Adequate Irrigation Amount per Application Is Required to Secure Uniform Water Management in Drip Irrigation Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Environments
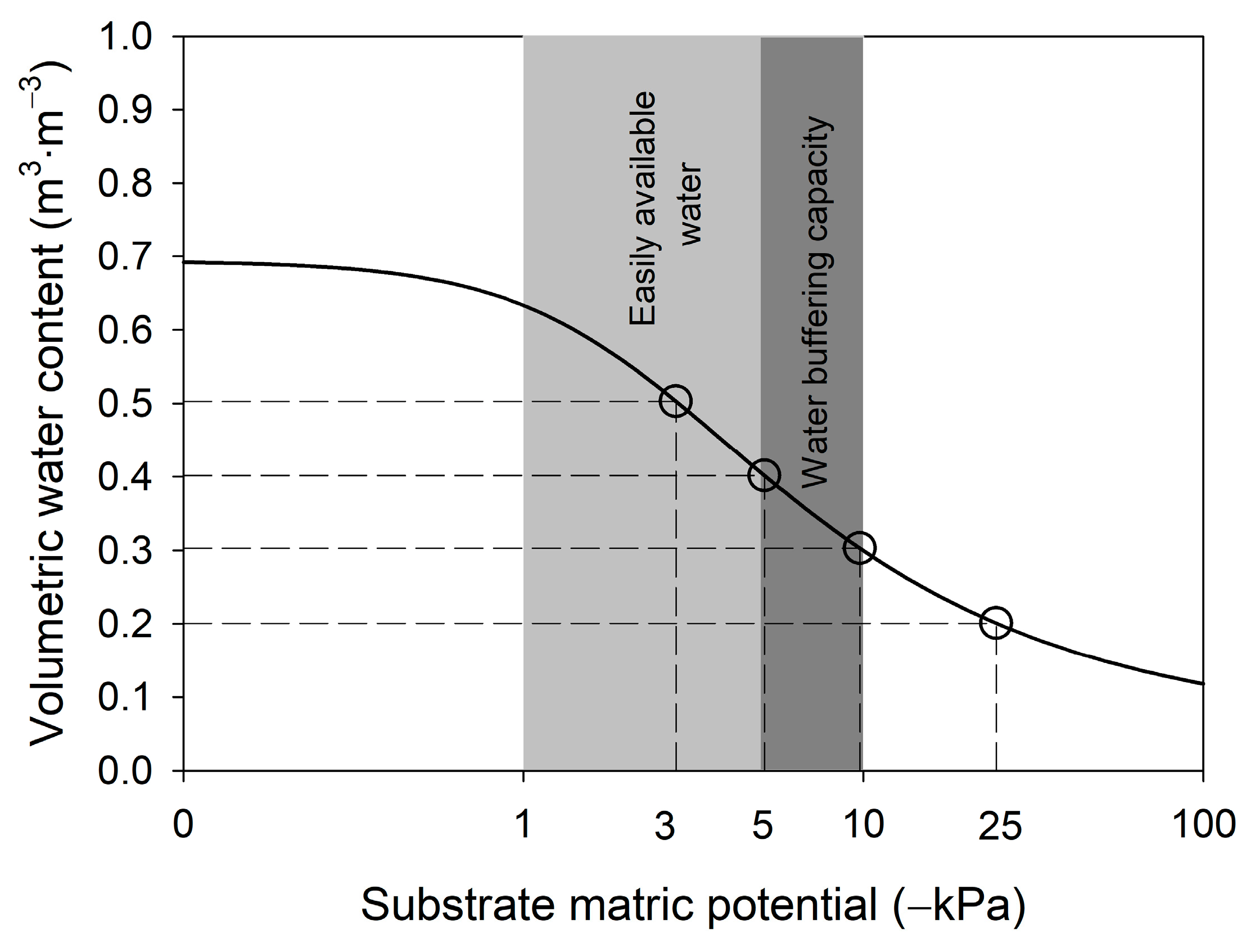
2.2. FDR Sensor-Based Drip Irrigation System
2.3. Irrigation Amount per Application Treatment
2.4. Plant Harvest and Growth Measurement
2.5. Quantifying the Variability of Substrate VWC and Plant Growth
2.6. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
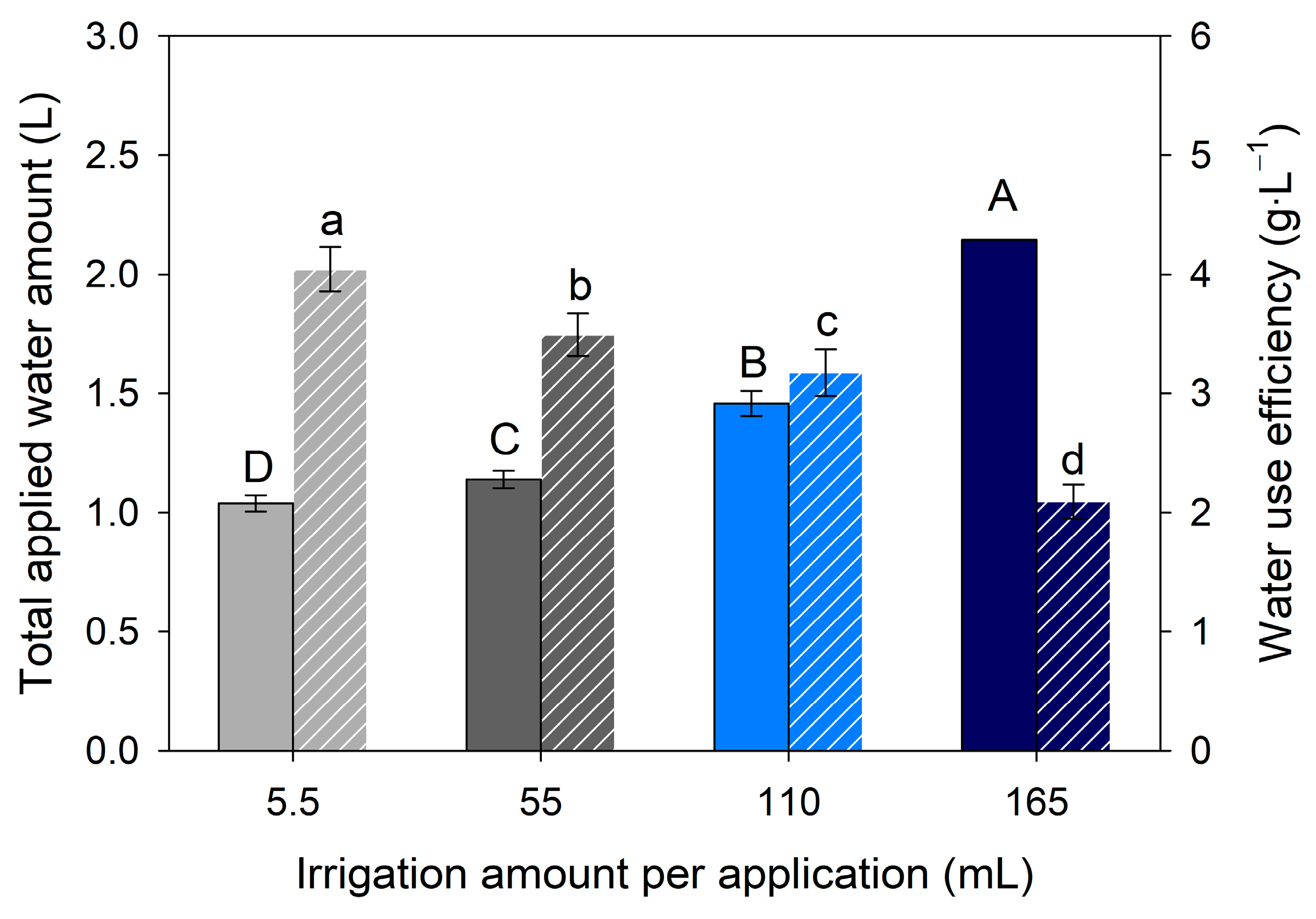
3.1. Effect of IA on the Variability of VWC
3.2. Effect of IA on the Variability of Sweet Basil Growth
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Water in Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. 2022. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/chapter/chapter-4/ (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- FAO. The State of the World’s Land And Water Resources For Food and Agriculture–Systems at Breaking Point in Synthesis Report 2021. 2021. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/items/55def12b-2a81-41e5-91dc-ac6c42f1cd0f (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Farooq, M.; Wahid, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Fujita, D.; Basra, S.M.A. Plant drought stress: Effects, mechanisms and management. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 29, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Malik, M.A.; Farooq, M.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Cheema, M.A. Improving drought tolerance by exogenous application of glycinebetaine and salicylic acid in sunflower. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2008, 194, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Vuong, T.D.; Vantoai, T.; Lee, J.D.; Wu, X.; Mian, M.A.R.; Dorrance, A.E.; Shannon, J.G.; Nguyen, H.T. Mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to Phytophthora sojae and flooding tolerance in soybean. Crop Sci. 2012, 52, 2481–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perata, P. Ethylene signaling controls fast oxygen sensing in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warsaw, A.L.; Fernandez, R.T.; Cregg, B.M.; Andresen, J.A. Container-grown ornamental plant growth and water runoff nutrient content and volume under four irrigation treatments. HortScience 2009, 44, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J.W.; Kay, M.G.; Weatherhead, E.K. Water regulation, crop production, and agricultural water management–Understanding farmer perspectives on irrigation efficiency. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 108, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcon, F.; Navarro, N.; de-Miguel, M.D.; Balbo, A.L. Drip irrigation technology: Analysis of adoption and diffusion processes. In Sustainable Solutions for Food; Sarkar, A., Sensarma, S., vanLoon, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 269–285. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J.; Patel, N.; Rajput, T.B.S. Development and integration of soil moisture sensor with drip system for precise irrigation scheduling through mobile phone. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2016, 8, 1959–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea-Cox, J.D. Using wireless sensor networks for precision irrigation scheduling. In Problems, perspectives and Challenges of Agricultural Water Management; Manish, K., Ed.; IntechOpen Press: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 233–258. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, H.G. Irrigation scheduling: Advantages and pitfalls of plant-based methods. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 2427–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Iersel, M.W.; Chappell, M.; Lea-Cox, J.D. Sensors for improved efficiency of irrigation in greenhouse and nursery production. HortTechnology 2013, 23, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, S.; Djaman, K.; Rudnick, D.R. Effect of full and limited irrigation amount and frequency on surface drip-irrigated maize evapotranspiration, yield, water use efficiency and yield response factors. Irrig. Sci. 2016, 34, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Kim, J. Sufficient light intensity is required for the drought responses in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Agronomy 2024, 14, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Hong, C.; An, S.K.; Kim, J. Low substrate water content is efficient for the performance of Ficus pumila ‘Variegata’ indoors. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2023, 64, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, R.R.; An, S.K.; Kim, J. Optimum moisture conditions for English lavender cuttings are drier for root development than shoot development. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, O.M.; Cohen, A.L.; Rieser, C.J.; Davis, A.G.; Taylor, J.M.; Adesanya, A.W.; Jones, M.S.; Meier, A.R.; Reganold, J.P.; Orpet, R.J.; et al. Organic farming provides reliable environmental benefits but increases variability in crop yields: A global meta-analysis. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Effects of drip system uniformity and irrigation amount on cotton yield and quality under arid conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 124, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, J.; Dančanin, P.; Krištof, K.; Maga, J.; Slaný, V. Evaluation of the quality of irrigation machinery by monitoring changes in the coefficients of uniformity and non-uniformity of irrigation. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Du, K.; Liu, N.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Yin, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z. Effect of dynamic pressure and emitter type on irrigation and fertigation uniformity of drip irrigation systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 312, 109418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Kang, S.; Kim, J. Maintaining a constant soil moisture level can enhance the growth and phenolic content of sweet basil better than fluctuating irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 238, 106203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhie, Y.H.; Kim, J. Changes in physical properties of various coir dust and perlite mixes and their capacitance sensor volumetric water content calibrations. HortScience 2017, 52, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, J.E. The uniformity of application of water by sprinkler systems. Agric. Eng. 1941, 22, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, J.; Xie, F.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Combined evaluation of agronomic and quality traits to explore heat germplasm in celery (Apium graveolens L.). Sci. Hortic. 2023, 317, 112039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chachar, S.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Guan, C. A comprehensive evaluation of genetic diversity in persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.) germplasms based on large-scale morphological traits and SSR markers. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 313, 111866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramjattan, R.; Umaharan, P. Interrelationships between yield and its components in hot pepper (Capsicum chinense Jacq.). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 287, 110254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
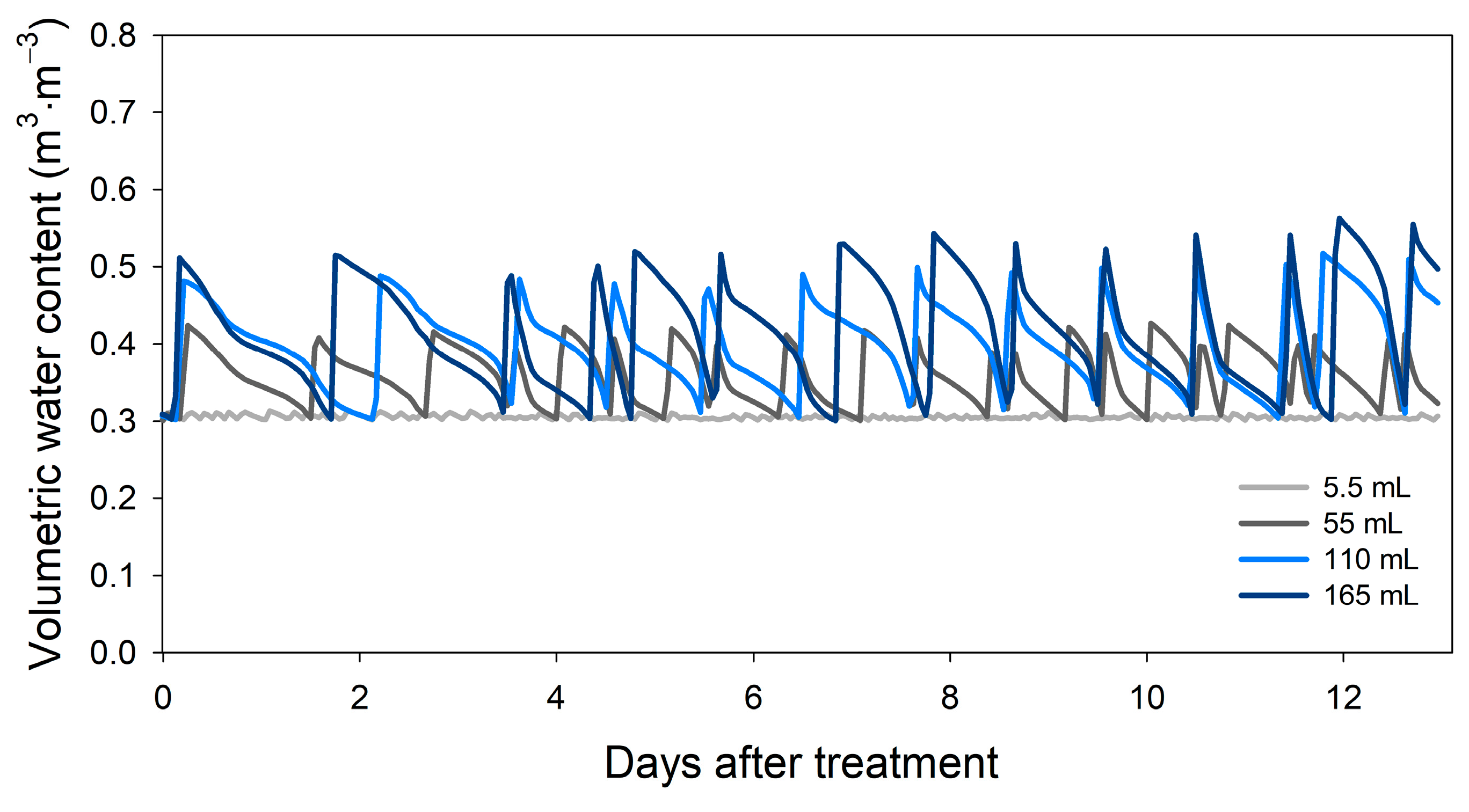
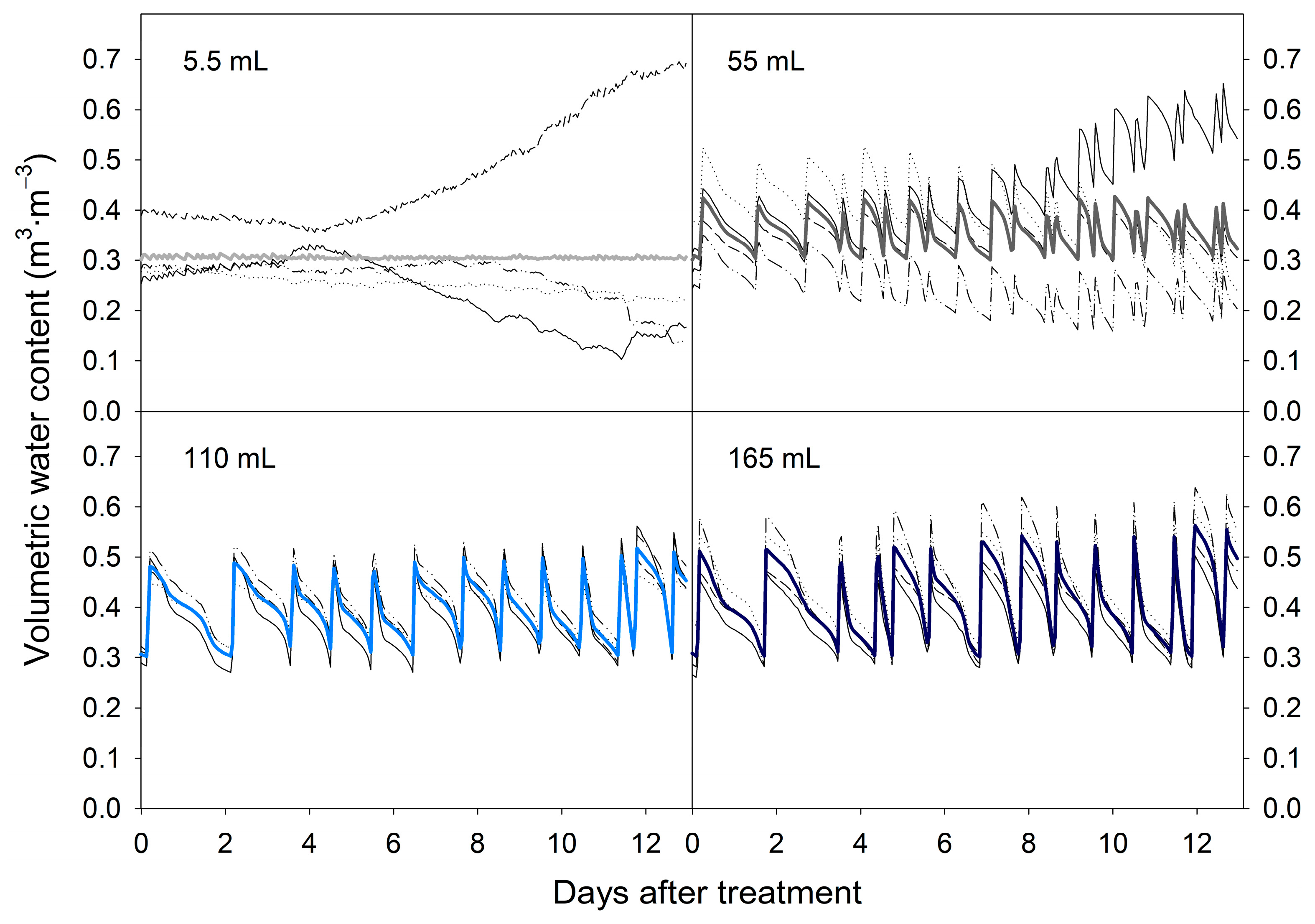
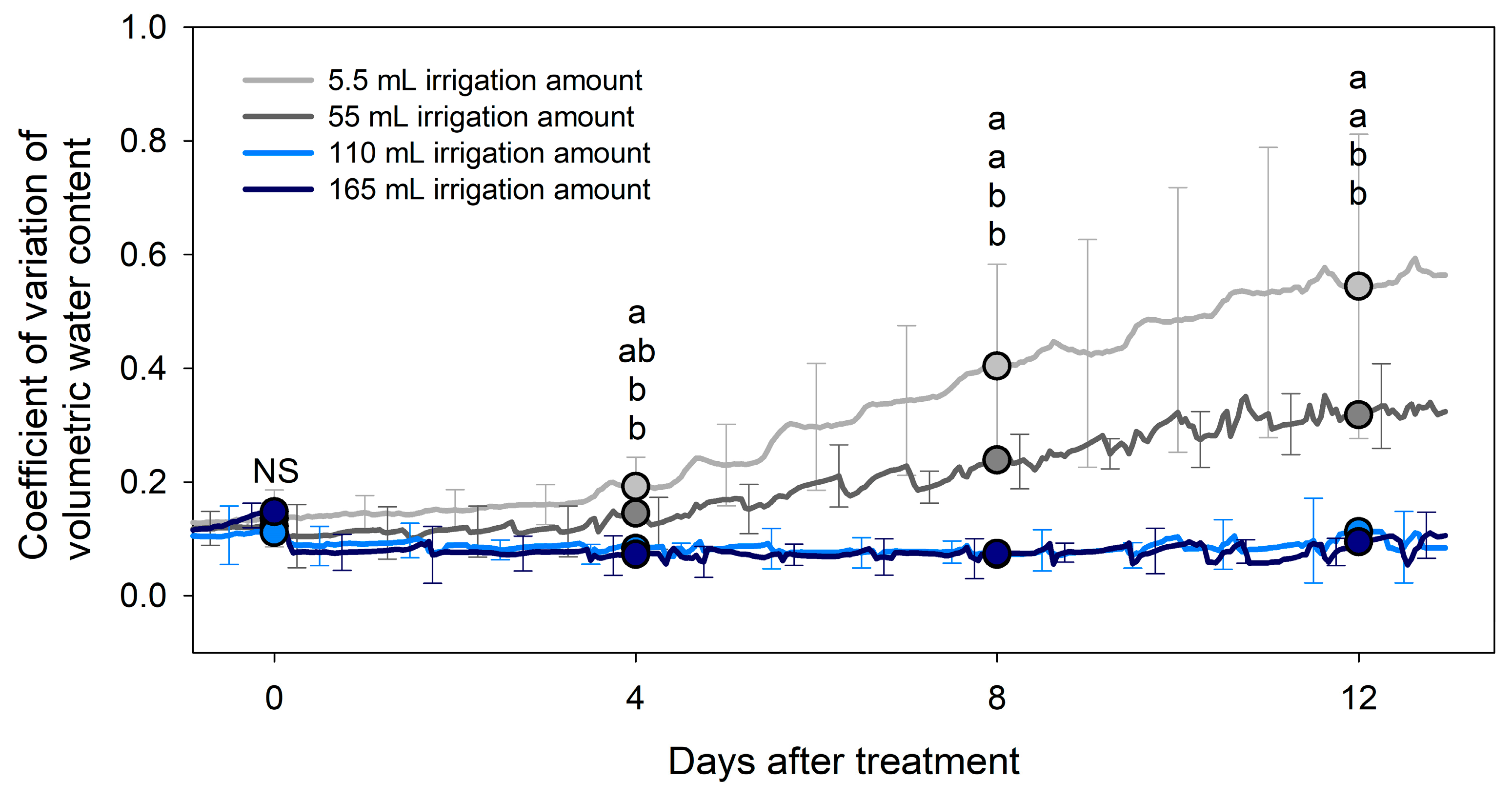
| DAT | Irrigation Amount per Application (mL) | Coefficient of Variation of Volumetric Water Content | ||||
| Mean | Standard Deviation | 95% Confidence Interval | Mean Separation | |||
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| 0 | 5.5 | 0.136 | 0.050 | 0.087 | 0.185 | NS |
