Effects of Cadmium Accumulation Along the Food Chain on the Fitness of Harmonia axyridis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plants and Sources of Experienced Insects
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Determination of Developmental Period and Body Weight of H. axyridis
2.4. Determination of Survival Rate, Pupation Rate, and Emergence Rate of H. axyridis
2.5. Determination of Deformity Rate and Sex Ratio as Well as Phenotype Photographs of H. axyridis
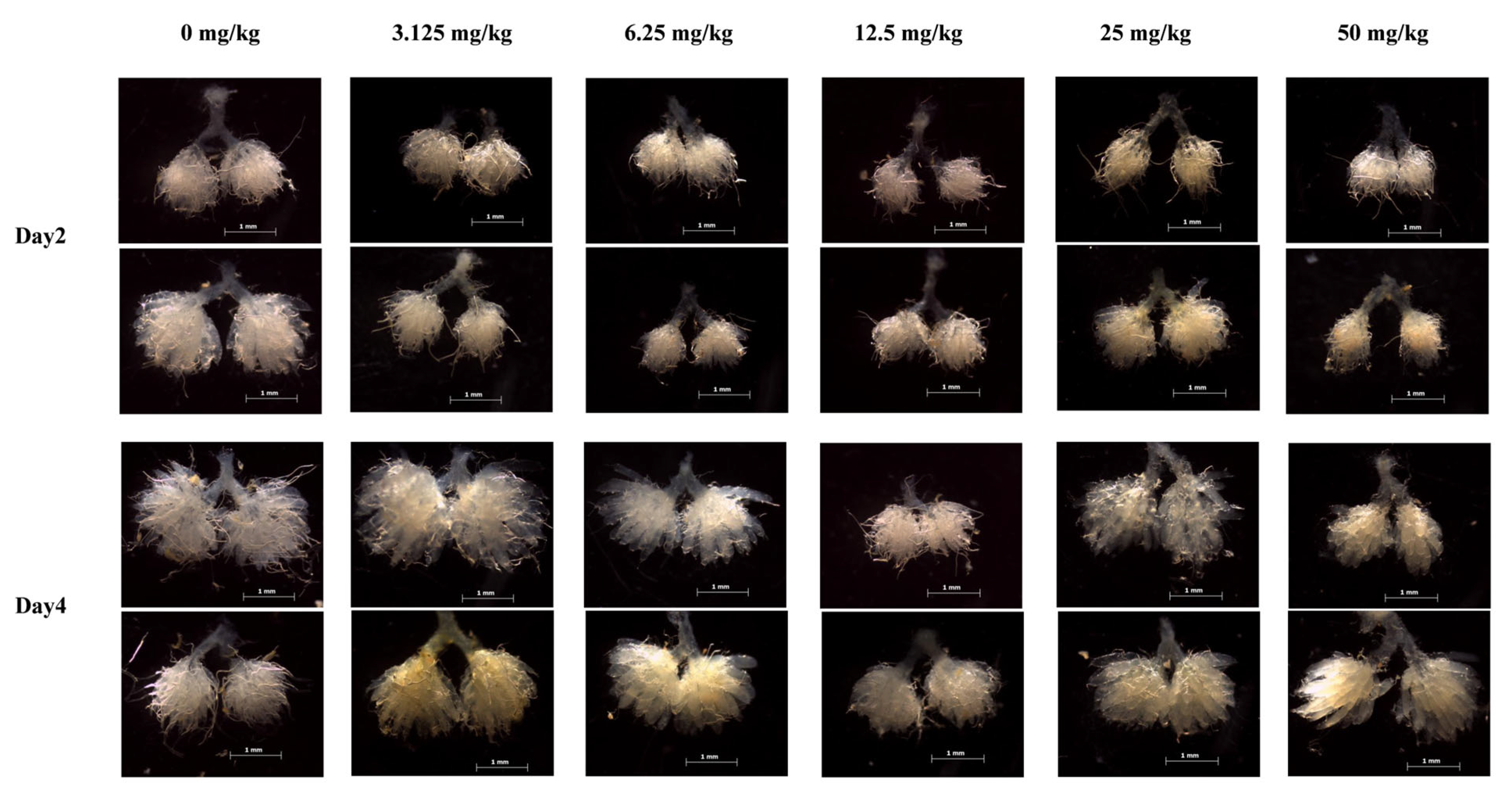
2.6. Observation and Photographing of Female Ovary Phenotype of H. axyridis
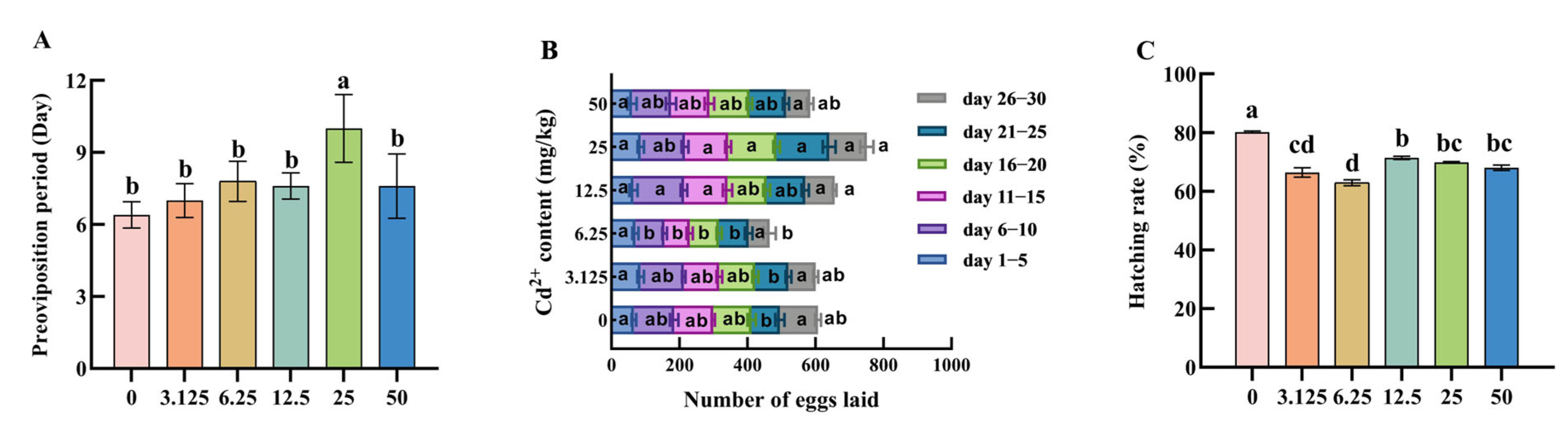
2.7. Determination of Preoviposition, Spawning Quantity, and Hatching Rate of H. axyridis
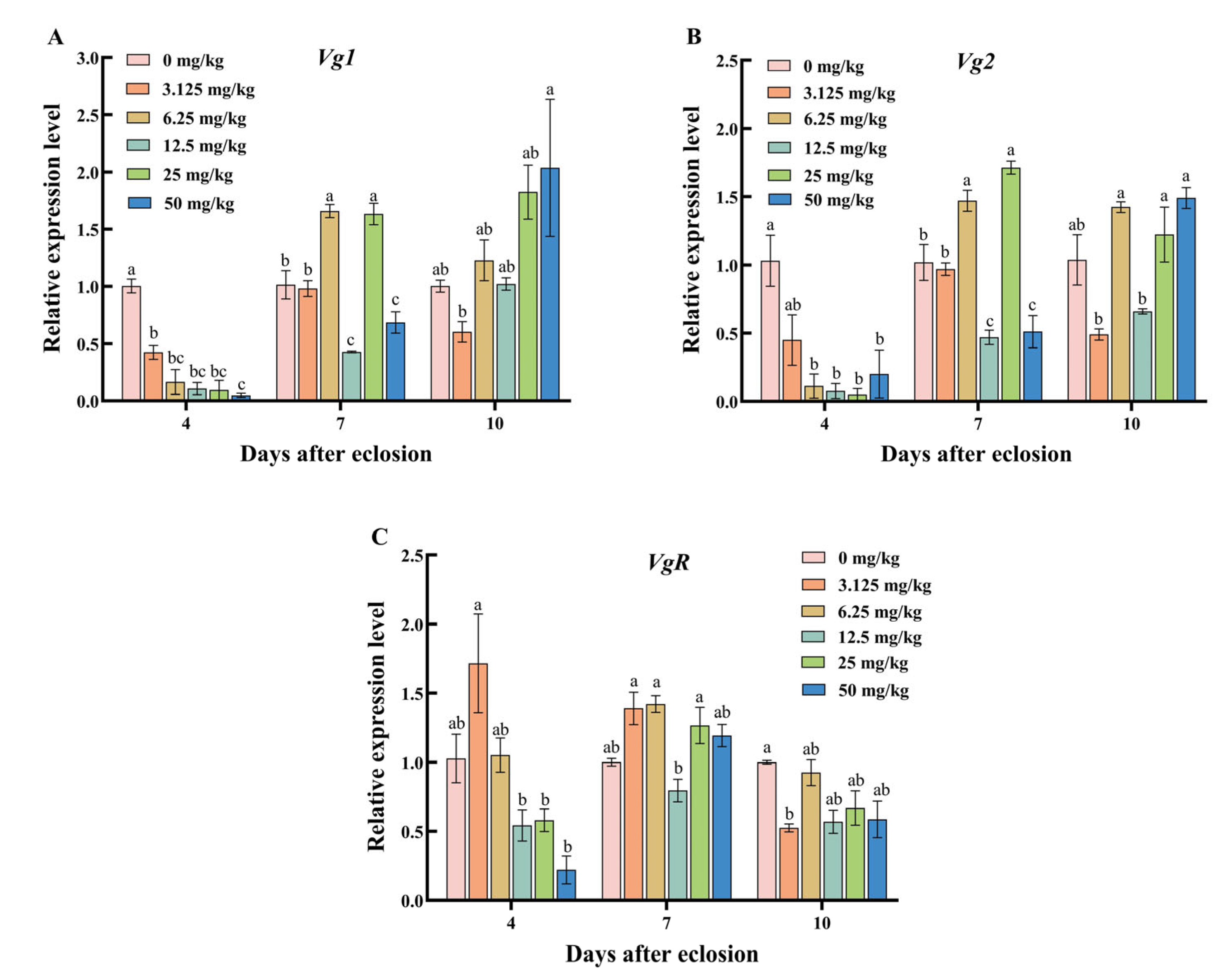
2.8. Determination of the Expression Levels of Vitellogenin and Vitellogenin Receptor Genes in Female H. axyridis
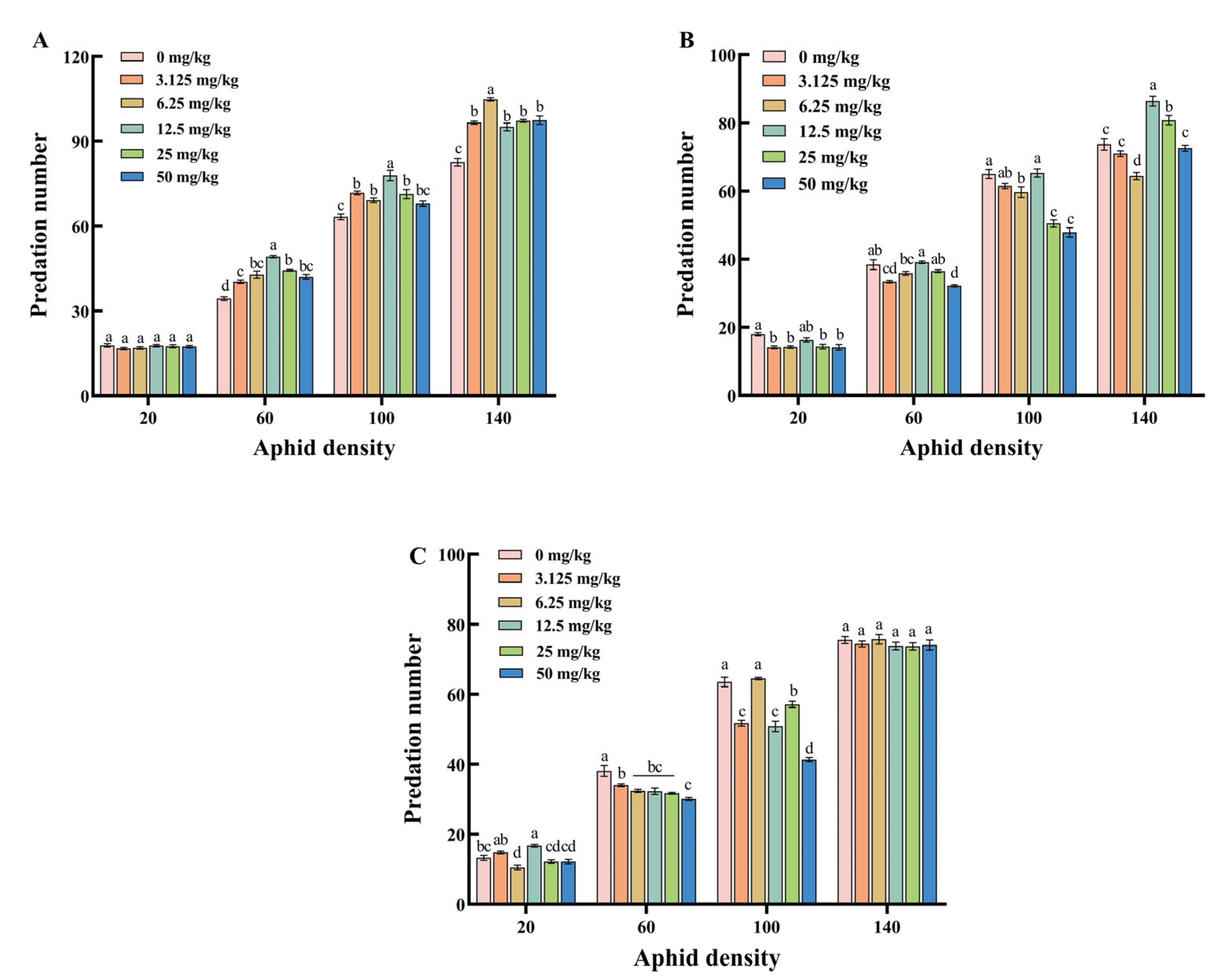
2.9. Determination of Predatory Capacity of H. axyridis
2.10. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Development Period and Body Weight of H. axyridis Under Cadmium Pollution
3.2. The Survival Rate, Pupation Rate, and Emergence Rate of H. axyridis Under Cd Pollution
3.3. Deformity Rate, Sex Ratio, and Abnormal Phenotype of H. axyridis Under Cadmium Pollution
3.4. Ovarian Phenotype of Female H. axyridis
3.5. The Preoviposition Period, the Number of Eggs and Hatching Rate of Female H. axyridis
3.6. Expression Levels of Vitellogenin and Vitellinogen Receptor Genes in Female H. axyridis
3.7. The Predation of H. axyridis Larvae and Adults Under Cadmium Pollution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.Q.; Zeng, X.M.; Feng, J.; Liu, Y.R. Characteristics and assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils of industrial regions in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Yue, X.; Ren, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K. Identification and hazard analysis of heavy metal sources in agricultural soils in ancient mining areas: A quantitative method based on the receptor model and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Yang, F.; Xu, C.; Yang, H.; Liu, W. Status of metal accumulation in farmland soils across China: From distribution to risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Jin, Q.; Kavan, P. A Study of Heavy Metal Pollution in China: Current Status, Pollution-Control Policies and Countermeasures. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5820–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y. Cadmium Enrichment Ability and Physiology of Kiwifruit Under Cadmium Stress and Preliminary Study on Cadmium Reduction Technology in the Soil. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Agriculture University, Changsha, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; Jia, X.; Wang, L.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhu, Y.G.