Study of Detection of Typical Pesticides in Paddy Water Based on Dielectric Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
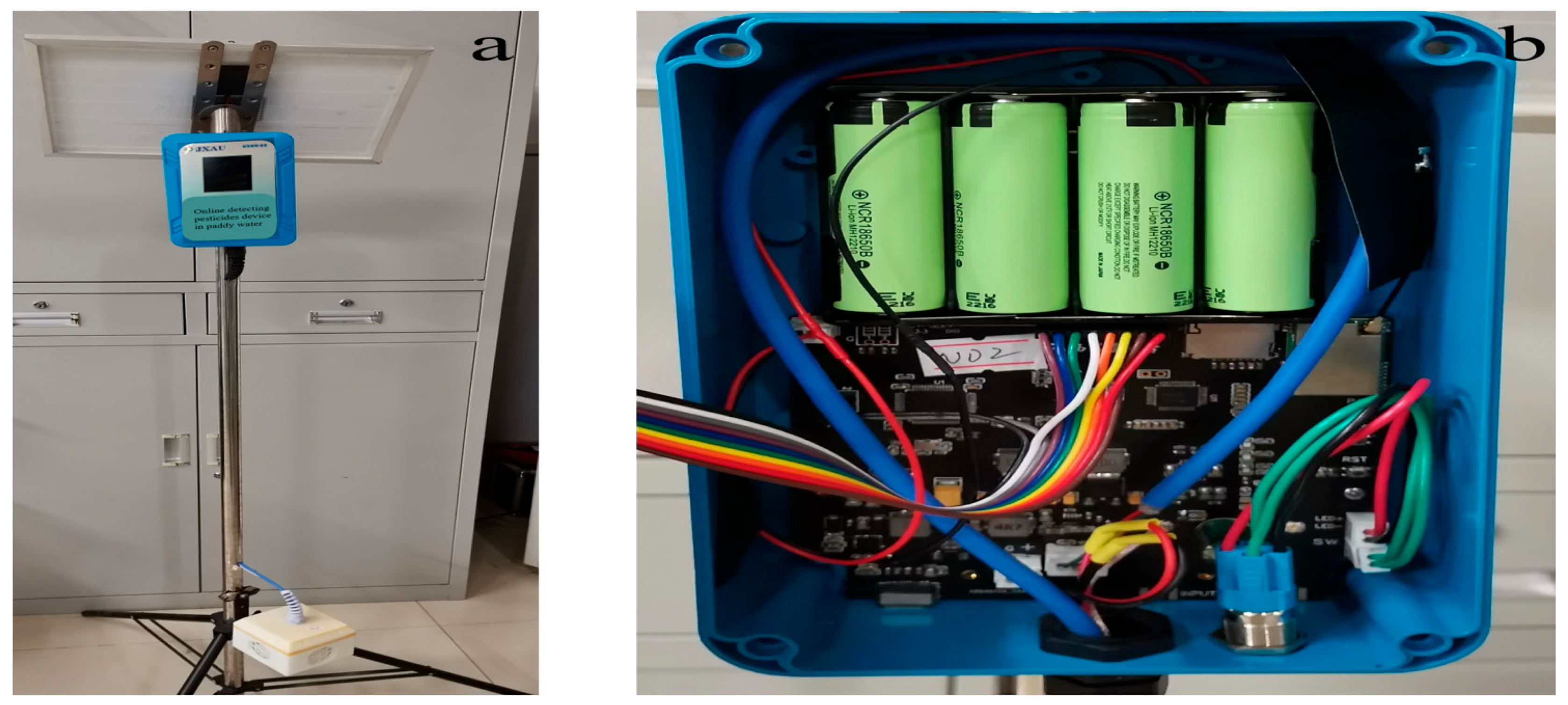
2.1. Test Apparatus and Reagents
2.2. Sensors for Detecting the Dielectric Properties of Pesticides in Paddy Water Bodies
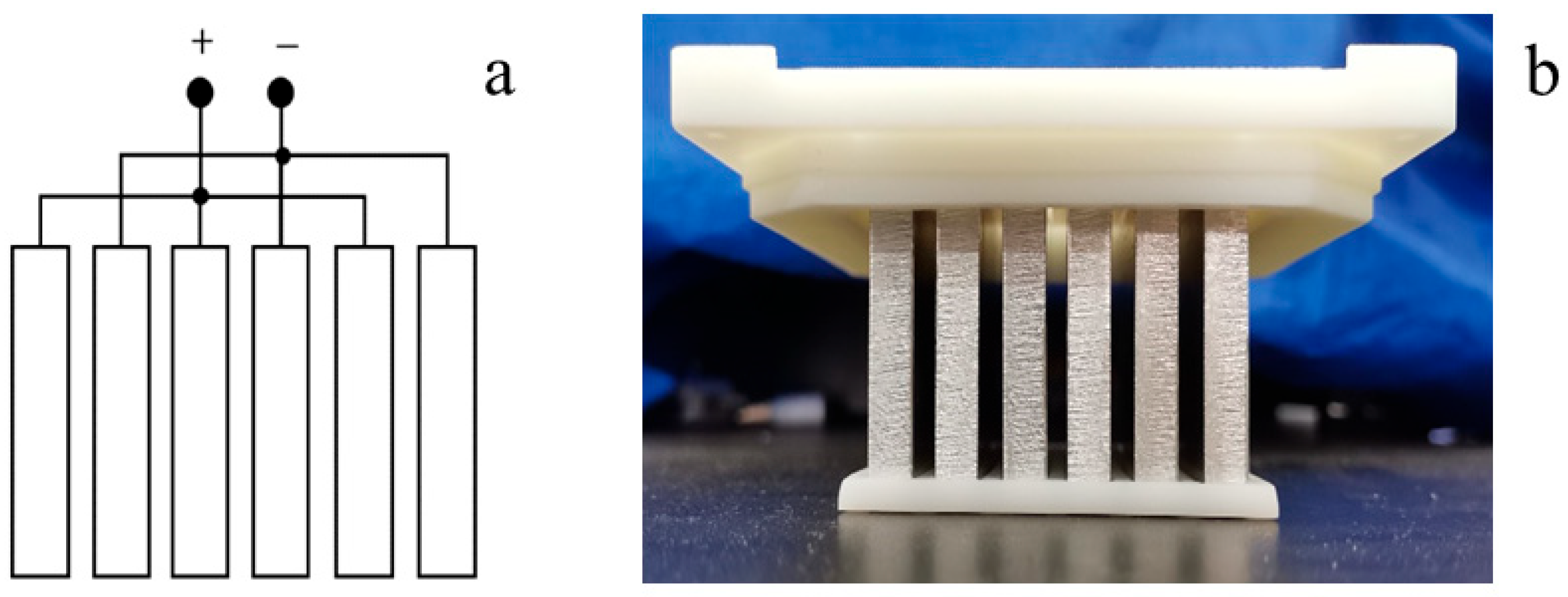
2.2.1. Theoretical Analysis of Dielectric Property Detection
2.2.2. Sensor for Detecting the Dielectric Properties of Pesticides in Paddy Water
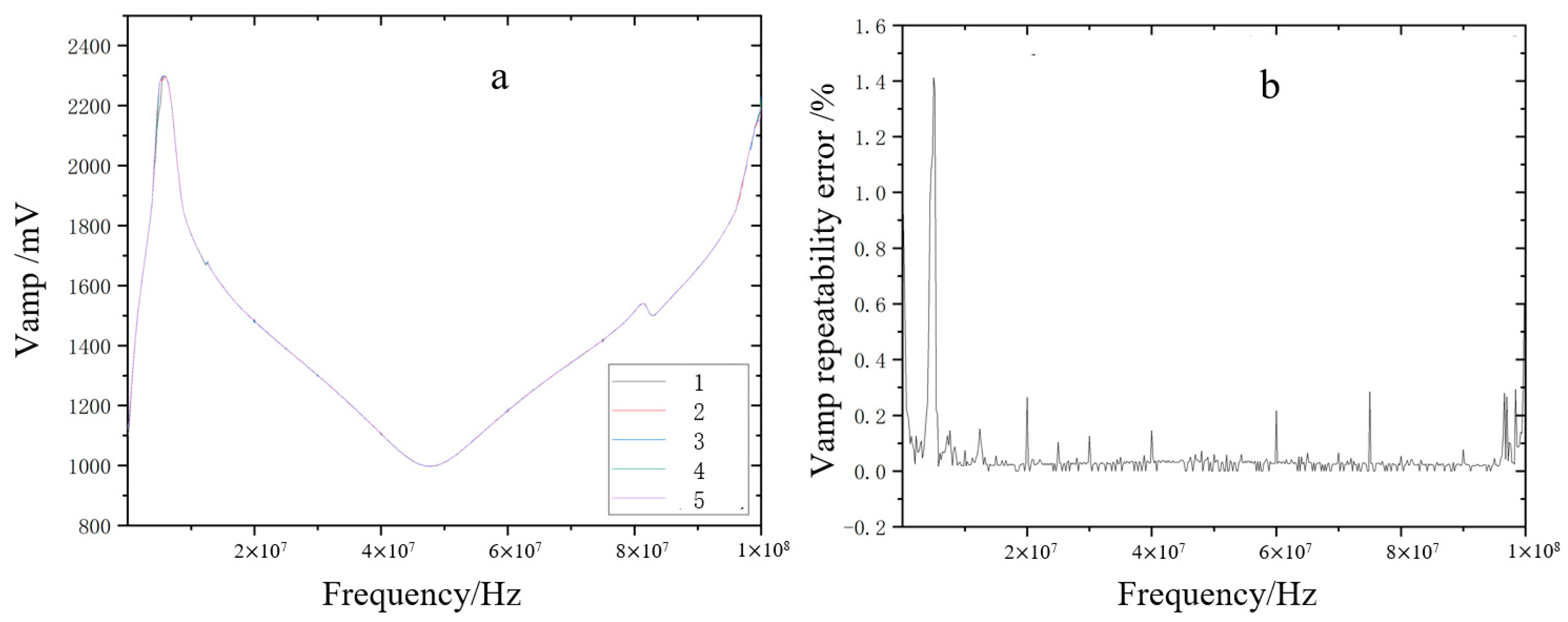
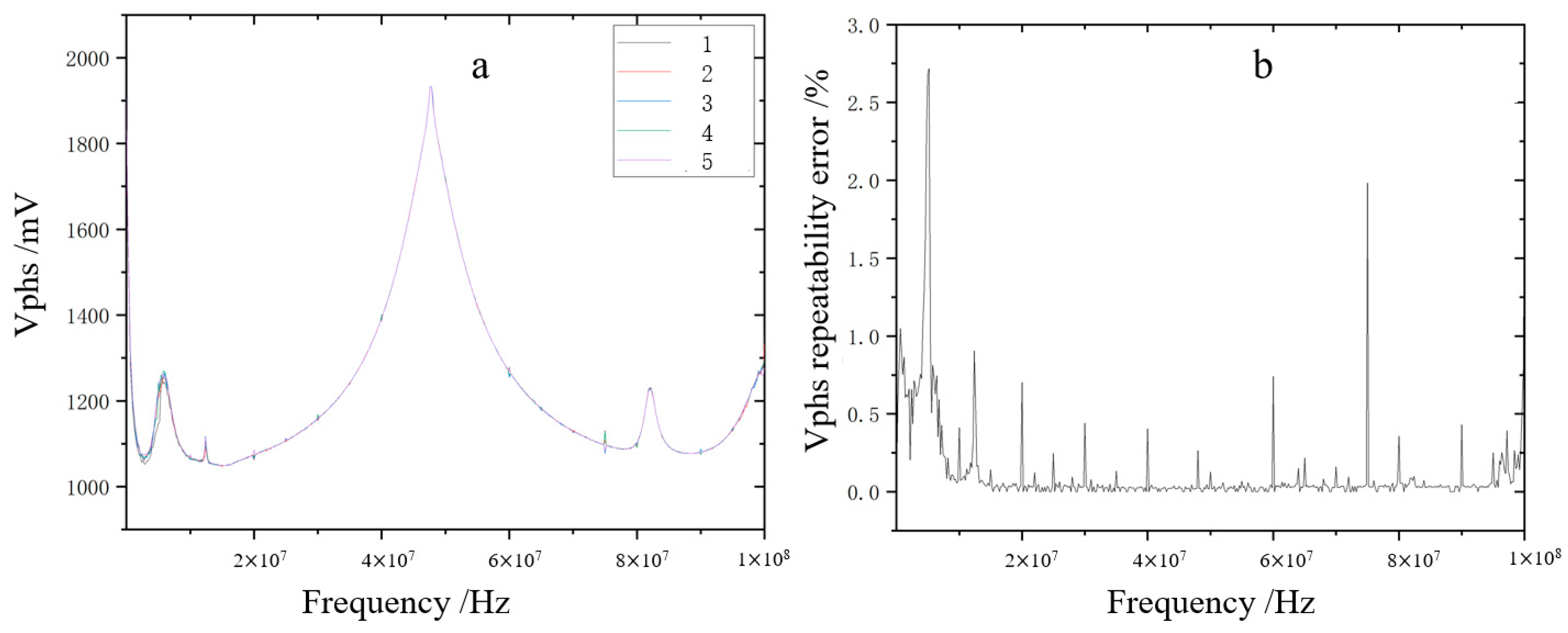
2.2.3. Repeatability Errors
2.3. Test Sample Preparation and Test Sample Profile
2.3.1. Preparation of Pesticide Stock Solutions in Paddy Water
2.3.2. Preparation of Pesticide Test Samples in Paddy Water
2.4. Frequency Response Data Acquisition
2.5. Data Handling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Repeatability Error Analysis
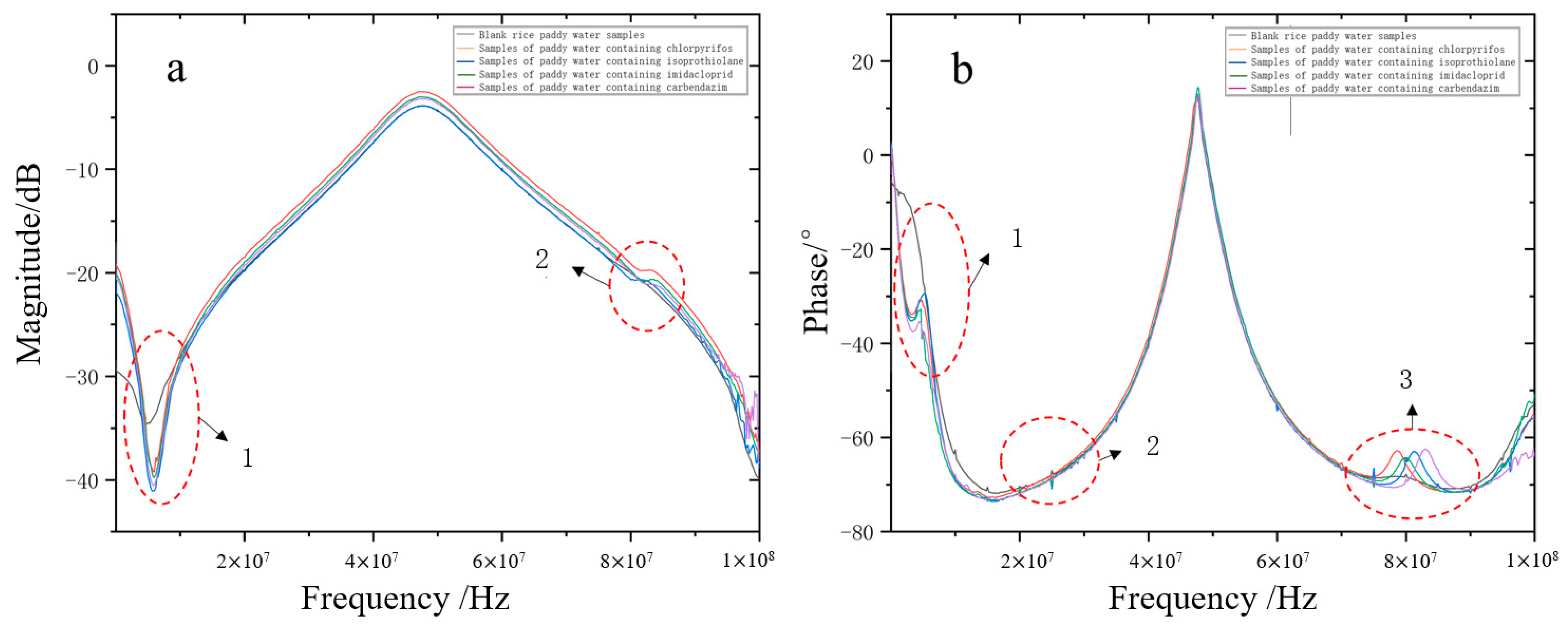
3.2. Frequency Response Analysis of Dielectric Properties of Pesticides in Paddy Water Bodies
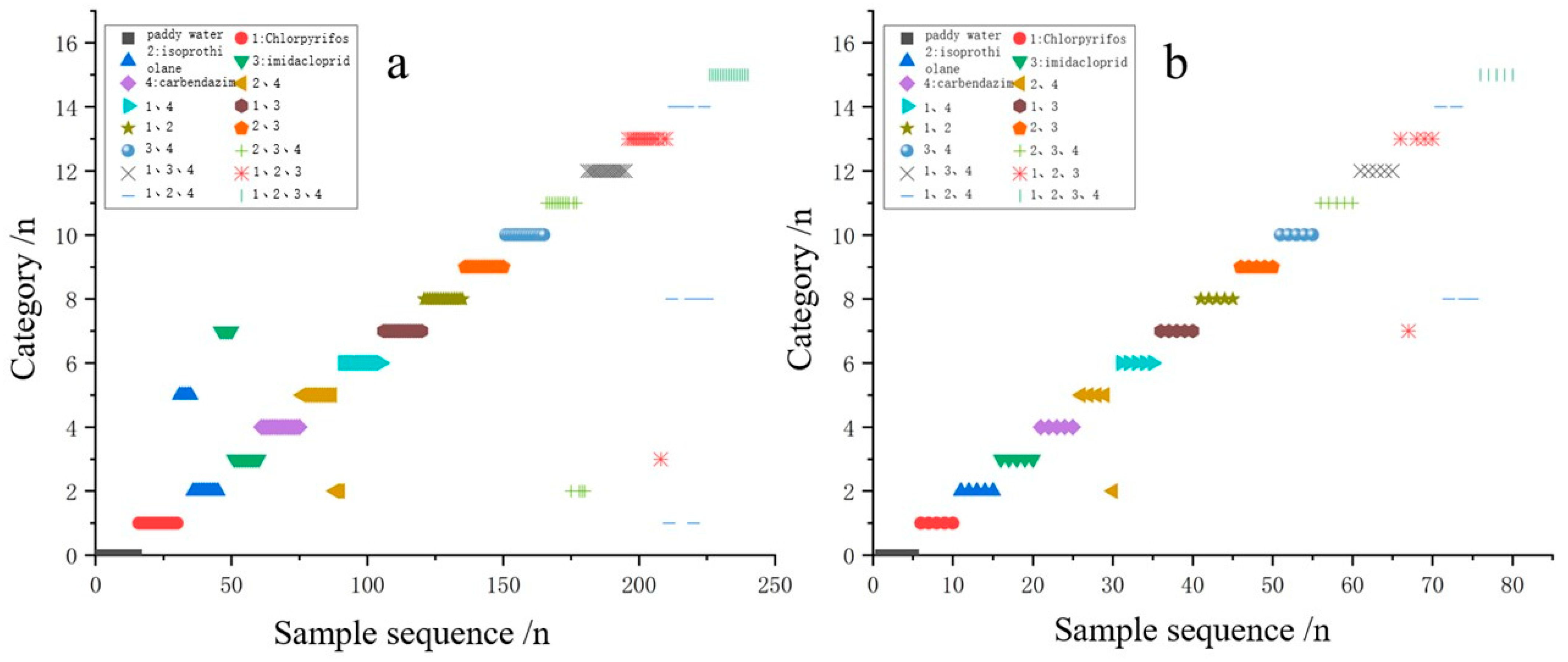
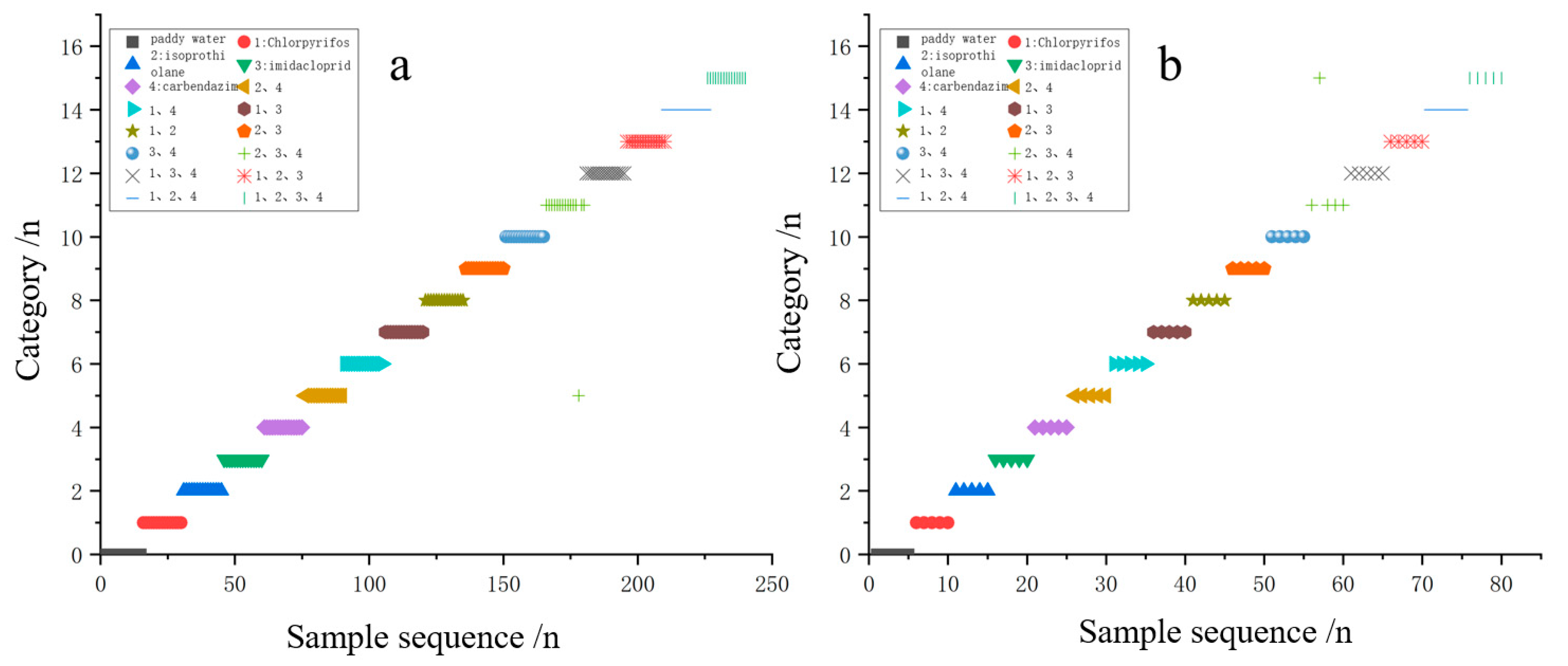
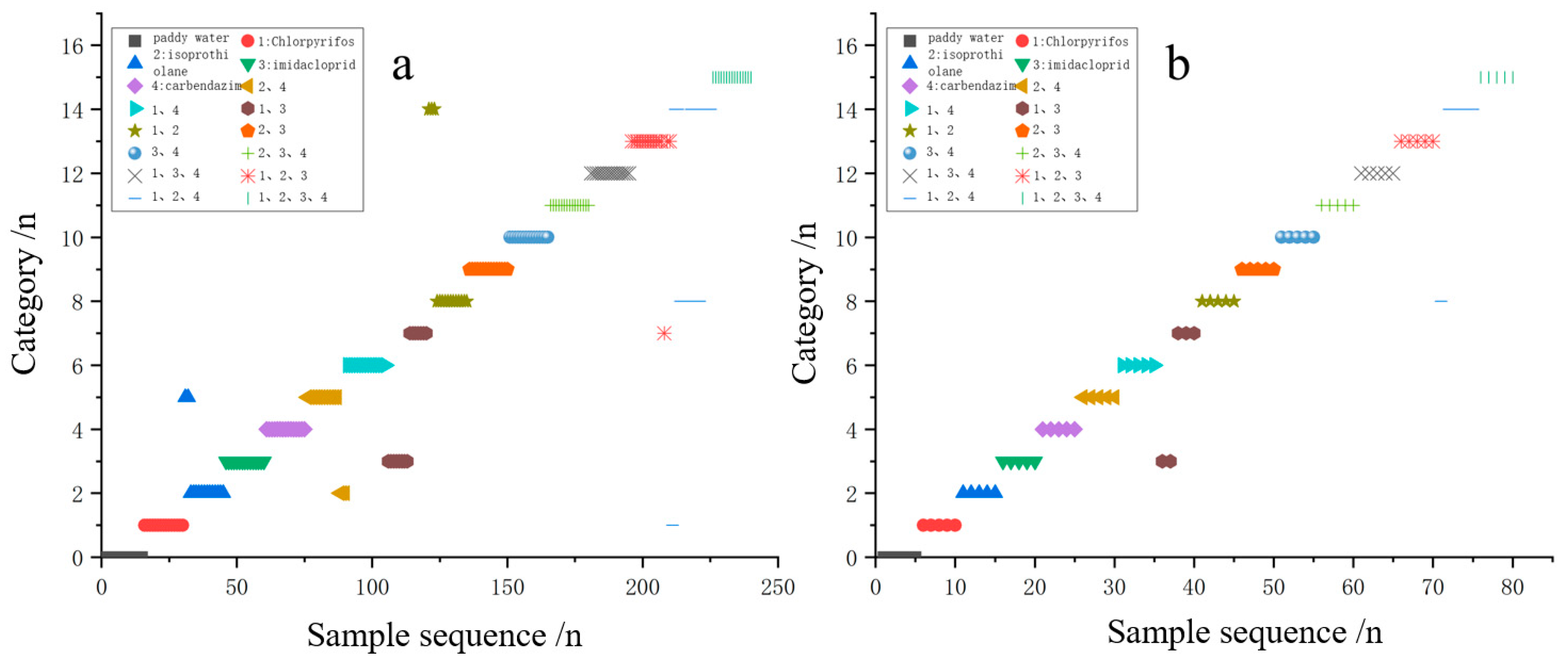
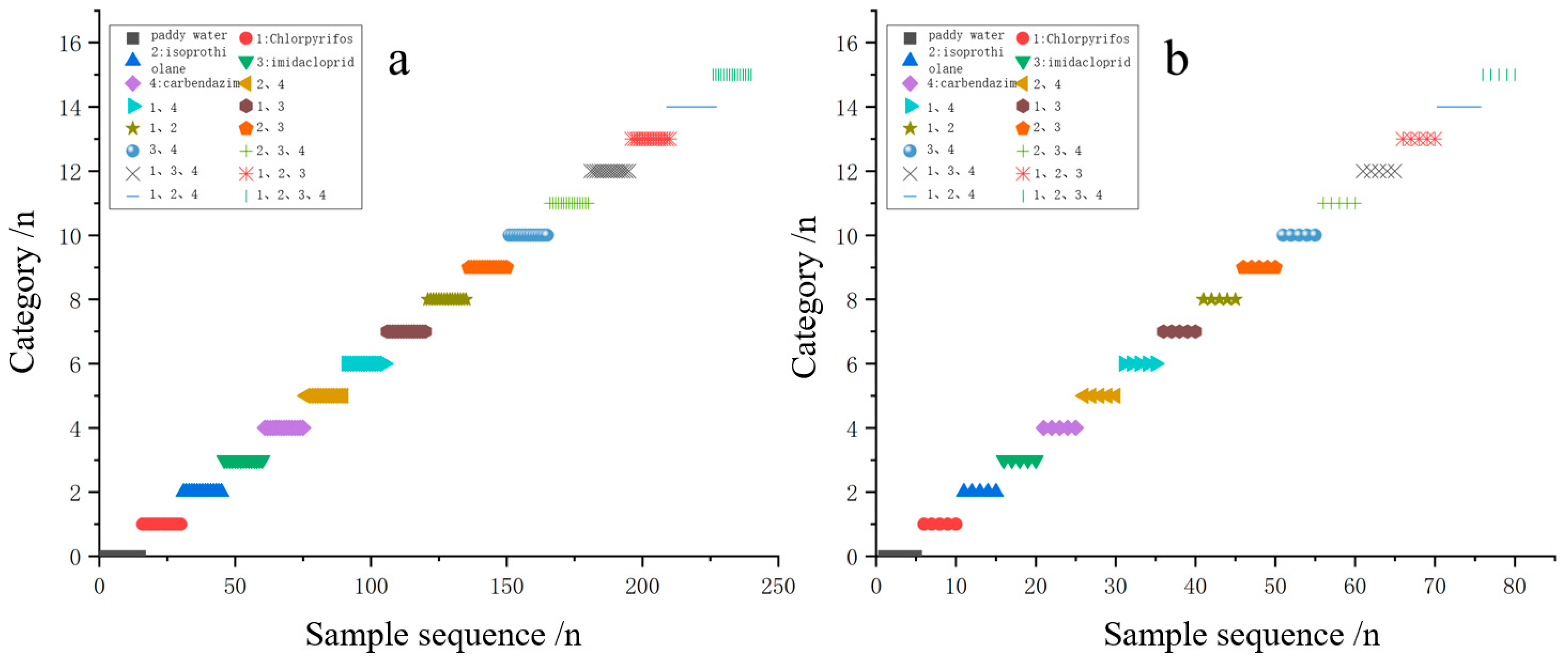
3.3. Characterization of Typical Pesticide Species in Paddy Water
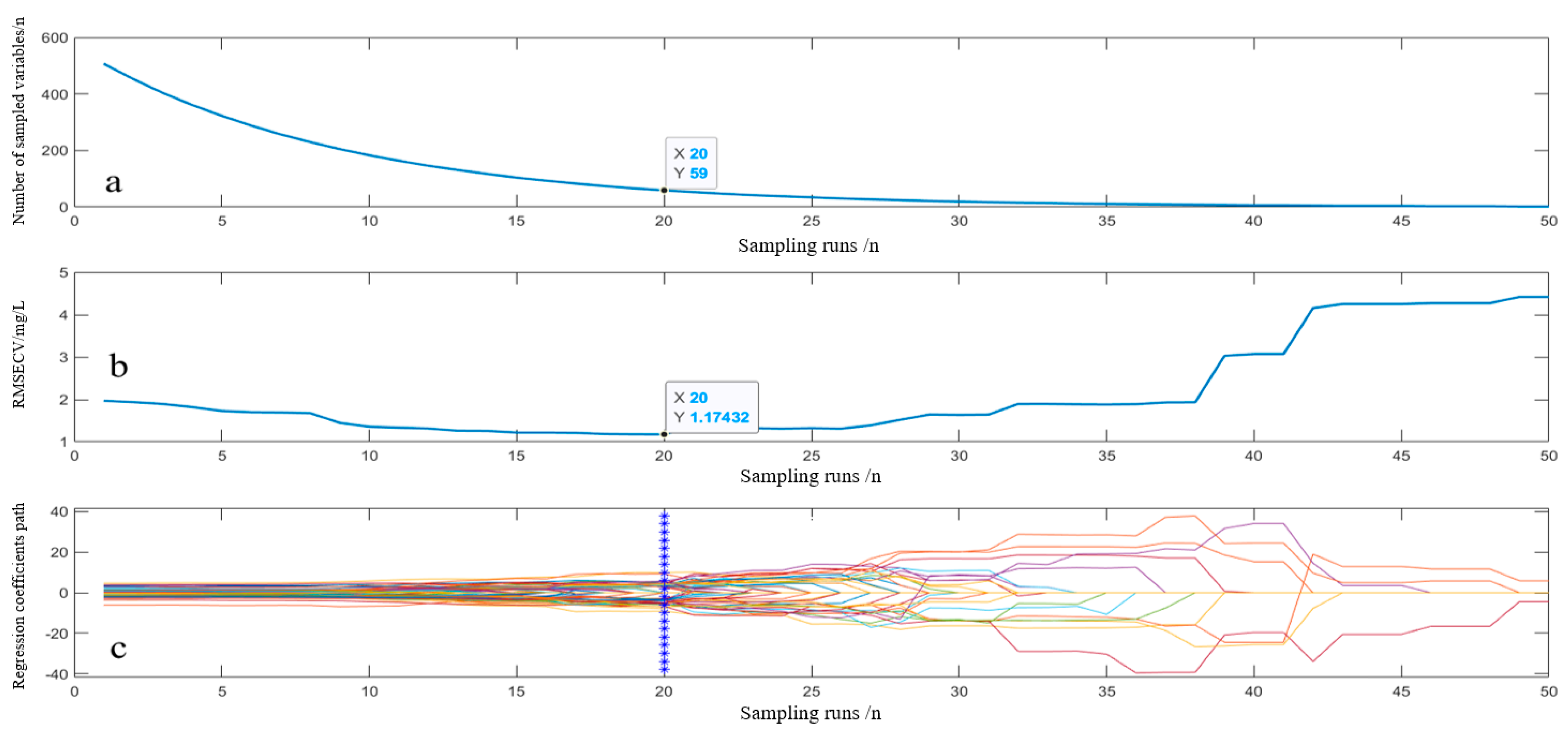
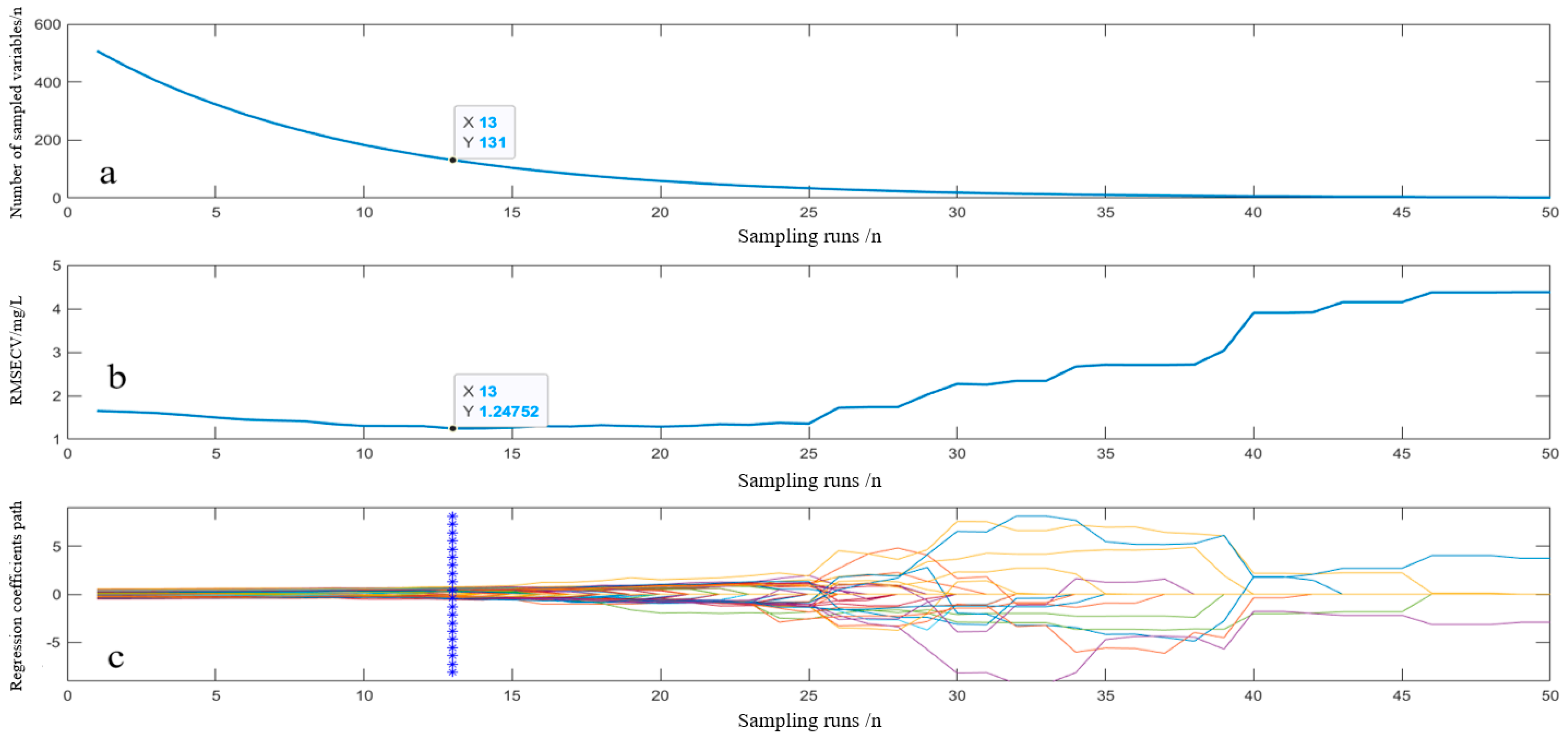
3.3.1. CARS Feature Extraction
3.3.2. PCA Feature Extraction
3.4. Modeling the Identification of Typical Pesticide Species in Paddy Water Bodies
3.4.1. Identification Models for CARS-SVM
3.4.2. Identification Model for PCA-SVM
3.4.3. Comparison of Species Identification Models
3.5. Detection of Typical Pesticide Content in Paddy Water Based on Dielectric Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shanthalakshmi, M.; Sandhiya, M.; Rajalakshmi, M.; Ratheesh, V. Paddy Disease Detection and Pesticide Recommender System for Farmers Using Multi SVM Technique. Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2019, 5, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapat, G.; Labade, C.; Chaudhari, A.; Zinjarde, S. Silica nanoparticle based techniques for extraction, detection, and degradation of pesticides. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 237, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, L.; Ye, B.; Gao, S.; Jin, N. Distribution and health risk assessment of pesticide pollution in raw water and drinking water within key river basins in China in 2022. J. Hyg. Res. 2024, 53, 726–733. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, B.; Hao, Y.; Wang, C.h.; He, H.; Li, J.; Tian, G.; Wei, Y.; Ding, G.; Xu, B. Pollution characteristics and ecological risks ofpesticides in surface water and sediments of Suzhou Ecological Conservation Area. Environ. Pollut. Control 2022, 44, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Maciej, T.; Andrzej, B. Improvement of the QuEChERS method coupled with GC–MS/MS for the determination of pesticide residues in fresh fruit and vegetables. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107794. [Google Scholar]
- Niki C, M.; George, B. Determination of Ethephon in Pesticide Formulations by Ion Exchange Chromatography with Indirect Spectrophotometric Detection. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 795–806. [Google Scholar]
- Ilić, M.; Pastor, K.; Romanić, R.; Vujić, Đ.; Ačanski, M. A New Challenge in Food Authenticity: Application of a Novel Mathematical Model for Rapid Quantification of Vegetable Oil Blends by Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). Anal. Lett. 2022, 55, 2752–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciej, T. Determination of Selected Priority Pesticides in High Water Fruits and Vegetables by Modified QuEChERS and GC-ECD with GC-MS/MS Confirmation. Molecules 2019, 24, 417. [Google Scholar]
