The Effects of Long-Term Land Use Changes on Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Northeast Mollisol Region of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Collection
2.3. Physicochemical Determination of the Soil
2.4. Sequence Generation for Characterization of the Bacterial Communities
2.5. Sequence Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties
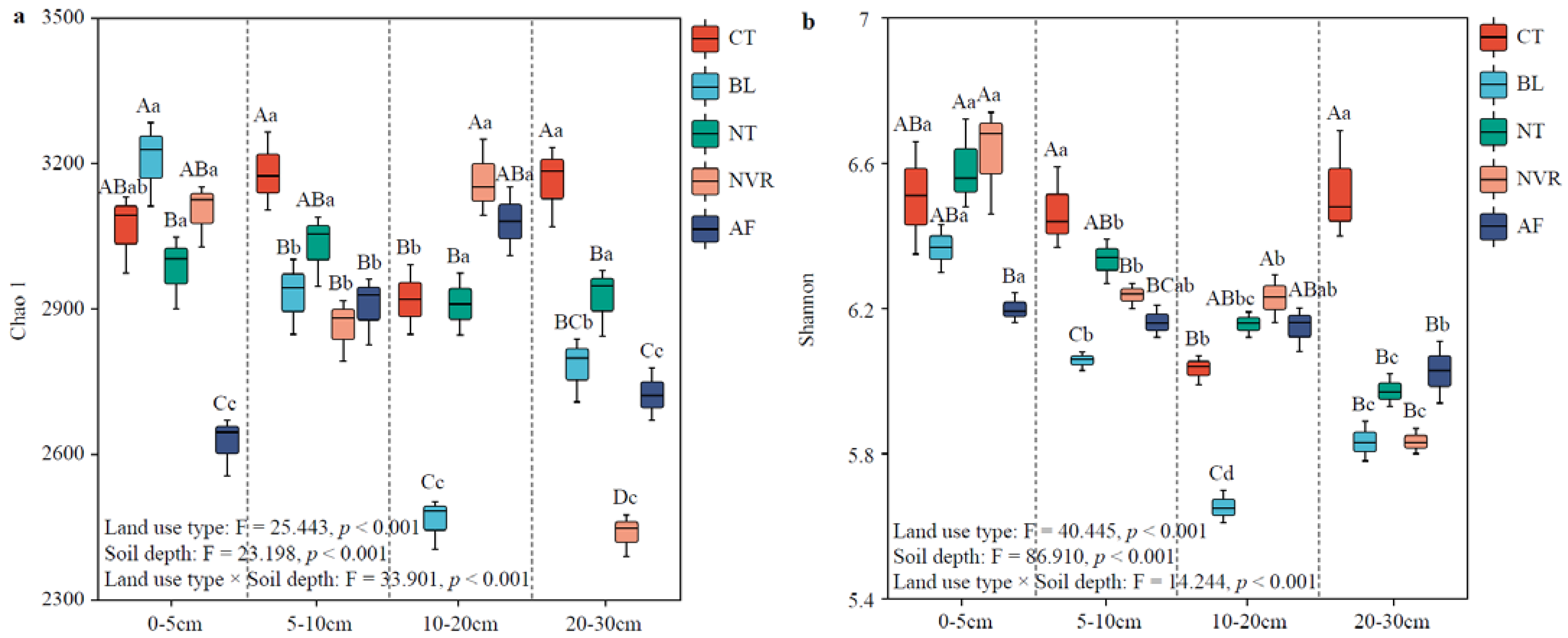
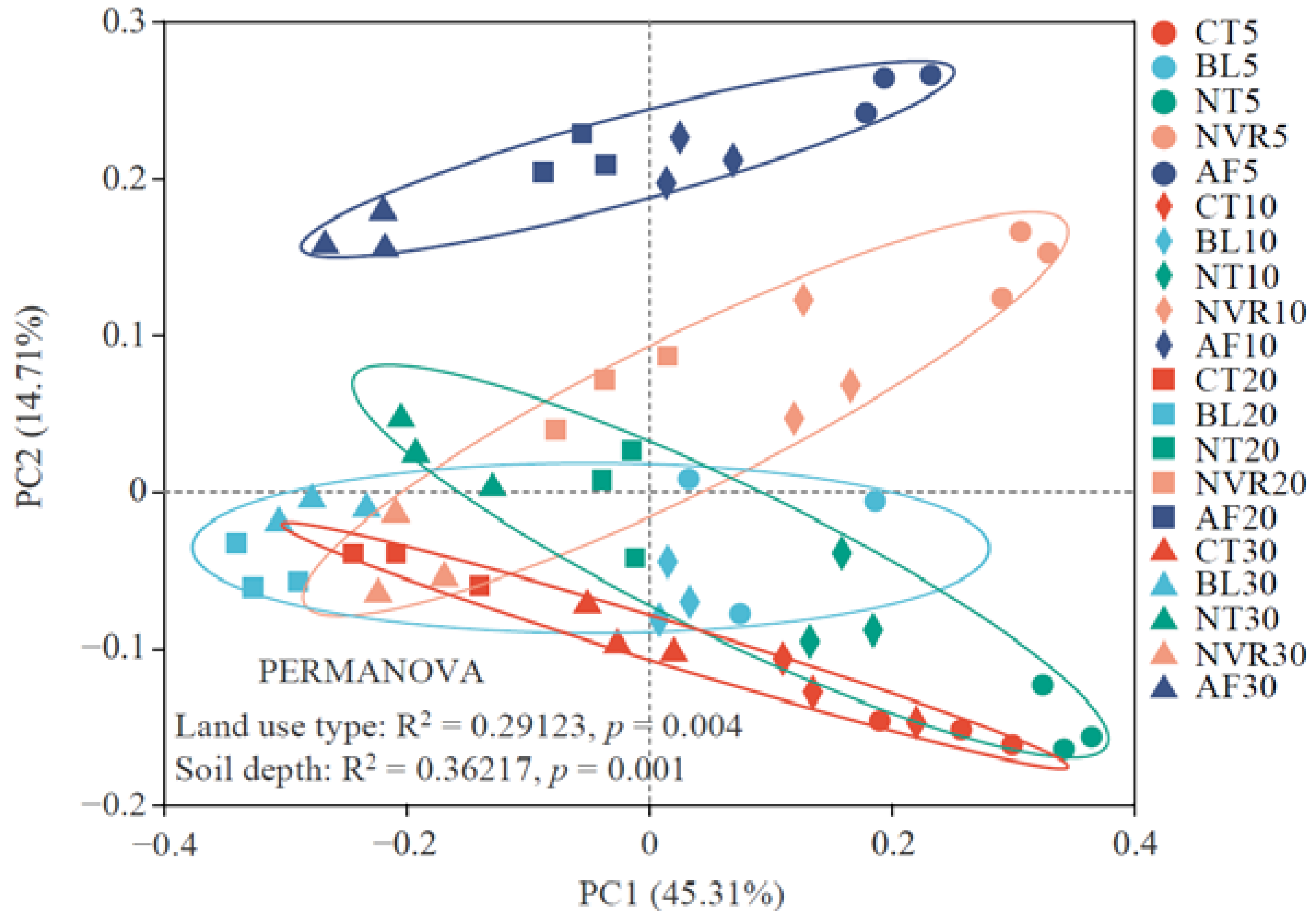
3.2. Characterization of the Soil Bacterial Community Diversity
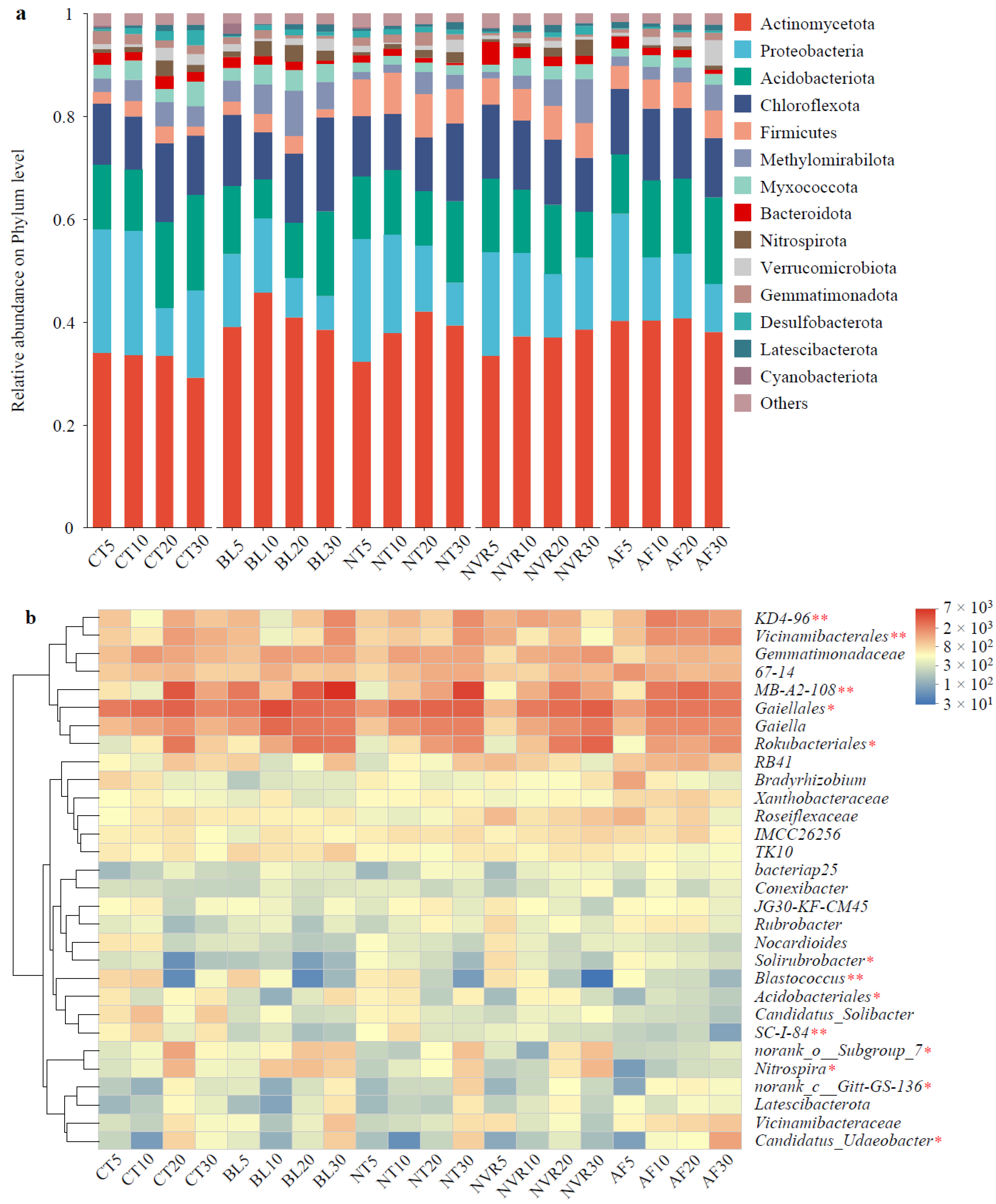
3.3. Composition of the Soil Bacterial Communities
3.4. KEGG Metabolic Pathway Analysis
3.5. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
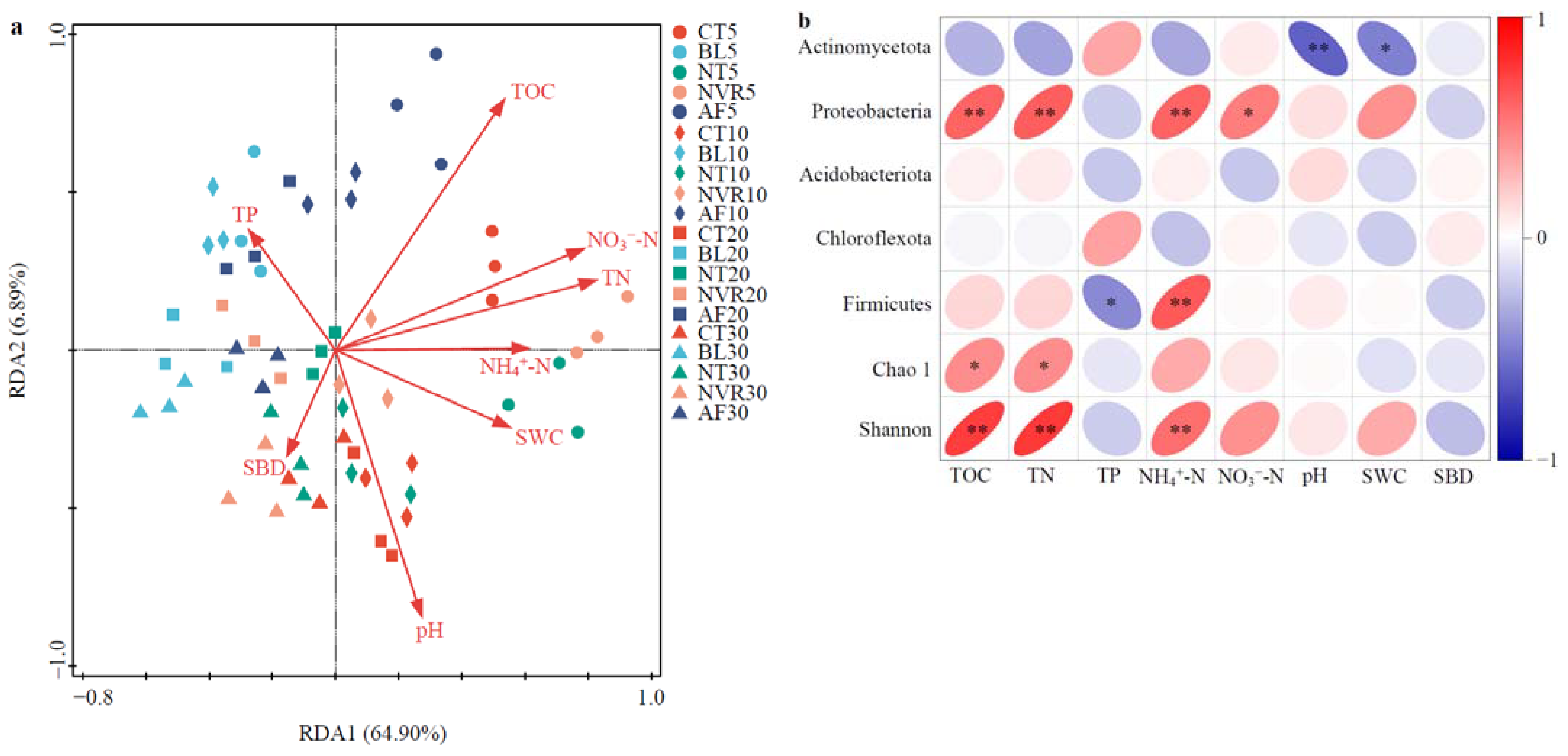
3.6. Relationships Between Soil Bacterial Community and Physicochemical Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliveira, E.M.; Wittwer, R.; Hartmann, M.; Keller, T.; Buchmann, N.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Effects of conventional, organic and conservation agriculture on soil physical properties, root growth and microbial habitats in a long-term field experiment. Geoderma 2024, 447, 116927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.C.; de Vries, W.; Liu, X.J.; Hao, T.X.; Zeng, M.F.; Shen, J.B.; Zhang, F.S. Enhanced acidification in Chinese croplands as derived from element budgets in the period 1980–2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.; Poch, R.M.; Lobb, D.A.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Alloush, G.; Eudoxie, G.D.; Anjos, L.H.C.; Castellano, M.; Ndzana, G.M.; Chenu, C.; et al. Status of the World’ s Soils. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2024, 49, 73–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárceles Rodríguez, B.; Durán-Zuazo, V.H.; Soriano Rodríguez, M.; García-Tejero, I.F.; Gálvez Ruiz, B.; Cuadros Tavira, S. Conservation Agriculture as a Sustainable System for Soil Health: A Review. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Ghassemi-Golezani, K.; Torabian, S. A short-term study of soil microbial activities and soybean productivity under tillage systems with low soil organic matter. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 168, 104122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, P.; Guo, X.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, L.J. Fifteen-year no tillage of a Mollisol with residue retention indirectly affects topsoil bacterial community by altering soil properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Sun, L.; Ren, J.H.; Yuan, Y.R.; Zang, S.Y. Influence of Tillage on the Mollisols Physicochemical Properties, Seed Emergence and Yield of Maize in Northeast China. Agriculture 2021, 11, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Rana, S.S.