Response of Alfalfa Yield to Rates and Ratios of N, P, and K Fertilizer in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions of China Based on Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Classification
2.2. Meta-Analysis
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Effect of N Application Rate on Alfalfa Yield
3.1.1. Effect of N Application Rate on Annual Yield of Alfalfa
3.1.2. Effect of N Application Rate on Alfalfa Yield at Different Cutting Cycles
3.1.3. Effect of N Application Rate on Percentage Change in Alfalfa Yield
3.2. Effect of P Application Rate on Alfalfa Yield
3.2.1. Effect of P Application Rate on Annual Yield of Alfalfa
3.2.2. Effect of P Application Rate on Alfalfa Yield at Different Cutting Cycles
3.2.3. Effect of P Application Rate on Percentage Change in Alfalfa Yield
3.3. Effect of K Application Rate on Alfalfa Yield
3.3.1. Effect of K Application Rate on Annual Alfalfa Yield
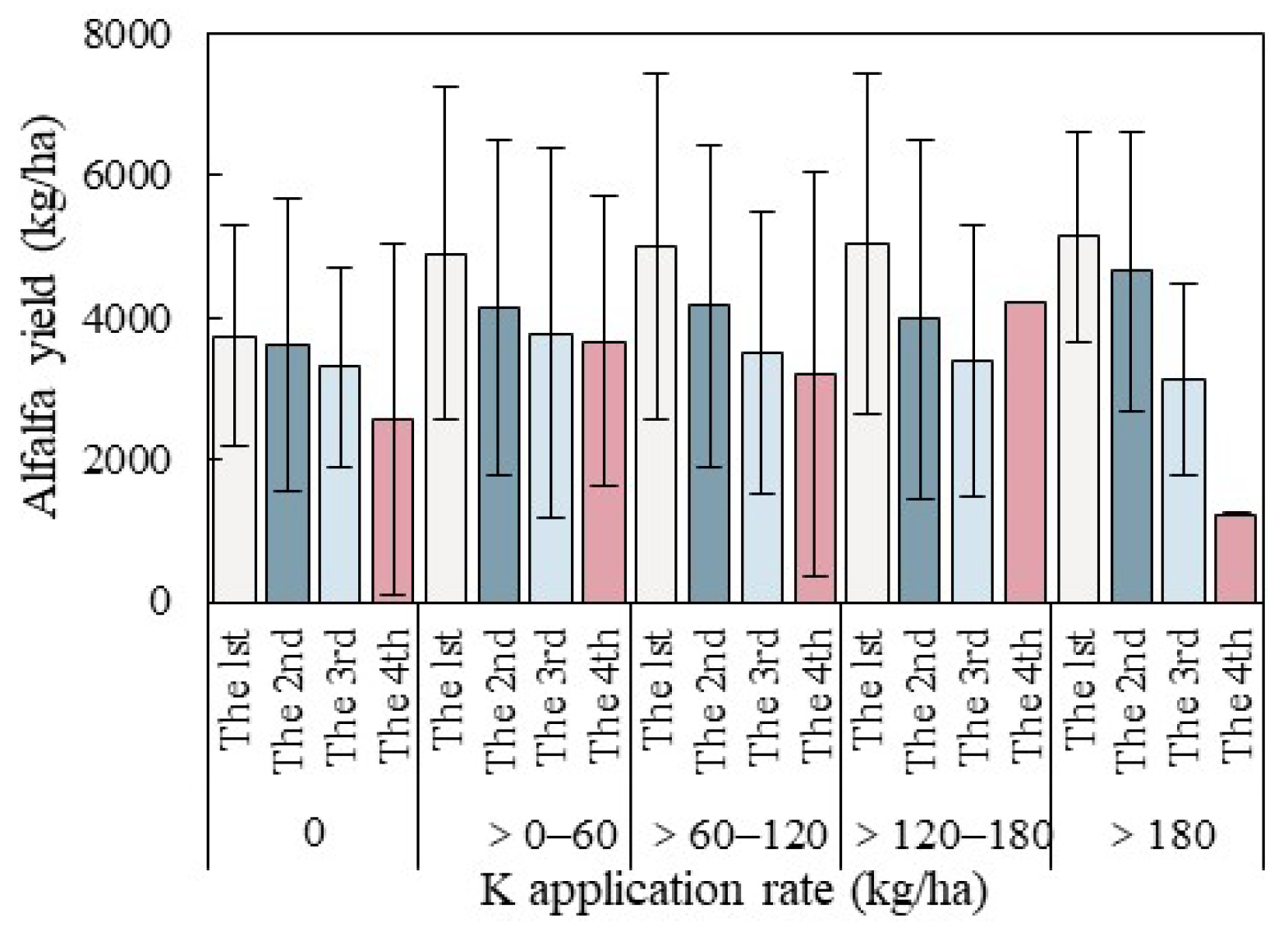
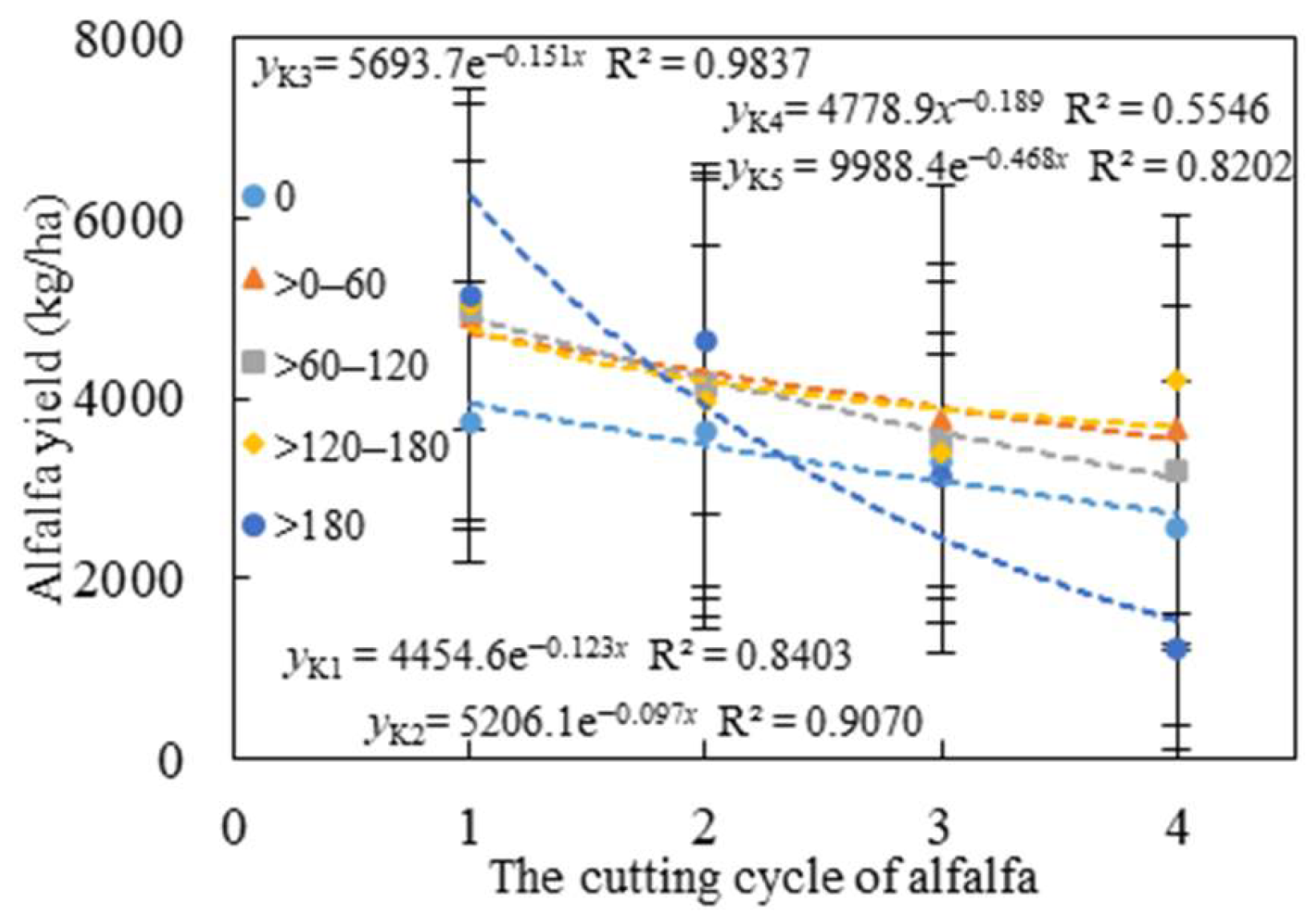
3.3.2. Effect of K Application Rate on Alfalfa Yield at Different Cutting Cycles
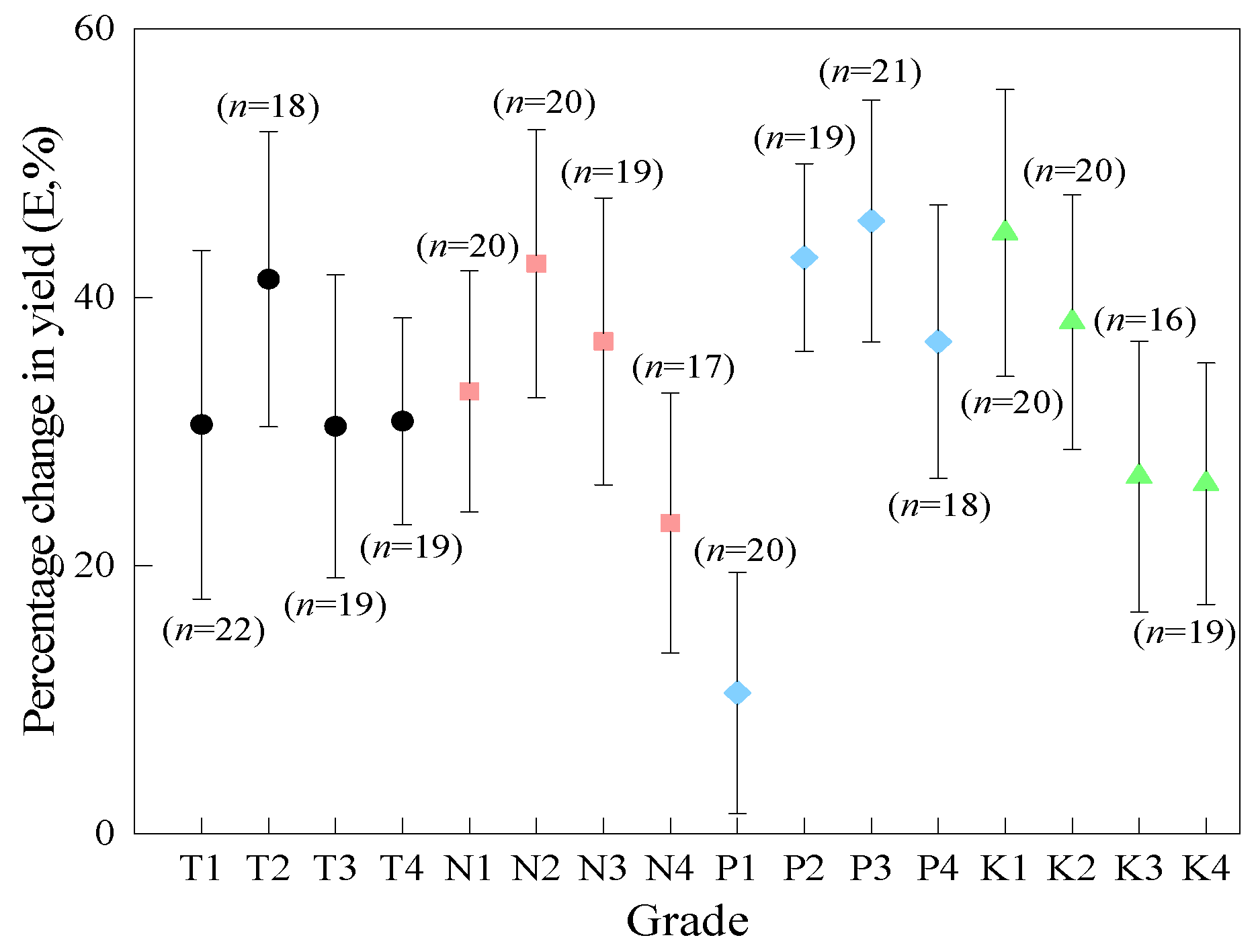
3.3.3. Effect of K Application Rate on Percentage Change in Alfalfa Yield
3.4. Effects of NPK Application Amount and Ratio on Alfalfa Yield
3.5. Contribution of N, P, and K Fertilizer on Alfalfa Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of N Application on Alfalfa Yield
4.2. Effects of P Application on Alfalfa Yield
4.3. Effects of K Application on Alfalfa Yield
4.4. Effects of NPK Application on Alfalfa Yield
4.5. Study Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the arid and semi-arid regions of China, the annual alfalfa yield increased and then decreased as the N application rate increased, but it increased with increasing P and K application rates. A significant factor affecting the annual and first and third cutting cycles yields was the NPK amount. For the second cutting cycle yield, the effect of P predominates, while K fertilization was the most important factor for the fourth cutting cycle yield.
- (2)
- The amounts of NPK and P had cumulative contributions to the annual alfalfa yield that exceeded 60%, indicating that these are key factors that influence the alfalfa yield in the arid and semi-arid regions of China. The contribution of P/NPK, N/NPK, and K/NPK to the annual yield of alfalfa decreases successively.
- (3)
