Drip Irrigation of Phosphorus Fertilizer Enhances Cotton Yield and Phosphorus Use Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling Methods and Measurements
2.3.1. Soil, Cotton Samples, and Phosphorus Content
2.3.2. Cotton Yield
2.3.3. Root Sampling
2.4. Phosphorus Fertilizer Use Efficiency and Calculation Methods
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Phosphorus Application Methods on Soil Phosphorus Availability
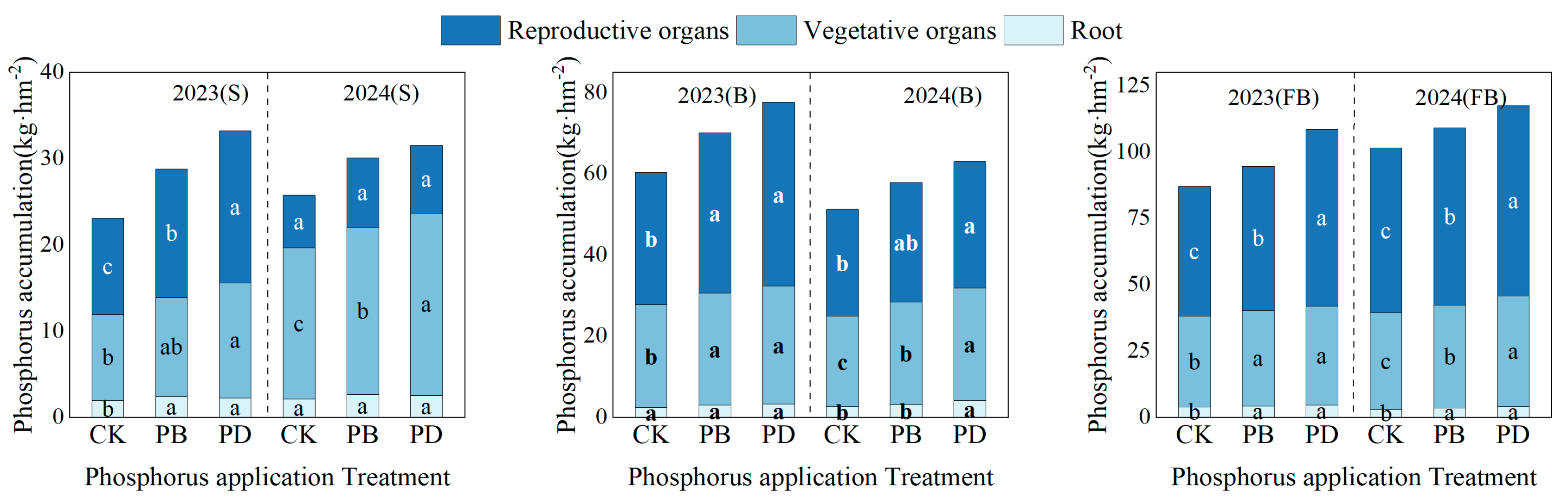
3.2. Impact of Phosphorus Application Methods on Phosphorus Accumulation
3.3. Impact of Phosphate Application Methods on Cotton Biomass and Yield
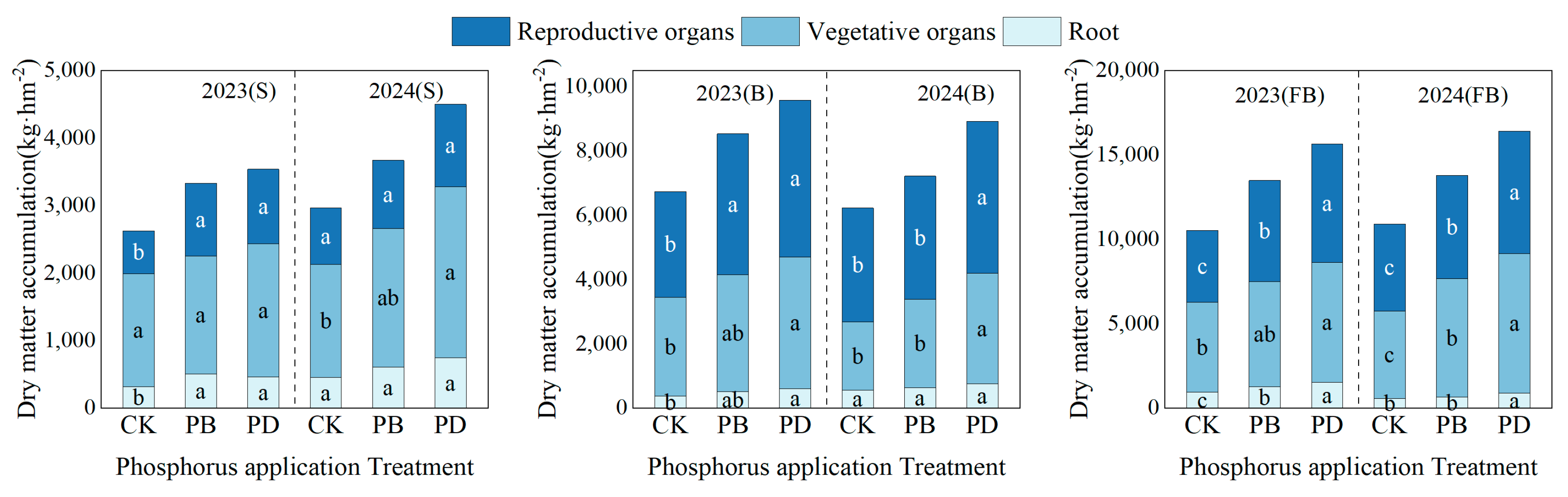
3.3.1. Impact of Phosphorus Application Methods on Cotton Biomass
3.3.2. Impact of Phosphorus Application Methods on Cotton Yield
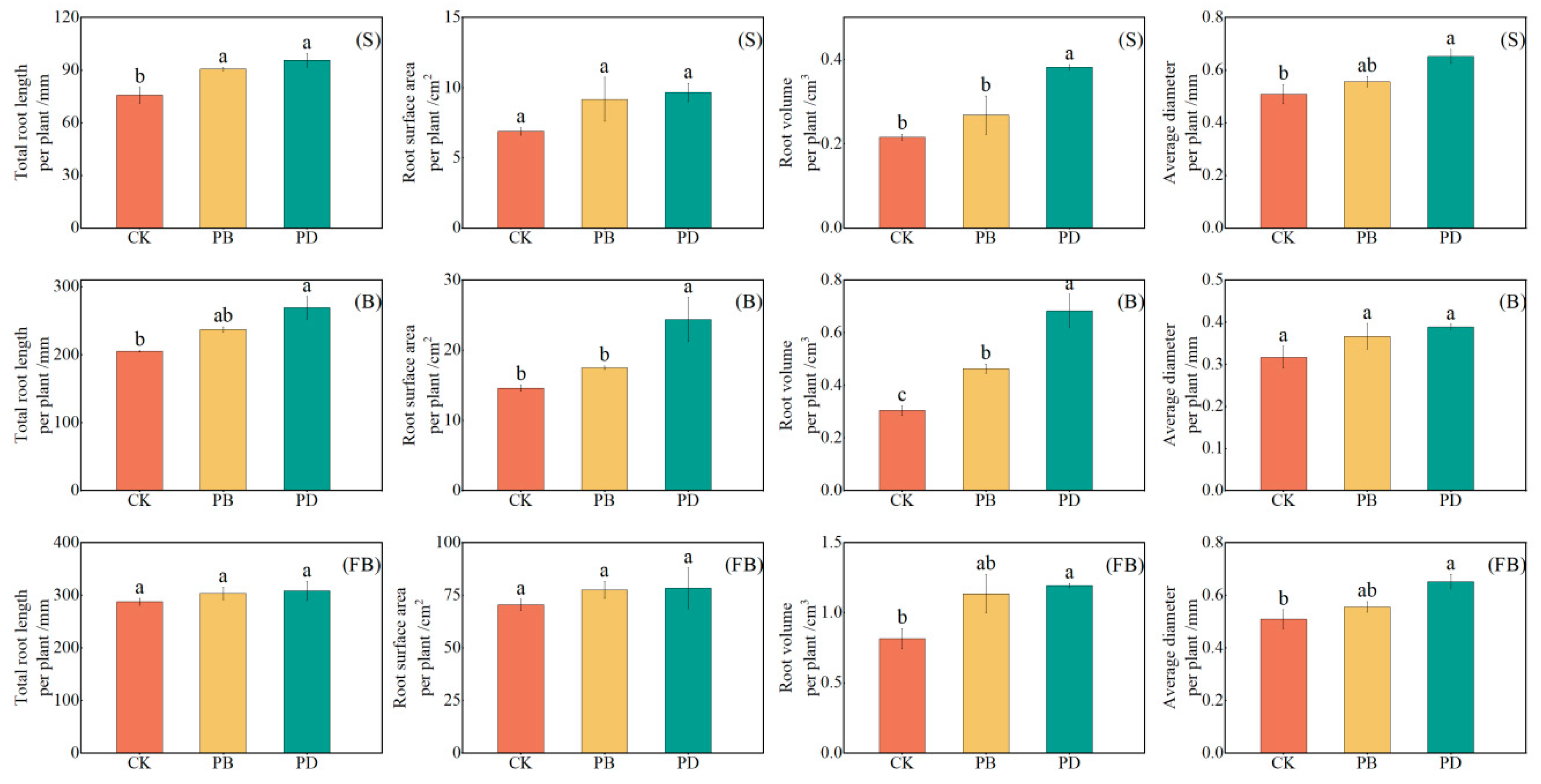
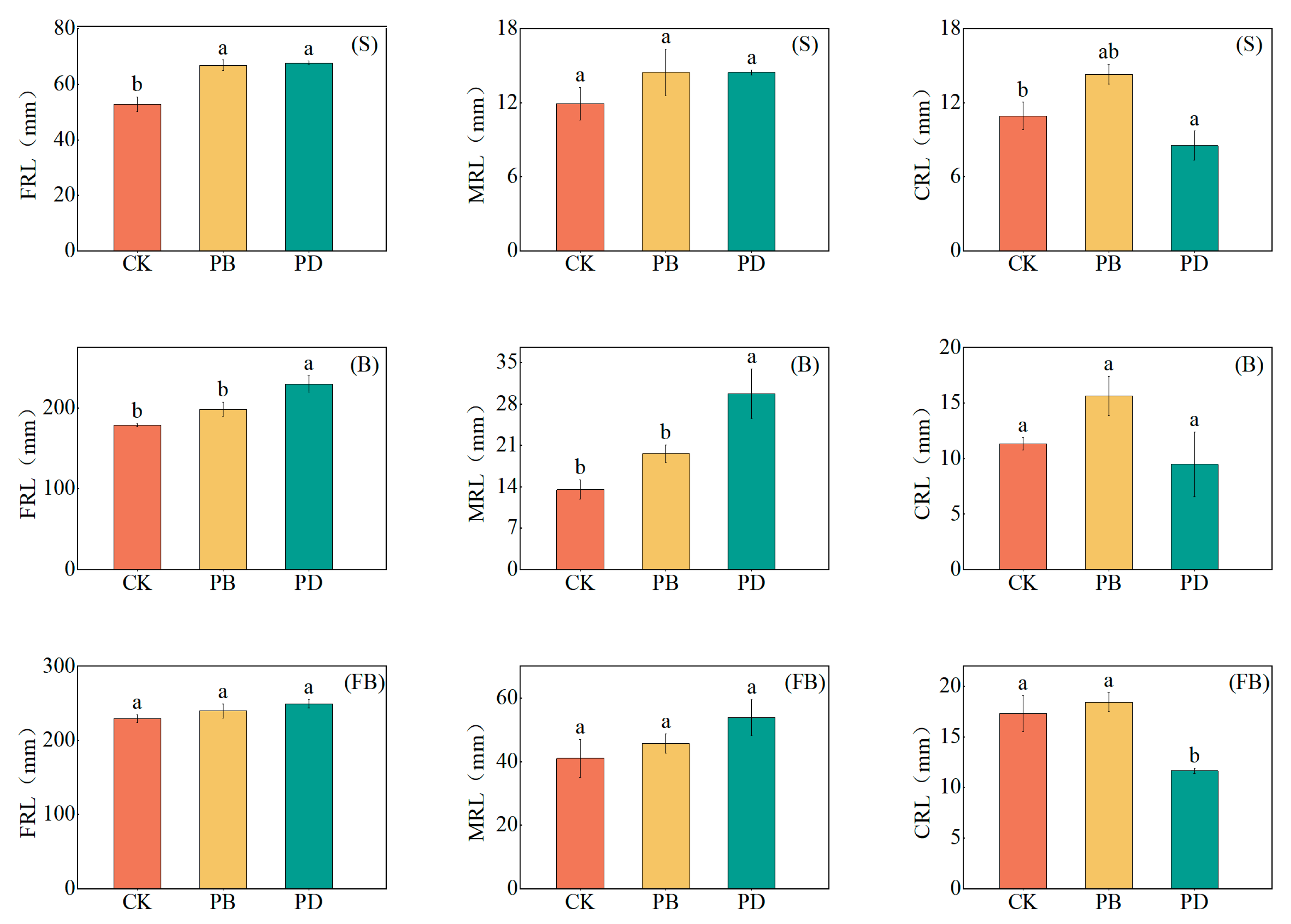
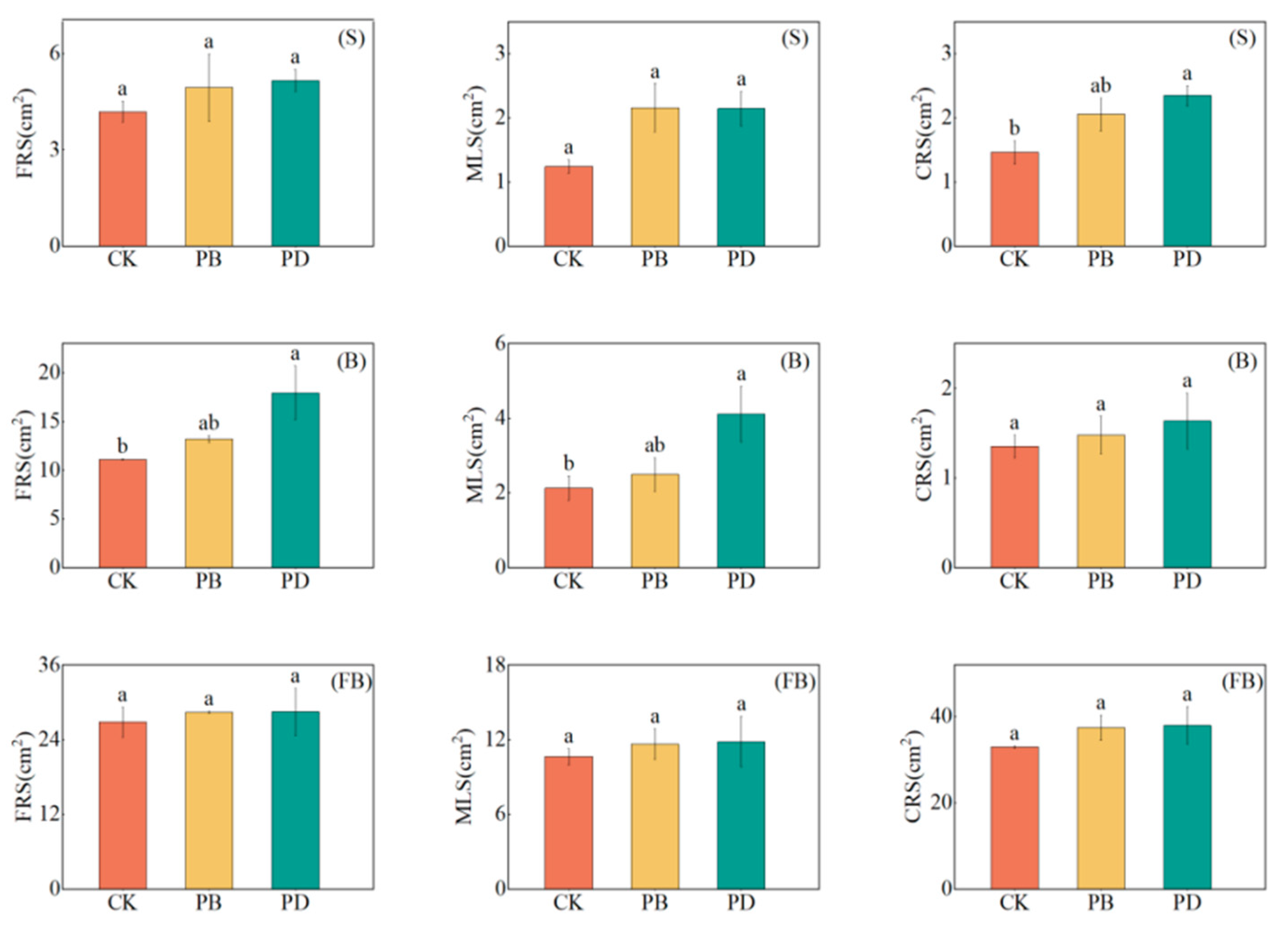
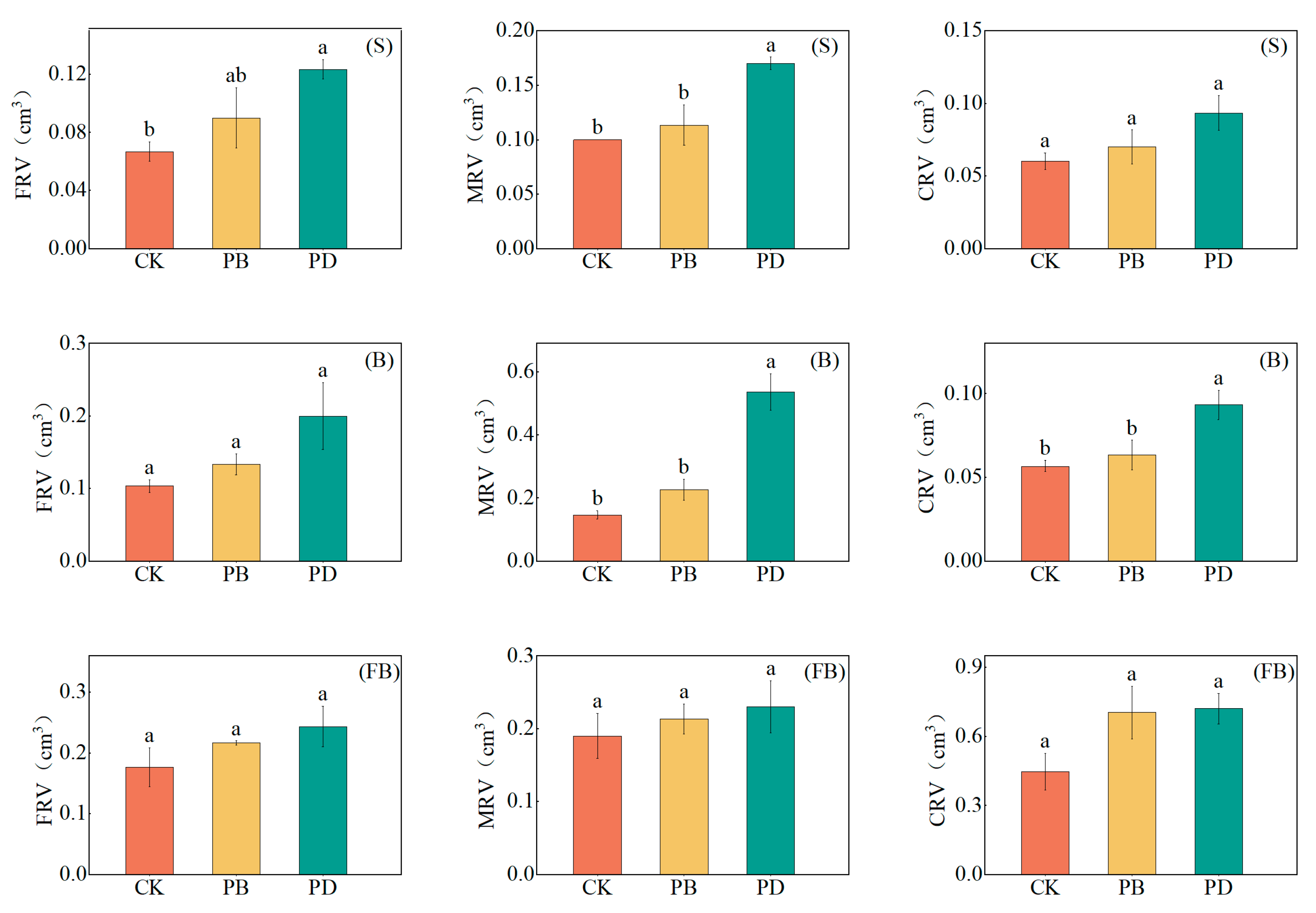
3.4. Impact of Phosphorus Application Methods on Root Morphological Parameters
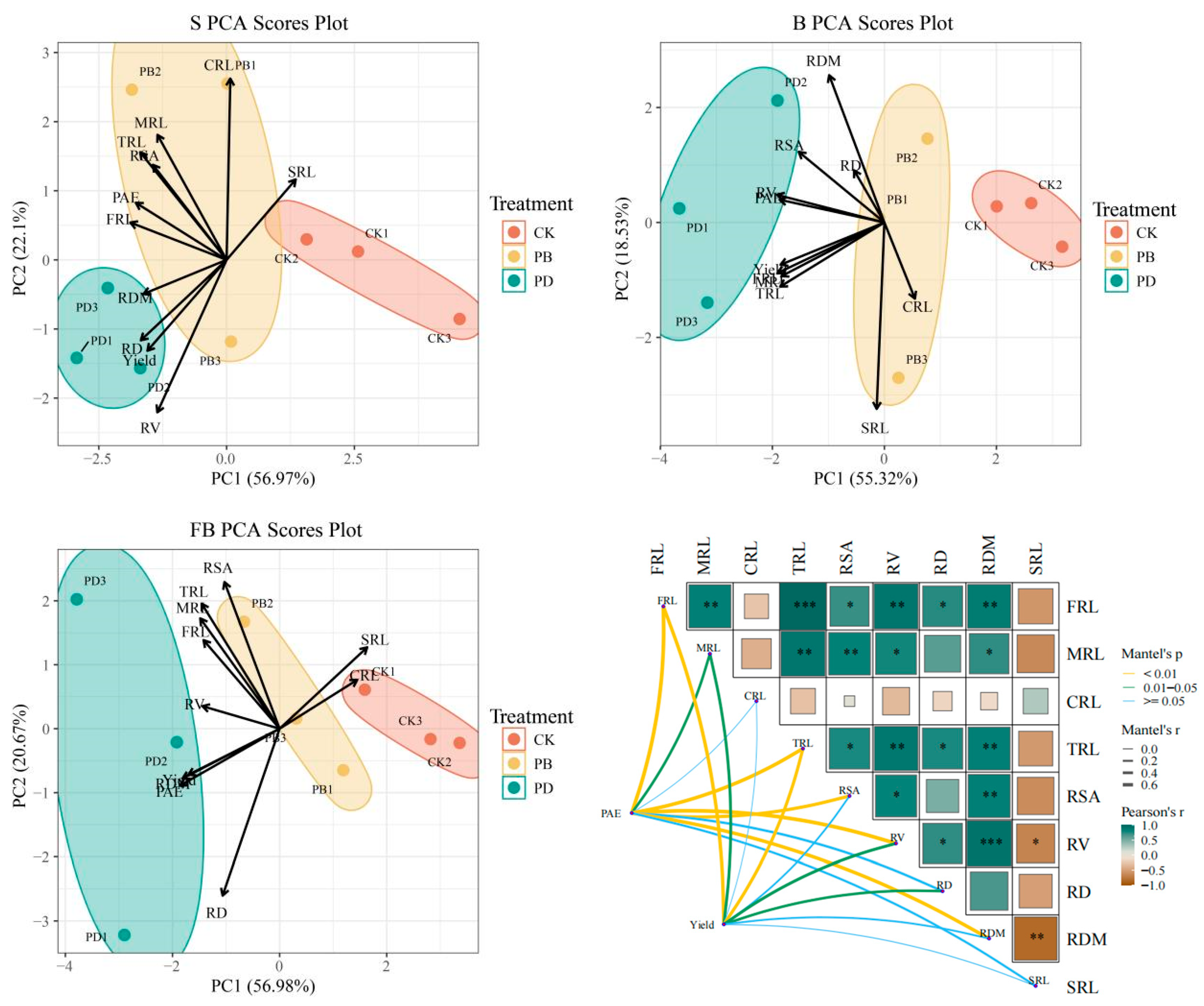
3.5. Correlations Between Total Root Morphological Parameters, P Accumulation, and Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Phosphorus Status, Phosphorus Uptake, and Use Efficiency
4.2. Cotton Dry Matter Accumulation and Distribution and Yield
4.3. Root Morphological Parameters Distribution
4.4. Correlations Between Total Root Morphological Parameters and P Accumulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, L. Effects of amendments on phosphor-ous status in soils with different phosphorous levels. Catena 2019, 172, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, B.; Kong, F.; Ullah, I.; Ali, S.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Khattak, W.A.; Zhou, Z. Phosphorus application improves the cotton yield by enhancing reproductive organ biomass and nutrient accumulation in two cotton cultivars with different phosphorus sensitivity. Agronomy 2020, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sheng, H.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Elser, J.J. Intensification of phosphorus cycling in China since the 1600s. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2609–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Vitousek, P.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Matson, P.; Zhang, F. Evidence for a historic change occurring in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.; Gai, J.; Feng, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Yi, K.; Li, Y. Strategies for improving fertilizer phosphorus use efficiency in Chinese cropping systems. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2019, 6, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, S.Z.; Bouwman, A.F.; Giller, K.E.; van Ittersum, M.K. Residual soil phosphorus as the missing piece in the global phosphorus crisis puzzle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6348–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Gao, P.; Yang, Z.; Su, L.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Xiao, Y. Biochar impacts on phosphorus cycling in rice ecosystem. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogollón, J.M.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Westhoek, H.; Bouwman, A.F. Future agricultural phosphorus demand according to the shared socioeconomic pathways. Glob. Environ. Change 2018, 50, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Cambardella, C.A. The soil management assessment framework: A quantitative soil quality evaluation method. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 1945–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.G.; Hansen, N.C. Phosphorus management in high-yield systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkebiwe, P.M.; Weinmann, M.; Bar-Tal, A.; Müller, T. Fertilizer placement to improve crop nutrient acqui-sition and yield: A review and meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuuren, D.P.; Bouwman, A.F.; Beusen, A.H.W. Phosphorus demand for the 1970–2100 period: A sce-nario analysis of resource depletion. Glob. Environ. Change 2010, 20, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabugao, K.G.; Timm, C.M.; Carrell, A.A.; Joanne, C.; Lu, T.S.; Pelletier, D.A.; Weston, D.J.; Norby, R.J. Root and rhizosphere bacterial phosphatase activity varies with tree species and soil phosphorus availability in Puerto Rico tropical forest. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zou, H.; Wang, H.; Li, G. Determining irrigation amount and fertilization rate to simultaneously optimize grain yield, grain nitrogen accumulation and economic benefit of drip-fertigated spring maize in northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, L.; Yan, S. Optimization of drip irrigation and fertilization regimes for high grain yield, crop water productivity and economic benefits of spring maize in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 230, 105986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, S.; Singh, A.K.; Lenka, N.K. Soil water and nitrogen interaction effect on residual soil nitrate and crop nitrogen recovery under maize–wheat cropping system in the semi-arid region of northern India. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 179, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Bian, C.; Liu, X.; Ma, C.; Liu, Q. Winter wheat grain yield and water use efficiency in wide-precision planting pattern under deficit irrigation in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 153, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cui, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Niu, W. Effects of manure fertilizer on crop yield and soil pro-perties in China: A meta-analysis. Catena 2020, 193, 104617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Sun, L.; Tian, H.; Rengel, Z.; Shen, J. Deep banding of phosphorus and nitrogen enhances Rosa multiflora growth and nutrient accumulation by improving root spatial distribution. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 277, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bauw, P.; Vandamme, E.; Senthilkumar, K.; Lupembe, A.; Smolders, E.; Merckx, R. Combining phosphorus placement and water saving technologies enhances rice production in phosphorus-deficient lowlands. Field Crops Res. 2019, 236, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Cai, T.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. Suitable fertilizer application depth can increase nitrogen use efficiency and maize yield by reducing gaseous nitrogen losses. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, J.Z.; Ma, K. An optimum combination of irrigation amount, irrigation water salinity and nitrogen application rate can improve cotton (for fiber) nitrogen uptake and final yield. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tao, X.; Khan, A.; Tan, D.K.; Luo, H. Biomass accumulation, photosynthetic traits and root development of cotton as affected by irrigation and nitrogen-fertilization. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Gutknecht, J.; Herman Herman, D.; Keck, D.C.; Firestone, M.K.; Cheng, W.X. Rhizosphere priming effects on soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 76, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D. Root developmental responses to phosphorus nutrition. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1065–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Fan, Y.; Yin, M.; Wang, F.; Cai, J.; Jiang, D.; Dai, T. Genetic Improvement of Root Growth and Its Relationship with Grain Yield of Wheat Cultivars in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River. Acta Agron. Sin. 2015, 41, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, L.; Luo, Q.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y. Spatial optimization of cotton cultivation in Xinjiang: A climate change perspective. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 124, 103523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunack, M.V.; Johnston, D.B.; Price, J.; Gauthier, E.J.F.C.R. Soil temperatureand soil water potential under thin oxodegradable plastie film impact on cottoncrop establishment and yield. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Fei, L.; Huang, D.; Zeng, J.; Chen, L.; Cai, Y. Coupling efects of irrigation andnitrogen levels on yield, water and nitrogen use efficiency ofsurge root irigated jujube in a semiarid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, T.; Chen, S.; Ye, R.; Chen, J.; Geng, C. Responses of rootphysiology and yield of apple tree to water and nitrogen amountsunder drip fertigation. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 2787–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Hu, T.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Sun, G.; Liu, J. Responses of soil reactivenitrogen pools and enzyme activities to water and nitrogen levels andtheir relationship with apple yield and quality under drip fertigation. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 324, 112632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, G.A.; Bange, M.P. The yield potential of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Field Crops Res. 2015, 182, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Maimaitiaili, B.; Feng, G.; Rengel, Z. Localized ammonium and phosphorus fertilization can improve cotton lint yield by decreasing rhizosphere soil pH and salinity. Field Crops Res. 2018, 217, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorter, H.; Bihler, J.; Van Dusschoten, D.; Climent, J.; Postma, J.A. Pot size matters: A meta-analysis of the effects of rooting volume on plant growth. Funct. Plant Biol. 2012, 39, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchenbuch, R.O.; Gerke, H.H.; Buczko, U. Spatial distribution of maize roots by complete 3D soil monolith sampling. Plant Soil 2009, 315, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Lu, J. Effect of depth of fertilizer banded-placement on growth, nutrient uptake and yield of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 62, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanello, D.D.; Kelly, S.J.; Bartoli, C.G.; Cano, M.G.; Alonso, S.M.; Guiamet, J.J. Plasticity of root growth and respiratory activity: Root responses to above-ground senescence, fruit removal or partial root pruning in soybean. Plant Sci. 2019, 290, 110296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Huang, F.; Ahmad, S.; Zhang, P.; et al. Suitable fertilization depth can improve the water productivity and maize yield by regulating development of the root system. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 271, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. Effects of phosphorus-fertigationon emitter clogging in drip irrigation system with saline water. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Cole, C.V.; Watanabe, F.S.; Dean, L.A. Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with NaHCO3. In United States Department of Agriculture Circular No. 939; US Government Printing Office: Washington DC, WA, USA, 1954; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Ye, Z.; Tang, X.; Chai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Sheng, J.; Feng, G. A comprehensive evaluation of the optimum amount of phosphate fertilizer for drip irrigation of cotton under mulch based on root morphology, physiology, and mycorrhizal symbiosis. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Maimaitiaili, B.; Kafle, A.; Khan, K.S.; Feng, G. Breeding practice improves the mycorrhizal responsiveness of cotton (Gossypium spp. L). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 780454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V.C. Enhancing nitrogen useefciency in crop plants. Adv. Agron. 2005, 88, 97–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Song, H.; Jiang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J. Managing fertiliser placement locations and source types to improve rice yield and the use efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus. Field Crops Res. 2019, 231, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yan, H.; Xu, S.; Lin, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, D. Moderately deep banding of phosphorus enhanced winter wheat yield by improving phosphorus availability, root spatial distribution, and growth. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, Q.; Yao, S.; Chen, Q.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; Feng, H.; Li, C. Controlled-release phosphate fertilizer improves soil fertility and soybean productivity by regulating soil microbial diversity and composition and increasing enzyme activities. Field Crops Res. 2025, 325, 109836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.J.; Kang, L.F.; Chu, G.X. Polymerization degree and rate of polyphosphate fertilizer affected the availability of phosphorus, Fe, Mn and Zn in calcareous soil. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2018, 24, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Zhang, G.; Chu, G. Split delivering phosphorus via fertigation to a calcareous soil increased P availability and maize yield (Zea mays L.) by reducing P fixation. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2287–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombi, E.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Johnston, C.; Armstrong, R.D.; Holloway, R.E. Mobility, solubility and lability of fluid and granular forms of P fertilizer in calcareous and non-calcareous soils under laboratory conditions. Plant Soil 2004, 269, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, I.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Holloway, R.E.; Armstrong, R.D.; McBeath, T. Changes in P bioavailabili-ty induced by the application on the liquid and powder sources of P, N and Zn fertilizers in alkaline soils. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2006, 74, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Dorante, L.O.; Claassen, N.; Steingrobe, B.; Olfs, H.W. Fertilizer-use efficiency of different inorga-nic polyphosphate sources: Effects on soil P availability and plant P acquisition during early growth of cor-n. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gal, A.; Dudley, L.M. Phosphorus availability under continuous point source irrigation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, F.; Li, Y. Effects of phophorus fertigation and lateral depths on distribution of Olsen-P in soil and yield of maize under subsurface drip irrigation. In 2017 ASABE Annual International Me-Eting; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St Joseph, MI, USA, 2017; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorahy, C.G.; Rochester, I.J.; Blair, G.J. Response of Field-grown Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) to phosphorus fertilisation on alkaline soils in eastern Australia. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2004, 42, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Dang, X.; Lin, X.; Ma, F.; Liu, Y. Integrated deep banding and fertigation of phosphorus improves cotton yield by regulating root spatial distribution and growth. Field Crops Res. 2024, 318, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Wang, H.W.; Jiang, W.Y.; Zhao, B.; Man, Y.P.; Zhang, K.Y. Effects of different planting patterns on dry matter accumulation, distribution and yield of maize. Maize Sci. 2021, 29, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lv, J.; Coulter, J.A.; Xie, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Niu, T.; Gan, Y. Slow-release fertilizer improves the growth, quality, and nutrient utilization of wintering Chinese chives (Allium-tuberosum Rottler ex Spreng.