0.42 a | 13.16 ± 0.26 b | 5.01 ± 0.08 b | 2.66 ± 0.05 a | 0.55 ± 0.03 a | 96.53 ± 1.18 a |
| Variety | Transparency | Percentage of Chalky Grains/% | Percentage of Chalky Grains (Area Ratio)/% | Percentage of Chalky Grains (LS/T 3247)/% | Chalkiness Degree/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LJ433 | 2 | 2.27 ± 0.51 g | 2.21 ± 0.45 f | 0.00 ± 0.00 g | 0.48 ± 0.11 g |
| JY653 | 2 | 8.33 ± 1.20 e | 7.80 ± 1.10 d | 2.00 ± 0.50 e | 2.91 ± 0.62 e |
| LJ218 | 2 | 6.69 ± 1.05 f | 5.96 ± 0.92 e | 0.84 ± 0.33 f | 1.47 ± 0.35 f |
| CK | 2 | 12.78 ± 1.80 d | 11.53 ± 1.63 c | 2.24 ± 0.61 d | 3.55 ± 0.75 d |
| LJ177 | 2 | 14.05 ± 2.02 c | 13.74 ± 1.93 b | 2.97 ± 0.70 b | 4.43 ± 0.90 c |
| LY66 | 2 | 16.51 ± 2.31 a | 16.52 ± 2.20 a | 2.36 ± 0.65 c | 4.74 ± 1.01 b |
| LX21 | 2 | 15.12 ± 2.15 b | 13.71 ± 1.85 b | 4.47 ± 1.15 a | 5.06 ± 1.10 a |
| Variety | Taste Value/Score | Mass (50 Grains)/g | Peak Area of Total Water/A | Peak Area of Bound Water/A21 | Peak Area of Free Water/A22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LJ433 | 89.00 ± 1.50 a | 0.99 ± 0.02 b | 8006.87 ± 210.56 c | 7926.23 ± 195.51 c | 80.65 ± 10.33 c |
| JY653 | 85.33 ± 1.20 b | 0.92 ± 0.01 d | 6861.31 ± 183.45 g | 6728.36 ± 175.42 g | 132.95 ± 15.28 a |
| LJ218 | 84.33 ± 1.30 b | 1.02 ± 0.03 a | 8423.68 ± 220.15 b | 8333.82 ± 210.38 b | 89.95 ± 12.55 b |
| CK | 82.67 ± 1.40 c | 0.91 ± 0.01 d | 7941.12 ± 190.42 d | 7869.9 ± 185.27 d | 71.22 ± 9.39 d |
| LJ177 | 80.67 ± 1.10 d | 0.92 ± 0.01 d | 7527.16 ± 171.23 f | 7482.6 ± 165.39 f | 44.58 ± 8.43 f |
| LY66 | 77.67 ± 1.00 e | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 8679.81 ± 195.36 a | 8636.13 ± 241.41 a | 43.68 ± 7.28 f |
| LX21 | 70.33 ± 1.20 f | 0.95 ± 0.01 c | 7815.55 ± 185.82 e | 7767.08 ± 183.76 e | 48.47 ± 8.37 e |
| Variety | Taste Value/Score | Amylose (mg/g) | Protein (mg/g) | Soluble Protein (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LJ433 | 89.00 ± 1.50 a | 148.55 ± 5.23 e | 68.71 ± 2.81 g | 6.41 ± 0.45 e |
| JY653 | 85.33 ± 1.20 b | 141.17 ± 4.81 f | 73.52 ± 3.02 f | 6.16 ± 0.42 f |
| LJ218 | 84.33 ± 1.30 b | 135.23 ± 4.32 g | 74.22 ± 3.15 e | 6.79 ± 0.53 d |
| CK | 82.67 ± 1.40 c | 154.35 ± 5.56 d | 75.18 ± 3.23 d | 7.38 ± 0.55 c |
| LJ177 | 80.67 ± 1.10 d | 162.02 ± 6.52 c | 76.33 ± 3.35 c | 7.45 ± 0.62 b |
| LY66 | 77.67 ± 1.00 e | 195.21 ± 7.05 a | 78.62 ± 3.52 b | 7.46 ± 0.65 b |
| LX21 | 70.33 ± 1.20 f | 177.38 ± 6.82 b | 78.29 ± 3.64 a | 8.25 ± 0.71 a |
| Quality-Related Traits | Correlation Coefficient | Quality-Related Traits | Correlation Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance characteristics (including broken rice) | Mean area | 0.29 | Chalkiness characteristics | Transparency | 0.51 |
| Mean perimeter | 0.36 | Percentage of chalky grains | −0.88 * | ||
| Mean length | 0.42 | Percentage of chalky grains (area ratio) | −0.86 * | ||
| Mean width | 0.35 | Percentage of chalky grains (LS/T 3247) | −0.83 * | ||
| Mean diameter | 0.46 | Chalkiness degree | −0.85 * | ||
| Mean roundness | 0.52 | Amplitudes of nuclear magnetic resonance signals | Mass (50 grains) | 0.59 | |
| Appearance characteristics of head rice | Mean area | 0.31 | Peak area of total water | 0.52 | |
| Mean perimeter | 0.42 | Peak area of bound water | 0.46 | ||
| Mean length | 0.49 | Peak area of free water | 0.85 * | ||
| Mean width | 0.43 | Chemical composition | Amylose | −0.82 * | |
| Mean roundness | 0.52 | Protein | −0.81 * | ||
| Head rice rate | 0.55 | Soluble Protein | −0.83 * | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Han, S.; Ma, Z.; Wang, L. Multi-Dimensional Analysis of Quality-Related Traits Affecting the Taste of Main Cultivated Japonica Rice Varieties in Northern China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081757
Yang H, Zhang L, Gao X, Han S, Ma Z, Wang L. Multi-Dimensional Analysis of Quality-Related Traits Affecting the Taste of Main Cultivated Japonica Rice Varieties in Northern China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081757
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hongwei, Liying Zhang, Xiangquan Gao, Shi Han, Zuobin Ma, and Lili Wang. 2025. "Multi-Dimensional Analysis of Quality-Related Traits Affecting the Taste of Main Cultivated Japonica Rice Varieties in Northern China" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081757
APA StyleYang, H., Zhang, L., Gao, X., Han, S., Ma, Z., & Wang, L. (2025). Multi-Dimensional Analysis of Quality-Related Traits Affecting the Taste of Main Cultivated Japonica Rice Varieties in Northern China. Agronomy, 15(8), 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081757