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, N. Effects of conservation tillage and weed management on soil microbial community and enzymatic activity. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2022, 51, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Ai, S.Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.Y.; Ding, J.H.; Yang, F. Effect of strip tillage widths on soil moisture, soil temperature and soil structure in northeast China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1404971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuenkamp, L.; de León, D.G.; Hamer, U.; Hölzel, N.; Mcgale, E.; Hannula, S.E. Comprehensive tools for ecological restoration of soils foster sustainable use and resilience of agricultural land. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodesová, R.; Jirku, V.; Kodes, V.; Mühlhanselová, M.; Nikodem, A.; Zigová, A. Soil structure and soil hydraulic properties of Haplic Luvisol used as arable land and grassland. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 111, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.H.; López-Vicente, M.; Wu, G.L. Effectiveness of re-vegetated forest and grassland on soil erosion control in the semi-arid Loess Plateau. Catena 2020, 195, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, D.R.; Huang, G.W. Isotope analysis reveals differential impacts of artificial and natural afforestation on soil organic carbon dynamics in abandoned farmland. Plant Soil 2022, 471, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Yao, F.Y.; Mi, G.H.; Wang, L.C.; Wu, H.Y.; Wang, Y.J. Crop rotation increases root biomass and promotes the correlation of soil dissolved carbon with the microbial community in the rhizosphere. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1081647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Song, D.X.; Liu, M.Z.; Li, Y.P.; Li, Y.A. Effects of earthworm activities on soil nutrients and microbial diversity under different tillage measures. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 222, 105441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, A.; Sombrero, A.; Santiago-Pajón, A.; Santiago-Calvo, Y.; Asensio-S-Manzanera, M.C. Effect of long-term conservation tillage management on microbial diversity under Mediterranean rainfed conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 236, 105923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Li, X.Y.; Guo, Q.C.; Yu, Z.X.; Yang, T.T.; Zhang, H.W. Long-term no-tillage and different residue amounts alter soil microbial community composition and increase the risk of maize root rot in northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.H.