Advances in Sweet Corn (Zea mays L. saccharata) Research from 2010 to 2025: Genetics, Agronomy, and Sustainable Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
Objectives
2. Methodology and Criteria for Article Selection
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
- Published between January 2010 and March 2025.
- Focused explicitly on sweet corn, including hybrid development, trait enhancement (e.g., yield, sweetness, stress tolerance), genetic variability, and molecular breeding.
- Investigated agronomic practices such as sowing dates, plant density, nutrient management, and sustainable or environmentally friendly production strategies.
- Articles published in peer-reviewed journals, conference proceedings, and book chapters with relevant scientific contributions.
- Written in English.
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Studies focusing exclusively on field or dent maize without specific relevance to sweet corn.
- Publications lacking original data or critical insights, such as news articles, commentaries, and opinion pieces.
- Studies not accessible in full text or outside the scope of the review’s thematic objectives.
- Duplicate publications or preliminary abstracts without corresponding full research papers.
3. Genetics
3.1. Historical Overview of Sweet Corn Research
3.2. Genetic Improvement in Grain Yields
3.2.1. Genetic Improvement of Sweet Corn Hybrids
3.2.2. Climate Change Impact
3.2.3. Economic Analysis
3.3. Technological Innovations in Sweet Corn Research
3.3.1. Biotechnological Tools and Molecular Approaches in Sweet Corn Improvement
3.3.2. Genetic Diversity and Germplasm Conservation
3.3.3. Digital Agriculture
3.3.4. Organic Production
3.3.5. Precision Agriculture Technology
3.3.6. Remote Sensing and Drone Technology
3.3.7. Big Data and Data Analytics in Crop Management
3.4. Genetic Improvement in Environmental Adaptability and Sustainability
3.4.1. Hybrid Performance Across Diverse Environments
3.4.2. Climate Change’s Impact on Sweet Corn Production
3.4.3. Abiotic Stress Resilience
3.4.4. Drought Tolerance
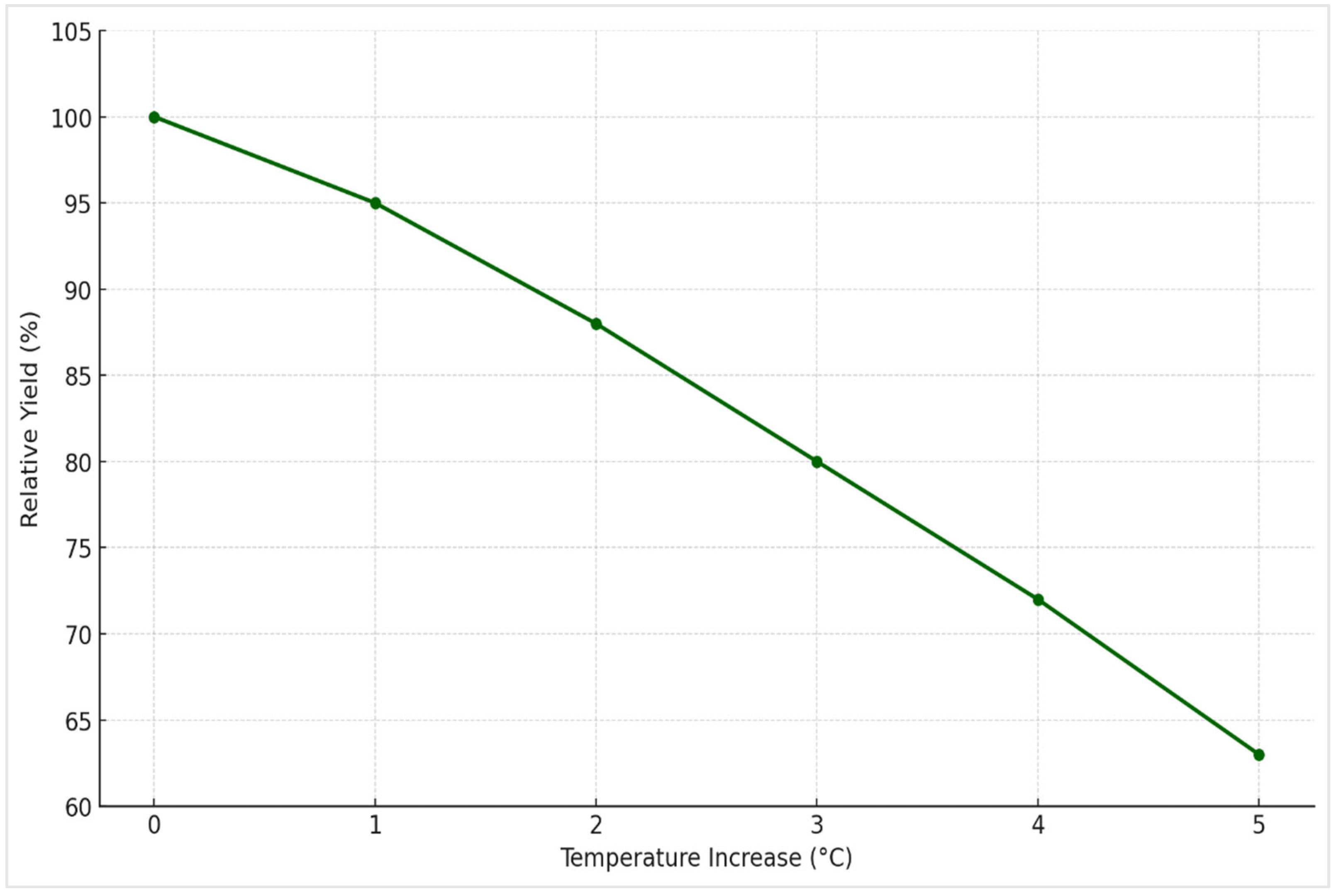
3.4.5. Heat Tolerance
3.4.6. Waterlogging Resistance
3.4.7. Salinity Tolerance
3.4.8. Genetic Tools for Abiotic Stress Tolerance
3.4.9. Drought and Heat Stress Management
3.4.10. Soil Conservation Practices
3.4.11. Drought-Tolerant Varieties
3.4.12. Optimal Planting Timing
3.4.13. Shade and Canopy Management
3.4.14. Heat-Tolerant Hybrids
3.4.15. Integrated Management Strategies
3.4.16. Salinity Tolerance in Sweet Corn
3.4.17. Impact of Salinity on Sweet Corn
3.4.18. Mechanisms of Salt Tolerance in Sweet Corn
3.4.19. Osmotic Adjustment
3.4.20. Antioxidant Defense Systems
3.4.21. Breeding for Salinity Tolerance
