Assessment of Wind-Related Parameters and Erodibility Potential Under Winter Wheat Canopy in Reclaimed Tidal Flat Land
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
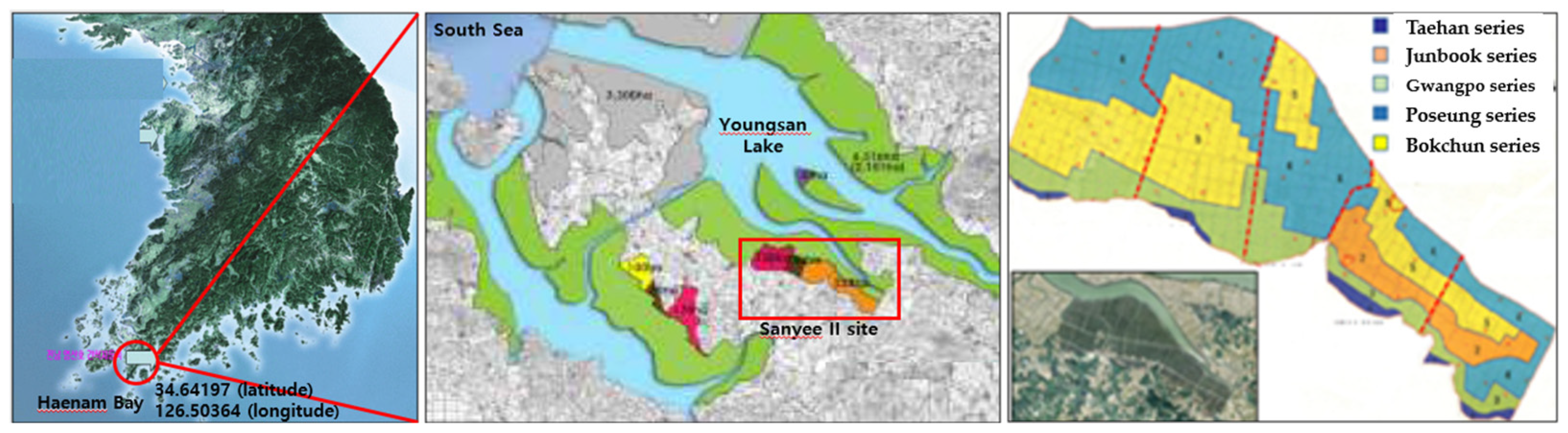
2.1. Experimental Field
2.2. Climatic Conditions
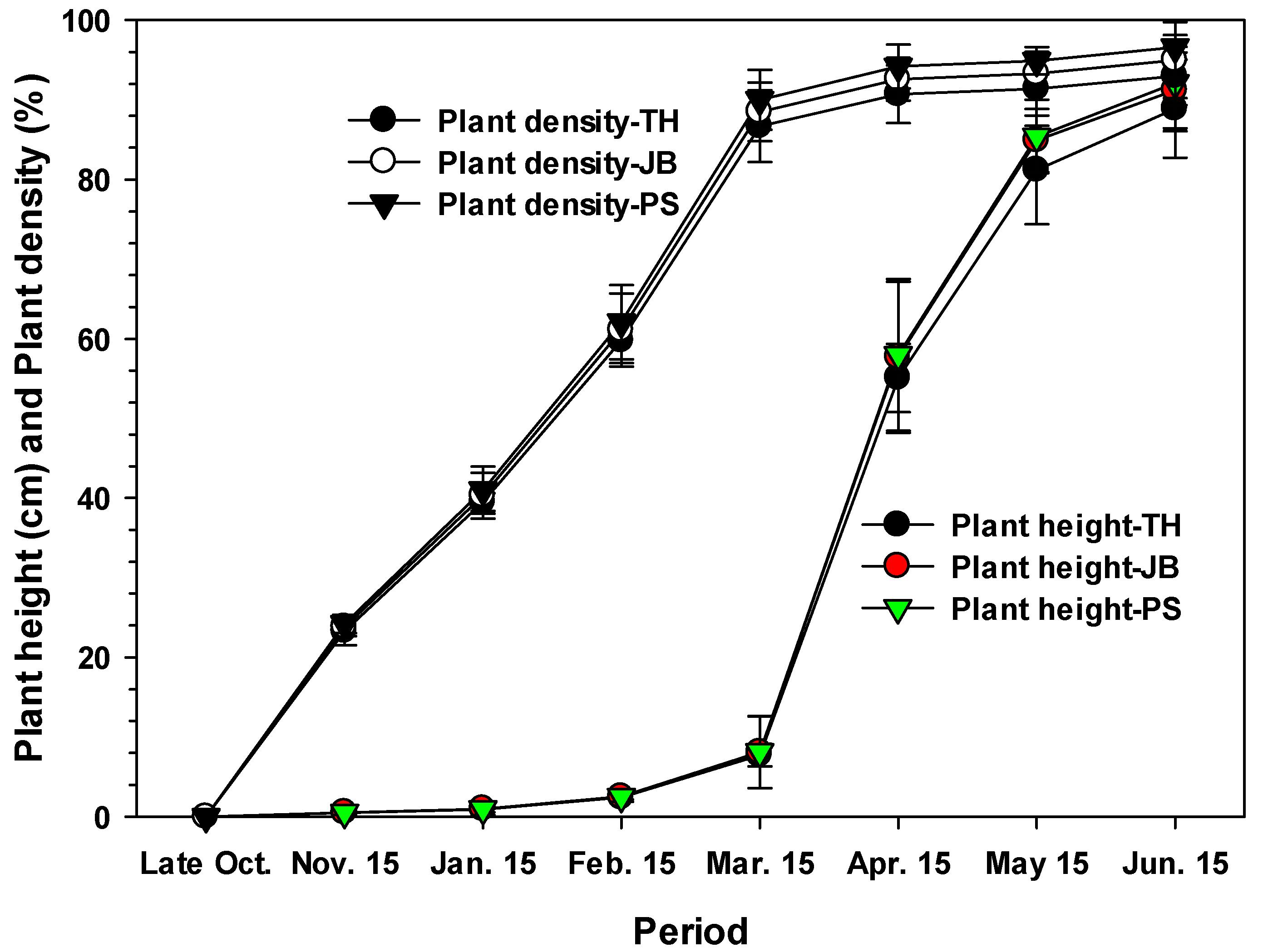
2.3. Plant Height and Canopy
2.4. Soil Characteristics
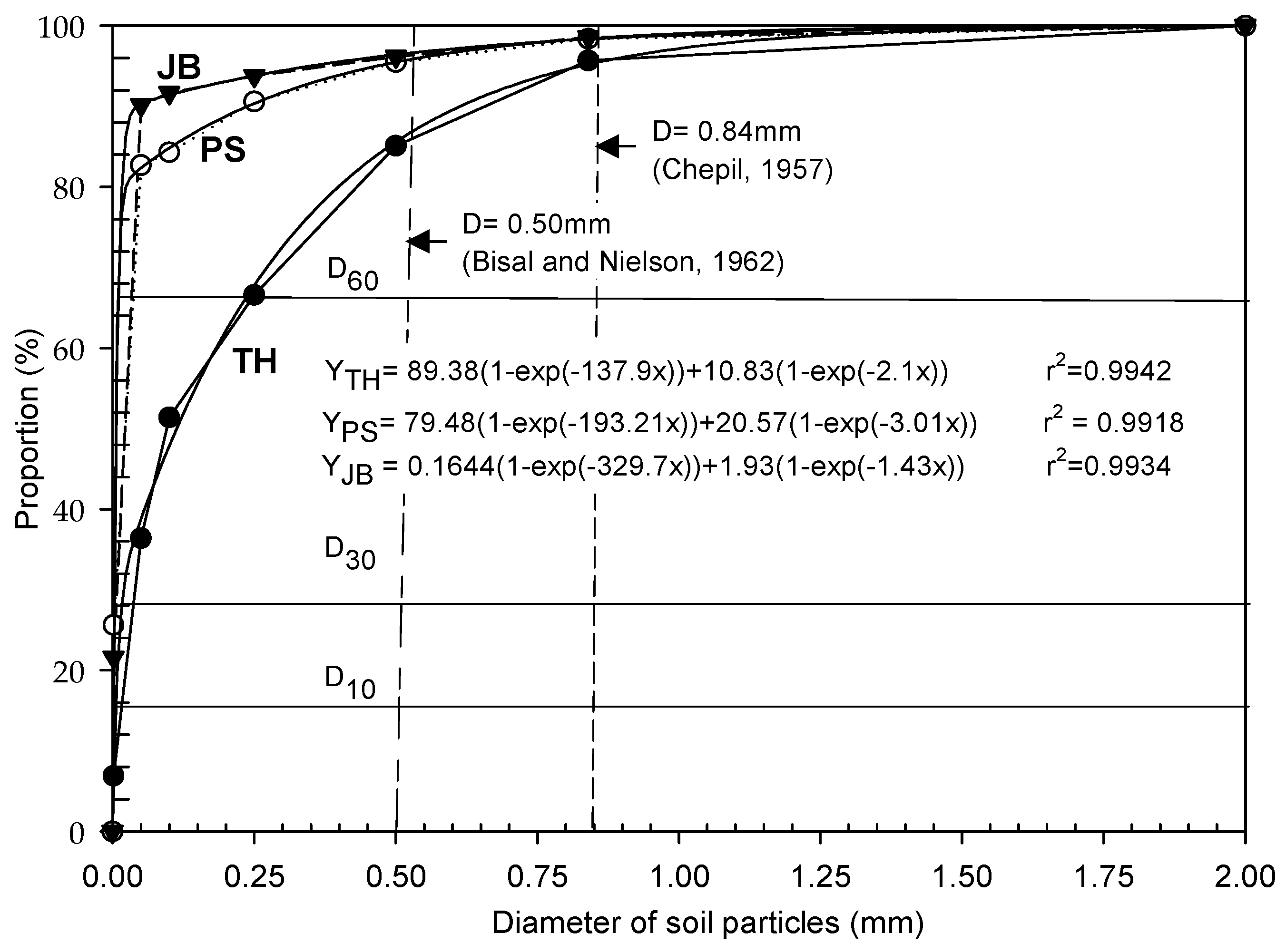
2.5. Soil Particle Distribution Curve
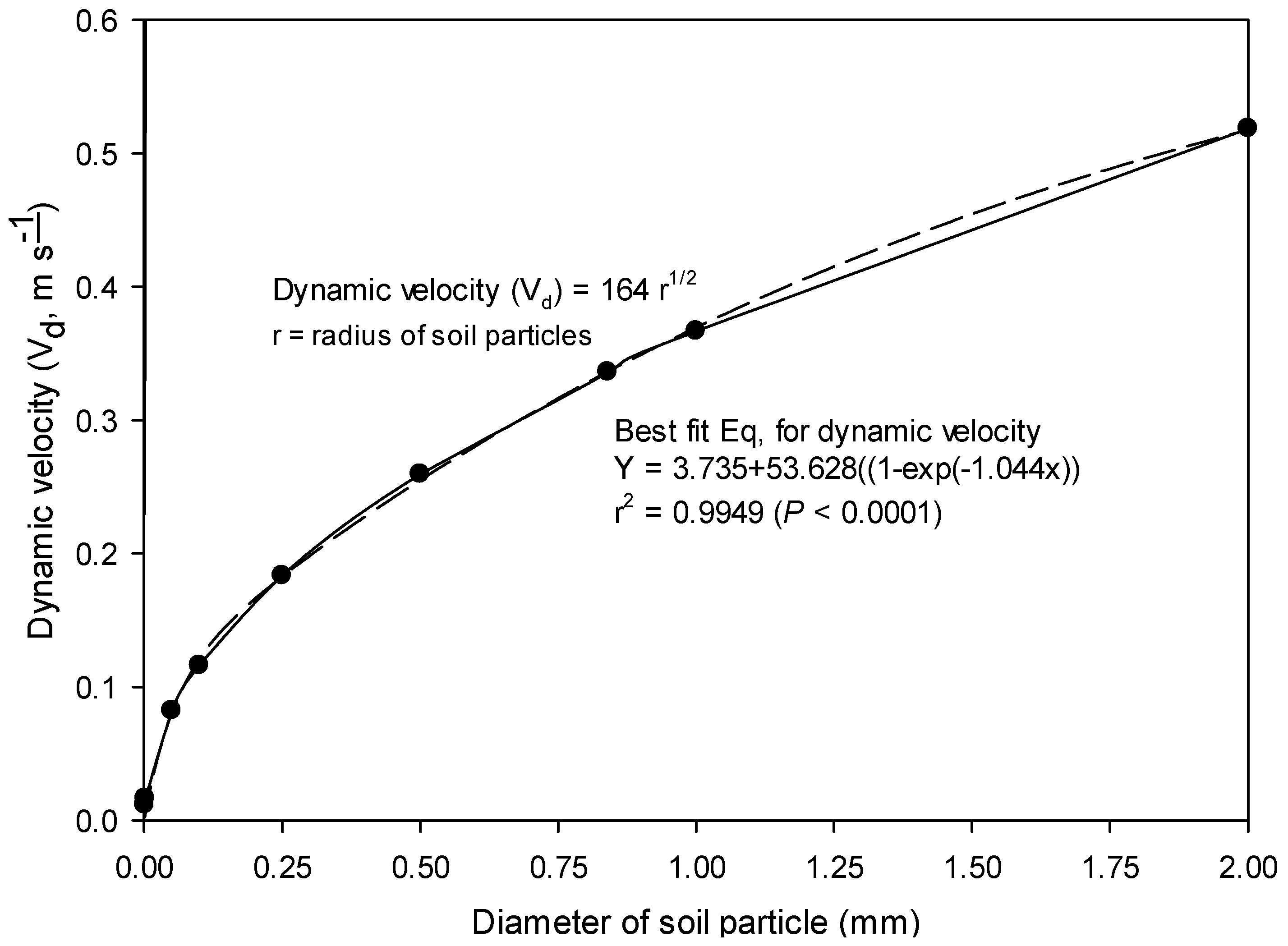
2.6. Estimation of Dynamic Velocity (Vd) and Wind Profile
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
Experimental Field and Climatic Condition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, D.Y.; Kim, H.; Park, M.; Lee, S.E. Characteristics of a reclaimed tidal soil for effective resalization at Saemangum and Youngsan-River. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2012, 45, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Seo, I.H.; Lee, S.P.; Jung, H.G.; Chung, D.Y. Simple assessment of wind erosion depending on the soil texture and threshold wind velocity in reclaimed tidal flat land. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 48, 843–853. [Google Scholar]
- Hagen, L.J.; Armbrust, D.V. Plant Canopy Effects on Wind Erosion Saltation. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Lu, H.A. Simple expression for wind erosion threshold friction velocity. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 22437–22443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharratt, B.S.; Vaddella, V.K. Threshold friction velocity of soils within the Columbia Plateau. Aeolian Res. 2012, 6, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Refahi, H.G. Wind Erosion and Conservation, 6th ed.; Tehran University Press: Tehran, Iran, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, N.P.; Siddoway, F.H. A wind erosion equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1965, 29, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyles, L.; Krauss, R.K. Threshold Velocities and Initial Particle Motion as Influenced by Air Turbulence. Trans. ASAE 1971, 14, 563–566. [Google Scholar]