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, J.D.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.B.; Wang, G.H. Responses of ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities to land-use and seasonal changes in Mollisols of Northeast China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 74, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Mohapatra, M.; Latare, A. Impact of land use changes on soil quality and species diversity in the Vindhyan dry tropical region of India. J. Trop. Ecol. 2020, 36, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Bharti, V. Importance of Dalbergia sissoo for restoration of degraded land: A case study of Indian dry tropical vindhyan regions. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 194, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.P.; Gao, D.X.; Fu, S.Y.; Lu, X.Q.; Wu, S.J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z. Long-term effects of vegetation and soil on the microbial communities following afforestation of farmland with Robinia pseudoacacia plantations. Geoderma 2020, 367, 114263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delelegn, Y.T.; Purahong, W.; Blazevic, A.; Yitaferu, B.; Wubet, T.; Göransson, H.; Godbold, D.L. Changes in land use alter soil quality and aggregate stability in the highlands of northern Ethiopia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louisson, Z.; Hermans, S.M.; Buckley, H.L.; Case, B.S.; Taylor, M.; Curran-Cournane, F.; Lear, G. Land use modification causes slow, but predictable, change in soil microbial community composition and functional potential. Environ. Microbiome 2023, 18, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.J. Land use and land cover change based on historical space-time model. Solid Earth 2016, 7, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Kirschbaum, M.U.F.; Eichler-Löbermann, B.; Gifford, R.M.; Liáng, L.L. The effect of land-use change on soil C, N, P, and their stoichiometries: A global synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 348, 108402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yao, S.H.; You, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Qiao, Y.F.; Zou, W.X.; Han, X.Z.; Zhang, B. Contrasting development of soil microbial community structure under no-tilled perennial and tilled cropping during early pedogenesis of a Mollisol. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 77, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, H.Z.; Dsouza, M.; Lou, J.; He, Y.; Dai, Z.M.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.M.; Gilbert, J.A. Geographic patterns of co-occurrence network topological features for soil microbiota at continental scale in eastern China. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.K.; Hao, Z.H.; Chen, L.; Sha, Y.; Wang, E.T.; Sui, X.H.; Mi, G.H. Conservation strip-till modifies rhizosphere ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria, increases nitrate accumulation and promotes maize growth at grain filling stage. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 234, 105821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H.; Liu, H.; Zhu, A.N.; Khan, M.H.; Hussain, S.; Cao, H. Conservation tillage practices affect soil microbial diversity and composition in experimental fields. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1227297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jia, S.X.; Liang, A.Z.; Chen, X.W.; Zhang, S.X.; Zhang, Y.; Mclaughlin, N.B.; Gao, Y.; Huang, D.D. Residue Return Effects Outweigh Tillage Effects on Soil Microbial Communities and Functional Genes in Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.J.; Liu, J.J.; Wei, D.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.; Zhou, B.K.; Chen, X.L.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.B.; Wang, G.H. Effects of over 30-year of different fertilization regimes on fungal community compositions in the black soils of northeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 248, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Y.; Wu, X.; Li, J.Y.; Guo, M.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, Q. Seasonal and Long-Term Variability in Soil Structure and Erodibility under Different Land-Use Patterns in the Mollisols Region of Northeast China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.Y.; Xie, R.F.; Ma, D.L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, L. Variations in soil microbial community structure and extracellular enzymatic activities along a forest-wetland ecotone in high-latitude permafrost regions. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Chen, J.H.; Tang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Effects of Soil Physical Properties on Soil Infiltration in Forest Ecosystems of Southeast China. Forests 2024, 15, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Martins, I.S.; Kastner, T.; Plutzar, C.; Theurl, M.C.; Eisenmenger, N.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Wood, R.; Stadler, K.; Bruckner, M.; et al. Increasing impacts of land use on biodiversity and carbon sequestration driven by population and economic growth. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.J.; Zeng, X.Z.; Chen, K.