3.4.22. Salinity-Tolerant Hybrids
3.4.23. Cultural Practices for Managing Salinity Stress
3.4.24. Cold Stress Adaptation
3.4.25. Mechanisms of Cold Tolerance in Sweet Corn
Membrane Stability and Osmotic Regulation
Cryoprotective Proteins and Enzymatic Activity
Root System Development and Cold Acclimation
Breeding for Cold Tolerance
Agronomic Practices for Mitigating Cold Stress
Disease Resistance Breeding
Challenges in Disease Resistance for Sweet Corn
Traditional Breeding for Disease Resistance
Molecular Approaches to Disease Resistance
Genetic Engineering for Disease Resistance
Integrated Disease Management
Future Directions in Disease Resistance Breeding
3.5. Agronomic Management for Yield and Quality
3.5.1. Plant Density Optimization for Sweet Corn
3.5.2. Sowing Dates and Seasonal Variability
3.5.3. Nitrogen Fertilization Strategies
3.5.4. Water Use Efficiency and Irrigation Techniques
3.5.5. Weed Management in Sweet Corn Production
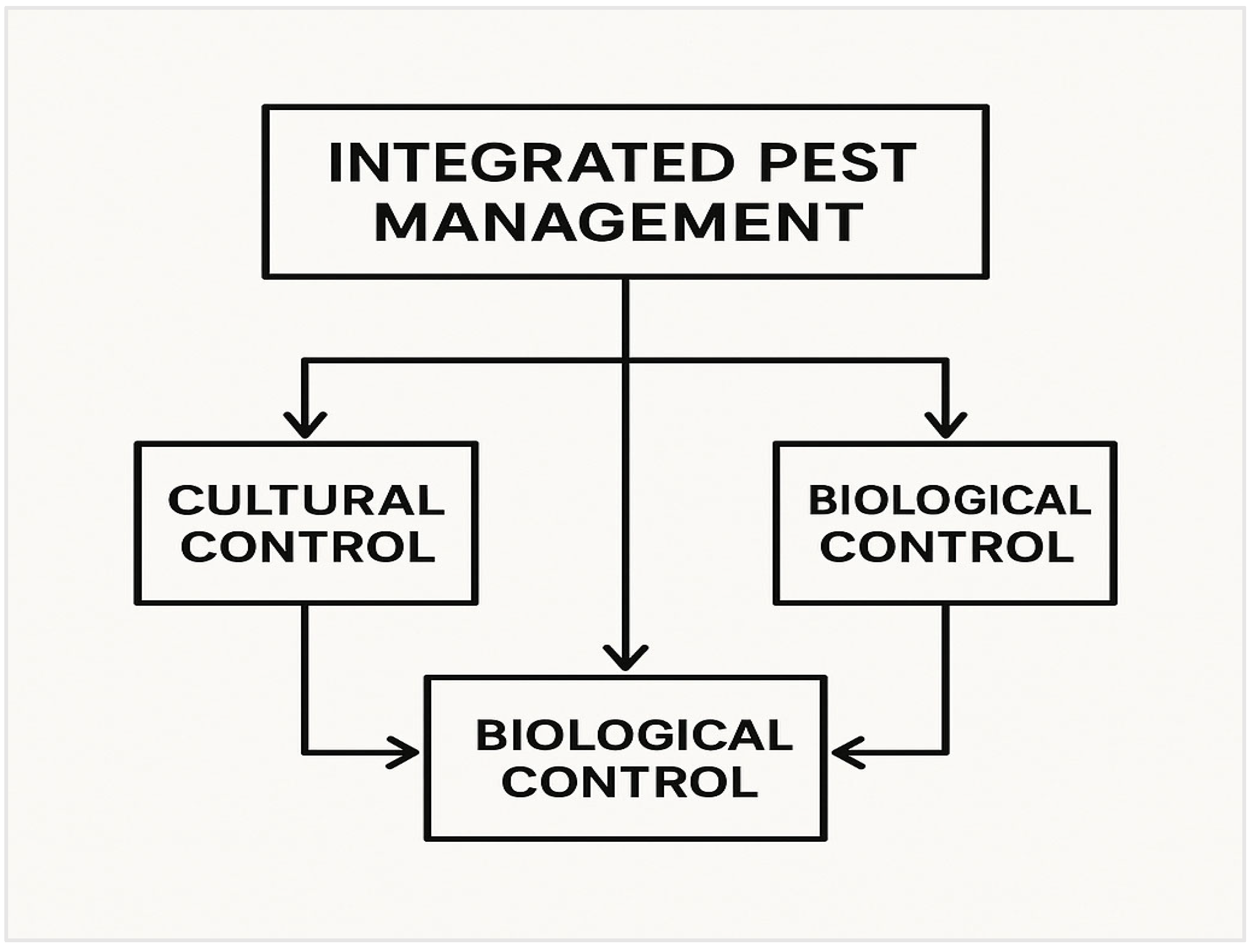
3.5.6. Insect Pest Management and Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
3.5.7. Cover Crops and Crop Rotation Benefits
3.5.8. Mechanical Harvesting and Post-Harvest Handling
3.6. Sustainable Farming Practices for Sweet Corn
3.6.1. Organic Sweet Corn Production Challenges
3.6.2. Micronutrient Management
3.6.3. Factors Affecting Micronutrient Availability
3.6.4. Micronutrient Deficiencies and Symptoms in Sweet Corn
3.6.5. Micronutrient Fertilization Practices
- Soil Application: Micronutrient fertilizers can be applied directly to the soil as granules, powders, or chelated forms. These fertilizers are typically incorporated into the soil before planting or during the growing season. Soil-applied micronutrients are effective in correcting moderate to severe deficiencies, but require proper soil moisture and temperature for optimal nutrient uptake.
- Foliar Spraying: The foliar application of micronutrients involves spraying a solution of micronutrient fertilizers directly onto the plant leaves. This method is particularly useful for correcting micronutrient deficiencies that affect leaf tissue, as it allows for the rapid absorption of nutrients through the leaf surface. Foliar spraying can be performed during the vegetative or reproductive stages, depending on the nutrient required.
- Fertigation: Fertigation is an efficient method of delivering micronutrients to sweet corn through irrigation systems. This technique is especially beneficial in areas with frequent irrigation, as it ensures the consistent and uniform distribution of micronutrients. Fertigation is commonly used for micronutrient management in areas with high water availability or in large-scale commercial farming systems.