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.P.; Ma, Z.M.; Xue, L. Effects of different kinds of organic fertilizer on fruit yield, quality and nutrient uptake of watermelon in gravel-mulched field. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Shen, W.; Kuzyakov, Y. Phosphatase activity and acidification in lupine and maize- rhizosphere depend on phosphorus availability and root properties: Coupling zymography with planar-optodes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 167, 104029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, D.; Zhang, S.; Gu, S.; Yan, Y.; Huang, S. Optimizing root system architecture to improve root anchorage strength and nitrogen absorption capacity under high plant density in maize. Field Crops Res. 2023, 303, 109109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X. Tracing the fate of nitrogen with 15N isotope considering suitable fertilizer rate related to yield and environment impacts in paddy field. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Khan, A.; Shi, X.; Hao, X.; Tan, D.K.Y.; Luo, H. Water-nutrient management enhances root morphophysiological functioning, phosphorus absorption, transportation and utilization of cotton in arid region. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 143, 111975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, M.; Feng, H.; Xiang, Y. Optimization of water and fertilizer management improves yield, water, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium uptake and use efficiency of cotton under drip fertigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jin, M.; Ferré, T.P.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Xian, Y. Soil conditions affect cotton root distribution and cotton yield under mulched drip irrigation. Field Crops Res. 2020, 249, 107743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ren, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Ren, B.; Wan, Y.; Liu, P. Deep phosphorus fertilizer placement increases maize productivity by improving root-shoot coordination and photosynthetic performance. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Chen, L.; Du, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Localized and moderate phosphorus application improves plant growth and phosphorus accumulation in Rosa multiflora thunb. ex murr. via efficient root system development. Forests 2020, 11, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.; Borie, F.; Cornejo, P.; López-Ráez, J.A.; López-García, Á.; Seguel, A. Phosphorus acquisition efficiency related to root traits: Is mycorrhizal symbiosis a key factor to wheat and barley cropping? Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Yu, M.; Fu, L.; Li, S.; Su, J.; Zhu, B. Root phosphatase activity aligns with the collaboration gradient of the root economics space. New Phytol. 2021, 234, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, H.; Wang, W.; Han, R.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Wang, D. Layered application of phosphate fertilizer increased winter wheat yield by promoting root proliferation and phosphorus accumulation. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 225, 105546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Layer (cm) | pH | Electrical Conductivity (μS/cm) | Soil Organic Matter (g/kg) | Alkali-Hydrolyzable Nitrogen (mg/kg) | Soil Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 | 8.09 | 389.4 | 14.20 | 19.10 | 14.27 |
| 20–40 | 8.13 | 380.5 | 10.90 | 17.30 | 12.30 |
| Year | Treatment | Single Boll Weight (g Boll−1) | Number of Bolls per Plant (Bolls Plant−1) | Number of Plants (plants) | Yield kg hm−2 | PRE × 100% | PFP (kg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | CK | 5.14 ± 0.15 a | 4.60 ± 0.26 b | 184 ± 10.55 a | 4356.19 ± 154.49 b | ||
| PB | 5.25 ± 0.08 a | 5.24 ± 0.15 ab | 189 ± 6.20 a | 5189.62 ± 199.72 a | 23.37 | 11.10 | |
| PD | 5.26 ± 0.34 a | 6.01 ± 0.47 a | 182 ± 5.73 a | 5681.03 ± 163.444 a | 28.52 | 17.66 | |
| 2024 | CK | 5.91 ± 0.59 a | 6.28 ± 0.13 a | 120 ± 7.77 b | 4385.32 ± 182.37 b | ||
| PB | 6.88 ± 0.72 a | 6.14 ± 0.45 a | 129 ± 8.76 b | 5368.30 ± 344.84 a | 22.09 | 13.10 | |
| PD | 5.8 ± 0.19 a | 5.45 ± 0.17 a | 194 ± 3.53 a | 6099.85 ± 48.78 a | 29.05 | 22.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, B. Drip Irrigation of Phosphorus Fertilizer Enhances Cotton Yield and Phosphorus Use Efficiency. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061328
Wu Y, Wu X, Zhang J, Zhou L, Chen B. Drip Irrigation of Phosphorus Fertilizer Enhances Cotton Yield and Phosphorus Use Efficiency. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061328
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuwen, Xiaoqian Wu, Jun Zhang, Leru Zhou, and Bolang Chen. 2025. "Drip Irrigation of Phosphorus Fertilizer Enhances Cotton Yield and Phosphorus Use Efficiency" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061328
APA StyleWu, Y., Wu, X., Zhang, J., Zhou, L., & Chen, B. (2025). Drip Irrigation of Phosphorus Fertilizer Enhances Cotton Yield and Phosphorus Use Efficiency. Agronomy, 15(6), 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061328