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Shangguan, Y.X.; Yu, H.; Tu, S.H.; Qin, Y.S. Long-term straw mulch effects on crop yields and soil organic carbon fractions at different depths under a no-till system on the Chengdu Plain, China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLauchlan, K. The nature and longevity of agricultural impacts on soil carbon and nutrients: A review. Ecosystems 2006, 9, 1364–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.Z.; Guo, M.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tian, J.Y.; Zhou, P.C.; Chen, Z.X. Comparison of the effects of five long-term land use and management practices on runoff, soil erosion, and nutrient loss under natural rainfall in the Mollisol region of Northeast China. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2024, 49, 1606–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.M.; Han, X.Z.; Hao, X.X.; Lu, X.C.; Yan, J.; Biswas, A.; Dunfield, K.; Zou, W.X. Impacts of land-use changes on the variability of microbiomes in soil profiles. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5056–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Eisenhauer, N.; Sierra, C.A.; Bessler, H.; Engels, C.; Griffiths, R.I.; Mellado-Vázquez, P.G.; Malik, A.A.; Roy, J.; Scheu, S.; et al. Plant diversity increases soil microbial activity and soil carbon storage. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, P.; Preece, C.; Peñuelas, J.; Giri, J. Soil carbon sequestration by root exudates. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miltner, A.; Bombach, P.; Schmidt-Brücken, B.; Kästner, M. SOM genesis: Microbial biomass as a significant source. Biogeochemistry 2012, 111, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, J.R.; Singh, B.P.; Cowie, A.L.; Fang, Y.Y.; Collins, D.; Badgery, W.; Dalal, R.C. Agricultural management practices impacted carbon and nutrient concentrations in soil aggregates, with minimal influence on aggregate stability and total carbon and nutrient stocks in contrasting soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 178, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yi, D.; Ye, Y.C.; Guo, X.; Liu, S.Y. Response of spatiotemporal variability in soil pH and associated influencing factors to land use change in a red soil hilly region in southern China. Catena 2022, 212, 106074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.X.; Liang, F.; Cao, W.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, J.S.; Guo, J.H. Meta-analysis reveals that returning crop straw to arable land causes soil acidification at the global scale. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, D.; McClure, R.; Jansson, J. Trends in Microbial Community Composition and Function by Soil Depth. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Eldridge, D.J.; García, C.; Png, G.K.; Bardgett, R.D.