Aluminum Sulfate and Straw Enhance Carbon Sequestration in Saline–Alkali Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Soil and Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Aggregate Composition
2.3.2. SOC Groups
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Salinization Properties of Saline–Alkali Soils
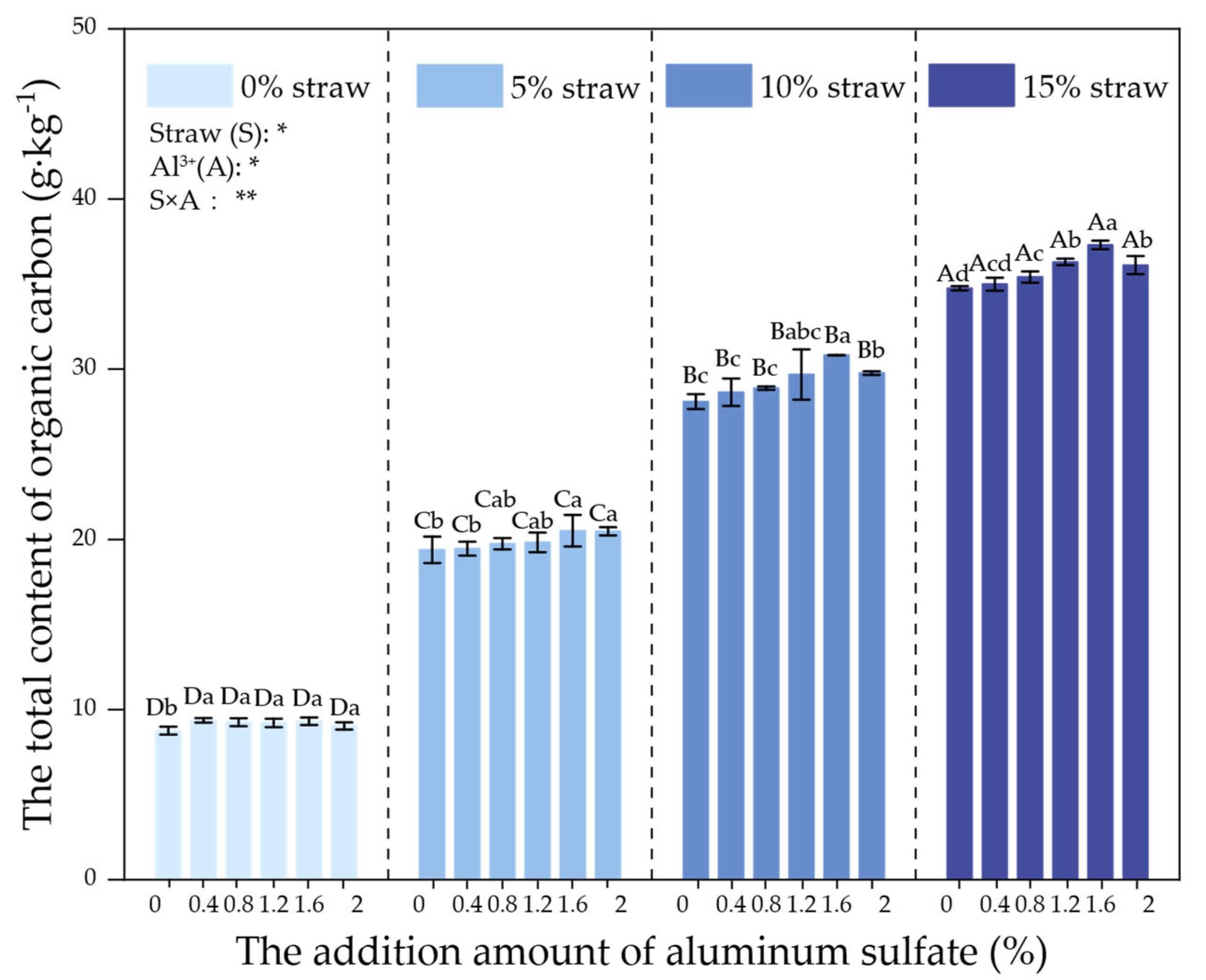
3.2. Effects of Al3+ on Straw C Sequestration
Changes in SOC
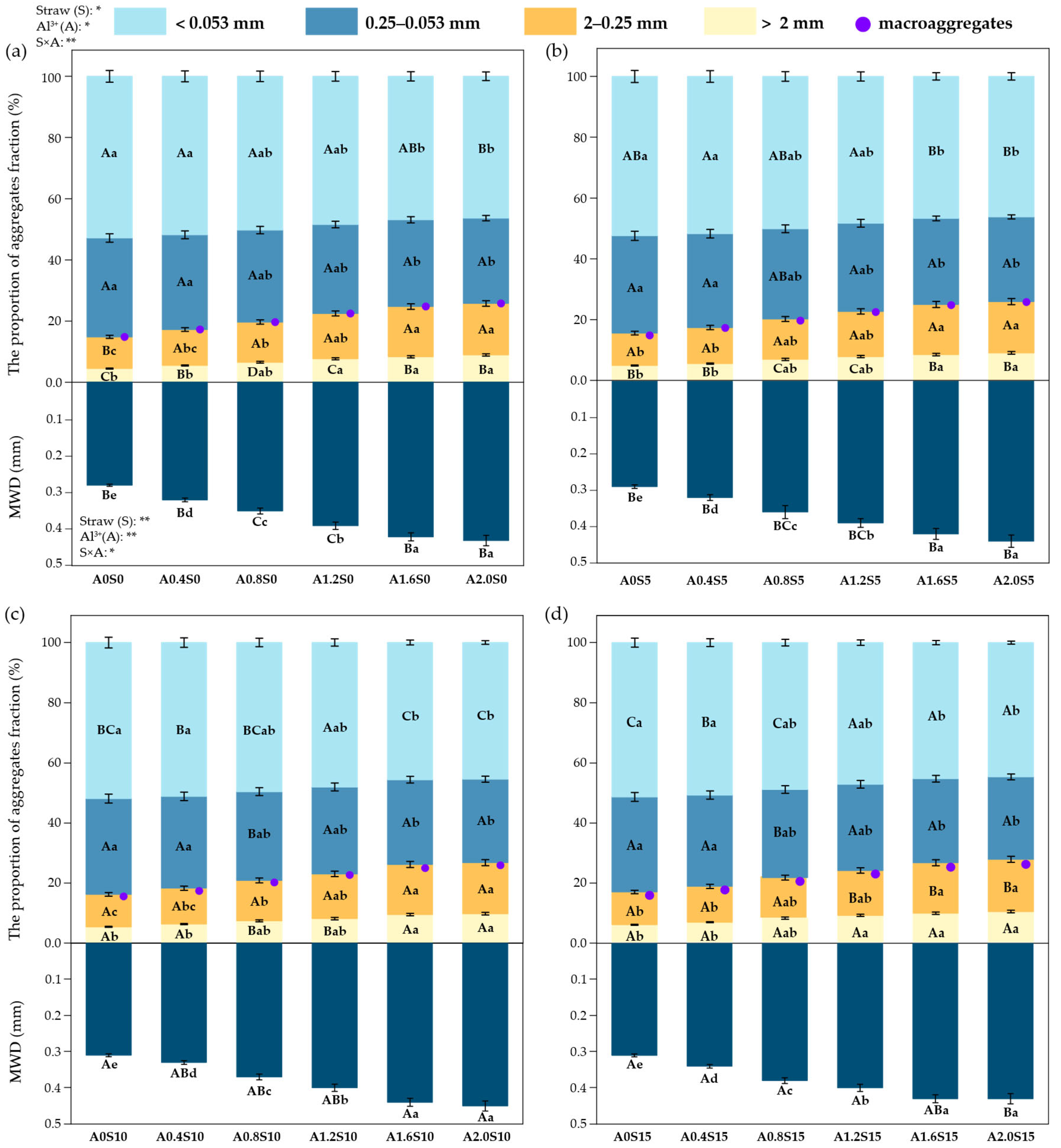
3.3. Changes in Aggregate Composition and OC Distribution
3.3.1. Aggregate Distribution
3.3.2. Aggregate-Associated SOC
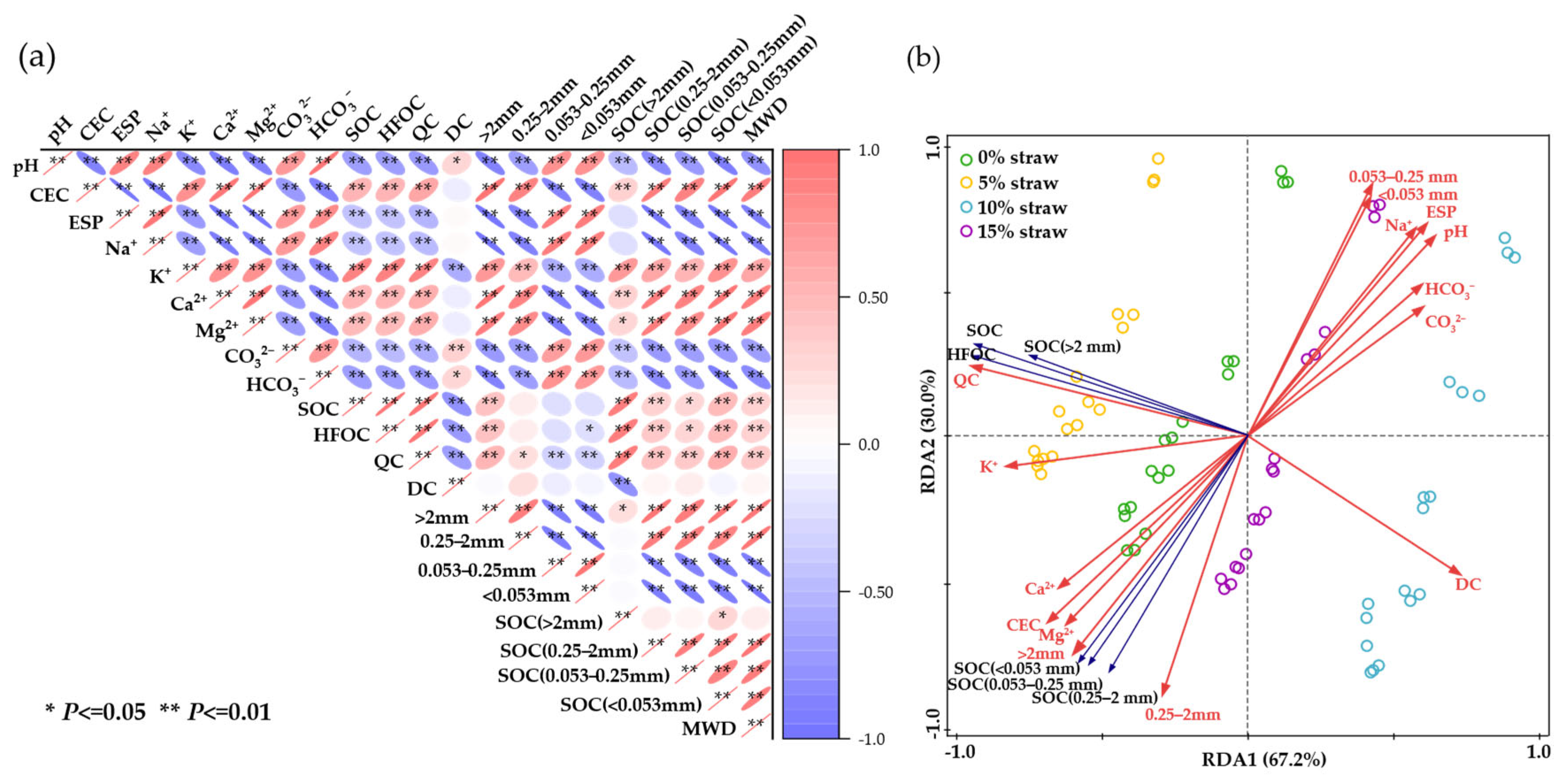
3.4. Associations and Relative Importance
3.4.1. Correlations Among Salinization Properties, Aggregate Characteristics and SOC
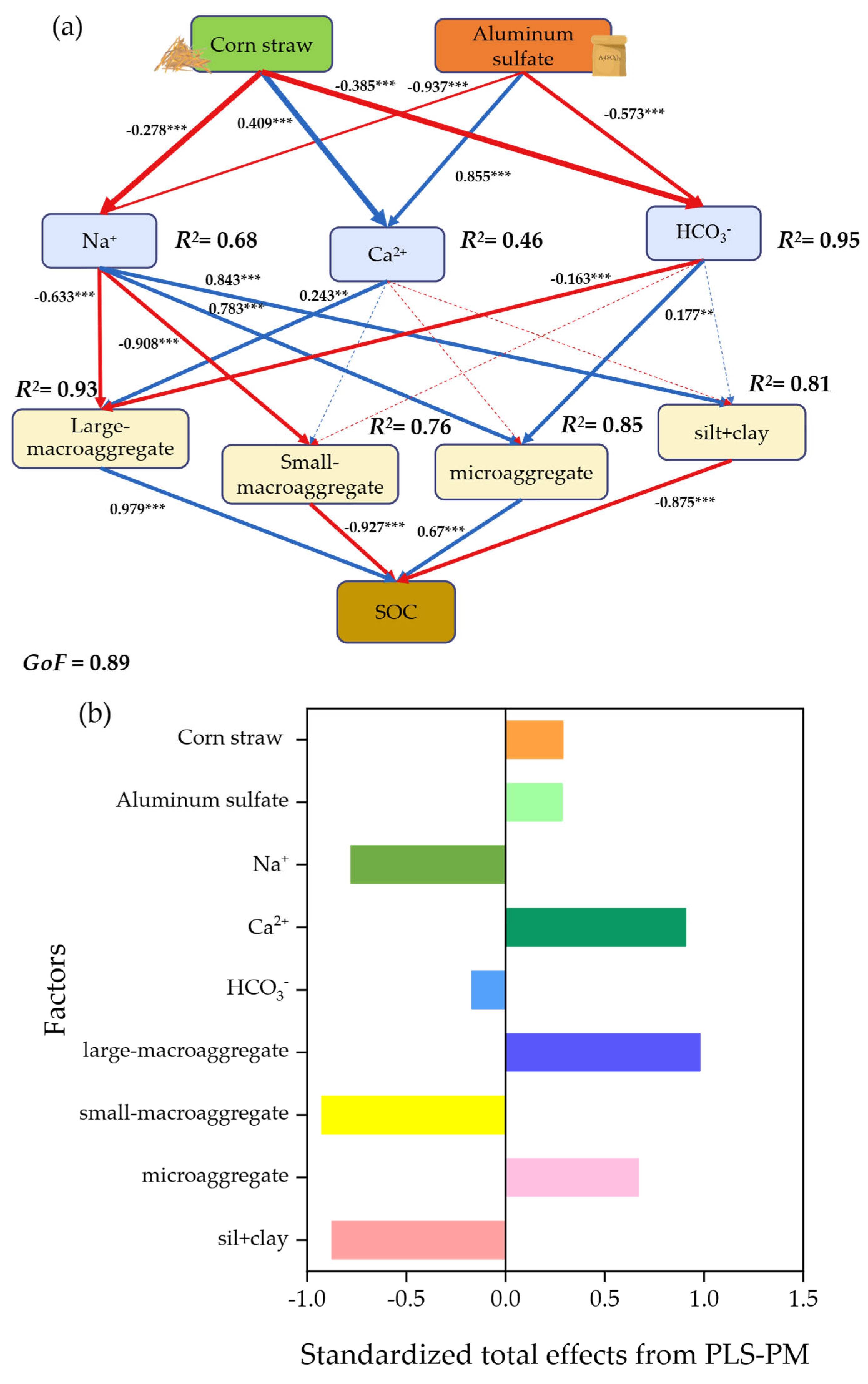
3.4.2. Driving Factors of the SOC
4. Discussion
4.1. Reduction in Soil Salinity–Sodality
4.2. Enhancement of Soil C Sequestration Performance
4.3. Comprehensive Effects of Straw and Al3+ on the Soil Aggregate Composition
4.4. Effects of Straw and Al3+ on C Sequestration in Soil Aggregates
4.5. Regulatory Mechanism of Soil C Sequestration
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qu, Y.; Tang, J.; Liu, B.; Lyu, H.; Duan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Rhizosphere Enzyme Activities and Microorganisms Drive the Transformation of Organic and Inorganic Carbon in Saline–Alkali Soil Region. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negacz, K.; Malek, Ž.; De Vos, A.; Vellinga, P. Saline Soils Worldwide: Identifying the Most Promising Areas for Saline Agriculture. J. Arid. Environ. 2022, 203, 104775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Sarkar, B.; Jat, H.S.; Sharma, P.C.; Bolan, N.S. Soil Salinity under Climate Change: Challenges for Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Heng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z. Effect of Salinity on Carbon Sequestration in Constructed Wetlands and Its Functional Mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 391, 129915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, J.; Yu, X.; Borjigin, Q.; Qu, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, D. Evaluation of the Microbial Community in Various Saline Alkaline-Soils Driven by Soil Factors of the Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lv, D.; Jiang, S.; Lin, H.; Sun, J.; Li, K.; Sun, J. Soil Salinity Regulation of Soil Microbial Carbon Metabolic Function in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudina, A.; Kuzyakov, Y. Dual Nature of Soil Structure: The Unity of Aggregates and Pores. Geoderma 2023, 434, 116478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Pan, H.; Zhuge, Y.; Ren, X.; Hu, S.; Li, C. Aggregate Stability and Organic Carbon Stock under Different Land Uses Integrally Regulated by Binding Agents and Chemical Properties in Saline-sodic Soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4151–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Hu, G.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Zhuge, Y. Straw-Returning Reduces the Contribution of Microbial Anabolism to Salt-Affected Soil Organic Carbon Accumulation over a Salinity Gradient. Soil. Ecol. Lett. 2023, 5, 220168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Song, X.; He, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J. Distribution of soil organic carbon density fractions in aggregates as influenced by salts and microbial community. Land 2023, 12, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Tian, L.; Chang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Tran, L.-S.P.; Tian, C. Grass and Maize Vegetation Systems Restore Saline-Sodic Soils in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, X.; Meng, Q.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Du, W.; Ma, X. Additional Application of Aluminum Sulfate with Different Fertilizers Ameliorates Saline-Sodic Soil of Songnen Plain in Northeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3521–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Ding, X. A Sustainable Option: Biochar Addition Can Improve Soil Phosphorus Retention and Rice Yield in a Saline–Alkaline Soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Zhang, W.; Sultana, T.; Akram, M.; Shoumik, B.A.A.; Khan, M.Z.; Farooq, M.A. Utilization of Sewage Sludge to Manage Saline–Alkali Soil and Increase Crop Production: Is It Safe or Not? Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Wen, X.; Guo, F.; Lou, S. Decision of Straw Deep Burial and Aluminum Sulfate Drip Irrigation in Soda Saline Soil Based on Grey Relation Analysis and TOPSIS Coupling. Agronomy 2024, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwari, G.; Tianxu, Y.; Alio Moussa, A.; Wentao, Z.; Mandozai, A.; Gamal, M.; El-Rahim, A.; Feng, J. Influence of Biochar and Aluminum Sulfate on Rice Growth and Production in Saline Soil Influence of Biochar and Aluminum Sulfate on Rice Growth and Production in Saline Soil. J. Crop. Improv. 2022, 37, 2151541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Zvobgo, G.; Zhang, G. A Review: The Beneficial Effect of Aluminum on Plant Growth in Acid Soil and the Possible Mechanisms. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 60345–60347. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H.; Duan, M.; Feng, L. China Effects of Different Soil Amendments on Physicochemical Property of Soda Saline-Alkali Soil and Crop Yield in Northeast China. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2022, 15, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Liao, B.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liao, P. Gypsum Application and Straw Incorporation Interact to Alleviate Methane Emissions in Coastal Saline-Alkali Rice Soils. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 4398–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, W.; Piao, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Jin, F. Response of Soil Physicochemical Properties, Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activity and Rice Yield to Rice Straw Returning in Highly Saline-alkali Paddy Soils. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 4396–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, X. Soil Carbon Storage and Carbon Sources under Different Spartina Alterniflora Invasion Periods in a Salt Marsh Ecosystem. Catena 2021, 196, 104831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Sui, B.; Zhao, L. Organic Carbon Content and Humus Composition after Application Aluminum Sulfate and Rice Straw to Soda Saline-Alkaline Soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 13746–13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Qu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, G. Contrasting Effects of Different Straw Return Modes on Net Ecosystem Carbon Budget and Carbon Footprint in Saline-Alkali Arid Farmland. Soil. Till Res. 2024, 239, 