- The optimal fertilization strategy for maximizing alfalfa yields in the arid and semi-arid regions of China was found to be an NPK amount > 225–310 kg/ha with N, P, and K proportions of 14.28–27.72%, 36.36–50%, and below 25%, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gámez, A.L.; Vatter, T.; Santesteban, L.G.; Araus, J.L.; Aranjuelo, I. Onfield estimation of quality parameters in alfalfa through hyperspectral spectrometer data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 216, 108463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhashemi, S.H. Use of a combination of two clustering and tree algorithms for investigating and predicting alfalfa yield under different conditions of deficit irrigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, M.R.I.; Alshallash, K.S.; Safhi, F.A.; Alatawi, A.; ALshamrani, S.M.; Dessoky, E.S.; Althobaiti, A.T.; Althaqafi, M.M.; Gharib, H.S.; Shafie, W.W.M.; et al. Genetic diversity, analysis of some agro-morphological and quality traits and utilization of plant resources of alfalfa. Genes 2022, 13, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.L.; Yang, Y.P.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T. Analysis on international development trends of alfalfa. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 56, 740–750. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.G.; Xu, W.P. Development characteristics and trend of alfalfa industry in China. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. High-quality forage looks forward to a strong “China core”. Farmer’s Daily, 7 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.P.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, M.Y.; Shen, H.H.; Xu, L.C.; Luo, Y.K.; Liu, Y.Z.; Xing, A.J.; Kang, J.; Jing, H.C.; et al. Yield and quality properties of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) and their influencing factors in China. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 141, 126637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.H.; Ma, Y.L.; Kang, Y.X.; Jia, Q.; Qi, G.P.; Wang, J.H. Effects of nitrogen application on alfalfa yield and quality in China—A meta-analysis. Acta Pratac. Sin. 2022, 31, 36–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kamran, M.; Yan, Z.G.; Jia, Q.M.; Chang, S.H.; Ahamd, I.; Ghani, M.U.; Hou, F.J. Irrigation and nitrogen fertilization influence on alfalfa yield, nutritive value, and resource use efficiency in an arid environment. Field Crops Res. 2022, 284, 108587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, F.G.; Zhu, Y.M.; Wu, H.; Ahmad, I.; Dong, G.C.; Zhou, G.S.; Wu, Y.Q. The Effects of planting density and nitrogen application on the growth quality of alfalfa forage in saline soils. Agriculture 2024, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, J.G.; Yu, L.Q.; Xu, Z.Y.; Samac, D.A. Overwintering and yield responses of two late-summer seeded alfalfa cultivars to phosphate supply. Agron. J. 2022, 12, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Z.Q. Fertilisation and environmental factors affect the yield and quality of alfalfa in China. Plant Soil Environ. 