- Abasalizadeh, A.; Sorouraddin, S.M.; Farajzadeh, M.A. Development of a green approach based on DµSPE combined with deep eutectic solvent-based DLLME for the extraction of some pesticides from vegetable samples prior to GC–FID and GC–MS. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2022, 19, 4699–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, Z. Development of a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer Quenchbody sensor for the detection of organophosphorus pesticides in water bodies. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmastas, A.; Umaz, A.; Pirinc, V.; Aydin, F. Quantitative determination and removal of pesticide residues in fresh vegetables and fruit products by LC–MS/MS and GC–MS/MS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Li, Z.; He, X.; Li, H. LingWu long jujube soluble solids content predicting model research based on dielectric spectra. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 369–375. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Wang, D.; Kong, F.; Li, L. Solids Content Detection of Soybean Milk Based on Permittivities. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2016, 47, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, X. Design of protein content detector for raw milk based on electrical properties. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Tao, Z.; Zeng, Y.; He, J. Moisture Content Prediction of Rice Husk in Ectopic Fermentation Bed Based on Dielectric Property. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2021, 50, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Development of rapid identification device for variety of macronutrient water soluble fertilizers based on dielectric characteristic frequency. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 06, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, X. Design and experiment of on-line measuring instrument for grain moisture based on dielectric properties. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2020, 41, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Samarghandi, M.R.; Mohammadi, M.; Karami, A.; Tabandeh, L.; Dargahi, A.; Amirian, F. Residue Analysis of Pesticides, Herbicides, and Fungicides in Various Water Sources Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Detection. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Zhu, W.; Dong, R.; Zheng, L.; Wang, F. Rapid Detection of Pesticide Residues in Paddy Water Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Sensors 2019, 19, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedeen, M.Z.; Sharma, M.; Kushwaha, H.S.; Gupta, R. Sensitive enzyme-free electrochemical sensors for the detection of pesticide residues in food and water. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. Regul. Ed. 2024, 176, 117729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaka, E.; Wariboko, M.A.; Johnson, N.A.N.; Aniagyei, O.N. Advanced visual sensing techniques for on-site detection of pesticide residue in water environments. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Lei, C.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y. Improved dielectric and energy storage properties of polymer composites with BNNSs/AgNPs hybrid nanofiller. Mater. Technol. 2022, 37, 2158–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, S.; Bano, S.; Bibi, I.; Alwadai, N.; Mohsin, I.U.; Al Huwayz, M.; Iqbal, M.; Nazir, A. Cationic distributions and dielectric properties of magnesium ferrites fabricated by sol-gel route and photocatalytic activity evaluation. De Gruyter 2023, 1, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.N.; Islam, M.T.; Samsuzzaman, M. Development of a microstrip based sensor aimed at salinity and sugar detection in water considering dielectric properties. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018, 60, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onelsons. Dielectric spectroscopy in agriculture. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2005, 351, 2940–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfe, M.H.; Hajian, M.; Toghraie, D.; Khaje khabaz, M.; Rahmanian, A.; Pirmoradian, M.; Rostamian, H. Prediction the dynamic viscosity of MWCNT-Al2O3 (30,70)/ Oil 5W50 hybrid nano-lubricant using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Egypt. Inform. J. 2022, 23, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, B.; Gabriele, S. Robust PCA via Regularized Reaper with a Matrix-Free Proximal Algorithm. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2021, 63, 626–649. [Google Scholar]
- Neshov, N.N.; Manolova, A.H.; Draganov, I.R.; Tonschev, K.T.; Boumbarov, O.L. Classification of Mental Tasks from EEG Signals Using Spectral Analysis, PCA and SVM. Cybern. Inf. Technol. 2018, 18, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, S.; Sun, G. Classification of ECG Arrhythmia Using CNN, SVM and LDA; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Jun Sun Yunnan Mo Chunxia Dai et, a.l. Detection of moisture content of tomato leaves based on dielectric properties and IRIV-GWO-SVR algorithm. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Song, K.; Han, W.; Xu, J.-H.; Guo, W.-C. Dielectric properties of Lousoil andmoisture content detection affected by frequency and temperature. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2013, 31, 713–718. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-H.; Zhang, K.-X.; Zhang, C. Coal and rock feature detection method based on CARS and PCA. J. Xi’an Univ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 760–768. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, J.K.C.; Puentes, Y.A.N.; Niño, D.D.C.; Acevedo, C.M.D. Detection of Pesticides in Water through an Electronic Tongue and Data Processing Methods. Water 2023, 15, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Luan, Y.; Tan, Z.; Wei, W. Pesticide Residue Detection in Broccoli Based on Hyperspectral Technology and Convolutional Neural Network. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2025, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