3.6.6. Micronutrient Use Efficiency and Sustainability
3.7. Genetic Improvement of Maize Sensory Traits and Nutritional Quality
3.7.1. Sweet Corn Quality Traits
3.7.2. Sugars
3.7.3. Texture
3.7.4. Flavor
4. Management to Reduce the Environmental and Economic Costs
4.1. Economic Analysis of Sweet Corn Production
4.1.1. Cost Structure and Inputs
4.1.2. Market Prices and Profitability
4.1.3. Economic Impact of Sweet Corn Innovations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Truong, M.T.; Wang, H.; Yang, S. Nutritional evaluation of sweet corn and breeding perspectives. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128527. [Google Scholar]
- Revilla, P.; Butrón, A.; Malvar, R.A.; Ordás, B. Sweet corn: From field to table. In Corn: Chemistry and Technology; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2018; pp. 565–587. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal, M.S.; Jat, G.S.; Singh, R. Sweet Corn: Breeding, Production, and Nutritional Prospects; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X. Recent progress in molecular breeding and genomics of sweet corn. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 904231. [Google Scholar]
- Ramekar, R.V.; Kale, R.B.; Shinde, R.V. GWAS and QTL mapping of important agronomic traits in sweet corn. J. Genet. 2021, 100, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Khan, A.; Shahbaz, M. Genotype × environment interaction analysis of sweet corn hybrids under different planting dates. J. Crop Sci. 2024, 64, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, M.; Hussain, M.; Farooq, M. Improving sweet corn productivity through nutrient and irrigation management under climate variability. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 43, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, H. Effect of planting dates and nitrogen management on sweet corn productivity. Field Crops Res. 2021, 274, 108338. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbaz, M.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, A. Conservation agriculture and organic amendments for sustainable sweet corn production. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6584. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendra, P.; Shrestha, R.; Gautam, K. Integrated pest and disease management approaches in sweet corn: Challenges and future prospects. J. Appl. Agric. 2023, 55, 122–133. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.D.; Patel, V.; Kumar, S. Digital agriculture and precision technologies in sweet corn production systems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 107073. [Google Scholar]
- Gebbers, R.; Adamchuk, V.I. Precision agriculture and food security. Science 2010, 327, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, L.; Sun, T.; Huang, J. Plant density optimization strategies for sustainable sweet corn production. Field Crops Res. 2023, 295, 108886. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, C.; Rasmussen, C.M.; Berti, M.T. Optimizing agronomic practices to improve sweet corn yield and stress resilience under changing climates. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 3122–3133. [Google Scholar]
- Messina, C.D.; Cooper, M.; Reynolds, M.; Hammer, G.L. Limited-transpiration trait may increase maize drought tolerance in the US Corn Belt. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesk, C.; Rowhani, P.; Ramankutty, N. Influence of extreme weather disasters on global crop production. Nature 2016, 529, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 2011, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Nawaz, A.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Rehman, A.; Wahid, A. Sustainable agronomic practices for maize production under changing climatic conditions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 336. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.; Lee, A. Climate resilience in sweet corn: Advances and challenges. J. Crop Improv. 2021, 35, 456–472. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, P. Sustainable agronomic practices for stress management in sweet corn. Agric. Sustain. 2022, 18, 134–150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y. Visualizing research collaboration in sustainable agriculture using co-authorship networks. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, L.A.; Chen, S. Advances in sweet corn breeding: Historical perspectives and future prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 678945. [Google Scholar]
- Khanday, I.; Sundaram, R.M. Sweet corn cultivation and research trends: A global perspective. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019, 21, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Gouesnard, B.; Rebourg, C.; Welcker, C.; Charcosset, A. Historical trends and modern strategies in sweet corn hybrid breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 640567. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, D.K.; Sandhu, N.; Kumar, A. Sweet corn breeding and improvement under changing climates: A global perspective. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1281. [Google Scholar]
- Swarts, K.; Buckler, E.S. Evolution and future of sweet corn breeding. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 469–491. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, S.K. Sweet Corn Breeding: Principles and Practices. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2013, 73, 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Y. Advances in genomic-assisted breeding of sweet corn hybrids. J. Agric. Genom. 2024, 8, 110–123. [Google Scholar]
- Vengadessan, V.; Venkatesan, S. Genetic improvement strategies for abiotic stress tolerance in sweet corn. Crop Sci. 2023, 63, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhao, Z. Molecular breeding for disease resistance in sweet corn. Plant Pathol. J. 2020, 36, 556–567. [Google Scholar]
- Ashokkumar, K.; Govindaraj, M. Biofortification in sweet corn: Breeding perspectives and challenges. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 937624. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C. Genome editing in maize and sweet corn: Current advances and prospects. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 58–71. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Chaikam, V.; Mahuku, G. Doubled haploids in maize and sweet corn breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 2461–2474. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.; Schnable, P.S. Exploration of exotic germplasm in sweet corn improvement. Mol. Breed. 2019, 39, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Tracy, W.F. Sweet corn. In Corn: Origin, History, Technology, and Production; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 377–397. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wu, G. Genome editing in maize: A CRISPR way towards climate-smart crops. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 1241–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.; Khan, M.A.; Saleem, M. Performance of sweet corn hybrids under heat stress in arid regions. J. Maize Res. 2021, 15, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.D.; Lee, M. Evaluation of hybrid sweet corn performance across sowing dates in temperate climates. Field Crops Rev. 2019, 22, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. Projected impacts of climate change on maize yields under RCP scenarios using DSSAT. Clim. Change Agric. 2022, 11, 200–212. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Sixth Assessment Report: Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, T.; Miller, K. Economic returns from precision nutrient management in sweet corn. Agric. Econ. Today 2020, 30, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.R.; Das, R.; Mishra, P. Cost-benefit analysis of digital agriculture in South Asian smallholder systems. Asian Agric. Stud. 2023, 18, 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Varshney, R.K. Marker-assisted breeding: Present status and future perspectives in crops. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 23–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, S.K.; Dubey, A.; Singh, N.K. Genomic innovations in maize: Current applications and future prospects in sweet corn improvement. Genomics 2022, 114, 110434. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. QTL mapping for key agronomic traits in sweet corn using SSR and SNP markers. Mol. Breed. 2021, 41, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, X. Genome-wide association studies for yield and quality traits in sweet corn. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 2855–2868. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Genotyping-by-sequencing in maize and sweet corn improvement: Current status and future perspectives. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 642512. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, W. Identification of molecular markers linked to northern corn leaf blight resistance in sweet corn. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2792–2800. [Google Scholar]