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Soil microbial diversity-biomass relationships are driven by soil carbon content across global biomes. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, F.Z. Diversity and Co-occurrence Patterns of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Seven Intercropping Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.Y.; Liu, E.K.; Yan, C.R.; Tian, J.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, Y.Q. Impact of no tillage vs. conventional tillage on the soil bacterial community structure in a winter wheat cropping succession in northern China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 80, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.K.; Wang, R.; Vyzmal, J.; Hu, Y.K.; Li, W.; Wang, J.Z.; Lei, Y.R.; Zhai, X.J.; Zhao, X.S.; Li, J.; et al. Shifts of active microbial community structure and functions in constructed wetlands responded to continuous decreasing temperature in winter. Chemosphere 2023, 335, 139080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komorek, D.; Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Zaborowska, M. Microbial Activity and Diversity in Soil Sown with Zea mays and Triticosecale. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechlivanis, N.; Karakatsoulis, G.; Kyritsis, K.; Tsagiopoulou, M.; Sgardelis, S.; Kappas, I.; Psomopoulos, F. Microbial co-occurrence network demonstrates spatial and climatic trends for global soil diversity. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.X.; Gu, H.D.; Yao, Q.; Jiao, F.; Liu, J.J.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.B.; Wang, G.H. Microbial communities in the diagnostic horizons of agricultural Isohumosols in northeast China reflect their soil classification. Catena 2022, 216, 106430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.G.; Jin, Y.Q.; Hu, Y.N.; Tang, J.W.; Xiong, Q.L.; Xu, M.X.; Bibi, F.; Beng, K.C. Drivers of soil bacterial community structure and diversity in tropical agroforestry systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 278, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Xu, J.J.; Yang, H.; Song, J.C.; Yu, X.J. Reduced Soil Quality but Increased Microbial Diversity in Cultivated Land Compared to Other Land-Use Types in the Longzhong Loess Plateau. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.Q.; Zhao, X.R.; Chen, Y.M.; Jiao, X.G.; Sui, Y.Y. Bacterial Communities, Network Complexity, and Multifunctionality Affected by Soil Types in Northeastern China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.M.; Cao, J.H.; Lan, G.Y.; Liang, Y.M.; Wang, H.; Li, Q. The Influence of Land Use Patterns on Soil Bacterial Community Structure in the Karst Graben Basin of Yunnan Province, China. Forests 2020, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Lu, X.R.; Chen, G.S.; Luo, N.N.; Sun, J.; Li, X.J.; Ngozi, E.A. The priming effect patterns linked to the dominant bacterial keystone taxa during different straw tissues incorporation into Mollisols in Northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 197, 105330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Liu, L.; Chen, Q.; Wen, X.X.; Liao, Y.C. Conservation tillage increases soil bacterial diversity in the dryland of northern China. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.K.; Song, S.Z.; Xiong, K.N. Effects of different grassland use patterns on soil bacterial communities in the karst desertification areas. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1208971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.N.; Chen, X.K.; Zhou, X.R.; Qian, Z.; Zhou, H.C.; Zhuang, G.Q.; Ma, A.Z. Effects of grazing in different intensities and 10-year grazing exclusion on soil bacterial community composition and interaction complexity in alpine grasslands of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 2274–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, K.X.; Cui, B.S. Bacterial Communities Present Distinct Co-occurrence Networks in Sediment and Water of the Thermokarst Lakes in the Yellow River Source Area. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 716732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Han, X.Z.; Pan, F.J.; Liu, H.; Yan, J.; Zou, W.X.; McLaughlin, N.B.; Hao, X.X. Land use alters diazotroph community structure by regulating bacterivores in Mollisols in Northeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 941170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.P.; Wang, Z.H.; Cai, K.; Wang, S.L.; Wright, A.L.; Jiang, X.J. Stability of nitrogen-cycling microbial communities and impact on microbial nitrogen function under different land use practices. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 204, 105729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.S.; Peng, J.; Ni, S.M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, J.G.; Cai, C.F. Erosion and deposition significantly affect the microbial diversity, co-occurrence network, and multifunctionality in agricultural soils of Northeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Han, X.Z.; Yan, J.; Zou, W.X.; Wang, E.T.; Lu, X.C.; Chen, X. Keystone Microbiomes Revealed by 14 Years of Field Restoration of the Degraded Agricultural Soil Under Distinct Vegetation Scenarios. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.C.; Xiong, J.B.; Zhang, H.Y.; Feng, Y.Z.; Lin, X.G.; Li, X.Y.; Liang, W.J.; Chu, H.Y. Soil pH drives the spatial distribution of bacterial communities along elevation on Changbai Mountain. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, W.J.; Asuming-Brempong, S.; Wang, Q.; Tourlousse, D.M.; Penton, C.R.; Deng, Y.; Rodrigues, J.L.M.; Adiku, S.G.K.; Jones, J.W.; Zhou, J.Z.; et al. Tropical agricultural land management influences on soil microbial communities through its effect on soil organic carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.L.; Zhou, W.D.; Gu, Y.J.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhou, Y.F.; Xue, Y.Y.; Shi, Z.G.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effects of tillage regime on soil aggregate-associated carbon, enzyme activity, and microbial community structure in a semiarid agroecosystem. Plant Soil 2024, 498, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machmuller, M.B.; Kramer, M.G.; Cyle, T.K.; Hill, N.; Hancock, D.; Thompson, A. Emerging land use practices rapidly increase soil organic matter. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

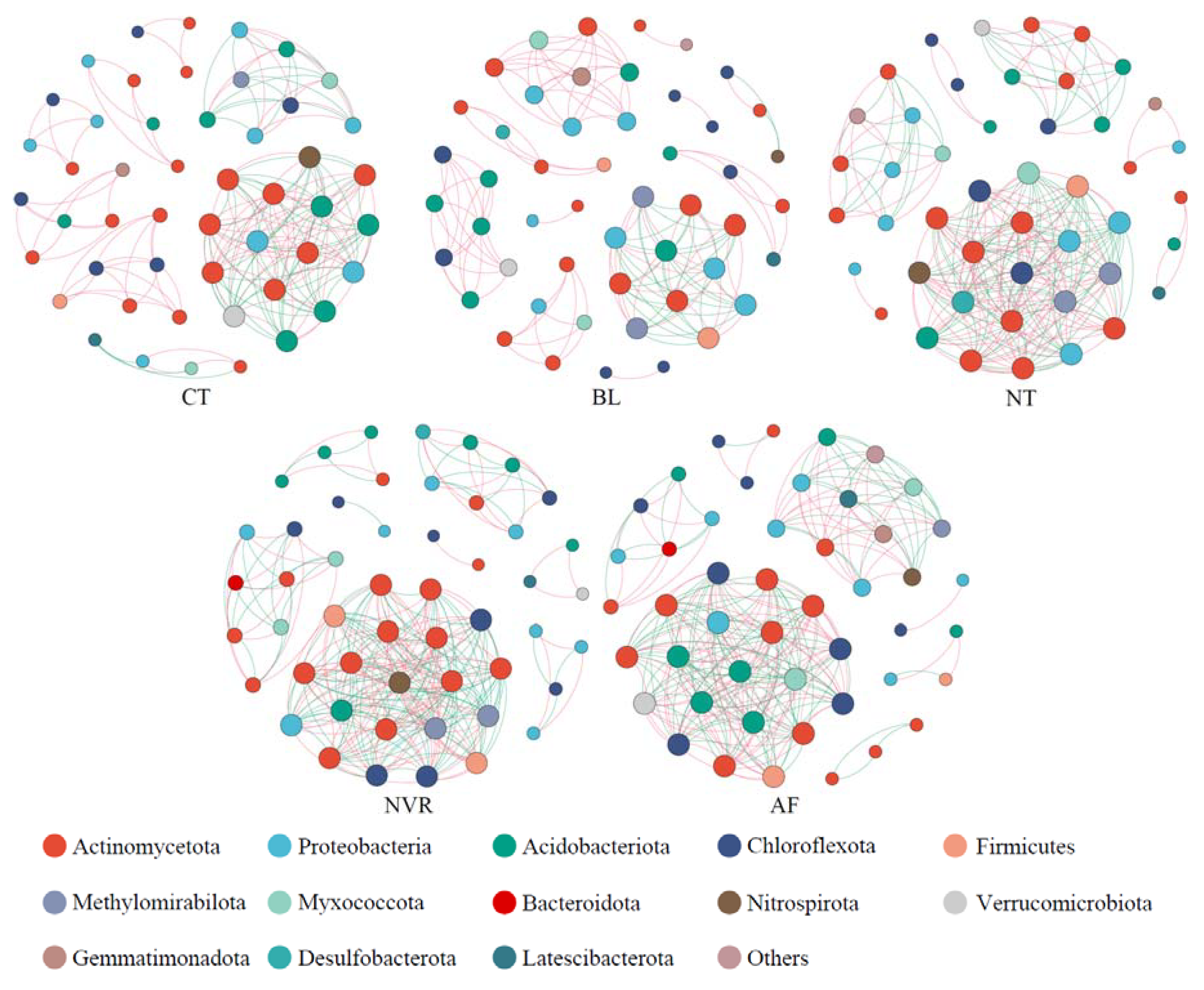
| Positive Links | Negative Links | Total Links | Average Degree | Network Density | Modularity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | 107 (59.78%) | 72 (40.22%) | 179 | 7.306 | 0.152 | 0.618 |
| BL | 101 (75.94%) | 32 (24.06%) | 133 | 5.320 | 0.109 | 0.749 |
| NT | 123 (51.90%) | 114 (48.10%) | 237 | 10.304 | 0.229 | 0.451 |
| NVR | 124 (48.44%) | 132 (51.56%) | 256 | 10.240 | 0.209 | 0.429 |
| AF | 122 (48.61%) | 129 (51.39%) | 251 | 10.681 | 0.232 | 0.484 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Yin, W.; Ma, D. The Effects of Long-Term Land Use Changes on Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Northeast Mollisol Region of China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051132
Wang X, Chen Q, Li Z, Yin W, Ma D. The Effects of Long-Term Land Use Changes on Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Northeast Mollisol Region of China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051132
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xu, Qiang Chen, Zhao Li, Weiping Yin, and Dalong Ma. 2025. "The Effects of Long-Term Land Use Changes on Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Northeast Mollisol Region of China" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051132
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, Q., Li, Z., Yin, W., & Ma, D. (2025). The Effects of Long-Term Land Use Changes on Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Northeast Mollisol Region of China. Agronomy, 15(5), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051132