| 55 | 0.122 | 0.039 | 0.084 | 0.160 | ||
| 110 | 0.111 | 0.056 | 0.056 | 0.166 | ||
| 165 | 0.148 | 0.020 | 0.128 | 0.168 | ||
| 4 | 5.5 | 0.192 | 0.052 | 0.141 | 0.243 | a |
| 55 | 0.145 | 0.055 | 0.092 | 0.199 | ab | |
| 110 | 0.083 | 0.029 | 0.111 | 0.111 | b | |
| 165 | 0.073 | 0.040 | 0.112 | 0.112 | b | |
| 8 | 5.5 | 0.404 | 0.179 | 0.228 | 0.579 | a |
| 55 | 0.239 | 0.034 | 0.205 | 0.273 | a | |
| 110 | 0.073 | 0.020 | 0.054 | 0.092 | b | |
| 165 | 0.075 | 0.031 | 0.045 | 0.104 | b | |
| 12 | 5.5 | 0.544 | 0.268 | 0.282 | 0.806 | a |
| 55 | 0.318 | 0.076 | 0.244 | 0.392 | a | |
| 110 | 0.113 | 0.069 | 0.045 | 0.180 | b | |
| 165 | 0.095 | 0.030 | 0.065 | 0.124 | b | |
| Irrigation Amount per Application (mL) | Plant Height (cm) | Leaf Area (cm2) | Shoot Fresh Weight (g) | Root Fresh Weight (g) | Shoot Dry Weight (g) | Root Dry Weight (g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | |
| 5.5 | 24.51 | 0.03 | 910.63 | 0.12 | 28.14 | 0.10 | 5.71 c | 0.13 | 3.80 | 0.09 | 0.66 bc | 0.09 |
| 55 | 24.26 | 0.04 | 922.52 | 0.13 | 28.43 | 0.11 | 5.94 bc | 0.10 | 3.63 | 0.11 | 0.65 c | 0.08 |
| 110 | 25.14 | 0.04 | 986.82 | 0.10 | 30.88 | 0.10 | 6.30 ab | 0.09 | 3.85 | 0.06 | 0.69 b | 0.09 |
| 165 | 24.96 | 0.04 | 983.16 | 0.10 | 30.30 | 0.10 | 6.44 a | 0.09 | 3.83 | 0.08 | 0.72 a | 0.07 |
| p value | 0.067 | >0.05 | 0.14 | >0.05 | 0.059 | >0.05 | 0.017 | >0.05 | 0.34 | >0.05 | 0.009 | >0.05 |
| Irrigation Amount per Application (mL) | Stomatal Conductance (mmol·m−2·s−1) | Maximum Quantum Yield of PS II (Fv/Fm) | Chlorophyll Content (SPAD) | Photosynthetic Rate (μmol·m−2·s−1) | Transpiration Rate (mmol·m−2·s−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | |
| 5.5 | 334.56 | 0.31 | 0.76 | 0.02 | 28.87 | 0.05 | 13.67 | 0.14 | 3.46 | 0.14 |
| 55 | 330.19 | 0.29 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 28.52 | 0.06 | 13.33 | 0.14 | 3.40 | 0.14 |
| 110 | 407.50 | 0.35 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 28.94 | 0.08 | 14.18 | 0.14 | 3.64 | 0.16 |
| 165 | 355.44 | 0.38 | 0.76 | 0.02 | 28.75 | 0.08 | 13.42 | 0.15 | 3.38 | 0.18 |
| p value | 0.45 | >0.05 | 0.97 | >0.05 | 0.94 | >0.05 | 0.69 | >0.05 | 0.67 | >0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Seymour, L.; Kim, J. Adequate Irrigation Amount per Application Is Required to Secure Uniform Water Management in Drip Irrigation Systems. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071639
Lee S, Seymour L, Kim J. Adequate Irrigation Amount per Application Is Required to Secure Uniform Water Management in Drip Irrigation Systems. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071639
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sooeon, Lynne Seymour, and Jongyun Kim. 2025. "Adequate Irrigation Amount per Application Is Required to Secure Uniform Water Management in Drip Irrigation Systems" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071639
APA StyleLee, S., Seymour, L., & Kim, J. (2025). Adequate Irrigation Amount per Application Is Required to Secure Uniform Water Management in Drip Irrigation Systems. Agronomy, 15(7), 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071639