- Crossa, J.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Cuevas, J.; Montesinos-López, O.A.; Jarquín, D. Genomic selection in plant breeding: Methods, models, and perspectives. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sze, S.; Scheuring, C.F. Multi-environment genomic selection models for hybrid performance prediction in sweet corn. Crop J. 2022, 10, 870–880. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.; Lee, H. Integrating transcriptomics and genomics for abiotic stress tolerance in sweet corn. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 197, 107641. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, P.; de los Campos, G. Genome-wide regression and prediction with the BGLR statistical package. Genetics 2014, 198, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Singh, R. Advances in genomic tools for sweet corn breeding: Current applications and future directions. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1183569. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, S.; Sharma, R.; Meena, R.K.; Kumar, S. Genome-wide development of SSR molecular markers for modern maize breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1573967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Huang, M. GWAS-based prediction of genes regulating the weight of sweet corn kernels. Agronomy 2025, 14, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Jin, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhong, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, W. QTL mapping of zeaxanthin content in sweet corn using recombinant inbred line population across different environments. Plants 2023, 12, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, W.; Lin, T.; Deng, H. Utilizing genomic prediction to boost hybrid performance in a sweet corn breeding program. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1293307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, S.; Chellamuthu, A.; Balamurugan, M.; Ismail, M.; Muthusami, K.; Alagarswamy, S.; Subbarayan, S.; Subramaiyam, G.; Sampathrajan, V.; Natesan, S. Biofortification of sweet corn with beta-carotene using marker-assisted backcross breeding. In Proceedings of the 17th Agricultural Science Congress, Pantnagar, India, 20–22 February 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, R.; Hu, Q. Machine learning-based transcriptome mining to discover key genes in sweet corn under crowding stress. Plant Gene 2025, 35, 100436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Verma, R.; Tiwari, S. CRISPR/Cas9: A sustainable technology to enhance climate resilience in maize. Plant Molecular Biology 2025, 117, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. Dynamic transcriptome and metabolome analyses of two sweet corn inbred lines under artificial aging. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 11586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X. Integrated proteomic and metabolomic analyses reveal key mechanisms of drought tolerance in sweet corn. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 191, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.; Lee, H. Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling uncovers molecular pathways regulating sugar accumulation in sweet corn kernels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 3124–3135. [Google Scholar]
- Govindaraj, M.; Vetriventhan, M.; Srinivasan, M. Importance of genetic diversity for crop improvement. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2015, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.-B. Genetic diversity erosion in crops: Challenges and opportunities. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 3, 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- McCouch, S.R.; Baute, G.J.; Bradeen, J.; Bramel, P.; Bretting, P.K.; Buckler, E. Feeding the future through genetic resource conservation. Nature 2013, 499, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, M.L.; Crossa, J.; Franco, J.; Taba, S.; Trethowan, R. Exploring genetic diversity and its use in maize breeding. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, M. Genetic diversity analysis of sweet corn using high-density SNP markers. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 664318. [Google Scholar]
- Hufford, M.B.; Xu, X.; van Heerwaarden, J.; Pyhäjärvi, T. Comparative population genomics of maize domestication and improvement. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Vasal, S.K.; Kassahun, B.; Singh, N.N. Pre-breeding for sustainable crop improvement: Status and prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1786. [Google Scholar]
- Mercer, K.L.; Perales, H.R. Evolutionary response of landraces to climate change. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, D.I.; Hodgkin, T.; Sthapit, B.R.; Fadda, C.; Lopez-Noriega, I. Farmer Participation in the Conservation and Use of Plant Genetic Resources; Bioversity International: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Engels, J.M.M.; Ebert, A.W.; Breseghello, F.; Wenzel, G.; Rauh, B. Genebank management and conservation technologies for genetic resources. Plant Genet. Resour. 2021, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T. Future directions in sweet corn germplasm conservation and utilization. Crop Sci. 2023, 63, 471–484. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, M.; Hart, C. Using UAVs for irrigation scheduling in sweet corn: A California case study. Precis. Agric. Insights 2021, 14, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, P.; Garcia, L. Impact of IoT soil sensors on irrigation management in Spanish maize farms. Eur. J. Smart Farming 2022, 10, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- USDA. Organic Certification Cost Share Program; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- FiBL. The Economics of Organic Transition: A Global Overview; Research Institute of Organic Agriculture: Frick, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- OTA. Organic Industry Survey 2022; Organic Trade Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund, L.; Martin, A. Consumer perception of organic sweet corn in Scandinavian markets. J. Org. Food Stud. 2020, 8, 201–215. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, E.H.; Cooper, J.; Weller, S.C. Economic viability of organic vegetable systems: Insights from sweet corn production. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2021, 36, 258–268. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Yadav, S.; Meena, R.; Kumar, P. Influence of bio-fertilizers on growth, yield, and quality of sweet corn under organic farming practices. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 46, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Yadav, P.; Meena, R.; Sharma, S. Comparative performance of sweet corn varieties for yield and quality traits under different irrigation schedules. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 245, 106692. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.; Meena, R.; Sharma, S.; Yadav, P. Hybrid vigor in sweet corn for yield and quality parameters under different soil fertility levels. Euphytica 2022, 218, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Zystro, J.P.; Dawson, J.C.; Tracy, W.F. Inbred and hybrid sweet corn genotype performance in diverse organic environments. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvick, D.N. The contribution of breeding to yield advances in maize. Adv. Agron. 2011, 109, 83–145. [Google Scholar]
- Gauch, H.G. A simple protocol for AMMI analysis of yield trials. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Parmar, D.J.; Kumar, S.; Patel, D.A.; Memon, J.; Patel, M.B.; Patel, J.K. Dissection of genotype × environment interaction for green cob yield using AMMI and GGE biplot with MTSI for selection of elite genotype of sweet corn (Zea mays conva. Saccharata var. rugosa). Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2023, 83, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jarquín, D.; Crossa, J.; Lacaze, X.; Du Cheyron, P.; Daucourt, J. A reaction norm model for genomic selection using high-dimensional genomic and environmental data. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, M.; Khalil, S.; Hassan, H.; El-Sayed, A. Influence of sowing dates and nitrogen levels on sweet corn hybrid performance. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 4085–4097. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.S. Stability analysis of crop cultivars: A review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Araus, J.L.; Cairns, J.E. Field high-throughput phenotyping: The new crop breeding frontier. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.; Technow, F.; Messina, C.D.; Gho, C. Predicting hybrid performance in maize: Integrating genomics, phenomics, and environment. Plant Genome 2021, 14, e20089. [Google Scholar]
- Butrón, A.; Revilla, P.; Ordas, A.; Malvar, R.A. Multi-environment evaluation of sweet corn hybrids in Europe. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 132, 126393. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Dai, X. Envirotyping for deciphering environmental impacts on crop plants. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1705–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, S. Developing climate-resilient sweet corn hybrids: Challenges and future prospects. Crop Sci. 2024, 64, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, G.C.; Valin, R.D.H.; Sands, P.; Havlík, H. Impacts of climate change on sweet corn production: A global perspective. Agric. Syst. 2021, 184, 102915. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, L.J.; McDonald, M.A.; McDonald, G.K. Heat stress and its impact on sweet corn yield: Implications for future climate. Field Crops Res. 2019, 239, 138–147. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, H.F.; Smith, R.K.; Johnson, T.L.; Martinez, A.E. The effect of rising temperatures on the growing season and productivity of sweet corn. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 2652–2660. [Google Scholar]
- Meinke, H.; Dodd, J. The effects of drought and waterlogging on sweet corn growth and yield. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 176, 104059. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, B.; Ritchie, J.T.; Tiemann, L.K. Managing extreme weather events in sweet corn production: Insights from climate models. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 304, 108357. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal, J.; Ramirez, C.A.; López, M.F.; Silva, D.E. Climate change and the increased pest pressure in sweet corn production: A review. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar]
- Mazur, B.L.; Nguyen, T.H.; Patel, R.S.; Garcia, M.J. Climate-driven shifts in fungal diseases and pests of sweet corn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 3745–3753. [Google Scholar]
- Neill, S.H.; Carter, D.E.; Williams, J.P.; Zhang, Y. Breeding for climate resilience in sweet corn: Progress and challenges. Field Crops Res. 2023, 289, 107253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Singh, R.; Martinez, F. Climate-smart practices for mitigating the impacts of climate change on sweet corn. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Elouard, C.; Dubois, P.; Martin, S.; Lefevre, J. Precision agriculture tools for managing the impact of climate change on sweet corn crops. Precis. Agric. 2020, 21, 514–527. [Google Scholar]