- Chepil, W.S. Soil Conditions that Influence Wind Erosion. USDA Technical Bulletin. 1958. Available online: https://www.agry.purdue.edu/soils_judging/new_manual/ch6-wind.html (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Fuchs, N.A. The Mechanics of Aerosols; Pergamon Press: London, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Bisal, F.; Nielsen, K.F. Movement of soil particles in saltation Canadian. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1962, 42, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.V. Wind erosion in agricultural soils: An example of limited supply of particles available for erosion. Catena 1998, 33, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevia, G.G.; Mendez, M.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Tillage affects soil aggregation parameters linked with wind erosion. Geoderma 2007, 140, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Cheng, H.; Kang, L.Q.; Wu, Y.Q. Cogitation on developing a dynamic model of soil wind erosion. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 462–473. [Google Scholar]
- Zobeck, T.M.; Van Pelt, S.; Stout, J.E.; Popham, T.W. Validation of the Revised Wind Erosion Equation (RWEQ) for Single Events and Discrete Periods. In Soil Erosion; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St Joseph, MI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrah, M.; Mayel, S.; Tatarko, J.; Funk, R.; Kuka, K. A review of wind erosion models: Data requirements, processes, and validity. Catena 2020, 187, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijóo, A.; Villanueva, D. Assessing wind speed simulation methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 473–483. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Pi, H.; Wagner, L.E.; Fox, F.; Li, S. Evaluating the ability of the Wind Erosion Prediction System (WEPS) to simulate near-surface wind speeds in the Inland Pacific Northwest, USA. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23712. Available online: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Schnarr, C.; Schipanski, M.; Tatarko, J. Crop residue cover dynamics for wind erosion control in a dryland, no-till system. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 77, 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Hagen, L.J. Crop Residue Effects on Aerodynamic Processes and Wind Erosion. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1996, 54, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, D.C.; Aiken, R.M. Wind speed above and within sunflower stalks varying in height and population. J. Soils Water Conserv. 1998, 53, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Spatial vegetation structure and its effect on wind erosion of Alxa dryland ecosystem” Environmental research letters. ERL 2023, 18, 044017. [Google Scholar]
- McMaster, G.S.; Aiken, R.M.; Nielsen, D.C. Optimizing wheat harvest cutting height for harvest efficiency and soil and water conservation. J. Agron. 2000, 92, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar]
- KMA. Current Weather of Korea. 2022. Available online: https://www.weather.go.kr/weather/observation/currentweather.jsp (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Aiken, R.M.; Nielsen, D.C.; Ahuja, L.R. Scaling Effects of Standing Crop Residues on the Wind Profile. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar]
- RDA (Rural Development Administration, Korea). Soil Series of a Reclaimed Tidal Soil. 2017. Available online: https://www.nongsaro.go.kr/portal/ps/psb/psbk/kidofcomdtyDtl.ps;jsessionid=Lc3cJtjh1sW6QdwMOvjgejWK0WLhvjXAOEPcSzAVZUarp3BcM6OFgxoebEBT74wD.nongsaro-web_servletengine1?menuId=PS00067&kidofcomdtyNo=20506 (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Kienast-Brown, S.; Libohova, Z.; Boettinger, J. Digital soil mapping. Soil Surv. Man. 2017, 18, 295–354. [Google Scholar]