106031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; ISBN 7-109-06644-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.K. Analysis Method of Soil Agricultural Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wicke, B.; Smeets, E.; Dornburg, V.; Vashev, B.; Gaiser, T.; Turkenburg, W.; Faaij, A. The Global Technical and Economic Potential of Bioenergy from Salt-Affected Soils. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2669–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LY/T1251-1999; Analysis methods of water soluble salts of forest soil. National Forestry and Grassland Administration: Beijing, China, 1999.
- Yang, H.; Xia, J.; Xie, W.; Wei, S.; Cui, Q.; Shao, P.; Sun, J.; Dong, K.; Qi, X. Effects of Straw Returning and Nitrogen Addition on Soil Quality of a Coastal Saline Soil: A Field Study of Four Consecutive Wheat-maize Cycles. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Gao, D.; Bai, T.; Geng, Y.; Shao, X.; Guo, L. Straw Return Alleviates the Negative Effects of Saline Sodic Stress on Rice by Improving Soil Chemistry and Reducing the Accumulation of Sodium Ions in Rice Leaves. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 342, 108253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.T. Aggregate Structure and Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Native and Cultivated Soils. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Ji, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, Y. Optimizing Organic Amendment Applications to Enhance Carbon Sequestration and Economic Benefits in an Infertile Sandy Soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Minggang, X.; Ali Shah, S.A.; Abrar, M.M.; Nan, S.; Baoren, W.; Zejiang, C.; Saeed, Q.; Naveed, M.; Mehmood, K.; et al. Soil Aggregation and Soil Aggregate Stability Regulate Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Storage in a Red Soil of Southern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, W.R.; Robarge, W.P.; Osmond, D.L.; Heitman, J.L. Comparing Four Methods of Measuring Soil Organic Matter in North Carolina Soils. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, S.; Holden, N. Determination of Soil Organic Matter and Carbon Fractions in Forest Top Soils Using Spectral Data Acquired from Visible–near Infrared Hyperspectral Images. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengky, L.; Joseph, F.H., Jr.; Richard, N. Partial Least Squares Path Modeling: Basic Concepts, Methodological Issues and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hua, J.; Xue, J. Salinity Drives Shifts in Soil Microbial Community Composition and Network Complexity along Vegetation Community Succession in Coastal Tidal Flats. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 276, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Lv, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Dong, H.; Gonsior, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Molecular Composition of Dissolved Organic Matter in Saline Lakes of the Qing-Tibetan Plateau. Org. Geochem. 2022, 167, 104400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, C.; Pang, H.; Liu, N.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Straw Layer Burial to Alleviate Salt Stress in Silty Loam Soils: Impacts of Straw Forms. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Xu, X.; Kong, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. The Combination of Straw Return and Appropriate K Fertilizer Amounts Enhances Both Soil Health and Rice Yield in Northeast China. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 5424–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Saline-Alkali Soil Applied with Vermicompost and Humic Acid Fertilizer Improved Macroaggregate Microstructure to Enhance Salt Leaching and Inhibit Nitrogen Losses. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2020, 156, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhuo, Y.Q.; Xu, L.Z. Research on Saline-Alkali Soil Amelioration with FGD Gypsum. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 121, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Flint, S.; Palmer, J. Magnesium and Calcium Ions: Roles in Bacterial Cell Attachment and Biofilm Structure Maturation. Biofouling 2019, 35, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.-Q.; Wang, L.-L.; Li, Q.-S.; Zhang, Q.-K.; He, B.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Qin, L.-P.; Li, S.-S. Improvement of hard saline–sodic soils using polymeric aluminum ferric sulfate (PAFS). Soil. Tillage Res. 2015, 149, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojórquez-Quintal, E.; Escalante-Magaña, C.; Echevarría-Machado, I.; Martínez-Estévez, M. Aluminum, a Friend or Foe of Higher Plants in Acid Soils. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Tripathi, D.K.; Singh, S.; Sharma, S.; Dubey, N.K.; Chauhan, D.K.; Vaculík, M. Toxicity of Aluminium on Various Levels of Plant Cells and Organism: A Review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 137, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, W.; Yumnam, J.S.; Sen, D.; Rai, M. Root Transcriptome Reveals Efficient Cell Signaling and Energy Conservation Key to Aluminum Toxicity Tolerance in Acidic Soil Adapted Rice Genotype. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y. The Effects of Exogenous Malic Acid in Relieving Aluminum Toxicity in Pinus Massoniana. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2020, 22, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Xie, J.; Hong, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, W.; Hong, J. Organic Matter Fractions Within Macroaggregates in Response to Long-term Fertilization in Calcareous Soil After Reclamation. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1636–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, F.; Li, Z. Soil Aggregate-Associated Organic Carbon Dynamics Subjected to Different Types of Land Use: Evidence from 13C Natural Abundance. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 122, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Yang, X.; Dou, Y.; Wang, B.; Xue, Z.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; An, S. Divergent Contribution of Particulate and Mineral-associated Organic Matter to Soil Carbon in Grassland. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, J.; Dai, A.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; et al. Long-Term Organic Fertilization Enhances Potassium Uptake and Yield of Sweet Potato by Expanding Soil Aggregates-Associated Potassium Stocks. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 358, 108701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gunina, A.; Zhang, F.; Cui, Z.; Tian, J. Fungal Necromass Increases Soil Aggregation and Organic Matter Chemical Stability under Improved Cropland Management and Natural Restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Y.; Chen, P.; Li, Z.-G.; Li, L.-Y.