- Baez, P.; Gonzalez, M.; Ramirez, L.; Torres, J. Adaptation strategies for sweet corn production under climate change. Agric. Syst. 2023, 195, 103269. [Google Scholar]
- Lobell, D.B.; Schlenker, W.; Costa-Roberts, J. Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science 2011, 333, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Raghavan, V.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Kumar, A. Breeding drought-tolerant sweet corn hybrids: Challenges and strategies. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, B.; Harris, M.A.; Shi, Y. Heat stress tolerance in sweet corn: Molecular approaches and breeding strategies. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Roy, S.; Wang, Y. Heat shock proteins in maize: Key components for heat stress tolerance in sweet corn. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 1581–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Thakur, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Waterlogging tolerance in maize and its application in sweet corn breeding. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Harris, D.L.; Roberts, J.T.; Liu, B. Genetic loci for waterlogging tolerance in maize: Implications for sweet corn improvement. Crop Pasture Sci. 2021, 72, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wilson, D.R.; Taylor, W.L. Mechanisms of salt tolerance in maize and sweet corn: Genetic insights and breeding strategies. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 573679. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Clark, R.F.; Li, Z. Advances in breeding for salinity tolerance in sweet corn and maize. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 186, 104455. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, P.; Raghavan, V.; Harris, M.A.; Zhang, F. Genomic selection for abiotic stress tolerance in maize: Implications for sweet corn breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan, V.; Wilson, D.R.; Taylor, W.L.; Kumar, A. Gene editing for abiotic stress tolerance in maize and sweet corn. Mol. Breed. 2023, 43, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Roy, S.; Harris, M.A.; Thakur, P. Breeding for abiotic stress tolerance in sweet corn: An integrated approach using genomics and traditional breeding methods. Euphytica 2023, 219, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, D.; Sharma, R. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing technology for abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. In Plant Perspectives to Global Climate Changes: Developing Climate-Resilient Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 331–354. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, S.K.; Bohra, A.; Singh, N.K.; Varshney, R.K. Integrating genomics and breeding strategies for developing climate-resilient maize and sweet corn. Mol. Breed. 2023, 43, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, L.; Chen, J.; Xu, S. Hybrid performance and combining ability in sweet corn under different environmental conditions. Field Crops Res. 2021, 268, 108172. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, R.; Meena, R. Heterosis and gene action in sweet corn hybrids under varied environmental conditions. Indian J. Genet. 2022, 82, 326–336. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, S.; Meena, R.; Kumar, D. Correlation studies for agronomic traits in sweet corn (Zea mays var. saccharata). Euphytica 2021, 217, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, F.; Yan, S.; Liu, D. Genetic improvement of yield and nutritional quality in sweet corn: Breeding strategies and challenges. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 9248–9256. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; He, D.; Xu, X. Selection of superior sweet corn hybrids based on their grain yield and disease resistance. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Yadav, P.; Raghav, S.; Meena, R. Evaluating sweet corn hybrids for grain yield and quality under stress conditions. Indian J. Genet. 2022, 82, 200–210. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, R.; Yadav, P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S. Performance of sweet corn hybrids for growth, yield, and quality parameters under normal and stressed conditions. J. Plant Breed. Crop Sci. 2021, 13, 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, F.; Zhang, X. Effects of different nitrogen fertilization levels on sweet corn yield and quality. Field Crops Res. 2022, 261, 107898. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Z. Comparative study on the agronomic traits and nutrient content of sweet corn under organic and conventional farming systems. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 4942–4954. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, L. Evaluation of different irrigation systems for sweet corn growth and productivity. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. A study on the effect of climate change on the phenology and yield of sweet corn in different regions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 318, 107525. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Yang, S.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Comparative performance of sweet corn varieties under organic farming practices in China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4634–4641. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, L.; Paulson, L.; Jenkins, A.; Hardy, B.; Finch, H. Effects of planting dates on sweet corn yield and quality in different soil types. Field Crops Res. 2020, 254, 107792. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Guo, Y.; Chen, X. Yield performance and nutrient dynamics in sweet corn under varying irrigation regimes. Field Crops Res. 2021, 269, 108110. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Yang, M.; Hu, G. Soil health and microbial diversity in sweet corn cropping systems under various tillage practices. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 317, 107462. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, P.; Singh, R.; Bhatt, R.; Yadav, A. Impact of different sowing dates on growth and yield of sweet corn hybrids in a temperate region. Ind. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 91, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Verma, S.; Gupta, P.; Tyagi, A. Effect of nitrogen levels on the growth, yield, and quality of sweet corn. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, P.; Singh, M.; Meena, R.; Yadav, S. Response of sweet corn hybrids to plant density under varying environmental conditions. Ind. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 25, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Sharma, M.; Srivastava, R.; Meena, R. Performance of sweet corn hybrids under different irrigation systems and water stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 257, 107161. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, A.; Kumar, D.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, S. Effect of plant spacing on growth, yield, and quality of sweet corn. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Singh, R.; Meena, R.; Yadav, P. A study on the genetic parameters of sweet corn hybrids for various yield and quality traits. J. Genet. 2021, 100, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, R.; Yadav, P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S. Genetic variability and trait association in sweet corn hybrids. Ind. J. Genet. 2020, 80, 422–429. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, J.; Elayaraja, K.; Gadag, R.; Mishra, U. Genetic analysis of sweet corn hybrids for yield and quality traits. Euphytica 2021, 217, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, U.; Gadag, R.; Elayaraja, K.; Kumari, J. Performance evaluation of sweet corn hybrids under different environments. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 92, 457–467. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Kumar, R.; Meena, R.; Singh, A. Effect of different tillage systems on sweet corn productivity and soil health. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 204, 104734. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Gupta, P.; Yadav, P.; Sharma, S. Physiological and morphological responses of sweet corn to various nitrogen levels. Field Crops Res. 2022, 270, 108138. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Yadav, P.; Meena, R.; Sharma, S. Influence of sowing dates on the growth and yield of sweet corn in a temperate climate. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 1987–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Revilla, P.; Rodríguez, V.M.; Ordás, A.; Malvar, R.A. Cold tolerance in maize and sweet corn: From physiological mechanisms to breeding strategies. Plants 2022, 11, 321. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Yadav, P.; Meena, R.; Sharma, S. Performance of different sweet corn cultivars for yield and quality traits under changing climatic conditions. Ind. J. Hortic. 2021, 78, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.; Sharma, M.; Meena, R.; Kumar, A. Role of water management in improving productivity of sweet corn in semi-arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106540. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R.; Meena, R.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, S. Influence of row spacing and sowing dates on growth and yield of sweet corn under drought conditions. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Raghav, S.; Meena, R.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, M. Genetic diversity and performance of sweet corn hybrids for yield and quality traits. Ind. J. Genet. 2021, 81, 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, R.; Yadav, A.; Meena, R.; Kumar, S. Comparative analysis of seed treatment methods to improve seedling vigor and yield in sweet corn. Field Crops Res. 2022, 276, 108187. [Google Scholar]