- Marticorena, B.; Bergametti, G.; Gillette, D.; Belnap, J. Factors controlling threshold friction velocity in semiarid and arid areas of the Unite States. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 23277–23287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, J.J.; James, G.B. Wind Profiles in Plant Canopies: Studies on an Analytical Model. J. Appl. Ecol. 1971, 8, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, A.S. Momentum absorption by vegetation. QJR Meteorol. Soc. 1971, 97, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.R.; Shaw, R.H. A numerical experiment on the mean wind structure inside canopies of vegetation. J. Agric. 1980, 22, 303–318. [Google Scholar]
- Szeicz, G.; Endrodi, G.; Tajchman, S. Aerodynamic and surface factors in evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 380–394. [Google Scholar]
- Stanhill, G. A Simple Instrument for the Field Measurement of Turbulent Diffusion Flux. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1969, 8, 509–513. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, N.J.; Blad, B.L.; Verma, S.B. Microclimate: The Biological Environment; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Dang, X.; Gao, Y.; Ren, X.; Ding, Y.; Wang, M. Interactive effects of wind speed, vegetation coverage and soil moisture in controlling wind erosion in a temperate desert steppe, Inner Mongolia of China. J. Arid. Land 2018, 10, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Wu, G.L.; Fang, N.F. Freeze/thaw and soil moisture effects on wind erosion. Geomorphology 2014, 207, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, F.; Li, H.; Cheng, D.; Sun, B. The Influence Mechanism of Freeze-Thaw on Soil Erosion: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Sun, C. Soil Erosion as Affected by Freeze-Thaw Regime and Initial Soil Moisture Content. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, Z. Wind tunnel test of the influence of moisture on the erodibility of loessial sandy loam soils by wind. J. Arid. Environ. 1996, 34, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. Physics of Wind Blown Sand and Desert Dunes; Methuen and Co., Ltd.: London, UK, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Cheng, H.; Liu, C.; Fang, Z.; Zou, X. A wind tunnel study of the effects of vegetation structural characteristics on the airflow field. Catena 2024, 242, 108064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary-Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1988; 382p. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, G.S. An Introduction to Environmental Biophysics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
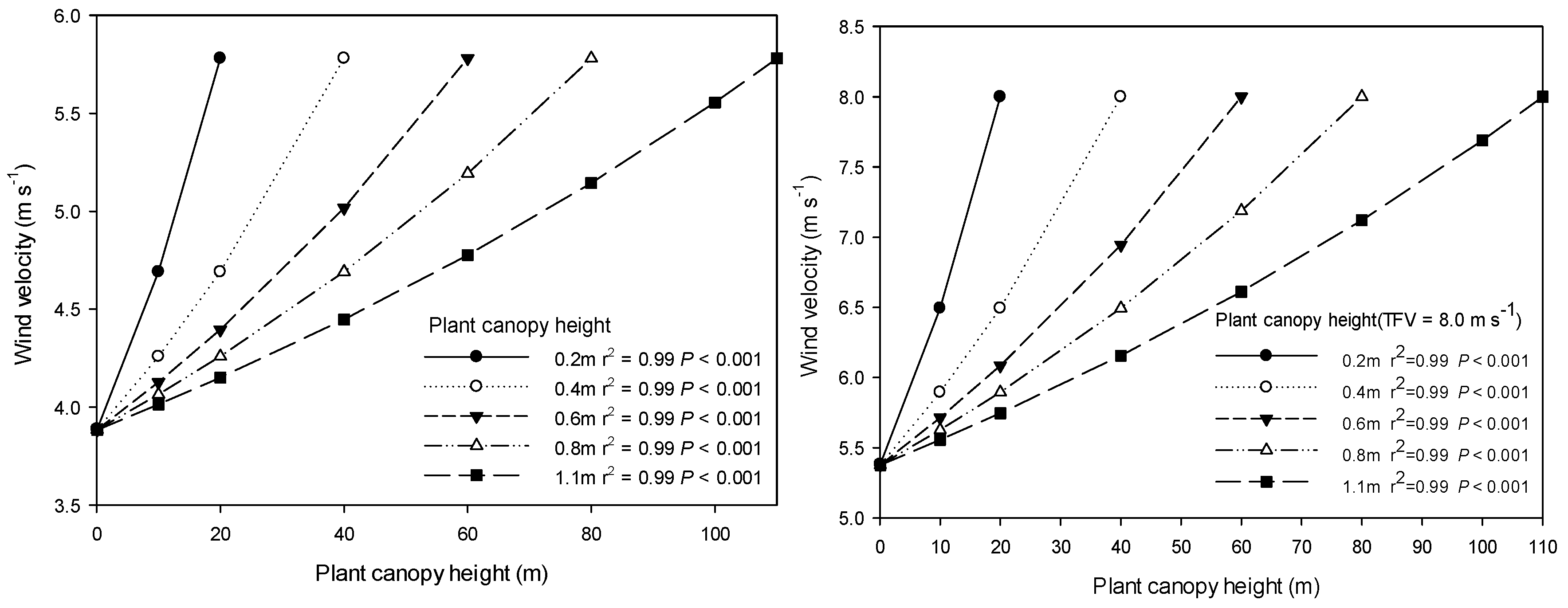
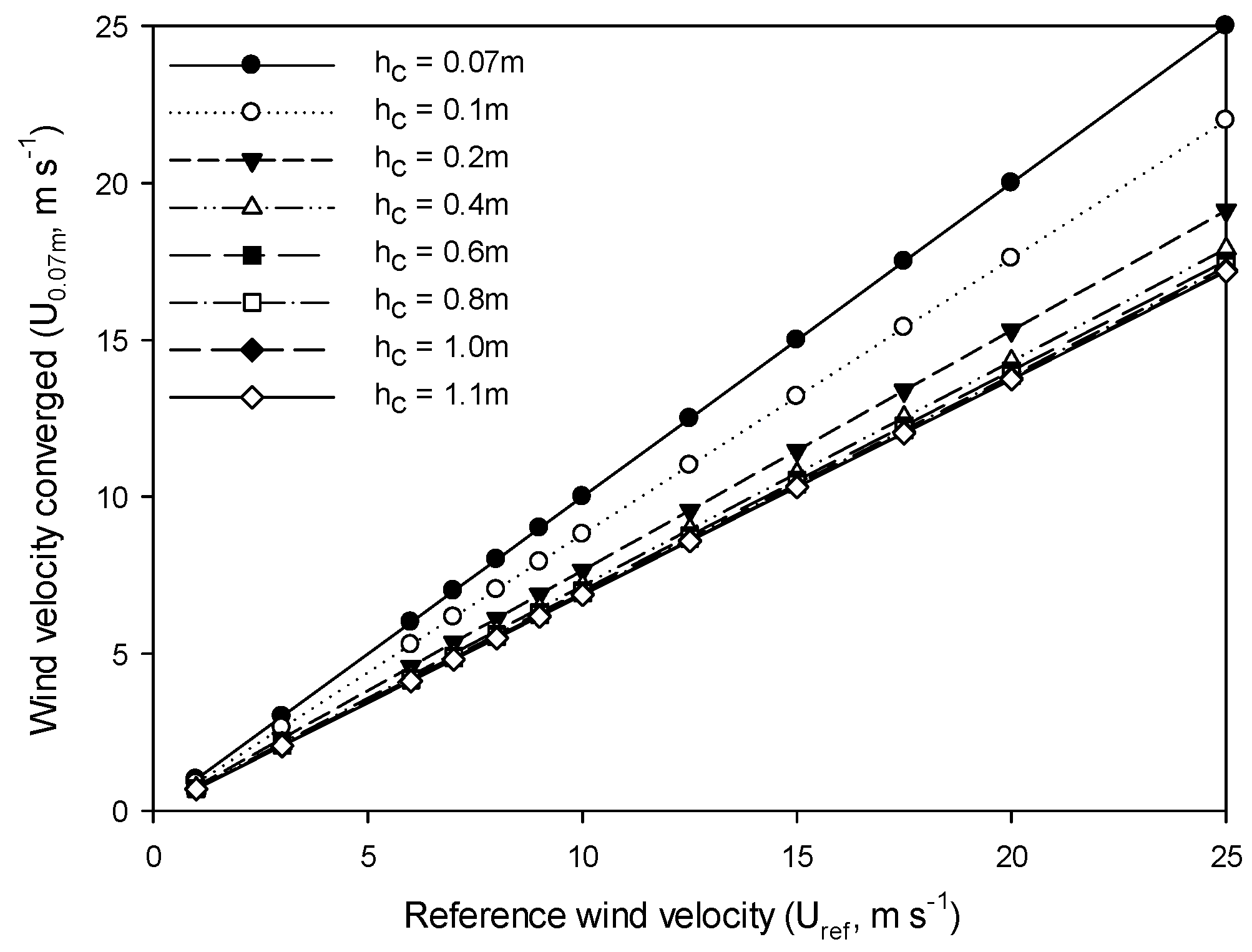

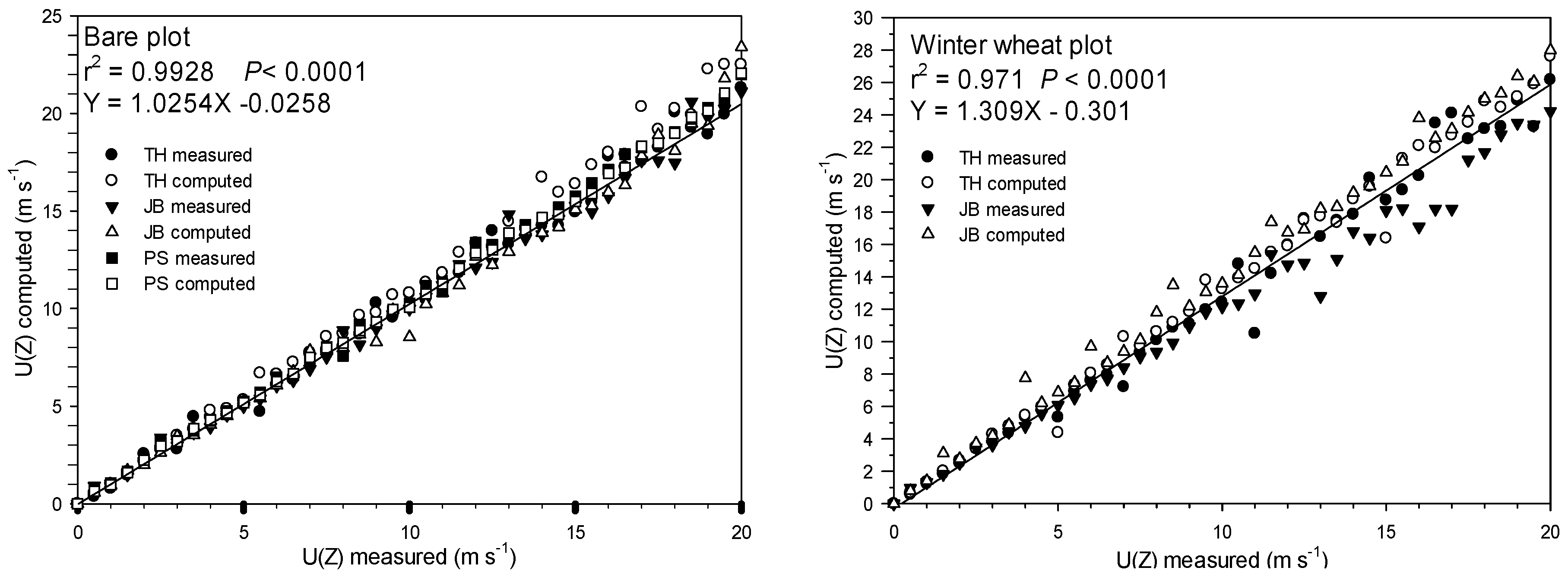
| Month. | October 2019–September 2020 | October 2020–September 2021 | October 2021–Sept. 2022 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. † (Day) | Total | Daily | No. (Day) | Total | Daily | No. (Day) | Total | Daily | ||||
| Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | |||||||
| (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | ||||||||||
| Oct. | 8 | 55.8 | 23.5 | 0.1 | 4 | 27.4 | 27.1 | 0.1 | 8 | 25.8 | 12.2 | 0.1 |
| Nov. | 5 | 12.8 | 7.26 | 0.2 | 5 | 6.92 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 6 | 77.9 | 23.5 | 0.2 |
| Dec. | 6 | 37.3 | 21.8 | 0.1 | 5 | 13.9 | 8.4 | 0.2 | 5 | 16.7 | 12.2 | 0.1 |
| Jan. | 6 | 45.8 | 26.2 | 0.1 | 7 | 36.3 | 13.9 | 0.1 | 4 | 5.18 | 1.95 | 0.1 |
| Feb. | 5 | 27.8 | 9.14 | 0.2 | 6 | 31.7 | 16.4 | 1.2 | 4 | 3.97 | 1.46 | 0.1 |
| Mar. | 6 | 27.1 | 9.72 | 0.1 | 8 | 97.2 | 34.6 | 0.1 | 8 | 83.7 | 29.6 | 0.4 |
| Apr. | 5 | 56.7 | 17.3 | 1.2 | 6 | 53.5 | 22.9 | 0.5 | 7 | 24.5 | 18.1 | 0.1 |