2024, 70, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.S.; Bai, T.C.; Zhi, J.H.; Xi, L.Q. Effects of different nitrogen levels on nutritional growth, yield and quality of alfalfa in Xinjiang region. Heilongjiang J. Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2017, 12, 174–175+178. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Y.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhao, J.W.; Liu, X.S.; Zhao, J.T.; Ma, C.H.; Zhang, Q.B. Effects of nitrogen addition on microbial quantity, enzyme activity in rhizosphere soil and alfalfa hay yield. Chin. J. Grassl. 2022, 44, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, W.F.; Li, Y.J.; Li, H.G. Yield and quality of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) in response to fertilizer application in China: A meta-analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1051725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Sun, L.L.; Xie, K.Y.; Liu, W.; Chu, H.Q.; Zhao, Y. Effects of irrigation, phosphorus application and am fungi on yield and water and phosphorus use efficiency of alfalfa. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2022, 30, 2356–2364. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.S.; Zhao, J.W.; Liu, J.Y.; Lu, W.H.; Ma, C.H.; Gu, X.L.; Zhang, Q.B. Water–phosphorus coupling enhances fine root turnover and dry matter yield of alfalfa under drip irrigation. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 4161–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Zhang, Z.M.; Wang, H. Study on the optimal application rate of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer of alfalfa in Hexi corridor area by applying “3414” design. Inform. Agric. Sci. Tech. 2021, 7, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.N.; Yu, S.Y.; Wang, X.; Song, W.X.; Wang, J.; Hu, P.F.; Wang, T.R.; Gao, X.Q.; Fu, B.Z. Effect of irrigation methods and phosphorus on the production performance and nutritional quality of alfalfa. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2024, 32, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.S.; Cao, M.J.; Li, C.L.; Li, F.S. Effects of superphosphate and potassium chloride fertilization on alfalfa. Grassl. Sci. 2003, 11, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, K.; Li, X.Y.; Ji, X.T.; Han, Y.Q.; Yun, L.; Mi, F.G. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on yield of caoyuan no.3 alfalfa. Chin. J. Grassl. 