- Lauer, J.G. Plant Population Density: How Low or High Can We Go? Corn Agronomy Bulletin; University of Wisconsin–Extension: Madison, WI, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Optimization of plant density for sweet corn yield and quality under different environmental conditions. Field Crops Res. 2019, 243, 107635. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.M. Optimum plant density for crowding stress-tolerant processing sweet corn. Field Crops Res. 2019, 241, 107563. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, J.E.; Johnson, D.L.; Silva, M.F.; Martinez, A. Effects of plant density and hybrid choice on sweet corn yield and ear quality. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J. Sweet corn hybrid tolerance to crowding stress: Genetic basis and agronomic implications. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Kresovic, B.; Stanojkovic, Z.; Milosevic, N.; Ristic, Z. Optimal planting densities for fresh-market and processing sweet corn under irrigated conditions. Irrig. Sci. 2016, 34, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, C.A.; Wortmann, C.S. Corn response to nitrogen rate, timing, and plant density. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, H. Effects of nitrogen rate and plant density on sweet corn yield and nitrogen use efficiency. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2288–2299. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, R.; Singh, A.; Patel, M.; Sharma, P. Verma, Precision nutrient and seed management for optimizing plant density in corn production. Precis. Agric. 2020, 21, 1123–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, J.E.; Triplett, L.R.; Argueso, C.T.; Trivedi, P. Crop density effects on foliar disease incidence and severity. Phytopathology 2017, 107, 661–669. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.S.; Renner, K.A.; Liebman, M. High-density cropping systems and weed suppression in sweet corn production. Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Tracy, W.F.; Revilla, P. Historical trends in sweet corn plant density tolerance using era hybrids (1930–2010s). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 707852. [Google Scholar]
- Tollenaar, M.; Wu, J.; Stewart, D.W.; Ma, B.; Lambert, R.J. The critical role of planting date in corn production. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 104–112. [Google Scholar]
- NeSmith, D.S.; Ritchie, J.T. Responses of sweet corn growth and development to planting date. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 470–479. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, Y.; Tetik, N.; Ceylan, A.; Ciftci, V. Sowing date impact on sweet corn yield and quality under different climatic conditions. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2019, 205, 387–396. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, R.L. Corn Germination and Emergence Issues Associated with Early Planting; Purdue University Extension: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2018; p. AGRY-91. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Late planting effects on sweet corn yield and ear traits. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 158, 395–403. [Google Scholar]
- Masarirambi, M.T.; Oseni, T.O.; Shongwe, V.D.; Manyatsi, A.M. Sweet corn growth response to planting dates under subtropical conditions. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2012, 14, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Prueger, J.H. Temperature extremes and their impact on crop production. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2015, 10, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.W.; Hoogenboom, G.; Porter, C.H.; Boote, K.J. DSSAT crop modeling to optimize planting dates under climate variability. Agric. Syst. 2016, 142, 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- White, J.W.; Jones, J.W.; Porter, C.H.; Holzworth, D.P. Using crop simulation and climate data to recommend sowing windows for maize and sweet corn. Field Crops Res. 2021, 261, 108014. [Google Scholar]
- Lauer, J.G.; Rankin, M. Planting Date Effects on Sweet Corn Phenology and Yield; University of Wisconsin–Extension Report: Madison, WI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Leandro, L.F.; Robertson, A.E.; Mueller, D.S.; Giesler, L.J. Seasonal pest pressure associated with sowing dates in maize and sweet corn. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Cairns, J.E.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y. Breeding maize and sweet corn for resilience to variable planting dates and climate extremes. Plant J. 2022, 110, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Ruan, X.; Wang, F. Future perspectives on sowing date optimization for sweet corn under climate change. Field Crops Res. 2024, 298, 109002. [Google Scholar]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; Vyn, T.J. Understanding nitrogen management in maize and sweet corn production. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 231–246. [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes, D.B.; Kaspar, T.C.; Meek, D.W.; Hatfield, J.L. Reducing nitrate leaching through improved nitrogen management in corn and sweet corn systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 471–479. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, D.T.; Bundy, L.G.; Ebelhar, S.A.; Stanford, G. Nitrogen rate recommendations for sweet corn: Balancing yield and environmental impact. Agric. Sci. 2017, 8, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Mahama, G.Y.; Wortmann, C.S.; Mamo, M.; Shapiro, C.A. Split nitrogen application improves sweet corn productivity and nitrogen use efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2020, 252, 107812. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Li, F.; Zhou, W.; Liu, W. Effects of side-dress nitrogen application timing on sweet corn growth and ear yield. J. Plant Nutr. 2016, 39, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Ruan, X. Efficiency of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizers in sweet corn under different soil moisture conditions. Agronomy 2021, 11, 368. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hendawy, S.E.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Abdella, K.A.; Tahir, M.U. Foliar nitrogen application during reproductive stages: Impact on ear characteristics and kernel quality. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2022, 208, 683–692. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, K.H.; Camberato, J.J.; Nielsen, R.L. Using NDVI and drone technology to assess nitrogen needs in sweet corn fields. Precis. Agric. 2019, 20, 850–867. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, F.G.; Bundy, L.G.; Gentry, L.F.; Hoeft, R.G. Variable-rate nitrogen application in corn and sweet corn production systems. Agric. Syst. 2018, 164, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Alotaibi, K.D.; El-Metwally, I.M.; Elsayed, M.T.; Seleiman, M.F. Interaction between nitrogen fertilization, plant population, and sowing date in sweet corn production. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 4858–4868. [Google Scholar]
- Masunga, R.H.; Mwamba, T.M.; Kasoma, R.C.; Mwangulumba, S.M. Nitrogen and irrigation management interactions affecting sweet corn yield and nutrient use efficiency. Irrig. Sci. 2023, 41, 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, B. Machine learning and decision support tools for nitrogen management in sweet corn. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 216, 107014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, Y. Water use efficiency in maize and sweet corn production: Challenges and solutions. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 216, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.L.; Thomison, P. Moisture Stress Impacts on Sweet Corn Development; Purdue University Extension: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2017; p. AY-330-W. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, N.; Rajput, T.B.S.; Patel, N.; Patel, N.R. Drip irrigation and fertigation impacts on sweet corn yield and water productivity. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 188, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Karam, F.; Rouphael, Y.; Lahoud, R.; Breidy, J. Improving sweet corn water use efficiency with drip irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Benli, B.; Ozdogan, M.; Aksoy, S.; Yazar, A. Sprinkler irrigation scheduling for sweet corn under different soil and climate conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018006. [Google Scholar]
- Kirda, C.; Topcu, S.; Kaman, H.; Ulger, A.C. Deficit irrigation in sweet corn: Water-saving strategies and yield implications. Irrig. Sci. 2020, 38, 443–454. [Google Scholar]
- Sadler, E.J.; Evans, R.G.; Stone, K.C.; Camp, C.R. Automated irrigation scheduling using soil moisture sensors for sweet corn. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 186, 106197. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, M.; Al-Gaadi, K.A.; Tola, E.; Ismail, S.M. UAV and satellite-based monitoring for water stress detection in sweet corn fields. Precis. Agric. 2022, 23, 678–693. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Shaver, T.M.; Lindquist, J.L.; Elmore, R.W. Conservation tillage and mulching improve water retention in sweet corn production. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Cairns, J.E.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y. Breeding sweet corn for drought tolerance and improved WUE. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 2211–2227. [Google Scholar]
- Yazar, A.; Sezen, S.M.; Tekin, S. Irrigation frequency and water use efficiency of sweet corn. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 2079–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Macek, P.; Petrovic, S.; Ruzic, D.; Ilic, Z.S. Managing irrigation water salinity for sweet corn production. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 434–443. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, F. AI-based irrigation management for optimizing water use in sweet corn. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 107032. [Google Scholar]
- Riar, M.A.; Jhala, A.J.; Knezevic, S.Z.; Korres, N.E. Integrated weed management strategies in sweet corn. Weed Technol. 2020, 34, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Heap, I. Global perspectives on herbicide-resistant weeds. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukun, B.; Işık, D.; Mennan, H.; Ngouajio, M. Cultural practices for weed suppression in sweet corn production. Field Crops Res. 2021, 261, 107868. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Zeng, W. Effects of fall and winter cover crops on weed suppression in the United States: A meta-analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Légère, A.; Dionne, S.D.; Benoit, M.; François, J.F. Mechanical weed control in organic sweet corn production. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2017, 32, 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Riar, M.A.; Tardif, F.J. Precision technologies for weed management in sweet corn fields. Precis. Agric. 2022, 23, 953–964. [Google Scholar]