| May | 9 | 188.1 | 59.4 | 0.1 | 8 | 128.9 | 39.9 | 0.2 | 5 | 55.2 | 13.3 | 0.1 |
| Jun. | 10 | 257.7 | 100.2 | 0.4 | 7 | 137.4 | 31.9 | 0.8 | 11 | 70.7 | 50.6 | 0.1 |
| Jul | 14 | 319.6 | 81.8 | 0.4 | 13 | 500.7 | 297.3 | 0.1 | 13 | 193.6 | 108.5 | 0.2 |
| Aug. | 10 | 153.7 | 85.4 | 0.7 | 12 | 172.3 | 29.1 | 0.3 | 12 | 115.6 | 37.7 | 0.4 |
| Sept. | 12 | 295.7 | 113.9 | 0.2 | 15 | 108.2 | 36.5 | 0.1 | 8 | 180 | 22.5 | 0.2 |
| Total | 96 | 1478.1 | 96 | 1314.4 | 91 | 852.8 | ||||||
| Month | Number of Wind Events | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| October 2019–September 2020 | October 2020–September 2021 | October 2021–September 2022 | ||||||||||||||||
| Velocity Range (m s−1) | Total | Velocity Range (m s−1) | Total | Velocity Range (m s−1) | Total | |||||||||||||
| <0.4 | 0.4~5.78 | 5.78~8.9 | 8.9< | 8.0< | <0.4 | 0.4~5.78 | 5.78~8.9 | 8.9< | 8.0< | <0.4 | 0.4~5.78 | 5.78~8.9 | 8.9< | 8.0< | ||||
| Oct. | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 14 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 15 |
| Nov. | 6 | 11 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 25 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 21 | 11 | 9 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 25 |
| Dec. | 9 | 12 | 8 | 1 | 3 | 30 | 6 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 25 | 14 | 9 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 34 |
| Jan. | 8 | 11 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 30 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 3 | 4 | 36 | 8 | 13 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 30 |
| Feb. | 12 | 12 | 11 | 3 | 7 | 38 | 9 | 12 | 11 | 4 | 8 | 36 | 10 | 13 | 10 | 4 | 6 | 37 |
| Mar. | 12 | 12 | 11 | 5 | 8 | 40 | 6 | 13 | 12 | 6 | 8 | 37 | 12 | 14 | 11 | 4 | 7 | 41 |
| Apr. | 9 | 15 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 32 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 31 | 8 | 11 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 28 |