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Hu, W.; Liu, Y. Soil Aggregate-Associated Organic Carbon Mineralization and Its Driving Factors in Rhizosphere Soil. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2023, 186, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wang, H.; Ye, W.; Tian, Y.; Hu, G.; Lou, Y.; Pan, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhuge, Y. Distinct Stabilization Characteristics of Organic Carbon in Coastal Salt-affected Soils with Different Salinity under Straw Returning. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Qian, X.; Zang, H.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Water-Stable Aggregates and Carbon Accumulation in Barren Sandy Soil Depend on Organic Amendment Method: A Three-Year Field Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.; Greenberg, I.; Ludwig, B.; Hippich, L.; Fischer, D.; Glaser, B.; Kaiser, M. Effect of Biochar and Compost on Soil Properties and Organic Matter in Aggregate Size Fractions under Field Conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 295, 106882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.K.; Ramachandran Nair, P.K.; Nair, V.D.; Mohan Kumar, B. Carbon Storage in Relation to Soil Size-Fractions under Tropical Tree-Based Land-Use Systems. Plant Soil. 2010, 328, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, M.; Xie, X.; Shi, X.; Xu, S.; Sun, W.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Q.; Pan, J.; Li, X.; et al. Sensitivity of Soil Aggregation to Soil Organic Carbon Fractions under Land-Use Conversion from Rice to Organic Vegetable Cultivation. Catena 2021, 207, 105661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, X.; Wu, X.; Zheng, F.; Li, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Man, X.; Degré, A. Microbial Regulation of Aggregate Stability and Carbon Sequestration under Long-Term Conservation Tillage and Nitrogen Application. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 44, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, R.; Gottschalk, P.; Smith, P.; Marschner, P.; Baldock, J.; Setia, D.; Smith, J. Soil Salinity Decreases Global Soil Organic Carbon Stocks. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fungo, B.; Lehmann, J.; Kalbitz, K.; Thionģo, M.; Okeyo, I.; Tenywa, M.; Neufeldt, H. Aggregate Size Distribution in a Biochar-Amended Tropical Ultisol under Conventional Hand-Hoe Tillage. Soil. Till Res. 2017, 165, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Basic Properties | Average Value | Analysis Methods |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 10.02 ± 0.35 | pH meter method (1:5 of soil to water) |