| Sample Overview | Chlorpyrifos | Isoprothiolane | Imidacloprid | Carbendazim |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration range (mg/L) | 1~98 | 1~125 | 1~125 | 2~250 |
| Samples at a temperature (n) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Temperature points (n) | 10 | |||
| Total single pesticide test samples (n) | 4000 | |||
| Sample Overview | Combination of Two Pesticides | Combination of Three Pesticides | Combination of Four Pesticides |
|---|---|---|---|
| Types | 6 | 4 | 1 |
| Per type sample at a temperature (n) | 40 | 40 | 90 |
| Total samples per type (n) | 240 | 160 | 90 |
| Total samples at a temperature (n) | 490 | ||
| Temperature points (n) | 10 | ||
| Total mixed pesticide test samples (n) | 4900 | ||
| Species Identification | Blank Paddy Water Sample | Added Single Pesticide Sample | Added Mixed Pesticide Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| Types | 1 | 4 | 11 |
| Per-type sample (n) | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Temperature points (n) | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Total samples per type (n) | 200 | 800 | 2200 |
| Total test samples (n) | 3200 | ||
| Content Prediction | Blank Paddy Water Sample | Added Single Pesticide Sample | Sample Containing a Certain Pesticide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Types | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Per-type sample number (n) | 1 | 100 | 330 |
| Total samples at a temperature (n) | 431 | ||
| Temperature points (n) | 10 | ||
| Total test samples (n) | 4310 | ||
| Temperature | PCA-SVM | CARS-SVM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Recognition Accuracy | Prediction Recognition Accuracy | Training Recognition Accuracy | Prediction Recognition Accuracy | |
| 5 °C | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| 10 °C | 100% | 100% | 100% | 98.75% |