| May | 5 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 16 |
| June | 9 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 7 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 9 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 |
| July | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Aug. | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 12 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 19 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 12 |
| Sep. | 9 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 20 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 23 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 18 |
| Total | 95 | 101 | 62 | 18 | 34 | 276 | 92 | 97 | 75 | 21 | 35 | 282 | 103 | 97 | 62 | 18 | 32 | 280 |
| Soil Series | Depth (cm) | Soil Texture | Soil Structure | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TH | 0~27 | sandy loam | single-grained, platy | tiny quartz particles |
| PS | 0~12 | silty loam | structureless | - |
| JB | 0~19 | silty loam | structureless, massive | mica |
| Soil Series | Sand | Silt | Clay | Soil | OM | BD | Porosity | Ksat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | Texture | (%) | (g cm−3) | (%) | (1×10−3 cm s−1) | ||||
| TH | Min~Max. | 58.8~68.3 | 27.4~34.3 | 5.30~8.90 | Sandy loam | 0.39~0.57 | 1.42~1.51 | 43.0~46.4 | 1.52~1.18 |
| Mean | 63.6 | 29.5 | 6.87 | 0.48 | 1.47 | 44.7 | 1.61 | ||
| SD | 4.53 | 3.54 | 1.80 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 1.71 | 0.02 | ||
| SE | 0.87 | 0.65 | 0.33 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.006 | ||
| PS | Min.~Max. | 13.8~21.2 | 52.9~62.9 | 21.1~29.1 | Silty loam | 0.71~1.23 | 1.34~1.42 | 46.4~49.4 | 1.39–1.59 |
| Mean | 16.8 | 57.1 | 25.6 | 0.97 | 1.38 | 47.9 | 1.48 | ||
| SD | 3.72 | 5.02 | 4.01 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 1.51 | 0.01 | ||