| EC (mS·cm−1) | 0.51 ± 0.07 | Conductivity meter method (1:5 of soil to water) |
| OC (g·kg−1) | 8.75 ± 0.82 | K2Cr2O7-H2SO4 method |
| CEC (cmol·kg−1) | 14.25 ± 1.00 | EDTA–ammonium acetate salt exchange method |
| Exchange Na+ (cmol·kg−1) | 8.26 ± 0.01 | Flame photometry |
| Soluble K+ (cmol·kg−1) | 0.02 ± 0.01 | Flame photometry |
| Soluble Na+ (cmol·kg−1) | 4.27 ± 0.18 | Flame photometry |
| Soluble Ca2+ (cmol·kg−1) | 0.63 ± 0.13 | EDTA titration |
| Soluble Mg2+ (cmol·kg−1) | 0.83 ± 0.31 | EDTA titration |
| Soluble CO32− (cmol·kg−1) | 0.35 ± 0.03 | Double-indicator titration |
| Soluble HCO3− (cmol·kg−1) | 0.69 ± 0.05 | Double-indicator titration |
| The Addition Amount of Al3+ (%) | The Addition Amount of Straw (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
| 0 | A0S0 | A0S5 | A0S10 | A0S15 |
| 0.4 | A0.4S0 | A0.4S5 | A0.4S10 | A0.4S15 |
| 0.8 | A0.8S0 | A0.8S5 | A0.8S10 | A0.8S15 |
| 1.2 | A1.2S0 | A1.2S5 | A1.2S10 | A1.2S15 |
| 1.6 | A1.6S0 | A1.6S5 | A1.6S10 | A1.6S15 |
| 2.0 | A2.0S0 | A2.0S5 | A2.0S10 | A2.0S15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Sui, B.; Zhao, X. Aluminum Sulfate and Straw Enhance Carbon Sequestration in Saline–Alkali Soils. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051200
Wang N, Guo X, Liu J, Zhao L, Wang H, Sui B, Zhao X. Aluminum Sulfate and Straw Enhance Carbon Sequestration in Saline–Alkali Soils. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051200
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Nan, Xinxin Guo, Jinhua Liu, Lanpo Zhao, Hongbin Wang, Biao Sui, and Xingmin Zhao. 2025. "Aluminum Sulfate and Straw Enhance Carbon Sequestration in Saline–Alkali Soils" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051200
APA StyleWang, N., Guo, X., Liu, J., Zhao, L., Wang, H., Sui, B., & Zhao, X. (2025). Aluminum Sulfate and Straw Enhance Carbon Sequestration in Saline–Alkali Soils. Agronomy, 15(5), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051200