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, F.J.; Bank, M.S.; O’Connor, D.; Nriagu, J. Global soil pollution by toxic metals threatens agriculture and human health. Science 2025, 388, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lux, A.; Martinka, M.; Vaculík, M.; White, P.J. Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: A review. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sall, M.L.; Diaw, A.K.D.; Gningue-Sall, D.; Efremova Aaron, S.; Aaron, J.J. Toxic heavy metals: Impact on the environment and human health, and treatment with conducting organic polymers, a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29927–29942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, S.; Yahya, M.; Aslam, S.; Hussain, R.; Shah, S.M.M.; Rauf, Z.; Zamir, A.; Ullah, R.; Shahzad, A. Environmental occurrence, hazards, and remediation strategies for the removal of cadmium from the polluted environment. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S.; Aarts, M.G.; Thomine, S.; Verbruggen, N. Plant science: The key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, T.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X. Cadmium accumulation characteristics and removal potentials of high cadmium accumulating rice line grown in cadmium-contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 15351–15357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Jing, H.; Wu, P.; Yang, W. Selection of rice and maize varieties with low cadmium accumulation and derivation of soil environmental thresholds in karst. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 247, 114244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DZ/T 0258-2014; Specification of Multi-Purpose Regional Geochemical Survey (1:250000). Ministry of Land and Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- Zhou, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.; Ma, T.; Huang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H. Effects of selenium fertilization on cadmium uptake and transport in rice crop in different cadmium-contaminated soils during two consecutive seasons. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 724–732. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, F.Q.; Chang, J.D.; Tang, Z.; Liu, W.J.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhao, F.J. Nramp5 expression and functionality likely explain higher cadmium uptake in rice than in wheat and maize. Plant Soil 2018, 433, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, N. The impact of Copper, Cadmium, Lead and Selenium on Individual and the Whole Colony Health of Apis mellifera L. (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Shanxi, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza-Cózatl, D.G.; Jobe, T.O.; Hauser, F.; Schroeder, J.I. Long-distance transport, vacuolar sequestration, tolerance, and transcriptional responses induced by cadmium and arsenic. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 4, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercè, L.; Roger, M.; Isabel, C.; Juan, B.; Charlotte, P. Cynara cardunculus a potentially useful plant for remediation of soils polluted with cadmium or arsenic. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 123, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Hesham, A.-L.; Qiao, M.; Rehman, S.; He, J.Z. Effects of Cd and Pb on soil microbial community structure and activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2010, 17, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Dai, L. Immobilization Effect and Its Physiology and Biochemical Mechanism of the Cadmium in Crop Roots. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2016, 49, 4323–4341. [Google Scholar]
- Konopka, J.K.; Hanyu, K.; Macfie, S.M.; McNeiol, J.N. Does the response of insect herbivores to cadmium depend on their feeding strategy? J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.K.; Primicerio, R.; Amundsen, P.A. Diversity and structure of Chironomidae (Diptera) communities along a gradient of heavy metal contamination in a subarctic watercourse. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 307, 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Hayford, B.L.; Ferrington, L.C. Biological Assessment of Cannon Creek, Missouri by Use of Emerging Chironomidae (Insecta: Diptera). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 2005, 78, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.X.; Chu, F.; Qin, F.J.; Liu, J.; He, Y.Q.; Liu, H. Effects of cadmium exposure on the lipid peroxide content and the antioxidant enzyme activity and mRNA expression in the fat body in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2014, 57, 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.Y.; Zhu, Q.H.; Zhu, H.H.; Xu, C.; Liu, S.L. Advances and prospects of safety agro-utilization of heavy metal contaminated farmland soil. Res. Agric. Mod. 2018, 39, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Naseer, S.; Cui, J.; Jahangir, S.; Noureen, M.; Wei, Z. Exploring the role of ligands in metal phytoremediation and its influence on metal availability and toxicity. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2025, 27, 953–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.U.; Wang, R.; Che, W.N.; Feng-Qi, L.I.; Zhao, H.P.; Wei, Y.Y.; Luo, C.; Ming, X. Identification and tissue distribution of odorant binding protein genes in Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 2204–2213. [Google Scholar]
- Cayrol, B.; Arnoldi, I.; Novak, V.; Epis, S.; Brilli, M.; Rahbé, Y.; Uzest, M.; Gabrieli, P. The development of the piercing mouth during the last molt of the diseases-transmitting aphids and mosquitoes as revealed by synchrotron X-ray microtomography. Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Wan, S.; Chen, L.; Dai, X.; Wang, R.; Desneux, N.; Zhi, J.; et al. Bioaccumulation and transferreing for impacts on Cd and Pb by aphid consumption of the broad bean, Vicia faba L, in soil heavy metal pollution. Chemosphere 2024, 360, 142429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.S.; Si, H.R.; Wan, S.J.; Li, G.Y.; Shu, Y.H.; Dai, X.Y.; Wang, R.J.; Wang, S.G.; Zhai, Y.F.; et al. Responses of aphid and ladybird to lead transfer through soil and broad beans. Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, W.; Xu, J.; Bashir, M.H.; Ali, S. Developmental responses of Cryptolaemus montrouzieri to heavy metals transferred across multi-trophic food chain. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Fan, Z.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Qiu, B.L. Distribution and accumulation of cadmium in different trophic levels affecting Serangium japonicum, the predatory beetle of whitefly Bemisia tabaci, biologically, physiologically and genetically: An experimental study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Wu, J.; Bashir, M.H.; Shaukat, M.; Ali, S. Heavy metals transported through a multi-trophic food chain influence the energy metabolism and immune responses of Cryptolaemus montrouzieri. Ecotoxicology 2019, 28, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Wan, S.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, S.; Dai, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Zhai, Y.; et al. Stress Response of Aphid Population Under Combined Stress of Cadmium and Lead and Its Effects on Development of Harmonia axyridis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, M.M.; Harwood, J.D. Influence of heavy metal contamination on urban natural enemies and biological control. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płachetka-Bożek, A.; Chwiałkowska, K.; Augustyniak, M. Molecular changes in vitellogenin gene of Spodoptera exigua after long-time exposure to cadmium—Toxic side effect or microevolution? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, T.; Duan, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z.; Mao, J. Testosterone maintains male longevity and female reproduction in Chrysopa pallens. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.; Nagaba, Y.; Elgendy, A.M.; Takeda, M. Regulation of vitellogenin genes in insects. Entomol. Sci. 2014, 17, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Snigirevskaya, E.S.; Raikhel, A.S. The cell biology of yolk protein precursor synthesis and secretion. Reprod. Biol. Invertebr. 2005, 12, 33–68. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tang, W.; Lu, K.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, G. Molecular characterization and expression pattern of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) vitellogenin, and its response to lead stress. J. Insect Physiol. 2009, 55, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Wan, S.; Chen, L.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, K.; Tao, S.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; et al. The Stress Response of Aphids to the Accumulation of Heavy Metals Along Vicia faba L. Under Cadmium Treatment. Insects 2024, 15, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, B.; Ashraf, U.; Azad, R.; Wu, J.; Ali, S. Biotransfer of Cd along a soil-plant-mealybug-ladybird food chain: A comparison with host plants. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zou, J.; Zhao, L.; Wu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F. Inhibitional effects of metal Zn2+ on the reproduction of Aphis medicaginis and its predation by Harmonia axyridis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, Z.R.; Tariq, K.; Mavian, C.; Ali, A.; Ullah, F.; Zang, L.S.; Ali, F.; Nazir, T.; Ali, S. Trophic transfer and toxicity of heavy metals from dengue mosquito Aedes aegypti to predator dragonfly Tramea cophysa. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malematja, E.; Manyelo, T.G.; Sebola, N.A.; Kolobe, S.D.; Mabelebele, M. The accumulation of heavy metals in feeder insects and their impact on animal production. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Di, N.; Huang, H.X.; Trumble, J.T.; Jaworski, C.C.; Wang, S.; Desneux, N.; Li, Y.X. Cadmium triggers hormesis in rice moth Corcyra cephalonica but different effects on two Trichogramma egg parasitoids. Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesketh, H.; Lahive, E.; Horton, A.A.; Robinson, A.G.; Svendsen, C.; Rortais, A.; Dorne, J.L.; Baas, J.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Heard, M.S. Extending standard testing period in honeybees to predict lifespan impacts of pesticides and heavy metals using dynamic energy budget modelling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.L.; Yi, Z.D.; Zhang, M. Toxicity effect of cadmium stress exposure to insects and defense mechanism of insects. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 29, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.L.; Sun, Q.M.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.Z.; Su, H.H. Effects of cadmium stress on juvenile hormone and molting hormone titers in Spodoptera exigua. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2023, 60, 2291–2297. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Zhu, Z.; Trumble, J.T.; Di, N.; Zang, L. Heavy metal exposure reduces larval gut microbiota diversity of the rice striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis. Ecotoxicology 2024, 33, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.I.; Green, I.D.; Naikoo, M.I.; Khan, F.A.; Ansari, A.A.; Lone, M.I. Assessment of biotransfer and bioaccumulation of cadmium, lead and zinc from fly ash amended soil in mustard–aphid–beetle food chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, M.I.; Dar, M.I.; Khan, F.A.; Raghib, F.; Rajakaruna, N. Trophic transfer and bioaccumulation of lead along soil-plant-aphid-ladybird food chain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 23460–23470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Veroli, A.; Santoro, F.; Pallottini, M.; Selvaggi, R.; Scardazza, F.; Cappelletti, D.; Goretti, E. Deformities of chironomid larvae and heavy metal pollution: From laboratory to field studies. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youbi, A.; Zerguine, K.; Houilia, A.; Farfar, K.; Soumati, B.; Berrebbah, H.; Djebar, M.R.; Souiki, L. Potential use of morphological deformities in Chironomus (Diptera: Chironomidae) as a bioindicator of heavy metals pollution in North-East Algeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8611–8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witeska, M.; Sarnowski, P.; Ługowska, K.; Kowal, E. The effects of cadmium and copper on embryonic and larval development of ide Leuciscus idus L. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Huang, Y.; Zang, L.; Wang, S.; Xiao, D. The role of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopa decarboxylase in melanin biosynthesis and metamorphosis in Coccinella septempunctata. Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ooik, T.; Rantala, M.J.; Saloniemi, I. Diet-mediated effects of heavy metal pollution on growth and immune response in the geometrid moth Epirrita autumnata. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkunas, I.; Woźniak, A.; Mai, V.C.; Rucińska-Sobkowiak, R.; Jeandet, P. The role of heavy metals in plant response to biotic stress. Molecules 2018, 23, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.I.; Khan, F.A.; Green, I.D.; Naikoo, M.I. The transfer and fate of Pb from sewage sludge amended soil in a multi-trophic food chain: A comparison with the labile elements Cd and Zn. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 16133–16142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, M.I.; Raghib, F.; Dar, M.I.; Khan, F.A.; Hessini, K.; Ahmad, P. Uptake, accumulation and elimination of cadmium in a soil-Faba bean (Vicia faba)-Aphid (Aphis fabae)-Ladybird (Coccinella transversalis) food chain. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafel, A.; Rozpędek, K.; Szulińska, E.; Zawisza-Raszka, A.; Migula, P. The effects of cadmium or zinc multigenerational exposure on metal tolerance of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 4705–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, N.; Hladun, K.R.; Zhang, K.; Liu, T.X.; Trumble, J.T. Laboratory bioassays on the impact of cadmium, copper and lead on the development and survival of honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) larvae and foragers. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.K.; Wang, S.S.; Pan, B.Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, B. Effects of zinc acquired through the plant-aphid-ladybug food chain on the growth, development and fertility of Harmonia axyridis. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Fu, W.; Yang, X.; Mu, Y.; Gu, W.; Zhang, M. Effects of cadmium on fecundity and defence ability of Drosophila melanogaster. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.W.; Shu, Y.H. Review on the effects of heavy metal pollution on herbivorous insects. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Han, S.; Qin, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; He, Y. Molecular identification and functional characterization of vitellogenin receptor from Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Gong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C. Sublethal concentrations of lambda-cyhalothrin reduce fecundity by affecting the hormone-vitellogenin signaling pathway in Chrysoperla sinica. Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 1459–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, A.; Cristina Maymó, A.; Martínez-Pardo, R.; Dolores Garcerá, M. Vitellogenesis inhibition in Oncopeltus fasciatus females (Heteroptera: Lygaeidae) exposed to cadmium. J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, A.; Maymó, A.C.; Martínez-Pardo, R.; Garcerá, M.D. Vitellogenin polypeptide levels in one susceptible and one cadmium-resistant strain of Oncopeltus fasciatus (Heteroptera: Lygaeidae), and its role in cadmium resistance. J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, A.; Maymó, A.C.; Sendra, M.; Martínez-Pardo, R.; Garcerá, M.D. Cadmium effects on development and reproduction of Oncopeltus fasciatus (Heteroptera: Lygaeidae). J. Insect Physiol. 2004, 50, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.Y. The effects of plumbum stress on reproduction and Vg of beet armyworm. Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Jiangsu, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, Y.; Shah, F.M.; Shah, M.A.; Khan, M.M.; Zhou, X.M. Temperature-dependent functional response of Harmonia axyridis (coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on the eggs of Spodoptera litura (lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in laboratory. Insects 2020, 11, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, L.A.; Grzywacz, D.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Frutos, R.; Brownbridge, M.; Goettel, M.S. Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Back to the future. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 132, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.C.; He, M.H.; Amalin, D.M.; Liu, W.; Alvindia, D.G.; Zhan, J. Biological Control of Plant Diseases: An Evolutionary and Eco-Economic Consideration. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhuo, R. Recent advances in phyto-combined remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 72, 108337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, Q.; Fang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhai, Y.; Tang, B. Megoura crassicauda promote the ability of Vicia faba L. to remediate cadmium pollution of water and soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, Y.M.; Hu, G.X. Effects of alfalfa applied with different mount potassium on the growth, development and fecundity of Acyrthosiphon pisum [J/OL]. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2025, 1–11. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3362.s.20250402.1644.004.html.