| SE | 0.68 | 0.92 | 0.73 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.003 | ||
| JB | Min.~Max | 7.90~11.6 | 63.4~74.2 | 17.8~26.2 | Silty loam | 0.84~1.05 | 1.35~1.44 | 45.7~49.1 | 1.48–1.69 |
| Mean | 9.89 | 68.6 | 21.6 | 0.95 | 1.4 | 47.4 | 1.53 | ||
| SD | 1.85 | 5.40 | 4.21 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 1.72 | 0.01 | ||
| SE | 0.34 | 0.99 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.004 | ||
| Soil Series | Proportion of Non-Erodible | Proportion of Erodible | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle Size (mm) | Sum | |||||||
| <0.025 (A) | 0.025~0.5 (B) | >0.84 (C) | (A + B) | (A + C) | D | E | 0.05~0.07 mm (F) | |
| TH | 32.5 | 14.9 | 10.6 | 47.4 | 43.1 | 52.6 | 56.9 | 11.5 |
| PS | 68.4 | 4.48 | 2.93 | 72.9 | 71.3 | 27.1 | 28.7 | 1.24 |
| JB | 72.9 | 3.82 | 1.45 | 76.7 | 74.4 | 23.3 | 25.7 | 1.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Jo, H.; Choi, W.; Cho, J.; Chung, D. Assessment of Wind-Related Parameters and Erodibility Potential Under Winter Wheat Canopy in Reclaimed Tidal Flat Land. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071504
Lee K, Lee J, Lee K, Jo H, Choi W, Cho J, Chung D. Assessment of Wind-Related Parameters and Erodibility Potential Under Winter Wheat Canopy in Reclaimed Tidal Flat Land. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071504
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kyosuk, Jaehan Lee, Kwangseung Lee, Hyunsuk Jo, Woojung Choi, Jinwoong Cho, and Dougyoung Chung. 2025. "Assessment of Wind-Related Parameters and Erodibility Potential Under Winter Wheat Canopy in Reclaimed Tidal Flat Land" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071504
APA StyleLee, K., Lee, J., Lee, K., Jo, H., Choi, W., Cho, J., & Chung, D. (2025). Assessment of Wind-Related Parameters and Erodibility Potential Under Winter Wheat Canopy in Reclaimed Tidal Flat Land. Agronomy, 15(7), 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071504