| 15 °C | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| 20 °C | 99.58% | 98.75% | 100% | 100% |
| 25 °C | 100% | 100% | 100% | 98.75% |
| 27 °C | 100% | 98.75% | 100% | 100% |
| 29 °C | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| 31 °C | 100% | 100% | 99.58% | 93.75% |
| 33 °C | 99.58% | 97.5% | 100% | 96.25% |
| 35 °C | 100% | 100% | 97.08% | 97.5% |
| Temperature | Amplitude | Phase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSEP (mg/L) | R2 | RMSEP (mg/L) | |
| 5 °C | 0.7783 | 26.2881 | 0.8186 | 23.3548 |
| 10 °C | 0.7783 | 25.9446 | 0.8011 | 26.0329 |
| 15 °C | 0.7761 | 25.6813 | 0.7837 | 24.9085 |
| 20 °C | 0.776 | 27.1139 | 0.7811 | 25.3296 |
| 25 °C | 0.8163 | 24.1919 | 0.8249 | 22.5937 |
| 27 °C | 0.7759 | 25.9639 | 0.7894 | 24.7322 |
| 29 °C | 0.7758 | 26.0133 | 0.7851 | 24.8585 |
| 31 °C | 0.7779 | 25.2470 | 0.8032 | 24.3347 |
| 33 °C | 0.7748 | 25.5194 | 0.8218 | 23.6387 |
| 35 °C | 0.801 | 23.907 | 0.7687 | 26.8571 |
| Temperature | Amplitude | Phase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSEP (mg/L) | R2 | RMSEP (mg/L) | |
| 5 °C | 0.7568 | 32.8584 | 0.8073 | 29.875 |
| 10 °C | 0.756 | 31.8154 | 0.8241 | 27.6818 |
| 15 °C | 0.7569 | 35.6823 | 0.8052 | 31.9389 |
| 20 °C | 0.7524 | 32.9548 | 0.8475 | 25.5785 |
| 25 °C | 0.7949 | 31.3452 | 0.8529 | 24.8319 |
| 27 °C | 0.7589 | 34.7517 | 0.8186 | 28.0793 |
| 29 °C | 0.7611 | 33.2808 | 0.8545 | 24.6119 |
| 31 °C | 0.79 | 29.6203 | 0.8639 | 24.7423 |
| 33 °C | 0.7698 | 30.9208 | 0.8373 | 26.6229 |
| 35 °C | 0.7885 | 29.9885 | 0.8537 | 26.112 |
| Temperature | Amplitude | Phase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSEP (mg/L) | R2 | RMSEP (mg/L) | |
| 5 °C | 0.8061 | 62.1691 | 0.8571 | 55.2072 |
| 10 °C | 0.8123 | 60.443 | 0.9028 | 55.0894 |
| 15 °C | 0.8019 | 62.0995 | 0.848 | 54.5977 |
| 20 °C | 0.799 | 62.8036 | 0.863 | 51.9813 |
| 25 °C | 0.8134 | 61.0351 | 0.9113 | 42.6253 |