| Gene Name | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| VgR | TGTAGGAGGCGAAGCAATGAT | TGGGATGTGACAGGGAAATAA |
| Vg1 | GCAACAGAGTCCGTGGTCTTT | GCTGCTTTCACCGTTCTTCAA |
| Vg2 | CAATCAAAACTCAAGCAAGGAGA | GTCAAAAACTGGATGGACAACAA |
| rp49 | GCGATCGCTATGGAAAACTC | TACGATTTTGCATCAACAGT |
| Developmental Stage INSTAR | Development Duration (d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 mg/kg | 3.125 mg/kg | 6.25 mg/kg | 12.5 mg/kg | 25 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | |
| 1st instar | 3.48 ± 0.16 ab | 2.92 ± 0.01 bc | 3.86 ± 0.28 a | 3.36 ± 0.19 ab | 2.21 ± 0.17 c | 2.67 ± 0.22 bc |
| 2nd instar | 1.91 ± 0.08 c | 2.33 ± 0.13 bc | 2.76 ± 0.27 ab | 2.55 ± 0.11 bc | 2.04 ± 0.10 bc | 3.36 ± 0.27 a |
| 3rd instar | 2.23 ± 0.08 a | 2.60 ± 0.12 a | 2.77 ± 0.13 a | 2.48 ± 0.10 a | 2.60 ± 0.24 a | 2.63 ± 0.20 a |
| 4th instar | 4.23 ± 0.12 b | 4.96 ± 0.23 ab | 5.60 ± 0.41 a | 5.55 ± 0.38 a | 5.11 ± 0.29 ab | 5.00 ± 0.22 ab |
| Prepupa | 0.88 ± 0.07 a | 0.86 ± 0.05 a | 0.95 ± 0.03 a | 0.93 ± 0.09 a | 0.77 ± 0.02 a | 0.94 ± 0.05 a |
| Pupa | 4.64 ± 0.08 a | 4.43 ± 0.14 a | 4.60 ± 0.05 a | 4.74 ± 0.08 a | 4.73 ± 0.06 a | 4.76 ± 0.06 a |
| Total duration from 1st instar to pupa | 17.37 ± 0.32 c | 17.89 ± 0.37 bc | 20.08 ± 0.55 a | 19.28 ± 0.47 ab | 17.12 ± 0.46 c | 18.38 ± 0.40 abc |
| Adult (lifespan) | 52.00 ± 6.34 a | 42.71 ± 4.96 a | 53.36 ± 5.17 a | 47.25 ± 5.92 a | 40.82 ± 6.07 a | 49.00 ± 4.06 a |
| F2 egg | 2.70 ± 0.15 a | 2.70 ± 0.15 a | 2.80 ± 0.13 a | 3.10 ± 0.18 a | 2.80 ± 0.13 a | 3.30 ± 0.15 a |
| Developmental Stage | Weight (mg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 mg/kg | 3.125 mg/kg | 6.25 mg/kg | 12.5 mg/kg | 25 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | |
| 2nd instar | 1.42 ± 0.25 a | 1.40 ± 0.10 a | 1.17 ± 0.08 a | 1.50 ± 0.09 a | 1.57 ± 0.09 a | 1.25 ± 0.11 a |
| 3rd instar | 4.11 ± 0.20 a | 4.14 ± 0.16 a | 3.77 ± 0.25 a | 4.45 ± 0.36 a | 4.54 ± 0.25 a | 3.93 ± 0.30 a |
| 4th instar | 11.71 ± 0.49 a | 13.09 ± 0.86 a | 12.68 ± 0.80 a | 13.11 ± 0.82 a | 13.18 ± 0.87 a | 12.01 ± 0.84 a |
| Prepupa | 34.26 ± 1.28 a | 32.61 ± 2.07 a | 28.29 ± 1.46 a | 29.03 ± 1.50 a | 29.32 ± 1.64 a | 31.08 ± 1.75 a |
| Pupa | 32.46 ± 1.22 a | 28.88 ± 1.67 ab | 26.26 ± 1.34 b | 26.70 ± 1.41 ab | 26.12 ± 1.45 b | 28.21 ± 1.45 ab |
| Adult | 27.91 ± 1.11 a | 24.27 ± 1.65 ab | 22.27 ± 1.20 ab | 22.60 ± 1.32 ab | 21.85 ± 1.38 b | 24.13 ± 1.38 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Q.; Wang, S.; Wan, S.; Guan, M.; Zhong, F.; Zhao, K.; Tao, S.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Effects of Cadmium Accumulation Along the Food Chain on the Fitness of Harmonia axyridis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051261
Shen Q, Wang S, Wan S, Guan M, Zhong F, Zhao K, Tao S, Zhou M, Li Y, Zhang W, et al. Effects of Cadmium Accumulation Along the Food Chain on the Fitness of Harmonia axyridis. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051261
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Qintian, Shasha Wang, Sijing Wan, Meiyan Guan, Fan Zhong, Keting Zhao, Shiyu Tao, Min Zhou, Yan Li, Weixing Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Cadmium Accumulation Along the Food Chain on the Fitness of Harmonia axyridis" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051261
APA StyleShen, Q., Wang, S., Wan, S., Guan, M., Zhong, F., Zhao, K., Tao, S., Zhou, M., Li, Y., Zhang, W., & Tang, B. (2025). Effects of Cadmium Accumulation Along the Food Chain on the Fitness of Harmonia axyridis. Agronomy, 15(5), 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051261