2019, 41, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Lin, F.; Tong, C.C. A data envelopment analysis study of alfalfa fertilization responses and economic return in the desert irrigation area of Hexi. Acta Pratac. Sin. 2020, 29, 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.F.; Liu, X.J.; Wu, Y.; Kuai, J.L. Fertilization effect of alfalfa high yield field and its recommended fertilizer application in northwest drought irrigated area. Acta Pratac. Sin. 2019, 28, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Zhao, Z.X.; Kang, J.M.; Long, R.C.; Lv, H.G.; Yang, Q.C.; Zhang, T.J. Effects of N, P and K fertilizer on alfalfa hay yield and quality. Chin. J. Grassl. 2019, 41, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, M.G.; Yang, H.M. Nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizations alter nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium resorption of alfalfa in the loess plateau of China. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 2234–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.Z.; Cartmill, A.D.; Lopez, I.F.; Ma, C.H.; Zhang, Q.B. Nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer use efficiency improves alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) production and performance in alkaline desert soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1526648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Q.Q.; Xie, J.H.; Yu, L.Q. Winter survival, yield and yield components of alfalfa as affected by phosphorus supply in two alkaline soils. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Jiang, Y.B.; Yin, M.H.; Ling, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Gan, Y.X.; Yue, C.F.; Ma, Y.L.; Kang, Y.X.; Qi, G.P.; et al. Optimizing phosphorus fertilization management is conducive to improving alfalfa yield and quality: A meta-analysis. Agriculture 2025, 15, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lv, W.S.; Bloszies, S.; Shi, Q.H.; Pan, X.H.; Zeng, Y.J. Effects of fertilizer management practices on yield-scaled ammonia emissions from croplands in China: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2016, 192, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Mai, W.X.; Tian, C.Y. Effects of organic fertilizer application on the improvement of saline soils: Meta analysis. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2023, 40, 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Coulter, J.A.; Xie, J.H.; Luo, Z.Z.; Zhang, R.Z.; Deng, X.P.; Li, L.L. Winter wheat yield and water use efficiency response to organic fertilization in northern China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 229, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.L. Effect of long-term destocking on soil fungal functional groups and interactions with plants. Plant Soil 2020, 448, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.F.; Lin, S.P.; Liu, S.H.; Zheng, X.; Bi, Y.F.; Xiao, Z.Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, A.K.; Du, X.H. Meta-analysis of the effect of fertilization on the yield of phyllostachys edulis forest. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Edn.) 2024, 48, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla, S.; Liebrenz, K.; Odorizzi, A.; Arolfo, V.; Maguire, V.; Moreno, V.; Ruiz, O.; Stritzler, M.; Serantes, L.; Soto, G. Exploring the cooperation between nitrogen-fixing and non-fixing alfalfa rhizobia. Symbiosis 2024, 93, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.R.; Wang, J.H.; Yin, M.H.; Kang, Y.X.; Ma, Y.L.; Jia, Q.; Qi, G.P.; Jiang, Y.B.; Lu, Q. Effects of planting and nitrogen application patterns on alfalfa yield, quality, water-nitrogen use efficiency, and economic benefits in the yellow river irrigation region of Gansu province, China. Water 2023, 15, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, F.; Long, R.C.; Li, M.N.; Wang, Z.; Kang, J.M.; Yang, Q.C. A global alfalfa diversity panel reveals genomic selection signatures in chinese varieties and genomic associations with root development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1937–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.L. Advance of alfalfa nodule bacteria research. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2005, 2, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H. The Effect of Nitrogen Application Rate on Nitrogen Fixation, Yield and Quality of Different Varieties of Alfalfa. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, W.Z.; Li, F.M.; Jia, Y. Soil nitrogen responses to the conversion of cropland from medicago sativa grassland in the semi-arid loess area. Acta Pratac. Sin. 2006, 5, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.L.; Wang, X.Z.; Ma, C.H.; Zhang, Q.B. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on agronomic characters, photosynthetic performance and anatomical structure of alfalfa in northern Xinjiang, China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Kuai, J.L.; Li, W.Q.; Ye, F.; Ren, H.Y.; Chen, L. Effects of NO3--N and NH4+-N on root growth, nodulation and nitrogen-fixation of alfalfa. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2011, 46, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.W.; Du, Y.L.; Wang, B.R.; Turner, N.C.; Wang, T.; Abbott, L.K.; Stefanova, K. Forage yield, soil water depletion, shoot nitrogen and phosphorus uptake and concentration, of young and old stands of alfalfa in response to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilisation in a semiarid environment. Field Crops Res. 2016, 198, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.T.; Wang, Y.Q.; Sun, S.N.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Qian, J.; Yan, X.B. Effects of nitrogen forms on nitrogen accumulation and utilization of alfalfa in different stubbles. Grassl. Sci. 2021, 38, 716–725. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.X.; Zhao, J.W.; Zhao, J.T.; Ma, C.H.; Zhang, Q.B. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on biochemical and stoichiometric characteristics of alfalfa fine roots and root collars. Chin. J. Grassl. 2023, 45, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.T.; Huang, R.Z.; Yang, K.X.; Ma, C.H.; Zhang, Q.B. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on photosynthetic properties of leaves and agronomic characters of alfalfa over three consecutive years. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; An, J.Y.; Hou, X.Y. Effects of six consecutive years of irrigation and phosphorus fertilization on alfalfa yield. Plants 2023, 12, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.B.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, X.S.; Sun, Y.L.; Li, S.Y.; Lu, W.H.; Ma, C.H. Optimizing the nutritional quality and phosphorus use efficiency of alfalfa under drip irrigation with nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 3129–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Han, X.Z. Advances in phosphorus in long-term fertilized soil. Soils 2009, 41, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.M.; Wu, R.X.; Li, Y.; You, Y.L.; Liu, G.B.; Zhai, L.J.; Yang, J.Z. Dynamic analyzing on the production performance of alfalfa between different cutting times and years. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2016, 24, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Jungers, J.M.; Kaiser, D.E.; Lamb, J.F.S.; Lamb, J.A.; Noland, R.L.; Samac, D.A.; Wells, M.S.; Sheaffer, C.C. Potassium fertilization affects alfalfa forage yield, nutritive value, root traits, and persistence. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2843–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tränkner, M.; Tavakol, E.; Jákli, B. Functioning of potassium and magnesium in photosynthesis, photosynthate translocation and photoprotection. Physiol. Plan. 2018, 163, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, E.A.; Balla-Kovács, A.; Ocwa, A.; Csajbók, J.; Kutasy, E. Enhancing alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) productivity: Exploring the significance of potassium nutrition. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielewicz, W.; Grzebisz, W.; Biber, M. Mutual effect of gypsum and potassium on nutrient productivity in the alfalfa-grass sward-a case study. Plants 2023, 12, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baidoo, M.M.; Islam, M.A. Potassium and harvest time interaction effect on alfalfa production and profitability. Agron. J. 2024, 116, 1670–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.H. The Affection of Fertilizer on Alfalfa and Analyzing of Economy. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Xu, Y.P.; Li, G.R.; Tian, B.H.; Li, Y.J.; Zhao, Z.X. Effects of different fertilization treatments on fresh grass yield in alfalfa. J. Grass Forage Sci. 2004, 8, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.H. Effects of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Fertilizers on Yield and Quality of Alfalfa Under Drip Irrigation. Master’s Thesis, Tarim University, Aksu, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Wang, L.L.; Luo, Z.Z.; Li, L.L.; Niu, Y.N.; Cai, L.Q.; Xie, J.H. Meta-analysis of yield effects of fertilization on alfalfa in China. Arid. Land Geogr. 2021, 44, 838–848. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.D.; Zhang, F.J.; Wang, T.; Xie, X.W.; Jia, X.H.; Xu, X. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on growth and leaf nitrogen metabolism of alfalfa in alkaline soil in Yinchuan plain of Hetao basin. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13261. [Google Scholar]
- Chtouki, M.; Laaziz, F.; Naciri, R.; Garré, S.; Nguyen, F.; Oukarroum, A. Interactive effect of soil moisture content and phosphorus fertilizer form on chickpea growth, photosynthesis, and nutrient uptake. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
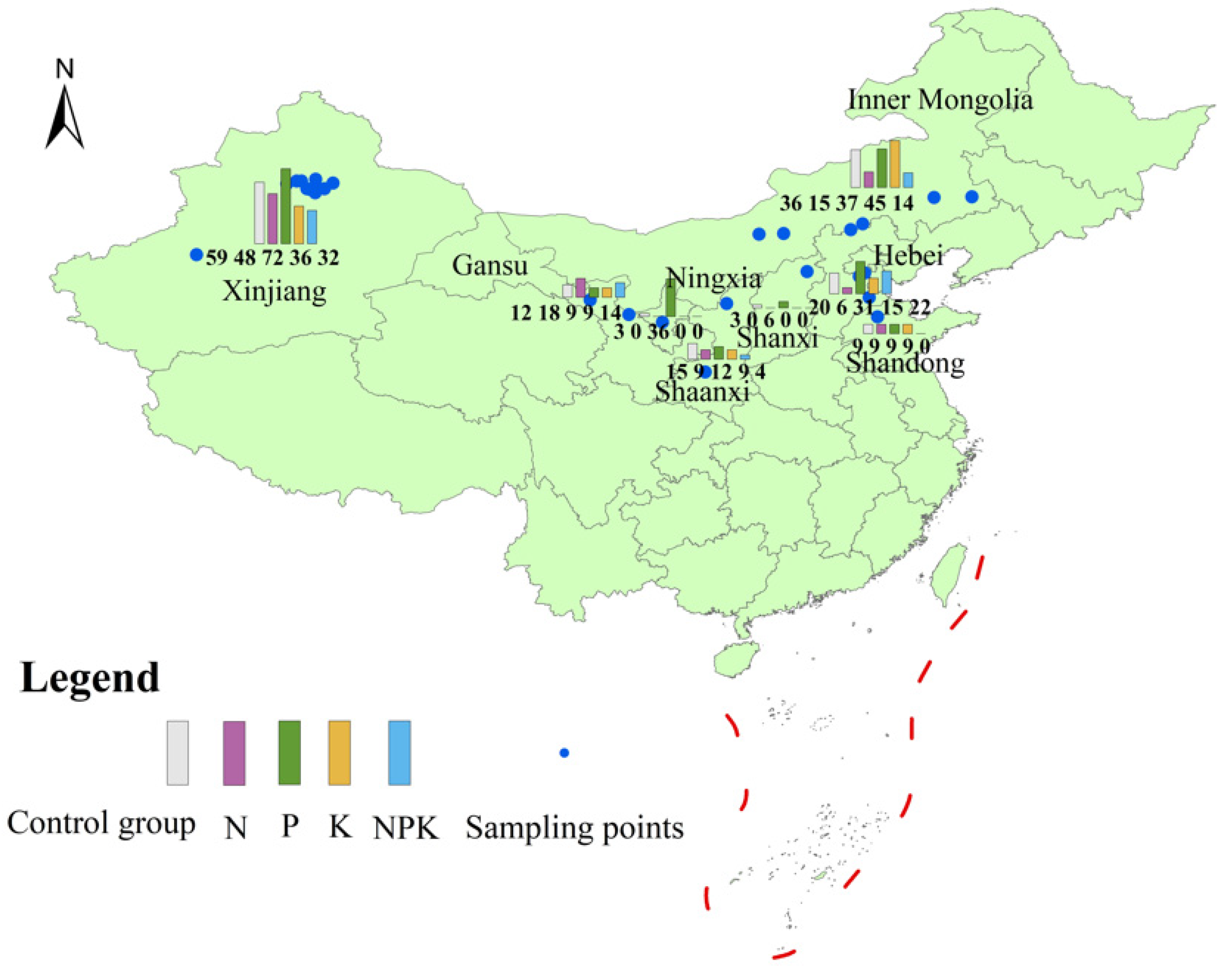
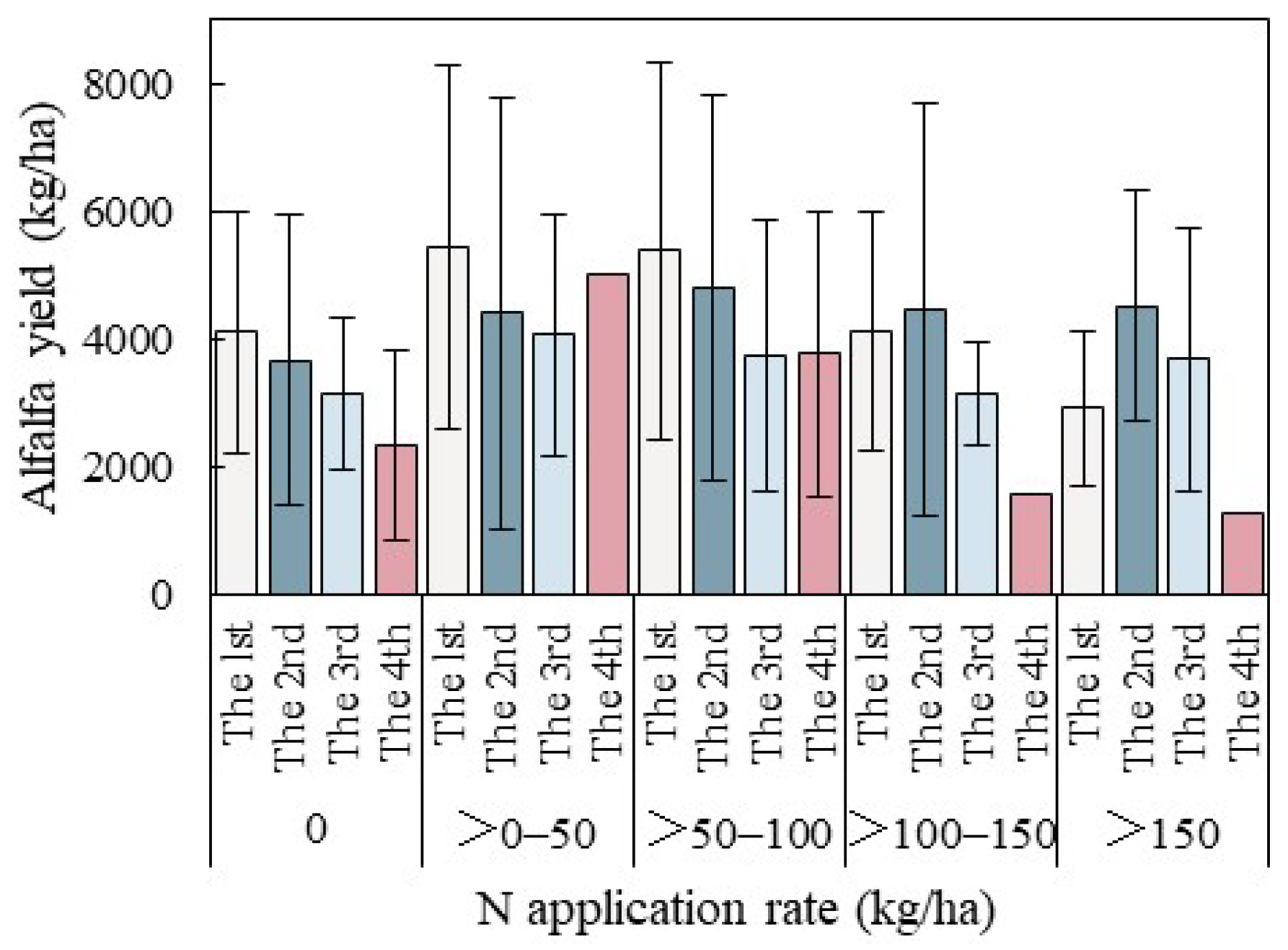

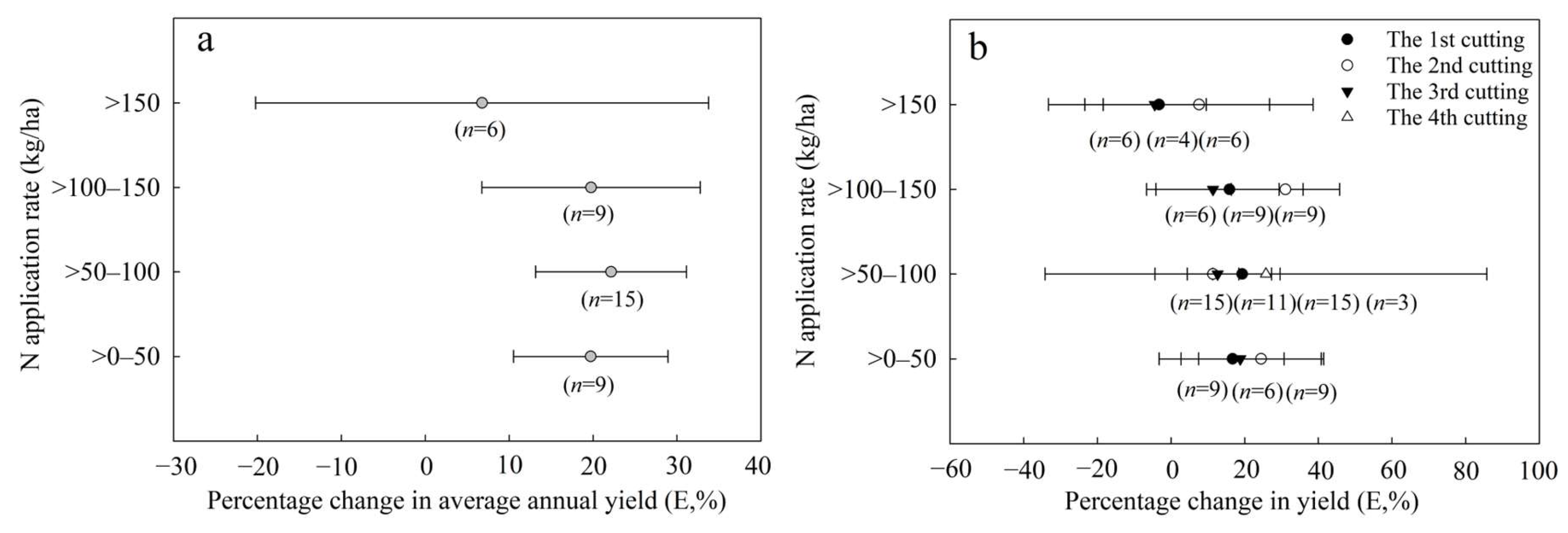


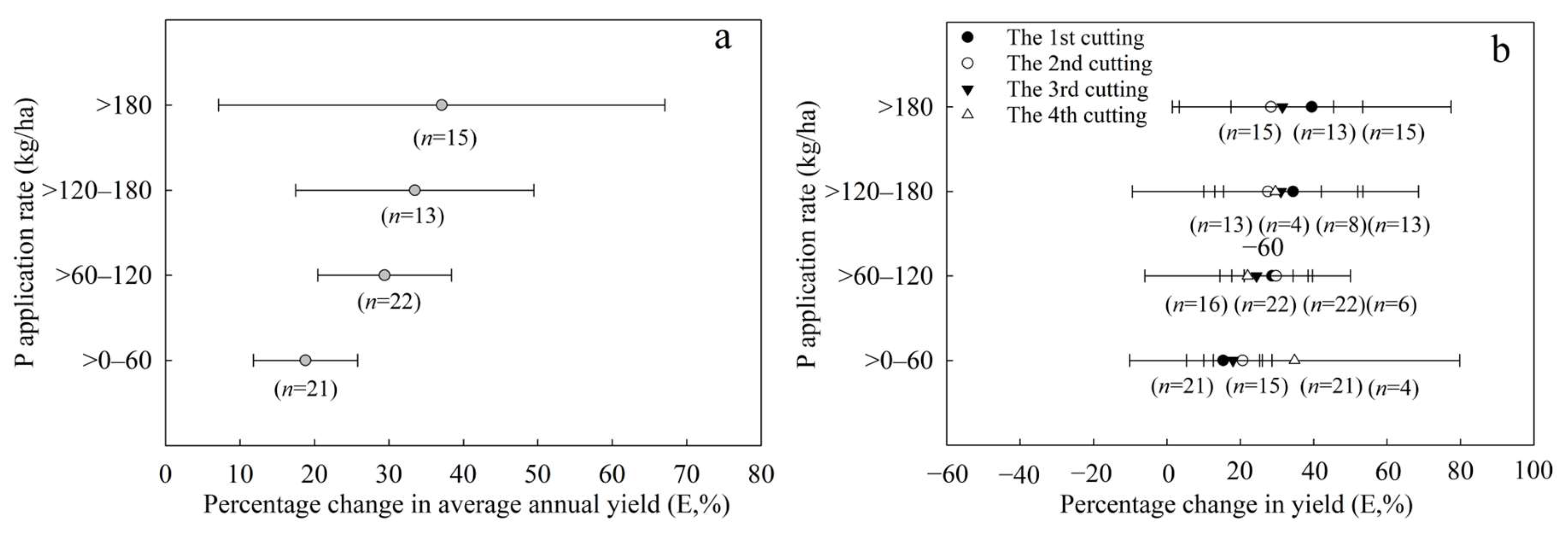


| Category | Min | Max | Mean | SD | 25th Quantile | 50th Quantile | 75th Quantile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 30.00 | 277.52 | 103.53 | 59.59 | 60.00 | 90.00 | 138.00 |
| P | 21.18 | 877.50 | 138.50 | 127.93 | 60.00 | 105.00 | 180.00 |
| K | 20.00 | 540.00 | 139.20 | 110.11 | 60.00 | 100.00 | 180.00 |
| NPK | 86.70 | 1334.25 | 386.70 | 263.94 | 225.00 | 310.00 | 447.30 |
| Category | N (kg/ha) | P (kg/ha) | ||||||||
| 0 | >0–50 | >50–100 | >100–150 | >150 | 0 | >0–60 | >60–120 | >120–180 | >180 | |
| Yield number | 41 | 23 | 40 | 22 | 20 | 78 | 61 | 66 | 38 | 47 |
| Category | K (kg/ha) | |||||||||
| 0 | >0–60 | >60–120 | >120–180 | >180 | ||||||
| Yield number | 38 | 34 | 40 | 17 | 32 | |||||
| Category | AR (kg/ha) | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV | 25th Quantile | 50th Quantile | 75th Quantile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 0 | 2776 | 22,011 | 10,588 | 5353 | 0.51 | 7374 | 9658 | 12,357 |
| >0–50 | 3458 | 31,415 | 13,738 | 8316 | 0.60 | 10,878 | 14,188 | 16,534 | |
| >50–100 | 3813 | 34,017 | 14,162 | 9056 | 0.64 | 7881 | 12,823 | 15,025 | |
| >100–150 | 3966 | 18,409 | 12,096 | 4619 | 0.38 | 8390 | 12,152 | 14,550 | |
| >150 | 3715 | 15,033 | 10,784 | 4626 | 0.43 | 7770 | 9230 | 14,814 | |