| 27 °C | 0.8312 | 57.4198 | 0.8618 | 51.9028 |
| 29 °C | 0.8064 | 61.4615 | 0.8662 | 51.0998 |
| 31 °C | 0.8071 | 61.2793 | 0.8851 | 48.1317 |
| 33 °C | 0.8143 | 60.1270 | 0.8459 | 55.1611 |
| 35 °C | 0.8107 | 61.7979 | 0.8393 | 60.3401 |
| Temperature | Amplitude | Phase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSEP (mg/L) | R2 | RMSEP (mg/L) | |
| 5 °C | 0.7925 | 32.6581 | 0.8368 | 28.9273 |
| 10 °C | 0.7909 | 32.7845 | 0.8087 | 31.34 |
| 15 °C | 0.7956 | 32.3876 | 0.803 | 31.8131 |
| 20 °C | 0.7956 | 32.4797 | 0.8034 | 31.6751 |
| 25 °C | 0.795 | 32.4193 | 0.8137 | 31.1361 |
| 27 °C | 0.7969 | 32.2742 | 0.8127 | 32.2792 |
| 29 °C | 0.7907 | 32.8365 | 0.8013 | 31.9277 |
| 31 °C | 0.7953 | 32.4028 | 0.8184 | 30.6263 |
| 33 °C | 0.7884 | 33.1951 | 0.8063 | 31.5378 |
| 35 °C | 0.7986 | 32.8135 | 0.8047 | 33.9902 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Yang, M.; Huang, J.; Shang, L.; Chen, Q.; Peng, F.; Liu, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J. Study of Detection of Typical Pesticides in Paddy Water Based on Dielectric Properties. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071666
Huang S, Yang M, Huang J, Shang L, Chen Q, Peng F, Liu M, Wu Y, Zhao J. Study of Detection of Typical Pesticides in Paddy Water Based on Dielectric Properties. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071666
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shuanggen, Mei Yang, Junshi Huang, Longwei Shang, Qi Chen, Fang Peng, Muhua Liu, Yan Wu, and Jinhui Zhao. 2025. "Study of Detection of Typical Pesticides in Paddy Water Based on Dielectric Properties" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071666
APA StyleHuang, S., Yang, M., Huang, J., Shang, L., Chen, Q., Peng, F., Liu, M., Wu, Y., & Zhao, J. (2025). Study of Detection of Typical Pesticides in Paddy Water Based on Dielectric Properties. Agronomy, 15(7), 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071666