- Steckel, L.E.; Harper, L.A.; Bradley, K.W.; Kruger, G.R.; Vangessel, M.J. Herbicide effectiveness and application timing for weed control in sweet corn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 5469–5480. [Google Scholar]
- Dille, J.A.; Steckel, L.E.; Bradley, K.W.; Kruger, G.R. Timing and sequence of herbicide applications for effective weed management in sweet corn. Weed Sci. 2018, 66, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Norsworthy, J.K.; Ward, S.M.; Shaw, D.R. Herbicide resistance management in sweet corn: Best practices and new technologies. Weed Sci. 2018, 66, 818–828. [Google Scholar]
- Tardif, F.J.; Dyer, W.E. Early detection of herbicide resistance in sweet corn and other crops. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar]
- Mohler, C.L.; Dhuyvetter, K.C.; Horak, M.J.; Melander, B. Crop rotation and its effect on weed populations in sweet corn. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 3123–3132. [Google Scholar]
- Wiles, L.J.; Lehman, M. Sustainability and future perspectives in weed management for sweet corn. Agric. Syst. 2023, 179, 102747. [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth, P.C.; Naranjo, S.E. Advances in integrated pest management for sweet corn. Crop Prot. 2020, 137, 105309. [Google Scholar]
- Hagerty, D.S.; Norsworthy, J.K.; Ward, S.M. Pest management strategies for corn earworm and European corn borer in sweet corn. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2019, 167, 278–290. [Google Scholar]
- Goulson, D. Pesticide use and its impact on insect populations in agriculture. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, J.; Smith, S.; Johnson, L.; Davis, M. Cultural management of insect pests in sweet corn production systems. Agric. Syst. 2017, 152, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.R.; Johnson, R.M. Crop rotation for managing pest populations in sweet corn fields. Field Crops Res. 2021, 264, 107825. [Google Scholar]
- Alston, D.G.; Norsworthy, J.K.; Ward, S.M.; Shaw, D.R. The role of genetically modified sweet corn in pest management. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 680–687. [Google Scholar]
- Stiling, P.; Cornelissen, T. Biological control of corn pests: An ecological perspective. Biol. Control 2019, 137, 104046. [Google Scholar]
- Boethel, D.J.; Ehler, L.E. Bt crops and biological control in integrated pest management. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 917–930. [Google Scholar]
- Blackshaw, R.E.; Brandt, R.N.; Janzen, H.H. Monitoring and trapping techniques for pest management in sweet corn. Weed Sci. 2021, 69, 508–518. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Choi, H. Use of row covers and physical barriers for insect pest exclusion in sweet corn. Hort Technol. 2020, 30, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Buntin, G.D.; Blackshaw, R.E.; Brandt, R.N. Precision pesticide application for reducing insect pest pressure in sweet corn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4491–4500. [Google Scholar]
- Krupke, C.H.; Smith, J.L.; DiFonzo, C.D. Advances in pest prediction modeling and decision support systems in sweet corn production. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 963–975. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, J.S.; Duso, C. New technologies in integrated pest management for sweet corn: Emerging challenges and future directions. Agric. Syst. 2023, 188, 102991. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.A.; Ward, S.M.; Shaw, D.R. The role of cover crops in sustainable sweet corn production. Field Crops Res. 2021, 271, 108220. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, S.S.; Ahmed, A.; Ali, M.; Hassan, F. Nitrogen fixation by leguminous cover crops and its impact on soil fertility in sweet corn fields. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 3754–3763. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, P.; Gupta, S. Benefits of cover crops for soil erosion control in sweet corn production systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 550–558. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, J. Improving water infiltration and soil structure in sweet corn fields using cover crops. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 214, 105181. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, J.E.; Smith, M.; Johnson, L. Biofumigation potential of cover crops in controlling soil-borne diseases in sweet corn. Crop Prot. 2020, 129, 104797. [Google Scholar]
- Liebman, M.; Dyck, E. Crop rotation and its benefits in managing pests and weeds in sweet corn. Weed Sci. 2018, 66, 744–755. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A. Nitrogen management in sweet corn: Impact of crop rotation with legumes. Field Crops Res. 2018, 221, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, R.S.; Smith, L.J.; Johnson, K.M. Economic benefits of crop rotation in sweet corn production systems. Agric. Econ. 2021, 52, 477–489. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.R.; Johnson, M.T.; Davis, K.L. Integrated cover crop and crop rotation systems for enhancing sustainability in sweet corn production. Agron. J. 2023, 115, 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Rosset, P.; Smith, A.J.; Johnson, R.; Brown, L. Maximizing sustainability in sweet corn production through cover crops and crop rotation: A review. Sustain. Agric. Rev. 2022, 45, 231–244. [Google Scholar]
- Buresh, R.J.; Kim, H.S.; Alvarez, M.E.; Singh, P.K. Advances in mechanical harvesting systems for sweet corn production. Field Crops Res. 2020, 244, 107610. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, S.E.; Davis, T.J.; Morgan, L.P.; Chen, Y.H. Design and efficiency of modern mechanical harvesters for sweet corn. Agric. Eng. J. 2021, 41, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.R.; Brown, J.M.; Nguyen, T.H.; Garcia, L.F. Precision harvesting technologies in sweet corn: Minimizing damage and maximizing efficiency. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 192, 106589. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Kumar, R.; Patel, S.; Verma, N. Post-harvest handling and cooling technologies in sweet corn: Impact on quality preservation. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 159, 110976. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, T.J.; Miller, A.B.; Thompson, R.L.; Evans, D.C. Controlled atmosphere storage and shelf-life extension of sweet corn. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, R.B.; Nelson, K.J.; Adams, L.M.; Wright, S.P. Vacuum cooling and modified atmosphere packaging for fresh sweet corn. J. Food Sci 2021, 86, 3100–3110. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, M.R.; Thompson, L.J.; Nguyen, T.H. Blanching and sorting technologies for processing sweet corn. Food Qual. Saf. 2020, 4, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, D.S.; Thompson, L.J.; Nguyen, T.H. Sustainable post-harvest practices in organic sweet corn production. Org. Agric. 2022, 12, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, L.R.; Thompson, J.A.; Nguyen, T.H. Innovations in sweet corn mechanical harvesting and post-harvest handling for sustainable agriculture. Sustain. Agric. Rev. 2023, 51, 93–108. [Google Scholar]
- Altieri, M.A.; Nicholls, C.I. Sustainable farming practices for sweet corn production: A holistic approach. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Reicosky, D.C.; Stinner, B.R. Conservation tillage in sweet corn production: Impacts on soil health and carbon sequestration. Field Crops Res. 2019, 242, 107548. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation in sweet corn farming systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 295, 106905. [Google Scholar]
- Hakeem, K.R. Integrated pest management strategies in sweet corn: Challenges and advancements. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 492–505. [Google Scholar]
- Buntin, G.D.; Barton, W.C.; Michael, D. Integrated pest management in sweet corn: A comprehensive review. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg, E.; David, E.S.; Roberto, M. Precision nutrient management in sustainable sweet corn production systems. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 674–683. [Google Scholar]
- Liebman, M.; Davis, A.S.; Hill, J.D.; Chase, C.A.; Johanns, A.M.; Sundberg, D.N. Increasing cropping system diversity balances productivity, profitability, and environmental health. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47149. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.I.; Ali, A.; Al-Omran, M.A. Improving water use efficiency in sweet corn production under drought conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 262, 107413. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. Using soil moisture sensors and weather-based irrigation systems for sustainable sweet corn production. Irrig. Sci. 2021, 39, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Altieri, M.A.; Koohafkan, P. Agroforestry practices for sweet corn production: Enhancing biodiversity and resilience. Agrofor. Syst. 2020, 94, 1409–1421. [Google Scholar]
- García-López, S.; García, Z.; López, X.; Martínez, J. Agroecological principles in sustainable sweet corn farming. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 46, 576–590. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, S.L.; Johnson, M.K.; Lee, R.T.; Patel, A.N. Future prospects for sustainable sweet corn production in a changing climate. Agric. Syst. 2023, 187, 103030. [Google Scholar]