| P | 0 | 1562 | 23,018 | 10,806 | 5089 | 0.47 | 8202 | 10,987 | 13,810 |
| >0–60 | 2802 | 32,416 | 12,484 | 5175 | 0.41 | 7800 | 12,688 | 14,808 | |
| >60–120 | 3287 | 32,516 | 13,082 | 6981 | 0.53 | 8390 | 13,139 | 15,655 | |
| >120–180 | 3216 | 35,017 | 13,755 | 9290 | 0.68 | 5729 | 12,726 | 16,708 | |
| >180 | 4248 | 17,765 | 14,028 | 3804 | 0.27 | 12,110 | 14,311 | 16,508 | |
| K | 0 | 2776 | 16,608 | 10,276 | 4365 | 0.42 | 8202 | 9311 | 13,070 |
| >0–60 | 2934 | 33,616 | 11,342 | 7714 | 0.68 | 9061 | 9871 | 10,890 | |
| >60–120 | 3813 | 34,017 | 12,184 | 7399 | 0.61 | 9230 | 10,149 | 14,933 | |
| >120–180 | 5574 | 26,563 | 13,196 | 8007 | 0.61 | 8905 | 12,106 | 12,833 | |
| >180 | 7344 | 27,013 | 13,422 | 5495 | 0.41 | 9483 | 13,678 | 14,814 |
| Category | Meaning | Level (Code) | Lower Limit (kg/ha) | Upper Limit (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPK (kg/ha) | N + P + K | Low (T1) | 0 | 225 |
| Medium–low (T2) | 225 | 310 | ||
| Medium–high (T3) | 310 | 447.30 | ||
| High (T4) | 447.30 | — | ||
| N Application Ratio (%) | N/NPK | Low (N1) | 0 | 14.28 |
| Medium–low (N2) | 14.28 | 27.72 | ||
| Medium–high (N3) | 27.72 | 39.48 | ||
| High (N4) | 39.48 | 100 | ||
| P Application Ratio (%) | P/NPK | Low (P1) | 0 | 18.63 |
| Medium–low (P2) | 18.63 | 36.36 | ||
| Medium–high (P3) | 36.36 | 50 | ||
| High (P4) | 50 | 100 | ||
| K Application Ratio (%) | K/NPK | Low (K1) | 0 | 25 |
| Medium–low (K2) | 25 | 36.36 | ||
| Medium–high (K3) | 36.36 | 49.17 | ||
| High (K4) | 49.17 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, H.; Ning, S.; Yan, A.; Zhao, Y.; Li, N.; Huo, T. Response of Alfalfa Yield to Rates and Ratios of N, P, and K Fertilizer in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions of China Based on Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051093
Ren H, Ning S, Yan A, Zhao Y, Li N, Huo T. Response of Alfalfa Yield to Rates and Ratios of N, P, and K Fertilizer in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions of China Based on Meta-Analysis. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051093
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Huipeng, Songrui Ning, An Yan, Yiqi Zhao, Ning Li, and Tingting Huo. 2025. "Response of Alfalfa Yield to Rates and Ratios of N, P, and K Fertilizer in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions of China Based on Meta-Analysis" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051093
APA StyleRen, H., Ning, S., Yan, A., Zhao, Y., Li, N., & Huo, T. (2025). Response of Alfalfa Yield to Rates and Ratios of N, P, and K Fertilizer in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions of China Based on Meta-Analysis. Agronomy, 15(5), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051093