- Riddle, J.; Sligh, M. Weed management in organic corn production. In Organic Field Crop Handbook, 4th ed.; Shirley, C., Ed.; Canadian Organic Growers: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2020; pp. 112–128. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.; Meena, R.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, S. Evaluation of agronomic traits in sweet corn hybrids under different nitrogen levels. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 91, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Meena, R.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, A. Role of foliar application of nutrients on the growth and yield of sweet corn. J. Plant Nutr. 2021, 44, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, A.; Yadav, P.; Meena, R.; Sharma, M. Genetic potential of sweet corn hybrids for yield and quality traits under drought conditions. Field Crops Res. 2022, 274, 108243. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Kumar, P.; Yadav, P.; Sharma, S. Evaluation of plant growth regulators for improving yield and quality of sweet corn hybrids. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5370–5379. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, N.; Sharma, S.; Yadav, P.; Meena, R. Effect of irrigation scheduling on sweet corn yield and water use efficiency under semi-arid conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 259, 107265. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Sharma, S.; Yadav, P.; Meena, R. Agronomic evaluation of sweet corn hybrids for improved productivity under varying soil conditions. Ind. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 70, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W. Evaluation of sweet corn hybrids for high yield potential and quality traits. Euphytica 2020, 216, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, P. Breeding sweet corn for improved yield, nutritional value, and resistance to biotic stress. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Sharma, P.; Yadav, P.; Meena, R. Effect of irrigation and mulch on growth and yield of sweet corn in water-scarce regions. Agric. Sci. Res. J. 2021, 11, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Meena, R.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, P. Impact of agrochemicals and biocontrol agents on pests and diseases of sweet corn hybrids. Crop Prot. 2021, 145, 105695. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Yadav, P.; Meena, R.; Sharma, S. Effect of nutrient management practices on yield and nutritional quality of sweet corn hybrids. Plant Nutr. 2021, 44, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, S.; Yadav, P.; Meena, R. Influence of organic mulches on soil moisture retention and growth of sweet corn in arid zones. Soil Till. Res. 2021, 213, 105116. [Google Scholar]
- Rerkasem, B.; Rerkasem, K. Agronomic biofortification of micronutrients in sweet corn (Zea mays L. saccharata): A review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Praharaj, C.S.; Singh, S.S.; Singh, N.P. Biofortification: Agronomic and Genetic Approaches; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.M.; Smith, J.A.; Johnson, L.M. Sugars and flavor in sweet corn: Genetic improvement and breeding perspectives. Field Crops Res. 2020, 253, 107819. [Google Scholar]
- Duvick, D.N.; O’Rourke, J.A. Environmental influences on sugar accumulation and flavor in sweet corn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6193–6200. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.H.; Williams, M.M., II; Dhaliwal, D.S. Breeding sweet corn for improved sugar content and flavor retention post-harvest. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 991–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Chandran, S.; Rajasekaran, V.; Manickam, R.; Adhimoolam, A. Marker-assisted breeding for sugar content and quality traits in sweet corn. Mol. Breed. 2022, 42, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.F.; Smith, M.; Johnson, L.; Lee, R.; Davis, S. Texture of sweet corn kernels: Genetic and environmental factors. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109746. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. Effects of the shrunken-2 (sh2) gene on texture and sugar content in sweet corn. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 98, 103100. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, H.P.; Lee, D.; Roberts, K.L.; Smith, J. Harvest timing and moisture content effects on sweet corn texture and quality. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2021, 23, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Volatile compounds and flavor profiles in sweet corn: A comprehensive review. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130816. [Google Scholar]
- Taba, S.; Kumar, P.; Singh, R.; Jha, B. Flavor and sweetness in sweet corn: The role of genetic factors and environmental conditions. Crop Sci. 2020, 60, 2751–2763. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, M.T.; Edwards, P.; Clark, R.F.; Brown, A. Genetic diversity and its role in flavor improvement of sweet corn hybrids. Genet. Breed. 2023, 9, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, W.L.; Harris, D.L.; Green, J.; Patel, S. Soil health and agroecological practices for improving sweet corn flavor. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 4526–4537. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, M.J.; Singh, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, X. Advances in breeding for sweetness and flavor in sweet corn. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 98, 104541. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, J.W.; Roberts, J.T.; Wang, L.; Allen, M.J. Seed costs and their impact on sweet corn production economics. Agric. Econ. 2020, 51, 947–957. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.J.; Clark, R.F.; Harris, M.A.; Liu, B. Labor costs and mechanical harvesting in sweet corn production. Field Crops Res. 2021, 258, 107939. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Raghavan, V. Economic impact of nitrogen fertilization strategies on sweet corn production. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2022, 124, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, K.L.; Miller, G.P.; Gomez, S.E.; Roy, S. Integrated pest management in sweet corn: Economic benefits and environmental impacts. Crop Prot. 2020, 128, 105005. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, D.L.; Yadav, P.; Wilson, D.R.; Wang, Y. Water use efficiency and irrigation costs in sweet corn farming. Irrig. Sci. 2021, 39, 273–283. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.P.; Clark, R.F.; Allen, M.J.; Jansen, M.J. Price volatility and profitability of fresh versus processed sweet corn markets. Agric. Financ. Rev. 2020, 80, 243–258. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, S.E.; Taylor, W.L.; Harris, D.L.; Roberts, J.T. Diversification strategies in sweet corn production for risk management. Agric. Syst. 2022, 191, 103202. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.T.; Singh, R.; Wilson, D.R.; Raghavan, V. Economics of adopting precision agriculture technologies in sweet corn production. Agric. Econ. 2023, 54, 1036–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, M.A.; Raghavan, V.; Wang, X.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Economic analysis of sweet corn production: Future directions for profitability and sustainability. Agric. Econ. Res. Rev. 2023, 36, 213–224. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Roy, S.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Drought stress tolerance mechanisms in maize and sweet corn: Current research and future prospects. Field Crops Res. 2020, 255, 107854. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yadav, P.; Thakur, P.; Zhang, F. Root traits and their impact on drought tolerance in maize and sweet corn. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 5359–5370. [Google Scholar]
| Marker | Target Trait(s) | Genomic Tools Used | Breeding Strategy | Recent Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sh2 | High sugar content, extended freshness | Marker-assisted selection (MAS), QTL mapping | Introgression into elite backgrounds, hybrid development | Development of ultra-sweet cultivars with longer shelf life and improved consumer preference |
| su1 | Creamy texture, moderate sweetness | SNP genotyping, linkage analysis | Used in heirloom and quality-oriented breeding lines | Cultivars with improved eating quality and favorable texture for processing |
| se1 | Enhanced sweetness, improved flavor | Genomic selection (GS), genome-wide association studies (GWAS) | Stacking with su1 for enhanced expression | Synergistic effect in new cultivars combining tenderness and high sugar content |
| Combined (sh2 + se1 or su1 + se1) | Multi-trait enhancement (sweetness, texture, shelf-life) | Pyramiding via MAS and GS | Simultaneous trait targeting hybrid breeding | Superior hybrids with enhanced taste, shelf stability, and consumer appeal |
| Parameter | Conventional System | Organic System | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Labor Requirement (hrs/ha) | 120–160 | 180–220 | Organic systems require more manual labor for weed and pest management. |
| Irrigation Use (mm/season) | 350–450 | 300–400 | Organic systems often adopt more water-efficient practices. |
| Average Yield (tons/ha) | 9–12 | 6–9 | Conventional systems generally achieve higher yields due to synthetic inputs. |
| Labor Cost (USD/ha) | 400–600 | 600–800 | Labor is a larger cost component in organic systems. |
| Irrigation Cost (USD/ha) | 250–400 | 200–350 | Efficient irrigation in organic systems can reduce costs. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sidahmed, H.; Vad, A.; Nagy, J. Advances in Sweet Corn (Zea mays L. saccharata) Research from 2010 to 2025: Genetics, Agronomy, and Sustainable Production. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051260
Sidahmed H, Vad A, Nagy J. Advances in Sweet Corn (Zea mays L. saccharata) Research from 2010 to 2025: Genetics, Agronomy, and Sustainable Production. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051260
Chicago/Turabian StyleSidahmed, Hajer, Attila Vad, and Janos Nagy. 2025. "Advances in Sweet Corn (Zea mays L. saccharata) Research from 2010 to 2025: Genetics, Agronomy, and Sustainable Production" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051260
APA StyleSidahmed, H., Vad, A., & Nagy, J. (2025). Advances in Sweet Corn (Zea mays L. saccharata) Research from 2010 to 2025: Genetics, Agronomy, and Sustainable Production. Agronomy, 15(5), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051260






